AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis
Abstract
1. Chemical Carcinogenesis
2. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR)
2.1. AhR Genomic Canonical Pathway
2.2. AhR Genomic Non-Canonical Pathway
2.3. AhR Non-Genomic Pathways
3. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3)
3.1. STAT3 Canonical Pathway
3.2. STAT3 Non-Canonical Pathways
3.3. STAT3 Pollutants
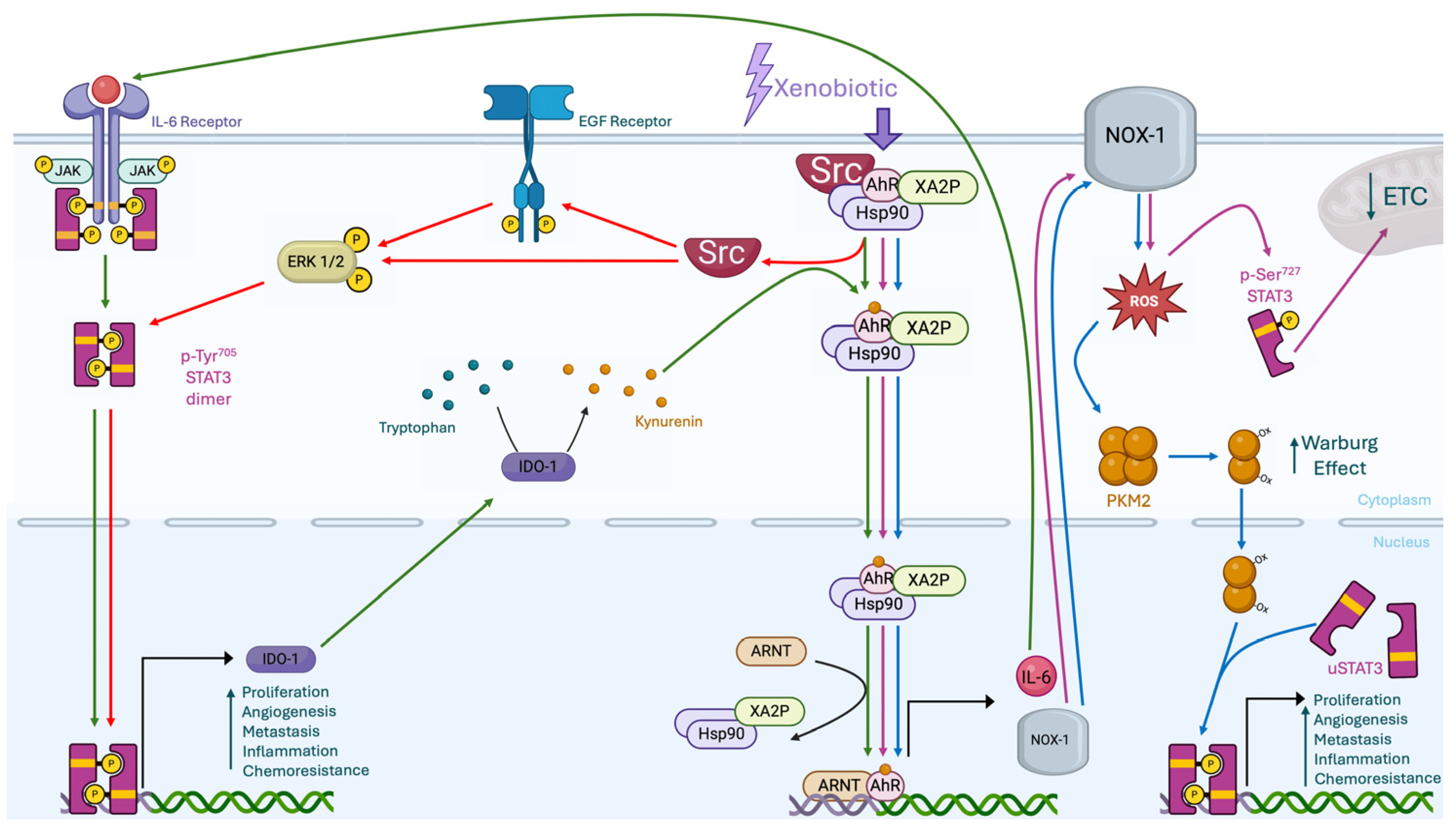
4. STAT3-AhR Interplays
4.1. Direct Interplay Between STAT3 and AhR
4.2. Indirect Interplay Between STAT3 and AhR
4.3. Potential Therapeutic Target in AhR- STAT3 Interplay
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wogan, G.N.; Hecht, S.S.; Felton, J.S.; Conney, A.H.; Loeb, L.A. Environmental and chemical carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2004, 14, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabirai, A.; Chahar, A.; Chahar, N.; Gupta, J. Chemical carcinogenesis: A brief review on mechanism & metabolism. J. Oral Med. Oral Surg. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 6, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, S.C.; Vaccari, M.; Al-Mulla, F.; Al-Temaimi, R.; Amedei, A.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H.; Brown, D.G.; Chapellier, M.; Christopher, J.; Curran, C.S.; et al. The effect of environmental chemicals on the tumor microenvironment. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, S160–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinek, R.; Lózsa, R.; Póti, Á.; Németh, E.; Várady, G.; Szabó, P.; Szüts, D. Comprehensive investigation of the mutagenic potential of six pesticides classified by IARC as probably carcinogenic to humans. Chemosphere 2024, 362, 142700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Jaros, A.; Gajdzińska, A.; Wojtyła-Buciora, P.; Szymański, I.; Szymaniak, J.; Janusz, W.; Walczak, I.; Jonaszka, G.; Bienert, A. The Dual Faces of Oestrogen: The Impact of Exogenous Oestrogen on the Physiological and Pathophysiological Functions of Tissues and Organs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Sharma, S.; Advani, D.; Khosla, A.; Kumar, P.; Ambasta, R.K. Unboxing the molecular modalities of mutagens in cancer. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 62111–62159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.C.; Miller, J.A. Mechanisms of chemical carcinogenesis. Cancer 1981, 47, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plošnik, A.; Vračko, M.; Dolenc, M.S. Mutagenic and carcinogenic structural alerts and their mechanisms of action. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2016, 67, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomar, A.; Barak, O.; Brenner, N. Cancer progression as a learning process. iScience 2022, 25, 103924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karidio, I.D.; Sanlier, S.H. Reviewing cancer’s biology: An eclectic approach. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 33, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolluri, S.K.; Jin, U.-H.; Safe, S. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as an anti-cancer drug target. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2497–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubini, E.; Altieri, F.; Chichiarelli, S.; Giamogante, F.; Carissimi, S.; Paglia, G.; Macone, A.; Eufemi, M. STAT3, a Hub Protein of Cellular Signaling Pathways, Is Triggered by β-Hexaclorocyclohexane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Zárate, E.; Sánchez-Pérez, Y.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.C.; Chirino, Y.I.; Osornio-Vargas, Á.R.; Morales-Bárcenas, R.; Souza-Arroyo, V.; García-Cuellar, C.M. Atmospheric particulate matter (PM10) exposure-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis evasion through STAT3 activation via PKCζ and Src kinases in lung cells. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuvoli, B.; Camera, E.; Mastrofrancesco, A.; Briganti, S.; Galati, R. Modulation of reactive oxygen species via ERK and STAT3 dependent signalling are involved in the response of mesothelioma cells to exemestane. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, H.Q.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, R.; Hahn, M.E.; Zhao, B. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: A predominant mediator for the toxicity of emerging dioxin-like compounds. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, E.J.; De Castro, K.P.; Joshi, A.D.; Elferink, C.J. Canonical and non-canonical aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakura, Y.; Tsutsumi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshida, T.; Maitani, T. Influence of food polyphenols on aryl hydrocarbon receptor-signaling pathway estimated by in vitro bioassay. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 3117–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebert, D.W. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR): “pioneer member” of the basic-helix/loop/helix per-Arnt-sim (bHLH/PAS) family of “sensors” of foreign and endogenous signals. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 67, 38–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.J.; Wei, W.-Q.; Baer, J.; Abnet, C.C.; Wang, G.-Q.; Sternberg, L.R.; Warner, A.C.; Johnson, L.L.; Lu, N.; Giffen, C.A.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Expression Is Associated with a Family History of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer in a High-Risk Population Exposed to Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2009, 18, 2391–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivanna, B.; Chu, C.; Moorthy, B. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR): A Novel Therapeutic Target for Pulmonary Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, H.-S.; Paloni, M.; Grandvuillemin, L.; Sirounian, S.; Ancelin, A.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Grimaldi, M.; Carivenc, C.; Lancey, C.; Ragan, T.J.; et al. Structural Insights into the Activation of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor by the Environmental Contaminant Benzo[a]pyrene and Structurally Related Compounds. J. Mol. Biol. 2024, 436, 168411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-Y.; Iwata, H.; Suda, T.; Tanabe, S.; Amano, M.; Miyazaki, N.; Petrov, E.A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and AHR nuclear translocator (ARNT) expression in Baikal seal (Pusa sibirica) and association with 2,3,7,8-TCDD toxic equivalents and CYP1 expression levels. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2005, 141, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollenz, R.S. The mechanism of AH receptor protein down-regulation (degradation) and its impact on AH receptor-mediated gene regulation. Chem. Interact. 2002, 141, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, B.R.; Karchner, S.I.; Allan, L.L.; Pollenz, R.S.; Tanguay, R.L.; Jenny, M.J.; Sherr, D.H.; Hahn, M.E. Repression of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) Signaling by AHR Repressor: Role of DNA Binding and Competition for AHR Nuclear Translocator. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.E.; Karchner, S.I.; Merson, R.R. Diversity as opportunity: Insights from 600 million years of AHR evolution. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2017, 2, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.D.; Nakka, M.; Grimm, S.L.; Coarfa, C.; Gorelick, D.A. Functional genomic analysis of non-canonical DNA regulatory elements of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; Joshi, A.D.; Elferink, C.J. The Tumor Suppressor Kruppel-Like Factor 6 Is a Novel Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor DNA Binding Partner. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 345, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.P.; Li, H.; Mitchell, K.A.; Joshi, A.D.; Elferink, C.J. Ah Receptor–Mediated Suppression of Liver Regeneration through NC-XRE–Driven p21Cip1 Expression. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 85, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinchmann, B.C.; Le Ferrec, E.; Bisson, W.H.; Podechard, N.; Huitfeldt, H.S.; Gallais, I.; Sergent, O.; Holme, J.A.; Lagadic-Gossmann, D.; Øvrevik, J. Evidence of selective activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor nongenomic calcium signaling by pyrene. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 158, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larigot, L.; Juricek, L.; Dairou, J.; Coumoul, X. AhR signaling pathways and regulatory functions. Biochim. Open 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puga, A.; Ma, C.; Marlowe, J.L. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor cross-talks with multiple signal transduction pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilla, M.N.; Malecki, K.M.C.; Hahn, M.E.; Wilson, R.H.; Bradfield, C.A. The Ah Receptor: Adaptive Metabolism, Ligand Diversity, and the Xenokine Model. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2020, 33, 860–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Snyder, M.; Kenison, J.E.; Yang, K.; Lara, B.; Lydell, E.; Bennani, K.; Novikov, O.; Federico, A.; Monti, S.; et al. How the AHR Became Important in Cancer: The Role of Chronically Active AHR in Cancer Aggression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guanizo, A.C.; Fernando, C.D.; Garama, D.J. STAT3: A multifaceted oncoprotein. Growth Factors 2018, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, R.L.; Lo, H.-W. STAT3 Target Genes Relevant to Human Cancers. Cancers 2014, 6, 897–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki-Ohara, K.; Hanada, T.; Yoshimura, A. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling and inflammatory diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2003, 3, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Liu, K. Unraveling the complexity of STAT3 in cancer: Molecular understanding and drug discovery. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diallo, M.; Pimenta, C.; Murtinheira, F.; Martins-Alves, D.; Pinto, F.R.; da Costa, A.A.; Letra-Vilela, R.; Martin, V.; Rodriguez, C.; Rodrigues, M.S.; et al. Asymmetric post-translational modifications regulate the nuclear translocation of STAT3 homodimers in response to leukemia inhibitory factor. Cell. Oncol. 2024, 47, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Wen, Z.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Stat3: A STAT Family Member Activated by Tyrosine Phosphorylation in Response to Epidermal Growth Factor and Interleukin-6. Science 1994, 264, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, X. The role of STAT3 in leading the crosstalk between human cancers and the immune system. Cancer Lett. 2018, 415, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Liao, X.; Agarwal, M.K.; Barnes, L.; Auron, P.E.; Stark, G.R. Unphosphorylated STAT3 accumulates in response to IL-6 and activates transcription by binding to NFκB. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1396–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Q.; Montgrain, P.R.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; Li, W.X. Unphosphorylated STAT3 in heterochromatin formation and tumor suppression in lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, J.; Potla, R.; Chwae, Y.-J.; Sepuri, N.B.V.; Zhang, Q.; Koeck, T.; Derecka, M.; Szczepanek, K.; Szelag, M.; Gornicka, A.; et al. Function of Mitochondrial Stat3 in Cellular Respiration. Science 2009, 323, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.A.; Larner, A.C. Toward a new STATe: The role of STATs in mitochondrial function. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.A.; Hyun, M.; Cantwell, M.; Raza, A.; Mertens, C.; Raje, V.; Sisler, J.; Tracy, E.; Torres-Odio, S.; Gispert, S.; et al. Stress-induced dynamic regulation of mitochondrial STAT3 and its association with cyclophilin D reduce mitochondrial ROS production. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaag2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marié, I.J.; Lahiri, T.; Önder, Ö.; Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Levy, D.E. Structural determinants of mitochondrial STAT3 targeting and function. Mitochondrial Commun. 2024, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, M.; Poli, V. PKM2, STAT3 and HIF-1α. JAK-STAT 2012, 1, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avalle, L.; Camporeale, A.; Morciano, G.; Caroccia, N.; Ghetti, E.; Orecchia, V.; Viavattene, D.; Giorgi, C.; Pinton, P.; Poli, V. STAT3 localizes to the ER, acting as a gatekeeper for ER-mitochondrion Ca2+ fluxes and apoptotic responses. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.K.; Dourlat, J.; Davies, A.M.; Long, A.; Liu, W.-Q.; Garbay, C.; Kelleher, D.; Volkov, Y. STAT3-Stathmin Interactions Control Microtubule Dynamics in Migrating T-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 12349–12362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Palmfeldt, J.; Lin, L.; Colaço, A.; Clemmensen, K.K.B.; Huang, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, X.; Maeda, K.; Luo, Y.; et al. STAT3 associates with vacuolar H+-ATPase and regulates cytosolic and lysosomal pH. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.; Nawrot, T.S.; Baccarelli, A.A. Hallmarks of Environmental Insults. Cell 2021, 184, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, J.; Wang, R.; Ramezani, K.; Bonakdar, M.; Moghimi, N.; Salimi, M.; Yao, Y.; Wang, K. Bisphenol A interacts with DLGAP5 and regulates IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway to promote tumorigenesis and progression of osteosarcoma. Chemosphere 2023, 312, 136545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A.V. A Common Feature of Pesticides: Oxidative Stress—The Role of Oxidative Stress in Pesticide-Induced Toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubini, E.; Paglia, G.; Cannella, D.; Macone, A.; Di Sotto, A.; Gullì, M.; Altieri, F.; Eufemi, M. β-Hexachlorocyclohexane: A Small Molecule with a Big Impact on Human Cellular Biochemistry. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorini, S.; Rubini, E.; Perugini, M.; Altieri, F.; Chichiarelli, S.; Meschiari, G.; Arrighetti, G.; Vijgen, J.; Natali, P.G.; Minacori, M.; et al. STAT3 Pathways Contribute to β-HCH Interference with Anticancer Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubini, E.; Minacori, M.; Paglia, G.; Altieri, F.; Chichiarelli, S.; Romaniello, D.; Eufemi, M. β-Hexachlorocyclohexane Drives Carcinogenesis in the Human Normal Bronchial Epithelium Cell Line BEAS-2B. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskalova, L.; Dvorak, Z.; Pavek, P. Endogenous and Exogenous Ligands of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor: Current State of Art. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meireson, A.; Devos, M.; Brochez, L. IDO Expression in Cancer: Different Compartment, Different Functionality? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 531491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.X.; Sotero-Esteva, W.D.; Taylor, M.W. Analysis of Transcription Factors Regulating Induction of Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase by IFN-gamma. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2000, 20, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litzenburger, U.M.; Opitz, C.A.; Sahm, F.; Rauschenbach, K.J.; Trump, S.; Winter, M.; Ott, M.; Ochs, K.; Lutz, C.; Liu, X.; et al. Constitutive IDO expression in human cancer is sustained by an autocrine signaling loop involving IL-6, STAT3 and the AHR. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1038–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.-T.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Zhao, S.; Song, C. Common mechanisms involved in lung cancer and depression: The dominant role of interleukin-6-IDO pathway in the lung-brain axis. J. Affect. Disord. Rep. 2023, 12, 100580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yan, L.; Lin, J.; Ke, K.; Yang, W. Constitutive TDO2 expression promotes liver cancer progression by an autocrine IL-6 signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Peng, Z.; Raufman, J.-P. Src-mediated aryl hydrocarbon and epidermal growth factor receptor cross talk stimulates colon cancer cell proliferation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G1006–G1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.X.; Yong, C.Y.; Ong, A.H.K.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y. Deciphering the roles of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in regulating carcinogenesis. Toxicology 2023, 495, 153596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, L.; Tian, L.; Yin, S.; Ma, X.; Cheng, S.; Tang, W.; Yu, J.; Ma, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes IL-10 Expression in Inflammatory Macrophages Through Src-STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishanova, A.Y.; Perepechaeva, M.L. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor in Oxidative Stress as a Double Agent and Its Biological and Therapeutic Significance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streeter, J.; Schickling, B.M.; Jiang, S.; Stanic, B.; Thiel, W.H.; Gakhar, L.; Houtman, J.C.; Miller, F.J., Jr. Phosphorylation of Nox1 Regulates Association with NoxA1 Activation Domain. Circ. Res. 2014, 115, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, D. Protein kinase function of pyruvate kinase M2 and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Guo, J.; Nie, H.; Xiong, H.; Xia, Y. Aberrant Energy Metabolism in Tumors and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2024, 63, e70008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrocco, I.; Altieri, F.; Rubini, E.; Paglia, G.; Chichiarelli, S.; Giamogante, F.; Macone, A.; Perugia, G.; Magliocca, F.M.; Gurtner, A.; et al. Shmt2: A Stat3 Signaling New Player in Prostate Cancer Energy Metabolism. Cells 2019, 8, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouédraogo, Z.G.; Müller-Barthélémy, M.; Kemeny, J.; Dedieu, V.; Biau, J.; Khalil, T.; Raoelfils, L.I.; Granzotto, A.; Pereira, B.; Beaudoin, C.; et al. STAT3 Serine 727 Phosphorylation: A Relevant Target to Radiosensitize Human Glioblastoma. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Chen, D.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; Jiao, H.; Duan, M.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, J.; Xu, L.; et al. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic significance of Tryptophan Metabolism and signaling in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhe, H.; Ma, J.-X.; Ye, F.-Z.; Song, C.-Y.; Chen, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Han, X.; Ma, L.-X.; Saiyin, H. IDO-1 inhibitor INCB24360 elicits distant metastasis of basal extruded cancer cells in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, J.; Chen, C. Ruxolitinib enhances gastric cancer to chemotherapy by suppressing JAK/STAT3 and inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2025, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, S.; Taha, M.O. Advances in the design and discovery of next-generation janus kinase-2 (JAK2) inhibitors for the treatment of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2024, 19, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, A.M.; Almalki, F.A.; Abdalla, A.N.; Abdelazeem, A.H.; Gouda, A.M. A Comprehensive Overview of Globally Approved JAK Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.-J.; Im, S.-A.; Oh, D.-Y.; Elvin, P.; Kim, H.-P.; Yoon, Y.-K.; Min, A.; Song, S.-H.; Han, S.-W.; Kim, T.-Y.; et al. Antitumor Activity of Saracatinib (AZD0530), a c-Src/Abl Kinase Inhibitor, Alone or in Combination with Chemotherapeutic Agents in Gastric Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucalp, A.; Sparano, J.A.; Caravelli, J.; Santamauro, J.; Patil, S.; Abbruzzi, A.; Pellegrino, C.; Bromberg, J.; Dang, C.; Theodoulou, M.; et al. Phase II Trial of Saracatinib (AZD0530), an Oral SRC-inhibitor for the Treatment of Patients with Hormone Receptor-negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2011, 11, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, T. Roles of Nox1 and other Nox isoforms in cancer development. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1382–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandierendonck, A.; Degroote, H.; Vanderborght, B.; Verhelst, X.; Geerts, A.; Devisscher, L.; Van Vlierberghe, H. NOX1 inhibition attenuates the development of a pro-tumorigenic environment in experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.J.; Kabeer, A.; Abbas, Z.; Siddiqui, H.A.; Calina, D.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cho, W.C. Interplay of oxidative stress, cellular communication and signaling pathways in cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, R.; Landrigan, P.J.; Balakrishnan, K.; Bathan, G.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Brauer, M.; Caravanos, J.; Chiles, T.; Cohen, A.; Corra, L.; et al. Pollution and health: A progress update. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e535–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niou, E.M.S.; Ordeshook, P.C. Alliances in Anarchic International Systems. Int. Stud. Q. 1994, 38, 167–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minacori, M.; Fiorini, S.; Perugini, M.; Iannetta, A.; Meschiari, G.; Chichiarelli, S.; Altieri, F.; Natali, P.G.; Eufemi, M. AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062744
Minacori M, Fiorini S, Perugini M, Iannetta A, Meschiari G, Chichiarelli S, Altieri F, Natali PG, Eufemi M. AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062744
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinacori, Marco, Sara Fiorini, Monia Perugini, Annamaria Iannetta, Giorgia Meschiari, Silvia Chichiarelli, Fabio Altieri, Pier Giorgio Natali, and Margherita Eufemi. 2025. "AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062744
APA StyleMinacori, M., Fiorini, S., Perugini, M., Iannetta, A., Meschiari, G., Chichiarelli, S., Altieri, F., Natali, P. G., & Eufemi, M. (2025). AhR and STAT3: A Dangerous Duo in Chemical Carcinogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062744








