A Multifaceted Giant Protein Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Subject No. | Mutation (Variant) | Domain (Region) | Symptoms of Disease | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | [c.15682 G>T p. (Asp5228Tyr)] | MTBD | Lissencephaly with brainstem hypoplasia and dysplasia | [15] |
| M2 | (g.39914279 C>G p. T-4642-S) Missense mutation | Spectrin repeats | Familial psychosis | [16] |
| M3, M4 | [c.1517 C>T (p.Thr506Ile)] and [c.11654 T>C (p. Ile3885Thr)] Heterozygous missense mutation | M3, plakin domain M4, spectrin repeats | Spectraplakinopathy type I: progressive spastic tetraplegia, dystonia, joint contracture, feeding difficulty, and developmental delay | [17] |
| M5 | A frame-shift mutation (p.V266fs) | Truncation after ABD | Bipolar disorder | [18] |



2. Roles of MACF1 in Cancers
2.1. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
2.2. Colorectal Cancer
2.3. Glioblastoma
2.4. Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
2.5. Lung Cancer
2.6. Melanoma
2.7. Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (MIBC)
2.8. Ovarian Cancer
2.9. Pancreatic Cancer
2.10. Vulvar Squamous Cell Carcinoma (VSCC)
3. Roles of MACF1 in Other Diseases
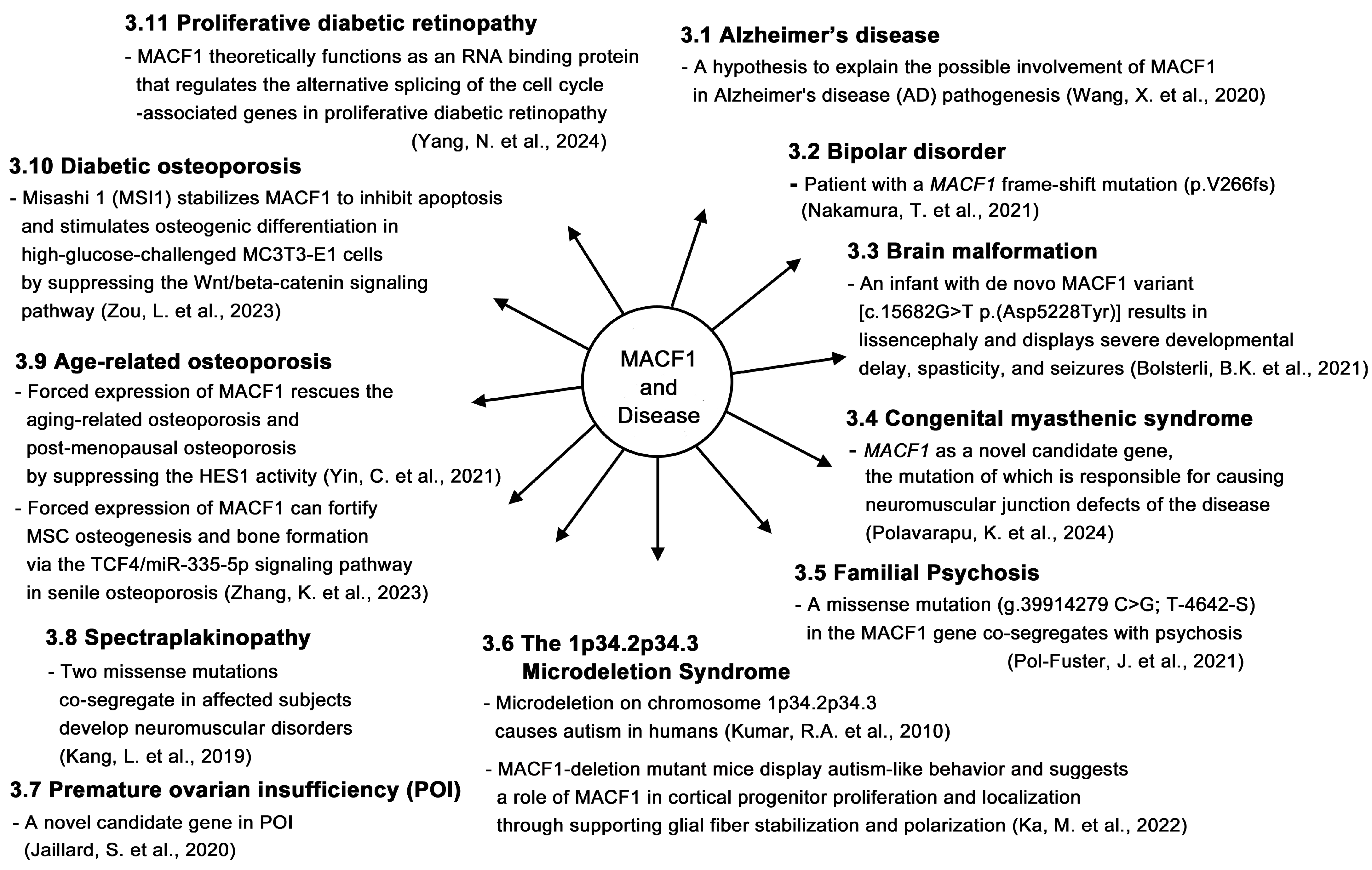
3.1. Alzheimer’s Disease
3.2. Bipolar Disorder
3.3. Brain Malformation
3.4. Congenital Myasthenic Syndrome
3.5. Familial Psychosis
3.6. The 1p34.2p34.3 Microdeletion Syndrome
3.7. Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
3.8. Spectraplakinopathy
3.9. Age-Related Osteoporosis
3.10. Diabetic Osteoporosis
3.11. Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
4. Physiological Roles of MACF1
4.1. Adhesome Architecture
4.2. Bone Formation
4.3. Neuronal Aging
4.4. Osteoblast Differentiation
4.5. Preosteoblast Migration
4.6. Tooth Development
5. Other Roles of MACF1
5.1. MACF1 as a Biomarker for Predicting Bloodstream Infections in Children with Burns
5.2. MACF1 SNP Is Associated with Eyebrow Thickness in the Male Pakistani Punjabi Population
5.3. MACF1 Serves as a Genetic Factor for Selection Signatures
5.4. Correlation of DNA Methylation Patterns of MACF1 Genes with Bull Offspring Development
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Kodama, A.; Karakesisoglou, I.; Wong, E.; Vaezi, A.; Fuchs, E. ACF7: An essential integrator of microtubule dynamics. Cell 2003, 115, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yue, J.; Wu, X. Spectraplakin family proteins-cytoskeletal crosslinkers with versatile roles. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 2447–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suozzi, K.C.; Wu, X.; Fuchs, E. Spectraplakins: Master orchestrators of cytoskeletal dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 197, 465–475. [Google Scholar]
- Cusseddu, R.; Robert, A.; Cote, J.F. Strength Through Unity: The Power of the Mega-Scaffold MACF1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnenberg, A.; Liem, R.K. Plakins in development and disease. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2189–2203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jefferson, J.J.; Leung, C.L.; Liem, R.K. Plakins: Goliaths that link cell junctions and the cytoskeleton. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 542–553. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.M.; Chen, H.J.; Leung, C.L.; Parry, D.A.; Liem, R.K. Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1b: A novel plakin that localizes to the Golgi complex. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118 Pt 16, 3727–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipworth, R.J.; Stewart, G.D.; Bhana, M.; Christie, J.; Sturgeon, C.M.; Guttridge, D.C.; Cronshaw, A.D.; Fearon, K.C.; Ross, J.A. Mass spectrometric detection of candidate protein biomarkers of cancer cachexia in human urine. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 36, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgo, A.; Proux-Gillardeaux, V.; Sotirakis, E.; Bun, P.; Casano, A.; Verraes, A.; Liem, R.K.; Formstecher, E.; Coppey-Moisan, M.; Galli, T. A molecular network for the transport of the TI-VAMP/VAMP7 vesicles from cell center to periphery. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 166–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakinuma, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Tsukada, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Toh, B.H. Interaction between p230 and MACF1 is associated with transport of a glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol-anchored protein from the Golgi to the cell periphery. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 298, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ka, M.; Kim, W.Y. Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 Is Required for Dendritic Arborization and Axon Outgrowth in the Developing Brain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6018–6032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Lin, C.M.; Lin, C.S.; Perez-Olle, R.; Leung, C.L.; Liem, R.K. The role of microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1 (MACF1) in the Wnt signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moffat, J.J.; Ka, M.; Jung, E.M.; Smith, A.L.; Kim, W.Y. The role of MACF1 in nervous system development and maintenance. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 69, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Ali, A.; Hu, L.; Zhao, F.; Yin, C.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.; Qian, A. Microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1, a novel potential target in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1953–1958. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bolsterli, B.K.; Steindl, K.; Kottke, R.; Steinfeld, R.; Boltshauser, E. Lissencephaly with Brainstem Hypoplasia and Dysplasia: Think MACF1. Neuropediatrics 2021, 52, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol-Fuster, J.; Canellas, F.; Ruiz-Guerra, L.; Medina-Dols, A.; Bisbal-Carrio, B.; Asensio, V.; Ortega-Vila, B.; Marzese, D.; Vidal, C.; Santos, C.; et al. Familial Psychosis Associated with a Missense Mutation at MACF1 Gene Combined with the Rare Duplications DUP3p26.3 and DUP16q23.3, Affecting the CNTN6 and CDH13 Genes. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 622886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y. Mutations of MACF1, Encoding Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking-Factor 1, Cause Spectraplakinopathy. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, T.; Nakajima, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Itohara, S.; Kasahara, T.; Tsuboi, T.; Kato, T. Functional and behavioral effects of de novo mutations in calcium-related genes in patients with bipolar disorder. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradzik, M.; Humphries, J.D.; Stojanovic, N.; Nestic, D.; Majhen, D.; Dekanic, A.; Samarzija, I.; Sedda, D.; Weber, I.; Humphries, M.J.; et al. KANK2 Links αVβ5 Focal Adhesions to Microtubules and Regulates Sensitivity to Microtubule Poisons and Cell Migration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.M.; Krantz, S.; Jambusaria, A.; Toth, P.T.; Moon, H.G.; Gunarathna, I.; Park, G.Y.; Rehman, J. Mitofusin-2 stabilizes adherens junctions and suppresses endothelial inflammation via modulation of β-catenin signaling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2736. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Ven, K.; Chastney, M.; Kokate, S.B.; Peranen, J.; Aaron, J.; Kogan, K.; Almeida-Souza, L.; Kremneva, E.; Poincloux, R.; et al. Focal adhesions contain three specialized actin nanoscale layers. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.X.; Ma, X.L.; Lin, X.; Zhao, F.; Li, D.J.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, K.W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, P.; Xiao, Y.Y.; et al. Deficiency of Macf1 in osterix expressing cells decreases bone formation by Bmp2/Smad/Runx2 pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liang, C.; Hu, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Lin, X.; et al. Silencing of miR-138-5p sensitizes bone anabolic action to mechanical stimuli. Theranostics 2020, 10, 12263–12278. [Google Scholar]
- Okenve-Ramos, P.; Gosling, R.; Chojnowska-Monga, M.; Gupta, K.; Shields, S.; Alhadyian, H.; Collie, C.; Gregory, E.; Sanchez-Soriano, N. Neuronal ageing is promoted by the decay of the microtubule cytoskeleton. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002504. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Yin, C.; Chen, D.; Wu, Z.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. MACF1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by sequestering repressors in cytoplasm. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2160–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, P.; Yin, C.; Li, D.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Pei, J.; Tian, Y.; Qian, A. MACF1 promotes preosteoblast migration by mediating focal adhesion turnover through EB1. Biol. Open 2020, 9, bio048173. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, W.; Lin, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Miao, Z.; Deng, X.; Duan, X.; et al. MACF1 deficiency suppresses tooth mineralization through IGF1 mediated crosstalk between odontoblasts and ameloblasts. Genes Dis. 2024, 11, 101103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurumi, A.; Flaherty, P.J.; Que, Y.A.; Ryan, C.M.; Banerjee, A.; Chakraborty, A.; Almpani, M.; Shankar, M.; Goverman, J.; Schulz, J.T., 3rd; et al. A Preventive Tool for Predicting Bloodstream Infections in Children with Burns. Shock 2023, 59, 393–399. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, M.; Adnan, A.; Rehman, R.A.; Nazir, S.; Adeyemo, O.A.; Amer, S.A.M.; Hadi, S.; Liu, F.; Wang, C.C.; Rakha, A. Evaluation of facial hair-associated SNPs: A pilot study on male Pakistani Punjabi population. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2023, 19, 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Huang, G.Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Teng, S.H.; Cao, Y.H.; Sun, J.L.; Hanif, Q.; Chen, N.B.; Lei, C.Z.; Liao, Y.Y. Selection signatures of Fuzhong Buffalo based on whole-genome sequences. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 674. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; An, X.; Yuan, C.; Guo, T.; Yue, Y. Genomic Selection for Live Weight in the 14th Month in Alpine Merino Sheep Combining GWAS Information. Animals 2023, 13, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.N.; Gao, Y.; Hatfield, M.J.; de Avila, J.M.; McClure, M.C.; Du, M. Cold exposure impacts DNA methylation patterns in cattle sperm. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1346150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F. The role of MACF1 on acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation is involved in Runx2-targeted PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 478, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, H.; Wang, J.; Hu, L.; Huang, Z. LRRC1 knockdown downregulates MACF1 to inhibit the malignant progression of acute myeloid leukemia by inactivating β-catenin/c-Myc signaling. J. Mol. Histol. 2024, 55, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafaie, S.; Xu, L.; Hu, T. Statistical methods with exhaustive search in the identification of gene-gene interactions for colorectal cancer. Genet. Epidemiol. 2021, 45, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, K.; Borlay, D.; Kutten, O.; Quick, Q.A. Inhibition of the Spectraplakin Protein Microtubule Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 Sensitizes Glioblastomas to Radiation. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2020, 8, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Duan, C.; Gui, Y.; Chen, D.; Su, X. Exosomal circMACF1 drives PI3K/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy suppression in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2024, 70, 179–185. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B. Identification of key genes in lung adenocarcinoma based on a competing endogenous RNA network. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, X.; Chen, C.; Tong, S.; Zhang, J. Circ_MACF1 targets miR-421 to upregulate FMO2 to suppress paclitaxel resistance and malignant cellular behaviors in lung adenocarcinoma. Thorac. Cancer 2023, 14, 3348–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jian, X.; Dou, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, F. Decreasing Microtubule Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1 Inhibits Melanoma Metastasis by Decreasing Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, G.; Bolkov, M.A.; Shinwari, K.; Tuzankina, I.A.; Chereshnev, V.A.; Wang, Z. Defining muscle-invasive bladder cancer immunotypes by introducing tumor mutation burden, CD8+ T cells, and molecular subtypes. Hereditas 2021, 158, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Hu, K.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, C.; Lv, J.; Lin, Z.; Wen, B. Expression and Clinical Significance of Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1 in Serous Ovarian Cancer. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheasley, D.; Nigam, A.; Zethoven, M.; Hunter, S.; Etemadmoghadam, D.; Semple, T.; Allan, P.; Carey, M.S.; Fernandez, M.L.; Dawson, A.; et al. Genomic analysis of low-grade serous ovarian carcinoma to identify key drivers and therapeutic vulnerabilities. J. Pathol. 2021, 253, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shi, W.; Zhu, S.; Yang, C. Construction of a 6-gene prognostic signature to assess prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer. Medicine 2020, 99, e22092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieske, K.; Alawi, M.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Jaeger, A.; Eylmann, K.; Burandt, E.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Joosse, S.A.; Woelber, L. Genomic characterization of vulvar squamous cell carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 158, 547–554. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, G.; Fu, C. Corrigendum to ‘Alteration of scaffold: Possible role of MACF1 in Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis’ [Med. Hypoth. 130 (2019) 109259]. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 136, 109509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Polavarapu, K.; Sunitha, B.; Topf, A.; Preethish-Kumar, V.; Thompson, R.; Vengalil, S.; Nashi, S.; Bardhan, M.; Sanka, S.B.; Huddar, A.; et al. Clinical and genetic characterisation of a large Indian congenital myasthenic syndrome cohort. Brain 2024, 147, 281–296. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.A.; Sudi, J.; Babatz, T.D.; Brune, C.W.; Oswald, D.; Yen, M.; Nowak, N.J.; Cook, E.H.; Christian, S.L.; Dobyns, W.B. A de novo 1p34.2 microdeletion identifies the synaptic vesicle gene RIMS3 as a novel candidate for autism. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ka, M.; Moffat, J.J.; Kim, W.Y. MACF1, Involved in the 1p34.2p34.3 Microdeletion Syndrome, is Essential in Cortical Progenitor Polarity and Brain Integrity. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 2187–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaillard, S.; Bell, K.; Akloul, L.; Walton, K.; McElreavy, K.; Stocker, W.A.; Beaumont, M.; Harrisson, C.; Jaaskelainen, T.; Palvimo, J.J.; et al. New insights into the genetic basis of premature ovarian insufficiency: Novel causative variants and candidate genes revealed by genomic sequencing. Maturitas 2020, 141, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, C.; Tian, Y.; Hu, L.; Yu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Miao, Z.; Qian, A. MACF1 alleviates aging-related osteoporosis via HES1. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 6242–6257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Qiu, W.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Lin, X.; Qian, A. MACF1 overexpression in BMSCs alleviates senile osteoporosis in mice through TCF4/miR-335-5p signaling pathway. J. Orthop. Translat. 2023, 39, 177–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, L.; Xiang, C.; Lu, M. MSI1 Stabilizes MACF1 to Inhibit Apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 Cells Induced by High Glucose and Promote Osteogenic Differentiation Through Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Mol. Biotechnol. 2023, 65, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Zhang, N.; Lu, G.; Zeng, S.; Xing, Y.; Du, L. RNA-binding proteins potentially regulate the alternative splicing of cell cycle-associated genes in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6731. [Google Scholar]
- Stubbins, R.J.; Francis, A.; Kuchenbauer, F.; Sanford, D. Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Review for General Practitioners in Oncology. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6245–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhuang, H.; Shi, X. Therapeutic efficacy of ferroptosis in the treatment of colorectal cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 563. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, C.M.; de Groot, J. Updates for newly diagnosed and recurrent glioblastoma: A review of recent clinical trials. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2024, 37, 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- Afghani, N.; Mehta, T.; Wang, J.; Tang, N.; Skalli, O.; Quick, Q.A. Microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1, a novel target in glioblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Cavaliere, M.; Bisogno, A.; Scarpa, A.; D’Urso, A.; Marra, P.; Colacurcio, V.; De Luca, P.; Ralli, M.; Cassandro, E.; Cassandro, C. Biomarkers of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: A review. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 54, 151787. [Google Scholar]
- Warth, A.; Muley, T.; Meister, M.; Stenzinger, A.; Thomas, M.; Schirmacher, P.; Schnabel, P.A.; Budczies, J.; Hoffmann, H.; Weichert, W. The novel histologic International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer/American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society classification system of lung adenocarcinoma is a stage-independent predictor of survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar]
- May, J.M.; Bylicky, M.; Chopra, S.; Coleman, C.N.; Aryankalayil, M.J. Long and short non-coding RNA and radiation response: A review. Transl. Res. 2021, 233, 162–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.X.; Wang, R.; Jin, X.Y.; Zeng, J.; Pan, J. LncRNA DGCR5 promotes lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) progression via inhibiting hsa-mir-22-3p. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 4126–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, C.; Cao, C.; Li, Q.; Jin, X.; Shi, H. Hsa_circ_RNA_0011780 Represses the Proliferation and Metastasis of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Decreasing FBXW7 via Targeting miR-544a. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarelli, N.; Aleman, S.J.; Mark, I.M.; Tran, J.T.; Kwak, S.; Botto, E.; Aflatooni, S.; Diaz, M.J.; Lipner, S.R. A Review of Current and Pipeline Drugs for Treatment of Melanoma. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumish, M.A.; Kohn, E.C.; Tew, W.P. Top advances of the year: Ovarian cancer. Cancer 2024, 130, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent advances in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, clinical trials and new drug development strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 211. [Google Scholar]
- Ka, M.; Jung, E.M.; Mueller, U.; Kim, W.Y. MACF1 regulates the migration of pyramidal neurons via microtubule dynamics and GSK-3 signaling. Dev. Biol. 2014, 395, 4–18. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Shen, Q.T.; Oristian, D.S.; Lu, C.P.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, H.W.; Fuchs, E. Skin stem cells orchestrate directional migration by regulating microtubule-ACF7 connections through GSK3β. Cell 2011, 144, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Vidal, G.S.; Djurisic, M.; William, C.M.; Birnbaum, M.E.; Garcia, K.C.; Hyman, B.T.; Shatz, C.J. Human LilrB2 is a β-amyloid receptor and its murine homolog PirB regulates synaptic plasticity in an Alzheimer’s model. Science 2013, 341, 1399–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, W.; Shi, J.; Yin, X.; Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I.; Gong, C.X.; Liu, F. PP2A regulates tau phosphorylation directly and also indirectly via activating GSK-3β. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 19, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Sanabria-Castro, A.; Alvarado-Echeverria, I.; Monge-Bonilla, C. Molecular Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: An Update. Ann. Neurosci. 2017, 24, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, T. Current understanding of bipolar disorder: Toward integration of biological basis and treatment strategies. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 526–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gordovez, F.J.A.; McMahon, F.J. The genetics of bipolar disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 544–559. [Google Scholar]
- Dobyns, W.B.; Aldinger, K.A.; Ishak, G.E.; Mirzaa, G.M.; Timms, A.E.; Grout, M.E.; Dremmen, M.H.G.; Schot, R.; Vandervore, L.; van Slegtenhorst, M.A.; et al. MACF1 Mutations Encoding Highly Conserved Zinc-Binding Residues of the GAR Domain Cause Defects in Neuronal Migration and Axon Guidance. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.; Hu, X.; Wu, H.M.; Ni, P.; Ren, H.; Deng, W.; Li, M.; Ma, X.; et al. Increased co-expression of genes harboring the damaging de novo mutations in Chinese schizophrenic patients during prenatal development. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18209. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, C.; Hu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, F.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; Ma, X.; Su, P.; Qiu, W.; et al. MACF1 Overexpression by Transfecting the 21 kbp Large Plasmid PEGFP-C1A-ACF7 Promotes Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Formation. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zanotti, S.; Smerdel-Ramoya, A.; Canalis, E. HES1 (hairy and enhancer of split 1) is a determinant of bone mass. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 2648–2657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hilton, M.J.; Tu, X.; Wu, X.; Bai, S.; Zhao, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Kronenberg, H.M.; Teitelbaum, S.L.; Ross, F.P.; Kopan, R.; et al. Notch signaling maintains bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors by suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padial-Molina, M.; de Buitrago, J.G.; Sainz-Urruela, R.; Abril-Garcia, D.; Anderson, P.; O’Valle, F.; Galindo-Moreno, P. Expression of Musashi-1 During Osteogenic Differentiation of Oral MSC: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, N.; Dekanic, A.; Paradzik, M.; Majhen, D.; Ferencak, K.; Ruscic, J.; Bardak, I.; Supina, C.; Tomicic, M.T.; Christmann, M.; et al. Differential Effects of Integrin α v Knockdown and Cilengitide on Sensitization of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Melanoma Cells to Microtubule Poisons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 1334–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Filadi, R.; Pendin, D.; Pizzo, P. Mitofusin 2: From functions to disease. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Su, P.; Li, R.; Yan, K.; Chen, Z.; Shang, P.; Qian, A. Knockdown of microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 inhibits cell proliferation in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. BMB Rep. 2015, 48, 583–588. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Su, P.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Yan, K.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by promoting β-catenin/TCF1/Runx2 signaling axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, L.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, D.; Zhao, F.; Su, P.; Ma, X.; Zhang, G.; et al. Mechanical unloading reduces microtubule actin crosslinking factor 1 expression to inhibit β-catenin signaling and osteoblast proliferation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5405–5419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Qiu, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; Su, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Ma, J.; et al. Mesenchymal MACF1 Facilitates SMAD7 Nuclear Translocation to Drive Bone Formation. Cells 2020, 9, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskildsen, T.; Taipaleenmaki, H.; Stenvang, J.; Abdallah, B.M.; Ditzel, N.; Nossent, A.Y.; Bak, M.; Kauppinen, S.; Kassem, M. MicroRNA-138 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human stromal (mesenchymal) stem cells in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6139–6144. [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa, J.; Ezura, Y.; Moriya, S.; Kawasaki, M.; Yamada, T.; Notomi, T.; Nakamoto, T.; Hayata, T.; Miyawaki, A.; Omura, K.; et al. Migration linked to FUCCI-indicated cell cycle is controlled by PTH and mechanical stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Cheong, H.; Lee, K.Y. Osterix represses adipogenesis by negatively regulating PPARγ transcriptional activity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35655. [Google Scholar]
- Zaoui, K.; Benseddik, K.; Daou, P.; Salaun, D.; Badache, A. ErbB2 receptor controls microtubule capture by recruiting ACF7 to the plasma membrane of migrating cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18517–18522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Wakamiya, M.; Shea, M.J.; Albrecht, U.; Behringer, R.R.; Bradley, A. Requirement for Wnt3 in vertebrate axis formation. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 361–365. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, O.G.; Pinson, K.I.; Skarnes, W.C. The Wnt co-receptors Lrp5 and Lrp6 are essential for gastrulation in mice. Development 2004, 131, 2803–2815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castanon, M.J.; Walko, G.; Winter, L.; Wiche, G. Plectin-intermediate filament partnership in skin, skeletal muscle, and peripheral nerve. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 140, 33–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Cao, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, N.; Xing, Y.; Yang, N. Role of mRNA-binding proteins in retinal neovascularization. Exp. Eye Res. 2024, 242, 109870. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-M.; Fu, R.-H.; Chen, H.-J. A Multifaceted Giant Protein Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073204
Lin C-M, Fu R-H, Chen H-J. A Multifaceted Giant Protein Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073204
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chung-Ming, Ru-Huei Fu, and Hui-Jye Chen. 2025. "A Multifaceted Giant Protein Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073204
APA StyleLin, C.-M., Fu, R.-H., & Chen, H.-J. (2025). A Multifaceted Giant Protein Microtubule-Actin Cross-Linking Factor 1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073204





