Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Multifaceted Roles of H2S in Synaptic Plasticity: Mechanisms, Behavioral Correlates, and Disease Implications
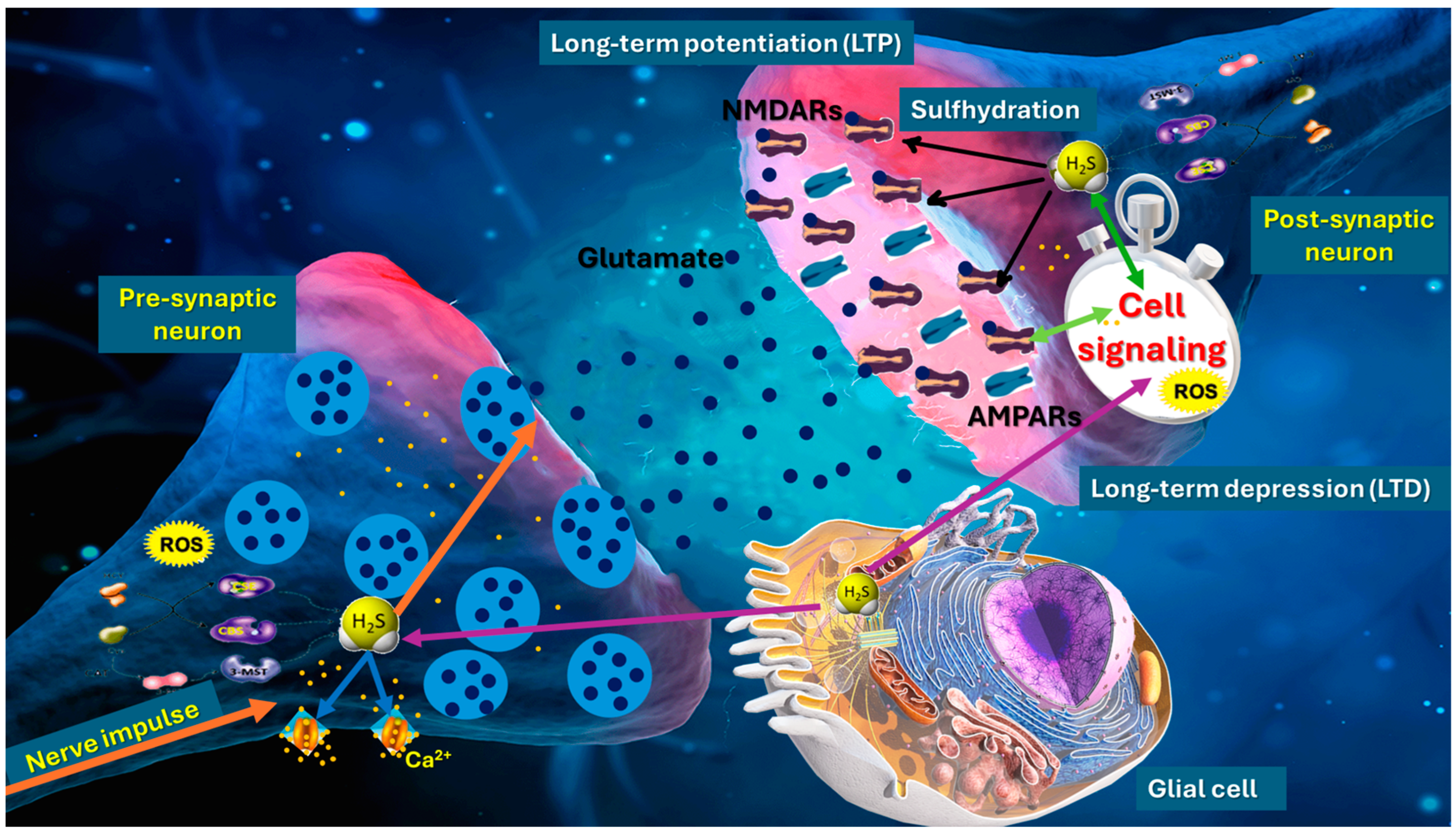
2.1. Presynaptic and Postsynaptic Modulation and Neurotransmitter Release
2.2. H2S Modulates NMDA Receptor Subunits and Calcium Influx
2.3. Effects on Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression
2.4. Redox-Dependent Mechanisms and Sulfhydration of Synaptic Proteins
2.5. Regional Specificity and Network-Level Outcomes
| Brain Region | H2S-Producing Enzymes | Principal Mechanisms | Observed Functional/Behavioral Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cortex | CBS, CSE, and possibly 3-MST | - Modulates excitatory versus inhibitory balance - Alters glutamate/GABA neurotransmission - Influences astroglial clearance of neurotransmitters | - Contributes to cortical plasticity and potentially to stress responsiveness - May interface with nitric oxide (NO) and carbon monoxide (CO) | [110,111,118] |
| Hippocampus | High CBS expression, CSE, and 3-MST | - Fine-tunes NMDA receptor function and presynaptic glutamate release - Facilitates LTP or LTD depending on concentration - Protein sulfhydration | - Enhances spatial learning, memory encoding, and synaptic consolidation - Modulates CA1–CA3 circuit excitability - Protective at moderate levels (neuroprotective); detrimental under high oxidative stress | [95,108,128,129] |
| Basal Ganglia (e.g., the striatum) | Primarily CSE (CBS is relatively lower) | - May influence dopaminergic and GABAergic pathways - Redox regulation of key proteins involved in motor control - Possible interactions with inflammatory processes | - Potential role in modulating motor coordination and reward-related behavior - Dysregulation could impact nigrostriatal pathways, contributing to motor deficits | [52,87] |
| Cerebellum | CBS and CSE in Purkinje cells/glia | - Adjusts synaptic plasticity at parallel fiber–Purkinje cell synapses - Modulates interplay of excitatory (glutamatergic) and inhibitory (GABAergic) inputs to Purkinje neurons | - Contributes to fine-tuning motor coordination and adaptive learning - Helps calibrate sensorimotor integration and error correction - Abnormal H2S signaling might exacerbate cerebellar dysfunctions | [114,117] |
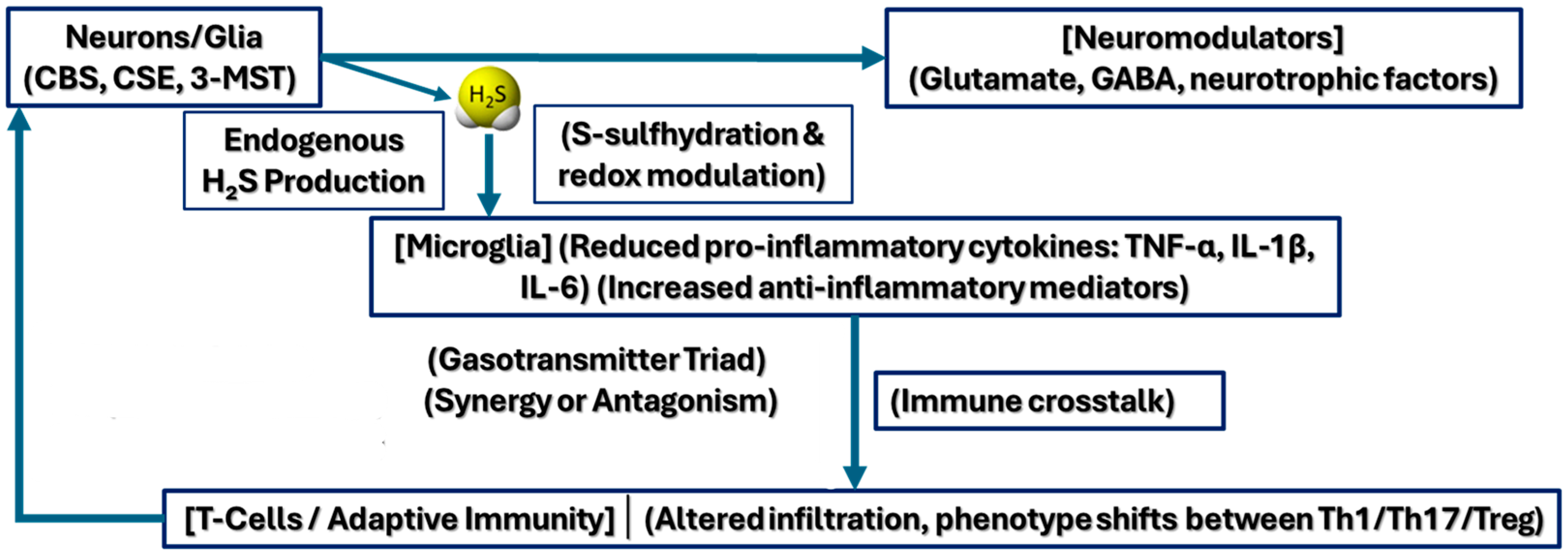
2.6. Synergistic and Antagonistic Interactions with Other Signaling Molecules
2.7. Behavioral Correlates of H2S-Mediated Synaptic Plasticity
2.8. Implications for Disease Models and Therapeutic Potential
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munteanu, C.; Turnea, M.A.; Rotariu, M. Hydrogen Sulfide: An Emerging Regulator of Oxidative Stress and Cellular Homeostasis—A Comprehensive One-Year Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Andrés Juan, C.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Chemistry of Hydrogen Sulfide—Pathological and Physiological Functions in Mammalian Cells. Cells 2023, 12, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Song, S.; Pan, L.; Muhammad Arslan, I.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S. Hydrogen sulfide: Recent progress and perspectives for the treatment of dermatological diseases. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 27, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Onose, G.; Rotariu, M.; Poștaru, M.; Turnea, M.; Galaction, A.I. Role of Microbiota-Derived Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) in Modulating the Gut–Brain Axis: Implications for Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, P.; Moore, P.K.; Zhu, Y.Z. H2S biosynthesis and catabolism: New insights from molecular studies. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1391–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrè, A.; Vicente, J.B. Hydrogen sulfide biochemistry and interplay with other gaseous mediators in mammalian physiology. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 6290931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Pandey, V. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) metabolism: Unraveling cellular regulation, disease implications, and therapeutic prospects for precision medicine. Nitric Oxide 2024, 144, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Iordan, D.A.; Hoteteu, M.; Popescu, C.; Postoiu, R.; Onu, I.; Onose, G. Mechanistic Intimate Insights into the Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Recent Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Xu, J.; Shen, H.; Yu, Z.; Chen, G. Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide in Parkinson’s disease. Med. Gas. Res. 2024, 14, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Tang, J.J.; Wang, L.X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Qiao, C. Hydrogen sulfide enhances adult neurogenesis in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolluru, G.K.; Shen, X.; Bir, S.C.; Kevil, C.G. Hydrogen sulfide chemical biology: Pathophysiological roles and detection. Nitric Oxide 2013, 35, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Onose, G.; Poștaru, M.; Turnea, M.; Rotariu, M.; Galaction, A.I. Hydrogen Sulfide and Gut Microbiota: Their Synergistic Role in Modulating Sirtuin Activity and Potential Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Popescu, C.; Vlădulescu-Trandafir, A.I.; Onose, G. Signaling Paradigms of H2S-Induced Vasodilation: A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Predmore, B.L.; Lefer, D.J.; Gojon, G. Hydrogen sulfide in biochemistry and medicine. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012, 17, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Kaundal, R.S.; Pandey, V. Biophysical characterization of hydrogen sulfide: A fundamental exploration in understanding significance in cell signaling. Biophys. Chem. 2024, 314, 107317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Signaling by hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and polysulfides (H2Sn) in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 126, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.P.; Dobariya, P.; Bellamkonda, H.; More, S.S. Role of 3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase (3-MST) in Physiology and Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myszkowska, J.; Derevenkov, I.; Makarov, S.V.; Spiekerkoetter, U.; Hannibal, L. Biosynthesis, quantification and genetic diseases of the smallest signaling thiol metabolite: Hydrogen sulfide. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Bhatia, M. Hydrogen Sulfide: A Versatile Molecule and Therapeutic Target in Health and Diseases. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Yu, D.; Yan, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, T. Neuroprotective Effect of Hydrogen Sulfide Subchronic Treatment Against TBI-Induced Ferroptosis and Cognitive Deficits Mediated Through Wnt Signaling Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 43, 4117–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagena, H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Interplay of hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression in enabling memory representations. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2024, 379, 20230229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, M.S.; Iezzi, E.; Gilio, L.; Centonze, D.; Buttari, F. Synaptic plasticity shapes brain connectivity: Implications for network topology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Production and physiological effects of hydrogen sulfide. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shefa, U.; Kim, M.S.; Jeong, N.Y.; Jung, J. Antioxidant and Cell-Signaling Functions of Hydrogen Sulfide in the Central Nervous System. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1873962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H.; Nagai, Y.; Umemura, K.; Kimura, Y. Physiological Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide: Synaptic Modulation, Neuroprotection, and Smooth Muscle Relaxation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 795–803. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide induces cyclic AMP and modulates the NMDA receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 267, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and polysulfide (H2Sn) signaling: The first 25 years. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen sulfide signalling in the CNS—Comparison with NO. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 5031–5045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Physiological role of hydrogen sulfide and polysulfide in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuie, H.; Kimura, Y.; Akaishi, T.; Yamada, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Saitoh, A.; Shibuya, N.; Watanabe, A.; Kusunose, N.; Mashimo, T.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide and polysulfides induce GABA/glutamate/d-serine release, facilitate hippocampal LTP, and regulate behavioral hyperactivity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S)/Polysulfides (H2Sn) Signalling and TRPA1 Channels Modification on Sulfur Metabolism. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Pessah, I.N.; Santana, C.M.; Purnell, B.S.; Li, R.; Buchanan, G.F.; Rumbeiha, W.K. Investigations into hydrogen sulfide-induced suppression of neuronal activity in vivo and calcium dysregulation in vitro. Toxicol. Sci. 2023, 192, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.B.; Lin, H.C. Hydrogen sulfide in physiology and diseases of the digestive tract. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 866–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, P.C.; Hendry-Hofer, T.B.; Witeof, A.E.; Brenner, M.; Mahon, S.B.; Boss, G.R.; Haouzi, P.; Bebarta, V.S. Hydrogen Sulfide Toxicity: Mechanism of Action, Clinical Presentation, and Countermeasure Development. J. Med. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.K.; Kalani, A.; Tyagi, N. Role of hydrogen sulfide in brain synaptic remodeling. In Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 555, pp. 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.Z.; Liu, Y.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen Sulfide and Cellular Redox Homeostasis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 6043038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R. Hydrogen sulfide: Redox metabolism and signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H.; Kashfi, K. Effects of hydrogen sulfide on mitochondrial function and cellular bioenergetics. Redox Biol. 2021, 38, 101772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, M.; Ohnishi, T.; Toyoshima, M.; Balan, S.; Maekawa, M.; Shimamoto-Mitsuyama, C.; Iwayama, Y.; Ohba, H.; Watanabe, A.; Ishii, T.; et al. Excess hydrogen sulfide and polysulfides production underlies a schizophrenia pathophysiology. EMBO Mol. Med. 2019, 11, e10695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.F.; Tang, X.Q. Hydrogen sulfide and nervous system regulation. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2011, 124, 3576–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschner, M.; Skalny, A.V.; Ke, T.; da Rocha, J.B.; Paoliello, M.M.; Santamaria, A.; Bornhorst, J.; Rongzhu, L.; Svistunov, A.A.; Djordevic, A.B.; et al. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Signaling as a Protective Mechanism against Endogenous and Exogenous Neurotoxicants. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 1908–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Turnea, M.; Blendea, C.D.; Rotariu, M.; Poștaru, M. Redox Homeostasis, Gut Microbiota, and Epigenetics in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Larsen, R.S.; Philpot, B.D.; Paulsen, O. Roles of Presynaptic NMDA Receptors in Neurotransmission and Plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2016, 39, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerasimova, E.; Lebedeva, J.; Yakovlev, A.; Zefirov, A.; Giniatullin, R.; Sitdikova, G. Mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) action on synaptic transmission at the mouse neuromuscular junction. Neuroscience 2015, 303, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austgen, J.R.; Hermann, G.E.; Dantzler, H.A.; Rogers, R.C.; Kline, D.D. Hydrogen sulfide augments synaptic neurotransmission in the nucleus of the solitary tract. J. Neurophysiol. 2011, 106, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. H2S signalling through protein sulfhydration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Fu, M.; Stokes, E.; Wu, L.; Yang, G. H2S-mediated protein S-Sulfhydration: A prediction for its formation and regulation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Kong, B.; Jung, Y.; Park, J.-B.; Oh, J.-M.; Hwang, J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kweon, D.-H. Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor-derived peptides for regulation of mast cell degranulation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, M.P.; Portalés, A.; SanJuan, M.P.; Jurado, S. Postsynaptic SNARE Proteins: Role in Synaptic Transmission and Plasticity. Neuroscience 2019, 420, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolphin, A.C. Functions of Presynaptic Voltage-gated Calcium Channels. Function 2021, 2, zqaa027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.F.; Luo, Z.D. Calcium channel functions in pain processing. Channels 2010, 4, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Qin, J.; Chang, X.; Yang, Z.; Bu, D.; Du, J. Modulating effect of hydrogen sulfide on gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor in recurrent febrile seizures in rats. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Q.; Xin, H.; Zhu, Y.Z. Hydrogen sulfide: Third gaseous transmitter, but with great pharmacological potential. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2007, 28, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, T.L. Hydrogen sulfide: Advances in understanding human toxicity. Int. J. Toxicol. 2010, 29, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Y.; Long, L.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Wu, P. Hydrogen Sulfide Promotes Surface Insertion of Hippocampal AMPA Receptor GluR1 Subunit via Phosphorylating at Serine-831/Serine-845 Sites Through a Sulfhydration-Dependent Mechanism. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, R.; Hulo, S.; Toni, N.; Madani, H.; Steimer, T.; Muller, D.; Vassalli, J. Enhanced hippocampal long-term potentiation and learning by increased neuronal expression of tissue-type plasminogen activator in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 3007–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.O.; Tu, H.Y.; Qian, H.C.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.P.; Xu, G.Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.F.; Wang, Y.L.; Hu, L.F. AMPK S-sulfuration contributes to H2S donors-induced AMPK phosphorylation and autophagy activation in dopaminergic cells. Neurochem. Int. 2021, 150, 105187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porokhya, M.V.; Abramochkin, D.V.; Abramov, A.A.; Kuzmin, V.S.; Sukhova, G.S. Inotropic Effects of Gaseous Transmitters in Isolated Rat Heart Preparation. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2012, 153, 856–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, C.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Fan, L.; Yu, Y.; Ji, X.; Gao, X.; Hou, K.; et al. Investigating the L-Glu-NMDA receptor-H2S-NMDA receptor pathway that regulates gastric function in rats’ nucleus ambiguus. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1389873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Tajima, N. Structural insights into NMDA receptor pharmacology. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2023, 51, 1713–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Kaundal, R.S.; Pandey, V. Mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide-mediated neuroprotection: Current understanding and future directions. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2024, 54, 1105–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilek, N.; Papapetropoulos, A.; Toliver-Kinsky, T.; Szabo, C. Hydrogen sulfide: An endogenous regulator of the immune system. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Rose, P.; Moore, P.K. Hydrogen sulfide and cell signaling. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2011, 51, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Du, J.; Tang, C.; Huang, Y.; Jin, H. H2S-induced sulfhydration: Biological function and detection methodology. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Snyder, S.H. H2S: A Novel Gasotransmitter that Signals by Sulfhydration. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.J.; Qian, L.; Li, K.; Qin, Y.Z.; Zhou, J.J.; Ji, X.Y.; Wu, D.D. Hydrogen sulfide-induced post-translational modification as a potential drug target. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iciek, M.; Kowalczyk-Pachel, D.; Bilska-Wilkosz, A.; Kwiecién, I.; Górny, M.; Wøodek, L. S-sulfhydration as a cellular redox regulation. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36, e00304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, F.; Ni, L.; Wu, P.; Chen, J. Targeting redox-altered plasticity to reactivate synaptic function: A novel therapeutic strategy for cognitive disorder. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.H.; Xi, Q.; Leffler, C.W.; Jaggar, J.H. Hydrogen sulfide activates Ca2+ sparks to induce cerebral arteriole dilatation. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2709–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, R. Interaction of H2S with calcium permeable channels and transporters. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 323269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaron, L.; Avanzato, D.; Moccia, F.; Mancardi, D. Hydrogen sulfide as a regulator of calcium channels. Cell Calcium 2013, 53, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokumitsu, H.; Sakagami, H. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase Kinase Signal Transduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ko, A.R.; Hyun, H.W.; Min, S.J.; Kim, J.E. PDI regulates seizure activity via NMDA receptor redox in rats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep42491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Lipton, S.A. Protein S-Nitrosylation as a Therapeutic Target for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibarov, D.A.; Boikov, S.I.; Karelina, T.V.; Antonov, S.M. GluN2 subunit-dependent redox modulation of NMDA receptor activation by homocysteine. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Foster, T.C. Linking redox regulation of NMDAR synaptic function to cognitive decline during aging. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 15710–15715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Poștaru, M.; Rotariu, M.; Turnea, M.; Blendea, C.D. Hydrogen Sulfide Modulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases and CD147/EMMPRIN: Mechanistic Pathways and Impact on Atherosclerosis Progression. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, N. Functional and Molecular Insights of Hydrogen Sulfide Signaling and Protein Sulfhydration. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marutani, E.; Sakaguchi, M.; Chen, W.; Sasakura, K.; Liu, J.; Xian, M.; Hanaoka, K.; Nagano, T.; Ichinose, F. Cytoprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide-releasing N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists mediated by intracellular sulfane sulfur. Medchemcomm 2014, 5, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marutani, E.; Kosugi, S.; Tokuda, K.; Khatri, A.; Nguyen, R.; Atochin, D.N.; Kida, K.; Van Leyen, K.; Arai, K.; Ichinose, F. A novel hydrogen sulfide-releasing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist prevents ischemic neuronal death. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 32124–32135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.T.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Mao, C.Y. Role of hydrogen sulfide in cognitive deficits: Evidences and mechanisms. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 849, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Guo, R.; Qiu, P.; Su, X.; Yan, G.; Feng, J. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide eliminates spatial memory retrieval impairment and hippocampal CA1 LTD enhancement caused by acute stress via promoting glutamate uptake. Neuroscience 2017, 350, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Z. Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Synaptic Plasticity from VD-Induced Damage via Akt/GSK-3β Pathway and Notch Signaling Pathway in Rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4159–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K.; Kimura, H. The Possible Role of Hydrogen Sulfide as an Endogenous Neuromodulator. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dallas, M.L.; Al-Owais, M.M.; Hettiarachchi, N.T.; Vandiver, M.S.; Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Scragg, J.L.; Boyle, J.P.; Steele, D.; Peers, C. Hydrogen sulfide regulates hippocampal neuron excitability via S-sulfhydration of Kv2.1. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Collins, R.; Huang, S.; Holmberg-Schiavone, L.; Anand, G.S.; Tan, C.H.; Van-Den-Berg, S.; Deng, L.-W.; Moore, P.K.; Karlberg, T.; et al. Structural basis for the inhibition mechanism of human cystathionine γ-lyase, an enzyme responsible for the production of H2S. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3076–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, L.; Linden, D.R.; Farrugia, G.; Szurszewski, J.H. Hydrogen sulfide selectively potentiates central preganglionic fast nicotinic synaptic input in mouse superior mesenteric ganglion. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 12638–12646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collingridge, G.L.; Isaac, J.T.R.; Yu, T.W. Receptor trafficking and synaptic plasticity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic plasticity: Multiple forms, functions, and mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 18–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.H.; Wong, P.T.H.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen sulfide: A novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 56, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.T. Hydrogen sulfide and environmental stresses. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 161, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tian, M.; Han, Y. Hydrogen sulfide: A multi-tasking signal molecule in the regulation of oxidative stress responses. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 2862–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, P.J.; Scott, J.D. Regulation of the phosphatase PP2B by protein-protein interactions. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2016, 44, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpure, B.V.; Bian, J.S. Brain, learning, and memory: Role of H2S in neurodegenerative diseases. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 230, 193–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Li, M.; Xie, J.; Li, S.; Xiang, S.S.; Liu, H.Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, P.; Kuang, X.; Tang, X.Q. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates postoperative cognitive dysfunction through promoting the pathway of Warburg effect-synaptic plasticity in hippocampus. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 409, 11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabil, O.; Motl, N.; Banerjee, R. H2S and its role in redox signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Proteins Proteom. 2014, 1844, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabil, O.; Banerjee, R. Redox biochemistry of hydrogen sulfide. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 21903–21907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oostrum, M.; Blok, T.M.; Giandomenico, S.L.; Dieck, S.T.; Tushev, G.; Fürst, N.; Langer, J.D.; Schuman, E.M. The proteomic landscape of synaptic diversity across brain regions and cell types. Cell 2023, 186, 5411–5427.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Reest, J.; Lilla, S.; Zheng, L.; Zanivan, S.; Gottlieb, E. Proteome-wide analysis of cysteine oxidation reveals metabolic sensitivity to redox stress. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabõ, C. Hydrogen sulphide and its therapeutic potential. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 917–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Liu, K.; He, J.; Tian, C.; Yu, X.; Yang, J. Direct Proteomic Mapping of Cysteine Persulfidation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R. Hydrogen sulfide, reactive sulfur species and coping with reactive oxygen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 140, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafaiee, R.; Khastar, H.; Garmabi, B.; Taleb, M.; Norouzi, P.; Khaksari, M. Hydrogen sulfide protects hippocampal CA1 neurons against lead mediated neuronal damage via reduction oxidative stress in male rats. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2021, 112, 101917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Hu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; He, Y. A Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Activated Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) Donor with Self-Reporting Fluorescence. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.G.; Schmidt, E.E. Sulfur Metabolism under Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 1158–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, T.; Pandey, V. Advancements in increasing efficiency of hydrogen sulfide in therapeutics: Strategies for targeted delivery as prodrugs. Nitric Oxide 2024, 152, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Lombó, C.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I.; Franco, R. Redox homeostasis, oxidative stress and mitophagy. Mitochondrion 2020, 51, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, W.J.; Fu, J.; Yin, H.Y.; Xu, N.G.; Tang, C.Z.; Liu, L.Z.; Yu, S.G.; Tang, Y. CBS-Induced H2S Generation in Hippocampus Inhibits EA-Induced Analgesia. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 5917910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Popescu, C.; Munteanu, D.; Hoteteu, M.; Iliescu, M.G.; Ionescu, E.V.; Stanciu, L.; Oprea, D.; Minea, M.; Oprea, C.; et al. Biological Evaluation of Balneotherapeutic Mud and Sulfurous Mineral Waters: Insights from In Vivo and In Vitro Studies. Balneo PRM Res. J. 2024, 15, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi Chameh, H.; Rich, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.D.; Zhang, L.; Carlen, P.L.; Tripathy, S.J.; Valiante, T.A. Diversity amongst human cortical pyramidal neurons revealed via their sag currents and frequency preferences. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyal, G.; Verhoog, M.B.; Testa-Silva, G.; Deitcher, Y.; Benavides-Piccione, R.; DeFelipe, J.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Segev, I. Human cortical pyramidal neurons: From spines to spikes via models. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 365369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-J.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Nie, X.-W.; Bian, J.-S. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide and Polysulfides in Neurological Diseases: Focus on Protein S-Persulfidation. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 19, 868–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Dargusch, R.; Schubert, D.; Kimura, H. Hydrogen Sulfide Protects HT22 Neuronal Cells from Oxidative Stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celnik, P. Understanding and Modulating Motor Learning with Cerebellar Stimulation. Cerebellum 2015, 14, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauk, M.D.; Medina, J.F.; Nores, W.L.; Ohyama, T. Cerebellar function: Coordination, learning or timing? Curr. Biol. 2000, 10, R522–R525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmolesky, M.T.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; Hansel, C. Climbing fiber synaptic plasticity and modifications in Purkinje cell excitability. Prog. Brain Res. 2005, 148, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishina, M.; Uemura, T.; Yasumura, M.; Yoshida, T. Molecular mechanism of parallel fiber-purkinje cell synapse formation. Front. Neural Circuits 2012, 6, 35288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittmann, W.; Häusser, M. Linking synaptic plasticity and spike output at excitatory and inhibitory synapses onto cerebellar Purkinje cells. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5559–5570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.; Pandey, D.; Naqvi, S.; Sharma, A. Critical role of hydrogen sulfide in the management of neurodegenerative disease. Nitric Oxide 2025, 154, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bian, J.S. Hydrogen sulfide: A neuromodulator and neuroprotectant in the central nervous system. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Pramanik, P.K.; Dwivedi, S.K.D.; Neizer-Ashun, F.; Kiss, T.; Ganguly, A.; Rice, H.; Mukherjee, P.; Xu, C.; Ahmad, M.; et al. A role for the cystathionine-β-synthase /H2S axis in astrocyte dysfunction in the aging brain. Redox Biol. 2023, 68, 102958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegle, J.H.; Moore, C.I. Cortical circuits: Finding balance in the brain. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R956–R957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbodio, J.I.; Snyder, S.H.; Bindu, P.D. Regulators of the transsulfuration pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirino, G.; Szabo, C.; Papapetropoulos, A. Physiological roles of hydrogen sulfide in mammalian cells, tissues, and organs. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 31–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B. Hydrogen sulfide in signaling pathways. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 439, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H.; Loy, A.C.M.; Cheah, K.W.; Chai, S.Y.W.; Ngu, L.H.; How, B.S.; Li, C.; Lock, S.S.M.; Wong, M.K.; Yiin, C.L.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) conversion to hydrogen (H2) and value-added chemicals: Progress, challenges and outlook. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 458, 141398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, K.R. Hydrogen sulfide as an oxygen sensor. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2015, 22, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T. Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide on Modulation of Theta–Gamma Coupling in Hippocampus in Vascular Dementia Rats. Brain Topogr. 2015, 28, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Qian, Z.; Ni, X.; Lu, J. Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents LPS-Induced Depression-like Behavior through the Suppression of NLRP3 Inflammasome and Pyroptosis and the Improvement of Mitochondrial Function in the Hippocampus of Mice. Biology 2023, 12, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursino, M.; Pirazzini, G. Theta–gamma coupling as a ubiquitous brain mechanism: Implications for memory, attention, dreaming, imagination, and consciousness. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2024, 59, 101433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweg, N.A.; Solomon, E.A.; Kahana, M.J. Theta Oscillations in Human Memory. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2020, 24, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, D.G.F.; Nunes, J.; Tomé, C.S.; Zuhra, K.; Costa, J.M.F.; Antunes, A.M.M.; Giuffrè, A.; Vicente, J.B. Human cystathionine γ-lyase is inhibited by s-nitrosation: A new crosstalk mechanism between NO and H2S. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaany, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, R. Crosstalk between hydrogen sulfide and nitric oxide in endothelial cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2013, 17, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, S.; Cao, L.; Sethi, G.; Bian, J.-s. The role of hydrogen sulfide in cyclic nucleotide signaling. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso-Pires, C.; Vieira, H.L.A. Carbon monoxide and mitochondria: Cell energy and fate control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, N.; Liu, D.; Nguyen, T.P.; Wang, B. Unraveling the Interplay of Dopamine, Carbon Monoxide, and Heme Oxygenase in Neuromodulation and Cognition. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Kumar, R.; Matson, J.B. Hydrogels for Gasotransmitter Delivery: Nitric Oxide, Carbon Monoxide, and Hydrogen Sulfide. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 24, e2300138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Lu, W.; Pan, M. Effects of NaHS and hydroxylamine on the expressions of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its receptors in rats after cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Scand. J. Trauma. Resusc. Emerg. Med. 2018, 26, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.D.; Pieper, A.A. Protective Roles of Hydrogen Sulfide in Alzheimer’s Disease and Traumatic Brain Injury. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthi, S.; Chung, H.J.; Jung, J.; Jeong, N.Y. Physiological importance of hydrogen sulfide: Emerging potent neuroprotector and neuromodulator. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9049782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, C. Hydrogen Sulfide, an Emerging Regulator of Acid-Sensing Ion Channels. Function 2021, 2, zqab014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Teng, H.; Yang, G.; Wu, L.; Wang, R. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the translational expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1492–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Yang, Y.; Wei, S.; Huang, X.; Peng, Z.; Ke, X.; Zeng, Z.; Song, Y. Hydrogen sulfide protects against high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury through activating PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, M.; Tian, W.; Wang, S.; Cui, L.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Ji, A.; Li, Y. Hydrogen sulfide acts as a double-edged sword in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through EGFR/ERK/MMP-2 and PTEN/AKT signaling pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, R.C.; Jaramillo-Riveri, S.; Luarte, A.; Moënne-Loccoz, C.; Fuentes, R.; Couve, A.; Maldonado, P.E. The Energy Homeostasis Principle: Neuronal Energy Regulation Drives Local Network Dynamics Generating Behavior. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, R.J.; Avramopoulos, D.; Jantzie, L.L.; McCallion, A.S. Neuroinflammation represents a common theme amongst genetic and environmental risk factors for Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Schwab, C.; Yu, S.; McGeer, E.; McGeer, P.L. Astrocytes produce the antiinflammatory and neuroprotective agent hydrogen sulfide. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Fang, F.; Liu, X.; Sheng, S.; Li, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, Z.; Wen, J. H2S Regulates the Phenotypic Transformation of Astrocytes Following Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion via Inhibiting the RhoA/ROCK Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 3179–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, A.; Long, D.; Li, J.; Ji, W.; Zhang, M.; Hong, L.; Liu, J. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates spatial memory impairment and hippocampal neuroinflammation in beta-amyloid rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Jiang, L.; Lan, F.; Tang, Y.Y.; Zhang, P.; Zou, W.; Chen, Y.J.; Tang, X.Q. Hydrogen sulfide antagonizes sleep deprivation-induced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors by inhibiting neuroinflammation in a hippocampal Sirt1-dependent manner. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 177, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, A.; Wills, D.N.; Ehlers, C.L. Ontogeny and adolescent alcohol exposure in Wistar rats: Open field conflict, light/dark box and forced swim test. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 122, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, S.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Miller, E.; Pieper, A.A.; Paul, B.D. Hydrogen sulfide signaling in neurodegenerative diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023; online version. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.J.; Li, X.; Tang, X.Q. Therapeutic benefits of H2S in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, B.D.; Pieper, A.A. Neuroprotective signaling by hydrogen sulfide and its dysregulation in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2024, 82, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.; Munteanu, C.; Anghelescu, A.; Ciobanu, V.; Spînu, A.; Andone, I.; Mandu, M.; Bistriceanu, R.; Băilă, M.; Postoiu, R.-L.; et al. Novelties on Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease–Focus on Gut and Oral Microbiota Involvement. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaorska, E.; Tomasova, L.; Koszelewski, D.; Ostaszewski, R.; Ufnal, M. Hydrogen sulfide in pharmacotherapy, beyond the hydrogen sulfide-donors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, R.X.; Zhou, T.T.; Jia, S.Y.; Li, W.G.; Wang, J.; Li, B.D.; Shan, Y.D.; Zhang, L.M.; Li, X.M. Hydrogen sulfide mitigates memory impairments via the restoration of glutamatergic neurons in a mouse model of hemorrhage shock and resuscitation. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 376, 114758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, A.H.; Iqbal, M.; Manhoosh, B.; Gholampoor, N.; Ma, D.; Marwah, M.; Sanchez-Aranguren, L. Hydrogen Sulphide-Based Therapeutics for Neurological Conditions: Perspectives and Challenges. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 1981–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, K.; Lee, S.W.; Bian, J.S.; Low, C.M.; Wong, P.T.H. Hydrogen sulfide: Neurochemistry and neurobiology. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, R.; Wu, L.; Yang, G. Hydrogen sulfide signaling in regulation of cell behaviors. Nitric Oxide 2020, 103, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Ying, J.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, C. The biologic effect of hydrogen sulfide and its function in various diseases. Medicine 2018, 97, e13065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinko, M.; Novaković, A. Hydrogen sulfide-releasing therapeutics: How far have we come in clinical studies? Arh. Farm. 2023, 73, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.C.J.; Grieder, F.B. The continued importance of animals in biomedical research. Lab Anim. 2024, 53, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Owais, M.M.; Hettiarachchi, N.T.; Dallas, M.L.; Scragg, J.L.; Lippiat, J.D.; Holden, A.V.; Steele, D.S.; Peers, C. Inhibition of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.5 by hydrogen sulfide attenuates remodeling through S-nitrosylation-mediated signaling. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munteanu, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Onose, G.; Turnea, M.; Rotariu, M. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073131
Munteanu C, Galaction AI, Onose G, Turnea M, Rotariu M. Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073131
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunteanu, Constantin, Anca Irina Galaction, Gelu Onose, Marius Turnea, and Mariana Rotariu. 2025. "Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073131
APA StyleMunteanu, C., Galaction, A. I., Onose, G., Turnea, M., & Rotariu, M. (2025). Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S- or H2Sn-Polysulfides) in Synaptic Plasticity: Modulation of NMDA Receptors and Neurotransmitter Release in Learning and Memory. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3131. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073131








