Universal Prime Editing Therapeutic Strategy for RyR1-Related Myopathies: A Protective Mutation Rescues Leaky RyR1 Channel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
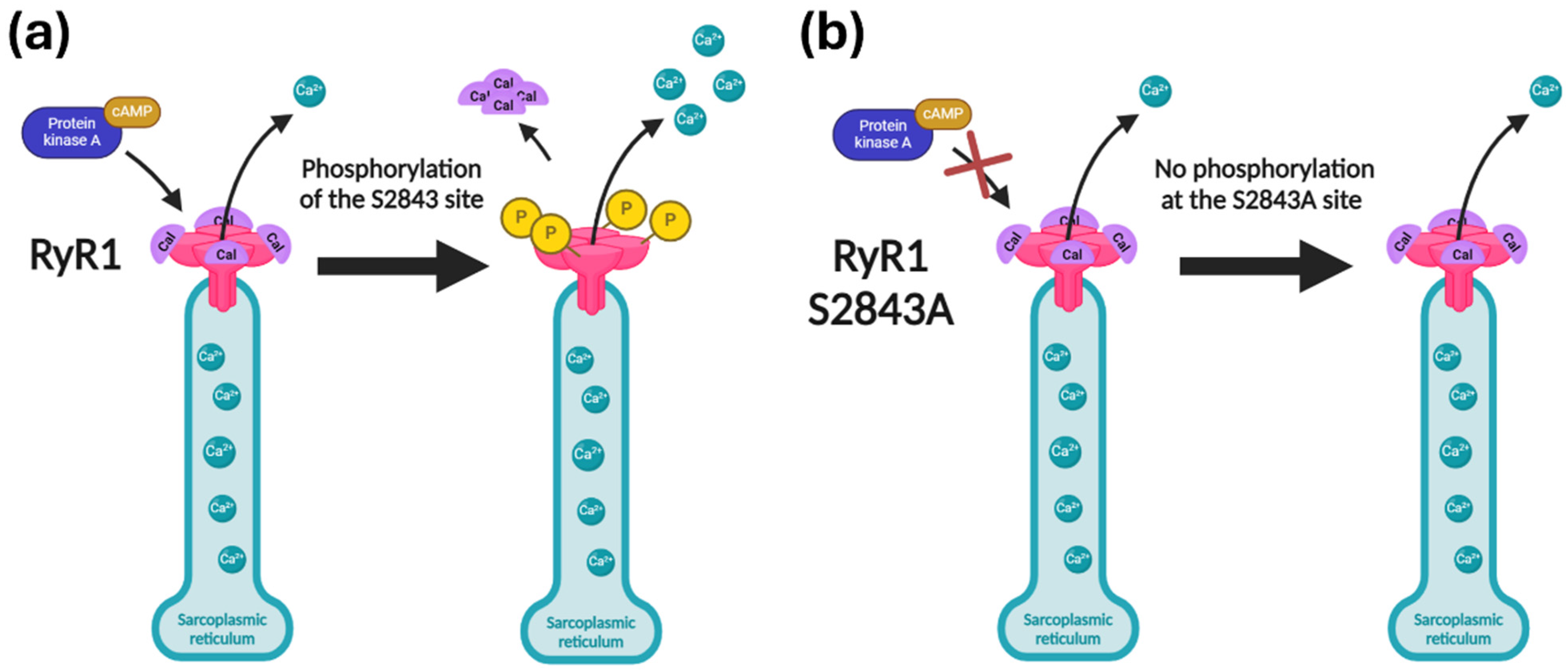
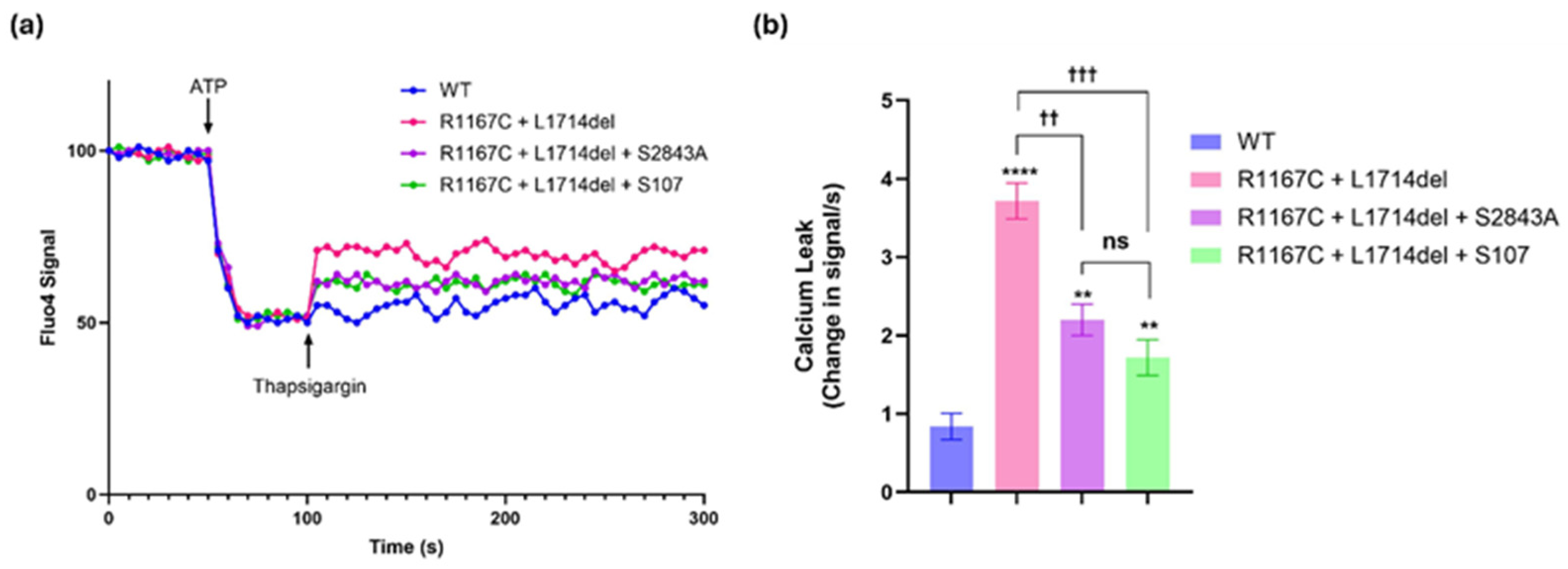
2.1. The S2843A Mutation Rescued the RyR1 Channel Leak Caused by Pathogenic Mutations in the RYR1 Gene
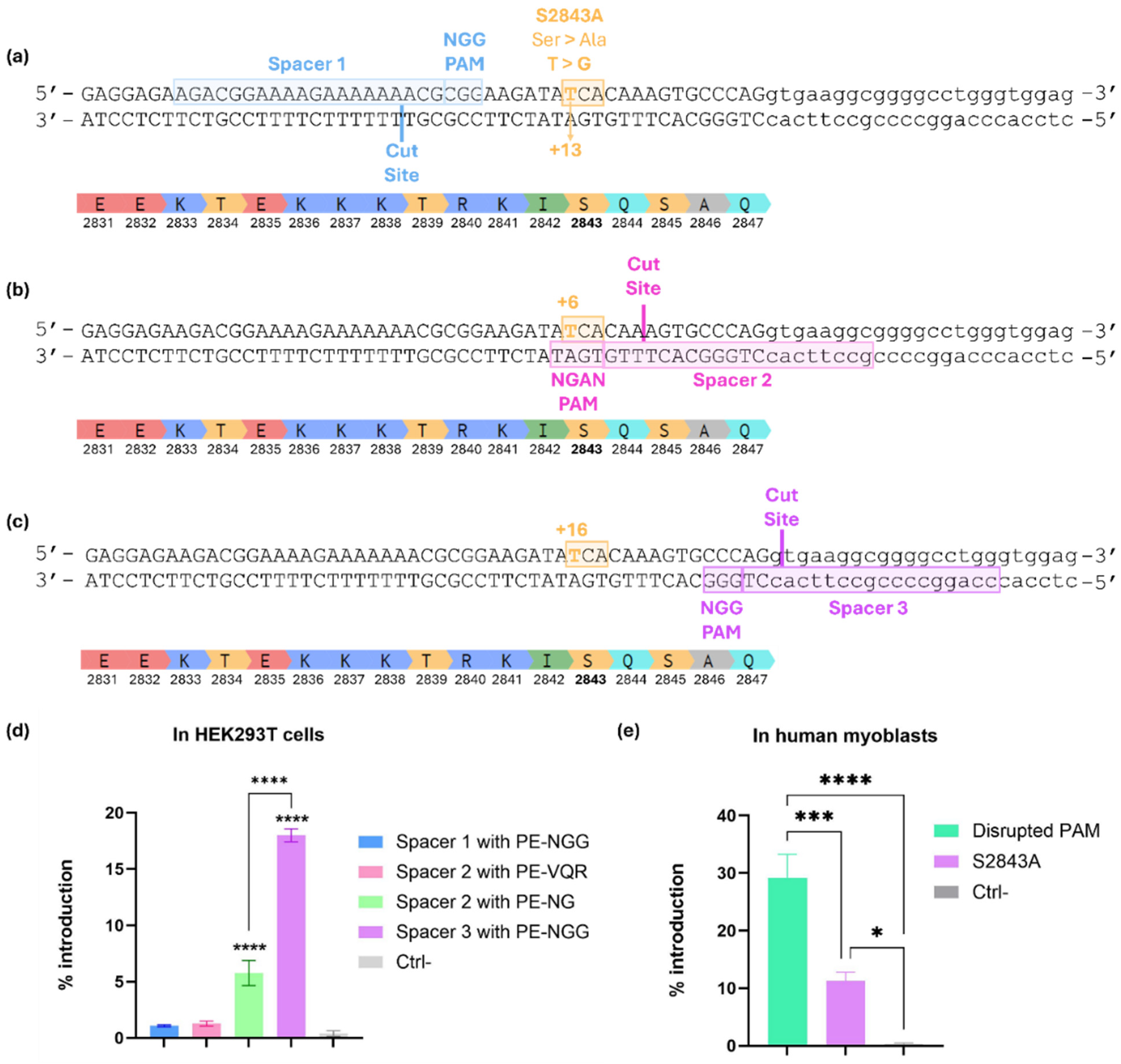
2.2. Prime Editing Design to Introduce the S2843A Mutation into the RYR1 Gene
2.3. Optimization of the epegRNA by Adding Silent Mutations Between the PAM and the +16 Position of the RTT
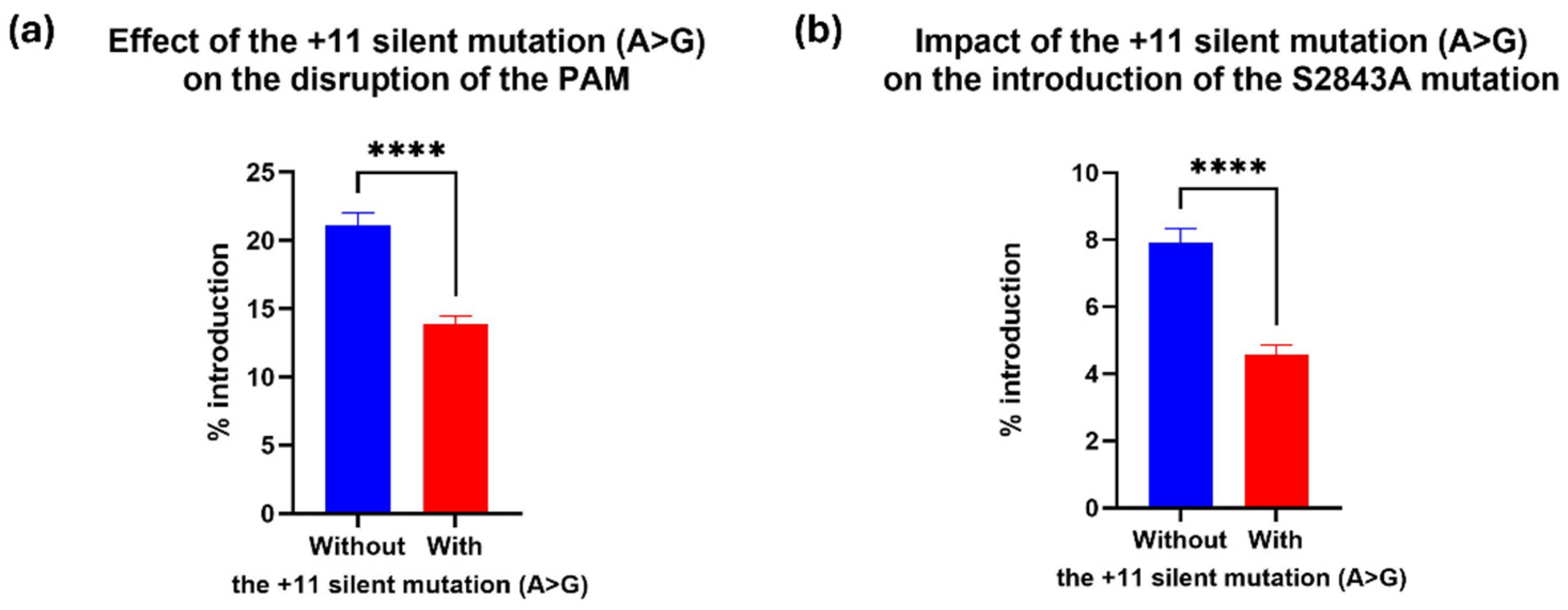
2.4. The +11 Silent Mutation in the RTT Decreased Prime Editing Efficiency
2.5. Assessing PE Variants to Improve Editing Efficiency
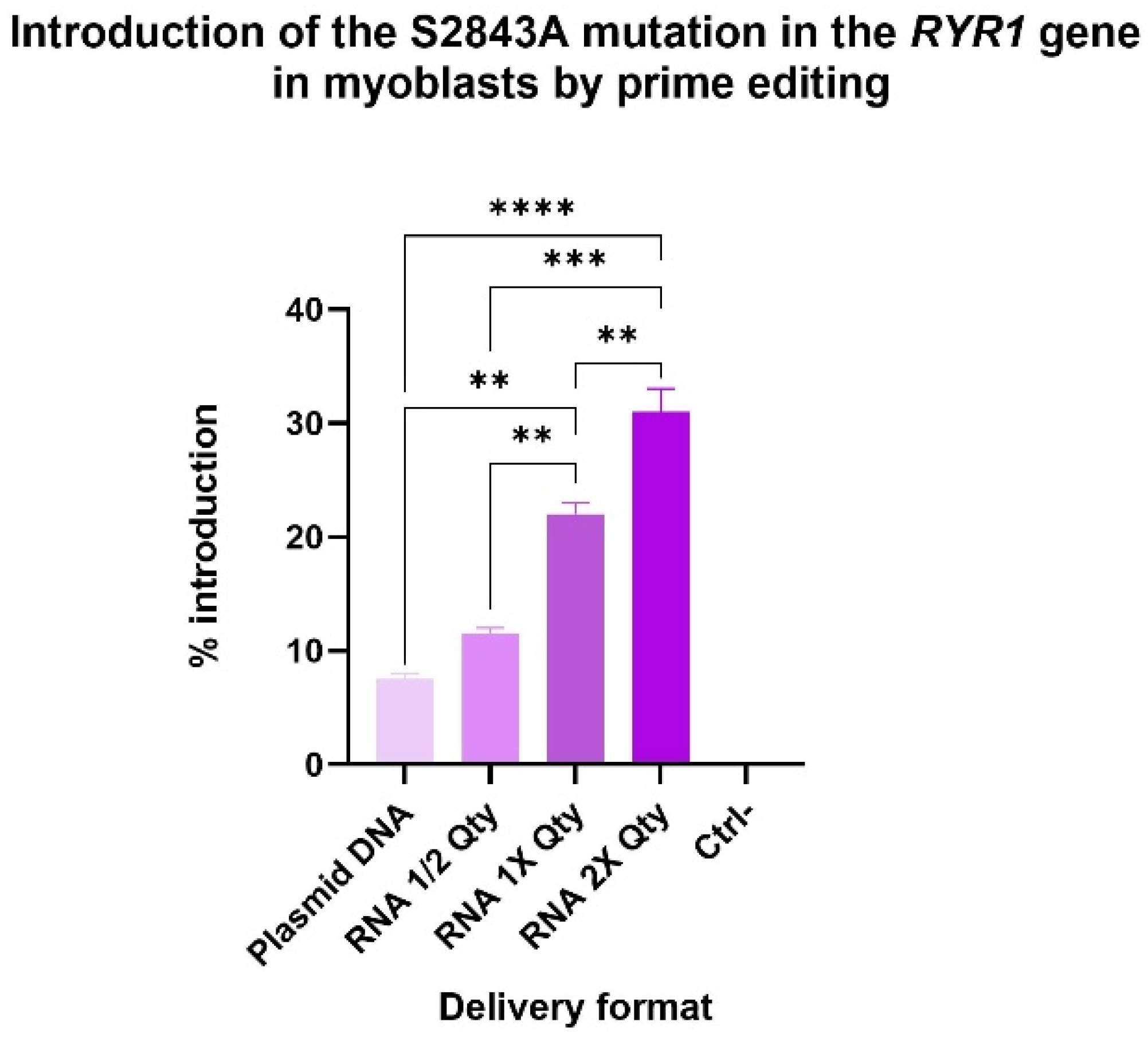
2.6. RNA Delivery Improved Prime Editing Efficiencies
2.7. Off-Target Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Prime Editing Technology
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Cell Line
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Ca2+ Leak Assay
4.6. Transfection of HEK293T Cells
4.7. Plasmid Electroporation in Myoblasts
4.8. PE mRNA In Vitro Transcription
4.9. RNA Electroporation in Myoblasts
4.10. Genomic DNA Preparation and PCR Amplification
4.11. Sanger Sequencing
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawal, T.A.; Todd, J.J.; Witherspoon, J.W.; Bonnemann, C.G.; Dowling, J.J.; Hamilton, S.L.; Meilleur, K.G.; Dirksen, R.T. Ryanodine receptor 1-related disorders: An historical perspective and proposal for a unified nomenclature. Skelet. Muscle 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungbluth, H.; Dowling, J.J.; Ferreiro, A.; Muntoni, F.; Consortium, R.Y.R.M. 217th ENMC International Workshop: RYR1-related myopathies, Naarden, The Netherlands, 29–31 January 2016. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2016, 26, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magyar, Z.E.; Hevesi, J.; Groom, L.; Dirksen, R.T.; Almassy, J. Function of a mutant ryanodine receptor (T4709M) linked to congenital myopathy. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 14659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, T.A.; Todd, J.J.; Meilleur, K.G. Ryanodine Receptor 1-Related Myopathies: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 885–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushnir, A.; Todd, J.J.; Witherspoon, J.W.; Yuan, Q.; Reiken, S.; Lin, H.; Munce, R.H.; Wajsberg, B.; Melville, Z.; Clarke, O.B.; et al. Intracellular calcium leak as a therapeutic target for RYR1-related myopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, J.J.; Lawal, T.A.; Chrismer, I.C.; Kokkinis, A.; Grunseich, C.; Jain, M.S.; Waite, M.R.; Biancavilla, V.; Pocock, S.; Brooks, K.; et al. Rycal S48168 (ARM210) for RYR1-related myopathies: A phase one, open-label, dose-escalation trial. eClinicalMedicine 2024, 68, 102433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Dridi, H.; Clarke, O.B.; Reiken, S.; Melville, Z.; Wronska, A.; Kushnir, A.; Zalk, R.; Sittenfeld, L.; Marks, A.R. RyR1-related myopathy mutations in ATP and calcium binding sites impair channel regulation. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.C.; Marks, A.R. Fixing ryanodine receptor Ca leak—A novel therapeutic strategy for contractile failure in heart and skeletal muscle. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2010, 7, e151–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, G. Regulation of Ryanodine Receptor Ion Channels Through Posttranslational Modifications. Curr. Top. Membr. 2010, 66, 91–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brillantes, A.B.; Ondrias, K.; Scott, A.; Kobrinsky, E.; Ondriasova, E.; Moschella, M.C.; Jayaraman, T.; Landers, M.; Ehrlich, B.E.; Marks, A.R. Stabilization of calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) function by FK506-binding protein. Cell 1994, 77, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suko, J.; Maurer-Fogy, I.; Plank, B.; Bertel, O.; Wyskovsky, W.; Hohenegger, M.; Hellmann, G. Phosphorylation of serine 2843 in ryanodine receptor-calcium release channel of skeletal muscle by cAMP-, cGMP- and CaM-dependent protein kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1175, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiken, S.; Lacampagne, A.; Zhou, H.; Kherani, A.; Lehnart, S.E.; Ward, C.; Huang, F.; Gaburjakova, M.; Gaburjakova, J.; Rosemblit, N.; et al. PKA phosphorylation activates the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) in skeletal muscle: Defective regulation in heart failure. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, A.M.; Reiken, S.; Dura, M.; Murphy, P.W.; Deng, S.X.; Landry, D.W.; Nieman, D.; Lehnart, S.E.; Samaru, M.; LaCampagne, A.; et al. Remodeling of ryanodine receptor complex causes “leaky” channels: A molecular mechanism for decreased exercise capacity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2198–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, L.; Kramer, H.F.; Tomberlin, G.H.; Townsend, C.; Meissner, G. Stabilization of the skeletal muscle ryanodine receptor ion channel-FKBP12 complex by the 1,4-benzothiazepine derivative S107. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreko-Pierce, T.; Azpurua, J.; Mahoney, R.E.; Eaton, B.A. Extension of Health Span and Life Span in Drosophila by S107 Requires the calstabin Homologue FK506-BP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26045–26055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stange, M.; Xu, L.; Balshaw, D.; Yamaguchi, N.; Meissner, G. Characterization of recombinant skeletal muscle (Ser-2843) and cardiac muscle (Ser-2809) ryanodine receptor phosphorylation mutants. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 51693–51702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherspoon, J.W.; Meilleur, K.G. Review of RyR1 pathway and associated pathomechanisms. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.A.; Hemez, C.; Lei, L.; Traore, S.; Kulhankova, K.; Newby, G.A.; Doman, J.L.; Oye, K.; Pandey, S.; Karp, P.H.; et al. Systematic optimization of prime editing for the efficient functional correction of CFTR F508del in human airway epithelial cells. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 9, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeck, B.J.; Gao, X.D.; McElroy, A.N.; Pandey, S.; Doman, J.L.; Riddle, M.J.; Xia, L.; Chen, W.; Eide, C.R.; Lengert, A.H.; et al. Twin Prime Editing Mediated Exon Skipping/Reinsertion for Restored Collagen VII Expression in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 2764–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.R.; Banskota, S.; Levy, J.M.; Newby, G.A.; Wang, X.; Anzalone, A.V.; Nelson, A.T.; Chen, P.J.; Hennes, A.D.; An, M.; et al. Efficient prime editing in mouse brain, liver and heart with dual AAVs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godbout, K.; Tremblay, J.P. Prime Editing for Human Gene Therapy: Where Are We Now? Cells 2023, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godbout, K.; Rousseau, J.; Tremblay, J.P. Successful Correction by Prime Editing of a Mutation in the RYR1 Gene Responsible for a Myopathy. Cells 2023, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, D.C.; Betzenhauser, M.J.; Reiken, S.; Umanskaya, A.; Shiomi, T.; Marks, A.R. Stress-induced increase in skeletal muscle force requires protein kinase A phosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 6381–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.W.; Randolph, P.B.; Shen, S.P.; Everette, K.A.; Chen, P.J.; Anzalone, A.V.; An, M.; Newby, G.A.; Chen, J.C.; Hsu, A.; et al. Engineered pegRNAs improve prime editing efficiency. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWeirdt, P.C.; McGee, A.V.; Zheng, F.; Nwolah, I.; Hegde, M.; Doench, J.G. Accounting for small variations in the tracrRNA sequence improves sgRNA activity predictions for CRISPR screening. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, R.; Li, X.; Chu, V.T.; Rajewsky, K. sgRNA Sequence Motifs Blocking Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Editing. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1098–1103.E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, Y.C.J.; Gierus, L.; Lushington, C.; Arudkumar, J.C.; Geiger, A.; Staker, L.G.; Robertson, L.J.; Pfitzner, C.; Kennedy, J.G.; Lee, R.H.B.; et al. Enhancing gRNA Transcript levels by Reducing the Scaffold Poly-T Tract for Optimal SpCas9- and SaCas9-mediated Gene Editing. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, J.; Yoon, J.K.; Jang, A.H.; Shin, H.R.; See, J.E.; Jang, G.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, Y. Engineered prime editors with PAM flexibility. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, N.; Allam, A.; Talas, A.; Kissling, L.; Benvenuto, E.; Schmidheini, L.; Schep, R.; Damodharan, T.; Balazs, Z.; Janjuha, S.; et al. Machine learning prediction of prime editing efficiency across diverse chromatin contexts. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, N.; Allam, A.; Kissling, L.; Marquart, K.F.; Schmidheini, L.; Solari, C.; Balazs, Z.; Krauthammer, M.; Schwank, G. Predicting prime editing efficiency and product purity by deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.J.; Hussmann, J.A.; Yan, J.; Knipping, F.; Ravisankar, P.; Chen, P.F.; Chen, C.; Nelson, J.W.; Newby, G.A.; Sahin, M.; et al. Enhanced prime editing systems by manipulating cellular determinants of editing outcomes. Cell 2021, 184, 5635–5652.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzalone, A.V.; Randolph, P.B.; Davis, J.R.; Sousa, A.A.; Koblan, L.W.; Levy, J.M.; Chen, P.J.; Wilson, C.; Newby, G.A.; Raguram, A.; et al. Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand breaks or donor DNA. Nature 2019, 576, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doman, J.L.; Pandey, S.; Neugebauer, M.E.; An, M.; Davis, J.R.; Randolph, P.B.; McElroy, A.; Gao, X.D.; Raguram, A.; Richter, M.F.; et al. Phage-assisted evolution and protein engineering yield compact, efficient prime editors. Cell 2023, 186, 3983–4002.E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDT. CRISPR-Cas9 Guide RNA Design Checker. Available online: https://www.idtdna.com/site/order/designtool/index/CRISPR_SEQUENCE (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Bock, D.; Rothgangl, T.; Villiger, L.; Schmidheini, L.; Matsushita, M.; Mathis, N.; Ioannidi, E.; Rimann, N.; Grisch-Chan, H.M.; Kreutzer, S.; et al. In vivo prime editing of a metabolic liver disease in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabl9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Hong, S.A.; Yu, J.; Eom, J.; Jang, K.; Yoon, S.; Hong, D.H.; Seo, D.; Lee, S.N.; Woo, J.S.; et al. Adenine base editing and prime editing of chemically derived hepatic progenitors rescue genetic liver disease. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1614–1624.E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Jo, D.H.; Cho, C.S.; Shin, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Yu, G.; Gopalappa, R.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.R.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Application of prime editing to the correction of mutations and phenotypes in adult mice with liver and eye diseases. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Huang, S.; Wu, S.; Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Huang, X.; Sun, Q.; et al. Modeling a cataract disorder in mice with prime editing. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhao, D.; Sui, T.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Chen, S.; Lai, L.; Li, Z. Efficient and precise generation of Tay-Sachs disease model in rabbit by prime editing system. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Raguram, A.; Du, S.W.; Banskota, S.; Davis, J.R.; Newby, G.A.; Chen, P.Z.; Palczewski, K.; Liu, D.R. Engineered virus-like particles for transient delivery of prime editor ribonucleoprotein complexes in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Kelly, K.; Cheng, H.; Dong, X.; Hedger, A.K.; Li, L.; Sontheimer, E.J.; Watts, J.K. In Vivo Prime Editing by Lipid Nanoparticle Co-Delivery of Chemically Modified pegRNA and Prime Editor mRNA. GEN Biotechnol. 2023, 2, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbout, K.; Tremblay, J.P. Delivery of RNAs to Specific Organs by Lipid Nanoparticles for Gene Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi Mbakam, C.; Rousseau, J.; Lu, Y.; Bigot, A.; Mamchaoui, K.; Mouly, V.; Tremblay, J.P. Prime editing optimized RTT permits the correction of the c.8713C>T mutation in DMD gene. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 30, 272–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happi Mbakam, C.; Rousseau, J.; Tremblay, G.; Yameogo, P.; Tremblay, J.P. Prime Editing Permits the Introduction of Specific Mutations in the Gene Responsible for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluesner, M.G.; Nedveck, D.A.; Lahr, W.S.; Garbe, J.R.; Abrahante, J.E.; Webber, B.R.; Moriarity, B.S. EditR: A Method to Quantify Base Editing from Sanger Sequencing. CRISPR J. 2018, 1, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godbout, K.; Dugas, M.; Reiken, S.R.; Ramezani, S.; Falle, A.; Rousseau, J.; Wronska, A.E.; Lamothe, G.; Canet, G.; Lu, Y.; et al. Universal Prime Editing Therapeutic Strategy for RyR1-Related Myopathies: A Protective Mutation Rescues Leaky RyR1 Channel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072835
Godbout K, Dugas M, Reiken SR, Ramezani S, Falle A, Rousseau J, Wronska AE, Lamothe G, Canet G, Lu Y, et al. Universal Prime Editing Therapeutic Strategy for RyR1-Related Myopathies: A Protective Mutation Rescues Leaky RyR1 Channel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072835
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodbout, Kelly, Mathieu Dugas, Steven R. Reiken, Sina Ramezani, Alexia Falle, Joël Rousseau, Anetta E. Wronska, Gabriel Lamothe, Geoffrey Canet, Yaoyao Lu, and et al. 2025. "Universal Prime Editing Therapeutic Strategy for RyR1-Related Myopathies: A Protective Mutation Rescues Leaky RyR1 Channel" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072835
APA StyleGodbout, K., Dugas, M., Reiken, S. R., Ramezani, S., Falle, A., Rousseau, J., Wronska, A. E., Lamothe, G., Canet, G., Lu, Y., Planel, E., Marks, A. R., & Tremblay, J. P. (2025). Universal Prime Editing Therapeutic Strategy for RyR1-Related Myopathies: A Protective Mutation Rescues Leaky RyR1 Channel. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2835. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072835








