Paeoniflorin Directly Targets ENO1 to Inhibit M1 Polarization of Microglia/Macrophages and Ameliorates EAE Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PF Ameliorates Clinical Symptoms in EAE Mice
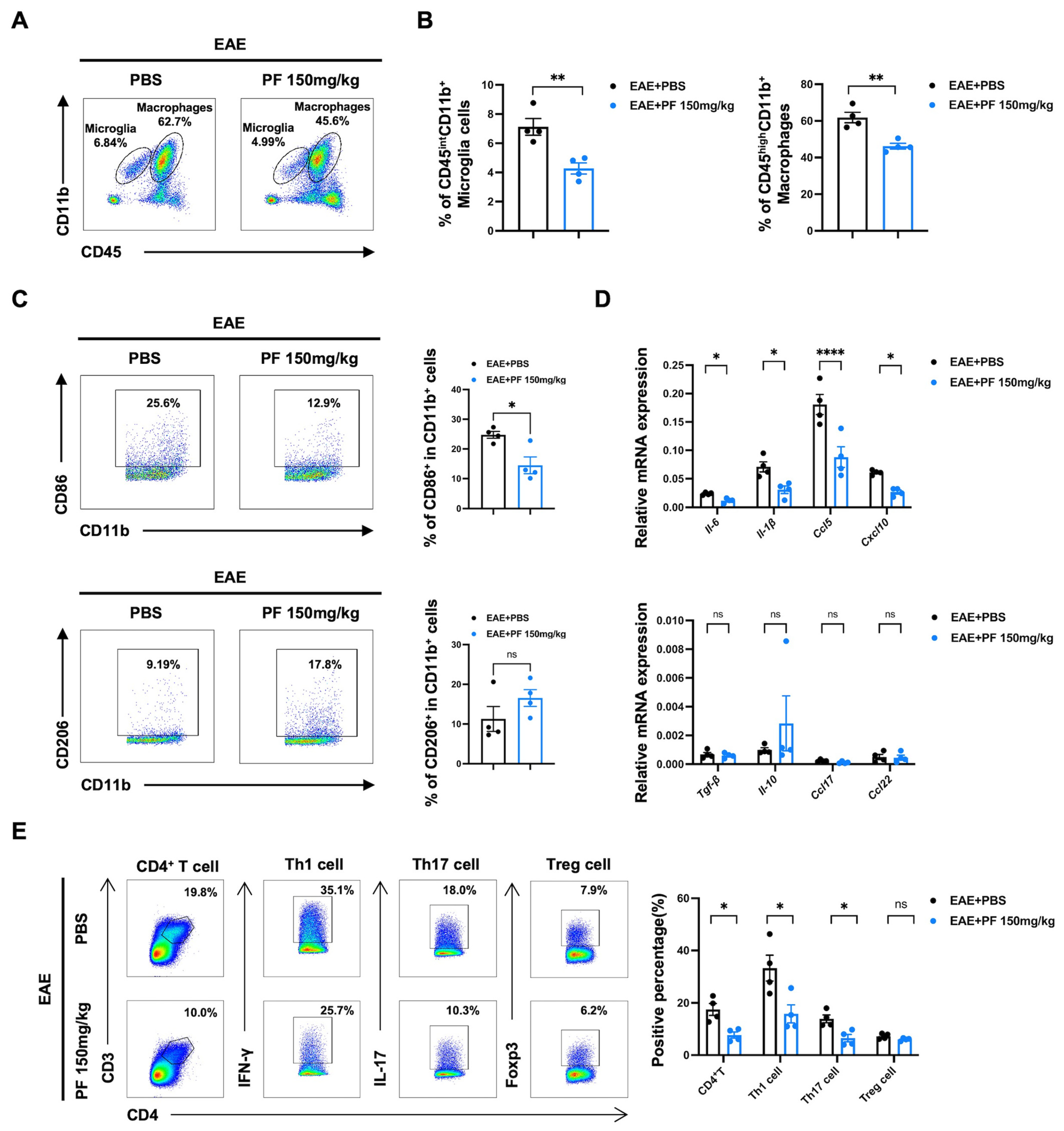
2.2. PF Inhibits the Polarization of Microglia/Macrophages to M1 Phenotype
2.3. PF Alleviates CNS Inflammation in EAE Mice by Reducing the Percentages of M1 Microglia/Macrophages and Pathogenic T Cells
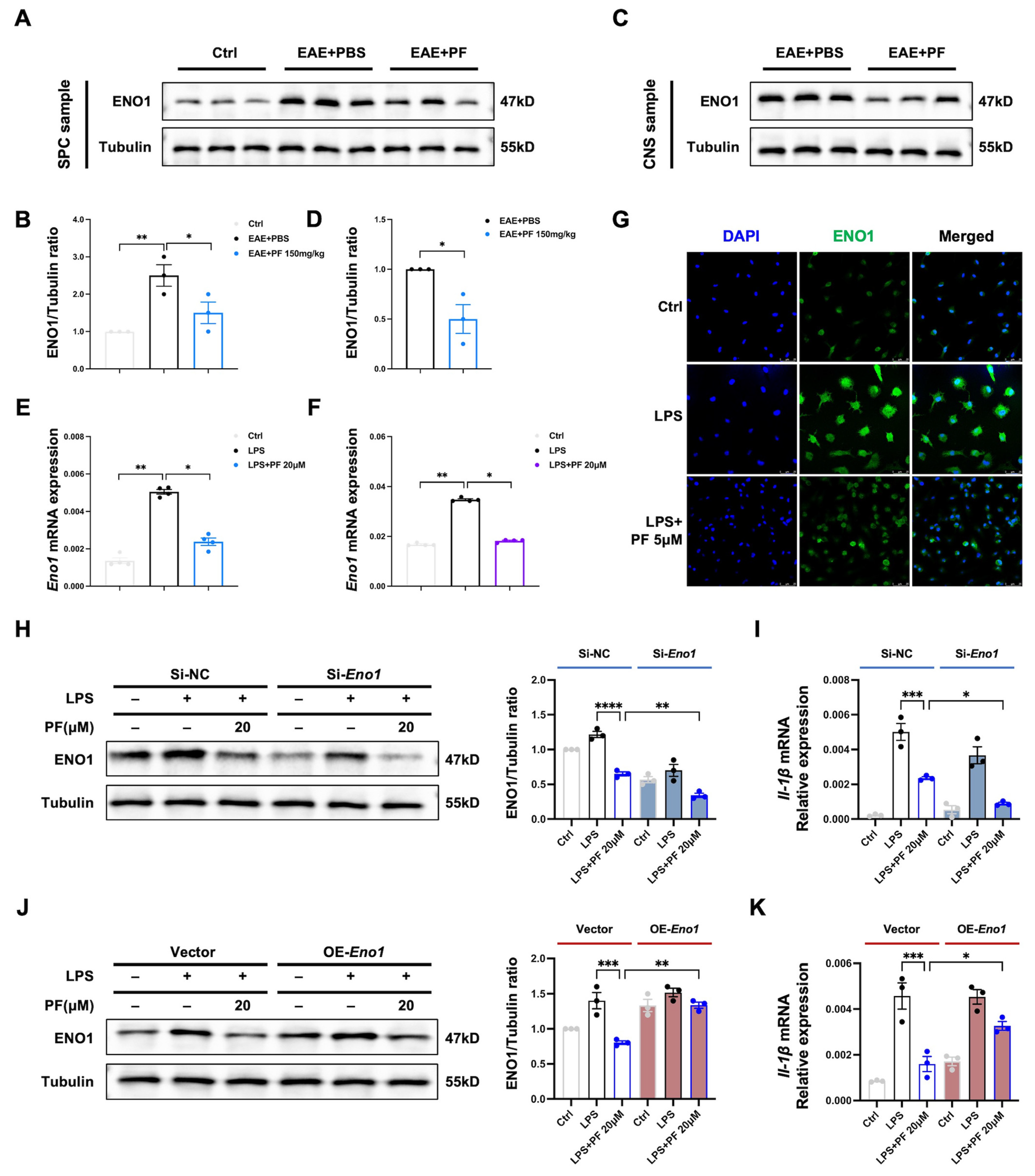
2.4. PF Targets ENO1 and Reduces Enzyme Activity as Well as Glycolysis Status of M1 Microglia/Macrophages
2.5. Downregulation of ENO1 Contributes to Anti-Inflammatory Function of PF in M1 Microglia/Macrophages
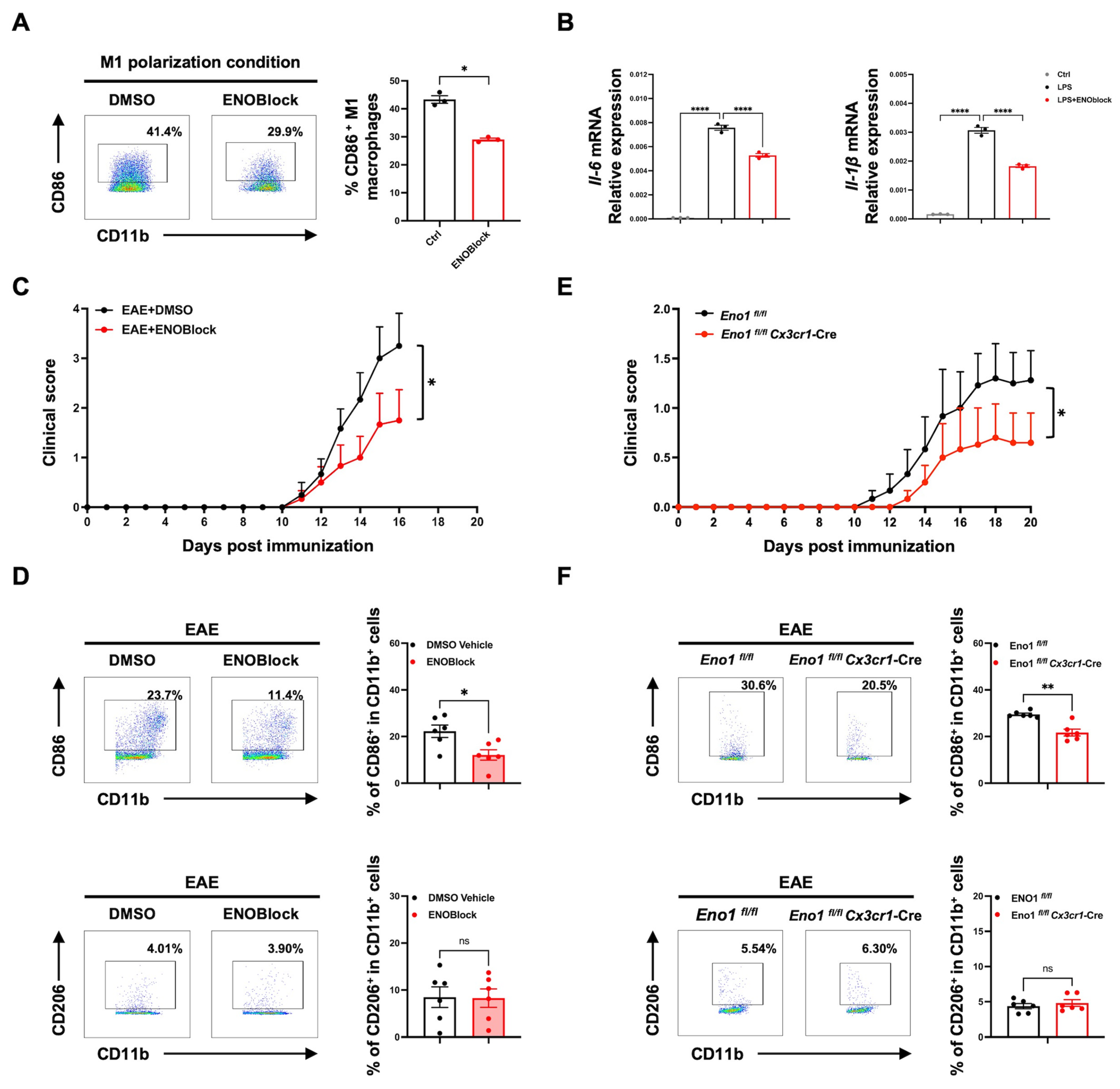
2.6. ENOBlock Treatment or Specific Knockout of Eno1 in Microglia Inhibits M1 Polarization and Alleviates EAE Progression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. EAE Induction, PF Treatment, and ENOBlock Administration
4.3. Histopathological Analysis of Spinal Cords
4.4. Cell Isolation
4.5. EAE CNS Mononuclear Cell RNA Sequencing and Analysis
4.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.7. CD4+ T Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Differentiation Assay
4.8. Microglia/Macrophage Polarization Assay
4.9. Immunofluorescence
4.10. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.11. ELISA
4.12. Western Blot
4.13. Drug Affinity Responsive Target Stability (DARTS) Assay
4.14. Microscale Thermophoresis (MST) Assay
4.15. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Assay
4.16. Molecular Docking of PF to ENO1
4.17. Enolase Activity Assay
4.18. Seahorse Extracellular Flux Analysis
4.19. Cell Transfection for Eno1 Silencing and Overexpression
4.20. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMDMs | bone marrow-derived macrophages |
| CFA | complete Freund’s adjuvant |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| DARTS | drug affinity responsive target stability |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DMTs | disease-modulatory therapies |
| EAE | experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis |
| ECAR | extracellular acidification rate |
| ENO1 | α-enolase |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin |
| HK2 | hexokinase 2 |
| LFB | luxol fast blue |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| MST | microscale thermophoresis |
| PF | paeoniflorin |
| PKM2 | pyruvate kinase M2 |
| SPR | surface plasmon resonance |
| WB | western blot |
References
- Wallin, M.T.; Culpepper, W.J.; Nichols, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Gebrehiwot, T.T.; Hay, S.I.; Khalil, I.A.; Krohn, K.J.; Liang, X.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of multiple sclerosis 1990-2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konen, F.F.; Mohn, N.; Witte, T.; Schefzyk, M.; Wiestler, M.; Lovric, S.; Hufendiek, K.; Schwenkenbecher, P.; Suhs, K.W.; Friese, M.A.; et al. Treatment of autoimmunity: The impact of disease-modifying therapies in multiple sclerosis and comorbid autoimmune disorders. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harding, K.; Williams, O.; Willis, M.; Hrastelj, J.; Rimmer, A.; Joseph, F.; Tomassini, V.; Wardle, M.; Pickersgill, T.; Robertson, N.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Escalation vs Early Intensive Disease-Modifying Therapy in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palace, J.; Duddy, M.; Bregenzer, T.; Lawton, M.; Zhu, F.; Boggild, M.; Piske, B.; Robertson, N.P.; Oger, J.; Tremlett, H.; et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of interferon beta and glatiramer acetate in the UK Multiple Sclerosis Risk Sharing Scheme at 6 years: A clinical cohort study with natural history comparator. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kaer, L.; Postoak, J.L.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Wu, L. Innate, innate-like and adaptive lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of MS and EAE. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2019, 16, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, N.; Nishihara, T.; Yorozuya, T.; Tanaka, J. Microglia and Macrophages in the Pathological Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems. Cells 2020, 9, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, M.; Koyama, R. Comparative Review of Microglia and Monocytes in CNS Phagocytosis. Cells 2021, 10, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haimon, Z.; Frumer, G.R.; Kim, J.S.; Trzebanski, S.; Haffner-Krausz, R.; Ben-Dor, S.; Porat, Z.; Muschaweckh, A.; Chappell-Maor, L.; Boura-Halfon, S.; et al. Cognate microglia-T cell interactions shape the functional regulatory T cell pool in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis pathology. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touil, H.; Li, R.; Zuroff, L.; Moore, C.S.; Healy, L.; Cignarella, F.; Piccio, L.; Ludwin, S.; Prat, A.; Gommerman, J.; et al. Cross-talk between B cells, microglia and macrophages, and implications to central nervous system compartmentalized inflammation and progressive multiple sclerosis. EBioMedicine 2023, 96, 104789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, N.; Katsara, M.; Tselios, T.; Androutsou, M.E.; de Courten, M.; Matsoukas, J.; Apostolopoulos, V. Multiple Sclerosis: Immunopathology and Treatment Update. Brain Sci. 2017, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charabati, M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Weiner, H.L.; Quintana, F.J. Multiple sclerosis: Neuroimmune crosstalk and therapeutic targeting. Cell 2023, 186, 1309–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, S.H.; Kang, S.; Lee, W.; Choi, H.; Chung, S.; Kim, J.I.; Mook-Jung, I. A Breakdown in Metabolic Reprogramming Causes Microglia Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 493–507 e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Islam, R.; Zhang, S.; Fang, J. Metabolic reprogramming of macrophages and its involvement in inflammatory diseases. EXCLI J. 2021, 20, 628–641. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yi, M.; Chu, Q.; Jiao, D.; Wu, K. Metabolic profiles of regulatory T cells and their adaptations to the tumor microenvironment: Implications for antitumor immunity. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijland, P.G.; Molenaar, R.J.; van der Pol, S.M.; van der Valk, P.; van Noorden, C.J.; de Vries, H.E.; van Horssen, J. Differential expression of glucose-metabolizing enzymes in multiple sclerosis lesions. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, J.; Luo, D.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. Covalent Inhibition of Pyruvate Kinase M2 Reprograms Metabolic and Inflammatory Pathways in Hepatic Macrophages against Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 5260–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, M.D.; Bhargava, P.; Kim, P.M.; Putluri, V.; Snowman, A.M.; Putluri, N.; Calabresi, P.A.; Snyder, S.H. Dimethyl fumarate targets GAPDH and aerobic glycolysis to modulate immunity. Science 2018, 360, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Hu, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Liu, L. Protective effects of paeoniflorin on cardiovascular diseases: A pharmacological and mechanistic overview. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1122969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yin, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, Z.; Niu, J. Antioxidant effects of Paeoniflorin and relevant molecular mechanisms as related to a variety of diseases: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 176, 116772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Feng, S.T.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, N.H.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y. Paeoniflorin: A neuroprotective monoterpenoid glycoside with promising anti-depressive properties. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Gong, X.H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C. A review on the pharmacokinetics of paeoniflorin and its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, F.; Aa, L.X.; Qi, Q.; Sun, R.B.; Yan, C.X.; Aa, J.Y.; Wang, G.J. Paeoniflorin inhibits Th1 and Th17 cells in gut-associated lymphoid tissues to produce anti-arthritis activities. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Song, L.; Yi, J. Paeoniflorin inhibits Rho kinase activation in joint synovial tissues of rats with collagen-induced rheumatoid arthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.Y.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, M. Elucidation of Transport Mechanism of Paeoniflorin and the Influence of Ligustilide, Senkyunolide I and Senkyunolide A on Paeoniflorin Transport through Mdck-Mdr1 Cells as Blood-Brain Barrier in Vitro Model. Molecules 2016, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Song, W.L.; Xu, Y.C.; Ye, Y.; Feng, L.Y. Paeoniflorin ameliorates ischemic neuronal damage in vitro via adenosine A1 receptor-mediated transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Z.; Ke, Y.; Sun, R.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhen, X.; Zheng, L.T. Early glycolytic reprogramming controls microglial inflammatory activation. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsson-McDermott, E.M.; Curtis, A.M.; Goel, G.; Lauterbach, M.A.R.; Sheedy, F.J.; Gleeson, L.E.; van den Bosch, M.W.M.; Quinn, S.R.; Domingo-Fernandez, R.; Johnston, D.G.W.; et al. Pyruvate Kinase M2 Regulates Hif-1alpha Activity and IL-1beta Induction and Is a Critical Determinant of the Warburg Effect in LPS-Activated Macrophages. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, G.; Wu, A.G.; Chen, X.L.; Tian, Y.; Lin, X.K. Enolase 1, a Moonlighting Protein, as a Potential Target for Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3981–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giralt, M.; Molinero, A.; Hidalgo, J. Active Induction of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) with MOG(35-55) in the Mouse. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1791, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lomenick, B.; Hao, R.; Jonai, N.; Chin, R.M.; Aghajan, M.; Warburton, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, R.P.; Gomez, F.; Loo, J.A.; et al. Target identification using drug affinity responsive target stability (DARTS). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21984–21989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhardt, J.; Santos-Martins, D.; Tillack, A.F.; Forli, S. AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2021, 61, 3891–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancholi, V. Multifunctional alpha-enolase: Its role in diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Nie, H. Paeoniflorin Directly Targets ENO1 to Inhibit M1 Polarization of Microglia/Macrophages and Ameliorates EAE Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083677
Sun Y, Wang G, Li S, Jiang Y, Liu Y, Gao Y, Yuan Y, Nie H. Paeoniflorin Directly Targets ENO1 to Inhibit M1 Polarization of Microglia/Macrophages and Ameliorates EAE Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083677
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Ying, Guojue Wang, Shengzhe Li, Yongshuai Jiang, Yunhui Liu, Yidan Gao, Yuanyang Yuan, and Hong Nie. 2025. "Paeoniflorin Directly Targets ENO1 to Inhibit M1 Polarization of Microglia/Macrophages and Ameliorates EAE Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083677
APA StyleSun, Y., Wang, G., Li, S., Jiang, Y., Liu, Y., Gao, Y., Yuan, Y., & Nie, H. (2025). Paeoniflorin Directly Targets ENO1 to Inhibit M1 Polarization of Microglia/Macrophages and Ameliorates EAE Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083677






