Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
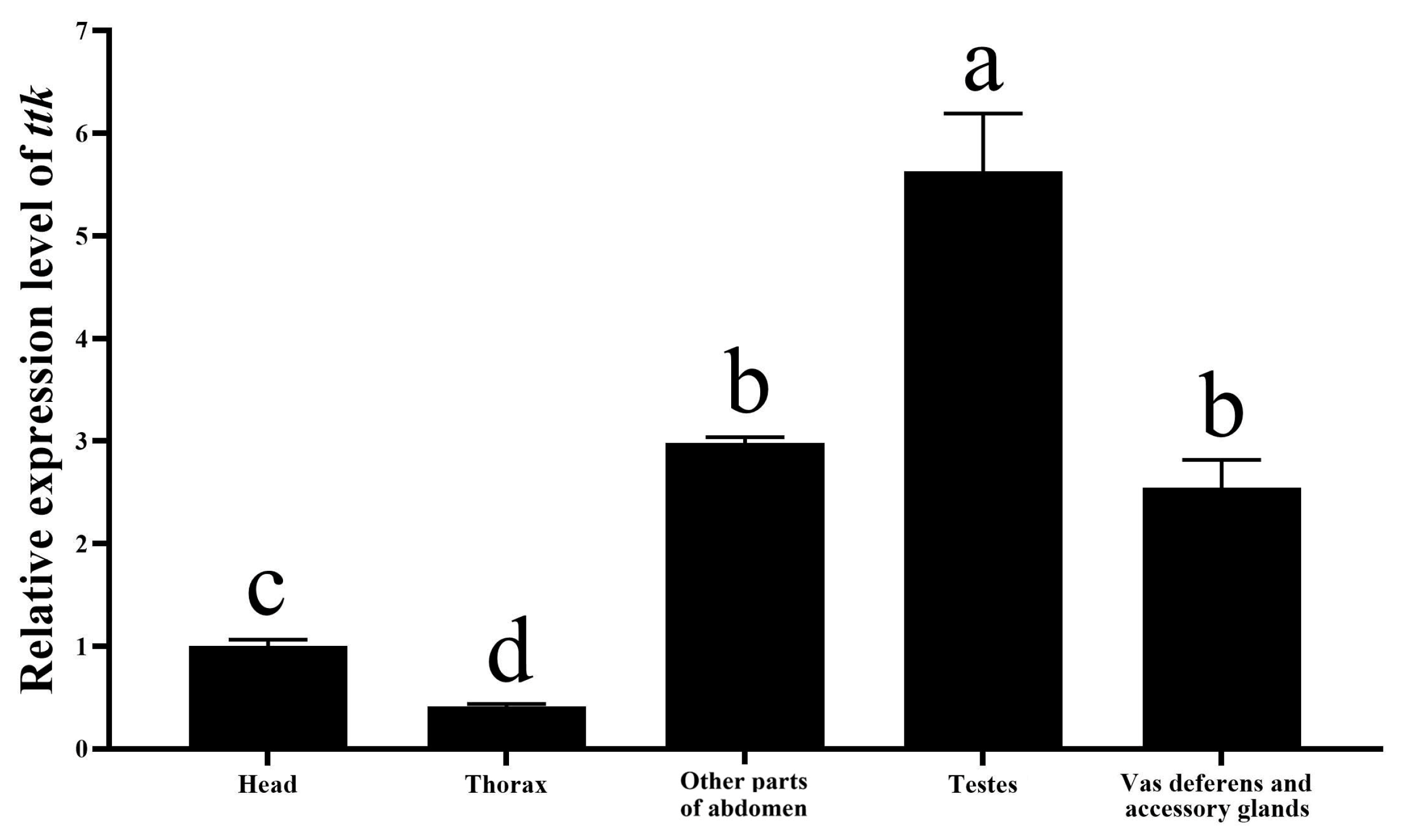
2.1. Expression of Ttk in Male Reproductive Organs
2.2. RNAi Efficiency of Dsttk in Fourth-Instar Male Nymphs
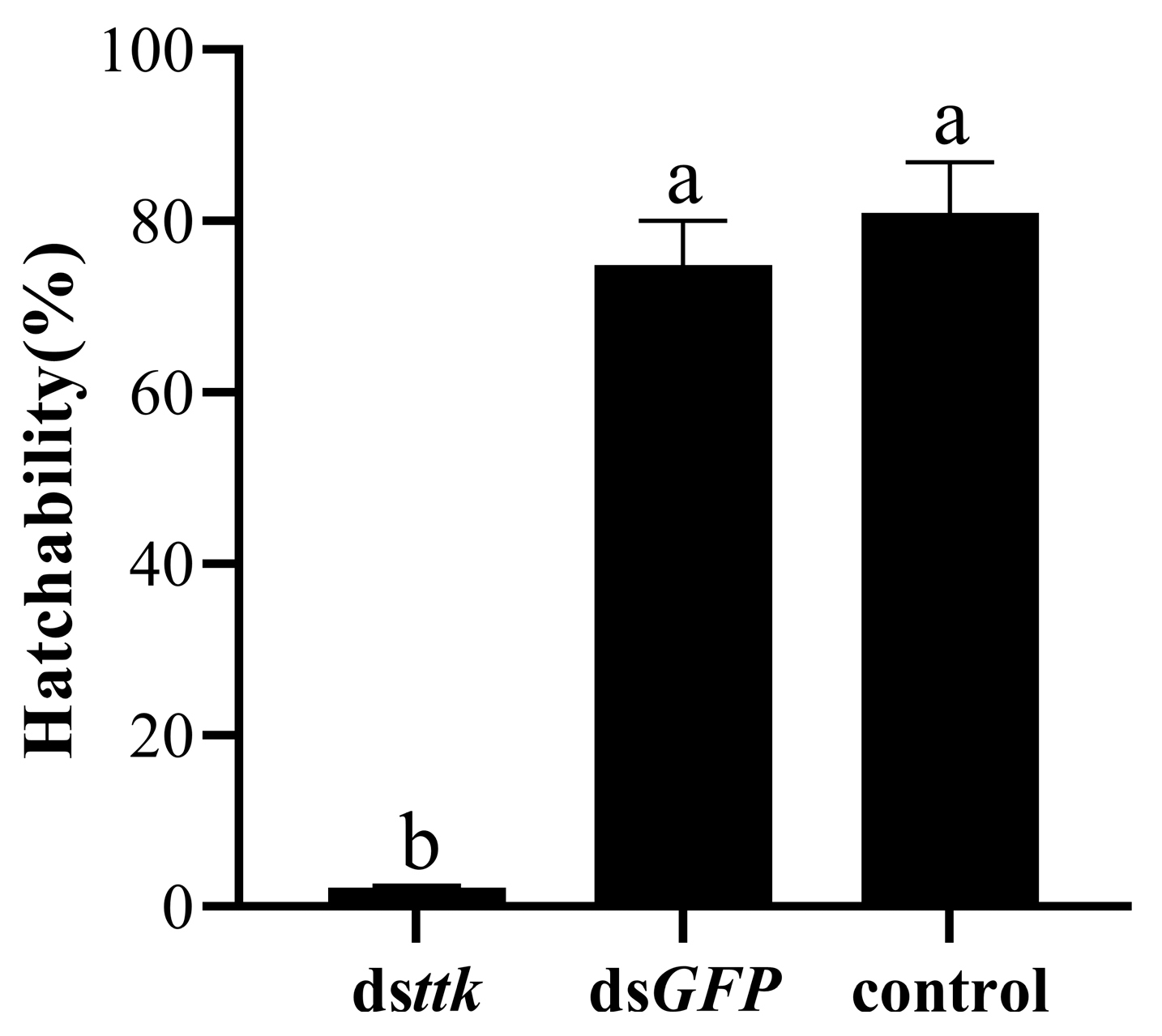
2.3. Hatching Rate of Eggs from Females Mated with Dsttk-Treated Males
2.4. Gonad Development
2.5. Spermatogenesis and Motility
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing
4.2. Primer Sequences for Ttk Amplification and RNAi
4.3. Ttk Expression in Body Regions and Male Reproductive Organs
4.4. DsRNA Synthesis and Injection
4.5. The Hatching Rate Assays of Eggs Laid by Female Adults Mated with Male Derived from Dsttk-Injected Nymphs
4.6. Gonad Morphometry
4.7. Sperm Analysis
4.8. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fabian, L.; Brill, J.A. Drosophila spermiogenesis: Big things come from little packages. Spermatogenesis 2012, 2, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryner, L.C.; Goodwin, S.F.; Castrillon, D.H.; Anand, A.; Villella, A.; Baker, B.S.; Hall, J.C.; Taylor, B.J.; Wasserman, S.A. Control of male sexual behavior and sexual orientation in Drosophila by the fruitless gene. Cell 1996, 87, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, M.; Nakata, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Iwami, M.; Takayanagi-Kiya, S.; Kiya, T. Fruitless is sex-differentially spliced and is important for the courtship behavior and development of silkmoth Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2023, 159, 103989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, E.A.; Puretskaia, O.A.; Terekhanova, N.V.; Labudina, A.; Bökel, C. Direct control of somatic stem cell proliferation factors by the Drosophila testis stem cell niche. Development 2018, 145, 156315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laktionov, P.P.; Maksimov, D.A.; Romanov, S.E.; Antoshina, P.A.; Posukh, O.V.; White-Cooper, H.; Koryakov, D.E.; Belyakin, S.N. Genome-wide analysis of gene regulation mechanisms during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Epigenet. Chromatin 2018, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Marca, J.E.; Diepstraten, S.T.; Hodge, A.L.; Wang, H.; Hart, A.H.; Richardson, H.E.; Somers, W.G. Strip and Cka negatively regulate JNK signalling during Drosophila spermatogenesis. Development 2019, 146, 174292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.C.; Wang, Z.J.; Chen, Z.Z.; Clarke, A.R.; Niu, C.Y. Bactrocera dorsalis male sterilization by targeted RNA interference of spermatogenesis: Empowering sterile insect technique programs. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Gurav, A.S.; Li, M.; Akbari, O.S.; Montell, C. Suppression of female fertility in Aedes aegypti with a CRISPR-targeted male-sterile mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105075118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.D.; Travers, A.A. The tramtrack gene encodes a Drosophila finger protein that interacts with the ftz transcriptional regulatory region and shows a novel embryonic expression pattern. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonichuk, A.; Benisov, S.; Georgiev, P.; Maksimenko, O. Drosophila BTB/POZ domains of “ttk Group” can form multimers and selectively interact with each other. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 412, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaharbakhshi, E.; Jemc, J.C. Broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-a-brac (BTB) proteins: Critical regulators of development. Genesis 2016, 54, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohl, M.; Ishii, K.; Asahina, K. Layered roles of fruitless isoforms in specification and function of male aggression-promoting neurons in Drosophila. eLife 2020, 9, e52702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althauser, C.; Jordan, K.C.; Deng, W.M.; Ruohola-Baker, H. Fringe-dependent notch activation and tramtrack function are required for specification of the polar cells in Drosophila. Dev. Dynam. 2005, 232, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arama, E.; Bader, M.; Rieckhof, G.E.; Steller, H. A ubiquitin ligase complex regulates caspase activation during sperm differentiation in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, N.C.; Thayer, N.H.; Kerr, S.A.; Tompa, M.; Berg, C.A. Following the ‘tracks’: Tramtrack69 regulates epithelial tube expansion in the Drosophila ovary through Paxillin, Dynamin, and the homeobox protein Mirror. Dev. Biol. 2013, 378, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, E.M.; Li, W.; Sun, J.J. Downregulation of homeodomain protein Cut is essential for Drosophila follicle maturation and ovulation. Development 2019, 146, dev179002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorum, S.M.; Simonette, R.A.; Alanis, R., Jr.; Wang, J.E.; Lewis, B.M.; Trejo, M.H.; Hanson, K.A.; Beckingham, K.M. The Drosophila BTB domain protein Jim Lovell has roles in multiple larval and adult behaviors. PLoS ONE 2013, 4, e61270. [Google Scholar]
- Boerjan, B.; Tobback, J.; De Loof, A.; Schoofs, L.; Huybrechts, R. Fruitless RNAi knockdown in males interferes with copulation success in Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem. Molec. Biol. 2011, 41, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomihara, K.; Kiuchi, T. Disruption of a BTB-ZF transcription factor causes female sterility and melanization in the larval body of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 159, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.J.; Li, X.R.; Pei, X.Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, X.F. Heat shock protein 90 maintains the stability and function of transcription factor Broad Z7 by interacting with its Broad-Complex-Tramtrack-Bric-a-brac domain. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 24, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Jacobs, C.G.; Mogollón Pérez, E.A.; Chen, D.; Sanden, J.T.; van de Bretscher, K.M.; Verweij, F.; Bosman, J.S.; Hackmann, A.; Merks, R.M.H.; et al. A life-history allele of large effect shortens developmental time in a wild insect population. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 8, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.H. Effects of ttk on development and courtship of male Nilaparvata lugens. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 6465–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.-X.; Yu, L.-L.; Fan, H.-W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.-J.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, Z.-R.; Zhou, W.-W.; et al. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Whitworth, C.; Pozmanter, C.; Neville, M.C.; Doren, M.V. Doublesex regulates fruitless expression to promote sexual dimorphism of the gonad stem cell niche. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerjan, B.; Tobback, J.; Vandersmissen, H.P.; Huybrechts, R.; Schoofs, L. Fruitless RNAi knockdown in the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Influences male fertility. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, M.; Chen, X.; Pringle, M.J.; Suchorolski, M.; Sancak, Y.; Viswanathan, S.; Bolival, B.; Lin, T.Y.; Marino, S.; Fuller, M.T. Testis-specific TAF homologs collaborate to control a tissue-specific transcription program. Development 2004, 131, 5297–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopova, B.; Jindra, M. Broad-Complex acts down-stream of Met in juvenile hormone signaling to coordinate primitive holometabolan metamorphosis. Development 2008, 135, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Tan, A.; Bai, H.; Palli, S.R. Transcription factor broad suppresses precocious development of adult structures during larval-pupal metamorphosis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Mech. Dev. 2008, 125, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fire, A.; Xu, S.Q.; Montgomery, M.K.; Kostas, S.A.; Driver, S.E.; Mello, C.C. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998, 391, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.Y.; Palli, S.R. Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA Interference. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2020, 65, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, O.; Niu, J.Z.; Taning, C.N.t. RNAi in insects: A revolution in fundamental research and pest control applications. Insects 2020, 11, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.Z.; Chen, R.Y.; Wang, J.J. RNA interference in insects: The link between antiviral defense and pest control. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.M.; Schutter, K.D. Biosafety aspects of RNAi-based pest control. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 3697–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Gong, F.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z. Photoperiod-regulated mitophagy in the germ cells of Brandt’s voles (Lasiopodomys brandtii). Integr. Zool. 2024, 19, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, E.; Benjamin, S.; Svetec, N.; Zhao, L. Testis single-cell RNA-seq reveals the dynamics of de novo gene transcription and germline mutational bias in Drosophila. eLife 2019, 8, e47138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Primer Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| dsttk-F | TCTTGCGATCCTGGTTTGA |
| dsttk-R | CAACTCACCATCGCACAAT |
| dsttk-T7F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGTCTTGCGATCCTGGTTTGA |
| dsttk-T7R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAACTCACCATCGCACAAT |
| dsGFP-F | CAAGAGTGCCATGCCCGAAG |
| dsGFP-R | CATGTGGTCACGCTTTTCGTT |
| dsGFP-2T7F | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGAGTGCCATGCCCGAAG |
| dsGFP-2T7R | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCATGTGGTCACGCTTTTCGTT |
| Qttk-F | CTTCCGCTGGTGACCTTCA |
| Qttk-R | TCAACCTCTTTCGCTACGC |
| β-actin-F | TCCCTCTCCACCTTCCAACA |
| β-actin-R | TCAGGTCCAGTTACACCGTC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, B.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F. Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083643
Feng B, Hu Y, Wang F. Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083643
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Bo, Yang Hu, and Fanghai Wang. 2025. "Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083643
APA StyleFeng, B., Hu, Y., & Wang, F. (2025). Reduction in Gonad Development and Sperm Motility in Male Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens via RNAi-Mediated Knockdown of tramtrack. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083643






