BRAF Targeting Across Solid Tumors: Molecular Aspects and Clinical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
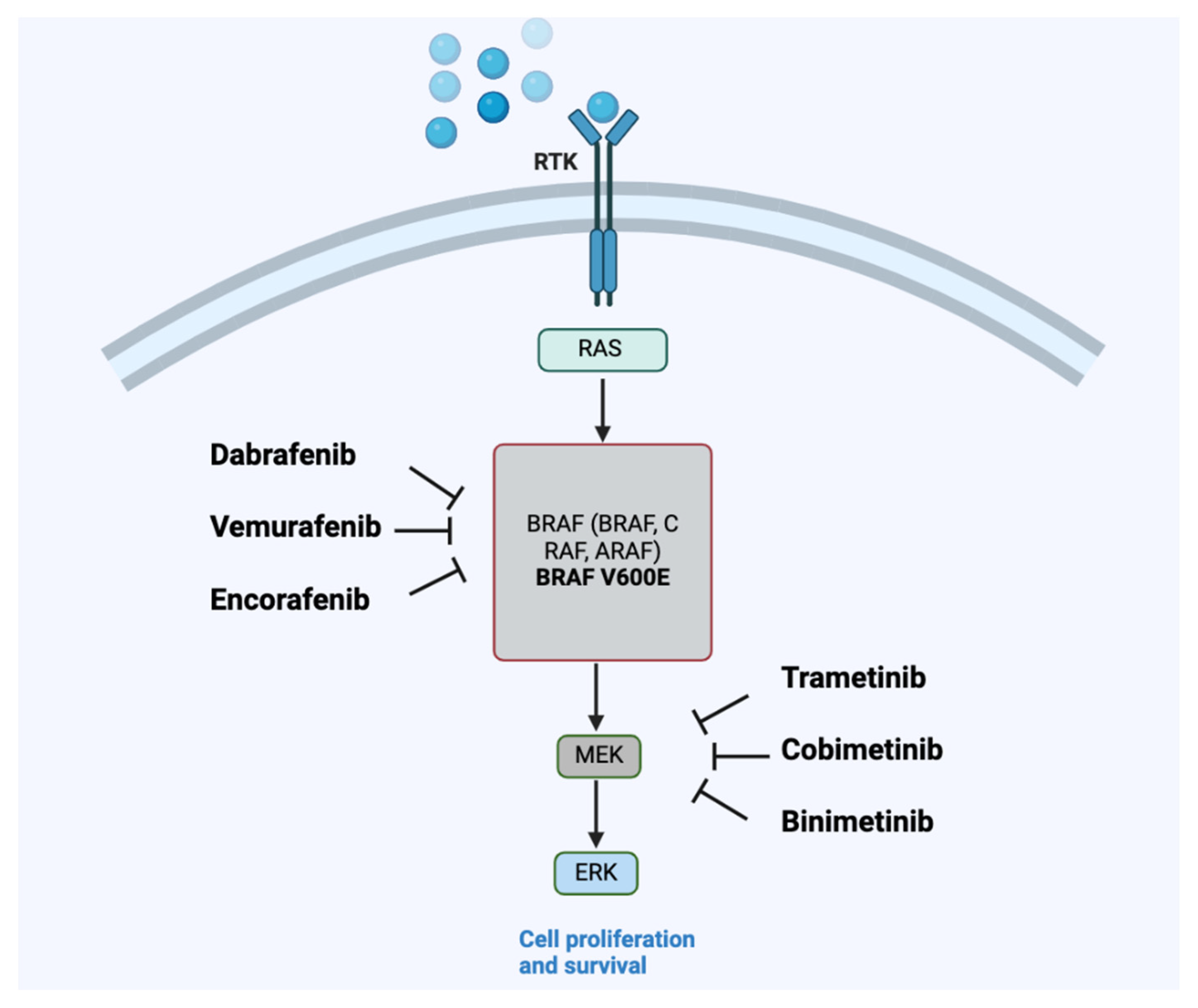
2. BRAF Biology and Its Therapeutical Implication
2.1. Impact of BRAF Mutation on Prognosis
2.2. Implication of BRAF Mutation on Immunotherapy Efficacy
3. Selected Strategies in BRAF-Mutated Solid Cancers
3.1. Melanoma
3.2. Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
3.3. Thyroid Cancer
3.4. Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
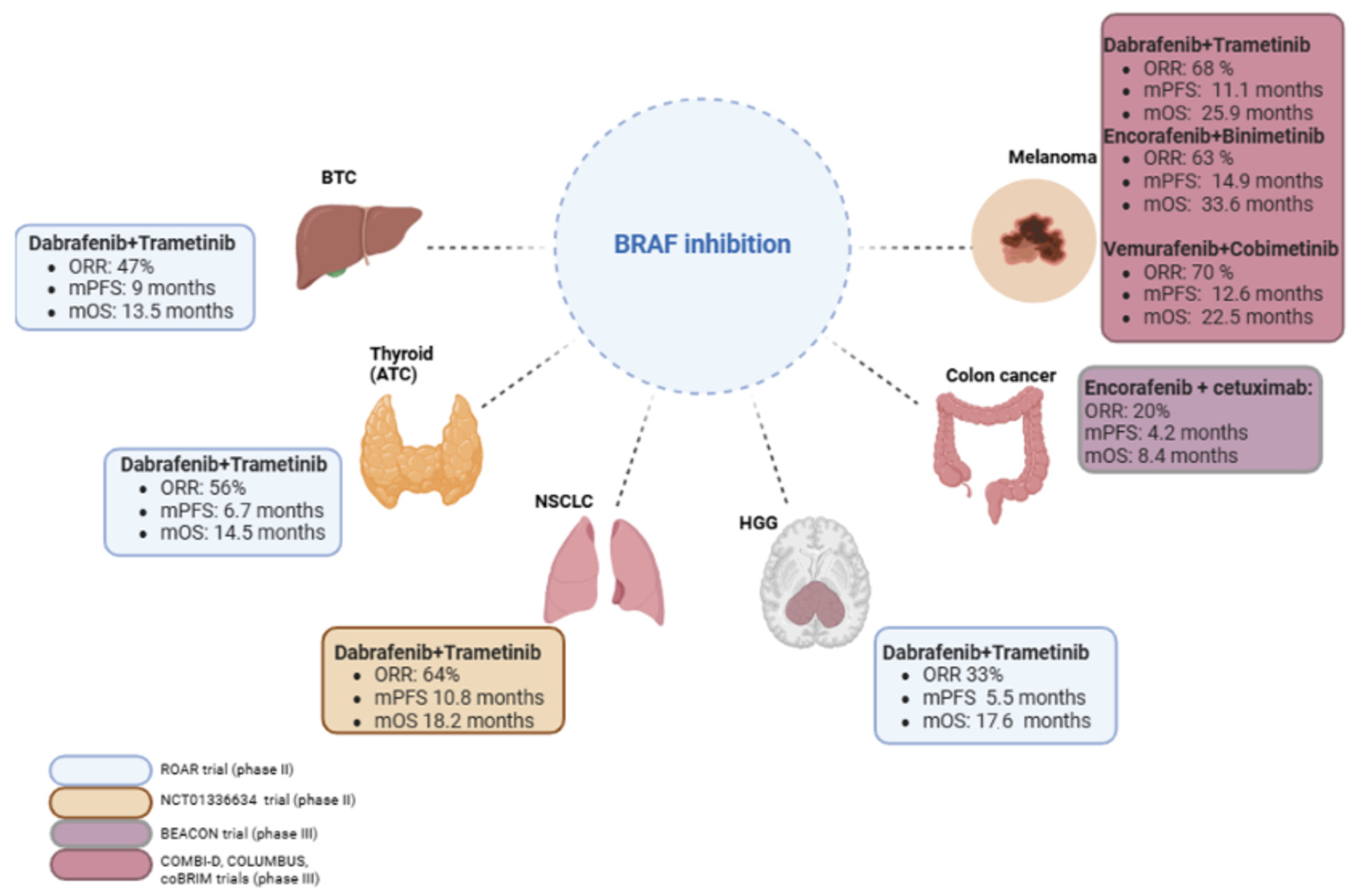
4. Agnostic Approach to BRAF Inhibition: Selected Examples of Rare Tumors
5. Mechanisms of Resistance
5.1. Intrinsic Resistance
5.2. Acquired Resistance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, H.; Bignell, G.R.; Cox, C.; Stephens, P.; Edkins, S.; Clegg, S.; Teague, J.; Woffendin, H.; Garnett, M.J.; Bottomley, W.; et al. Mutations of the BRAF Gene in Human Cancer. Nature 2002, 417, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leicht, D.T.; Balan, V.; Kaplun, A.; Singh-Gupta, V.; Kaplun, L.; Dobson, M.; Tzivion, G. Raf Kinases: Function, Regulation and Role in Human Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 1196–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, A.; Wu, W.; Bivona, T.G. Targeting Oncogenic BRAF: Past, Present, and Future. Cancers 2019, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanrahan, A.J.; Chen, Z.; Rosen, N.; Solit, D.B. BRAF—A Tumour-Agnostic Drug Target with Lineage-Specific Dependencies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 224–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, M.E.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, D.R. Targeting the RAS/RAF/MAPK Pathway for Cancer Therapy: From Mechanism to Clinical Studies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desideri, E.; Cavallo, A.L.; Baccarini, M. Alike but Different: RAF Paralogs and Their Signaling Outputs. Cell 2015, 161, 967–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, M.; Chen, W.; Cobb, M.H. Differential Regulation and Properties of MAPKs. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3100–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Lovly, C.M. Mechanisms of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation in Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibb, N.J.; Dilworth, S.M.; Mol, C.D. Switching on Kinases: Oncogenic Activation of BRAF and the PDGFR Family. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaeger, R.; Corcoran, R.B. Targeting Alterations in the RAF–MEK Pathway. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lito, P.; Pratilas, C.A.; Joseph, E.W.; Tadi, M.; Halilovic, E.; Zubrowski, M.; Huang, A.; Wong, W.L.; Callahan, M.K.; Merghoub, T.; et al. Relief of Profound Feedback Inhibition of Mitogenic Signaling by RAF Inhibitors Attenuates Their Activity in BRAFV600E Melanomas. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 668–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzies, A.M.; Haydu, L.E.; Visintin, L.; Carlino, M.S.; Howle, J.R.; Thompson, J.F.; Kefford, R.F.; Scolyer, R.A.; Long, G.V. Distinguishing Clinicopathologic Features of Patients with V600E and V600K BRAF-Mutant Metastatic Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3242–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, M.L.; Vidwans, S.J.; Janku, F.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; Munoz, J.; Schwab, R.; Subbiah, V.; Rodon, J.; Kurzrock, R. Genomically Driven Tumors and Actionability across Histologies: BRAF-Mutant Cancers as a Paradigm. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Yaeger, R.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.S.; Tao, A.; Torres, N.M.; Chang, M.T.; Drosten, M.; Zhao, H.; Cecchi, F.; Hembrough, T.; et al. Tumours with Class 3 BRAF Mutants Are Sensitive to the Inhibition of Activated RAS. Nature 2017, 548, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisone, D.; Friedlaender, A.; Malapelle, U.; Banna, G.; Addeo, A. A BRAF New World. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2020, 152, 103008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özgü, E.; Kaplan, B.G.; Sivakumar, S.; Sokol, E.S.; Aydın, E.; Tokat, Ü.M.; Adibi, A.; Karakoç, E.G.; Hu, J.; Kurzrock, R.; et al. Therapeutic Vulnerabilities and Pan-Cancer Landscape of BRAF Class III Mutations in Epithelial Solid Tumors. BJC Rep. 2024, 2, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.M.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Patients with Previously Untreated BRAFV600E-Mutant Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Kreitman, R.J.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Gazzah, A.; Lassen, U.; Stein, A.; Wen, P.Y.; Dietrich, S.; De Jonge, M.J.A.; Blay, J.-Y.; et al. Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in BRAFV600E-Mutated Rare Cancers: The Phase 2 ROAR Trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.E.; Edmiston, S.N.; Alexander, A.; Groben, P.A.; Parrish, E.; Kricker, A.; Armstrong, B.K.; Anton-Culver, H.; Gruber, S.B.; From, L.; et al. Association Between NRAS and BRAF Mutational Status and Melanoma-Specific Survival Among Patients with Higher-Risk Primary Melanoma. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires Da Silva, I.; Wang, K.Y.X.; Wilmott, J.S.; Holst, J.; Carlino, M.S.; Park, J.J.; Quek, C.; Wongchenko, M.; Yan, Y.; Mann, G.; et al. Distinct Molecular Profiles and Immunotherapy Treatment Outcomes of V600E and V600K BRAF-Mutant Melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, A.P.; Tang, Y.H.; Armour, N.; Dutton-Regester, K.; Krause, L.; Loffler, K.A.; Lambie, D.; Burmeister, B.; Thomas, J.; Smithers, B.M.; et al. BRAF Mutation Status Is an Independent Prognostic Factor for Resected Stage IIIB and IIIC Melanoma: Implications for Melanoma Staging and Adjuvant Therapy. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.N.; Kopetz, E.S. BRAF Mutant Colorectal Cancer as a Distinct Subset of Colorectal Cancer: Clinical Characteristics, Clinical Behavior, and Response to Targeted Therapies. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2015, 6, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Riordan, E.; Bennett, M.W.; Daly, L.; Power, D.G. The Implication of BRAF Mutation in Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 191, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibodeau, S.N.; French, A.J.; Cunningham, J.M.; Tester, D.; Burgart, L.J.; Roche, P.C.; McDonnell, S.K.; Schaid, D.J.; Vockley, C.W.; Michels, V.V.; et al. Microsatellite Instability in Colorectal Cancer: Different Mutator Phenotypes and the Principal Involvement of hMLH1. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar]
- Bond, C.E.; Whitehall, V.L.J. How the BRAF V600E Mutation Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Colorectal Cancer: Molecular and Clinical Implications. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 9250757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremolini, C.; Loupakis, F.; Antoniotti, C.; Lupi, C.; Sensi, E.; Lonardi, S.; Mezi, S.; Tomasello, G.; Ronzoni, M.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. FOLFOXIRI plus Bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus Bevacizumab as First-Line Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Updated Overall Survival and Molecular Subgroup Analyses of the Open-Label, Phase 3 TRIBE Study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samowitz, W.S.; Sweeney, C.; Herrick, J.; Albertsen, H.; Levin, T.R.; Murtaugh, M.A.; Wolff, R.K.; Slattery, M.L. Poor Survival Associated with the BRAF V600E Mutation in Microsatellite-Stable Colon Cancers. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6063–6069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lochhead, P.; Kuchiba, A.; Imamura, Y.; Liao, X.; Yamauchi, M.; Nishihara, R.; Qian, Z.R.; Morikawa, T.; Shen, J.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; et al. Microsatellite Instability and BRAF Mutation Testing in Colorectal Cancer Prognostication. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taieb, J.; Le Malicot, K.; Shi, Q.; Penault Lorca, F.; Bouché, O.; Tabernero, J.; Mini, E.; Goldberg, R.M.; Folprecht, G.; Luc Van Laethem, J.; et al. Prognostic Value of BRAF and KRAS Mutations in MSI and MSS Stage III Colon Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, D.; Vitiello, P.P.; Cardone, C.; Martini, G.; Troiani, T.; Martinelli, E.; Ciardiello, F. Immunotherapy of Colorectal Cancer: Challenges for Therapeutic Efficacy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2019, 76, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, C.E.; Umapathy, A.; Buttenshaw, R.L.; Wockner, L.; Leggett, B.A.; Whitehall, V.L.J. Chromosomal Instability in BRAF Mutant, Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Federico, A.D.; Ricci, A.D.; Frega, G.; Palloni, A.; Pagani, R.; Tavolari, S.; Marco, M.D.; Brandi, G. Targeting BRAF-Mutant Biliary Tract Cancer: Recent Advances and Future Challenges. Cancer Control 2020, 27, 107327482098301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cui, Y.; Yin, F.; Peng, L.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wen, S.; Shi, J.; Lei, M.; et al. BRAF Mutation in Chinese Biliary Tract Cancer Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S15), e16678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannapfel, A. Mutations of the BRAF Gene in Cholangiocarcinoma but Not in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2003, 52, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, S.; Hyder, O.; Dodson, R.; Nayar, S.K.; Poling, J.; Beierl, K.; Eshleman, J.R.; Lin, M.-T.; Pawlik, T.M.; Anders, R.A. The Frequency of KRAS and BRAF Mutations in Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinomas and Their Correlation with Clinical Outcome. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2768–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, A.; Felicioni, L.; Malatesta, S.; Grazia Sciarrotta, M.; Guetti, L.; Chella, A.; Viola, P.; Pullara, C.; Mucilli, F.; Buttitta, F. Clinical Features and Outcome of Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3574–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imielinski, M.; Berger, A.H.; Hammerman, P.S.; Hernandez, B.; Pugh, T.J.; Hodis, E.; Cho, J.; Suh, J.; Capelletti, M.; Sivachenko, A.; et al. Mapping the Hallmarks of Lung Adenocarcinoma with Massively Parallel Sequencing. Cell 2012, 150, 1107–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlaender, A.; Banna, G.; Malapelle, U.; Pisapia, P.; Addeo, A. Next Generation Sequencing and Genetic Alterations in Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma: Where Are We Today? Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, J. A Large-Scale, Multicenter Characterization of BRAF G469V/A-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chen, W.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Su, W.-C. Durable Response to Combined Dabrafenib and Trametinib in a Patient with BRAF K601E Mutation-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Tseng, L.-H.; Chen, G.; Haley, L.; Illei, P.; Gocke, C.D.; Eshleman, J.R.; Lin, M.-T. Clinical Detection and Categorization of Uncommon and Concomitant Mutations Involving BRAF. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faehling, M.; Schwenk, B.; Kramberg, S.; Eckert, R.; Volckmar, A.-L.; Stenzinger, A.; Sträter, J. Oncogenic Driver Mutations, Treatment, and EGFR-TKI Resistance in a Caucasian Population with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Survival in Clinical Practice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77897–77914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguera, G.; Majem, M. BRAF Inhibitors in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M. BRAF Mutation in Thyroid Cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2005, 12, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Shugard, E.; Khanafshar, E.; Quivey, J.M.; Garsa, A.A.; Yom, S.S. Association Between BRAF V600E Mutation and Decreased Survival in Patients Locoregionally Irradiated for Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, E356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Alzahrani, A.S.; Carson, K.A.; Viola, D.; Elisei, R.; Bendlova, B.; Yip, L.; Mian, C.; Vianello, F.; Tuttle, R.M.; et al. Association Between BRAF V600E Mutation and Mortality in Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer. JAMA 2013, 309, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufano, R.P.; Teixeira, G.V.; Bishop, J.; Carson, K.A.; Xing, M. BRAF Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Cancer and Its Value in Tailoring Initial Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2012, 91, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Hu, S.; Hou, P.; Jiang, D.; Condouris, S.; Xing, M. Suppression of BRAF/MEK/MAP Kinase Pathway Restores Expression of Iodide-Metabolizing Genes in Thyroid Cells Expressing the V600E BRAF Mutant. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D. Synergistic Inhibition of MEK/ERK and BRAF V600E with PD98059 and PLX4032 Induces Sodium/Iodide Symporter (NIS) Expression and Radioiodine Uptake in BRAF Mutated Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cells. Thyroid. Res. 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Bojdani, E.; Xing, M. Induction of Thyroid Gene Expression and Radioiodine Uptake in Thyroid Cancer Cells by Targeting Major Signaling Pathways. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Kim, T.W.; Van Cutsem, E.; Geva, R.; Jäger, D.; Hara, H.; Burge, M.; O’Neil, B.; Kavan, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Phase II Open-Label Study of Pembrolizumab in Treatment-Refractory, Microsatellite Instability-High/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: KEYNOTE-164. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichenthal, M.; Svane, I.M.; Kandolf Sekulovic, L.; Mangana, J.; Mohr, P.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; Schmidt, H.; Ziogas, D.C.; Bender, M.; Ellebaek, E.; et al. EMRseq: Registry-Based Outcome Analysis on 1,000 Patients with BRAF V600–Mutated Metastatic Melanoma in Europe Treated with Either Immune Checkpoint or BRAF-/MEK Inhibition. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 9540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, T.; Lonardi, S.; Wong, K.Y.M.; Lenz, H.-J.; Gelsomino, F.; Aglietta, M.; Morse, M.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; McDermott, R.; Hill, A.; et al. Nivolumab plus Low-Dose Ipilimumab in Previously Treated Patients with Microsatellite Instability-High/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: 4-Year Follow-up from CheckMate 142. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, T.; Shiu, K.-K.; Kim, T.W.; Jensen, B.V.; Jensen, L.H.; Punt, C.; Smith, D.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Benavides, M.; Gibbs, P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Microsatellite-Instability-High Advanced Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechahougui, H.; Friedlaender, A. Unraveling the Nexus: Oncogenic Drivers and Immunotherapy Efficacy in Cancer Treatment. Immunotherapy 2024, 16, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.; Lopes, L.; Lee, S.; Riano, I.; Saeed, A. The Prognostic and Predictive Impact of BRAF Mutations in Deficient Mismatch Repair/Microsatellite Instability-High Colorectal Cancer: Systematic Review/Meta-Analysis. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngoc, T.; Bouchaab, H.; Adjei, A.A.; Peters, S. BRAF Alterations as Therapeutic Targets in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Cheng, G.; Xie, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, Y.; Xi, W.; Fan, Y. Tumor Immune Microenvironment and Immunotherapy Efficacy in BRAF Mutation Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Drilon, A.; Lusque, A.; Mhanna, L.; Cortot, A.B.; Mezquita, L.; Thai, A.A.; Mascaux, C.; Couraud, S.; Veillon, R.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Patients with Advanced Lung Cancer and Oncogenic Driver Alterations: Results from the IMMUNOTARGET Registry. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, L.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.S.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Solomon, B.J.; et al. Oncogene-Addicted Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-Up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Schachter, J.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2521–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comin-Anduix, B.; Chodon, T.; Sazegar, H.; Matsunaga, D.; Mock, S.; Jalil, J.; Escuin-Ordinas, H.; Chmielowski, B.; Koya, R.C.; Ribas, A. The Oncogenic BRAF Kinase Inhibitor PLX4032/RG7204 Does Not Affect the Viability or Function of Human Lymphocytes across a Wide Range of Concentrations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6040–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holderfield, M.; Nagel, T.E.; Stuart, D.D. Mechanism and Consequences of RAF Kinase Activation by Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Vence, L.; Falchook, G.; Radvanyi, L.G.; Liu, C.; Goodman, V.; Legos, J.J.; Blackman, S.; Scarmadio, A.; Kurzrock, R.; et al. BRAF(V600) Inhibitor GSK2118436 Targeted Inhibition of Mutant BRAF in Cancer Patients Does Not Impair Overall Immune Competency. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2326–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuske, M.; Westphal, D.; Wehner, R.; Schmitz, M.; Beissert, S.; Praetorius, C.; Meier, F. Immunomodulatory Effects of BRAF and MEK Inhibitors: Implications for Melanoma Therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 136, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Simeone, E.; Sileni, V.C.; Del Vecchio, M.; Marchetti, P.; Cappellini, G.C.A.; Ridolfi, R.; de Rosa, F.; Cognetti, F.; Ferraresi, V.; et al. Sequential Treatment with Ipilimumab and BRAF Inhibitors in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma: Data from the Italian Cohort of the Ipilimumab Expanded Access Program. Cancer Investig. 2014, 32, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, M.B.; Lee, S.J.; Chmielowski, B.; Tarhini, A.A.; Cohen, G.I.; Truong, T.-G.; Moon, H.H.; Davar, D.; O’Rourke, M.; Stephenson, J.J.; et al. Combination Dabrafenib and Trametinib Versus Combination Nivolumab and Ipilimumab for Patients with Advanced BRAF-Mutant Melanoma: The DREAMseq Trial—ECOG-ACRIN EA6134. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Gogas, H.; Levchenko, E.; De Braud, F.; Larkin, J.; Garbe, C.; Jouary, T.; Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.-J.; et al. Dabrafenib and Trametinib versus Dabrafenib and Placebo for Val600 BRAF-Mutant Melanoma: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.-J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. Dabrafenib in BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma: A Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 3 Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortot, A.B.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Molinier, O.; Le Moulec, S.; Barlesi, F.; Zalcman, G.; Dumont, P.; Pouessel, D.; Poulet, C.; Fontaine-Delaruelle, C.; et al. Weekly Paclitaxel plus Bevacizumab versus Docetaxel as Second- or Third-Line Treatment in Advanced Non-Squamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results of the IFCT-1103 ULTIMATE Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 131, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopetz, S.; Grothey, A.; Yaeger, R.; Van Cutsem, E.; Desai, J.; Yoshino, T.; Wasan, H.; Ciardiello, F.; Loupakis, F.; Hong, Y.S.; et al. Encorafenib, Binimetinib, and Cetuximab in BRAF V600E–Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1632–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Massari, F.; MacLennan, G.T.; Montironi, R. Molecular Testing for BRAF Mutations to Inform Melanoma Treatment Decisions: A Move toward Precision Medicine. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Baik, C.; Kirkwood, J.M. Clinical Development of BRAF plus MEK Inhibitor Combinations. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheault, T.R.; Stellwagen, J.C.; Adjabeng, G.M.; Hornberger, K.R.; Petrov, K.G.; Waterson, A.G.; Dickerson, S.H.; Mook, R.A.; Laquerre, S.G.; King, A.J.; et al. Discovery of Dabrafenib: A Selective Inhibitor of Raf Kinases with Antitumor Activity against B-Raf-Driven Tumors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellani, G.; Buccarelli, M.; Arasi, M.B.; Rossi, S.; Pisanu, M.E.; Bellenghi, M.; Lintas, C.; Tabolacci, C. BRAF Mutations in Melanoma: Biological Aspects, Therapeutic Implications, and Circulating Biomarkers. Cancers 2023, 15, 4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; McKee, A.E.; Ning, Y.-M.; Hazarika, M.; Theoret, M.; Johnson, J.R.; Xu, Q.C.; Tang, S.; Sridhara, R.; Jiang, X.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Vemurafenib for Treatment of Unresectable or Metastatic Melanoma with the BRAFV600E Mutation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4994–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved Survival with Vemurafenib in Melanoma with BRAF V600E Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Robert, C.; Larkin, J.; Haanen, J.B.; Ribas, A.; Hogg, D.; Hamid, O.; Ascierto, P.A.; Testori, A.; Lorigan, P.C.; et al. Vemurafenib in Patients with BRAFV600 Mutation-Positive Metastatic Melanoma: Final Overall Survival Results of the Randomized BRIM-3 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, G.A.; Maio, M.; Arance, A.; Nathan, P.; Blank, C.; Avril, M.-F.; Garbe, C.; Hauschild, A.; Schadendorf, D.; Hamid, O.; et al. Vemurafenib in Metastatic Melanoma Patients with Brain Metastases: An Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase 2, Multicentre Study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.J.; Demidov, L.V.; Jouary, T.; Gutzmer, R.; Millward, M.; Rutkowski, P.; Blank, C.U.; Miller, W.H.; Kaempgen, E.; et al. An Update on BREAK-3, a Phase III, Randomized Trial: Dabrafenib (DAB) versus Dacarbazine (DTIC) in Patients with BRAF V600E-Positive Mutation Metastatic Melanoma (MM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31 (Suppl. S15), 9013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, K.T.; Robert, C.; Hersey, P.; Nathan, P.; Garbe, C.; Milhem, M.; Demidov, L.V.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; Mohr, P.; et al. Improved Survival with MEK Inhibition in BRAF-Mutated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Flaherty, K.; Nathan, P.; Hersey, P.; Garbe, C.; Milhem, M.; Demidov, L.; Mohr, P.; Hassel, J.C.; Rutkowski, P.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes from a Phase 3 METRIC Study in Patients with BRAF V600 E/K–Mutant Advanced or Metastatic Melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 109, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Gogas, H.; Levchenko, E.; De Braud, F.; Larkin, J.; Garbe, C.; Jouary, T.; Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.J.; et al. Combined BRAF and MEK Inhibition versus BRAF Inhibition Alone in Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1877–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Dréno, B.; Atkinson, V.; Liszkay, G.; Maio, M.; Mandalà, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. Combined Vemurafenib and Cobimetinib in BRAF-Mutated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; McArthur, G.A.; Dréno, B.; Atkinson, V.; Liszkay, G.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; Mandalà, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. Cobimetinib Combined with Vemurafenib in Advanced BRAFV600-Mutant Melanoma (coBRIM): Updated Efficacy Results from a Randomised, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Dréno, B.; Larkin, J.; Ribas, A.; Liszkay, G.; Maio, M.; Mandalà, M.; Demidov, L.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Thomas, L.; et al. 5-Year Outcomes with Cobimetinib plus Vemurafenib in BRAF V600 Mutation–Positive Advanced Melanoma: Extended Follow-up of the coBRIM Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 5225–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Stroyakovsky, D.L.; Gogas, H.; Levchenko, E.; De Braud, F.; Larkin, J.M.G.; Garbe, C.; Jouary, T.; Hauschild, A.; Grob, J.J.; et al. COMBI-d: A Randomized, Double-Blinded, Phase III Study Comparing the Combination of Dabrafenib and Trametinib to Dabrafenib and Trametinib Placebo as First-Line Therapy in Patients (Pts) with Unresectable or Metastatic BRAF V600E/K Mutation-Positive Cutaneous Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32 (Suppl. S15), 9011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Flaherty, K.T.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Gogas, H.; Levchenko, E.; De Braud, F.; Larkin, J.; Garbe, C.; Jouary, T.; Hauschild, A.; et al. Dabrafenib plus Trametinib versus Dabrafenib Monotherapy in Patients with Metastatic BRAF V600E/K-Mutant Melanoma: Long-Term Survival and Safety Analysis of a Phase 3 Study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Karaszewska, B.; Schachter, J.; Rutkowski, P.; Mackiewicz, A.; Stroiakovski, D.; Lichinitser, M.; Dummer, R.; Grange, F.; Mortier, L.; et al. Improved Overall Survival in Melanoma with Combined Dabrafenib and Trametinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A.; Saiag, P.; Robert, C.; Grob, J.-J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Arance, A.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Thomas, L.; Lesimple, T.; Mortier, L.; et al. Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Patients with BRAFV600-Mutant Melanoma Brain Metastases (COMBI-MB): A Multicentre, Multicohort, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, G.V.; Hauschild, A.; Santinami, M.; Atkinson, V.; Mandalà, M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Larkin, J.; Nyakas, M.; Dutriaux, C.; Haydon, A.; et al. Adjuvant Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Stage III BRAF-Mutated Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Encorafenib plus Binimetinib versus Vemurafenib or Encorafenib in Patients with BRAF -Mutant Melanoma (COLUMBUS): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Overall Survival in Patients with BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Receiving Encorafenib plus Binimetinib versus Vemurafenib or Encorafenib (COLUMBUS): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, R.; Flaherty, K.T.; Robert, C.; Arance, A.; De Groot, J.W.B.; Garbe, C.; Gogas, H.J.; Gutzmer, R.; Krajsová, I.; Liszkay, G.; et al. COLUMBUS 5-Year Update: A Randomized, Open-Label, Phase III Trial of Encorafenib Plus Binimetinib Versus Vemurafenib or Encorafenib in Patients with BRAF V600–Mutant Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 4178–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudnik, E.; Peled, N.; Nechushtan, H.; Wollner, M.; Onn, A.; Agbarya, A.; Moskovitz, M.; Keren, S.; Popovits-Hadari, N.; Urban, D.; et al. BRAF Mutant Lung Cancer: Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression, Tumor Mutational Burden, Microsatellite Instability Status, and Response to Immune Check-Point Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Facchinetti, F.; Rossi, G.; Minari, R.; Conti, A.; Friboulet, L.; Tiseo, M.; Planchard, D. BRAF in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): Pickaxing Another Brick in the Wall. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2018, 66, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Martinez, P.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ambrogio, C.; Ferris, L.A.; Lydon, C.; Nguyen, T.; Jessop, N.A.; Iafrate, A.J.; Johnson, B.E.; et al. Impact of BRAF Mutation Class on Disease Characteristics and Clinical Outcomes in BRAF-Mutant Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankner, M.; Lajoie, M.; Moldoveanu, D.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Savage, P.; Rajkumar, S.; Huang, X.; Lvova, M.; Protopopov, A.; Vuzman, D.; et al. Dual MAPK Inhibition Is an Effective Therapeutic Strategy for a Subset of Class II BRAF Mutant Melanomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6483–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautschi, O.; Milia, J.; Cabarrou, B.; Bluthgen, M.-V.; Besse, B.; Smit, E.F.; Wolf, J.; Peters, S.; Früh, M.; Koeberle, D.; et al. Targeted Therapy for Patients with BRAF-Mutant Lung Cancer Results from the European EURAF Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Gervais, R.; Riely, G.; Hollebecque, A.; Blay, J.-Y.; Felip, E.; Schuler, M.; Gonçalves, A.; Italiano, A.; Keedy, V.; et al. Efficacy of Vemurafenib in Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with BRAF V600 Mutation: An Open-Label, Single-Arm Cohort of the Histology-Independent VE-BASKET Study. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazieres, J.; Montané, L.; Barlesi, F.; Coudert, B.; Souquet, P.J.; Otto, J.; Gervais, R.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Monnet, I.; Brain, E.; et al. OA12.05 Vemurafenib in Patients Harboring V600 and Non V600 BRAF Mutations: Final Results of the NSCLC Cohort from the AcSé Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, S348–S349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazieres, J.; Cropet, C.; Montané, L.; Barlesi, F.; Souquet, P.J.; Quantin, X.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Otto, J.; Favier, L.; Avrillon, V.; et al. Vemurafenib in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients with BRAFV600 and BRAFnonV600 Mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, R.; Mayo-de-las-Casas, C.; Teixidó, C.; Cabrera, C.; Marín, E.; Vollmer, I.; Jares, P.; Garzón, M.; Molina-Vila, M.Á.; Reguart, N. Clinical Benefit From BRAF/MEK Inhibition in a Double Non-V600E BRAF Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Case Report. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e219–e223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, H.; Adachi, Y.; Kitai, H.; Tomida, S.; Bando, H.; Faber, A.C.; Yoshino, T.; Voon, D.C.; Yano, S.; Ebi, H. Distinct Dependencies on Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in the Regulation of MAPK Signaling between BRAF V600E and Non-V600E Mutant Lung Cancers. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereno, M.; Moreno, V.; Moreno Rubio, J.; Gómez-Raposo, C.; García Sánchez, S.; Hernández Jusdado, R.; Falagan, S.; Zambrana Tébar, F.; Casado Sáenz, E. A Significant Response to Sorafenib in a Woman with Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma and a BRAF Non-V600 Mutation. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2015, 26, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadei Gardini, A.; Chiadini, E.; Faloppi, L.; Marisi, G.; Delmonte, A.; Scartozzi, M.; Loretelli, C.; Lucchesi, A.; Oboldi, D.; Dubini, A.; et al. Efficacy of Sorafenib in BRAF-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and No Response in Synchronous BRAF Wild Type-Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Case Report. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.W.; Eder, J.P.; Ryan, D.; Lathia, C.; Lenz, H.-J. Safety and Pharmacokinetics of the Dual Action Raf Kinase and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitor, BAY 43-9006, in Patients with Advanced, Refractory Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 5472–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.J.; Infante, J.R.; Janku, F.; Wong, D.J.L.; Sosman, J.A.; Keedy, V.; Patel, M.R.; Shapiro, G.I.; Mier, J.W.; Tolcher, A.W.; et al. First-in-Class ERK1/2 Inhibitor Ulixertinib (BVD-523) in Patients with MAPK Mutant Advanced Solid Tumors: Results of a Phase I Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, S.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Ding, H.; Pan, Y. Development of Small-Molecule Therapeutics and Strategies for Targeting RAF Kinase in BRAF-Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutuka, C.S.A.; Andrews, M.C.; Mariadason, J.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Hudson, C.; Cebon, J.; Behren, A. PLX8394, a New Generation BRAF Inhibitor, Selectively Inhibits BRAF in Colonic Adenocarcinoma Cells and Prevents Paradoxical MAPK Pathway Activation. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, R.J.; Hollebecque, A.; Flaherty, K.T.; Shapiro, G.I.; Rodon Ahnert, J.; Millward, M.J.; Zhang, W.; Gao, L.; Sykes, A.; Willard, M.D.; et al. A Phase I Study of LY3009120, a Pan-RAF Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.; Shin, S.J.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, Y.J.; Han, H.S.; Lee, S.J.; Lim, H.-S.; Hong, Y.; Noh, Y.S.; et al. Belvarafenib, a Novel Pan-RAF Inhibitor, in Solid Tumor Patients Harboring BRAF, KRAS, or NRAS Mutations: Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S15), 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboulleux, S.; Benisvy, D.; Taieb, D.; Attard, M.; Bournaud, C.; Terroir, M.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Lamartina, L.; Schlumberger, M.J.; Godbert, Y.; et al. 1743MO MERAIODE: A Redifferentiation Phase II Trial with Trametinib Followed by Radioactive Iodine for Metastatic Radioactive Iodine Refractory Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Patients with a RAS Mutation. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leboulleux, S.; Benisvy, D.; Taieb, D.; Attard, M.; Bournaud, C.; Terroir-Cassou-Mounat, M.; Lacroix, L.; Anizan, N.; Schiazza, A.; Garcia, M.E.; et al. MERAIODE: A Phase II Redifferentiation Trial with Trametinib and 131 I in Metastatic Radioactive Iodine Refractory RAS Mutated Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2023, 33, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Kreitman, R.J.; Wainberg, Z.A.; Cho, J.Y.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Soria, J.C.; Wen, P.Y.; Zielinski, C.C.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Boran, A.; et al. Dabrafenib plus Trametinib in Patients with BRAF V600E-Mutant Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Updated Analysis from the Phase II ROAR Basket Study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brose, M.S.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Cohen, E.E.W.; Wirth, L.J.; Riehl, T.; Yue, H.; Sherman, S.I.; Sherman, E.J. Vemurafenib in Patients with BRAFV600E-Positive Metastatic or Unresectable Papillary Thyroid Cancer Refractory to Radioactive Iodine: A Non-Randomised, Multicentre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.E.; Johnson, B.; Kugathasan, L.; Morris, V.K.; Raghav, K.; Swanson, L.; Lim, H.J.; Renouf, D.J.; Gill, S.; Wolber, R.; et al. Population-Based Screening for BRAF V600E in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Reveals Increased Prevalence and Poor Prognosis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4599–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.C.; Renfro, L.A.; Al-Shamsi, H.O.; Schrock, A.B.; Rankin, A.; Zhang, B.Y.; Kasi, P.M.; Voss, J.S.; Leal, A.D.; Sun, J.; et al. Non-V600 BRAF Mutations Define a Clinically Distinct Molecular Subtype of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2624–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osterlund, E.; Ristimäki, A.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Kytölä, S.; Kononen, J.; Pfeiffer, P.; Soveri, L.; Keinänen, M.; Sorbye, H.; Nunes, L.; et al. Atypical (non-V600E) BRAF Mutations in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Population and Real-world Cohorts. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 154, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.M.; Esmail, A.; Abdelrahim, M. Triple-Regimen of Vemurafenib, Irinotecan, and Cetuximab for the Treatment of BRAFV600E-Mutant CRC: A Case Report and Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 795381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, S.; Basu, G.D.; Hall, D.W.; Gatalica, Z. Tumor-Type Agnostic, Targeted Therapies: BRAF Inhibitors Join the Group. Acta Medica Acad. 2023, 51, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamarca, A.; Edeline, J.; Goyal, L. How I Treat Biliary Tract Cancer. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Kwong, L.N.; Javle, M. Genomic Profiling of Biliary Tract Cancers and Implications for Clinical Practice. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2016, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, A.K.S.; Li, S.; Macrae, E.R.; Park, J.-I.; Mitchell, E.P.; Zwiebel, J.A.; Chen, H.X.; Gray, R.J.; McShane, L.M.; Rubinstein, L.V.; et al. Dabrafenib and Trametinib in Patients with Tumors with BRAF V600E Mutations: Results of the NCI-MATCH Trial Subprotocol H. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3895–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nunno, V.; Gatto, L.; Tosoni, A.; Bartolini, S.; Franceschi, E. Implications of BRAF V600E Mutation in Gliomas: Molecular Considerations, Prognostic Value and Treatment Evolution. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1067252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklener, K.; Mazurek, M.; Wieteska, M.; Wacławska, M.; Bilski, M.; Mańdziuk, S. New Directions in the Therapy of Glioblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittapalli, R.K.; Vaidhyanathan, S.; Dudek, A.Z.; Elmquist, W.F. Mechanisms Limiting Distribution of the Threonine-Protein Kinase B-RaFV600E Inhibitor Dabrafenib to the Brain: Implications for the Treatment of Melanoma Brain Metastases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N.F.; Carter, T.; Kitchen, N.; Mulholland, P. Dabrafenib and Trametinib in BRAFV600E Mutated Glioma. CNS Oncol. 2017, 6, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim-Fat, M.J.; Song, K.W.; Iorgulescu, J.B.; Andersen, B.M.; Forst, D.A.; Jordan, J.T.; Gerstner, E.R.; Reardon, D.A.; Wen, P.Y.; Arrillaga-Romany, I. Clinical, Radiological and Genomic Features and Targeted Therapy in BRAF V600E Mutant Adult Glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol 2021, 152, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaley, T.; Touat, M.; Subbiah, V.; Hollebecque, A.; Rodon, J.; Lockhart, A.C.; Keedy, V.; Bielle, F.; Hofheinz, R.-D.; Joly, F.; et al. BRAF Inhibition in BRAFV600-Mutant Gliomas: Results From the VE-BASKET Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadducci, A.; Cosio, S. Therapeutic Approach to Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma: State of Art and Perspectives of Clinical Research. Cancers 2020, 12, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwimpfer, T.A.; Tal, O.; Geissler, F.; Coelho, R.; Rimmer, N.; Jacob, F.; Heinzelmann-Schwarz, V. Low Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer—A Rare Disease with Increasing Therapeutic Options. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 112, 102497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, T.J.; Bell, J.L.; Bruce, J.P.; Doherty, G.J.; Galvin, M.; Green, M.F.; Hunter-Zinck, H.; Kumari, P.; Lenoue-Newton, M.L.; Li, M.M.; et al. AACR Project GENIE: 100,000 Cases and Beyond. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2044–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, B.J.; Grisham, R.N.; Banerjee, S.; Kalbacher, E.; Mirza, M.R.; Romero, I.; Vuylsteke, P.; Coleman, R.L.; Hilpert, F.; Oza, A.M.; et al. MILO/ENGOT-Ov11: Binimetinib Versus Physician’s Choice Chemotherapy in Recurrent or Persistent Low-Grade Serous Carcinomas of the Ovary, Fallopian Tube, or Primary Peritoneum. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3753–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisham, R.N.; Vergote, I.; Banerjee, S.; Drill, E.; Kalbacher, E.; Mirza, M.R.; Romero, I.; Vuylsteke, P.; Coleman, R.L.; Hilpert, F.; et al. Molecular Results and Potential Biomarkers Identified from the Phase 3 MILO/ENGOT-Ov11 Study of Binimetinib versus Physician Choice of Chemotherapy in Recurrent Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4068–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershenson, D.M.; Miller, A.; Brady, W.E.; Paul, J.; Carty, K.; Rodgers, W.; Millan, D.; Coleman, R.L.; Moore, K.N.; Banerjee, S.; et al. Trametinib versus Standard of Care in Patients with Recurrent Low-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer (GOG 281/LOGS): An International, Randomised, Open-Label, Multicentre, Phase 2/3 Trial. Lancet 2022, 399, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechahougui, H.; Michael, M.; Friedlaender, A. Precision Oncology in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 4648–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.R.; Fridlyand, J.; Yan, Y.; Penuel, E.; Burton, L.; Chan, E.; Peng, J.; Lin, E.; Wang, Y.; Sosman, J.; et al. Widespread Potential for Growth-Factor-Driven Resistance to Anticancer Kinase Inhibitors. Nature 2012, 487, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turajlic, S.; Furney, S.J.; Stamp, G.; Rana, S.; Ricken, G.; Oduko, Y.; Saturno, G.; Springer, C.; Hayes, A.; Gore, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Reveals Complex Mechanisms of Intrinsic Resistance to BRAF Inhibition. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalley, K.S.M.; Lioni, M.; Palma, M.D.; Xiao, M.; Desai, B.; Egyhazi, S.; Hansson, J.; Wu, H.; King, A.J.; Van Belle, P.; et al. Increased Cyclin D1 Expression Can Mediate BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in BRAF V600E–Mutated Melanomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2876–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagle, N.; Van Allen, E.M.; Treacy, D.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Cooper, Z.A.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Rosenberg, M.; Goetz, E.M.; Sullivan, R.J.; Farlow, D.N.; et al. MAP Kinase Pathway Alterations in BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Patients with Acquired Resistance to Combined RAF/MEK Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, S.R.; Theurillat, J.-P.; Van Allen, E.; Wagle, N.; Hsiao, J.; Cowley, G.S.; Schadendorf, D.; Root, D.E.; Garraway, L.A. A Genome-Scale RNA Interference Screen Implicates NF1 Loss in Resistance to RAF Inhibition. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Sucker, A.; Treacy, D.J.; Johannessen, C.M.; Goetz, E.M.; Place, C.S.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Whittaker, S.; Kryukov, G.V.; et al. The Genetic Landscape of Clinical Resistance to RAF Inhibition in Metastatic Melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Sabnis, A.J.; Chan, E.; Olivas, V.; Cade, L.; Pazarentzos, E.; Asthana, S.; Neel, D.; Yan, J.J.; Lu, X.; et al. The Hippo Effector YAP Promotes Resistance to RAF- and MEK-Targeted Cancer Therapies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellano, C.P.; White, M.G.; Andrews, M.C.; Chelvanambi, M.; Witt, R.G.; Daniele, J.R.; Titus, M.; McQuade, J.L.; Conforti, F.; Burton, E.M.; et al. Androgen Receptor Blockade Promotes Response to BRAF/MEK-Targeted Therapy. Nature 2022, 606, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakadia, S.; Yarlagadda, N.; Awad, R.; Kundranda, M.; Niu, J.; Naraev, B.; Mina, L.; Dragovich, T.; Gimbel, M.; Mahmoud, F. Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors and Clinical Update of US Food and Drug Administration-Approved Targeted Therapy in Advanced Melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7095–7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, K.L.; Martin, A.-M.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Greshock, J.; Letrero, R.; D’Andrea, K.; O’Day, S.; Infante, J.R.; Falchook, G.S.; Arkenau, H.-T.; et al. Tumor Genetic Analyses of Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Treated with the BRAF Inhibitor Dabrafenib (GSK2118436). Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4868–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dummer, R.; Brase, J.C.; Garrett, J.; Campbell, C.D.; Gasal, E.; Squires, M.; Gusenleitner, D.; Santinami, M.; Atkinson, V.; Mandalà, M.; et al. Adjuvant Dabrafenib plus Trametinib versus Placebo in Patients with Resected, BRAFV600-Mutant, Stage III Melanoma (COMBI-AD): Exploratory Biomarker Analyses from a Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton-Ward, T.; Middleton, G. The Impact of Genomic Context on Outcomes of Solid Cancer Patients Treated with Genotype-Matched Targeted Therapies: A Comprehensive Review. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 1113–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Chen, J.Q.; Liu, C.; Malu, S.; Creasy, C.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Xu, C.; McKenzie, J.A.; Zhang, C.; Liang, X.; et al. Loss of PTEN Promotes Resistance to T Cell–Mediated Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuger, I.Z.M.; Slieker, R.C.; Van Groningen, T.; Van Doorn, R. Therapeutic Strategies for Targeting CDKN2A Loss in Melanoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 18–25.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinetti, F.; Lacroix, L.; Mezquita, L.; Scoazec, J.-Y.; Loriot, Y.; Tselikas, L.; Gazzah, A.; Rouleau, E.; Adam, J.; Michiels, S.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors in BRAFV600E Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 132, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanrè, V.; Bellinato, F.; Cardile, A.; Passarini, C.; Di Bella, S.; Menegazzi, M. BRAF-Mutated Melanoma Cell Lines Develop Distinct Molecular Signatures After Prolonged Exposure to AZ628 or Dabrafenib: Potential Benefits of the Antiretroviral Treatments Cabotegravir or Doravirine on BRAF-Inhibitor-Resistant Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, W.; Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Sang, L.; Hao, Q.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; et al. EGF/EGFR-YAP 1/TEAD 2 Signaling Upregulates STIM 1 in Vemurafenib Resistant Melanoma Cells. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 4969–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondru, A.K.; Wilkinson, B.; Aljasir, M.A.; Alrumayh, A.; Greaves, G.; Emmett, M.; Albohairi, S.; Pritchard-Jones, R.; Cross, M.J. The ERK5 Pathway in BRAFV600E Melanoma Cells Plays a Role in Development of Acquired Resistance to Dabrafenib but Not Vemurafenib. FEBS Lett. 2024, 598, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Jobe, N.; Satapathy, S.R.; Mohapatra, P.; Andersson, T. Increased MARCKS Activity in BRAF Inhibitor-Resistant Melanoma Cells Is Essential for Their Enhanced Metastatic Behavior Independent of Elevated WNT5A and IL-6 Signaling. Cancers 2022, 14, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blateau, P.; Coyaud, E.; Laurent, E.; Béganton, B.; Ducros, V.; Chauchard, G.; Vendrell, J.A.; Solassol, J. TERT Promoter Mutation as an Independent Prognostic Marker for Poor Prognosis MAPK Inhibitors-Treated Melanoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Gutierrez, M.; Anders, C.K.; Ansstas, G.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Monga, V.; Forsyth, P.A.J.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Chandra, S.; Tsai, K.K.; et al. Trial in Progress: Phase 1a/b Study of PF-07284890 (Brain-Penetrant BRAF Inhibitor) with/without Binimetinib in Patients with BRAF V600-Mutant Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39 (Suppl. S15), TPS3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirven, I.; Pierre, E.; Vander Mijnsbrugge, A.-S.; Vounckx, M.; Kessels, J.I.; Neyns, B. Regorafenib Combined with BRAF/MEK Inhibitors for the Treatment of Refractory Melanoma Brain Metastases. Cancers 2024, 16, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Z.; Gao, Y.; Su, W.; Yaeger, R.; Tao, J.; Na, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Rymar, A.; Tao, A.; et al. RAF Inhibitor PLX8394 Selectively Disrupts BRAF Dimers and RAS-Independent BRAF-Mutant-Driven Signaling. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, G.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; Rad, R.; Saur, D. Tissue-Specific Tumorigenesis: Context Matters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer Type | Treatment Regimen | Main AEs, Any Grade | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic melanoma | Dabrafenib + trametinib | Pyrexia (52%), alanine aminotransferase increase (10%), fatigue (27%), rash (24%), cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (3%), decreased ejection fraction (4%) | [69] |
| Chemotherapy (dacarbazine) | Nausea (14%), vomiting (5%), fatigue (5%), diarrhea (15%), hematological toxicities (>15%) | [70] | |
| Metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | Dabrafenib + trametinib | Pyrexia (46%), nausea (40%), vomiting (35%), asthenia (28%), rash (19%), squamous cell carcinoma of skin (4%) | [18] |
| Standard second-line chemotherapy (paclitaxel, bevacizumab) | Hematological toxicity (73,4%), neuropathy (49,5%), alopecia (29,4%), vomiting (13,8%) | [71] | |
| Metastatic colorectal cancer | Encorafenib + binimetinib + cetuximab | Diarrhea (62%), acneiform dermatitis (49%), nausea (45%), vomiting (38%), pyrexia (20%) | [72] |
| Standard chemotherapy (FOLFIRI–cetuximab) | Diarrhea (48%), acneiform dermatitis (39%), nausea (41%), vomiting (29%), pyrexia (14%) | [72] |
| Tumor Type | Patient Population | Intervention | Phase | Trial Designation | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | Patients with resectable stage IIIB-C BRAF V600 mutation-positive melanoma | Dabrafenib + trametinib | II | NCT01972347 | NR |
| Metastatic or unresectable melanoma carrying a BRAF V600 mutation and having relapsed on a BRAF/MEK inhibitor therapy | Dabrafenib + trametinib | I | NCT04903119 | R | |
| Advanced melanoma patients with BRAF V600E/K mutation | HL-085 + vemurafenib | II | NCT05263453 | R | |
| Unresectable BRAF-mutated stage III/IV melanoma | XL888 + vemurafenib + cobimetinib | II | NCT02721459 | NR | |
| Metastatic or unresectable melanoma carrying a BRAF V600 mutation and having relapsed on a BRAF/MEK inhibitor therapy | Nilotinib + dabrafenib/trametinib or encorafenib/binimetinib | I | NCT04903119 | R | |
| Chinese patients with stage III BRAF V600 mutation positive melanoma after complete resection | Dabrafenib + trametinib | II | NCT04666272 | R | |
| High-risk patients with stage II melanoma with BRAF mutations (COLUMBUS-AD) | Encorafenib + binimetinib | III | NCT05270044 | NR | |
| Treatment-naive patients with advanced/metastatic melanoma with BRAF alterations (STEABOARD) | Encorafenib + binimetinib + pembrolizumab | III | NCT04657991 | NR | |
| BRAF mutant metastatic melanoma (CELEBRATE) | Encorafenib + binimetinib + palbociclib | I/II | NCT04720768 | R | |
| Patients with pretreated advanced melanoma (RegoMel) | Regorafenib | II | NCT05370807 | R | |
| BRAFV600-mutated melanoma with CNS metastasis | E6201 + dabrafenib | I | NCT05388877 | NR | |
| mCRC | First-line metastatic colorectal cancer with BRAFV600E mutation | Encorafenib + cetuximab + mFOLFOX6 | III | NCT04607421 | NR |
| Metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) with BRAF V600E mutation after first-line treatment | HLX208 (BRAF V600E Inhibitor) + cetuximab | II | NCT04984369 | NR | |
| First-line treatment for RAS/BRAF wild-type advanced colorectal cancer | Sintilimab + cetuximab + chemotherapy | I/II | NCT06776757 | R | |
| Previously treated MSS mCRC with BRAFV600E mutation | Encorafenib + cetuximab + nivolumab | II | NCT05308446 | R | |
| Previously untreated metastatic CRC (BREAKWATER) | Encorafenib + cetuximab +/− chemotherapy | III | NCT04607421 | NR | |
| Previously untreated BRAFV600E mutant, MSI high/DMMR metastatic CRC (SEAMARK) | Encorafenib + cetuximab + pembrolizumab vs. pembrolizumab alone | II | NCT05217446 | NR | |
| BRAF V600E-mutated MSS initially resectable/potentially resectable advanced colorectal cancer | Cetuximab + encorafenib + binimetinib | II | NCT06207656 | R | |
| Thyroid | High-risk BRAFV600E-mutant differentiated thyroid carcinoma (pre-radioiodine therapy) | Vemurafenib + cobimetinib | II | NCT06440850 | R |
| Radioiodine-refractory BRAFV600E-mutant differentiated thyroid cancer (post-VEGFR TKI) | Dabrafenib + trametinib vs. cabozantinib | III | NCT06475989 | R | |
| Previously treated patients with locally advanced/metastatic, RAI-refractory BRAFV600E-mutated differentiated thyroid cancer | Dabrafenib + trametinib | III | NCT04940052 | NR | |
| Patients with metastatic radioiodine refractory BRAFV600 mutant thyroid cancer | Encorafenib + binimetinib +/− nivolumab | II | NCT04061980 | NR | |
| NSCLC | Metastatic NSCLC with BRAF V600E mutation (no prior BRAF/MEK inhibitors) | Encorafenib + binimetinib | II | NCT03915951 | NR |
| Untreated metastatic NSCLC with BRAFV600E mutation | Encorafenib + binimetinib | II | NCT04526782 | NR | |
| Patients with NSCLC, solid tumors, melanoma, high-grade gliomas | Dabrafenib + trametinib | IV | NCT03340506 | R | |
| Advanced NSCLC | Binimetinib + pembrolizumab | I | NCT03991819 | R | |
| Other solid tumors | Advanced solid tumors with non-V600E BRAF mutations (e.g., class II/III alterations) | Encorafenib + binimetinib | II | NCT03839342 | NR |
| Relapsed or progressive pediatric low-grade glioma with BRAF alterations (V600E or BRAF fusions) | Tovorafenib | II | NCT04775485 | R | |
| Advanced solid tumors with oncogenic BRAF (class I/II/III) or RAS/MAPK pathway mutations | BDTX-4933 (pan-RAF/RAS inhibitor) | I | NCT05786924 | NR | |
| adults with BRAF/NRAS-mutated advanced or metastatic solid tumors | KIN-2787 | I | NCT04913285 | R | |
| Advanced solid tumors with BRAFV600 mutations (monotherapy dose escalation; combination with trametinib in expansion) | CFT1946 (BRAF V600 degrader) ± trametinib | I/II | NCT05668585 | R | |
| Recurrent/progressive low-grade ovarian or peritoneal cavity cancer | Trametinib vs. standard of care | II/III | NCT02101788 | NR | |
| Patients with BRAF and other RAS/MAPK mutation-positive neoplasms | BDTX-4933 | I | NCT05786924 | NR | |
| Advanced solid tumors with BRAF, KRAS, and/or NRAS mutations | VS6766 +/− everolimus | I | NCT02407509 | R | |
| Advanced/metastatic malignancies harboring RAS or RAF oncogenic mutations | IMM-6-415 | I/II | NCT06208124 | R | |
| Advanced/recurrent low-grade glioma or pancreatic cancer with BRAF fusion/rearrangement | Binimetinib | II | NCT06159478 | R |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mechahougui, H.; Gutmans, J.; Gouasmi, R.; Smekens, L.; Friedlaender, A. BRAF Targeting Across Solid Tumors: Molecular Aspects and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083757
Mechahougui H, Gutmans J, Gouasmi R, Smekens L, Friedlaender A. BRAF Targeting Across Solid Tumors: Molecular Aspects and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083757
Chicago/Turabian StyleMechahougui, Hiba, James Gutmans, Roumaïssa Gouasmi, Laure Smekens, and Alex Friedlaender. 2025. "BRAF Targeting Across Solid Tumors: Molecular Aspects and Clinical Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083757
APA StyleMechahougui, H., Gutmans, J., Gouasmi, R., Smekens, L., & Friedlaender, A. (2025). BRAF Targeting Across Solid Tumors: Molecular Aspects and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3757. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083757






