Comprehensive Multi-Omics Analysis of Muscle Tissue Alterations in Male Macrobrachium rosenbergii Induced by Frequent Mating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
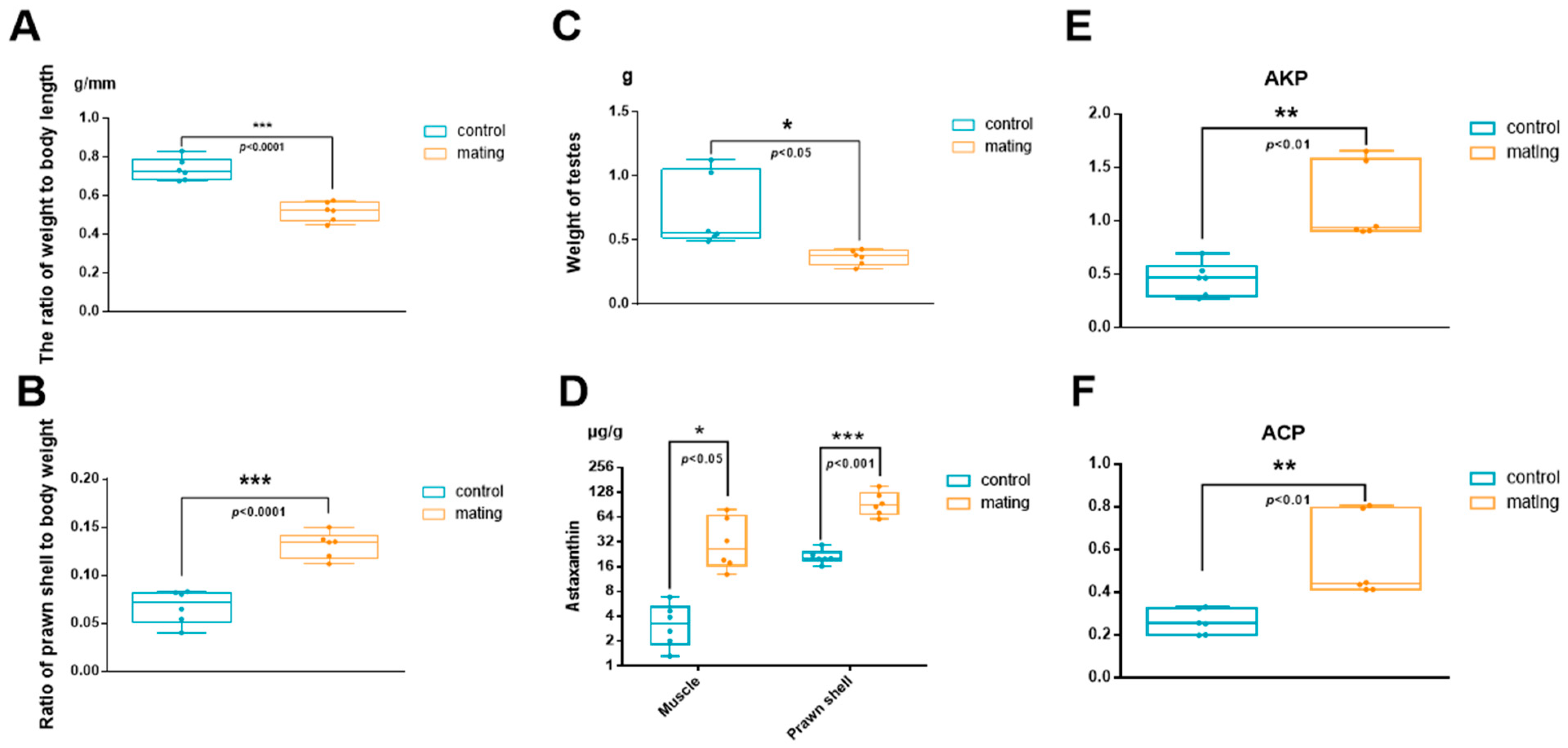
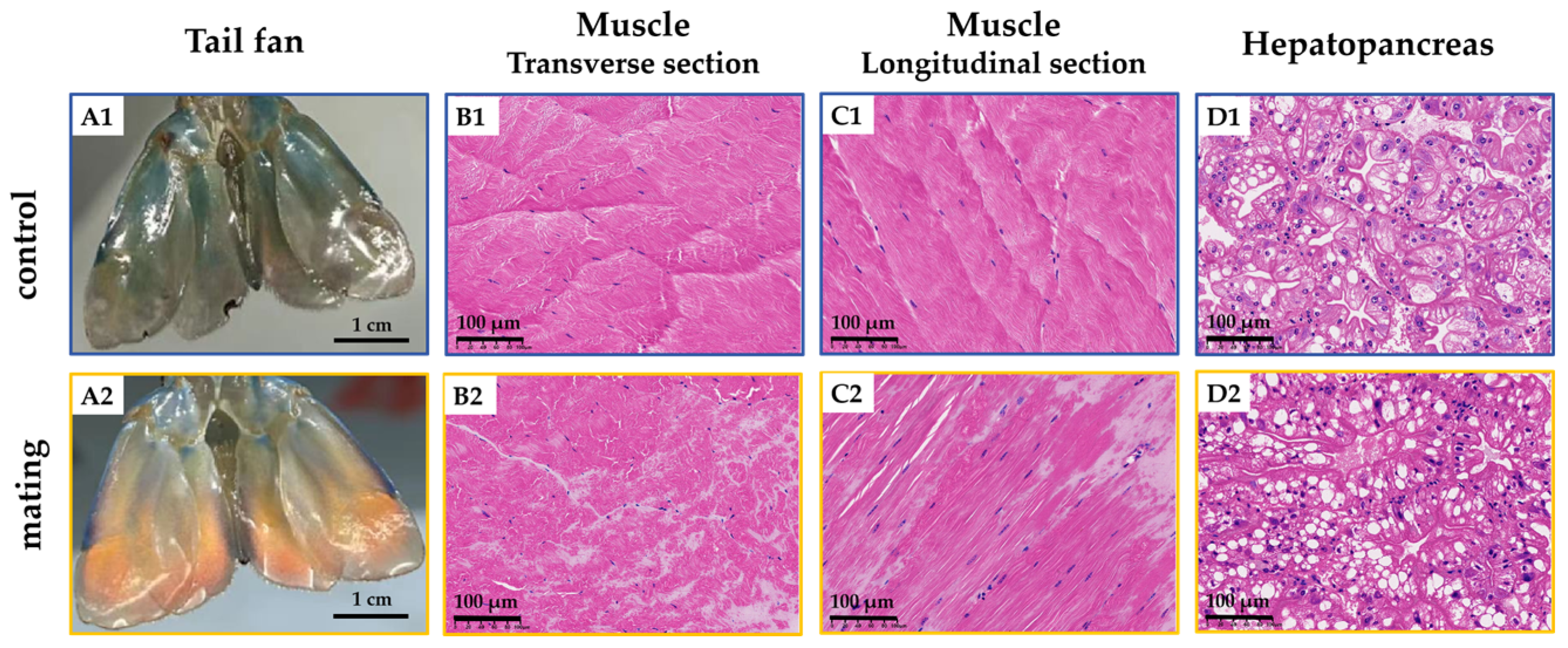
2.1. Altered Physiological Status
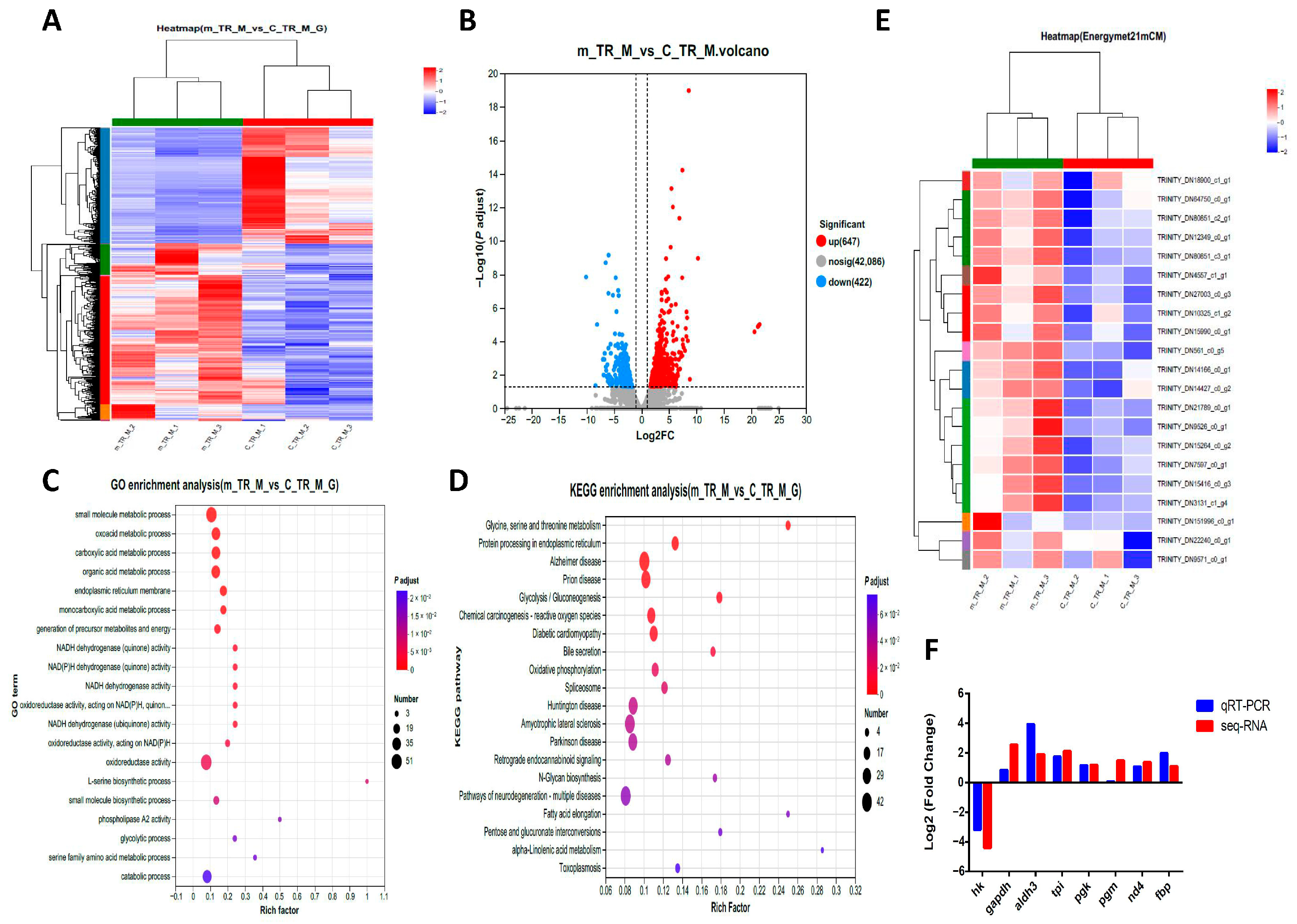
2.2. Transcriptome Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs)
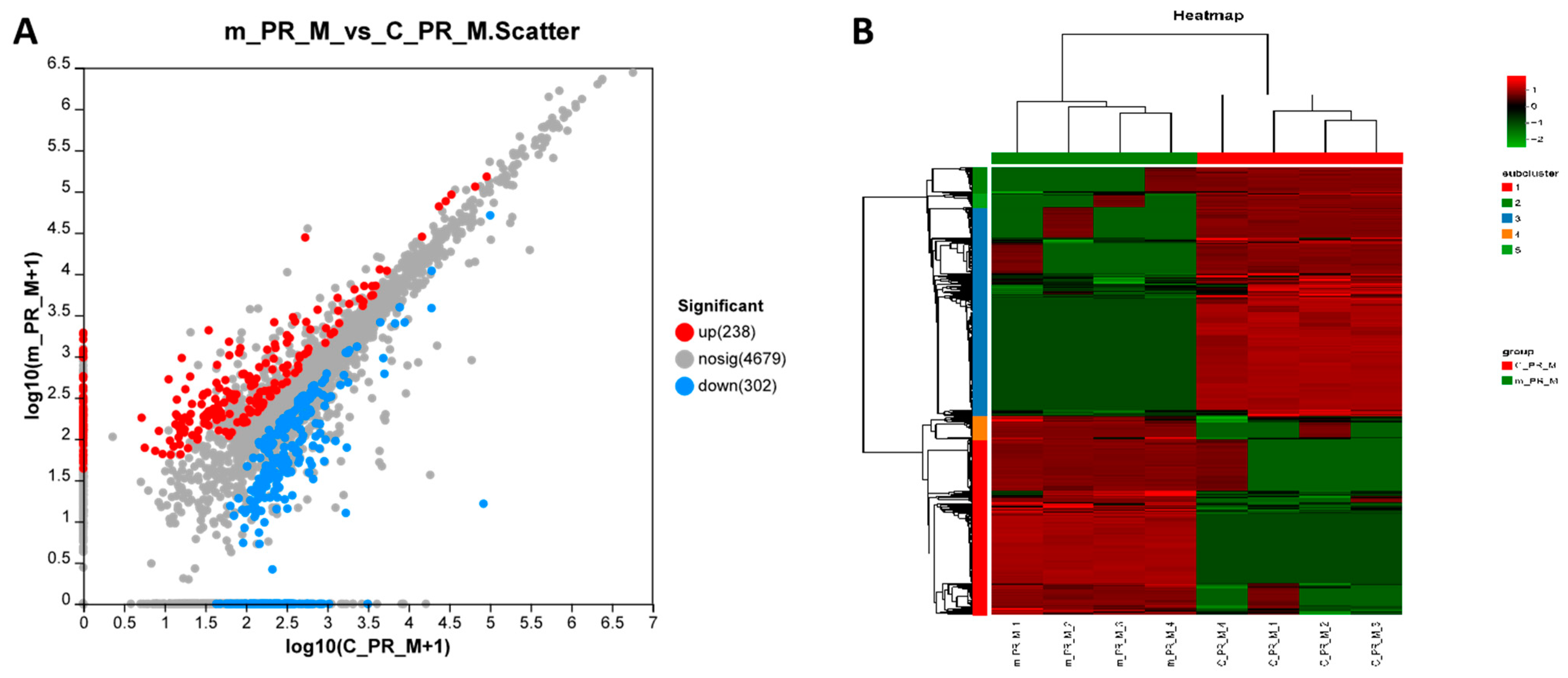
2.3. Proteomic Analysis
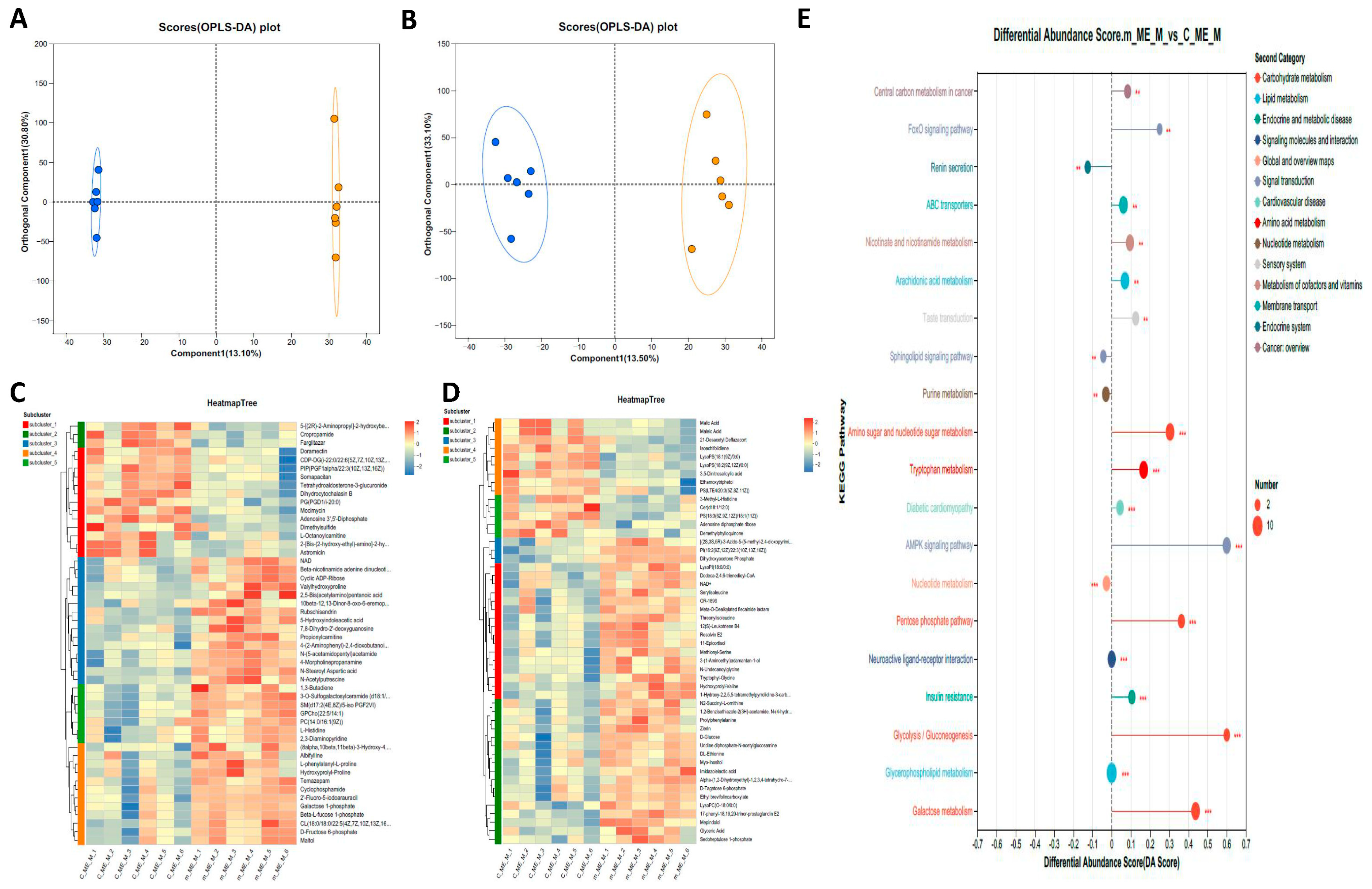
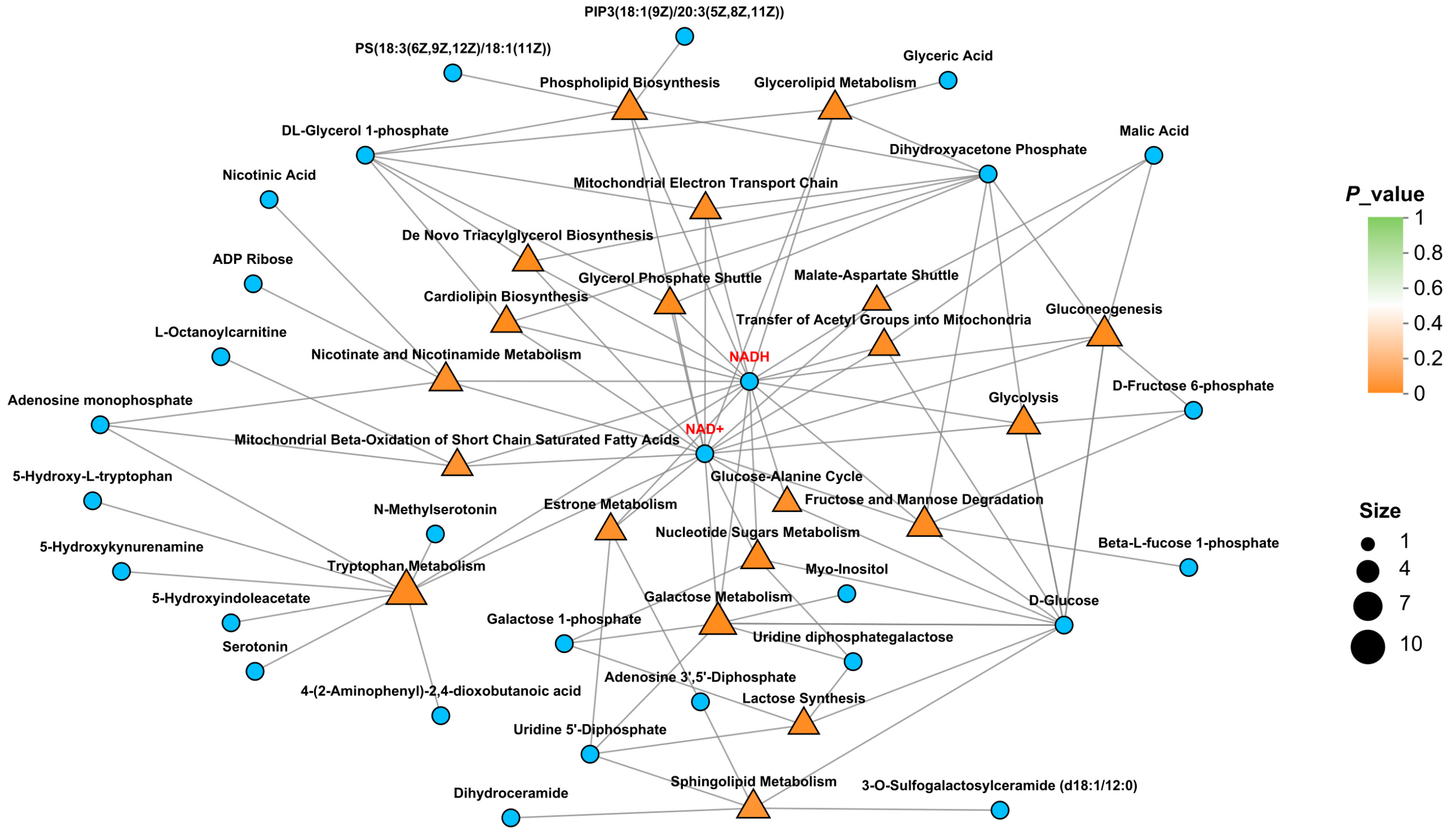
2.4. Metabolome Analysis
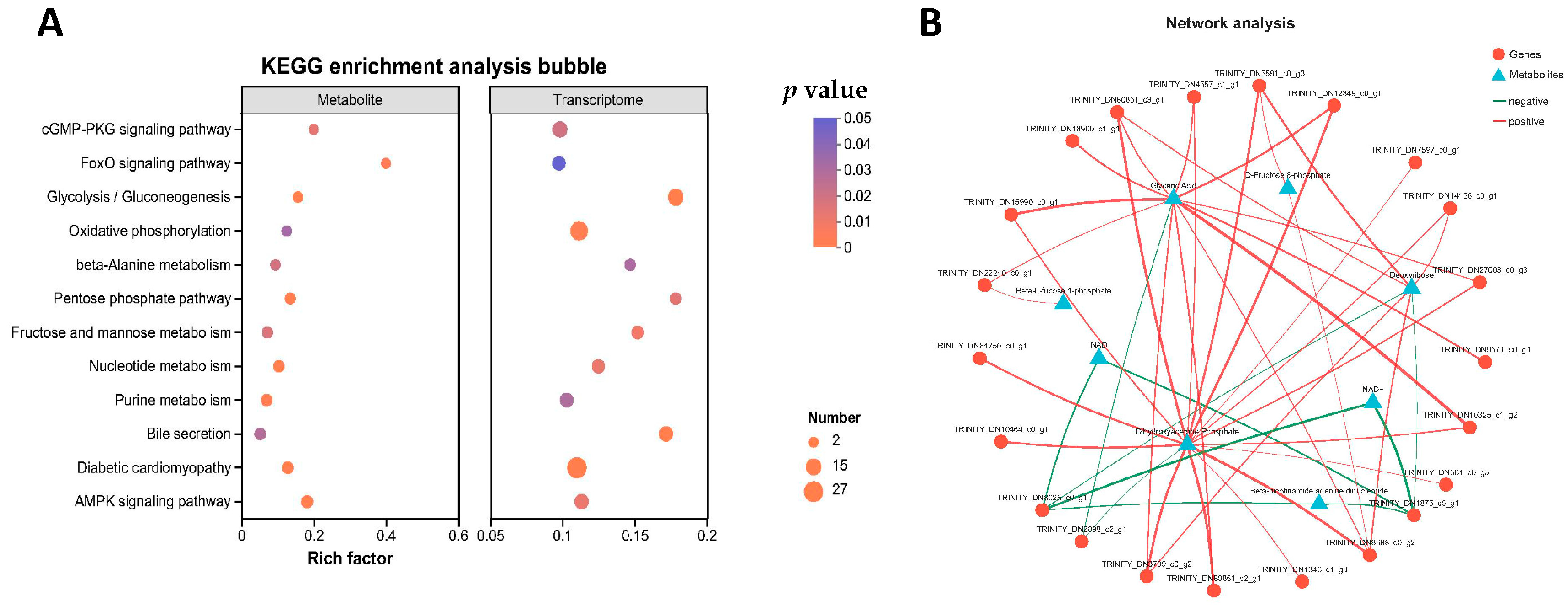
2.5. Multi-Omics Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experiment Design
4.2. Determination of Astaxanthin Content
4.3. Measurement of Alkaline Phosphatase (AKP) and Acid Phosphatase (ACP) Activity
4.4. Histological Observation
4.5. Sequencing and Analysis
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis of Gene Expression
4.7. Statiscical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| M. rosenbergii | Macrobrachium rosenbergii |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| DEPs | differentially expressed proteins |
| DEMs | differentially expressed metabolites |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| MSEA | Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis |
| aldh3 | aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family member A1 |
| fbp | fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase |
| hk | hexokinase |
| nd4 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 |
| pgk | phosphoglycerate kinase |
| pgm | phosphoglucomutase |
| tpi | triosephosphate isomerase |
| gapdh | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| rps18 | ribosomal protein S18 |
Appendix A
| Metabolite | p_Value | Log2FC(m_ME_M/C_ME_M) | Significant | Regulate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAD | 0.008888 | 0.0599 | yes | up |
| NAD+ | 0.01724 | 0.0613 | yes | up |
| Serotonin | 0.006341 | 0.3161 | yes | up |
| N-Methylserotonin | 0.04121 | 0.6014 | yes | up |
| Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate | 0.001331 | 0.0909 | yes | up |
| Glyceric Acid | 0.02769 | 0.0986 | yes | up |
| D-Glucose | 0.0382 | 0.0475 | yes | up |
| NR_Description | Gene(log2FC) | Protein(log2FC) |
|---|---|---|
| fructose-bisphosphate aldolase-like | 2.49 | 1.243 |
| transketolase-like protein 2 | 3.918 | 7.624 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC113813620 | 2.732 | 7.624 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC113812620 | 2.636 | 2.378 |
| C-reactive protein 1.1-like | 3.063 | 7.624 |
| antilipopolysaccharide factor | 3.732 | 7.624 |
| RNA-binding protein with serine-rich domain 1-A | 1.892 | 7.624 |
| X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 5-like isoform X3 | 2.491 | 7.624 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC122257736 | 2.265 | 7.624 |
| V-type proton ATPase proteolipid subunit | 1.345 | 1.604 |
| mid1-interacting protein 1A-like isoform X2 | 4.131 | 2.154 |
| peroxisomal membrane protein PMP34-like | 3.208 | 7.624 |
| vacuolar fusion protein MON1 homolog A-like isoform X2 | 1.701 | 7.624 |
| talin-2-like isoform X1 | 1.697 | 7.624 |
| sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 4-like | 1.676 | 7.624 |
| serine protease inhibitor 88Ea-like | 3.591 | 7.624 |
| hypothetical protein C7M84_025254 | 2.971 | 7.624 |
| venom protease-like | 2.626 | 7.624 |
| F-box-like/WD repeat-containing protein TBL1XR1 isoform X2 | 1.676 | 7.624 |
| coiled-coil domain-containing protein 56 | 1.776 | 7.624 |
| very low-density lipoprotein receptor-like | 2.115 | 7.624 |
| metaxin-1-like isoform X1 | 1.852 | 7.624 |
| protein PTCD3 homolog, mitochondrial-like | 2.368 | 7.624 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC113804706 isoform X2 | 1.685 | 1.483 |
| epoxide hydrolase 4-like | 2.559 | 7.624 |
| acylglycerol kinase, mitochondrial-like | 1.865 | 7.624 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC121857022 isoform X12 | 2.965 | 0.9386 |
| cytosolic non-specific dipeptidase-like isoform X2 | 2.276 | 7.624 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC123770307 | 4.642 | 2.102 |
| protein qua-1-like | −1.466 | −16.61 |
| fibrillin-3-like isoform X2 | −2.351 | −2.179 |
| iodotyrosine deiodinase 1-like | −2.145 | −16.61 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC123763680 | −2.486 | −0.679 |
| periodic tryptophan protein 1 homolog | −1.836 | −1.432 |
| unconventional myosin-IXa-like isoform X1 | −2.054 | −16.61 |
| rab11 family-interacting protein 1-like | −2.002 | −16.61 |
| DnaJ C2 | −2.371 | −2.764 |
| nuclear RNA export factor 1-like | −2.435 | −1.548 |
| serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 2-like isoform X5 | −1.819 | −16.61 |
| 4′-phosphopantetheine phosphatase-like isoform X3 | −1.479 | −0.8173 |
| synapse-associated protein 1 | −1.284 | −16.61 |
| unnamed protein product | −4.851 | −2.539 |
| leucine-rich repeat protein SHOC-2-like isoform X1 | −2.67 | −16.61 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC123773768 | −2.068 | −2.554 |
| equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1-like isoform X3 | −2.091 | −16.61 |
| monocarboxylate transporter 3-like isoform X1 | −1.536 | −1.413 |
| endophilin-A-like isoform X5 | −2.636 | −0.9748 |
| uncharacterized protein ZK1073.1-like isoform X3 | −1.991 | −0.7415 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC113817296 | −3.43 | −2.708 |
| troponin C, isotype gamma-like isoform X5 | −5.5 | −0.844 |
| protein stum homolog | −2.843 | −16.61 |
| tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 9-like isoform X3 | −1.628 | −1.585 |
| soluble calcium-activated nucleotidase 1-like | −2.356 | −16.61 |
| golgin subfamily A member 2-like | −1.806 | −16.61 |
| protein quiver-like isoform X2 | −2.448 | −0.8967 |
| probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase IM isoform X3 | −1.542 | −0.9456 |
| 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase delta-4-like | −1.787 | −1.369 |
| Arf-GAP domain and FG repeat-containing protein 1-like | −2.003 | −0.737 |
| uncharacterized protein LOC122248415 isoform X1 | −1.684 | −0.7171 |
| low-quality protein: MOG-interacting and ectopic P-granules protein 1-like | −2.206 | −16.61 |
| crustacyanin-A1 | −4.871 | −1.673 |
References
- Puttasan, M.; Nipitwattanaphon, M.; Rungsin, W.; Swatdipong, A. Instinctive mate choice with genetically different partners assists sustaining genetic diversity in giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Fish. Res. 2023, 262, 106648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.; Levy, T.; Ventura, T.; Sagi, A. Monosex Populations of the Giant Freshwater Prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii—From a Pre-Molecular Start to the Next Generation Era. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Cheng, Y. Mating capacity of male Macrobrachium rosenbergii with different morphotypes. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2010, 21, 1043. [Google Scholar]
- Ra’Anan, Z.; Sagi, A. Alternative mating strategies in male morphotypes of the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man). Biol. Bull. 1985, 169, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Macias, L.H.; Garcia, L.R. Unraveling the hierarchical structure of posture and muscle activity changes during mating of Caenorhabditis elegans. PNAS Nexus 2024, 3, pgae032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.P.; Marucci, R.C. Mating Behavior and Reproductive Success in Doru luteipes (Dermaptera: Forficulidae). J. Insect Behav. 2025, 38, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tian, N.; Chang, P.; Zhang, W. Mating reconciles fitness and fecundity by switching diet preference in flies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, H.; Toltesi, R.; Eng, M.; Garg, D.; Merritt, T.J.S.; Rajpurohit, S. No water, no mating: Connecting dots from behaviour to pathways. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.C.; Hwang, P.P. Some insights into energy metabolism for osmoregulation in fish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. Cbp 2008, 148, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horscroft, J.A.; Murray, A.J. Skeletal muscle energy metabolism in environmental hypoxia: Climbing towards consensus. Extrem. Physiol. Med. 2014, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, M.; Han, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Y. Chromosome level genome assembly of giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Sci. Data 2023, 11, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, B.R.; Ponzoni, R.W.; Das Mahapatra, K.; Panda, D. Genetic improvement of giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii: A review of global status. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, L.; Li, Q. Insights into the mechanism of color formation of the freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) revealed by de novo assembly transcriptome analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2024, 50, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhao, Q.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhou, H.; Hu, J.; Gu, L.; Hu, Y.W.; Zeng, F.; Zhao, F.; Yue, C.C. Pathogenesis, multi-omics research, and clinical treatment of psoriasis. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 133, 102916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitmaier, P.; Katsoula, G.; Zeggini, E. Insights from multi-omics integration in complex disease primary tissues. Trends Genet. 2023, 39, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, D.; Jones, N.C.; Schittenhelm, R.B.; Anderson, A.; Casillas-Espinosa, P.M. Multi-omics integration and epilepsy: Towards a better understanding of biological mechanisms. Prog. Neurobiol. 2023, 227, 102480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, R.; Tian, S.; Yu, Y.; Ren, L.; Hou, W.; Zhu, F. Multi-omics data integration using ratio-based quantitative profiling with Quartet reference materials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianann, T.; Weimin, W. The early life culture and gonadal development of giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii: A review. Aquaculture 2022, 559, 738357. [Google Scholar]
- Sui, J.; Luan, S.; Yang, G.; Xia, Z.; Tang, Q.; Luo, K.; Meng, X.; Kong, J. Effects of the individual rearing stage on the growth traits of candidate giant freshwater prawns (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Aquac. Int. 2022, 30, 1659–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuc, T.H.; Vu, N.T.; Nga, N.T.K.; Ky, N.T.; Nguyen, N.H. Assessment of a long-term selective breeding program for giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii since 2007. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, B.; Shen, P.; Cheng, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Q. Regulation and Response Mechanism of Acute Low-Salinity Stress during Larval Stages in Macrobrachium rosenbergii Based on Multi-Omics Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Cao, L.; Gao, J.; Li, Q.; Nie, Z.; Sun, Y.; Xu, G.; Du, J. Integration of metabolomics and transcriptomics reveals the toxicological mechanism of deltamethrin exposure in Chinese mitten crab Eriocheir sinensis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 176975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Cui, D.; Sun, X.; Shi, J.; Xu, N. Primary metabolism is associated with the astaxanthin biosynthesis in the green algae Haematococcus pluvialis under light stress. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, J.E.; Boutin, S.; Speakman, J.R.; Humphries, M.M. Energetic costs of male reproduction in a scramble competition mating system. J. Anim. Ecol. 2010, 79, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, N.; Xue, M.; Thornalley, P.J. Hexokinase-2-Linked Glycolytic Overload and Unscheduled Glycolysis—Driver of Insulin Resistance and Development of Vascular Complications of Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachsmuth, H.; Weninger, S.N.; Duca, F. Role of the gut–brain axis in energy and glucose metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.J. NADH/NAD + Redox Imbalance and Diabetic Kidney Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Hu, S.W.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; He, P.; Kohlmeier, K.A.; Zhu, Y. Sex peptide regulates female receptivity through serotoninergic neurons in Drosophila. iScience 2023, 26, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirovich, D.B.; Da’dara, A.A.; Skelly, P.J. Multifunctional fructose 1, 6-bisphosphate aldolase as a therapeutic target. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 719678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, K.A.; Tossing, G.; Mulroe, F.; Simmons, C.; Butler, K.M.; Schreiber, A.; Alsadah, A.; Neilson, D.E.; Naess, K.; Wedell, A. ATP6V0C variants impair V-ATPase function causing a neurodevelopmental disorder often associated with epilepsy. Brain 2023, 146, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, L.; Brandt, J.; Ushakov, D.S.; Bodmer, B.S.; Pickin, M.J.; Groseth, A.; Hoenen, T. Evidence for viral mRNA export from Ebola virus inclusion bodies by the nuclear RNA export factor NXF1. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e00900-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.G.; Raduwan, H.; Carlet, J.; Soto, M.C. The RhoGAP HUM-7/Myo9 integrates signals to modulate RHO-1/RhoA during embryonic morphogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 2018, 145, dev168724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, J.M.; Krawczyk, P.A.; Scaria, S.M.; Cangelosi, A.L.; Chan, S.H.; Kunchok, T.; Lewis, C.A.; Sabatini, D.M. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate signals glucose availability to mTORC1. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Li, D.D.; Yang, K.L.; Zhu, X.F. Regulation of glycolytic metabolism by autophagy in liver cancer involves selective autophagic degradation of HK2 (hexokinase 2). Autophagy 2017, 14, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. siRNA-Mediated MrIAG Silencing Induces Sex Reversal in Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Shi, C.; Liu, L.; Han, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fu, W.; Gao, H.; Huang, H. Majorbio Cloud 2024: Update single-cell and multiomics workflows. iMeta 2024, 3, e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| GO Description | NES | p-Value | Lead|Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| structural constituent of ribosome | −2.15175 | 0 | 78|89 |
| structural molecule activity | −2.01916 | 0 | 117|162 |
| peptide biosynthetic process | −1.90523 | 0 | 74|88 |
| ribosome | −1.85941 | 0 | 60|76 |
| translation | −1.91465 | 0 | 73|86 |
| ribosomal subunit | −1.86037 | 0.00173 | 30|34 |
| amide biosynthetic process | −1.87565 | 0 | 78|98 |
| cellular response to chemical stimulus | −1.80275 | 0.00169 | 7|19 |
| ribonucleoprotein complex | −1.79437 | 0 | 108|189 |
| peptide metabolic process | −1.80315 | 0 | 75|95 |
| cellular protein metabolic process | −1.81616 | 0 | 89|122 |
| microtubule cytoskeleton organization | −1.78661 | 0.00338 | 9|19 |
| response to chemical | −1.80472 | 0.00173 | 13|35 |
| cellular amide metabolic process | −1.76313 | 0 | 77|121 |
| response to oxidative stress | −1.75177 | 0.0049 | 12|25 |
| cysteine-type peptidase activity | −1.68567 | 0.00333 | 13|53 |
| aminopeptidase activity | −1.69007 | 0.00671 | 7|19 |
| hydrolase activity, hydrolyzing O-glycosyl compounds | −1.64148 | 0.00326 | 17|58 |
| response to organic substance | −1.64371 | 0.00858 | 8|24 |
| endopeptidase complex | 1.73946 | 0.00472 | 16|20 |
| respiratory chain complex | 1.72275 | 0.01256 | 19|21 |
| proteasome complex | 1.71102 | 0.01946 | 16|20 |
| peroxidase activity | −1.62955 | 0.01544 | 8|19 |
| transferase activity, transferring sulfur-containing groups | 1.68865 | 0.00515 | 11|21 |
| carboxylic acid binding | 1.7413 | 0.01446 | 2|17 |
| respiratory electron transport chain | 1.75704 | 0.00699 | 16|20 |
| generation of precursor metabolites and energy | 1.76887 | 0.00272 | 33|55 |
| lipase activity | 1.59569 | 0.03373 | 2|18 |
| mitochondrial protein complex | 1.58684 | 0.01961 | 25|40 |
| organic acid binding | 1.65345 | 0.00948 | 2|19 |
| whole membrane | 1.59702 | 0.00532 | 14|49 |
| tricarboxylic acid cycle | 1.63374 | 0.02232 | 12|18 |
| proteasomal protein catabolic process | 1.60833 | 0.01887 | 13|17 |
| extracellular region part | 1.5984 | 0.00543 | 10|85 |
| inner mitochondrial membrane protein complex | 1.63885 | 0.02 | 23|35 |
| electron transport chain | 1.81405 | 0 | 19|23 |
| peptidase complex | 1.60913 | 0.02353 | 17|24 |
| citrate metabolic process | 1.61652 | 0.03 | 12|18 |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | 1.77131 | 0.00726 | 22|33 |
| sulfotransferase activity | 1.83354 | 0 | 11|18 |
| Gene | Function | Primer Pairs (5′-3′) | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| aldh3 | To convert aldehydes to the corresponding carboxylic acids. | F: TGTACGTCGAGAACGAGCAG R: CGCCCATAACGAGAACCACT | XM_067104159.1 |
| fbp | It catalyzes the conversion of fructose-1, 6-diphosphate to fructose6-phosphate, which is the rate-limiting step in the gluconeogenesis pathway. | F: GCAGGTCGAGTACGAGGATG R: ATGATGGGCATCCAGACAGC | XM_067125270.1 |
| hk | It catalyzes the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate, the first step in glycolysis. | F: CTCCAAACGCTCCCCATTCT R: TACAACTGGCACGCTCATGT | XM_067093332.1 |
| nd4 | It is involved in the electron transport chain and is responsible for the transfer of electrons from NADH to ubiquinone. | F: GCCCAGGCTTTCAGTCATCT R: AGACACCTGCACAGCTAACC | XM_067108213.1 |
| pgk | It catalyzes the conversion of 1, 3-diphosphoglycerate to 3-phosphoglycerate, along with the generation of ATP, and is a key enzyme in the glycolytic and gluconeogenic pathways. | F: GGATGGGCCTTGATTGTGGA R: CGTGCATCCTTTGGTTGTGG | XM_067098515.1 |
| pgm | It catalyzes the conversion between glucose-1-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate. | F: ATTCCTGGGTGCCGATCTTG R: GGTGGCCCTAATGCTGACTT | XM_067133232.1 |
| tpi | It catalyzes the interconversion between dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate. | F: CAAATGAAGGCGCTGGTTCC R: CACCTGGGCACTGACGTTAT | XM_067106417.1 |
| gapdh | It catalyzes the oxidation and phosphorylation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and is a key enzyme in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis pathways. | F: TGAAGCCCGAGAACATTCCATG R: GTTCACGCCGCAGACGAACATG | XM_067126079.1 |
| rps18 | It encodes the ribosomal protein S18, a component of the small ribosomal subunit. | F: TACCTACGACCCACACCCTT R: TATCAACGCACCGCCAAGAT | XM_067093923.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Cheng, H.; Li, X.; Yuan, H.; Cai, X.; Tang, L.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H. Comprehensive Multi-Omics Analysis of Muscle Tissue Alterations in Male Macrobrachium rosenbergii Induced by Frequent Mating. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093995
Fan Y, Gao Q, Cheng H, Li X, Yuan H, Cai X, Tang L, Yuan X, Zhang G, Zhang H. Comprehensive Multi-Omics Analysis of Muscle Tissue Alterations in Male Macrobrachium rosenbergii Induced by Frequent Mating. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):3995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093995
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yunpeng, Qiang Gao, Haihua Cheng, Xilian Li, Huwei Yuan, Xue Cai, Lin Tang, Xiudan Yuan, Guangjing Zhang, and Haiqi Zhang. 2025. "Comprehensive Multi-Omics Analysis of Muscle Tissue Alterations in Male Macrobrachium rosenbergii Induced by Frequent Mating" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 3995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093995
APA StyleFan, Y., Gao, Q., Cheng, H., Li, X., Yuan, H., Cai, X., Tang, L., Yuan, X., Zhang, G., & Zhang, H. (2025). Comprehensive Multi-Omics Analysis of Muscle Tissue Alterations in Male Macrobrachium rosenbergii Induced by Frequent Mating. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 3995. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26093995






