High Mobility Group Box 1 Is Potential Target Therapy for Inhibiting Metastasis and Enhancing Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Overexpression of HMGB1 in Tumor Tissues and Patients with Metastasis
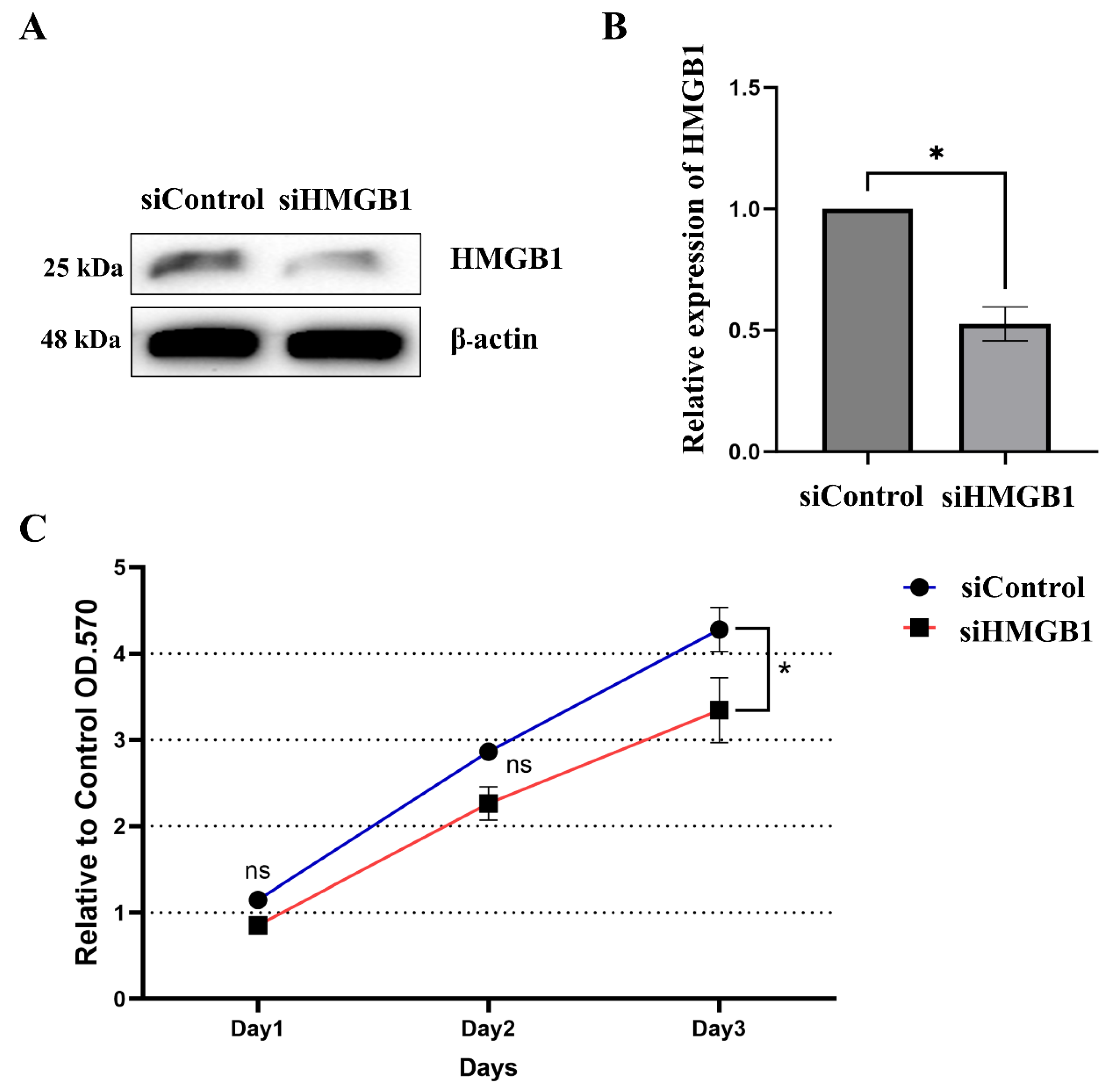
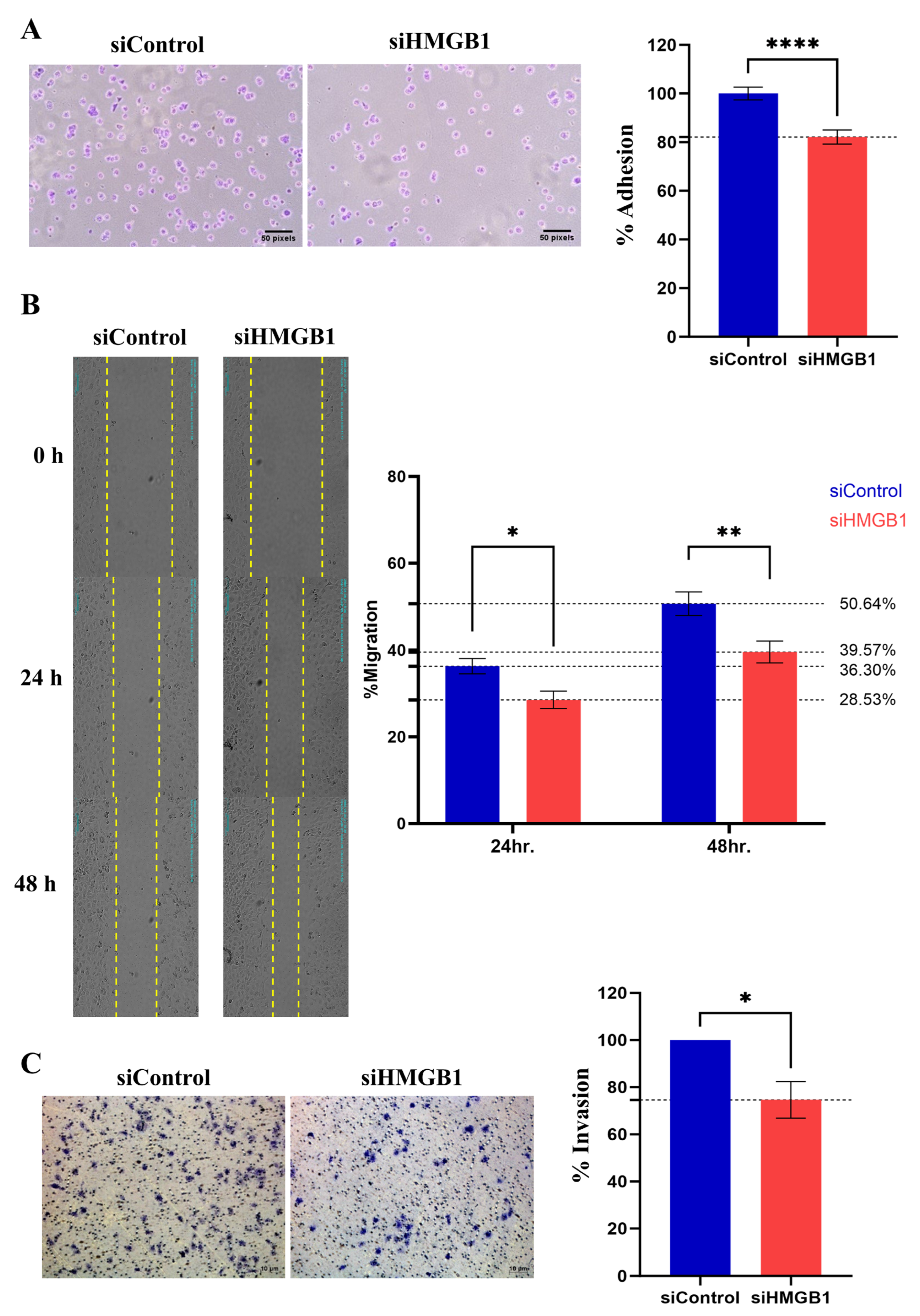
2.2. HMGB1 Plays a Crucial Role in HCC Cell Proliferation and Metastasis
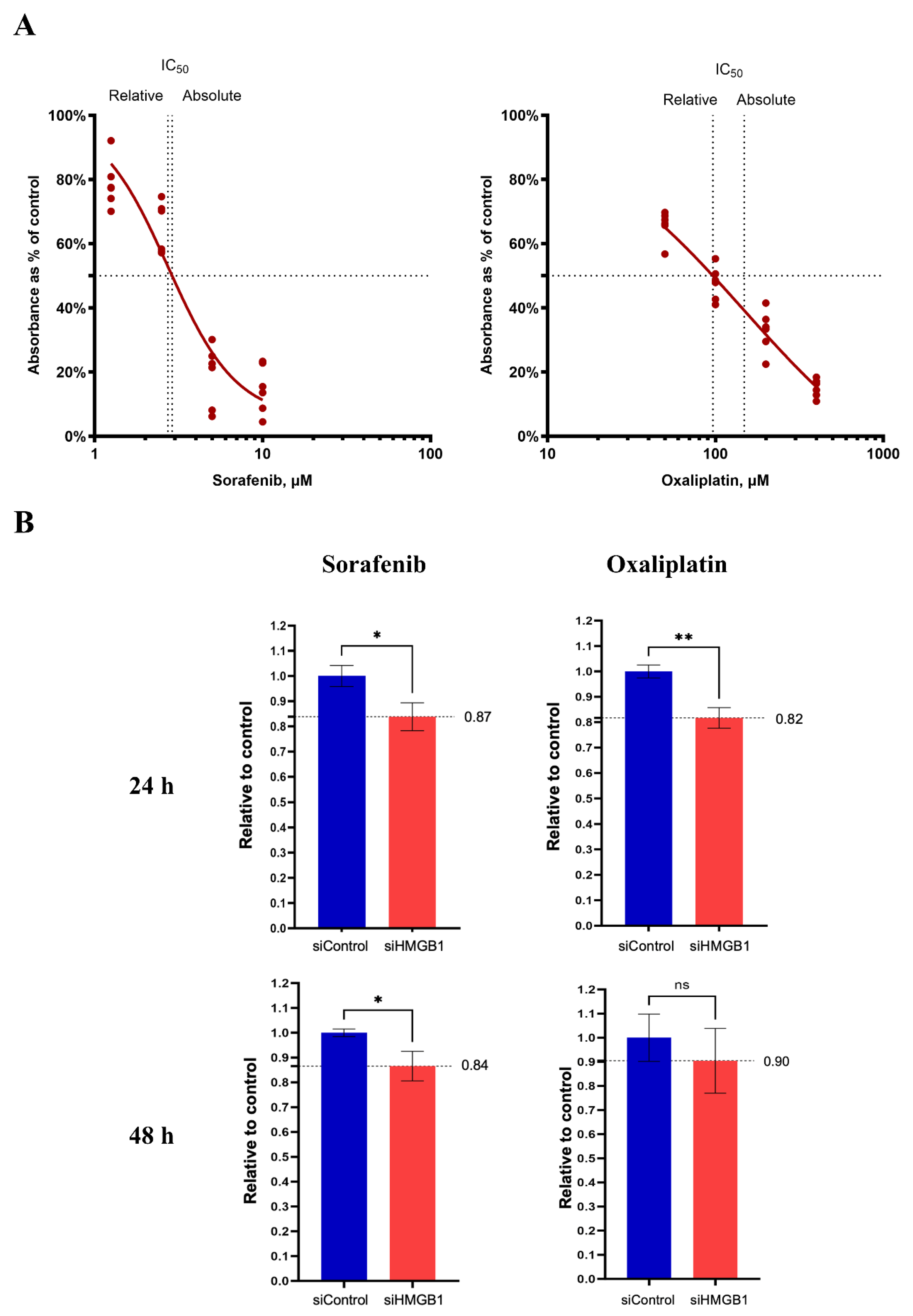
2.3. Inhibition of HMGB1 Increases Drug Sensitivity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Patients and Tissue Samples
4.3. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.4. siRNA Transfection
4.5. Cell Adhesion Assay
4.6. Cell Scratch Assay
4.7. Cell Invasion Assay
4.8. Drug Challenge Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratana-Amornpin, S.; Vilaichone, R.K.; Miftahussurur, M.; Aumpan, N.; Kaewkarnjanarat, K.; Nun-Anan, P.; Chonprasertsuk, S.; Siramolpiwat, S.; Bhanthumkomol, P.; Pornthisarn, B.; et al. Clinical Features and Overall Survival of Females with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Retrospective Study and Review of the Literature in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. Int. J. Womens Health 2021, 13, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindson, J. Combined TACE and sorafenib for HCC treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhao, S.; Zeng, X.; Sun, R.; Zheng, R. Optimal timing of combining sorafenib with trans-arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 14, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahim, M.; Victor, D.; Esmail, A.; Kodali, S.; Graviss, E.A.; Nguyen, D.T.; Moore, L.W.; Saharia, A.; McMillan, R.; Fong, J.N.; et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Plus Sorafenib Compared to TACE Alone in Transplant Recipients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Institution Experience. Cancers 2022, 14, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Yan, T.; Liu, F.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, H.; Jiang, S. Link of sorafenib resistance with the tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma: Mechanistic insights. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 991052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Song, G.; Xu, Z.; Bu, Y.; Chang, F.; Jia, F.; Xiao, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, M.; Jia, Q. Oxaliplatin resistance is enhanced by saracatinib via upregulation Wnt-ABCG1 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klune, J.R.; Dhupar, R.; Cardinal, J.; Billiar, T.R.; Tsung, A. HMGB1: Endogenous Danger Signaling. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Fu, Y.; Yao, M.; Cui, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Lin, Y.; He, S. The HN1/HMGB1 axis promotes the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma and attenuates the chemosensitivity to oxaliplatin. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 6400–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Chen, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.; Duan, L.; Yin, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Sun, M.; et al. HMGB1-mediated elevation of KLF7 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis through upregulating TLR4 and PTK2. Theranostics 2023, 13, 4042–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, P.; Roncarati, P.; Demoulin, S.; Pilard, C.; Ancion, M.; Reynders, C.; Lerho, T.; Bruyere, D.; Lebeau, A.; Radermecker, C.; et al. Extracellular HMGB1 blockade inhibits tumor growth through profoundly remodeling immune microenvironment and enhances checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Shi, X. Extracellular HMGB1 promotes CD44 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating miR-21. Aging 2021, 13, 8380–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Zhang, S.Y.; Shi, M.; Xu, X.P. HMGB1 Promotes the Proliferation and Metastasis of Lung Cancer by Activating the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820948054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, L.; Sun, H.; Xie, K. High-Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Promotes Angiogenesis and Tumor Migration by Regulating Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 (HIF-1α) Expression via the Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)/AKT Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.-H.; Zhu, L.; Wang, M.; Ning, Y.; Chen, F.-Q.; Gao, X.-Q.; Yang, C.-T.; Wang, H.-W.; Li, H.-L. Mechanisms involved in the HMGB1 modulation of tumor multidrug resistance (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2023, 52, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, C.; Huebener, P.; Pradere, J.P.; Antoine, D.J.; Friedman, R.A.; Schwabe, R.F. HMGB1 links chronic liver injury to progenitor responses and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2436–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Chang, Y.; Liang, X.; Cardinal, J.S.; Huang, H.; Thorne, S.H.; Monga, S.P.; Geller, D.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Tsung, A. High-mobility group box 1 activates caspase-1 and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasiveness and metastases. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.-D.; Cui, L.; Peng, C.-H.; Cheng, D.-F.; Han, B.-S.; Huang, F. Expression and clinical significance of HMGB1 in human liver cancer: Knockdown inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaser, A.M.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.R.; Hu, G.S.; Xiao, M.F.; Huang, Z.B.; Duan, C.J.; Tian, W.; Tang, D.L.; Fan, X.G. The Role of receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (RAGE) in the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5982–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, K.E.I.; Sakoda, M.; Ueno, S.; Hiwatashi, K.; Iino, S.; Minami, K.; Kawasaki, Y.; Hashiguchi, M.; Tanoue, K.; Mataki, Y.; et al. Clinical Implication of the Relationship Between High Mobility Group Box-1 and Tumor Differentiation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, W.; Tohme, S.; Chen, M.; Fu, Y.; Tian, D.; Lotze, M.; Tang, D.; Tsung, A. Hypoxia induced HMGB1 and mitochondrial DNA interactions mediate tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma through Toll-like receptor 9. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Q.; Huang, B.-F.; Wang, Y.; Tang, C.-H.; Jin, H.-C.; Shao, F.; Shao, J.-K.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Y. Subcellular localization of HMGB1 in colorectal cancer impacts on tumor grade and survival prognosis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idoudi, S.; Bedhiafi, T.; Pedersen, S.; Elahtem, M.; Alremawi, I.; Akhtar, S.; Dermime, S.; Merhi, M.; Uddin, S. Role of HMGB1 and its associated signaling pathways in human malignancies. Cell. Signal. 2023, 112, 110904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Cheng, J.; Cai, T.; Wu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Qi, S.; Qi, Z. Calunduloside E inhibits HepG2 cell proliferation and migration via p38/JNK-HMGB1 signalling axis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 147, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Xu, B.; Pang, H.; Xiao, L.; Mei, Q.; He, X. Ozonated Water Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Invasion and Metastasis by Regulating the HMGB1/NF-κB/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.W.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, H.; Hong, D.J.; Chung, J.B.; Stroncek, D.; Lim, J.-B. Serum high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) is closely associated with the clinical and pathologic features of gastric cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.H.; Jia, C.Q.; Tian, H.; Xiao, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.H.; Dong, L.; Lin, D.J. Serum high mobility group box protein 1 as a clinical marker for non-small cell lung cancer. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 1949–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Raoul, J.L.; Sherman, M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Bolondi, L.; Craxi, A.; Galle, P.R.; Santoro, A.; Beaugrand, M.; Sangiovanni, A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Subanalyses of a phase III trial. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Rong, D.; Reiter, F.P.; et al. The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Sun, L.; Fu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Hu, X.; Zhou, P.; Quan, J.; Li, N.; Fan, X.-G. High mobility group box 1 promotes sorafenib resistance in HepG2 cells and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Dai, W.; Wang, F.; Lu, J.; Shen, M.; Chen, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, J.; et al. Ethyl pyruvate inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulation of the HMGB1–RAGE and AKT pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Guan, X.-W.; Gribben, J.G.; Liu, F.-T.; Jia, L. Blockade of HMGB1 signaling pathway by ethyl pyruvate inhibits tumor growth in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z. Ethyl pyruvate inhibits glioblastoma cells migration and invasion through modulation of NF-κB and ERK-mediated EMT. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
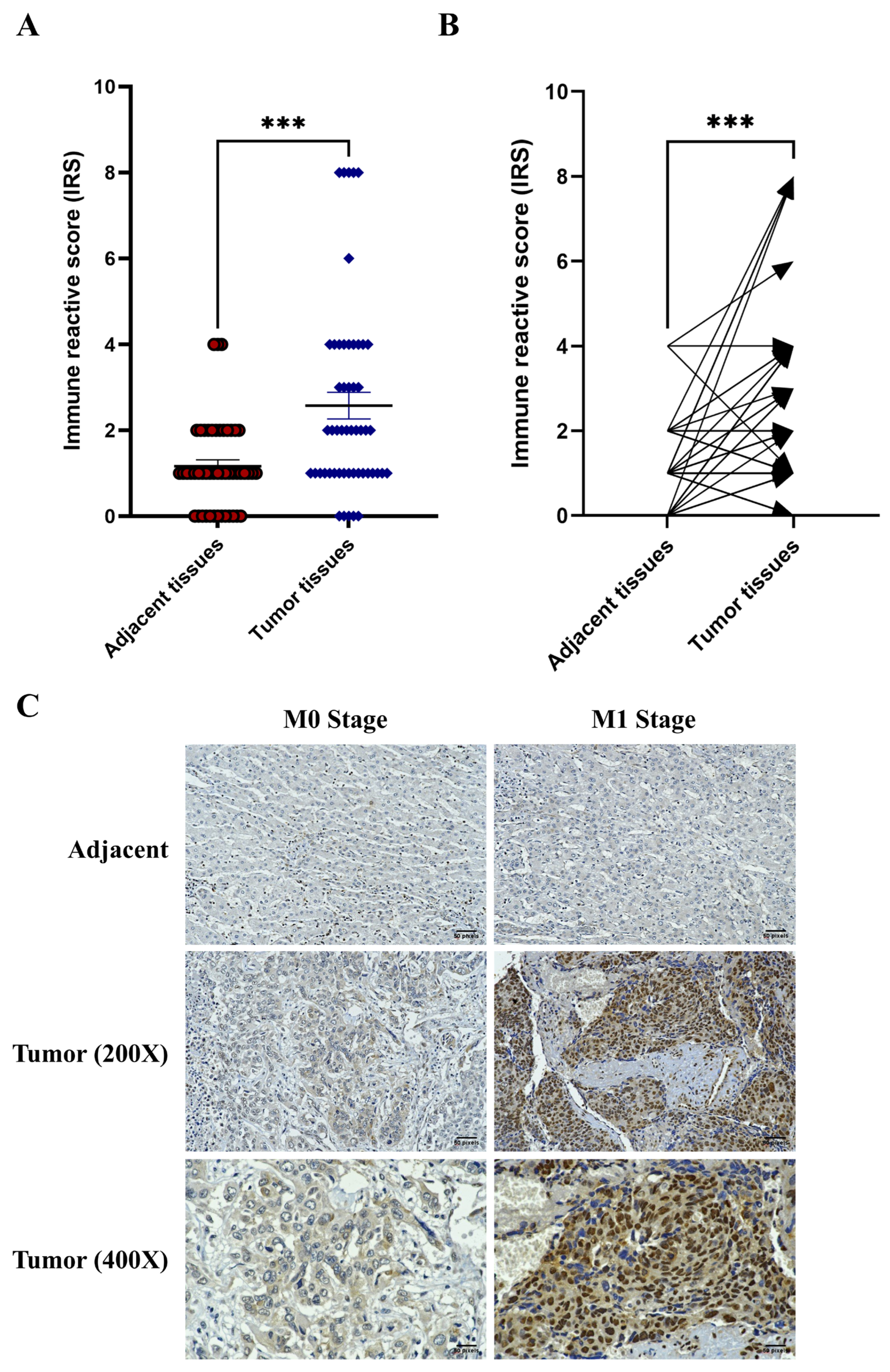
| Variables | n (%) | Mean IRS | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 35 (73%) | 3.029 | 0.6982 |
| Female | 13 (27%) | 2.692 | |
| Age | |||
| <60 | 13 (27%) | 3.154 | 0.7323 |
| ≥60 | 35 (73%) | 2.857 | |
| T staging | |||
| T1 | 26 (55%) | 3.269 | 0.3416 |
| T2 | 16 (33%) | 2.000 | |
| T3 | 1 (2%) | 3.000 | |
| T4 | 5 (10%) | 4.200 | |
| M Staging | |||
| M0 | 44 (92%) | 2.614 | 0.0035 * |
| M1 | 4 (8%) | 6.500 | |
| Tumor extension | |||
| Confined to liver | 43 (90%) | 2.791 | 0.2610 |
| Involves visceral peritoneum | 5 (10%) | 4.200 | |
| Vascular invasion | |||
| Not identified | 30 (62%) | 3.400 | 0.1166 |
| Present | 18 (38%) | 2.167 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiraviriyakul, A.; Nensat, C.; Promchai, S.; Chaiaun, Y.; Hoiraya, Y.; Yamnak, N.; Khutanthong, S.; Singpan, N.; Songjang, W. High Mobility Group Box 1 Is Potential Target Therapy for Inhibiting Metastasis and Enhancing Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083491
Jiraviriyakul A, Nensat C, Promchai S, Chaiaun Y, Hoiraya Y, Yamnak N, Khutanthong S, Singpan N, Songjang W. High Mobility Group Box 1 Is Potential Target Therapy for Inhibiting Metastasis and Enhancing Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083491
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiraviriyakul, Arunya, Chatchai Nensat, Samitanan Promchai, Yanisa Chaiaun, Yanisa Hoiraya, Nutnicha Yamnak, Suphakit Khutanthong, Nun Singpan, and Worawat Songjang. 2025. "High Mobility Group Box 1 Is Potential Target Therapy for Inhibiting Metastasis and Enhancing Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083491
APA StyleJiraviriyakul, A., Nensat, C., Promchai, S., Chaiaun, Y., Hoiraya, Y., Yamnak, N., Khutanthong, S., Singpan, N., & Songjang, W. (2025). High Mobility Group Box 1 Is Potential Target Therapy for Inhibiting Metastasis and Enhancing Drug Sensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083491







