Rare Case with Pathogenic Variant in DHX16 Gene Causing Neuromuscular Disease and Oculomotor Anomalies
Abstract
1. Introduction
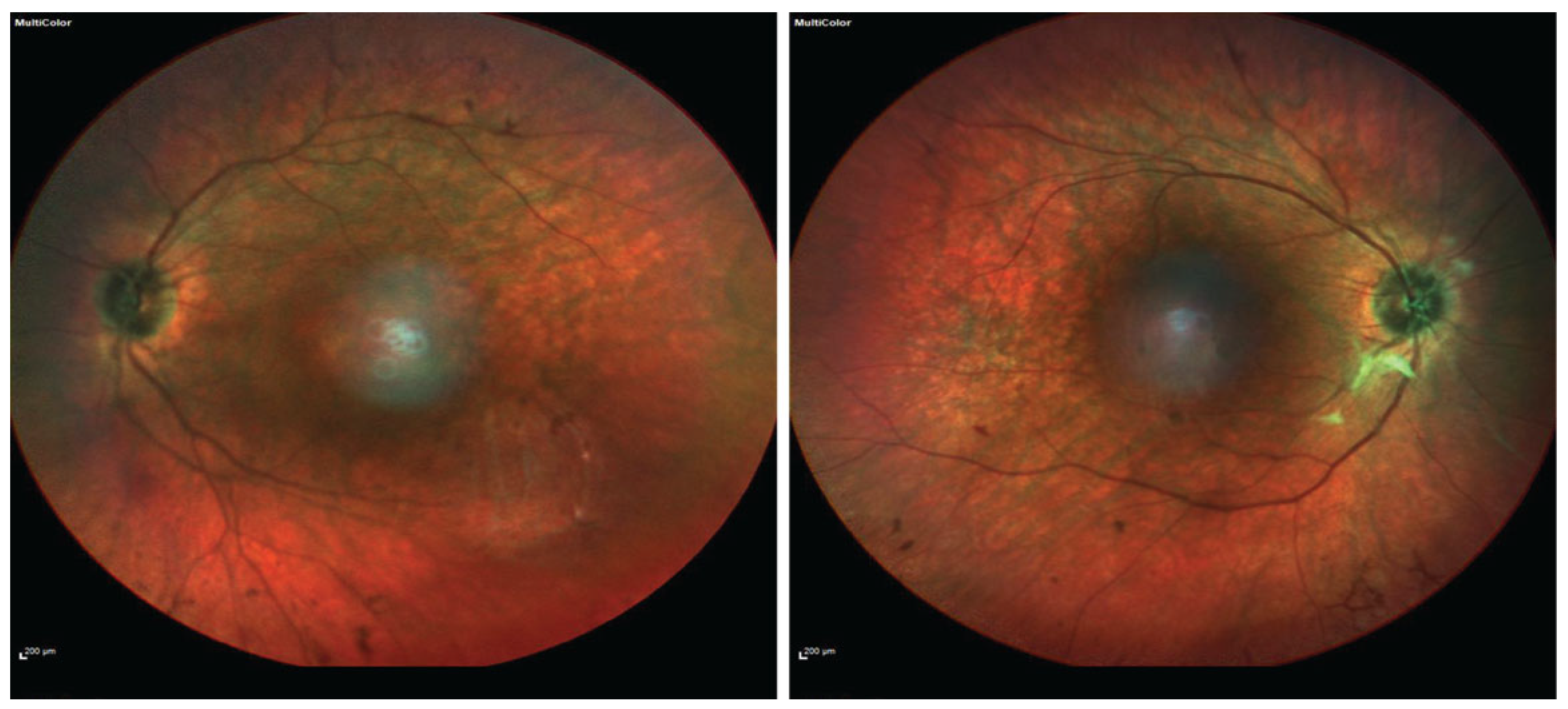
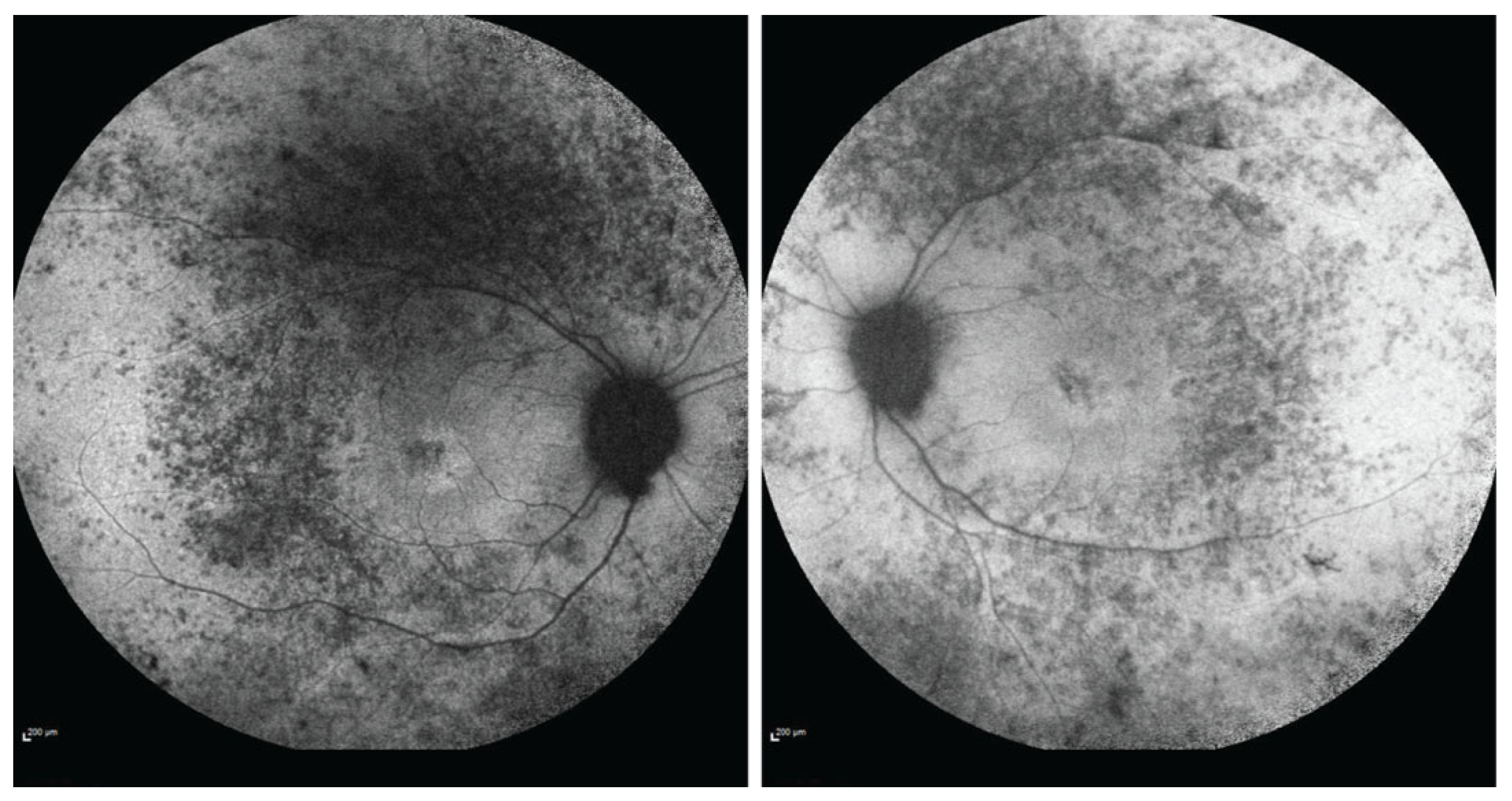
2. Case Presentation
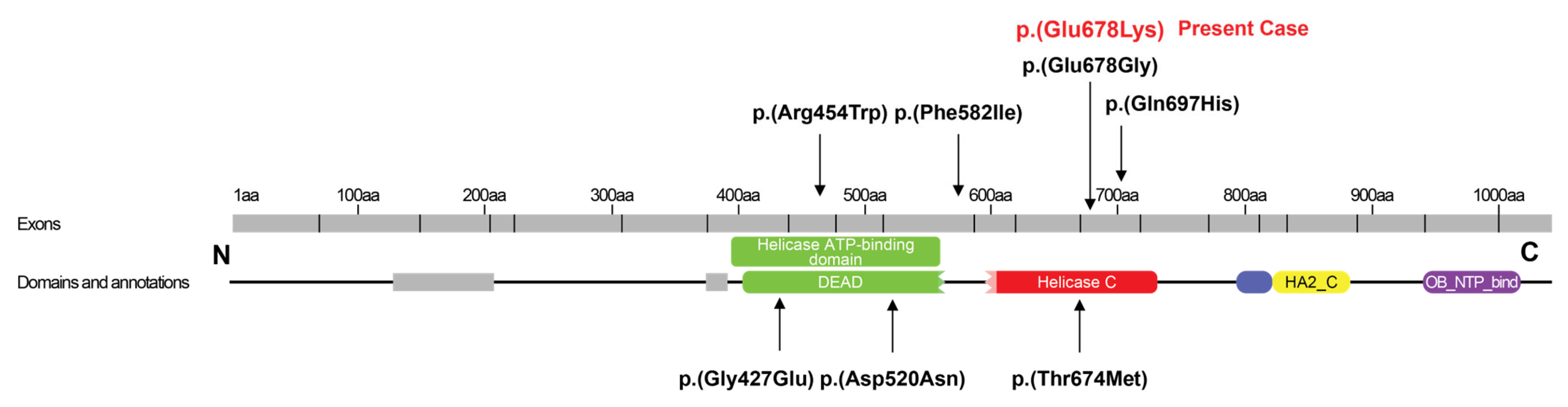
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bourgeois, C.F.; Mortreux, F.; Auboeuf, D. The multiple functions of RNA helicases as drivers and regulators of gene expression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankowsky, E. RNA helicases at work: Binding and rearranging. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gencheva, M.; Kato, M.; Newo, A.N.; Lin, R.J. Contribution of DEAH-box protein DHX16 in human pre-mRNA splicing. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paine, I.; Posey, J.E.; Grochowski, C.M.; Jhangiani, S.N.; Rosenheck, S.; Kleyner, R.; Marmorale, T.; Yoon, M.; Wang, K.; Robison, R.; et al. Paralog Studies Augment Gene Discovery: DDX and DHX Genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 302–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Drackley, A.; De Simone, L.; Kuntz, N.; Rahmani, S.; Ing, A.; Rao, V.K.; Rathbun, P.; Yap, K.L. Expansion of the phenotypic spectrum associated with pathogenic missense variation in DHX16. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2024, 194, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gencheva, M.; Lin, T.Y.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Richard, C.; Jones, M.; Lin, S.B.; Lin, R.J. Nuclear retention of unspliced pre-mRNAs by mutant DHX16/hPRP2, a spliceosomal DEAH-box protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 35624–35632. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Snijders Blok, L.; Madsen, E.; Juusola, J.; Gilissen, C.; Baralle, D.; Reijnders, M.R.; Venselaar, H.; Helsmoortel, C.; Cho, M.T.; Hoischen, A.; et al. Mutations in DDX3X Are a Common Cause of Unexplained Intellectual Disability with Gender-Specific Effects on Wnt Signaling. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 97, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Posey, J.E.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Bacino, C.A.; Scaglia, F.; Immken, L.; Harris, J.M.; Hickey, S.E.; Mosher, T.M.; Slavotinek, A.; et al. Phenotypic expansion in DDX3X—A common cause of intellectual disability in females. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Jang, S.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Sim, H.; Jeon, H.; Hong, S.E.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Jeon, E.Y.; et al. Systematic analysis of inheritance pattern determination in genes that cause rare neurodevelopmental diseases. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 990015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archana, A.; Selvan, T.; Kumar, V.R.; Abinaya, K.; Kasturi, N. A Rare Case of Neuromuscular Oculoauditory Syndrome. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2022, 25, 780–781. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hautakangas, M.R.; Widgren, P.; Korpelainen, P.; Kangas, S.M.; Komulainen, T.; Vieira, P.; Rahikkala, E.; Pylkäs, K.; Tuominen, H.; Kokkonen, H.; et al. Infantile onset encephalomyopathy, retinopathy, optic atrophy, and mitochondrial DNA depletion associated with a novel pathogenic DHX16 variant. Clin. Genet. 2023, 104, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alli, Z.; Ackerley, C.; Chen, Y.; Al-Saud, B.; Abdelhaleem, M. Nuclear and mitochondrial localization of the putative RNA helicase DHX32. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2006, 81, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsetos, C.D.; Koutzaki, S.; Melvin, J.J. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neuromuscular disorders. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 20, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, A.M.; Stroek, K.; Abeling, N.G.; Waterham, H.R.; Ijlst, L.; Wanders, R.J. The Brown-Vialetto-Van Laere and Fazio Londe syndrome revisited: Natural history, genetics, treatment and future perspectives. Orphanet. J. Rare. Dis. 2012, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, B.; Bosch, A.M. Clinical presentation and outcome of riboflavin transporter deficiency: Mini review after five years of experience. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2016, 39, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Chen, W.X.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, C.; Ni, Y.; Duan, B.; Wang, H.; Xu, Z.M. Recessive LOXHD1 variants cause a prelingual down-sloping hearing loss: Genotype-phenotype correlation and three additional children with novel variants. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 145, 110715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, K.; Nishio, S.Y.; Abe, S.; Goto, S.I.; Honkura, Y.; Iwasaki, S.; Kanda, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Oka, S.I.; Okami, M.; et al. Mutational Spectrum and Clinical Features of Patients with LOXHD1 Variants Identified in an 8074 Hearing Loss Patient Cohort. Genes 2019, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Authors, Year | Pathogenic Variant | DHX16 Domain | Inheritance | Gender | Age of Onset | Age of Diagnosis | Neurological Symptoms | Other Features | MRI Brain | First Symptom | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paine et al., 2019 [4] individual 6 | c.1744 T > A p.(Phe582Ile) heterozygous | C-terminal | De novo | Female | 10 weeks | n/a | Hypotonia, poor head control, poor visual tracking, infantile spasms | Sensorineural hearing loss, chorioretinal lacunae, depigmentation around optic nerve | Corpus callosum agenesis, subependymal heterotopia | Infantile spasms | n/a |
| Paine et al., 2019 [4] individual 7 | c.2091G > T p.(Gln697His) heterozygous | C-terminal | De novo | Female | Birth | Infancy | n/a | Small length, short limbs, dysmorphic facial features (bilateral epicanthal folds, simple auricles), enlarged cystic kidneys | n/a | Decreased fetal heart tones, reduced birth length, dysmorphic features | Death 16 days after birth |
| Paine et al., 2019 [4] individual 8 | c.1280G > A p.(Gly427Glu) heterozygous | ATP-binding area | De novo | Male | Birth | Infancy | Sensorimotor neuropathy, horizontal nystagmus | Sensorineural hearing loss, bilateral equinovarus, feeding difficulties, respiratory distress, flexion contractures | Normal | Severe hypotonia, skeletal abnormalities | Death at the age of 4 months |
| Paine et al., 2019 [4] individual 9 | c.2021C > T p.(Thr674Met) heterozygous | C-terminal | De novo | Male | 10 months | Infancy | Epilepsy, developmental delay, myopathy, peripheral neuropathy, hypertrophic calves, ataxic gait, unable to walk | Sensorineural hearing loss, retinopathy, complete vision loss, contractures | Normal | Febrile seizure | At age 34 wheelchair-bound, blind, deaf |
| Archana et al., 2022 [12] | c.1445G > A p.(Arg482His) heterozygous | ATP-binding area | Unknown | Male | 18 months | Toddler (18 months) | Hypotonia, nystagmus, developmental delay, infantile spasms | Sensorineural hearing loss, blindness, retinal pigmentary spotting | Normal | Sensorineural deafness at 4 months of age | n/a |
| Park et al., 2022 [11] | c.2021C > T p.(Thr674Met) heterozygous | C-terminal | De Novo | n/a | Birth | n/a | Myopathy | n/a | n/a | n/a | n/a |
| Hautakangas et al. 2023 [13] | c.1360C>T p.(Arg454Trp) heterozygous additional homozygous missense variant c.1378C>G p.(Arg460Gly) in CHRNB2 gene | ATP-binding area | De Novo | Female | Infancy (3 months) | n/a | Hypotonia, lack of eye contact, elevated CPK, constant nystagmus, spasticity | Sensorineural hearing loss, dysmorphic features (epicanthal folds, single palmar crease, sandal gaps), poor weight gain, pale fundi with pigmentation and depigmentation, failure to thrive | Normal | Dysmorphic features | Death at 4 years |
| Drackley et al., 2024 [5] | c.2033A > G p.(Glu678Gly) heterozygous | C-terminal | De novo | Female | Birth | 15 years | Hypotonia, motor delay, sensorimotor axonal neuropathy, myopathy, ADHD | Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss, retinitis pigmentosa, premature adrenarche, primary ovarian insufficiency | n/a | Bilateral sensorineural hearing loss | n/a |
| Present case | c.2032G>A, p.(Glu678Lys) heterozygous | C-terminal | De novo | Female | Birth | 36 years | Facial palsy, swallowing difficulties, nasal speech, myopathy, flaccid tetraparesis | Sensorineural deafness, retinitis pigmentosa, primary ovarian deficiency | Normal | Sensorineural hearing loss | Deaf, wheelchair-bound |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalampokini, S.; Goulis, D.G.; Pepe, G.; Koukoula, S.; Frontistis, A.; Moschou, M.; Arnaoutoglou, M.; Papaliagkas, V.; Kimiskidis, V.K. Rare Case with Pathogenic Variant in DHX16 Gene Causing Neuromuscular Disease and Oculomotor Anomalies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062812
Kalampokini S, Goulis DG, Pepe G, Koukoula S, Frontistis A, Moschou M, Arnaoutoglou M, Papaliagkas V, Kimiskidis VK. Rare Case with Pathogenic Variant in DHX16 Gene Causing Neuromuscular Disease and Oculomotor Anomalies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062812
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalampokini, Stefania, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Georgia Pepe, Stavrenia Koukoula, Antonis Frontistis, Maria Moschou, Marianthi Arnaoutoglou, Vasileios Papaliagkas, and Vasilios K. Kimiskidis. 2025. "Rare Case with Pathogenic Variant in DHX16 Gene Causing Neuromuscular Disease and Oculomotor Anomalies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062812
APA StyleKalampokini, S., Goulis, D. G., Pepe, G., Koukoula, S., Frontistis, A., Moschou, M., Arnaoutoglou, M., Papaliagkas, V., & Kimiskidis, V. K. (2025). Rare Case with Pathogenic Variant in DHX16 Gene Causing Neuromuscular Disease and Oculomotor Anomalies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062812










