Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Molecular Physiology
2.1. Fatty Acid Uptake: Key Transporters
2.2. Lipogenesis: Synthesis of New Lipids
2.3. Fatty Acid Oxidation: A Metabolic Counterbalance
2.4. Safe Storage of Lipid Droplets: Droplets of Hepatic Lipid Balance
2.5. Lipid Exportation: Pathways of Hepatic Lipid Clearance
2.6. Role of Adipokines in the Pathogenesis and Progression of MASLD/MASH
2.7. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Drivers of Liver Injury and Fibrosis
2.8. Mitochondrial Dysfunction: The Energy Crisis in MASLD
2.9. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress: A Cellular Stressor in Liver Disease
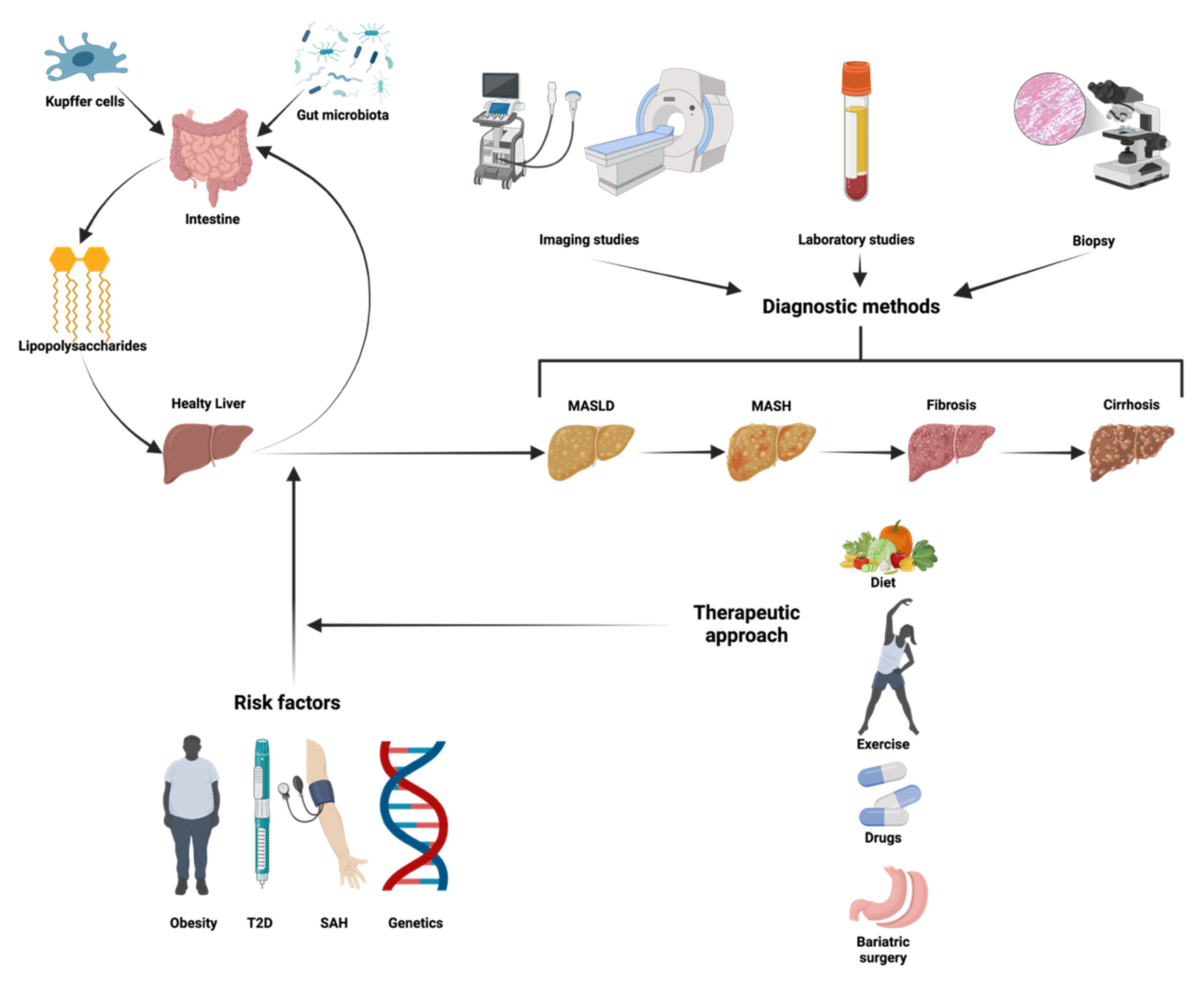
2.10. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: The Gut–Liver Axis in MASLD Progression
2.11. Unraveling the Spleen–Liver Axis
2.12. Genetic and Epigenetic Factors: Molecular Determinants of Disease Susceptibility
3. Clinic Manifestations
3.1. Early Stages of MASLD
3.2. The Silent Progression of MASLD (MASH)
3.3. Screening and Diagnostic Approach for MASLD
4. Approaches to Managing MASLD and Halting Its Progression
4.1. Drugs in Development and Research for MASLD and MASH Treatmen
4.1.1. Resmetirom
4.1.2. PPAR
4.1.3. SGLT2
4.1.4. FXR Agonist
4.1.5. Obeticholic Acid
4.1.6. GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
4.1.7. DPP-4
4.1.8. FGF Analogs
4.1.9. Statins
4.1.10. Metformin
4.1.11. Promising New Medications
| Target | Action | Drugs Name | Benefits | Side Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THRβ | Agonist | Resmetirom * | ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ LDL, ↓ TG, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ GGT | Diarrhea, nausea, pruritus, vomit | [138] |
| PPAR | PPARα agonist | Pemafibrate | ↓ Liver stiffness, ↓ ALT, ↓ TG, ↑HDL | Diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, CKD, AKI, skin rashes, muscle pain | [140] |
| Saroglitazar | ↓ TC, ↓ TG, ↓ LDL, ↓ VLDL | Diarrhea, cough, abdominal pain, fatigue, nausea, dyspepsia | [141] | ||
| Fenofibrate | ↓ TG, ↓ LDL, ↑HDL, ↓ ALP, ↓ GGT, ↓ Insulin resistance | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, abdominal pain, headache, dizziness, rashes | [140] | ||
| PPARγ agonist | Pioglitazone | ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ FPG, ↓ Insulin resistance, ↓ TG, ↓ LDL | Weight gain, fluid retention, nausea, vomit, lethargy, insomnia | [145] | |
| PanPPAR agonist | Lanifibranor | ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ TG, ↑HDL, ↓ Insulin resistance, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ FPG | Nausea, diarrhea, anemia, peripheral edema, weight gain | [141] | |
| SGLT2 | Inhibitor | Canagliflozin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ TG, ↑Insulin Sensitivity, ↑Insulin secretion, ↓ Body and fat mass, ↓ Liver enzymes, ↓ Visceral fat | Nausea, diarrhea, constipation, UTIs, genital mycotic infections, increased urination, increased thirst | [148] |
| Dapagliflozin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Pancreatic fat content, ↓ Inflammatory cytokine ↓ ALT, ↓ Visceral fat ↓ Body weight, ↑Insulin sensitivity | UTIs, genital mycotic infections, increased urination, episodes of hypotension, upper respiratory tract infections, headache, rash | [144] | ||
| Empagliflozin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ Visceral fat, ↓ AST, ↓ ALT, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ Body weight | UTIs, genital mycotic infections, increased urination | [179] | ||
| Ipragliflozin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ Visceral fat, ↑HDL, ↓ TG, ↓ FPG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ Blood pressure, ↓ Liver enzymes, ↓ Uric acid | UTIs, hypoglycemia, increase urinary glucose excretion, genital mycotic infections | [143] | ||
| Licogliflozin | ↓ Steatosis ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ GGT, ↓ Body weight, ↓ HbA1c, ↑eGFR | Diarrhea, flatulence, abdominal distension, renal impairment, UTIs, genital mycotic infections | [146] | ||
| Ertugliflozin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ GGT, ↓ TG, ↓ Body weight, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ Uric acid | Genital mycotic infections, UTIs, headache, back pain | [149] | ||
| FXR | Agonist | EDP-305 | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ GGT, ↓ TG, ↓ FPG | Pruritus, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, gastroesophageal reflux, headache, dizziness, vomit | [150] |
| Obeticholic acid | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ Body weight, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ GGT | Pruritus, fatigue, abdominal pain and discomfort, increases in LDL-C, dizziness, constipation, arthralgia, eczema, thyroid function abnormality | [154] | ||
| Vonafexor | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ Body weight, ↓ ALT, ↓ GGT, ↑eGFR | Pruritus, increased LDL-C, dyslipidemia, nausea, fatigue | [152] | ||
| Cilofexor | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST | Pruritus, dyslipidemia, nausea, diarrhea, vomit, constipation and decreased appetite, increased LDL-C, increases TG | [153] | ||
| FGF | 19 analogue | Aldafermin | ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↑Insulin sensitivity | Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, altered bowel function, increased appetite, increased LDL-C, fatigue, headache, constipation | [171] |
| 21 analogue | Pegbelfermin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST | Diarrhea, nausea, increased appetite, local reactions, headache, fatigue, hypoglycemia | [168] | |
| Pegozafermin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ TG, ↑HDL, ↓ LDL, ↓ ALT, ↓ HbA1c, ↑Insulin sensitivity | Diarrhea, nausea, vomit, increased appetite, local reactions | [169] | ||
| Efruxifermin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ TG, ↓ LDL, ↑HDL, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ Uric acid | Diarrhea, nausea, increased appetite, local reactions | [170] | ||
| DPP4 | Inhibitor | Sitagliptin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Liver stiffness, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ FPG, ↓ TG, ↓ LDL, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ Atherosclerosis | Upper respiratory tract infections, headache, diarrhea, UTIs, joint pain | [147] |
| Vildagliptin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Liver stiffness, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ FPG, ↓ Lipid profile, ↓ ALT, ↓ Atherosclerosis | Upper respiratory tract infections, headache, diarrhea, nausea, dizziness | [166] | ||
| Evogliptin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ FPG, ↑ Insulin sensitivity, ↓ AST, ↓ ALT | Hypoglycemia, nasopharyngitis, headache, gastrointestinal disturbance | [142] | ||
| Saxagliptin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ FPG, ↓ Liver enzymes, ↓ Adipose tissue | Upper respiratory tract infections, UTIs, diarrhea, vomit, abdominal pain, headache, hypoglycemia, lymphopenia | [167] | ||
| HMG-CoA | Inhibitor | Atorvastatin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ LDL, ↑ HDL, ↓ TG, ↑Insulin sensitivity ↓ CRP, ↓ VLDL | Myalgia, myopathy, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, insomnia, drowsiness | [172] |
| Rosuvastatin | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ LDL, ↓ TG, ↑HDL, ↓ VLDL | Muscle toxicity, dizziness, headache, myalgia, gastrointestinal issues | [173] | ||
| AMPK | Agonist | Metformin | ↓ Steatosis, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ TG, ↓ Body weight, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, | Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence, vomit, metallic taste | [175] |
| GLP-1 | Agonist | Semaglutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ Body weight, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ CRP, ↓ TG, ↓ LDL, ↓ VLDL | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, headache, fatigue, dyspepsia, dizziness, hypoglycemia | [135] |
| Dulaglutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ HbA1c, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, decreased appetite, headache | [155] | ||
| Liraglutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ Body weight, ↓ TG, ↓ HbA1c, ↑Insulin sensitivity | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, abdominal pain | [156] | ||
| Exenatide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Liver enzymes, ↓ Body weight, ↑Insulin sensitivity | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, hypoglycemia, local reactions, upper respiratory symptoms | [157] | ||
| Cotadutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ Body weight, ↓ HbA1c | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, constipation, decreased appetite, hypoglycemia | [158] | ||
| Beinaglutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ Body weight, ↓ FPG, ↓ HbA1c | Diarrhea, nausea, vomit, dizziness | [159] | ||
| GLP-1/GIP | Dual agonist | Tirzepatide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ FPG, ↓ HbA1c, ↓ Body weight, ↓ TG, ↑HDL, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ OSA | Nausea, diarrhea, vomit, abdominal pain, constipation, decreased appetite, dyspepsia | [162] |
| GLP-1/Glucagon | Dual agonist | Survodutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Liver stiffness, ↓ Body weight, ↓ HbA1c | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, dehydration, angioedema | [164] |
| Pemvidutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ Body weight, ↓ Blood pressure, ↓ Liver volume, ↓ Lipid profile | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, constipation | [161] | ||
| GLP-1/Glucagon/GIP | Triple agonist | Retatrutide | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ Body weight, ↓ Adipose tissue | Nausea, diarrhea, vomit, constipation, change in bowel habits, skin hyperesthesia | [163] |
| Efocipegtrutide | ↓ MASH | Hyperglycemia, gastrointestinal issues | [165] | ||
| ACC | Inhibitor | Firsocostat | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ Body weight, ↓ Blood pressure, ↓ Liver volume, ↓ Lipid profile | Hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, nauseas, diarrhea, pruritus | [153] |
| PDE | Inhibitor | Pentoxifylline | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST | Nausea, vomit, diarrhea, anorexia, dizziness, headache, chest pain, tachycardia, skin reactions | [180] |
| SCD1 | Partial inhibitor | Aramchol | ↓ Steatosis, ↓ MASH, ↓ Fibrosis, ↓ ALT, ↓ AST, ↓ HbA1c, ↑Insulin sensitivity | Skin disorders, eye disorders, atherosclerosis, hair loss, hypothermia | [176] |
| ASK1 | Inhibitor | Selonsertib | ↓ Liver stiffness, ↓ MASH | Headache, nausea, sinusitis, nasopharyngitis, upper abdominal pain, back pain, fatigue | [177] |
| Ketohexokinase | Inhibitor | PF-06835919 | ↓ Steatosis, ↑Insulin sensitivity, ↓ FPG | Headache, nausea, insomnia, back pain, dyspepsia, fatigue | [178] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| MASLD | metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| AASLD | American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases |
| EASL | European Association for the Study of the Liver |
| ALEH | Asociación Latinoamericana para el Estudio del Hígado |
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| BMI | body mass index |
| MASH | metabolic-dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| NASH | non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| MetALD | metabolic alcoholic liver disease |
| CD36 | Cluster Differentiation 36 |
| FATP2 | Fatty Acid Transport Protein 2 |
| INSIG2 | Insulin-Induced Gene 2 |
| SREBP1 | Sterol Regulatory Element-Binding Protein 1 |
| FAS | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| SCD-1 | Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 |
| ACC1 | Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase |
| NAT10 | N-Acetyltransferase 10 |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| GSK-3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| ACLY | ATP Citrate Lyase |
| ACCα | acetyl-CoA carboxylase alpha |
| PPAR | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-kappa B |
| ACSL5 | Acyl-CoA Synthetase Family Member 5 |
| USP29 | Ubiquitin-Specific Protease 29 |
| PLIN2 | Perilipin 2 |
| DGAT2 | Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase 2 |
| ATG3 | Autophagy-related 3 |
| GSTA1 | Glutathione S-Transferase A1 |
| FABP1 | Fatty Acid Binding Protein 1 |
| PGC1α | Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Coactivator 1-Alpha |
| LXR | Liver X Receptor |
| CX3CL1 | C-X3-C Motif Ligand 1 |
| CCL2 | C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 |
| CCR2 | Chemokine Receptor 2 |
| MTTP | Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein |
| VLDL | very low-density lipoproteins |
| TMEM41B | Transmembrane protein 41B |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ATF3 | Activating transcription factor 3 |
| IL | interleukin |
| SOCS2 | Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 2 |
| MT1B | Metallothionein-1B |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| STING | Stimulator of Interferon Genes |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| JNK | inhibiting Jun N-terminal kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| FNDC4 | Fibronectin Type III Domain Containing Protein 4 |
| GPx7 | glutathione peroxidase 7 |
| HFD | high-fat diet |
| CMKLR1 | Chemokine-like receptor 1 |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead box protein O1 |
| YAP | Yes-associated protein |
| NOTCH1 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 |
| β-HAD | β-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| Drp1 | Dynamin-related protein 1 |
| OPA1 | Optic Atrophy 1 |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| SIRT1 | silent information regulator 1 |
| BNIP3 | BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa-interacting protein 3 |
| TIM22 | Translocase of the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane 22 |
| VLDLR | very-low-density lipoprotein receptors |
| ATF4 | Activating Transcription Factor 4 |
| BRD4 | Bromodomain-containing protein 4 |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| Hsp70 | heat shock protein 70 |
| DAMP | damage-associated molecular pattern |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharides |
| STK39 | serine-threonine kinase 39 |
| PNPLA3 | Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 |
| ND6 | NADH dehydrogenase 6 |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| GGT | gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| THR-β | thyroid hormone receptor beta |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| SGLT | sodium-glucose cotransporter |
| FXR | farnesoid X receptor |
| OCA | Obeticholic acid |
| FGF19 | fibroblast growth factor 19 |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| DPP-4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 |
| FGF | Fibroblast growth factor |
| CYP7A1 | cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase |
| SCD1 | stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 |
| THRβ | Thyroid hormone receptor-beta |
| SGLT2 | Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 |
| DPP4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 |
| HMG-CoA | Hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A |
| GIP | Gastric inhibitory polypeptide |
| ACC | Acetyl-Coenzyme A carboxylase |
| PDE | Phosphodiesterase |
| ASK1 | Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1C |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| OSA | Obstructive sleep apnea |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| UTIs | urinary tract infections |
References
- Kalligeros, M.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Victor, D.W.; Mylonakis, E.; Noureddin, M. Prevalence of Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD, MetALD, and ALD) in the United States: NHANES 2017–2020. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 22, 1330–1332.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Carbone, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Perseghin, G. Exploring the Landscape of Steatotic Liver Disease in the General US Population. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2425–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A Multisociety Delphi Consensus Statement on New Fatty Liver Disease Nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, L.A.; Lazarus, J.V.; Fuentes-López, E.; Idalsoaga, F.; Ayares, G.; Desaleng, H.; Danpanichkul, P.; Cotter, T.G.; Dunn, W.; Barrera, F.; et al. Disparities in Steatosis Prevalence in the United States by Race or Ethnicity According to the 2023 Criteria. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripongpun, P.; Kaewdech, A.; Udompap, P.; Kim, W.R. Characteristics and Long-Term Mortality of Individuals with MASLD, MetALD, and ALD, and the Utility of SAFE Score. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, M.; Miyaaki, H.; Nakao, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Haraguchi, M.; Takahashi, K.; Ozawa, E.; Miuma, S.; Akazawa, Y.; Soyama, A.; et al. Characterizing Alcohol-Related and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Cirrhosis via Fibrotic Pattern Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canivet, C.M.; Boursier, J.; Loomba, R. New Nomenclature for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Understanding Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, Metabolic Dysfunction- and Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease, and Their Implications in Clinical Practice. Semin. Liver Dis. 2024, 44, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Ye, J.; Mo, S.; Ye, M.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Impact of Nomenclature as Metabolic Associated Steatotic Liver Disease on Steatotic Liver Disease Prevalence and Screening: A Prospective Population Survey in Asians. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 39, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Price, J.K.; Owrangi, S.; Gundu-Rao, N.; Satchi, R.; Paik, J.M. The Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 1999–2010.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Li, J.; Huang, D.Q.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Kam, L.Y.; Tan, X.X.E.; et al. Global Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes of Non-Obese or Lean Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.S. Differences in the Prevalence of NAFLD, MAFLD, and MASLD According to Changes in the Nomenclature in a Health Check-up Using MRI-Derived Proton Density Fat Fraction. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 3036–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F.; Horn, P.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Ratziu, V.; Bugianesi, E.; Francque, S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Valenti, L.; Roden, M.; Schick, F.; et al. EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amernia, B.; Moosavy, S.H.; Banookh, F.; Zoghi, G. FIB-4, APRI, and AST/ALT Ratio Compared to FibroScan for the Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Bandar Abbas, Iran. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Kechagias, S.; Ekstedt, M. Risk for Hepatic and Extra-hepatic Outcomes in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K.; Isaacs, S.; Barb, D.; Basu, R.; Caprio, S.; Garvey, W.T.; Kashyap, S.; Mechanick, J.I.; Mouzaki, M.; Nadolsky, K.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Primary Care and Endocrinology Clinical Settings. Endocr. Pract. 2022, 28, 528–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M. From Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome to Cardiovascular-Renal-Hepatic-Metabolic Syndrome: Proposing an Expanded Framework. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Simon, T.G.; Rinella, M.E. Extrahepatic Outcomes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Nonhepatocellular Cancers. Clin. Liver Dis. 2023, 27, 251–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Qin, H.; Liao, M.; Zheng, E.; Luo, X.; Xiao, A.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wei, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. CD36 Promotes de Novo Lipogenesis in Hepatocytes through INSIG2-Dependent SREBP1 Processing. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Yang, X.; Kuang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Tan, X.; Lan, J.; Qiang, Z.; Feng, T. HBx Induced Upregulation of FATP2 Promotes the Development of Hepatic Lipid Accumulation. Exp. Cell Res. 2023, 430, 113721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blériot, C.; Barreby, E.; Dunsmore, G.; Ballaire, R.; Chakarov, S.; Ficht, X.; De Simone, G.; Andreata, F.; Fumagalli, V.; Guo, W.; et al. A Subset of Kupffer Cells Regulates Metabolism through the Expression of CD36. Immunity 2021, 54, 2101–2116.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Jang, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Choi, S.S.; Khim, K.W.; Eom, H.-J.; Hyun, J.; Shin, K.J.; Chae, Y.C.; Kim, H.; et al. Hepatic MIR20B Promotes Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing PPARA. eLife 2021, 10, e70472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Tang, Y.; Su, H.; Lu, F.; Dong, H.; Fang, K. Diosgenin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Type 2 Diabetes through Regulating SIRT6-Related Fatty Acid Uptake. Phytomedicine 2023, 111, 154661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dille, M.; Nikolic, A.; Wahlers, N.; Fahlbusch, P.; Jacob, S.; Hartwig, S.; Lehr, S.; Kabra, D.; Klymenko, O.; Al-Hasani, H.; et al. Long-Term Adjustment of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism after Chronic Stress and the Role of FGF21. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yuan, B.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Ding, N.; Liu, C.; Gao, M.; Yao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. The Methyltransferase METTL3 Negatively Regulates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Progression. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozen, E.; Demirel-Yalciner, T.; Sari, D.; Avcilar, C.; Samanci, T.F.; Ozer, N.K. Deficiency of SREBP1c Modulates Autophagy Mediated Lipid Droplet Catabolism during Oleic Acid Induced Steatosis. Metab. Open 2021, 12, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, M.; Kim, H.-G.; Chowdhury, K.; Gao, J.; Liu, S.; Wan, J.; Wei, L.; Dong, X.C. SIRT6 Controls Hepatic Lipogenesis by Suppressing LXR, ChREBP, and SREBP1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N.; Luo, Y.; Ma, M.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, M.-H.; Ruan, C.-C.; et al. Improvement of MASLD and MASH by Suppression of Hepatic N-Acetyltransferase 10. Mol. Metab. 2024, 89, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.-H.; Hu, L.-K.; Yan, Y.-X. Identification of Metabolism-Related Proteins as Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance and Potential Mechanisms of M6A Modification. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zywno, H.; Bzdega, W.; Kolakowski, A.; Kurzyna, P.; Harasim-Symbor, E.; Sztolsztener, K.; Chabowski, A.; Konstantynowicz-Nowicka, K. The Influence of Coumestrol on Sphingolipid Signaling Pathway and Insulin Resistance Development in Primary Rat Hepatocytes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, M.; Guo, Q.; Furuta, K.; Correia, C.; Meroueh, C.; Kim Lee, H.S.; Warasnhe, K.; Valenzuela-Pérez, L.; Mazar, A.P.; Kim, I.; et al. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Activity Enhances Liver Inflammation in MASH. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Ji, P.-X.; Ni, X.-X.; Chen, Y.-X.; Sheng, L.; Lian, M.; Guo, C.-J.; Hua, J. Regulation of PPAR-γ Activity in Lipid-Laden Hepatocytes Affects Macrophage Polarization and Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theys, C.; Vanderhaeghen, T.; Van Dijck, E.; Peleman, C.; Scheepers, A.; Ibrahim, J.; Mateiu, L.; Timmermans, S.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Francque, S.M.; et al. Loss of PPARα Function Promotes Epigenetic Dysregulation of Lipid Homeostasis Driving Ferroptosis and Pyroptosis Lipotoxicity in Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Front. Mol. Med. 2024, 3, 1283170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Régnier, M.; Polizzi, A.; Smati, S.; Lukowicz, C.; Fougerat, A.; Lippi, Y.; Fouché, E.; Lasserre, F.; Naylies, C.; Bétoulières, C.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific Deletion of Pparα Promotes NAFLD in the Context of Obesity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, K.; Shi, H.; Qin, F.; Zhang, T.; Tian, S.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qin, J.; et al. USP29 Alleviates the Progression of MASLD by Stabilizing ACSL5 through K48 Deubiquitination. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 31, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliterni, C.; Vari, F.; Schifano, E.; Tacconi, S.; Stanca, E.; Friuli, M.; Longo, S.; Conte, M.; Salvioli, S.; Gnocchi, D.; et al. Lipotoxicity of Palmitic Acid Is Associated with DGAT1 Downregulation and Abolished by PPARα Activation in Liver Cells. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 65, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, R.; Zehnder, S.V.; Watts, R.; Lian, J.; Das, C.; Nelson, R.; Lehner, R. Preferential Lipolysis of DGAT1 over DGAT2 Generated Triacylglycerol in Huh7 Hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA—Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2023, 1868, 159376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.; Xia, M.; Vale, G.; Wang, S.; Kim, C.-W.; Li, S.; McDonald, J.G.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Horton, J.D. DGAT2 Inhibition Blocks SREBP-1 Cleavage and Improves Hepatic Steatosis by Increasing Phosphatidylethanolamine in the ER. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 617–629.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Lima, N.; Fondevila, M.F.; Nóvoa, E.; Buqué, X.; Mercado-Gómez, M.; Gallet, S.; González-Rellan, M.J.; Fernandez, U.; Loyens, A.; Garcia-Vence, M.; et al. Inhibition of ATG3 Ameliorates Liver Steatosis by Increasing Mitochondrial Function. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, H.; Tang, M.; Lei, L.; Li, H.-Y.; Dong, B.; Li, J.-R.; Wang, X.-K.; Sun, H.; Li, J.-Y.; et al. Upregulation of Hepatic Glutathione S-Transferase Alpha 1 Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatosis by Degrading Fatty Acid Binding Protein 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinin, E.; Arconzo, M.; Matrella, M.L.; Cariello, M.; Polizzi, A.; Lippi, Y.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Guillou, H.; Loiseau, N.; Villani, G.; et al. Intestinal Pgc1α Ablation Protects from Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis. JHEP Rep. 2023, 5, 100853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhuge, F.; Ni, L.; Nagata, N.; Yamashita, T.; Mukaida, N.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T.; Nagashimada, M. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 Interaction Protects against Lipotoxicity-Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Regulating Macrophage Migration and M1/M2 Status. Metabolism 2022, 136, 155272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Loor, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, B.; Cao, J.; et al. Regulation of Cholesterol Metabolism during High Fatty Acid–Induced Lipid Deposition in Calf Hepatocytes. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 5835–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Pottekat, A.; Duffey, A.; Jang, I.; Chang, B.H.; Cho, J.; Finck, B.N.; Davidson, N.O.; Kaufman, R.J. Conditional Hepatocyte Ablation of PDIA1 Uncovers Indispensable Roles in Both APOB and MTTP Folding to Support VLDL Secretion. Mol. Metab. 2024, 80, 101874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Feng, T.; Tao, W.; Sun, H.; Wen, H.; Lu, X.; Zhu, Q.; et al. Cytoplasmic SIRT6-Mediated ACSL5 Deacetylation Impedes Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Facilitating Hepatic Fatty Acid Oxidation. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 4099–4115.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Xu, B.; Liu, L.; Wu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ghanbarpour, A.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.-J.; Lyu, J.; Hu, Y.; et al. TMEM41B Acts as an ER Scramblase Required for Lipoprotein Biogenesis and Lipid Homeostasis. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1655–1670.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strøm, T.B.; Asprusten, E.; Laerdahl, J.K.; Øygard, I.; Hussain, M.M.; Bogsrud, M.P.; Leren, T.P. Missense Mutation Q384K in the APOB Gene Affecting the Large Lipid Transfer Module of ApoB Reduces the Secretion of ApoB-100 in the Liver without Reducing the Secretion of ApoB-48 in the Intestine. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2023, 17, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jadhav, K.; Pan, X.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, S.; Chen, L.; Tang, Y.; Wang, H.H.; et al. Hepatocyte ATF3 Protects against Atherosclerosis by Regulating HDL and Bile Acid Metabolism. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 59–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, H.; Ding, W.; Yu, X.; Hou, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, X. Adipokines Regulate the Development and Progression of MASLD through Organellar Oxidative Stress. Hepatol. Commun. 2025, 9, e0639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Zhuang, Q.; Ye, X.; Ning, M.; Wu, S.; Lu, L.; Wan, X. Adiponectin Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis via AMPK-JNK/ErK1/2-NFκB/ROS Signaling Pathways. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 546445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Xu, A.; Tam, P.K.H.; Lam, K.S.L.; Huang, B.; Liang, Y.; Lee, I.-K.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y. Upregulation of UCP2 by Adiponectin: The Involvement of Mitochondrial Superoxide and HnRNP K. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ganini, D.; Tokar, E.J.; Kumar, A.; Das, S.; Corbett, J.; Kadiiska, M.B.; Waalkes, M.P.; Diehl, A.M.; Mason, R.P. Leptin Is Key to Peroxynitrite-Mediated Oxidative Stress and Kupffer Cell Activation in Experimental Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, M.D.L.; Gao, J.; Yang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Gromada, J. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Regulates Energy Metabolism by Activating the AMPK–SIRT1–PGC-1α Pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12553–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Bai, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zou, D.; Qu, S.; Tian, G.; Song, L.; Zhang, T.; et al. Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF21) Protects Mouse Liver against d-Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress and Apoptosis via Activating Nrf2 and PI3K/Akt Pathways. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 403, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Mu, D.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Song, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xia, M. Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Induces Hepatic Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Promotes Hepatic Steatosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4338–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.-M.; Ying, H.-Z.; Zhang, H.-H.; Qiu, F.-S.; Wu, J.-Q.; Yu, C.-H. Exosomal RBP4 Potentiated Hepatic Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in High-Fat-Diet-Fed Mice by Promoting M1 Polarization of Kupffer Cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 195, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-J.; Kim, D.-I.; Choi, J.-H.; Heo, Y.-R.; Park, S.-H. New Role of Irisin in Hepatocytes: The Protective Effect of Hepatic Steatosis in Vitro. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batirel, S.; Bozaykut, P.; Mutlu Altundag, E.; Kartal Ozer, N.; Mantzoros, C.S. The Effect of Irisin on Antioxidant System in Liver. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 75, S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, R.; Feder, S.; Haberl, E.M.; Rein-Fischboeck, L.; Weiss, T.S.; Spirk, M.; Bruckmann, A.; McMullen, N.; Sinal, C.J.; Buechler, C. Chemerin Overexpression in the Liver Protects against Inflammation in Experimental Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, A.; Wada, J.; Iseda, I.; Teshigawara, S.; Higashio, K.; Murakami, K.; Kanzaki, M.; Inoue, K.; Terami, T.; Katayama, A.; et al. Vaspin Is an Adipokine Ameliorating ER Stress in Obesity as a Ligand for Cell-Surface GRP78/MTJ-1 Complex. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, H.; Adhikari, B.K.; Wang, S.; Yang, N.; Liu, W.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. The Role of Apelin–APJ System in Diabetes and Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 820002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, W.; Xin, Y. Serum Resistin Levels in Adult Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2021, 9, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.J.; Choi, S.-E.; Jeon, J.Y.; Han, S.J.; Kim, D.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, H.J. Visfatin Induces Inflammation and Insulin Resistance via the NF-κB and STAT3 Signaling Pathways in Hepatocytes. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 4021623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Garza, R.G.; Morales-Garza, L.A.; Martin-Estal, I.; Castilla-Cortazar, I. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Deficiency and Cirrhosis Establishment. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Kang, S.; Lee, A.-R.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.E.; Kim, H.R. Stachydrine Derived from Fermented Rice Prevents Diet-Induced Obesity by Regulating Adipsin and Endoplasmic Reticulum Homeostasis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 107, 109036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, N.; Wang, J.; Di, Z.; Liu, Z.; Jia, X.; Yan, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Qian, Y. The Effects of Intelectin-1 on Antioxidant and Angiogenesis in HUVECs Exposed to Oxygen Glucose Deprivation. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuratovskaia, D.; Komar, A.; Vulf, M.; Quang, H.V.; Shunkin, E.; Volkova, L.; Gazatova, N.; Zatolokin, P.; Litvinova, L. IL-6 Reduces Mitochondrial Replication, and IL-6 Receptors Reduce Chronic Inflammation in NAFLD and Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Viswanathan, S.; Adami, E.; Singh, B.K.; Chothani, S.P.; Ng, B.; Lim, W.W.; Zhou, J.; Tripathi, M.; Ko, N.S.J.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific IL11 Cis-Signaling Drives Lipotoxicity and Underlies the Transition from NAFLD to NASH. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Han, S.; Jin, K.; Yu, T.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, G. SOCS2 Suppresses Inflammation and Apoptosis during NASH Progression through Limiting NF-ΚB Activation in Macrophages. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4165–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zou, X.; Shi, W.; Gao, J.; Yang, C.; Ge, Y.; Xu, Z.; Bi, S.; Zhong, X. Metallothionein 1B Attenuates Inflammation and Hepatic Steatosis in MASH by Inhibiting the AKT/PI3K Pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2024, 66, 100701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, Y.; An, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. STING-Mediated Inflammation in Kupffer Cells Contributes to Progression of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 129, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fuda, H.; Tsukui, T.; Wu, X.; Shen, N.; Saito, N.; Chiba, H.; Hui, S.-P. Oxidative Stress Linked Organ Lipid Hydroperoxidation and Dysregulation in Mouse Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Revealed by Lipidomic Profiling of Liver and Kidney. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauchbach, E.; Zeigerman, H.; Abu-Halaka, D.; Tirosh, O. Cholesterol Induces Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Damage and Death in Hepatic Stellate Cells to Mitigate Liver Fibrosis in Mice Model of NASH. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Pozada, E.E.; Ramos-Tovar, E.; Rodriguez-Callejas, J.D.; Cardoso-Lezama, I.; Galindo-Gómez, S.; Talamás-Lara, D.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Arellanes-Robledo, J.; Tsutsumi, V.; Villa-Treviño, S.; et al. Caffeine Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by Downregulating TLR4/MAPK/NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway in an Experimental NASH Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, G.; Becerril, S.; Valentí, V.; Moncada, R.; Catalán, V.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Colina, I.; Silva, C.; Escalada, J.; Frühbeck, G.; et al. FNDC4 Reduces Hepatocyte Inflammatory Cell Death via AMPKα in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 2221–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.; Fang, S.; Kim, W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.-W. GPx7 Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Regulating Oxidative Stress. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Dou, Z.; Li, N.; Suo, Y.; Ma, Y.; Sun, M.; Tian, Z.; Xu, L. Chemerin/CMKLR1 Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Promoting Autophagy and Alleviating Oxidative Stress through the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway. Peptides 2021, 135, 170422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmerie, A.; Martens, L.; Thoné, T.; Castoldi, A.; Seurinck, R.; Pavie, B.; Roels, J.; Vanneste, B.; De Prijck, S.; Vanhockerhout, M.; et al. Osteopontin Expression Identifies a Subset of Recruited Macrophages Distinct from Kupffer Cells in the Fatty Liver. Immunity 2020, 53, 641–657.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidman, J.S.; Troutman, T.D.; Sakai, M.; Gola, A.; Spann, N.J.; Bennett, H.; Bruni, C.M.; Ouyang, Z.; Li, R.Z.; Sun, X.; et al. Niche-Specific Reprogramming of Epigenetic Landscapes Drives Myeloid Cell Diversity in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Immunity 2020, 52, 1057–1074.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.; Baba, I.; Poupel, L.; Dussaud, S.; Moreau, M.; Gélineau, A.; Marcelin, G.; Magréau-Davy, E.; Ouhachi, M.; Lesnik, P.; et al. Impaired Kupffer Cell Self-Renewal Alters the Liver Response to Lipid Overload during Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Immunity 2020, 53, 627–640.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Qu, X.; Yang, T.; Sheng, M.; Bian, X.; Zhan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. The Foxo1-YAP-Notch1 Axis Reprograms STING-Mediated Innate Immunity in NASH Progression. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Kwon, H.; Han, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Ma, W.; Dash, S.; Gandhi, C.R.; Wu, T. Yes-Associated Protein in Kupffer Cells Enhances the Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines and Promotes the Development of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajaz, S.; McPhail, M.J.; Gnudi, L.; Trovato, F.M.; Mujib, S.; Napoli, S.; Carey, I.; Agarwal, K. Mitochondrial Dysfunction as a Mechanistic Biomarker in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Mitochondrion 2021, 57, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.P.; Cunningham, R.P.; Meers, G.M.; Johnson, S.A.; Wheeler, A.A.; Ganga, R.R.; Spencer, N.M.; Pitt, J.B.; Diaz-Arias, A.; Swi, A.I.A.; et al. Compromised Hepatic Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation and Reduced Markers of Mitochondrial Turnover in Human NAFLD. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1452–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frietze, K.K.; Brown, A.M.; Das, D.; Franks, R.G.; Cunningham, J.L.; Hayward, M.; Nickels, J.T. Lipotoxicity Reduces DDX58/Rig-1 Expression and Activity Leading to Impaired Autophagy and Cell Death. Autophagy 2022, 18, 142–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Teker, S.; Cunza, N.L.; Theusch, E.; Yang, N.; Venkatesan, L.; Su, J.; Krauss, R.M.; Lakkaraju, A.; Mattis, A.N.; et al. Loss of TMEM55B Modulates Lipid Metabolism through Dysregulated Lipophagy and Mitochondrial Function. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, J.; Ngo, J.; Wang, S.-P.; Williams, K.; Kramer, H.F.; Ho, G.; Rodriguez, C.; Yekkala, K.; Amuzie, C.; Bialecki, R.; et al. The Mitochondrial Fission Protein Drp1 in Liver Is Required to Mitigate NASH and Prevents the Activation of the Mitochondrial ISR. Mol. Metab. 2022, 64, 101566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Murata, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Anders, R.; Rosenberg, A.Z.; Kaplan, J.; Hamilton, J.P.; Aghajan, M.; Levi, M.; Wang, N.-Y.; et al. Prevention and Regression of Megamitochondria and Steatosis by Blocking Mitochondrial Fusion in the Liver. iScience 2022, 25, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Huang, F.; Chen, B.; Kang, J.; Yao, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T.; Peng, D.; et al. A Classical Herbal Formula Alleviates High-Fat Diet Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) via Targeting Mitophagy to Rehabilitate Dysfunctional Mitochondria, Validated by UPLC-HRMS Identification Combined with in Vivo Experiment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Wang, K.; Jiang, H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, L.; Fan, X.; Zou, Q.; Yu, J.; Dong, H.; Cheng, S.; et al. AGK Regulates the Progression to NASH by Affecting Mitochondria Complex I Function. Theranostics 2022, 12, 3237–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyman, M.; Babin-Ebell, A.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, R.; Rigon, M.; Aguilar-Recarte, D.; Villarroya, J.; Planavila, A.; Villarroya, F.; Palomer, X.; Barroso, E.; et al. SIRT1 Regulates Hepatic Vldlr Levels. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Chen, P.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; et al. Phocaeicola vulgatus Alleviates Diet-Induced Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Progression by Downregulating Histone Acetylation Level via 3-HPAA. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2309683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Saha, P.; Bose, D.; Trivedi, A.; More, M.; Xiao, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Chatterjee, S. Hepatic NLRP3-Derived Hsp70 Binding to TLR4 Mediates MASLD to MASH Progression upon Inhibition of PP2A by Harmful Algal Bloom Toxin Microcystin, a Second Hit. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhu, M.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Oleic Acid Ameliorates Palmitic Acid Induced Hepatocellular Lipotoxicity by Inhibition of ER Stress and Pyroptosis. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochumon, S.; Malik, M.Z.; Sindhu, S.; Arefanian, H.; Jacob, T.; Bahman, F.; Nizam, R.; Hasan, A.; Thomas, R.; Al-Rashed, F.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis Shaped by Cocoa Butter-Based Sucrose-Free HFD Leads to Steatohepatitis, and Insulin Resistance in Mice. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xie, Z.; Yu, H.; Du, H.; Wang, X.; Cai, J.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, R.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Z.; et al. TLR2 Inhibition Ameliorates the Amplification Effect of LPS on Lipid Accumulation and Lipotoxicity in Hepatic Cells. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didenko, V.I.; Klenina, I.A.; Tatarchuk, O.M.; Hrabovska, O.I.; Petishko, O.P. Specificities of Lipotoxicity of Free Fatty Acids and Cytokine Profile in Patients with Chronic Diffuse Liver Diseases. Regul. Mech. Biosyst. 2021, 13, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qi, M.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W. Ghrelin Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Induced by Chronic Low-grade Inflammation via Blockade of Kupffer Cell M1 Polarization. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 5121–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, F.; Wu, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y. Suppression of STK39 Weakens the MASLD/MASH Process by Protecting the Intestinal Barrier. Biosci. Trends 2024, 18, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Mitra, P.; Lahiri, A.; Das, T.; Sarkar, J.; Paul, S.; Chakrabarti, P. Butyrate Limits Inflammatory Macrophage Niche in NASH. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgesson, S.; Tarai, S.; Langner, T.; Ahlström, H.; Johansson, L.; Kullberg, J.; Lundström, E. Spleen Volume Is Independently Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Liver Volume and Liver Fibrosis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutaiba, N.; Chung, W.; Goodwin, M.; Testro, A.; Egan, G.; Lim, R. The Impact of Hepatic and Splenic Volumetric Assessment in Imaging for Chronic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Insights Imaging 2024, 15, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wan, D.; Zhu, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, X.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Shang, Q.; Zhang, C.; et al. CD11b + CD43 Hi Ly6C Lo Splenocyte-Derived Macrophages Exacerbate Liver Fibrosis via Spleen-Liver Axis. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, D.J.; Liu, L.; Mamrosh, J.L.; Xie, J.; Ferbas, J.; Lomenick, B.; Ladinsky, M.S.; Verma, R.; Rulifson, I.C.; Deshaies, R.J. The Fatty Liver Disease–Causing Protein PNPLA3-I148M Alters Lipid Droplet–Golgi Dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2318619121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Tussy, P.; Cardelo, M.P.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J.; Price, N.L.; Boutagy, N.E.; Goedeke, L.; Cadena-Sandoval, M.; Xirouchaki, C.E.; Brown, W.; et al. MiR-33 Deletion in Hepatocytes Attenuates MASLD-MASH-HCC Progression. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e168476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theys, C.; Ibrahim, J.; Mateiu, L.; Mposhi, A.; García-Pupo, L.; De Pooter, T.; De Rijk, P.; Strazisar, M.; İnce, İ.A.; Vintea, I.; et al. Mitochondrial GpC and CpG DNA Hypermethylation Cause Metabolic Stress-Induced Mitophagy and Cholestophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Wong, V.W.; Anstee, Q.M.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Trauner, M.H.; Harrison, S.A.; Lawitz, E.J.; Okanoue, T.; Camargo, M.; Kersey, K.; et al. Fatigue and Pruritus in Patients with Advanced Fibrosis Due to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: The Impact on Patient-Reported Outcomes. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1637–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Myers, R.P.; Younossi, I.; Henry, L. The Potential Role of Fatigue in Identifying Patients with NASH and Advanced Fibrosis Who Experience Disease Progression. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 21, 970–977.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Flores-García, N.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Chalasani, N.P. Occult Liver Disease: A Multinational Perspective. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 29, 101480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doward, L.C.; Balp, M.-M.; Twiss, J.; Slota, C.; Cryer, D.; Brass, C.A.; Anstee, Q.M.; Sanyal, A.J. Development of a Patient-Reported Outcome Measure for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH-CHECK): Results of a Qualitative Study. Patient 2020, 14, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, S.; Das, S.; Samajdar, S.S.; Joshi, S.R. Role of Semaglutide in the Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease or Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2023, 17, 102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Paik, J.M.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Y.; Henry, L.; Nader, F. The Impact of Fatigue on Mortality of Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Data from National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2005–2010 and 2017–2018. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2646–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.A.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, H.Y. Evolution of Characteristics of MASLD with and without Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Placebo Arms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, X.; Ge, A.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Zeng, L.; Ge, J. Efficacy and Safety of Dietary Polyphenol Supplementation in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 949746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, G.; Peng, X.; Li, X.; An, K.; He, H.; Fu, X.; Li, S.; An, Z. Unmasking the Enigma of Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Mechanism to the Clinic. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1294267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, H.M.; Ain, H.B.U.; Tufail, T.; Hanif, A.; Malik, T. Impact of Silymarin-supplemented Cookies on Liver Enzyme and Inflammatory Markers in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 7273–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the Clinical Assessment and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besutti, G.; Valenti, L.; Ligabue, G.; Bassi, M.C.; Pattacini, P.; Guaraldi, G.; Rossi, P.G. Accuracy of Imaging Methods for Steatohepatitis Diagnosis in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: A Systematic Review. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1521–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arzehgar, A.; Nia, R.G.N.N.; Dehdeleh, V.; Roudi, F.; Eslami, S. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Diagnosis with Multi-Group Factors. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2023, 305, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjærgaard, K.; Mikkelsen, A.C.D.; Landau, A.M.; Eriksen, P.L.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Magnusson, N.E.; Thomsen, M.B.; Chen, F.; Vilstrup, H.; Mookerjee, R.P.; et al. Cognitive Dysfunction in Early Experimental Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease Is Associated with Systemic Inflammation and Neuroinflammation. JHEP Rep. 2023, 6, 100992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerome, N.E.; Edwards, N.E.; Ding, Q. Impact of Mediterranean Dietary Education on Symptoms for Adults at Risk for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2023, 46, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Garibay, V.M.; Chavez-Tapia, N.C. The Rationale for the Aggressive Progression of MASLD in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Ann. Hepatol. 2025, 30, 101778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salva-Pastor, N.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Uribe, M.; Nuño-Lámbarri, N. The Diagnostic and Initial Approach of the Patient with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Role of the Primary Care Provider. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2019, 12, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nadolsky, K.; Cryer, D.R.; Articolo, A.; Fisher, T.; Schneider, J.; Rinella, M. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Diagnosis and Treatment from the Perspective of Patients and Primary Care Physicians: A Cross-Sectional Survey. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2211349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaró, C.M.; Bouzas, C.; Montemayor, S.; Casares, M.; Gómez, C.; Ugarriza, L.; Borràs, P.-A.; Martínez, J.A.; Tur, J.A. Association between Stages of Hepatic Steatosis and Physical Activity Performance in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Analysis in FLIPAN Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Sasso, M.; Deeks, J.J.; Paredes, A.; Boursier, J.; Chan, W.-K.; Yilmaz, Y.; Czernichow, S.; Zheng, M.-H.; Wong, V.W.-S.; et al. FibroScan-AST (FAST) Score for the Non-Invasive Identification of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis with Significant Activity and Fibrosis: A Prospective Derivation and Global Validation Study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armandi, A.; Bugianesi, E. Extrahepatic Outcomes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Liver Dis. 2023, 27, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarus, J.V.; Alazawi, W.; Basuroy, R.; Castera, L.; Estulin, D.; Koulla, Y.; Prasad, P.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Takahashi, H.; Wong, V.W.-S.; et al. A Social Media Listening Study of Patients’ Experiences Relating to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: The LISTEN-MASLD Study. Ann. Hepatol. 2024, 30, 101741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, A.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.R.; Samadi, M.; Qorbani, M.; Merat, S.; Adibi, H.; Poustchi, H.; Hekmatdoost, A. Effects of Supplementation with Main Coffee Components Including Caffeine and/or Chlorogenic Acid on Hepatic, Metabolic, and Inflammatory Indices in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannotti, L.; Stanca, E.; Di Chiara Stanca, B.; Spedicato, F.; Massaro, M.; Quarta, S.; Del Rio, D.; Mena, P.; Siculella, L.; Damiano, F. Coffee Bioactive N-Methylpyridinium: Unveiling Its Antilipogenic Effects by Targeting De Novo Lipogenesis in Human Hepatocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2400338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, U.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Okut, H.; Afroz, S.; Tasleem, S.; Haris, A. The Effect of Coffee Consumption on the Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis: A Meta-Analysis of 11 Epidemiological Studies. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 100254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, T.L.; Hagemann, C.A.; Wei, C.; Kazankov, K.; Thomsen, K.L.; Knop, F.K.; Grønbæk, H. Bariatric Surgery in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease—From Pathophysiology to Clinical Effects. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassailly, G.; Caiazzo, R.; Ntandja-Wandji, L.-C.; Gnemmi, V.; Baud, G.; Verkindt, H.; Ningarhari, M.; Louvet, A.; Leteurtre, E.; Raverdy, V.; et al. Bariatric Surgery Provides Long-Term Resolution of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Regression of Fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 1290–1301.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, R.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Bedossa, P.; Ponnaiah, M.; Oppert, J.; Siksik, J.; Genser, L.; Charlotte, F.; Thabut, D.; Clement, K.; et al. Persistence of Severe Liver Fibrosis despite Substantial Weight Loss with Bariatric Surgery. Hepatology 2022, 76, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornia Matavelli, C.; Echeverria, L.S.; Pereira, L.M.; Chrispim, I.; Mounzer, D.L.S.; Chaim, F.D.M.; Chaim, E.A.; Utrini, M.P.; Gestic, M.A.; Callejas-Neto, F.; et al. Short-Term Evolution of MASLD Following Roux-En-Y Gastric Bypass: A Focus on Fibrotic MASH. Obes. Surg. 2025, 35, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Okanoue, T.; Palle, M.S.; Sejling, A.; Tawfik, M.; Roden, M. Similar Weight Loss with Semaglutide Regardless of Diabetes and Cardiometabolic Risk Parameters in Individuals with Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Post Hoc Analysis of Three Randomised Controlled Trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 27, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, J.; Kim, Y.; Parisé, H.; Bercaw, E.; Smith, Z. Budget Impact of Resmetirom for the Treatment of Adults with Noncirrhotic Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) with Moderate to Advanced Liver Fibrosis (Consistent with Stages F2 to F3 Fibrosis). J. Med. Econ. 2024, 27, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E. A New Treatment and Updated Clinical Practice Guidelines for MASLD. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 22, 88–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Chávez-Tapia, N. Resmetirom, the Long-Awaited First Treatment for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis? Med 2024, 5, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Nogami, A.; Ogawa, Y.; Imajo, K.; Sakai, E.; Nakada, Y.; Koyama, S.; Kurihashi, T.; Oza, N.; et al. Pemafibrate for Treating MASLD Complicated by Hypertriglyceridaemia: A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Controlled Trial Study Protocol. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e088862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Parmar, D.; Sheikh, F.; Sarin, S.K.; Cisneros, L.; Gawrieh, S.; Momin, T.; Duseja, A.; Sanyal, A.J. Saroglitazar, a Dual PPAR α/γ Agonist, Improves Atherogenic Dyslipidemia in Patients with Non-Cirrhotic Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Pooled Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 2597–2605.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, E.; Huh, J.H.; Lee, E.Y.; Bae, J.C.; Chun, S.W.; Yu, S.H.; Kwak, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Lee, B. Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Multicentre, Double-blind, Randomized, Comparative Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 24, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, K.; Koshizaka, M.; Ishibashi, R.; Shoji, M.; Horikoshi, T.; Sakurai, K.; Yokote, K. Effects of the SGLT2 Inhibitor Ipragliflozin and Metformin on Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Fibrosis: Sub-analysis of a Randomized Controlled Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2025, 27, 2056–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guo, X.; Qiao, Q.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on Liver and Pancreatic Fat in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2023, 37, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, D.; Shimizu, S.; Haisa, A.; Yanagisawa, S.; Inoue, K.; Saito, D.; Sumita, T.; Yanagisawa, M.; Uchida, Y.; Inukai, K.; et al. Long-term Effects of Ipragliflozin and Pioglitazone on Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: 5 Year Observational Follow-up of a Randomized, 24 Week, Active-controlled Trial. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Manghi, F.P.; Smith, W.B.; Alpenidze, D.; Aizenberg, D.; Klarenbeek, N.; Chen, C.-Y.; Zuckerman, E.; Ravussin, E.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; et al. Licogliflozin for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2a Study. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, M.; Sasaki, J.; Tanimura-Inagaki, K.; Sakuma, I.; Sugihara, H.; Oikawa, S. Ipragliflozin and Sitagliptin Differentially Affect Lipid and Apolipoprotein Profiles in Type 2 Diabetes: The SUCRE Study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshino, A.; Oshima, M.; Arnott, C.; Fletcher, R.A.; Bakris, G.L.; Jardine, M.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Perkovic, V.; Pollock, C.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; et al. Effects of Canagliflozin on Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Post Hoc Analysis of the CREDENCE Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, A.; Badshah, H.; Shah, Y.; Rehman, I.U.; Khan, K.U.; Ming, L.C.; Cheng, M.H. The Effect of Ertugliflozin in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicine 2024, 103, e40356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Lawitz, E.; Denham, D.; Kayali, Z.; Sheikh, A.; Kowdley, K.V.; Desta, T.; Elkhashab, M.; et al. EDP-305 in Patients with NASH: A Phase II Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Dose-Ranging Study. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternostro, R.; Trauner, M. Current Treatment of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 190–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratziu, V.; Harrison, S.A.; Loustaud-Ratti, V.; Bureau, C.; Lawitz, E.; Abdelmalek, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Francque, S.; Girma, H.; Darteil, R.; et al. Hepatic and Renal Improvements with FXR Agonist Vonafexor in Individuals with Suspected Fibrotic NASH. J. Hepatol. 2022, 78, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; Herring, R.; Kabler, H.; Kayali, Z.; Hassanein, T.; Kohli, A.; Huss, R.S.; Zhu, Y.; Billin, A.N.; Damgaard, L.H.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Combination Therapy with Semaglutide, Cilofexor and Firsocostat in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Randomised, Open-Label Phase II Trial. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhouri, N.; LaCerte, C.; Edwards, J.; Poordad, F.; Lawitz, E.; Lee, L.; Karan, S.; Sawhney, S.; Erickson, M.; MacConell, L.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Obeticholic Acid in Subjects with Fibrosis or Cirrhosis from NASH. Liver Int. 2024, 44, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xin, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhou, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Reduction of Hepatic Fat Content by Dulaglutide for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: A Two-Centre Open, Single-Arm Trial. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2024, 8, e70021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tian, W.; Lin, L.; Xu, X. Liraglutide or Insulin Glargine Treatments Improves Hepatic Fat in Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Twenty-Six Weeks: A Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 170, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Repetto, E.; Guja, C.; Hardy, E.; Han, J.; Jabbour, S.A.; Ferrannini, E. Exenatide and Dapagliflozin Combination Improves Markers of Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 22, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, V.E.R.; Robertson, D.; Erazo-Tapia, E.; Havekes, B.; Phielix, E.; De Ligt, M.; Roumans, K.H.M.; Mevenkamp, J.; Sjoberg, F.; Schrauwen-Hinderling, V.B.; et al. Cotadutide Promotes Glycogenolysis in People with Overweight or Obesity Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 2086–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Xia, M.; Yan, H.; Li, X.; Chang, X. Efficacy of Beinaglutide in the Treatment of Hepatic Steatosis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Open-label, Controlled Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 26, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Sanyal, A.J.; Engebretsen, K.A.; Kliers, I.; Østergaard, L.; Vanni, D.; Bugianesi, E.; Rinella, M.E.; Roden, M.; Ratziu, V. Semaglutide 2.4 mg in Participants with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis: Baseline Characteristics and Design of the Phase 3 ESSENCE Trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Browne, S.K.; Suschak, J.J.; Tomah, S.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Yang, J.; Roberts, M.S.; Harris, M.S. Effect of Pemvidutide, a GLP-1/Glucagon Dual Receptor Agonist, on MASLD: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. J. Hepatol. 2024, 82, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuppalanchi, R.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Nikooie, A.; Tang, Y.; Robins, D.A.; Brouwers, B.; Hartman, M.L. Randomised Clinical Trial: Design of the SYNERGY-NASH Phase 2b Trial to Evaluate Tirzepatide as a Treatment for Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatohepatitis and Modification of Screening Strategy to Reduce Screen Failures. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frias, J.P.; Brouwers, B.; Wu, Q.; Thomas, M.K.; Harris, C.; Schloot, N.C.; Du, Y.; Mather, K.J.; et al. Triple Hormone Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Randomized Phase 2a Trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2037–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawitz, E.J.; Fraessdorf, M.; Neff, G.W.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Noureddin, M.; Alkhouri, N.; Schmid, B.; Andrews, C.P.; Takács, I.; Hussain, S.A.; et al. Efficacy, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of Survodutide, a Glucagon/Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Dual Agonist, in Cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A.; Sanchez, W.; Lawitz, E.; Filozof, C.; Cho, H.; Baek, E.; Choi, J.; Baek, S. A Phase 2, Adaptive Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter, 52-Week Study of HM15211 in Patients with Biopsy-Confirmed Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis—Study Design and Rationale of HM-TRIA-201 Study. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2023, 130, 107176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElKabbany, Z.A.; Ismail, E.A.R.; Hamed, E.T.; Elbarbary, N.S. The Impact of Vildagliptin as an Add-on Therapy on Matrix Metalloproteinase-14 Levels, Liver Stiffness and Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes and Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 5857–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.; Hockings, P.D.; Johnsson, E.; Dronamraju, N.; Maaske, J.; Garcia-Sanchez, R.; Wilding, J.P.H. Dapagliflozin plus Saxagliptin Add-on to Metformin Reduces Liver Fat and Adipose Tissue Volume in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalek, M.F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Nakajima, A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Goodman, Z.D.; Lawitz, E.J.; Harrison, S.A.; Jacobson, I.M.; Imajo, K.; Gunn, N.; et al. Pegbelfermin in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Compensated Cirrhosis (FALCON 2): A Randomized Phase 2B Study. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 22, 113–123.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.L.; Balic, K.; Charlton, R.W.; Margalit, M.; Mansbach, H.; Savic, R.M. Population Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Pegozafermin in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 114, 1323–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Frias, J.P.; Neff, G.; Abrams, G.A.; Lucas, K.J.; Sanchez, W.; Gogia, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Behling, C.; Bedossa, P.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Once-Weekly Efruxifermin versus Placebo in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (HARMONY): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2b Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lieu, H.D.; Kowdley, K.V.; Goodman, Z.D.; Alkhouri, N.; Lawitz, E.; Ratziu, V.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Younes, Z.H.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Aldafermin in Patients with NASH and Compensated Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2023, 79, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athyros, V.G.; Tziomalos, K.; Gossios, T.D.; Griva, T.; Anagnostis, P.; Kargiotis, K.; Pagourelias, E.D.; Theocharidou, E.; Karagiannis, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P. Safety and Efficacy of Long-Term Statin Treatment for Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Abnormal Liver Tests in the Greek Atorvastatin and Coronary Heart Disease Evaluation (GREACE) Study: A Post-Hoc Analysis. Lancet 2010, 376, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lyu, L.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ping, F.; Li, Y. Impact of Rosuvastatin on Metabolic Syndrome Patients with Moderate to Severe Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease without Overt Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2024, 18, 103126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Newby, L.K.; Arnold, S.V.; Bittner, V.; Brewer, L.C.; Demeter, S.H.; Dixon, D.L.; Fearon, W.F.; Hess, B.; Johnson, H.M.; et al. 2023 AHA/ACC/ACCP/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline for the Management of Patients With Chronic Coronary Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2023, 148, E9–E119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liang, E.; Liu, T.; Mao, J. Effect of Metformin on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Based on Meta-Analysis and Network Pharmacology. Medicine 2022, 101, e31437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratziu, V.; De Guevara, L.; Safadi, R.; Poordad, F.; Fuster, F.; Flores-Figueroa, J.; Arrese, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Bashat, D.B.; Lackner, K.; et al. Aramchol in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2b Trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Okanoue, T.; Bzowej, N.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Younes, Z.; Kohli, A.; Sarin, S.; Caldwell, S.H.; Alkhouri, N.; et al. Selonsertib for Patients with Bridging Fibrosis or Compensated Cirrhosis Due to NASH: Results from Randomized Phase III STELLAR Trials. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.R.; Lyle, S.; Khavandi, K.; Qiu, R.; Whitlock, M.; Esler, W.P.; Kim, A.M. A Phase 2a, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Three-arm, Parallel-group Study to Assess the Efficacy, Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacodynamics of PF-06835919 in Patients with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 25, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, S.; Shigiyama, F.; Kumashiro, N. Empagliflozin versus Sitagliptin for Ameliorating Intrahepatic Lipid Content and Tissue-specific Insulin Sensitivity in Patients with Early-stage Type 2 Diabetes with Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Prospective Randomized Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouda, A.; Abdelaziz, A.E.; Hussien, M.; Ali, A.A.; Abdelkawy, K.S.; Elbarbry, F. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Effects of Vitamin E, Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Egyptian Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 7449–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carli, F.; Della Pepa, G.; Sabatini, S.; Vidal Puig, A.; Gastaldelli, A. Lipid Metabolism in MASLD and MASH: From Mechanism to the Clinic. JHEP Rep. 2024, 6, 101185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Ye, J.; Xu, Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y. Updated Mechanisms of MASLD Pathogenesis. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Priority Level | Molecular Mechanism | Key Processes and Players | Relevance to MASLD Progression |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Core Driver) | Dysregulated Lipid Metabolism | Excessive fatty acid uptake (CD36, FATP2), enhanced de novo lipogenesis (SREBP1, FAS), impaired lipid export (MTTP, ApoB) | Central to hepatic steatosis; initiates lipid accumulation, leading to metabolic overload |
| 2 (Core Driver) | Insulin Resistance and Hyperinsulinemia | Reduced AKT phosphorylation, increased SREBP1 activation, impaired glycogen synthesis | Amplifies lipogenesis and reduces lipid oxidation, promoting steatosis and metabolic stress |
| 3 (Core Driver) | Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress | Impaired β-oxidation (PPARα, ACSL5), reduced ATP production, increased ROS, mitophagy defects (BNIP3, p62) | Directly drives hepatocyte injury, apoptosis, and fibrogenesis |
| 4 (Major Amplifier) | Chronic Inflammation | Kupffer cell activation, cytokine release (TNF-α, IL-6, CX3CL1), inflammasome activation (NLRP3) | Links metabolic dysfunction to liver fibrosis; perpetuates hepatocyte injury |
| 5 (Major Amplifier) | Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress | ATF4-VLDLR axis, SIRT1 downregulation, unfolded protein response (UPR) | Exacerbates lipid accumulation and inflammatory signaling |
| 6 (Major Amplifier) | Adipokine Dysregulation | ↓ Adiponectin, FGF21; ↑ Leptin, Resistin, RBP4 | Creates a pro-inflammatory, pro-fibrotic microenvironment in the liver |
| 7 (Important Contributor) | Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis | ↑ Intestinal permeability, ↑ LPS, ↑ TLR4/NF-κB signaling | Triggers hepatic inflammation via gut–liver axis |
| 8 (Modifier of Susceptibility) | Genetic Factors | PNPLA3 I148M, TM6SF2, MBOAT7 | Genetic variants modify lipid handling, inflammation, and fibrosis risk |
| 9 (Modifier of Disease Course) | Epigenetic Modifications | miR-33 (↓ mitochondrial function), hypermethylation of ND6 (mitochondrial DNA) | Shapes disease severity through regulation of lipid metabolism, inflammation, and fibrosis |
| Category | Treatment/Research | Mechanism/Target | Clinical Status/Research Goal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid Hormone Receptor Beta (THR-β) Agonists | Resmetirom (MGL-3196) | Liver-targeted THR-β agonist; reduces hepatic lipid content and fibrosis | Phase III (MAESTRO-NASH); evaluating efficacy in MASH patients with fibrosis |
| VK2809 | THR-β agonist; reduces liver fat content | Phase IIb; assessing efficacy in liver fat reduction | |
| Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) Analogues | Efruxifermin (EFX) | FGF21 analogue; reverses liver fibrosis, improves insulin sensitivity | Phase IIb; showing fibrosis reversal, progressing to Phase III |
| Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists | Semaglutide | GLP-1 receptor agonist; improves liver fibrosis, promotes weight loss | Phase III; demonstrated improvement in fibrosis, seeking regulatory approval |
| Dual GLP-1 and Glucagon Receptor Agonists | Survodutide | Dual GLP-1 and glucagon receptor agonist; targets liver fibrosis and metabolic dysfunction | Phase III; received FDA Breakthrough Therapy designation |
| Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 (SCD1) Inhibitors | Denifanstat | SCD1 inhibitor; reduces hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation | Phase III; evaluating in non-cirrhotic MASH patients |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mejía-Guzmán, J.E.; Belmont-Hernández, R.A.; Chávez-Tapia, N.C.; Uribe, M.; Nuño-Lámbarri, N. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072959
Mejía-Guzmán JE, Belmont-Hernández RA, Chávez-Tapia NC, Uribe M, Nuño-Lámbarri N. Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072959
Chicago/Turabian StyleMejía-Guzmán, Jeysson E., Ramón A. Belmont-Hernández, Norberto C. Chávez-Tapia, Misael Uribe, and Natalia Nuño-Lámbarri. 2025. "Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072959
APA StyleMejía-Guzmán, J. E., Belmont-Hernández, R. A., Chávez-Tapia, N. C., Uribe, M., & Nuño-Lámbarri, N. (2025). Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Emerging Therapeutic Strategies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072959






