The Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporter HAP12 Is Critical in Toxoplasma gondii Survival and Virulence
Abstract
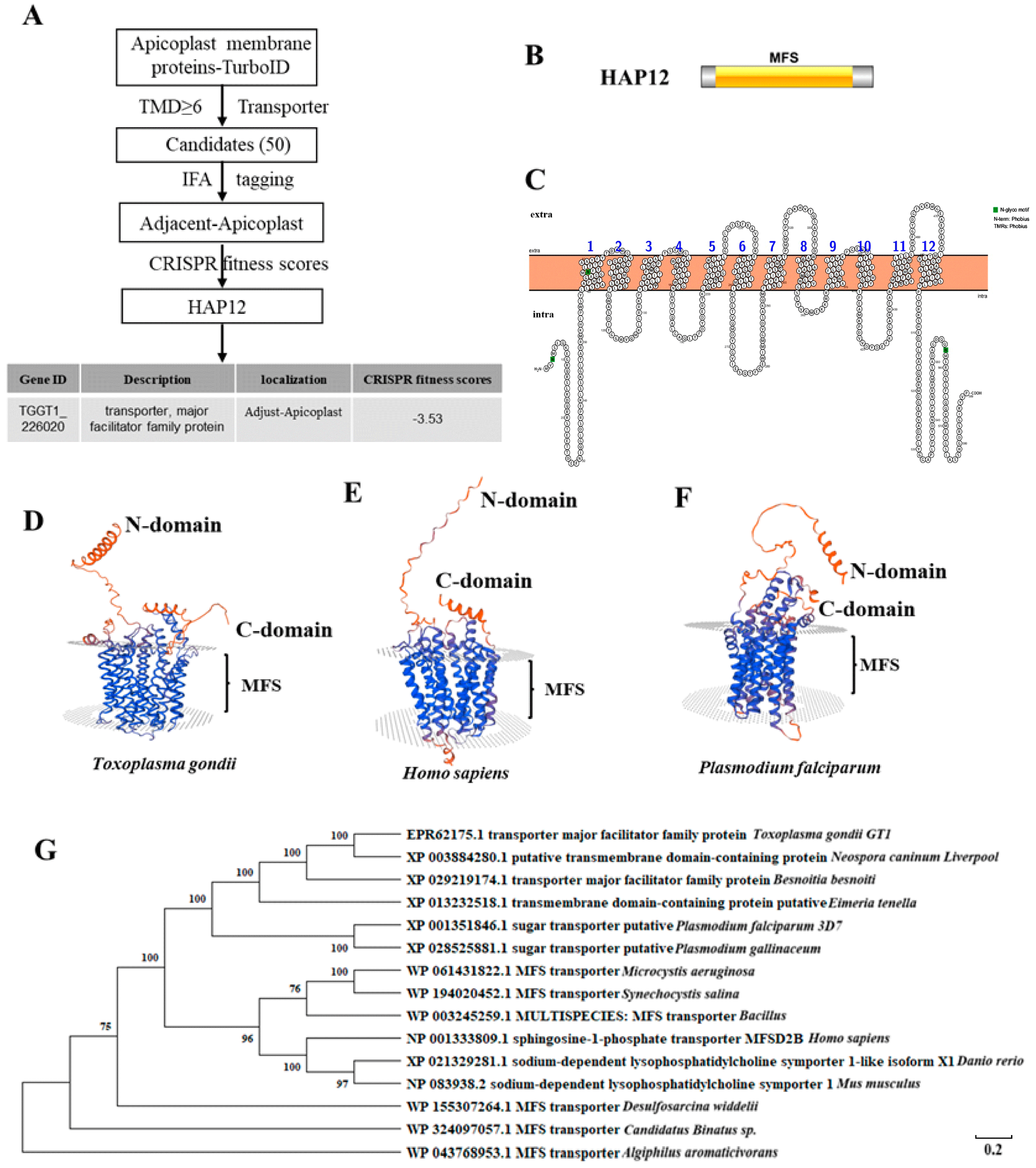
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HAP12 Is a Highly Conserved Apicoplast MSF Protein in Toxoplasma gondii
2.2. Inducible Degradation of HAP12 Impairs Parasite Invasion and Survival
2.3. Inducible Degradation of HAP12 Results in a Characteristic Delayed-Death Phenotype
2.4. Inducible Degradation of HAP12 Shows No Detectable Effect on Apicoplast Integrity or Other Organelles
2.5. Inducible Degradation of HAP12 in Mice Reveals Its Critical Role in Parasite Virulence
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.2. Plasmid Construction
4.3. Parasites and Host Cell Culture
4.4. IFA
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Plaque Assay
4.7. Parasite Replication
4.8. Invasion Assay
4.9. In Vivo Assay
4.10. Statistics
4.11. Availability of Data and Materials
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blackman, M.J.; Biddau, M.; Bouchut, A.; Major, J.; Saveria, T.; Tottey, J.; Oka, O.; van-Lith, M.; Jennings, K.E.; Ovciarikova, J.; et al. Two essential Thioredoxins mediate apicoplast biogenesis, protein import, and gene expression in Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, G.; Webster, J.P.; Walker, M. Toxoplasma gondii: AnUnderestimated Threat? Trends Parasitol. 2020, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, D.; Sobrosa, P.; Morais Passos, R.; Silva, F.; Ferreira, A.; Corga da Silva, R.; Silva, D. Cerebral Toxoplasmosis Mimicking a Brain Neoplasm in an Inaugural HIV-Positive Patient: The Importance of Early Decision-Making and Background Assessment in the Emergency Department. Cureus 2025, 17, e76936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Rahimi, A.; Zarei, H.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Rasoulpoor, S.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. Global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.; McFadden, G.I. The evolution, metabolism and functions of the apicoplast. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 749–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Suo, X.; Zhu, G.; Shen, B. The apicoplast biogenesis and metabolism: Current progress and questions. Trends Parasitol. 2024, 40, 1144–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janouškovec, J.; Horák, A.; Oborník, M.; Lukeš, J.; Keeling, P.J. A common red algal origin of the apicomplexan, dinoflagellate, and heterokont plastids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10949–10954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Cui, J.; Yang, X.; Xia, N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gupta, N.; Shen, B. Acquisition of exogenous fatty acids renders apicoplast-based biosynthesis dispensable in tachyzoites of Toxoplasma. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7743–7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadian, K.; Gupta, Y.; Singh, H.V.; Kempaiah, P.; Rawat, M. Apicoplast Metabolism: Parasite’s Achilles’ Heel. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeber, F.; Feagin, J.E.; Parsons, M.; van Dooren, G.G. The apicoplast and mitochondrion of Toxoplasma gondii. In The Model Apicomplexan: Perspectives and Methods; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 499–545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Jia, H. Biogenesis and maintenance of the apicoplast in model apicomplexan parasites. Parasitol. Int. 2021, 81, 102270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, A.; Mastud, P.; Patankar, S. Dually localised proteins found in both the apicoplast and mitochondrion utilize the Golgi-dependent pathway for apicoplast targeting in Toxoplasma gondii. Biol. Cell 2021, 113, 58–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.H.; King, T.P.; Ayong, L.; Asady, B.; Cai, X.; Rahman, T.; Vella, S.A.; Coppens, I.; Patel, S.; Moreno, S.N.J. A plastid two-pore channel essential for inter-organelle communication and growth of Toxoplasma gondii. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, Y.; Xia, N.; Fan, B.; Niu, Z.; He, Z.; Wang, X.; Yuan, J.; Gupta, N.; Shen, B. A pyruvate transporter in the apicoplast of apicomplexan parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2314314121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnataki, A.; Derocher, A.; Coppens, I.; Nash, C.; Feagin, J.E.; Parsons, M. Cell cycle-regulated vesicular trafficking of Toxoplasma APT1, a protein localized to multiple apicoplast membranes. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 63, 1653–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheiner, L.; Fellows, J.D.; Ovciarikova, J.; Brooks, C.F.; Agrawal, S.; Holmes, Z.C.; Bietz, I.; Flinner, N.; Heiny, S.; Mirus, O.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii Toc75 Functions in Import of Stromal but not Peripheral Apicoplast Proteins. Traffic 2015, 16, 1254–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, S.; van Dooren, G.G.; Agrawal, S.; Brooks, C.F.; McFadden, G.I.; Striepen, B.; Higgins, M.K. Tic22 is an essential chaperone required for protein import into the apicoplast. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 39505–39512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yang, J.; He, K.; Zheng, W.B.; Lai, D.H.; Liu, J.; Ding, H.Y.; Wu, R.B.; Brown, K.M.; Hide, G.; et al. The Toxoplasma monocarboxylate transporters are involved in the metabolism within the apicoplast and are linked to parasite survival. Elife 2024, 12, RP88866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Brown, K.M.; Drewry, L.L.; Anthony, B.; Phan, I.Q.H.; Sibley, L.D. Calmodulin-like proteins localized to the conoid regulate motility and cell invasion by Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.M.; Long, S.; Sibley, L.D. Plasma Membrane Association by N-Acylation Governs PKG Function in Toxoplasma gondii. mBio 2017, 8, e00375-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Lindsay, D.S.; Speer, C.A. Structures of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites, bradyzoites, and sporozoites and biology and development of tissue cysts. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1998, 11, 267–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, F.; Soldati-Favre, D. Metabolic Pathways in the Apicoplast of Apicomplexa. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 281, 161–228. [Google Scholar]
- Kloehn, J.; Lacour, C.E.; Soldati-Favre, D. The metabolic pathways and transporters of the plastid organelle in Apicomplexa. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2021, 63, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiny, S.R.; Pautz, S.; Recker, M.; Przyborski, J.M. Protein Traffic to the Plasmodium falciparum apicoplast: Evidence for a sorting branch point at the Golgi. Traffic 2014, 15, 1290–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaderi, S.; Levkau, B. An erythrocyte-centric view on the MFSD2B sphingosine-1-phosphate transporter. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 249, 108483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perland, E.; Bagchi, S.; Klaesson, A.; Fredriksson, R. Characteristics of 29 novel atypical solute carriers of major facilitator superfamily type: Evolutionary conservation, predicted structure and neuronal co-expression. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, N.; Pain, A.; Berriman, M.; Churcher, C.; Harris, B.; Harris, D.; Mungall, K.; Bowman, S.; Atkin, R.; Baker, S.; et al. Sequence of Plasmodium falciparum chromosomes 1, 3-9 and 13. Nature 2002, 419, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E.; Pino, P.; Foth, B.J.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Sheiner, L.; Schepers, R.; Soldati, T.; Soldati-Favre, D. Dual Targeting of Antioxidant and Metabolic Enzymes to the Mitochondrion and the Apicoplast of Toxoplasma gondii. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Shen, B. Transcriptomic analyses reveal distinct response of porcine macrophages to Toxoplasma gondii infection. Parasitol. Res. 2020, 119, 1819–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelenska, J.; Crawford, M.J.; Harb, O.S.; Zuther, E.; Haselkorn, R.; Roos, D.S.; Gornicki, P. Subcellular localization of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2723–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, S.; Shunmugam, S.; Berry, L.; Arnold, C.S.; Katris, N.J.; Duley, S.; Pierrel, F.; Cesbron-Delauw, M.F.; Yamaryo-Botté, Y.; Botté, C.Y. Toxoplasma LIPIN is essential in channeling host lipid fluxes through membrane biogenesis and lipid storage. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, L.; Mo, X.; Pan, M.; Shen, B.; Fang, R.; Hu, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, Y. Essential Functions of Calmodulin and Identification of Its Proximal Interacting Proteins in Tachyzoite-Stage Toxoplasma gondii via BioID Technology. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0136322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, K.; Crisafulli, E.M.; Ralph, S.A. Delayed Death by Plastid Inhibition in Apicomplexan Parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, N.; Shrestha, A.; Ruttkowski, B.; Beck, T.; Vogl, C.; Tomley, F.; Blake, D.P.; Joachim, A. The genome of the protozoan parasite Cystoisospora suis and a reverse vaccinology approach to identify vaccine candidates. Int. J. Parasitol. 2017, 47, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocamora, F.; Gupta, P.; Istvan, E.S.; Luth, M.R.; Carpenter, E.F.; Kümpornsin, K.; Sasaki, E.; Calla, J.; Mittal, N.; Carolino, K.; et al. PfMFR3: A Multidrug-Resistant Modulator in Plasmodium falciparum. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, Q.; Yu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Min, H.; Qiu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Miao, J.; Cui, L.; et al. An MFS-Domain Protein Pb115 Plays a Critical Role in Gamete Fertilization of the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium berghei. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, W.; Dong, H.; Lai, D.H.; Yang, J.; He, K.; Tang, X.; Liu, Q.; Hide, G.; Zhu, X.Q.; Sibley, L.D.; et al. The Toxoplasma micropore mediates endocytosis for selective nutrient salvage from host cell compartments. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Tang, T.; Ding, H.; Dong, H.; Long, S.; Suo, X. The Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporter HAP12 Is Critical in Toxoplasma gondii Survival and Virulence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083910
Chen X, Tang T, Ding H, Dong H, Long S, Suo X. The Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporter HAP12 Is Critical in Toxoplasma gondii Survival and Virulence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083910
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaowei, Tao Tang, Huiyong Ding, Hui Dong, Shaojun Long, and Xun Suo. 2025. "The Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporter HAP12 Is Critical in Toxoplasma gondii Survival and Virulence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083910
APA StyleChen, X., Tang, T., Ding, H., Dong, H., Long, S., & Suo, X. (2025). The Major Facilitator Superfamily Transporter HAP12 Is Critical in Toxoplasma gondii Survival and Virulence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083910





