The Elongation Factor 1 Alpha Promoter Drives the Functional Expression of Kir2A in Plutella xylostella Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
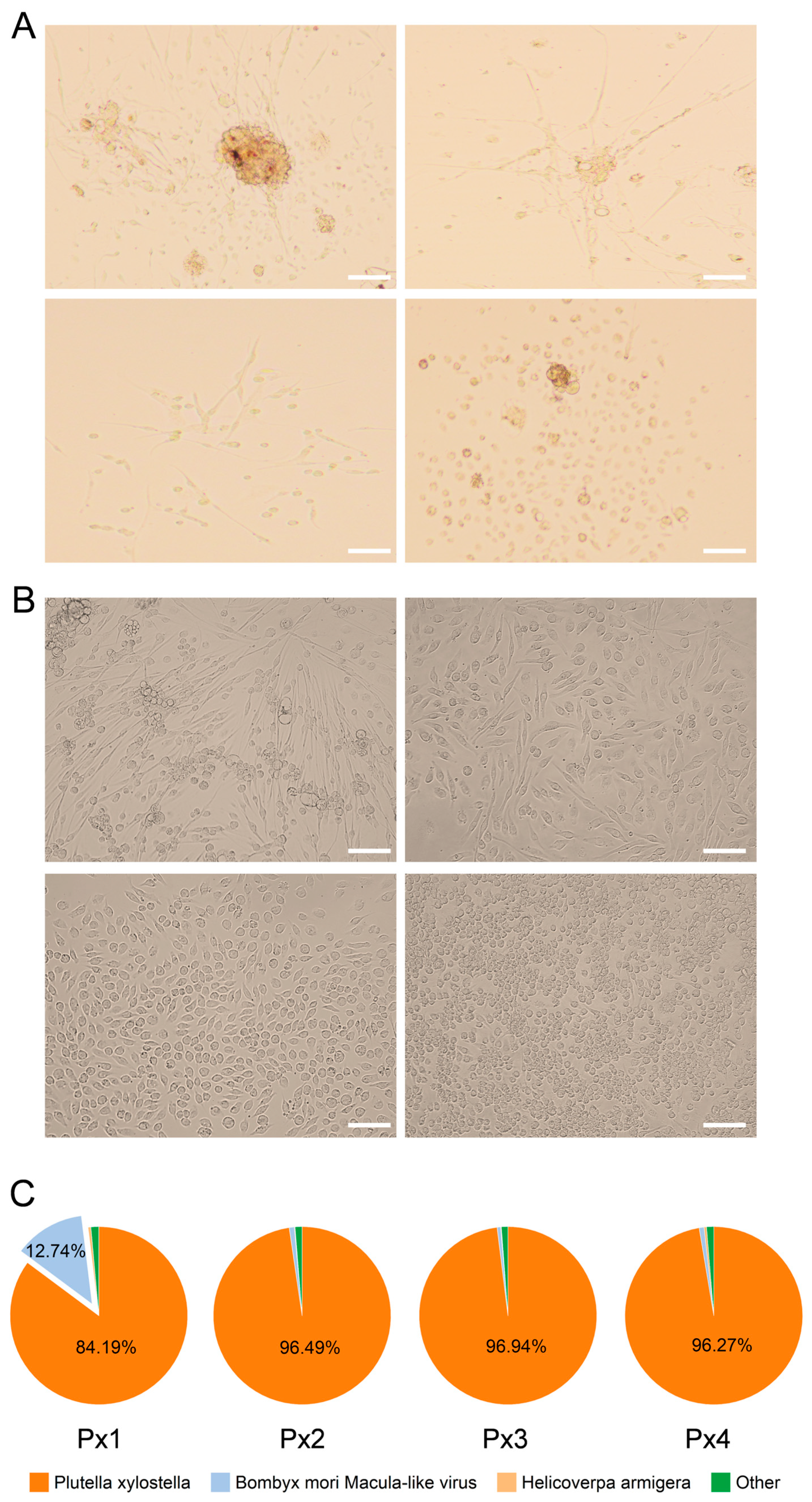
2.1. Establishment of P. xylostella Cell Lines
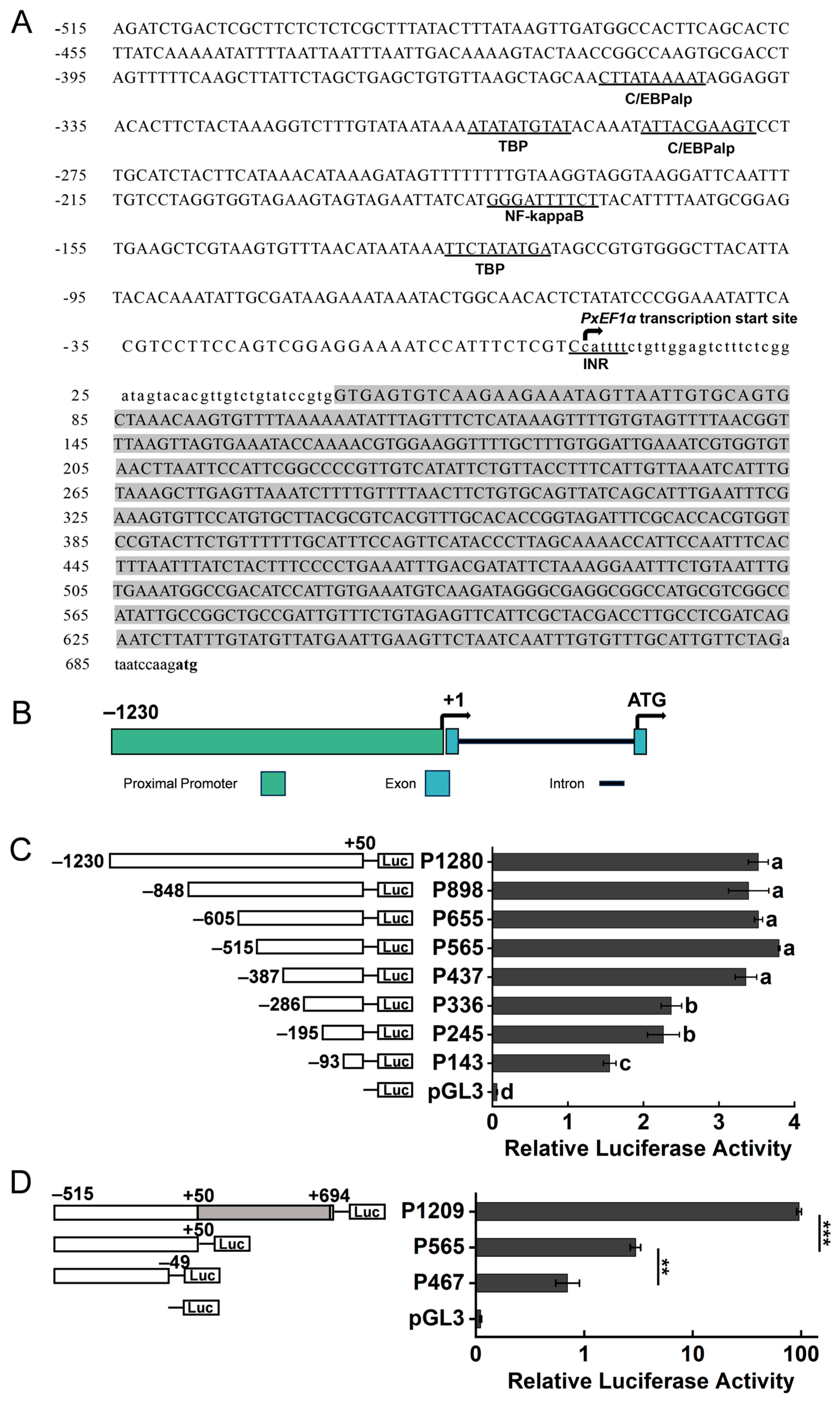
2.2. Analysis of PxEF1α Promoter Activity
2.3. Promoters Regulate the Expression of Firefly Luciferase in Various Insect Cell Types
2.4. Promoters Regulate the Expression of EGFP in Various Insect Cells
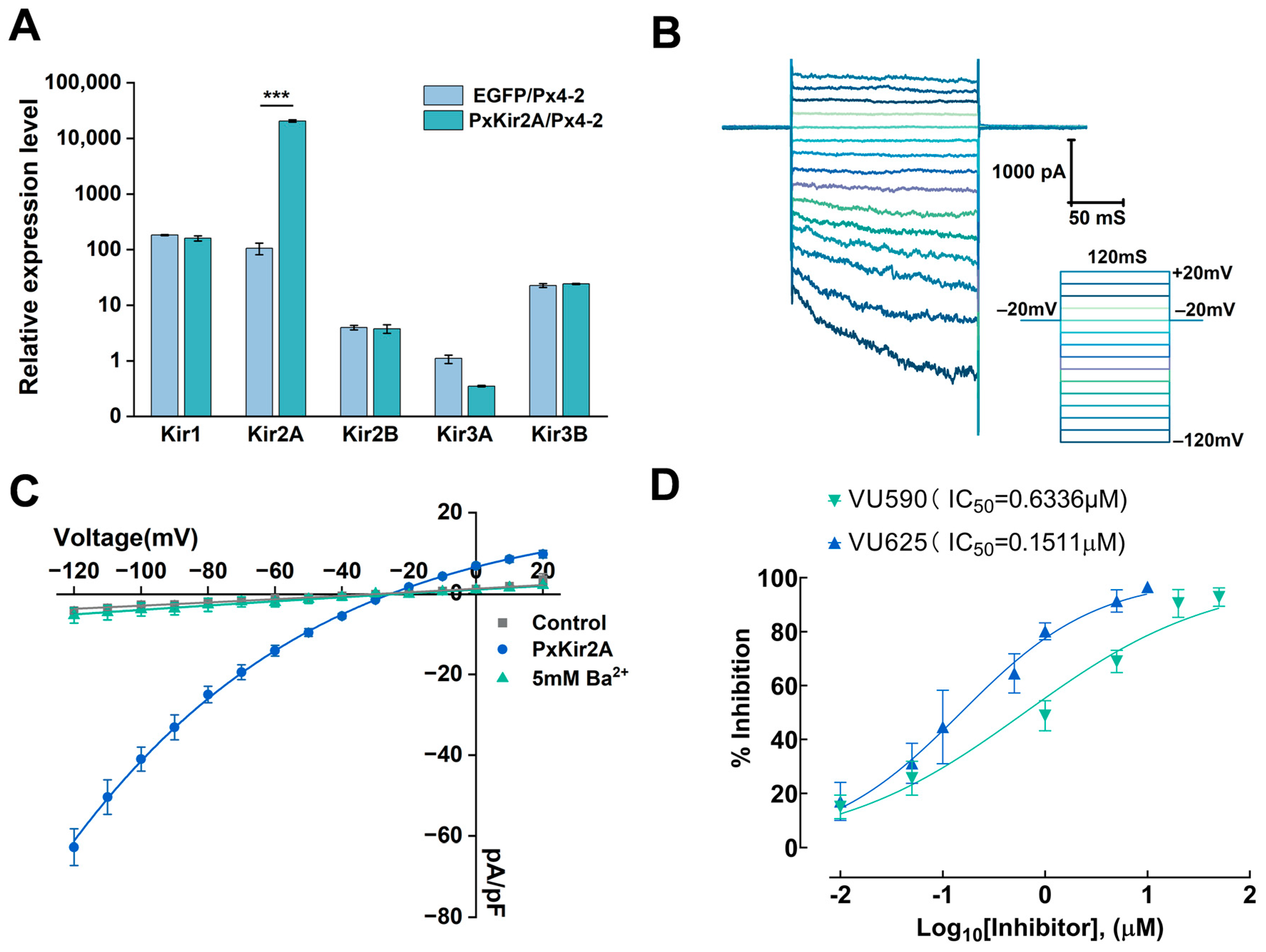
2.5. The PxEF1α Promoter Regulates the Expression of the Kir2A Gene in Px4-2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insects, Cells, and Chemicals
4.2. Primary Cell Culture and Cell Line Isolation
4.3. RNA Sequencing
4.4. 5′ RNA Ligase-Mediated Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends (5′ RLM-RACE)
4.5. Cloning of the Promoter
4.6. Plasmid Construction
4.7. Cell Transfection and Photography
4.8. Dual-Luciferase Activity Assay
4.9. Electrophysiological Assays
4.10. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, X.; Lu, L.; Huang, P.; Yu, B.; Peng, L.; Zou, L.; Ren, Y. Insect Cell-Based Models: Cell Line Establishment and Application in Insecticide Screening and Toxicology Research. Insects 2023, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, J.L.; Goodwin, R.H.; Tompkins, G.J.; McCawley, P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro 1977, 13, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sudeep, A.B.; Mourya, D.T.; Shouche, Y.S.; Pidiyar, V.; Pant, U. A new cell line from the embryonic tissue of Helicoverpa armigera HBN. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2002, 38, 262–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi, J. A Continuous Cell Line from Pupal Ovaries of the Common Cutworm, Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1995, 30, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hink, W.F. Established Insect Cell Line from the Cabbage Looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature 1970, 226, 466–467. [Google Scholar]
- Grace, T.D. Establishment of a line of cells from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Nature 1967, 216, 613. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.L.; He, W.Y.; Wang, P.; You, M.-S. Cell lines from diamondback moth exhibiting differential susceptibility to baculovirus infection and expressing midgut genes. Insect Sci. 2017, 26, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Senderskiy, I.V.; Tsarev, A.A.; Zhuravlyov, V.S.; Pavlova, O.A.; Dolgikh, V.V. Heterologous expression of Nosema bombycis hexokinase in the baculovirus-Sf9 insect cell system confirms its accumulation in the host nuclei and secretion by the microsporidian parasite. Protistology 2020, 14, 23–31. [Google Scholar]
- Chaves, L.C.S.; Ribeiro, B.M.; Blissard, G.W. Production of GP64-free virus-like particles from baculovirus-infected insect cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 265–274. [Google Scholar]
- Geisler, C.; Jarvis, D.L. Adventitious viruses in insect cell lines used for recombinant protein expression. Protein Expres. Purif. 2018, 144, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, D.E.; Harrison, R.L. Available Lepidopteran Insect Cell Lines. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1350, 119–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Goodman, C.L.; Ringbauer, J., Jr.; Song, Q.; Beerntsen, B.; Stanley, D. Establishment of two midgut cell lines from the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2020, 56, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Baum, B.J. All human EF1α promoters are not equal: Markedly affect gene expression in constructs from different sources. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 11, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fraser, M.J. Insect Transgenesis: Current Applications and Future Prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 267–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.C.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Wang, C.H.; Nai, Y.S. Transient Expression of Foreign Genes in Insect Cells (sf9) for Protein Functional Assay. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 132, 56693. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, B.; Liu, X.; James, A.A.; Tan, A. Engineering a complex, multiple enzyme-mediated synthesis of natural plant pigments in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2306322120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Guo, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, K.; Yao, Q. Investigation and application of promoters of insects and their virus. J. Biol. 2012, 29, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.S.; Wang, Z.H.; Li, W.S.; Xu, W.H. FoxO induces pupal diapause by decreasing TGFβ signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210404119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Li, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, G.; Guo, X.; Ma, Y.; Yao, Q. Characterization of the Promoter Elements of Bombyx mori Bidensovirus Nonstructural Gene 1. Curr. Microbiol. 2012, 65, 643–648. [Google Scholar]
- Miyata, Y.; Tokumoto, S.; Sogame, Y.; Deviatiiarov, R.; Okada, J.; Cornette, R.; Gusev, O.; Shagimardanova, E.; Sakurai, M.; Kikawada, T. Identification of a novel strong promoter from the anhydrobiotic midge, Polypedilum vanderplanki, with conserved function in various insect cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7004. [Google Scholar]
- Piermarini, P.M.; Denton, J.S.; Swale, D.R. The Molecular Physiology and Toxicology of Inward Rectifier Potassium Channels in Insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2022, 67, 125–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hibino, H.; Inanobe, A.; Furutani, K.; Murakami, S.; Findlay, I.; Kurachi, Y. Inwardly rectifying potassium channels: Their structure, function, and physiological roles. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 291–366. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.R.; Jahangir, A.; Alekseev, A.E.; Terzic, A. Channelopathies of inwardly rectifying potassium channels. FASEB J. 1999, 13, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Döring, F.; Wischmeyer, E.; Kühnlein, R.P.; Jäckle, H.; Karschin, A. Inwardly rectifying K+ (Kir) channels in Drosophila. A crucial role of cellular milieu factors Kir channel function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25554–25561. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhier, M.F.; Raphemot, R.; Denton, J.S.; Piermarini, P.M. Pharmacological validation of an inward-rectifier potassium (Kir) channel as an insecticide target in the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100700. [Google Scholar]
- Raphemot, R.; Estévez-Lao, T.Y.; Rouhier, M.F.; Piermarini, P.M.; Denton, J.S.; Hillyer, J.F. Molecular and functional characterization of Anopheles gambiae inward rectifier potassium (Kir1) channels: A novel role in egg production. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 51, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, M.; Niu, J.; Hu, B.; Wei, Q.; Zheng, C.; Tian, X.; Gao, C.; He, B.; Dong, K.; Su, J. Block of Kir channels by flonicamid disrupts salivary and renal excretion of insect pests. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 99, 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Piermarini, P.M.; Inocente, E.A.; Acosta, N.; Hopkins, C.R.; Denton, J.S.; Michel, A.P. Inward rectifier potassium (Kir) channels in the soybean aphid Aphis glycines: Functional characterization, pharmacology, and toxicology. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 110, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sourisseau, F.; Chahine, C.; Pouliot, V.; Cens, T.; Charnet, P.; Chahine, M. Cloning, functional expression, and pharmacological characterization of inwardly rectifying potassium channels (Kir) from Apis mellifera. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7834. [Google Scholar]
- Piermarini, P.M.; Rouhier, M.F.; Schepel, M.; Kosse, C.; Beyenbach, K.W. Cloning and functional characterization of inward-rectifying potassium (Kir) channels from Malpighian tubules of the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 75–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, X.; Xu, J.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X. Identification and Expression of Inward-Rectifying Potassium Channel Subunits in Plutella xylostella. Insects 2020, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, A.H.; Grasela, J.J.; Matted, R.L. Identification of insect cell lines by DNA amplification fingerprinting (DAF). Insect Mol. Biol. 1996, 5, 187–195. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Li, L.L. The p35 and ie1 of Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus could rescue late gene expression of Plutella xylostella granulovirus in nonpermissive cell lines. Virus Genes 2014, 48, 343–355. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, L.L. Homologous region 1 of Plutella xylostella granulovirus functions as an enhancer for early gene expression. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2429–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiong, L.; Xie, C.; Shen, L.; Chen, X.; Ye, M.; Sun, L.; Yang, X.; Yao, S.; Yue, Z.; et al. Optimization and Application of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing in a Cosmopolitan Pest, Diamondback Moth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innami, K.; Aizawa, T.; Tsukui, T.; Katsuma, S.; Imanishi, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Iwanaga, M. Infection studies of nontarget mammalian cell lines with Bombyx mori macula-like virus. J. Virol. Methods 2016, 229, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Katsuma, S.; Kawamoto, M.; Shoji, K.; Aizawa, T.; Kiuchi, T.; Izumi, N.; Ogawa, M.; Mashiko, T.; Kawasaki, H.; Sugano, S.; et al. Transcriptome profiling reveals infection strategy of an insect maculavirus. DNA Res. 2018, 25, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Chereddy, S.C.R.R.; Gurusamy, D.; Palli, S.R. Identification and characterization of highly active promoters from the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 126, 103455. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, J.; Banno, Y.; Mita, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ando, T.; Fujiwara, H. Periodic Wnt1 expression in response to ecdysteroid generates twin-spot markings on caterpillars. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1857. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, T.; Liu, R.; Luo, Q.; Ma, J.; Ou, Y.; Zeng, W.; Feng, L.; Xu, H. The intronic promoter of Actin4 mediates high-level transgene expression mainly in the wing and epidermis of silkworms. Transgenic Res. 2020, 29, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, X.Y.; Lu, W.J.; Qiao, X.; Huang, J. Genome editing efficiency of four Drosophila suzukii endogenous U6 promoters. Insect Mol. Biol. 2021, 30, 420–426. [Google Scholar]
- Calloe, K.; Rognant, S.; Friis, S.; Shaughnessy, C.; Klaerke, D.A.; Trachsel, D. Compounds commonly used in equine medicine inhibits the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv11.1. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 123, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Man, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ma, H. Electrophysiological and pharmacological properties of the slowpoke channel in the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 200, 105824. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.; Ma, H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Identification and pharmacological characterization of the voltage-gated potassium channel Shab in diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, T.R.; Wickham, T.J.; McKenna, K.A.; Granados, R.R.; Shuler, M.L.; Wood, H.A. Comparative recombinant protein production of eight insect cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1993, 29, 388–390. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, G.L.; Li, C.Y.; Zhou, H.X.; Li, S.W.; Li, G.X.; Xue, M. Establishment of two new cell lines from the embryonic tissue of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and their responses to baculovirus infection. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2010, 53, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.F.; Liu, Z.G.; Sun, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Feng, Y. Screening of single-cell clonal lines from Papilio demoleus Linnaeus cell lines for exogenous protein expression and adaptation in serum-free culture. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2020, 56, 444–451. [Google Scholar]
- Klonaros, D.; Dresch, J.M.; Drewell, R.A. Transcriptome profile in Drosophila Kc and S2 embryonic cell lines. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2023, 13, jkad054. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, F.; Yang, T.; Han, Z.; Gao, T. Transcriptome analysis for identification of candidate genes related to sex determination and growth in Charybdis japonica. Gene 2018, 677, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Ma, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, W.; Man, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. C/EBPα Regulates PxTreh1 and PxTreh2 Trehalase-Related Bt Resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). Insects 2022, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene_ID | Description | Px2 | Px3 | Px4 | AVE. (fpkm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC105391374 | elongation factor 1-alpha | 6779.87 | 6455.37 | 6476.86 | 6570.70 |
| LOC105383306 | heat shock 70 kDa protein cognate 4 | 6083.09 | 3606.12 | 3578.88 | 4422.70 |
| LOC105380966 | tubulin beta-1 chain | 4481.64 | 3106.23 | 4111.85 | 3899.91 |
| LOC105395368 | 40S ribosomal protein S26 | 3673.93 | 3278.9 | 4185.09 | 3712.64 |
| LOC105387458 | 60S ribosomal protein L32 | 3927.65 | 3106.78 | 3704 | 3579.48 |
| LOC105398657 | 40S ribosomal protein S25 | 3459.16 | 1732.38 | 4772.07 | 3321.20 |
| LOC105393825 | 60S ribosomal protein L13 | 3301.49 | 2304.95 | 3595.51 | 3067.32 |
| LOC105397135 | 60S ribosomal protein L40 | 2758.34 | 2063.79 | 3681.04 | 2834.39 |
| LOC105386998 | 60S ribosomal protein L30 | 4097.38 | 2158.8 | 2229.32 | 2828.50 |
| LOC105392651 | 60S ribosomal protein L18 | 3183.03 | 2915.76 | 1925.27 | 2674.69 |
| LOC105386163 | 40S ribosomal protein S10 | 2881.14 | 2508.21 | 2434.86 | 2608.07 |
| LOC105398808 | ADP, ATP carrier protein 2 | 2243.29 | 2849.8 | 2616.7 | 2569.93 |
| LOC105391828 | 60S ribosomal protein L23 | 3002.74 | 2520.08 | 2024.39 | 2515.74 |
| LOC105382338 | 60S ribosomal protein L24 | 3021.33 | 1746.83 | 2401.96 | 2390.04 |
| LOC105387239 | 60S ribosomal protein L35 | 4011.06 | 1746.09 | 1404.56 | 2387.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, P.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Man, Y.; Zhou, X. The Elongation Factor 1 Alpha Promoter Drives the Functional Expression of Kir2A in Plutella xylostella Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073042
Wang Y, Ma H, Liu Z, Zhao P, Liu J, Zhu H, Zhou Y, Man Y, Zhou X. The Elongation Factor 1 Alpha Promoter Drives the Functional Expression of Kir2A in Plutella xylostella Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073042
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yinna, Haihao Ma, Zheming Liu, Piao Zhao, Jia Liu, Hang Zhu, Yong Zhou, Yilong Man, and Xiaomao Zhou. 2025. "The Elongation Factor 1 Alpha Promoter Drives the Functional Expression of Kir2A in Plutella xylostella Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073042
APA StyleWang, Y., Ma, H., Liu, Z., Zhao, P., Liu, J., Zhu, H., Zhou, Y., Man, Y., & Zhou, X. (2025). The Elongation Factor 1 Alpha Promoter Drives the Functional Expression of Kir2A in Plutella xylostella Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073042






