Agmatine Enhances Dorsal Raphe Serotonergic Neuronal Activity via Dual Regulation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A Receptors
Abstract
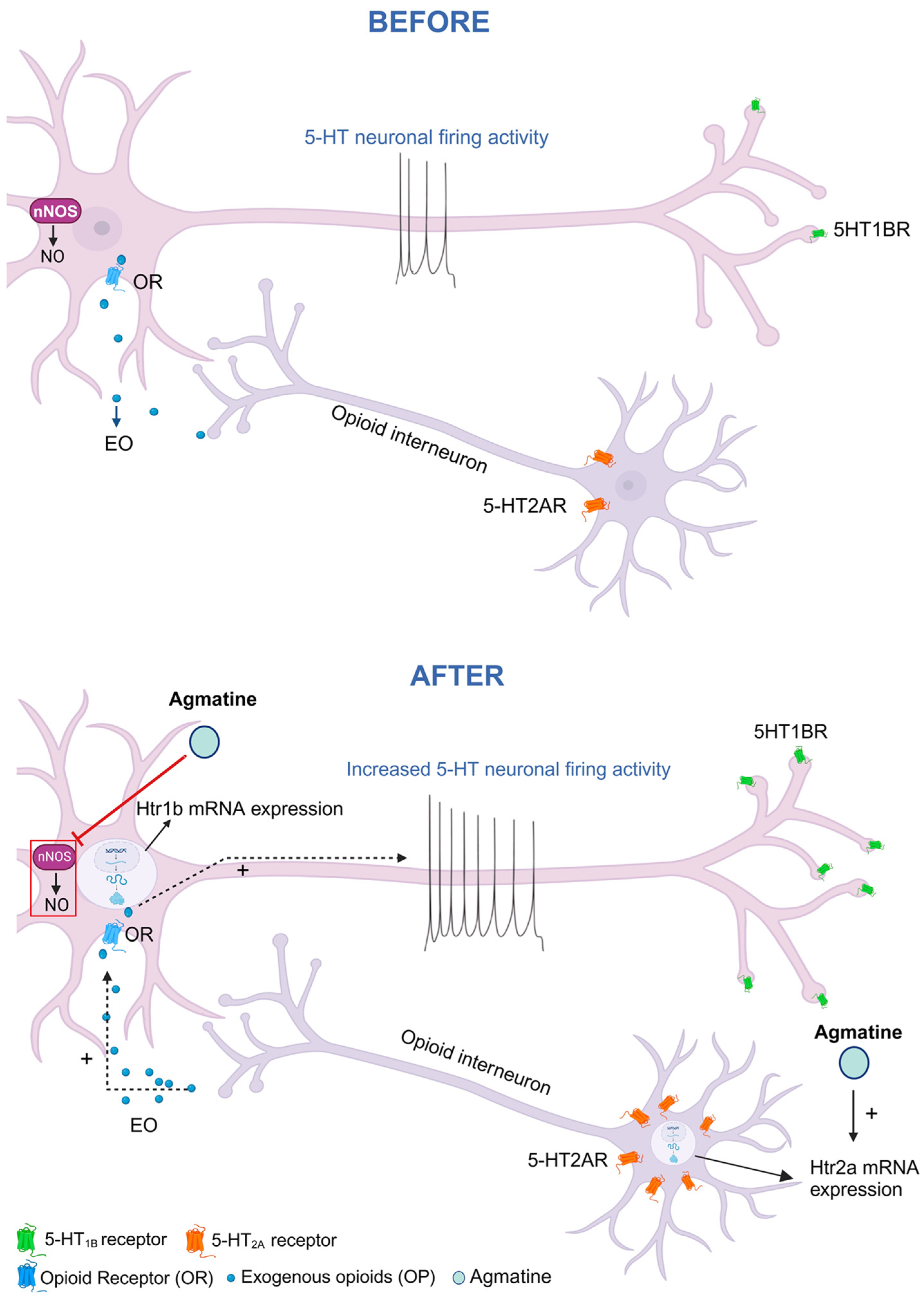
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects Acute and Chronic Agmatine Treatment on the Firing Activity of 5-HT Neurons in the DRN
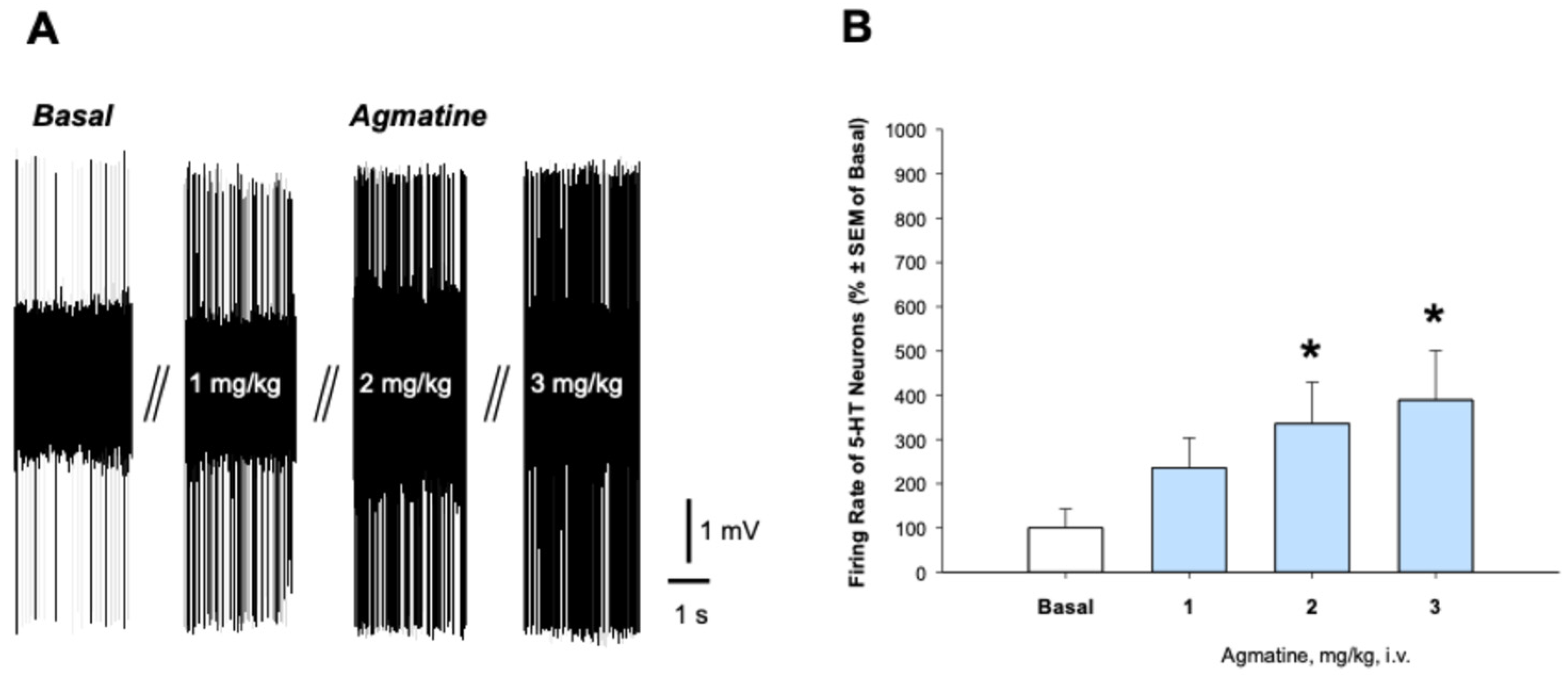
2.2. Effects of Chronic Agmatine Treatment on the Firing Activity of 5-HT Neurons in the DRN
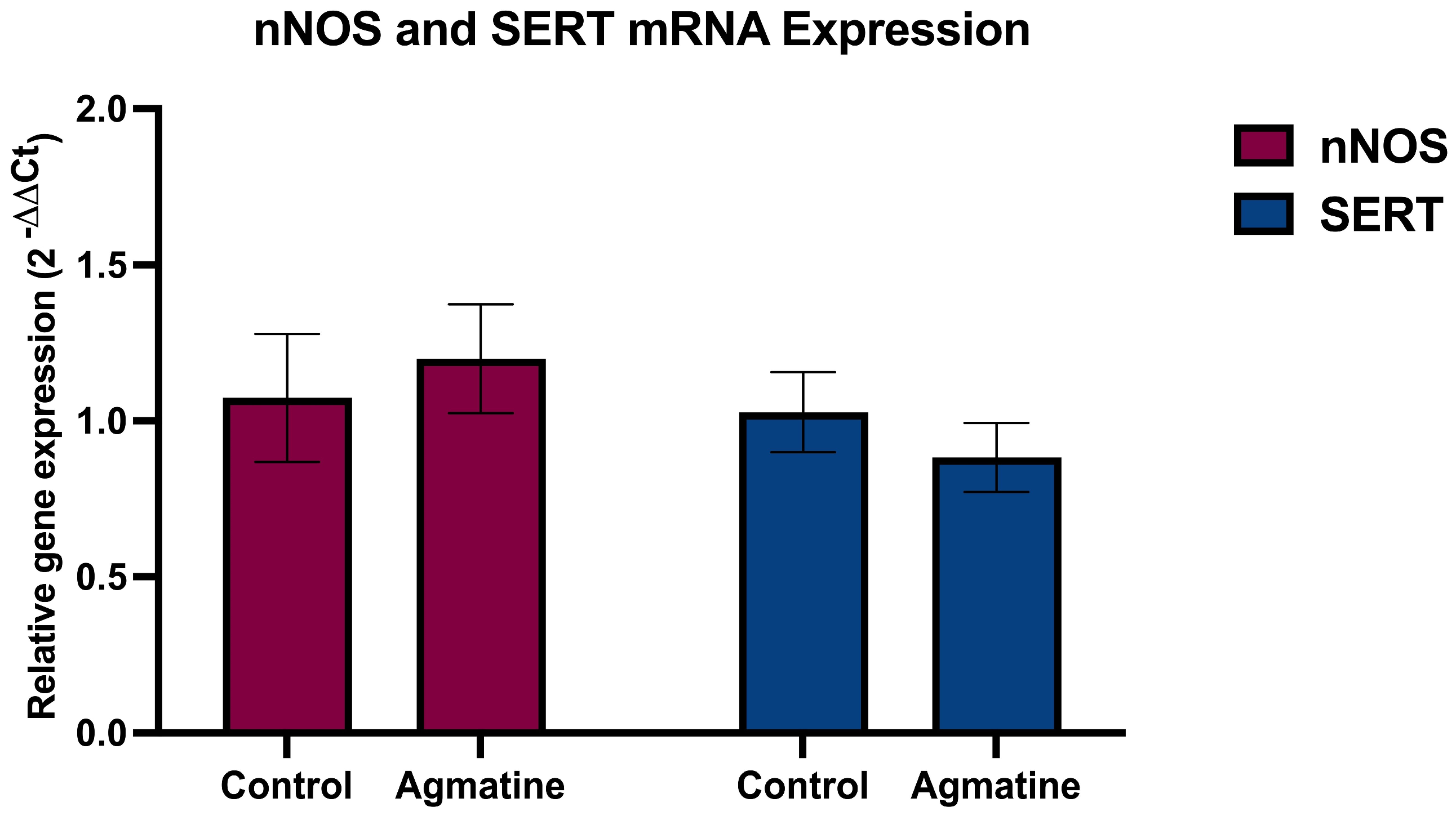
2.3. Effects of Chronic Agmatine Treatment on the nNOS and SERT mRNA Expression in the DRN
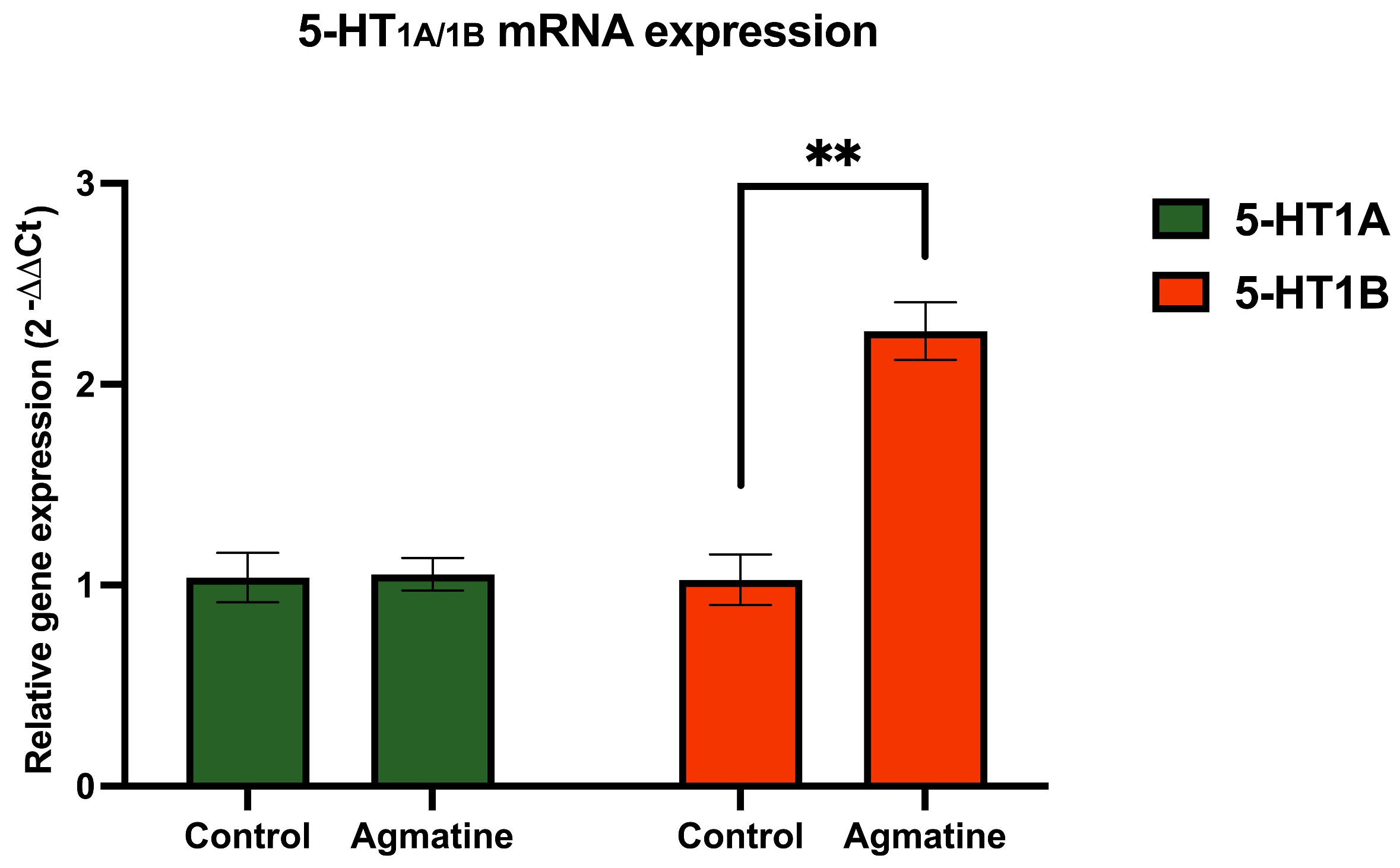
2.4. Effects of Chronic Agmatine Treatment on the Expression of the DRN 5-HT Receptors Belonging to the 5-HT1 Subfamily
2.5. Effects of Chronic Agmatine Treatment on the Expression of the DRN 5-HT Receptors Belonging to the 5-HT2 Subfamily
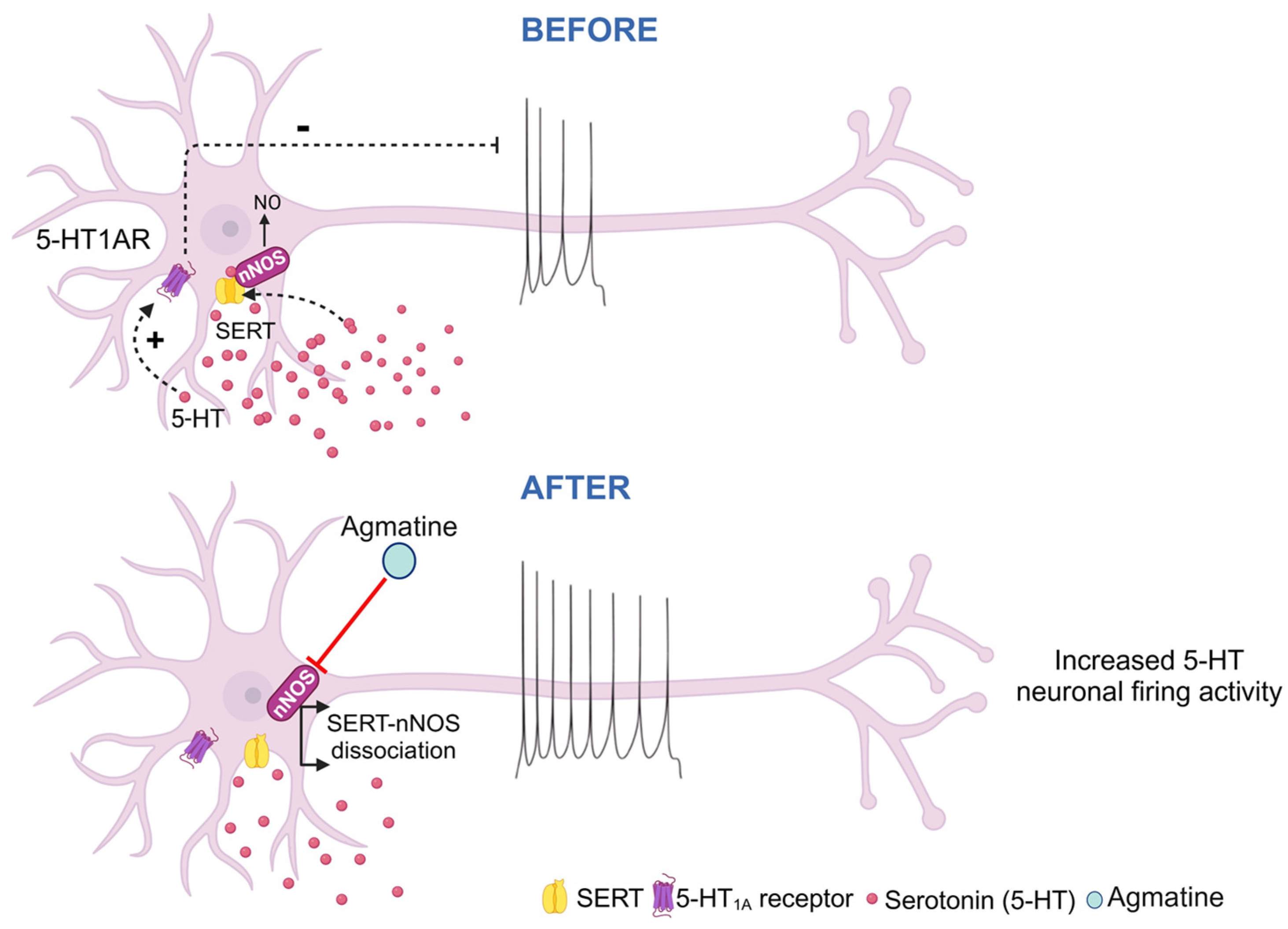
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. Electrophysiology
4.4. Assessment of the Acute Agmatine Effect on 5-HT Neuronal Firing Activity
4.5. Assessment of the Chronic Agmatine Effect on 5-HT Neuronal Firing Activity
4.6. Assessment of Target Gene Expression in DRN Using Multiplex RT-qPCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | Serotonin |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| nNOS | Neuronal nitric oxide synthase |
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| SERT | 5-HT transporter |
| SSRIs | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
| TAAR1 | Trace amine associated receptor 1 |
References
- Molderings, G.J.; Haenisch, B. Agmatine (decarboxylated l-arginine): Physiological role and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piletz, J.E.; Aricioglu, F.; Cheng, J.-T.; Fairbanks, C.A.; Gilad, V.H.; Haenisch, B.; Halaris, A.; Hong, S.; Lee, J.E.; Li, J.; et al. Agmatine: Clinical applications after 100 years in translation. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 880–893. [Google Scholar]
- Galea, E.; Regunathan, S.; Eliopoulos, V.; Feinstein, D.L.; Reis, D.J. Inhibition of mammalian nitric oxide synthases by agmatine, an endogenous polyamine formed by decarboxylation of arginine. Biochem. J. 1996, 316 Pt 1, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gadkari, T.V.; Cortes, N.; Madrasi, K.; Tsoukias, N.M.; Joshi, M.S. Agmatine induced NO dependent rat mesenteric artery relaxation and its impairment in salt-sensitive hypertension. Nitric Oxide 2013, 35, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demady, D.R.; Jianmongkol, S.; Vuletich, J.L.; Bender, A.T.; Osawa, Y. Agmatine enhances the NADPH oxidase activity of neuronal NO synthase and leads to oxidative inactivation of the enzyme. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 59, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.J.; Li, F.; Zhu, D.Y. nNOS and Neurological, Neuropsychiatric Disorders: A 20-Year Story. Neurosci. Bull. 2023, 39, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Grinchii, D.; Dremencov, E. Mechanism of Action of Atypical Antipsychotic Drugs in Mood Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garthwaite, J. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase and the serotonin transporter get harmonious. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7739–7740. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Qin, Y.-J.; Xu, C.; Xia, T.; Du, Z.-W.; Zheng, L.-P.; Li, A.-a.; Meng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J. Design of fast-onset antidepressant by dissociating SERT from nNOS in the DRN. Science 2022, 378, 390–398. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, A.E.; Egea, J.; Buendia, I.; Gómez-Rangel, V.; Parada, E.; Navarro, E.; Casas, A.I.; Wojnicz, A.; Ortiz, J.A.; Cuadrado, A.; et al. Agmatine, by Improving Neuroplasticity Markers and Inducing Nrf2, Prevents Corticosterone-Induced Depressive-Like Behavior in Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 3030–3045. [Google Scholar]
- Aglawe, M.M.; Kale, M.B.; Rahangdale, S.R.; Kotagale, N.R.; Umekar, M.J.; Taksande, B.G. Agmatine improves the behavioral and cognitive impairments associated with chronic gestational ethanol exposure in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 167, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin Ozkartal, C.; Tuzun, E.; Kucukali, C.I.; Ulusoy, C.; Giris, M.; Aricioglu, F. Antidepressant-like effects of agmatine and NOS inhibitors in chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in rats: The involvement of NLRP inflammasomes. Brain Res. 2019, 1725, 146438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neis, V.B.; Moretti, M.; Bettio, L.E.; Ribeiro, C.M.; Rosa, P.B.; Gonçalves, F.M.; Lopes, M.W.; Leal, R.B.; Rodrigues, A.L. Agmatine produces antidepressant-like effects by activating AMPA receptors and mTOR signaling. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 959–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.Z.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Chen, H.X.; Li, J.; Wang, N.P. 5-HT1A/1B receptors, alpha2-adrenoceptors and the post-receptor adenylate cyclase activation in the mice brain are involved in the antidepressant-like action of agmatine. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2008, 43, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gartside, S.E.; Yurttaser, A.E.; Burns, A.L.; Jovanović, N.; Smith, K.J.; Amegashiti, N.S.; Olthof, B.M.J. A role for nitric oxide in serotonin neurons of the midbrain raphe nuclei. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 51, 1881–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremencov, E.; Jezova, D.; Barak, S.; Gaburjakova, J.; Gaburjakova, M.; Kutna, V.; Ovsepian, S.V. Trophic factors as potential therapies for treatment of major mental disorders. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 764, 136194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.S.; Vincow, E.S.; Sexton, T.J.; Neumaier, J.F. Increased expression of 5-HT1B receptor in dorsal raphe nucleus decreases fear-potentiated startle in a stress dependent manner. Brain Res. 2004, 1007, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burlet, S.; Leger, L.; Cespuglio, R. Nitric oxide and sleep in the rat: A puzzling relationship. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léger, L.; Gay, N.; Burlet, S.; Charnay, Y.; Cespuglio, R. Localization of nitric oxide-synthesizing neurons sending projections to the dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 257, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dremencov, E.; El Mansari, M.; Blier, P. Distinct electrophysiological effects of paliperidone and risperidone on the firing activity of rat serotonin and norepinephrine neurons. Psychopharmacology 2007, 194, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinchii, D.; Hoener, M.C.; Khoury, T.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Nejati Bervanlou, R.; Jezova, D.; Dremencov, E. Effects of acute and chronic administration of trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) ligands on in vivo excitability of central monoamine-secreting neurons in rats. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4861–4868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tiger, M.; Varnäs, K.; Okubo, Y.; Lundberg, J. The 5-HT(1B) receptor—A potential target for antidepressant treatment. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1317–1334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinton, C.M.; Fallon, S.L. Electrophysiological evidence for a functional differentiation between subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 157, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Hertel, P.; Lindblom, N.; Nomikos, G.G.; Svensson, T.H. Receptor-mediated regulation of serotonin output in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus: Effects of risperidone. Psychopharmacology 2001, 153, 307–314. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.D.; Menescal-de-Oliveira, L. Nociceptive vocalization response in guinea pigs modulated by opioidergic, GABAergic and serotonergic neurotransmission in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Brain Res. Bull. 2014, 106, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Vázquez, F.; Garduño, J.; Hernández-López, S. GABAergic modulation of serotonergic neurons in the dorsal raphe nucleus. Rev. Neurosci. 2019, 30, 289–303. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, A.R.; Gadotti, V.M.; Oliveira, G.L.; Tibola, D.; Paszcuk, A.F.; Neto, A.; Spindola, H.M.; Souza, M.M.; Rodrigues, A.L.; Calixto, J.B. Mechanisms involved in the antinociception caused by agmatine in mice. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freitas, A.E.; Egea, J.; Buendía, I.; Navarro, E.; Rada, P.; Cuadrado, A.; Rodrigues, A.L.; López, M.G. Agmatine induces Nrf2 and protects against corticosterone effects in hippocampal neuronal cell line. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 1504–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Hajós, M.; Hajós-Korcsok, E.; Sharp, T. Role of the medial prefrontal cortex in 5-HT1A receptor-induced inhibition of 5-HT neuronal activity in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 126, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Grinchii, D.; Janáková Csatlósová, K.; Viñas-Noguera, M.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Paliokha, R.; Lacinová, Ľ.; Dremencov, E.; Dubovický, M. Effects of pre-gestational exposure to the stressors and perinatal bupropion administration on the firing activity of serotonergic neurons and anxiety-like behavior in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 459, 114796. [Google Scholar]
- Dremencov, E.; Oravcova, H.; Grinchii, D.; Romanova, Z.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Lacinova, L.; Jezova, D. Maternal treatment with a selective delta-opioid receptor agonist during gestation has a sex-specific pro-cognitive action in offspring: Mechanisms involved. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1357575. [Google Scholar]
- Hajós, M.; Allers, K.A.; Jennings, K.; Sharp, T.; Charette, G.; Sík, A.; Kocsis, B. Neurochemical identification of stereotypic burst-firing neurons in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus using juxtacellular labelling methods. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Target Gene | Forward | Reverse | Probe |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | 5′-TGG GTA CTC TCA TTT TCT G-3′ | 5′-CAG CAC TGA TAC CAT GAG-3′ | FAM-TCA GTA ACC GCC AAG GAG CC-BHQ_1 |
| 5-HT2A | 5′-CAG AGT TCT CTG TCA TCA-3′ | 5′-GCA CCA CAT TAC AAC AAA-3′ | HEX-TCC AAC GGT CCA TCC ACA GAG-BHQ_1 |
| nNOS | 5′-GGC GAA CAA CTC CCT CAT TA-3′ | 5′-TTG GAA AGA CCT TGG GTC AG-3′ | ROX-TCC TCT TCC AGC TTC GGT CAT TGC-BHQ_2 |
| 5-HT1B | 5′-GGT GGA CTA TTC TGC TAA A-3′ | 5′-GGA GTA GAC CGT GTA GAG-3′ | FAM-AAG CAG TCC AGC ACC TCC TC-BHQ_1 |
| 5-HT2B | 5′-CTG TGT CCT GCC TGG TTA TT-3′ | 5′-GCA CTG ATT GGC CTG AAT TG-3′ | FAM-TGT GCC ATT TCC CTG GAT CGC TAT-BHQ_1 |
| 5-HT2C | 5′-GCA CGG GAC TGT GAT GTT AT-3′ | 5′-GTA GAT GAG CAG AGC GAG AAT C-3′ | HEX-ACA CCT AAA TGG ACA GAT TCA GTG GCA-BHQ_1 |
| SERT | 5′-CAC CGT AAT CTA CTT TAG C-3′ | 5′-GAC AGA GAG GAC AAT GTA-3′ | ROX-CCA CAC CAC CTT GCC AGA TG-BHQ_2 |
| GAPDH | 5′-CTC CCT GTT CTA GAG ACA-3′ | 5′-CCA TGT AGT TGA GGT CAA-3′ | Cy5-CAG TGC CAG CCT CGT CTC ATA-BHQ_2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Özbaşak, H.; Paliokha, R.; Dekhtiarenko, R.; Grinchii, D.; Dremencov, E. Agmatine Enhances Dorsal Raphe Serotonergic Neuronal Activity via Dual Regulation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073087
Özbaşak H, Paliokha R, Dekhtiarenko R, Grinchii D, Dremencov E. Agmatine Enhances Dorsal Raphe Serotonergic Neuronal Activity via Dual Regulation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073087
Chicago/Turabian StyleÖzbaşak, Hande, Ruslan Paliokha, Roman Dekhtiarenko, Daniil Grinchii, and Eliyahu Dremencov. 2025. "Agmatine Enhances Dorsal Raphe Serotonergic Neuronal Activity via Dual Regulation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A Receptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073087
APA StyleÖzbaşak, H., Paliokha, R., Dekhtiarenko, R., Grinchii, D., & Dremencov, E. (2025). Agmatine Enhances Dorsal Raphe Serotonergic Neuronal Activity via Dual Regulation of 5-HT1B and 5-HT2A Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3087. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073087






