Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase-3 Immunopositivity in Human Model of Asphyxial Death
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
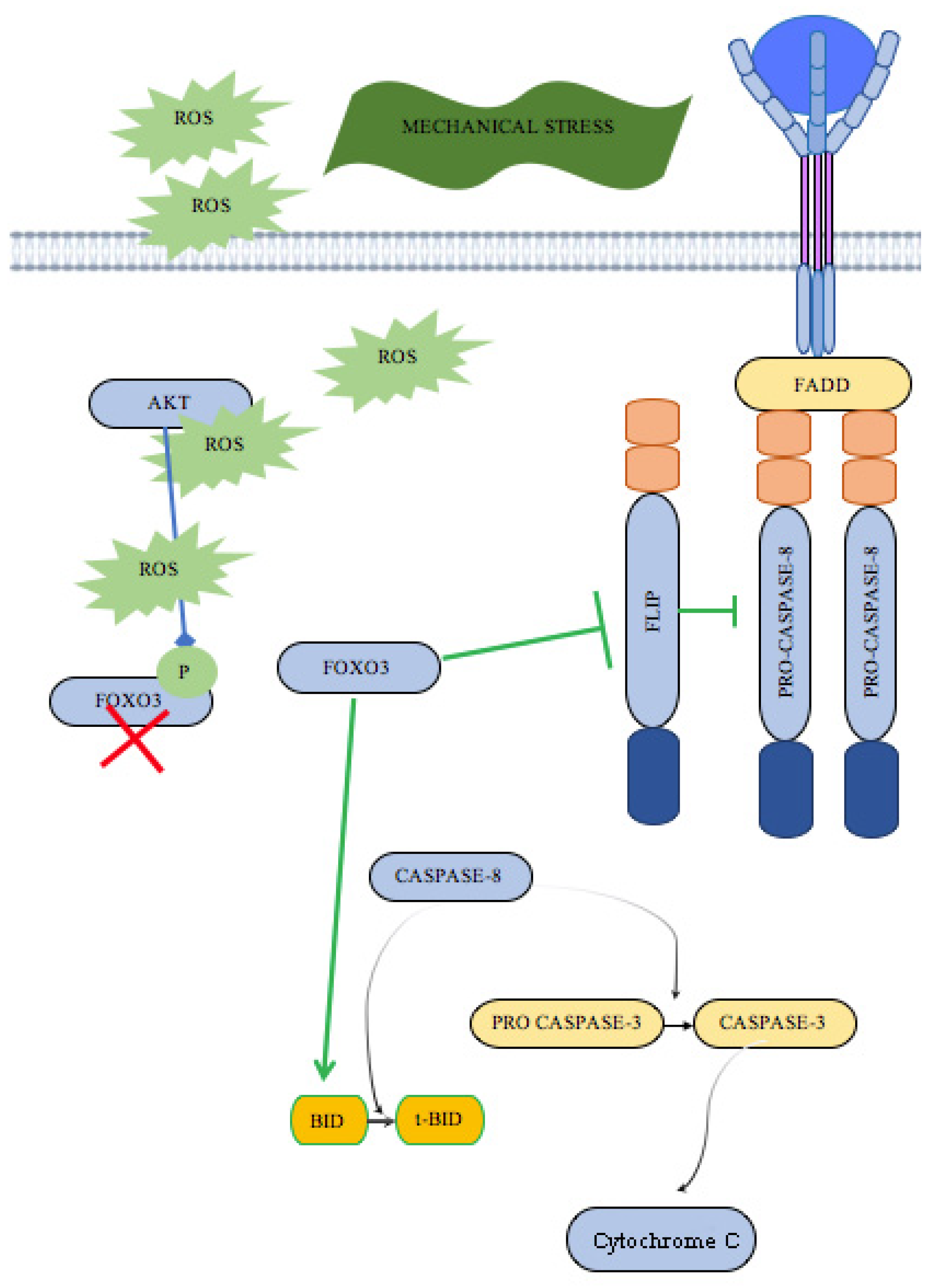
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Group Selection and Samples Collection
4.2. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.3. Quantitative Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cade, C.E.; Clark, A.C. Caspases—Key Players in Apoptosis. In Proteases in Apoptosis: Pathways, Protocols and Translational Advances; Bose, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 31–51. ISBN 978-3-319-19497-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mahara, A.; Morimoto, N.; Sakuma, T.; Fujisato, T.; Yamaoka, T. Complete Cell Killing by Applying High Hydrostatic Pressure for Acellular Vascular Graft Preparation. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 379607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamaraeva, M.V.; Sabirov, R.Z.; Maeno, E.; Ando-Akatsuka, Y.; Bessonova, S.V.; Okada, Y. Cells Die with Increased Cytosolic ATP during Apoptosis: A Bioluminescence Study with Intracellular Luciferase. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madea, B. (Ed.) Estimation of the Time Since Death, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 978-0-429-16620-4. [Google Scholar]
- Madea, B. Importance of Supravitality in Forensic Medicine. Forensic Sci. Int. 1994, 69, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauvageau, A. True and Simulated Homicidal Hangings: A Six-Year Retrospective Study. Med. Sci. Law 2009, 49, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, C.T.; Cadden, G.A.; Margolius, K.A. Death by Hanging in Western Australia. Pathology 1995, 27, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, A.; Marshall, T.K. Hanging in Northern Ireland—A Survey. Med. Sci. Law 1986, 26, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, D.A. Hanging—A Review. Forensic Sci. Int. 1982, 20, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.L.; Reay, D.T.; Eisele, J.W.; Bonnell, H.J. Correlation of Circumstances with Pathological Findings in Asphyxial Deaths by Hanging: A Prospective Study of 61 Cases from Seattle, WA. J. Forensic Sci. 1985, 30, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Elfawal, M.A.; Awad, O.A. Deaths from Hanging in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia. Med. Sci. Law 1994, 34, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmak, D. Asphyxial Deaths: A Retrospective Study and Review of the Literature. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2006, 27, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meel, B. Epidemiology of Suicide by Hanging in Transkei, South Africa. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2006, 27, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Peñaranda, J.M.; Álvarez, T.; Miguéns, X.; Rodríguez-Calvo, M.S.; De Abajo, B.L.; Cortesão, M.; Cordeiro, C.; Vieira, D.N.; Muñoz, J.I. Characterization of Lesions in Hanging Deaths. J. Forensic Sci. 2008, 53, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luke, J.L. Asphyxial Deaths by Hanging in New York City, 1964-1965. J. Forensic Sci. 1967, 12, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maiese, A.; Manetti, A.C.; Santoro, P.; Del Duca, F.; De Matteis, A.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. FOXO3 Depletion as a Marker of Compression-Induced Apoptosis in the Ligature Mark: An Immunohistochemical Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Duca, F.; Manetti, A.C.; Maiese, A.; Napoletano, G.; Ghamlouch, A.; Pascale, N.; Giorgio, B.; Paola, F.; Russa, R.L. Death Due to Anaphylactic Reaction: The Role of the Forensic Pathologist in an Accurate Postmortem Diagnosis. Medicina 2023, 59, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Duca, F.; Maiese, A.; Spina, F.; Visi, G.; La Russa, R.; Santoro, P.; Pignotti, M.S.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemorrhage in Infancy: A Case Report and Literature Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Duca, F.; Napoletano, G.; Volonnino, G.; Maiese, A.; La Russa, R.; Di Paolo, M.; De Matteis, S.; Frati, P.; Bonafè, M.; Fineschi, V. Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown, Central Nervous System Cell Damage, and Infiltrated T Cells as Major Adverse Effects in CAR-T-Related Deaths: A Literature Review. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1272291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Kuninaka, Y.; Nosaka, M.; Shimada, E.; Hata, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Hashizume, Y.; Kimura, A.; Furukawa, F.; Kondo, T. Forensic Application of Epidermal AQP3 Expression to Determination of Wound Vitality in Human Compressed Neck Skin. Int. J. Legal Med. 2018, 132, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legaz Pérez, I.; Falcón, M.; Gimenez, M.; Diaz, F.M.; Pérez-Cárceles, M.D.; Osuna, E.; Nuno-Vieira, D.; Luna, A. Diagnosis of Vitality in Skin Wounds in the Ligature Marks Resulting From Suicide Hanging. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2017, 38, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turillazzi, E.; Vacchiano, G.; Luna-Maldonado, A.; Neri, M.; Pomara, C.; Rabozzi, R.; Riezzo, I.; Fineschi, V. Tryptase, CD15 and IL-15 as Reliable Markers for the Determination of Soft and Hard Ligature Marks Vitality. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 1539–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputo, F.; Barranco, R.; Ventura, F.; Fracasso, T. Immunohistochemical Detection of Fibronectin, P-Selectin, FVIII, HSP-70 and MRP-8 in the Skin of Ligature Marks of Suicidal Hangings. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2023, 96, 102524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudnyk, V. Immunohistochemical Diagnosis of the Viability of the Strangulation Furrow. EUREKA Health Sci. 2021, 3, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focardi, M.; Bugelli, V.; Venturini, M.; Bianchi, I.; Defraia, B.; Pinchi, V.; Bacci, S. Increased Expression of iNOS by Langerhans Cells in Hanging Marks. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 2022, 54, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ishida, Y.; Ishigami, A.; Nosaka, M.; Kuninaka, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Kofuna, A.; Matsuki, J.; Osako, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. Forensic Application of Epidermal Expression of HSP27 and HSP70 for the Determination of Wound Vitality in Human Compressed Neck Skin. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, M.; Fabbri, M.; D’Errico, S.; Di Paolo, M.; Frati, P.; Gaudio, R.M.; La Russa, R.; Maiese, A.; Marti, M.; Pinchi, E.; et al. Regulation of miRNAs as New Tool for Cutaneous Vitality Lesions Demonstration in Ligature Marks in Deaths by Hanging. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetti, A.C.; Maiese, A.; Baronti, A.; Mezzetti, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V.; Turillazzi, E. MiRNAs as New Tools in Lesion Vitality Evaluation: A Systematic Review and Their Forensic Applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiese, A.; De Matteis, A.; Bolino, G.; Turillazzi, E.; Frati, P.; Fineschi, V. Hypo-Expression of Flice-Inhibitory Protein and Activation of the Caspase-8 Apoptotic Pathways in the Death-Inducing Signaling Complex Due to Ischemia Induced by the Compression of the Asphyxiogenic Tool on the Skin in Hanging Cases. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-R.; Teng, D.-H.; Dong, G.-K.; Yin, W.-J.; Cai, H.-X. Expression of caspase-3 and HAX-1 after cerebral contusion in rat. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015, 31, 7–10, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, Q.-Y.; Yang, G.-M.; Zhang, P.; Dong, W.-J.; Jing, D.; Hou, Z.-P.; Peng, Y.-X.; Yu, Y.; Li, L.-H.; Hong, S.-J. Nrf2 Expression, Mitochondrial Fission, and Neuronal Apoptosis in the Prefrontal Cortex of Methamphetamine Abusers and Rats. Brain Res. 2024, 1837, 148973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, T.; Yar Saglam, A.S.; Göçün, P.U.; Alp, E.; Konac, E.; Menevşe, A. Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase Levels in Estimation of the Wound Age. Turk. J. Biochem. 2018, 43, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.R.; Pollok, K.E. Targeting the Anti-Apoptotic Protein c-FLIP for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2011, 3, 1639–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safa, A.; Day, T.; Wu, C.-H. Cellular FLICE-Like Inhibitory Protein (C-FLIP): A Novel Target for Cancer Therapy. CCDT 2008, 8, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, S.; Schleich, K.; Lavrik, I.N. Cellular FLICE-like Inhibitory Proteins (c-FLIPs): Fine-Tuners of Life and Death Decisions. Exp. Cell Res. 2012, 318, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheau, O.; Lens, S.; Gaide, O.; Alevizopoulos, K.; Tschopp, J. NF-κB Signals Induce the Expression of c-FLIP. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 5299–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, N.; Yu, M.; Shen, B.; Xiang, J.; Lin, A. Cyclic AMP Inhibits JNK Activation by CREB-Mediated Induction of c-FLIPL and MKP-1, Thereby Antagonizing UV-Induced Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, S.; Candi, E.; Alotto, D.; Castagnoli, C.; Melino, G.; Viganò, M.A.; Mantovani, R. P63 Regulates the Caspase-8-FLIP Apoptotic Pathway in Epidermis. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safa, A.R. Roles of C-FLIP in Apoptosis, Necroptosis, and Autophagy. J. Carcinog. Mutagen. 2013, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skurk, C.; Maatz, H.; Kim, H.-S.; Yang, J.; Abid, M.R.; Aird, W.C.; Walsh, K. The Akt-Regulated Forkhead Transcription Factor FOXO3a Controls Endothelial Cell Viability through Modulation of the Caspase-8 Inhibitor FLIP. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacko, A.; Gupta, C.; Palimar, V.; Nayak, M.D. Epidemiological, Gross Morphological, And Histopathological Analysis of Postmortem Cases of Hanging—An Observational Study. F1000Research 2025, 13, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

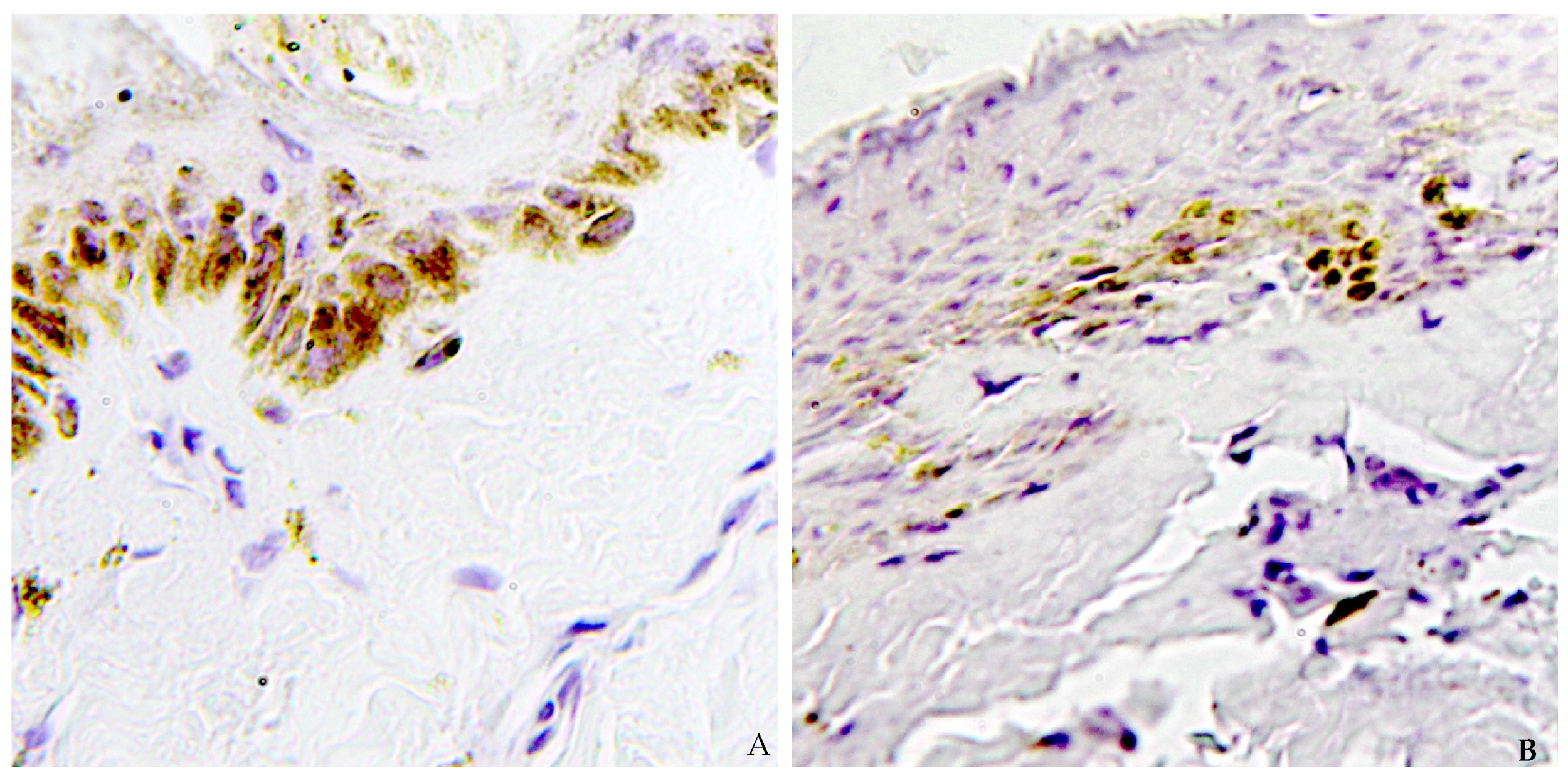
| n° | Sex | Ligature Mark Caspase-3 | Uninjured Skin Caspase-3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 3 | 0 |
| 2 | F | 2 | 1 |
| 3 | M | 2 | 0 |
| 4 | M | 3 | 0 |
| 5 | M | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | M | 2 | 1 |
| 7 | F | 2 | 0 |
| 8 | F | 2 | 0 |
| 9 | F | 3 | 0 |
| 10 | M | 3 | 0 |
| 11 | M | 2 | 1 |
| 12 | F | 3 | 0 |
| 13 | M | 2 | 0 |
| 14 | M | 3 | 0 |
| 15 | M | 3 | 0 |
| 16 | F | 2 | 1 |
| 17 | M | 2 | 0 |
| 18 | M | 2 | 0 |
| 19 | M | 2 | 1 |
| 20 | F | 3 | 0 |
| 21 | M | 3 | 0 |
| Grade | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 3 | Positive staining |
| 2 | Minimal decrease in staining compared to normally stained tissue |
| 1 | A clear decrease in staining with some positivity (brown color) remaining |
| 0 | No positive staining |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Duca, F.; Treglia, M.; La Russa, R.; De Simone, S.; Cipolloni, L.; Maiese, A.; Frati, P. Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase-3 Immunopositivity in Human Model of Asphyxial Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073317
Del Duca F, Treglia M, La Russa R, De Simone S, Cipolloni L, Maiese A, Frati P. Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase-3 Immunopositivity in Human Model of Asphyxial Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073317
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Duca, Fabio, Michele Treglia, Raffaele La Russa, Stefania De Simone, Luigi Cipolloni, Aniello Maiese, and Paola Frati. 2025. "Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase-3 Immunopositivity in Human Model of Asphyxial Death" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073317
APA StyleDel Duca, F., Treglia, M., La Russa, R., De Simone, S., Cipolloni, L., Maiese, A., & Frati, P. (2025). Evaluation of Apoptotic Caspase-3 Immunopositivity in Human Model of Asphyxial Death. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3317. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073317








