Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of hsa_piR_022710, hsa_piR_019822, and hsa_piR_020840 in Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Recurrence and Survival in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Pathological Characteristics of Patients
2.2. Patient Prognostic Predictors
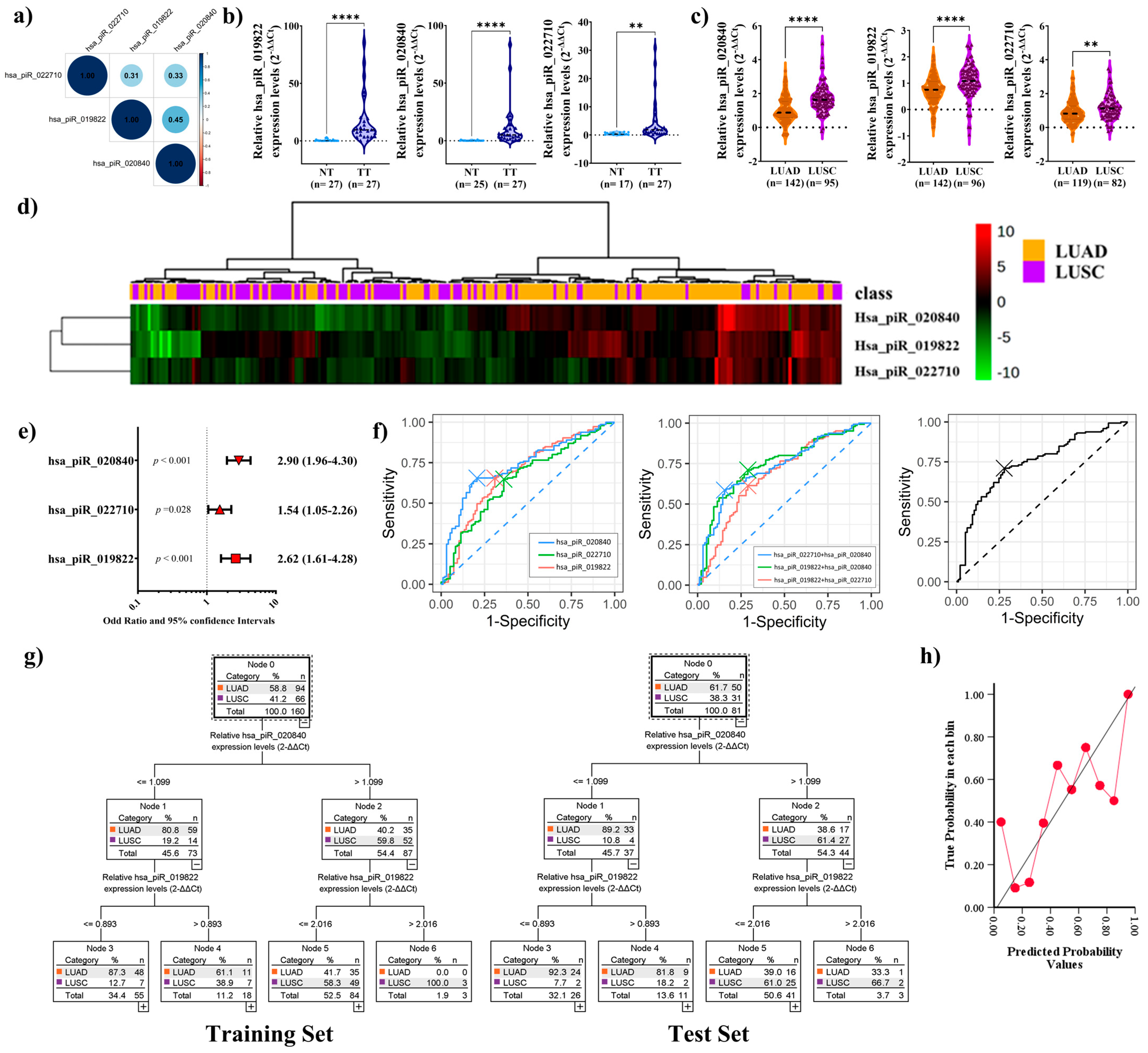
2.3. PiRNAs Expression in Patient Sample
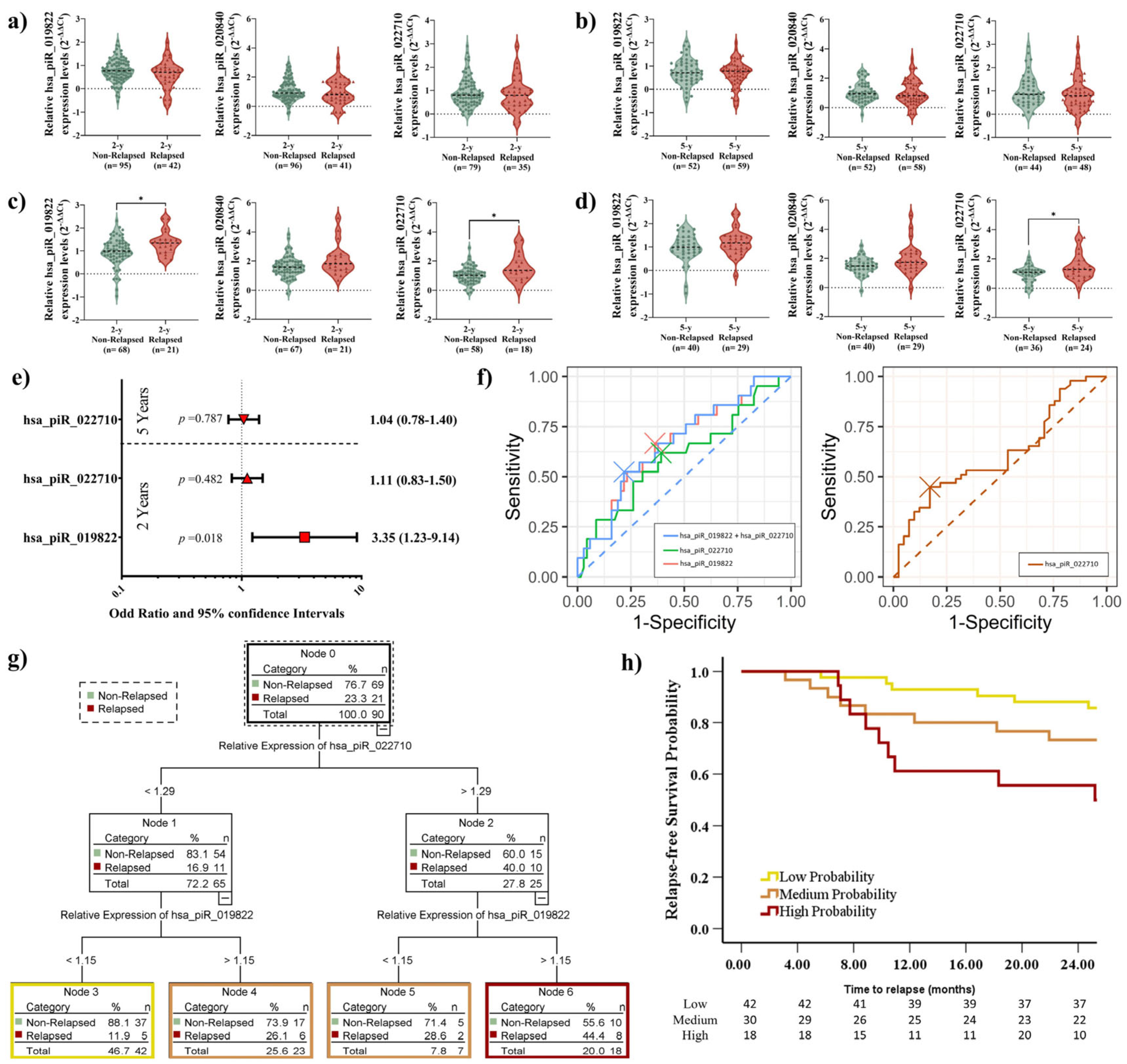
2.4. Elevated piRNA Expression Levels Correlate with Higher Recurrence Risk in LUSC Patients
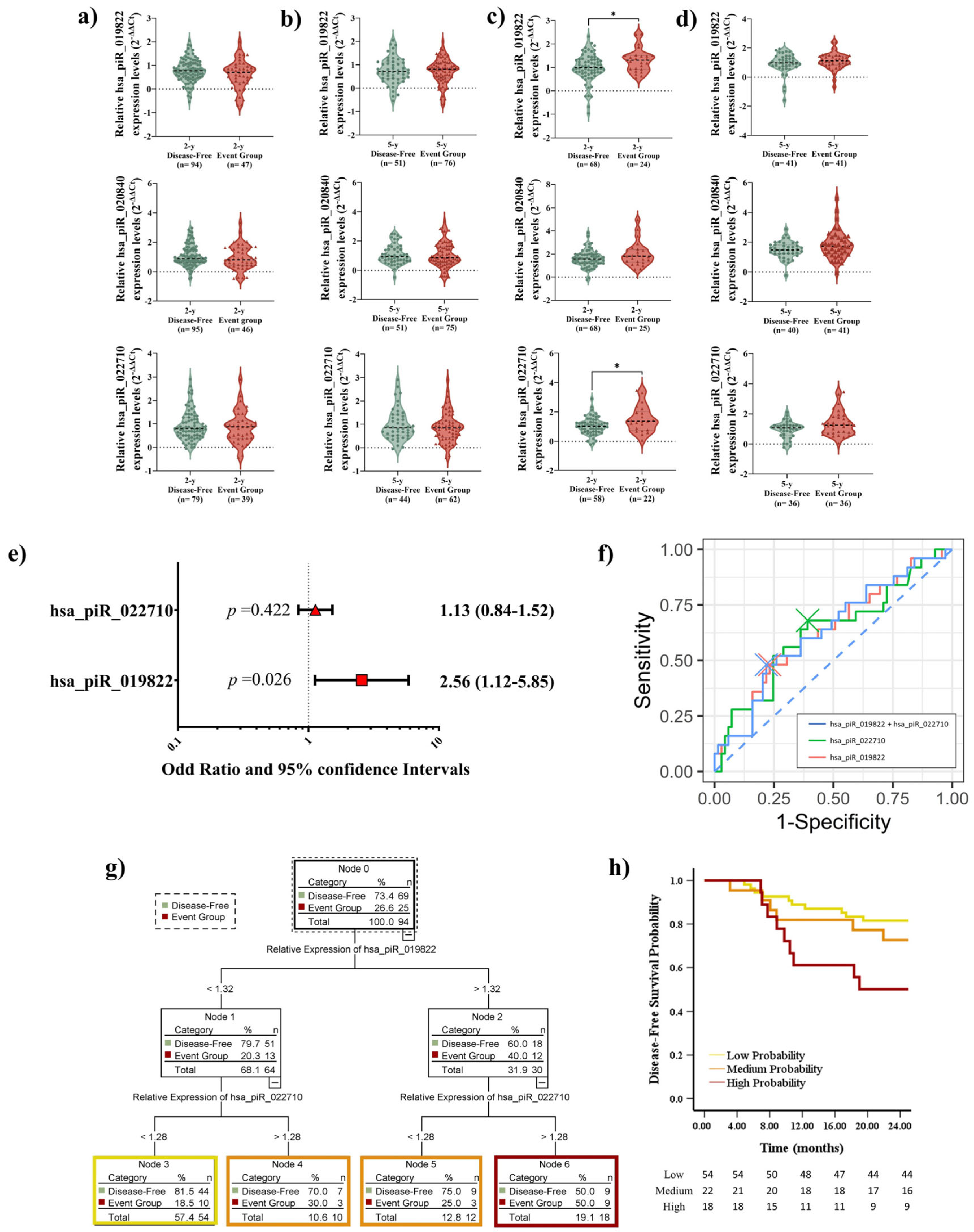
2.5. Elevated piRNA Expression Levels Correlate with Poor DFS in LUSC Patients During Short-Term Follow-Up
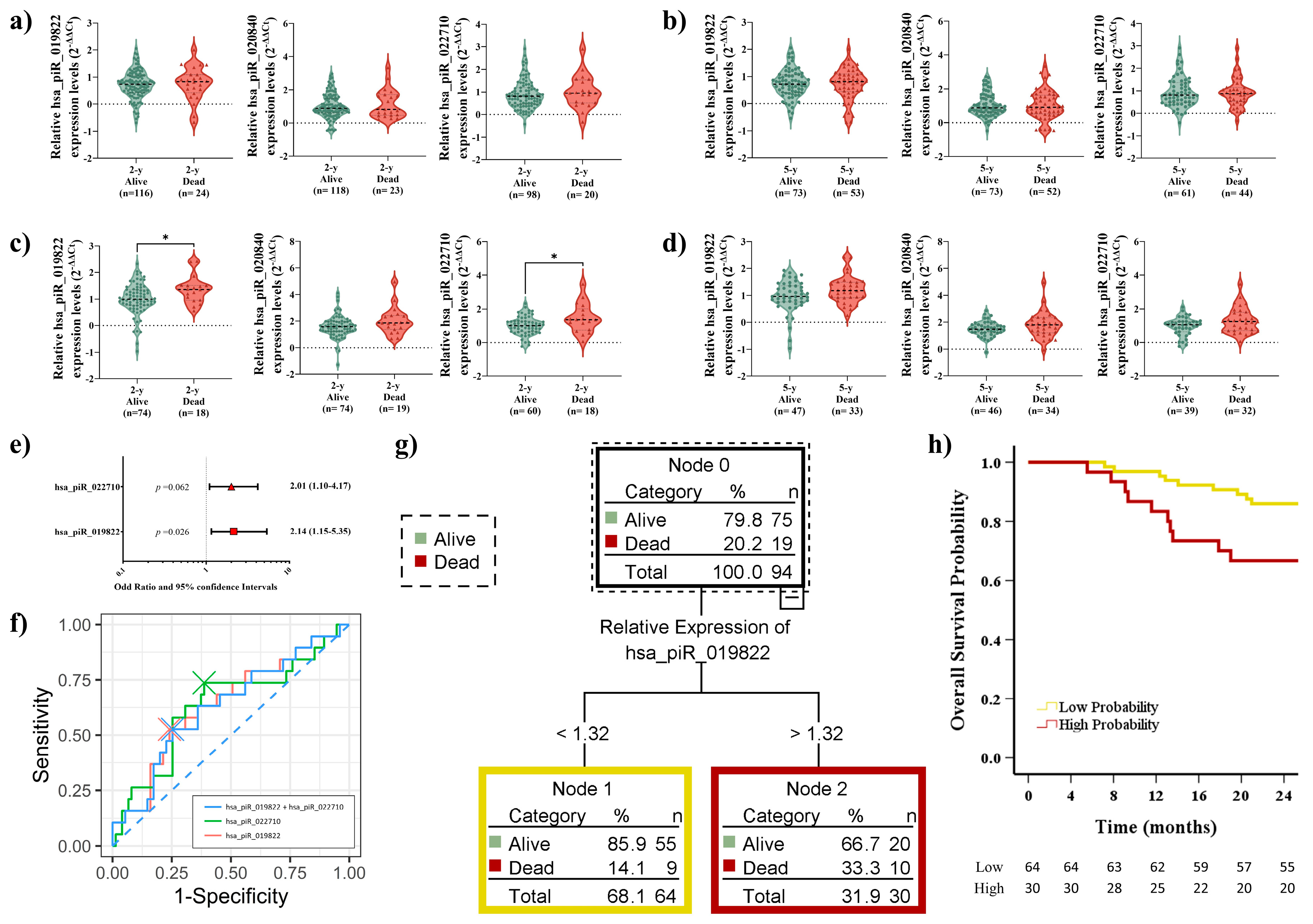
2.6. Elevated piRNA Expression Levels Correlate with Poor OS in LUSC Patients During Short-Term Follow-Up
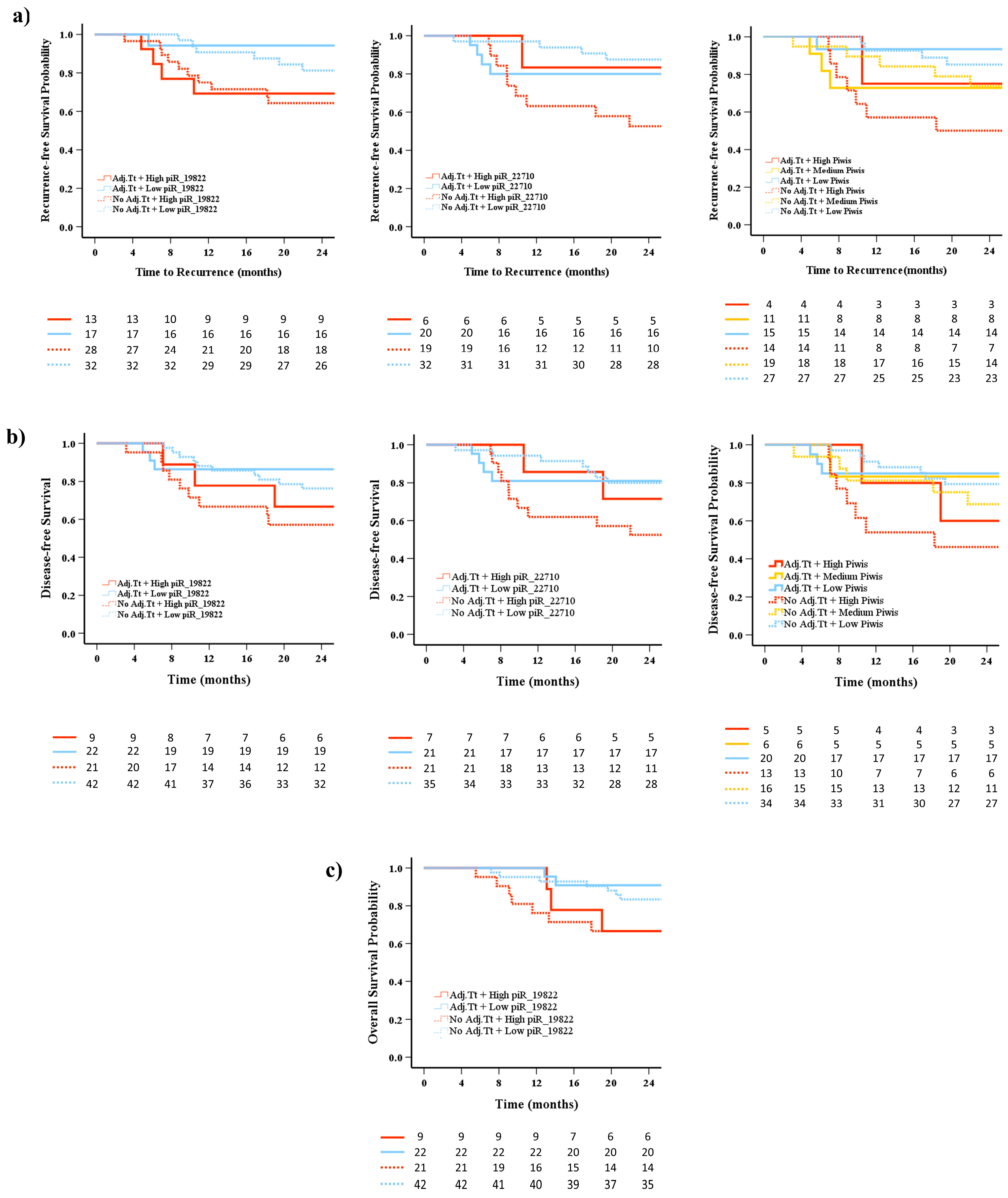
2.7. Prognostic Impact of piRNA Expression Levels on Recurrence, Survival, and the Role of Adjuvant Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Sample
4.2. RNA Extraction and piRNA Quantification
4.3. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| piRNAs | PIWI-interacting RNAs |
| OS | Overall survival |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| LUSC | Lung squamous cell carcinoma |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| LUAD | Lung adenocarcinoma |
| TTR | Time to Relapse |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| RT | Reverse transcription |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar]
- Leiter, A.; Veluswamy, R.R.; Wisnivesky, J.P. The global burden of lung cancer: Current status and future trends. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 624–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yan, B.; He, S. Advances and challenges in the treatment of lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115891. [Google Scholar]
- Osarogiagbon, R.U.; Veronesi, G.; Fang, W.; Ekman, S.; Suda, K.; Aerts, J.G.; Donington, J. Early-stage NSCLC: Advances in thoracic oncology 2018. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 968–978. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Vaccarella, S.; Morgan, E.; Li, M.; Etxeberria, J.; Chokunonga, E.; Manraj, S.S.; Kamate, B.; Omonisi, A.; Bray, F. Global variations in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype in 2020: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 1206–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotow, J.; Bivona, T.G. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 637–658. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, A.; Liu, S.V.; Subramaniam, D.S.; Giaccone, G. Refining the treatment of NSCLC according to histological and molecular subtypes. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 511–526. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Moreno, P.; Brambilla, E.; Thomas, R.; Soria, J.-C. Squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: Molecular subtypes and therapeutic opportunities. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.W.; Dhahbi, J. Lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma cancer classification, biomarker identification, and gene expression analysis using overlapping feature selection methods. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.; Pan, Y.; Velcheti, V.; Wong, K.K. Squamous cell lung cancer: Current landscape and future therapeutic options. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Uramoto, H.; Tanaka, F. Recurrence after surgery in patients with NSCLC. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganti, A.K.; Klein, A.B.; Cotarla, I.; Seal, B.; Chou, E. Update of incidence, prevalence, survival, and initial treatment in patients with non–small cell lung cancer in the US. Jama Oncol. 2021, 7, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Šutić, M.; Vukić, A.; Baranašić, J.; Försti, A.; Džubur, F.; Samaržija, M.; Jakopović, M.; Brčić, L.; Knežević, J. Diagnostic, predictive, and prognostic biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) management. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundage, M.D.; Davies, D.; Mackillop, W.J. Prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer: A decade of progress. Chest 2002, 122, 1037–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.A.; Hubbs, J.L.; Kim, D.W.; Hollis, D.; Marks, L.B.; Kelsey, C.R. Timing of local and distant failure in resected lung cancer: Implications for reported rates of local failure. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 211–214. [Google Scholar]
- Taft, R.J.; Pang, K.C.; Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.; Mattick, J.S. Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. J. Pathol. A J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2010, 220, 126–139. [Google Scholar]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. Non-coding RNAs: Classification, biology and functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Girard, A.; Sachidanandam, R.; Hannon, G.J.; Carmell, M.A. A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 2006, 442, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, W.; Bian, Y.; Gou, A.; Zhang, W.; Fu, K.; Shi, W. Emerging roles of piRNAs in cancer: Challenges and prospects. Aging 2019, 11, 9932. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.; Wan, H.; Zhao, S.; Xu, H.; Tang, T.; Oware, K.A.; Qu, S. Role of PIWI-interacting RNAS on cell survival: Proliferation, apoptosis, and cycle. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weick, E.-M.; Miska, E.A. piRNAs: From biogenesis to function. Development 2014, 141, 3458–3471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olivas, W.M.; Muhlrad, D.; Parker, R. Analysis of the yeast genome: Identification of new non-coding and small ORF-containing RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4619–4625. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Wu, Q.; Sun, C.; Ai, L.; Deng, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Chu, Z.; Tang, B.; Wang, K. piRNA-823 contributes to tumorigenesis by regulating de novo DNA methylation and angiogenesis in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2015, 29, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, A.; Jacobs, D.I.; Hoffman, A.E.; Zheng, T.; Zhu, Y. PIWI-interacting RNA 021285 is involved in breast tumorigenesis possibly by remodeling the cancer epigenome. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1094–1102. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, D.; Ding, P.; Tan, L.; Zhang, J.; Pan, Z.; Bai, R.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, W. PIWI-interacting RNA-54265 is oncogenic and a potential therapeutic target in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5213. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, A.; Tejero, R.; Viñolas, N.; Cordeiro, A.; Marrades, R.M.; Fuster, D.; Caritg, O.; Moises, J.; Muñoz, C.; Molins, L.; et al. The significance of PIWI family expression in human lung embryogenesis and non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31544–31556. [Google Scholar]
- exRNADisease Database. hsa_piR_020840 in exRNA Disease Database. Available online: http://origin-gene.cn/database/exRNAdisease/detail.php?entry_ID=exR0752394 (accessed on 2 November 2024).
- Mei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kumari, P.; Shetty, A.C.; Clark, D.; Gable, T.; MacKerell, A.D.; Ma, M.Z.; Weber, D.J.; Yang, A.J. A piRNA-like small RNA interacts with and modulates p-ERM proteins in human somatic cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7316. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, J.; Mallick, B. Investigating piwi-interacting RNA regulome in human neuroblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2018, 57, 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, R.; Yoshida, J.; Ishii, G.; Hishida, T.; Nishimura, M.; Nagai, K. Prognostic impact of histology on early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Chest 2011, 140, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kris, M.G.; Gaspar, L.E.; Chaft, J.E.; Kennedy, E.B.; Azzoli, C.G.; Ellis, P.M.; Lin, S.H.; Pass, H.I.; Seth, R.; Shepherd, F.A. Adjuvant systemic therapy and adjuvant radiation therapy for stage I to IIIA completely resected non-small-cell lung cancers: American Society of Clinical Oncology/Cancer Care Ontario clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2960–2974. [Google Scholar]
- Consonni, D.; Pierobon, M.; Gail, M.H.; Rubagotti, M.; Rotunno, M.; Goldstein, A.; Goldin, L.; Lubin, J.; Wacholder, S.; Caporaso, N.E. Lung cancer prognosis before and after recurrence in a population-based setting. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodard, G.A.; Jones, K.D.; Jablons, D.M. Lung cancer staging and prognosis. Lung Cancer Treat. Res. 2016, 170, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.K.; Walsh, B.; Timilsina, M.; Torrente, M.; Franco, F.; Provencio, M.; Janik, A.; Costabello, L.; Minervini, P.; Stenetorp, P. On predicting recurrence in early stage non-small cell lung cancer. In Proceedings of the American Medical Informatics Association Annual Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 5–9 November 2022; p. 853. [Google Scholar]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, W.; Miller, V.; Zakowski, M.; Doherty, J.; Politi, K.; Sarkaria, I.; Singh, B.; Heelan, R.; Rusch, V.; Fulton, L. EGF receptor gene mutations are common in lung cancers from “never smokers” and are associated with sensitivity of tumors to gefitinib and erlotinib. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13306–13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardarella, S.; Johnson, B.E. The impact of genomic changes on treatment of lung cancer. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, A.; Maiello, M.R.; D’Alessio, A.; Pergameno, M.; Normanno, N. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications for therapeutic approaches. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, S17–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derman, B.A.; Mileham, K.F.; Bonomi, P.D.; Batus, M.; Fidler, M.J. Treatment of advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: A review. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 524. [Google Scholar]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Stitkovcova, K.; Radova, L.; Sachlova, M.; Kosarova, Z.; Slaba, K.; Kala, Z.; Svoboda, M.; Kiss, I.; Vyzula, R. Circulating PIWI-interacting RNAs piR-5937 and piR-28876 are promising diagnostic biomarkers of colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2018, 27, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Guo, J.-M.; Xiao, B.-X.; Miao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.-N. piRNA, the new non-coding RNA, is aberrantly expressed in human cancer cells. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1621–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relli, V.; Trerotola, M.; Guerra, E.; Alberti, S. Abandoning the notion of non-small cell lung cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinolas, N.; Aya, F.; Navarro, A.; Marrades, R.M.; Cordeiro, A.; Fernandez, A.; Chic, N.; Gimferrer, J.M.; Ramirez, J.; Molins, L. piRNA-651 as a prognostic marker in surgically resected non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 11043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Ichinose, Y.; Ohta, M.; Hata, E.; Tsubota, N.; Tada, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Wada, H.; Tsuboi, M.; Hamajima, N. A randomized trial of adjuvant chemotherapy with uracil–tegafur for adenocarcinoma of the lung. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pignon, J.-P.; Tribodet, H.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Shepherd, F.A.; Stephens, R.J.; Dunant, A.; Torri, V.; Rosell, R.; Seymour, L.; et al. Lung adjuvant cisplatin evaluation: A pooled analysis by the LACE Collaborative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3552–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, S.H.; Chen, W.T.; Chung, C.L.; Chou, Y.T.; Lin, S.E.; Hong, S.Y.; Chang, J.H.; Chang, T.H.; Chien, L.N. Comparative survival analysis of platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the lung. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, R.S.; Song, Y.; Amann, K.J.; Gerbin, S.C.; Pollard, T.D.; Chang, D.D. EPLIN regulates actin dynamics by cross-linking and stabilizing filaments. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, R.S.; Chang, D.D. EPLIN, epithelial protein lost in neoplasm. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7838–7841. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, R.J.; Jiang, W.G.; Hargest, R.; Mason, M.D.; Sanders, A.J. EPLIN: A fundamental actin regulator in cancer metastasis? Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 753–764. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Lü, J.; Zhao, Q.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Z.; Ma, W.; Liu, P.; Pestell, R.G.; Liang, C. piRNA-823 is involved in cancer stem cell regulation through altering DNA methylation in association with luminal breast cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641052. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, Y.; Xu, H.; Pang, D.; Duan, C.; Liu, C. The expression of stem cell protein Piwil2 and piR-932 in breast cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 22, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Camp, R.L.; Dolled-Filhart, M.; Rimm, D.L. X-tile: A new bio-informatics tool for biomarker assessment and outcome-based cut-point optimization. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7252–7259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | Total Patients N = 260 (%) | LUAD Patients N = 145 (%) | LUSC Patients N = 97 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 191 (73.5) | 89 (61.4) | 88 (90.7) |
| Female | 69 (26.5) | 56 (38.6) | 9 (9.3) |
| Age (years), mean (range) | 67 (32–85) | 66 (32–85) | 68 (50–83) |
| ≤65 | 109 (41.9) | 65 (44.8) | 37 (38.1) |
| >65 | 151 (58.1) | 80 (55.2) | 60 (61.9) |
| ECOG PS | |||
| 0 | 65 (25) | 35 (24.1) | 24 (24.79) |
| 1 | 188 (72.3) | 108 (74.5) | 72 (74.2) |
| 2 | 7 (2.7) | 2 (1.4) | 1 (1) |
| Tumor size (pT) | |||
| ≤30 mm | 115 (44.3) | 70 (48.3) | 39 (40) |
| 31–50 mm | 85 (32.7) | 44 (30.3) | 36 (37) |
| 51–70 mm | 43 (16.5) | 22 (15.2) | 19 (20) |
| >70 mm | 17 (6.5) | 9 (6.2) | 3 (3.1) |
| Lymph node status (pN) | |||
| 0 | 190 (73.1) | 109 (75.2) | 68 (70.1) |
| 1 | 52 (20) | 24 (16.6) | 23 (23.7) |
| 2 | 17 (6.5) | 11 (7.6) | 6 (6.2) |
| 3 | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.7) | 0 |
| Lymph node status (pN) | |||
| Negative | 190 (73.1) | 109 (75.2) | 68 (70.1) |
| Positive | 70 (26.9) | 36 (24.8) | 29 (29.9) |
| Stage | |||
| I | 157 (60.4) | 91 (62.8) | 55 (56.7) |
| II | 57 (21.9) | 25 (17.2) | 28 (28.9) |
| III | 46 (17.7) | 29 (20) | 14 (14.4) |
| Histology | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 145 (55.8) | ||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 97 (37.3) | ||
| Others | 18 (6.9) | ||
| Smoking history | |||
| Current smoker | 97 (37.3) | 51 (35.2) | 39 (40.2) |
| Former smoker | 134 (51.6) | 67 (46.2) | 58 (59.8) |
| Non-smoker | 29 (11.2) | 27 (18.6) | 0 |
| Type of surgery | |||
| Lobectomy | 206 (79.2) | 121 (83.4) | 72 (74.2) |
| Pneumonectomy | 17 (6.6) | 7 (4.8) | 9 (9.3) |
| Bilobectomy | 7 (2.7) | 2 (1.4) | 4 (4.1) |
| Atypical resection | 16 (6.2) | 9 (6.2) | 5 (5.2) |
| Typical segmentectomy | 14 (5.4) | 6 (4.1) | 7 (7.2) |
| Adjuvant treatment | |||
| Yes | 79 (30.4) | 42 (29) | 31 (32) |
| No | 181 (69.6) | 103 (71) | 66 (68) |
| Relapse | |||
| Yes | 106 (40.8) | 65 (44.8) | 32 (33) |
| No | 154 (59.2) | 80 (55.2) | 65 (67) |
| Average follow-up time (months) | 58 | 65 | 56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Altuna-Coy, A.; Acosta-Plasencia, M.; Molins, L.; Sánchez-Lorente, D.; Martinez, D.; Díaz, T.; Na, R.; Marrades, R.M.; Navarro, A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of hsa_piR_022710, hsa_piR_019822, and hsa_piR_020840 in Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Recurrence and Survival in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072870
He Y, Altuna-Coy A, Acosta-Plasencia M, Molins L, Sánchez-Lorente D, Martinez D, Díaz T, Na R, Marrades RM, Navarro A. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of hsa_piR_022710, hsa_piR_019822, and hsa_piR_020840 in Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Recurrence and Survival in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072870
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yangyi, Antonio Altuna-Coy, Melissa Acosta-Plasencia, Laureano Molins, David Sánchez-Lorente, Daniel Martinez, Tania Díaz, Risha Na, Ramón M. Marrades, and Alfons Navarro. 2025. "Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of hsa_piR_022710, hsa_piR_019822, and hsa_piR_020840 in Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Recurrence and Survival in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072870
APA StyleHe, Y., Altuna-Coy, A., Acosta-Plasencia, M., Molins, L., Sánchez-Lorente, D., Martinez, D., Díaz, T., Na, R., Marrades, R. M., & Navarro, A. (2025). Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of hsa_piR_022710, hsa_piR_019822, and hsa_piR_020840 in Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Implications for Recurrence and Survival in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2870. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072870








