Impact of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Mental Illness: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
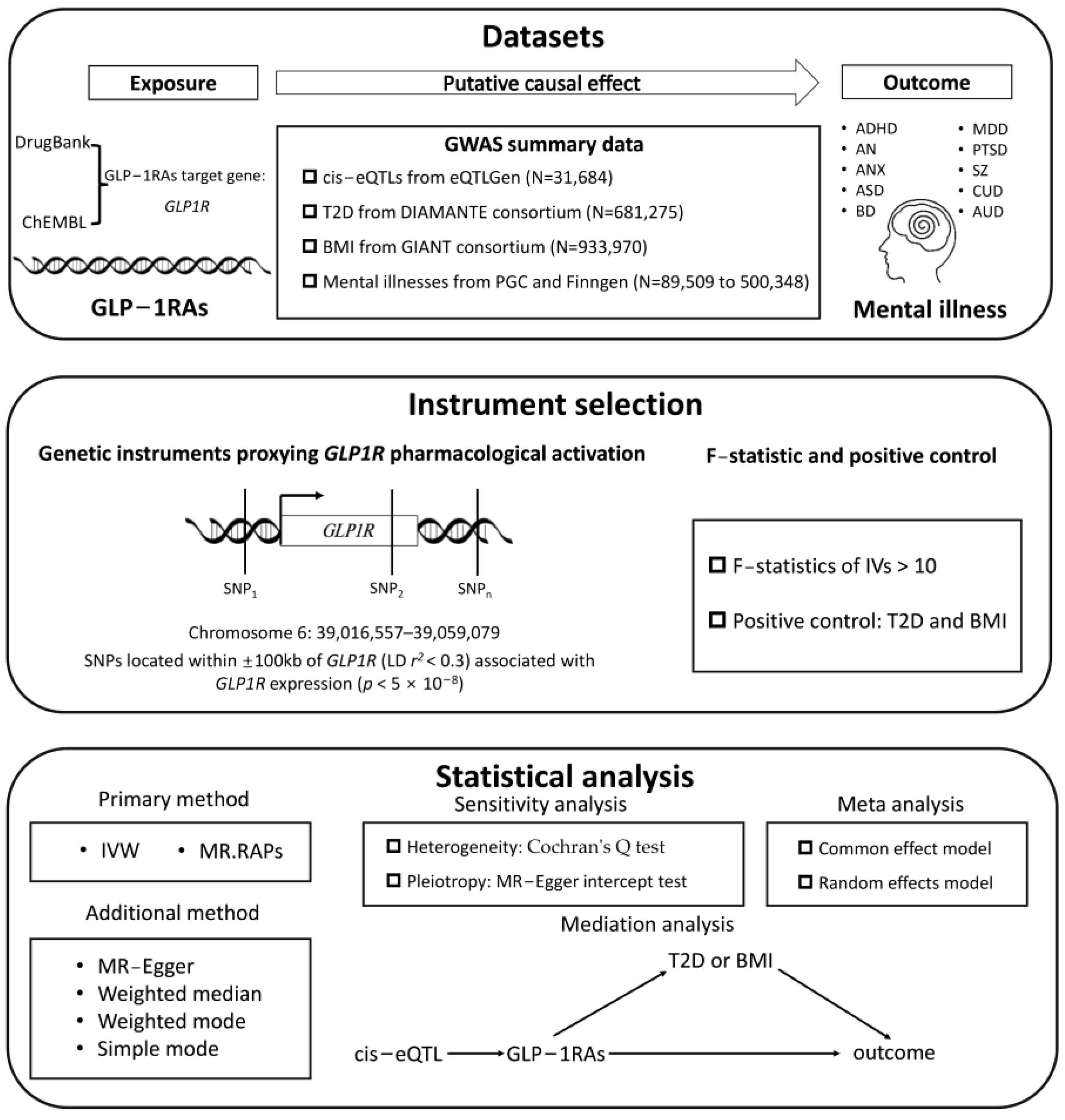
2.1. Selection of Genetic Instruments
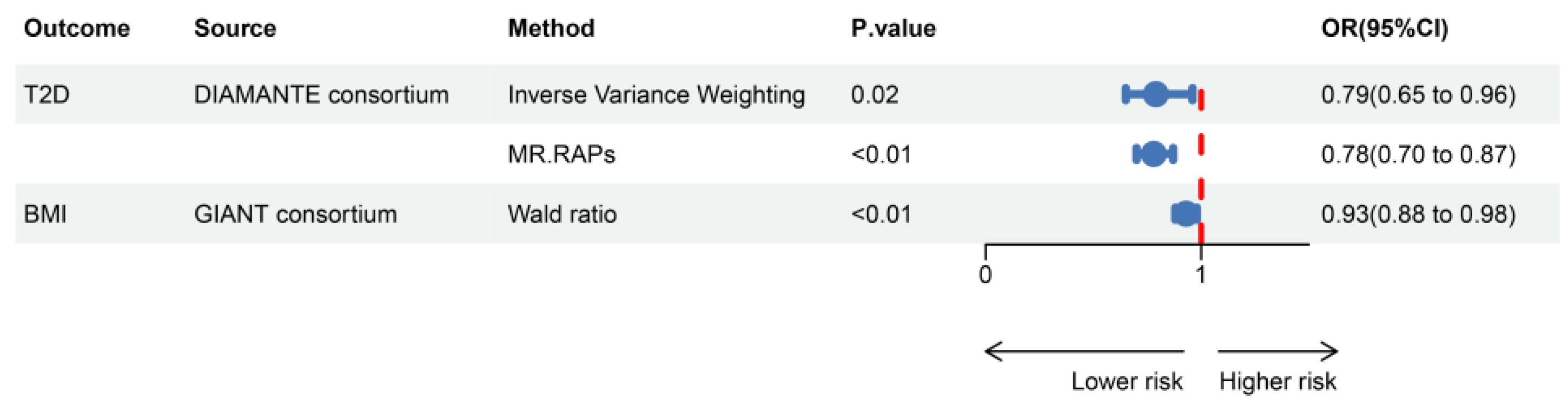
2.2. Causal Relationship Between GLP1RA and Mental Illnesses
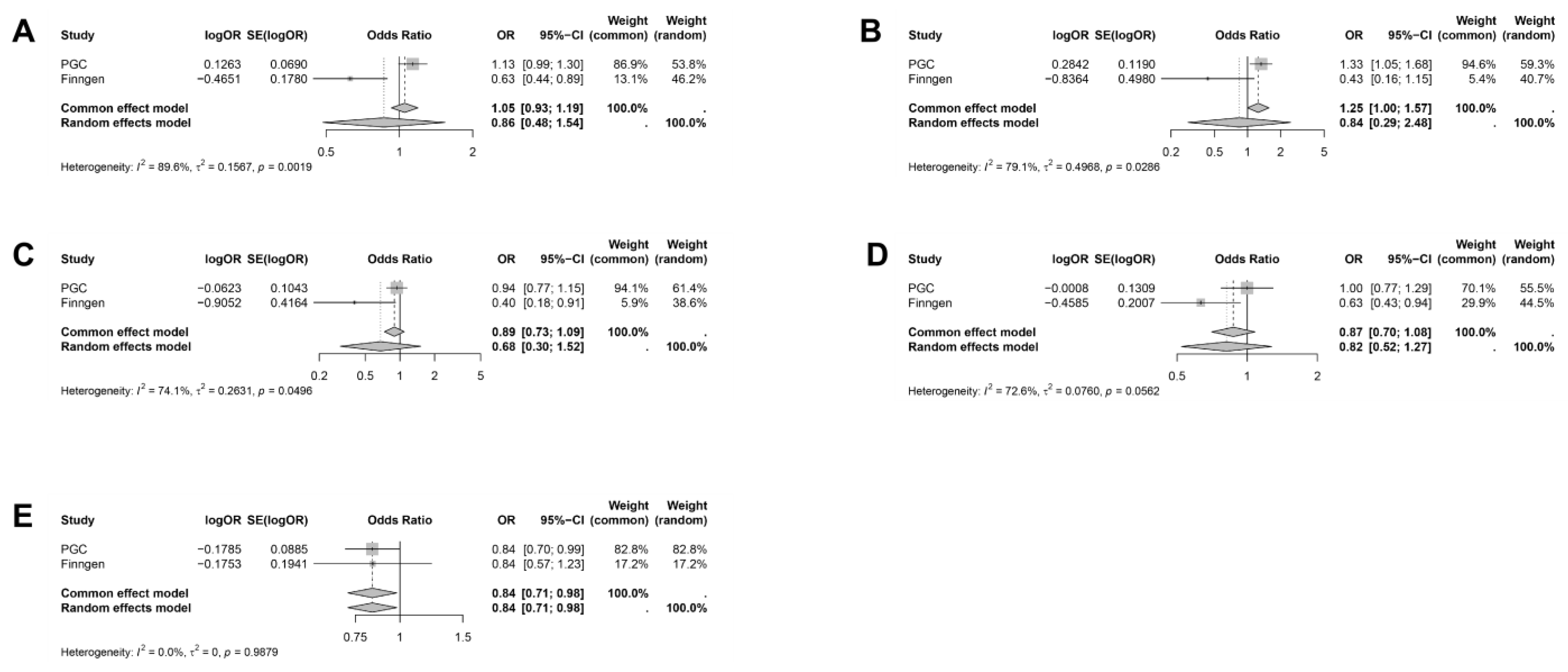
2.3. Meta-Analysis
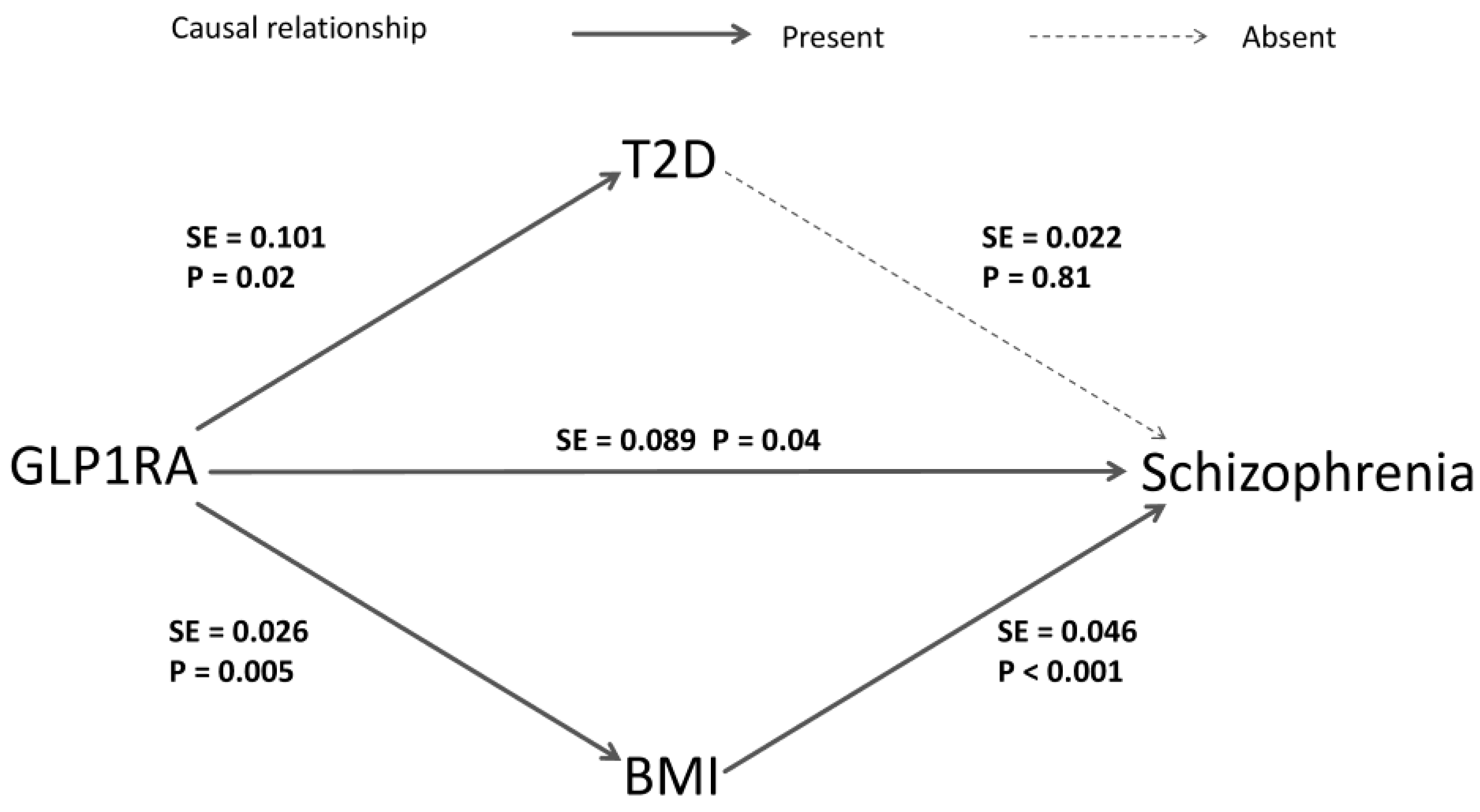
2.4. Meditation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Data Source
4.3. Genetic Instrumental Selection
4.4. MR and Sensitivity Analysis
4.5. Meta Analysis
4.6. Mediation Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| GLP1R | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor |
| GLP1RA | Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist |
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| ADHD | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| AN | Anorexia nervosa |
| ANX | Anxiety |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| BD | Bipolar disorder |
| MDD | Major depressive disorder |
| PTSD | Post-traumatic stress disorder |
| SZ | Schizophrenia |
| CUD | Cannabis use disorder |
| AUD | Alcohol use disorder |
| IVW | Inverse variance weighting |
| MR.RAPs | Mendelian randomization robust adjusted profile scores |
References
- Calsolaro, V.; Edison, P. Novel GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) Analogues and Insulin in the Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases. CNS Drugs 2015, 29, 1023–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.; Vaduganathan, M.; Chiu, N.; Bhatt, D.L. Potential implications of the FDA approval of semaglutide for overweight and obese adults in the United States. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 68, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.; Lund, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, F.; van Ommeren, M.; Flaxman, A.; Cornett, J.; Whiteford, H.; Saxena, S. New WHO prevalence estimates of mental disorders in conflict settings: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2019, 394, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, Z.; Marnane, C.; Iranpour, C.; Chey, T.; Jackson, J.W.; Patel, V.; Silove, D. The global prevalence of common mental disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis 1980–2013. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 476–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1789–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigo, D.; Thornicroft, G.; Atun, R. Estimating the true global burden of mental illness. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.H.; Sung, F.C.; Chiu, L.T.; Shih, Y.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Wu, S.I. Decreased risk of anxiety in diabetic patients receiving glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist: A nationwide, population-based cohort study. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 765446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, C.; Xue, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: Beyond Their Pancreatic Effects. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 721135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, N.; Hölscher, C. The neuroprotective effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: An in-depth review. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 970925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, O.Y.; Song, J. Alleviation of Depression by Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Through the Regulation of Neuroinflammation, Neurotransmitters, Neurogenesis, and Synaptic Function. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansur, R.B.; Ahmed, J.; Cha, D.S.; Woldeyohannes, H.O.; Subramaniapillai, M.; Lovshin, J.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, J.H.; Brietzke, E.; Reininghaus, E.Z.; et al. Liraglutide promotes improvements in objective measures of cognitive dysfunction in individuals with mood disorders: A pilot, open-label study. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 207, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadini, F.; Simeone, P.G.; Boccatonda, A.; Guagnano, M.T.; Liani, R.; Tripaldi, R.; Di Castelnuovo, A.; Cipollone, F.; Consoli, A.; Santilli, F.; et al. Liraglutide improves memory in obese patients with prediabetes or early type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled study. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderberg, R.H.; Richard, J.E.; Hansson, C.; Nissbrandt, H.; Bergquist, F.; Skibicka, K.P. GLP-1 is both anxiogenic and antidepressant; divergent effects of acute and chronic GLP-1 on emotionality. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 65, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Choi, T.; Al-Aly, Z. Mapping the effectiveness and risks of GLP1R agonists. Nat. Med. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanassoulis, G.; O’Donnell, C.J. Mendelian randomization: Nature’s randomized trial in the post-genome era. JAMA 2009, 301, 2386–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Ebrahim, S. ’Mendelian randomization’: Can genetic epidemiology contribute to understanding environmental determinants of disease? Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, V.M.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Martin, R.M. Mendelian randomization: A novel approach for the prediction of adverse drug events and drug repurposing opportunities. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 2078–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.F.; Finan, C.; Gordillo-Marañón, M.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Freitag, D.F.; Patel, R.S.; Tyl, B.; Chopade, S.; Faraway, R.; Zwierzyna, M.; et al. Genetic drug target validation using Mendelian randomisation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ference, B.A.; Ray, K.K.; Catapano, A.L.; Ference, T.B.; Burgess, S.; Neff, D.R.; Oliver-Williams, C.; Wood, A.M.; Butterworth, A.S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; et al. Mendelian Randomization Study of ACLY and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofat, R.; Hingorani, A.D.; Smeeth, L.; Humphries, S.E.; Talmud, P.J.; Cooper, J.; Shah, T.; Sandhu, M.S.; Ricketts, S.L.; Boekholdt, S.M.; et al. Separating the mechanism-based and off-target actions of cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors with CETP gene polymorphisms. Circulation 2010, 121, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, A.D.; Kuan, V.; Finan, C.; Kruger, F.A.; Gaulton, A.; Chopade, S.; Sofat, R.; MacAllister, R.J.; Overington, J.P.; Hemingway, H.; et al. Improving the odds of drug development success through human genomics: Modelling study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarmolinsky, J.; Bouras, E.; Constantinescu, A.; Burrows, K.; Bull, C.J.; Vincent, E.E.; Martin, R.M.; Dimopoulou, O.; Lewis, S.J.; Moreno, V.; et al. Genetically proxied glucose-lowering drug target perturbation and risk of cancer: A Mendelian randomisation analysis. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1481–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Thambisetty, M.; Ferrucci, L.; Johnell, K.; Hägg, S. Genetic Variation in Targets of Antidiabetic Drugs and Alzheimer Disease Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Neurology 2022, 99, e650–e659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Pang, X.; Du, R.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X. Genetically proxied antidiabetic drugs targets and stroke risk. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Si, S.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Duong, V.; Cai, Q.; Li, G.; Oo, W.M.; Zheng, X.; Boer, C.G.; et al. Exploring antidiabetic drug targets as potential disease-modifying agents in osteoarthritis. EBioMedicine 2024, 107, 105285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.M.; Goldberg, R.W.; McNary, S.W.; Dixon, L.B.; Lehman, A.F. Cognitive correlates of job tenure among patients with severe mental illness. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 1395–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, P.M.; Correll, C.U. The acute efficacy of antipsychotics in schizophrenia: A review of recent meta-analyses. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 8, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskind, D.; Hahn, M.; Correll, C.U.; Fink-Jensen, A.; Russell, A.W.; Bak, N.; Broberg, B.V.; Larsen, J.; Ishøy, P.L.; Vilsbøll, T.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists for antipsychotic-associated cardio-metabolic risk factors: A systematic review and individual participant data meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, H.; Xu, G.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J. Liraglutide improves cognitive impairment via the AMPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in type 2 diabetic rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2449–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.; Suzuki, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Mori, K.; Mogi, Y.; Oka, J.-I. The influences of juvenile diabetes on memory and hippocampal plasticity in rats: Improving effects of glucagon-like peptide-1. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 64, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palleria, C.; Leo, A.; Andreozzi, F.; Citraro, R.; Iannone, M.; Spiga, R.; Sesti, G.; Constanti, A.; De Sarro, G.; Arturi, F.; et al. Liraglutide prevents cognitive decline in a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes independently from its peripheral metabolic effects. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 321, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Sun, J.; Zhao, G.; Guo, A.; Chen, Y.; Fu, R.; Deng, Y. Liraglutide Improves Water Maze Learning and Memory Performance While Reduces Hyperphosphorylation of Tau and Neurofilaments in APP/PS1/Tau Triple Transgenic Mice. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 2326–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long-Smith, C.M.; Manning, S.; McClean, P.L.; Coakley, M.F.; O’Halloran, D.J.; Holscher, C.; O’Neill, C. The diabetes drug liraglutide ameliorates aberrant insulin receptor localisation and signalling in parallel with decreasing both amyloid-β plaque and glial pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med. 2013, 15, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Hölscher, C. Neuroprotective effects of a triple GLP-1/GIP/glucagon receptor agonist in the APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2018, 1678, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves Filho, A.M.; Cunha, N.L.; de Souza, A.G.; Verde-Ramo Soares, M.; Jucá, P.M.; de Queiroz, T.; Souza Oliveira, J.V.; Valvassori, S.S.; Barichello, T.; Quevedo, J.; et al. The GLP1R agonist liraglutide reverses mania-like alterations and memory deficits induced by D-amphetamine and augments lithium effects in mice: Relevance for bipolar disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 99, 109872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutlu, M.D.; Kose, S.; Akillioglu, K. GLP-1 agonist Liraglutide prevents MK-801-induced schizophrenia-like behaviors and BDNF, CREB, p-CREB, Trk-B expressions in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in Balb/c mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 445, 114386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flintoff, J.; Kesby, J.P.; Siskind, D.; Burne, T.H. Treating cognitive impairment in schizophrenia with GLP1RA: An overview of their therapeutic potential. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Tang, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, B.; et al. Investigating the shared genetic architecture between schizophrenia and body mass index. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 2312–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rødevand, L.; Rahman, Z.; Hindley, G.L.; Smeland, O.B.; Frei, O.; Tekin, T.F.; Kutrolli, G.; Bahrami, S.; Hoseth, E.Z.; Shadrin, A.; et al. Characterizing the Shared Genetic Underpinnings of Schizophrenia and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. Am. J. Psychiatry 2023, 180, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, R.; Saito, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Shimasaki, A.; Ashizawa, T.; Ito, K.; Ikeda, M.; Iwata, N. Shared genetic components between metabolic syndrome and schizophrenia: Genetic correlation using multipopulation data sets. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 76, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Rashidy-Pour, A.; Atkin, S.L.; Jamialahmadi, T.; Sahebkar, A. GLP-1 mimetics and cognition. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, E.; Akdede, B.B.; Alptekin, K. The relationship between cognitive impairment in schizophrenia and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2017, 47, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocarsly, M.E.; Fasolino, M.; Kane, G.A.; LaMarca, E.A.; Kirschen, G.W.; Karatsoreos, I.N.; McEwen, B.S.; Gould, E. Obesity diminishes synaptic markers, alters microglial morphology, and impairs cognitive function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15731–15736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari Laurindo, L.; Barbalho, S.M.; Guiguer, E.L.; Soares de Souza, M.S.; de Souza, G.A.; Fidalgo, T.M.; Araújo, A.C.; de Souza Gonzaga, H.F.; de Bortoli Teixeira, D.; de Oliveira Silva Ullmann, T.; et al. GLP-1a: Going beyond Traditional Use. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detka, J.; Głombik, K. Insights into a possible role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of depression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Guo, L.; Pan, Q. The Antidepressant Effects of GLP1R Agonists: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2024, 32, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.R.; Cao, J.; Wei, J.; Geng, W. Case Report: Semaglutide-associated depression: A report of two cases. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1238353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, A.; Dai, J.; Driskill, J.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H. Depression and obesity: Focus on factors and mechanistic links. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2025, 1871, 167561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobaiqy, M.; Elkout, H. Psychiatric adverse events associated with semaglutide, liraglutide and tirzepatide: A pharmacovigilance analysis of individual case safety reports submitted to the EudraVigilance database. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2024, 46, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElroy, S.L.; Mori, N.; Guerdjikova, A.I.; Keck, P.E. Would glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists have efficacy in binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa? A review of the current literature. Med. Hypotheses 2018, 111, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Gao, W.; Hu, H.; Zhou, S. Why 90% of clinical drug development fails and how to improve it? Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.; Georgakis, M.K.; Walker, V.M.; Schmidt, A.F.; Gkatzionis, A.; Freitag, D.F.; Finan, C.; Hingorani, A.D.; Howson, J.M.; Burgess, S.; et al. Mendelian randomization for studying the effects of perturbing drug targets. Wellcome Open Res. 2021, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Malarstig, A.; Thompson, S.G. Use of Mendelian randomisation to assess potential benefit of clinical intervention. BMJ 2012, 345, e7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Võsa, U.; Claringbould, A.; Westra, H.J.; Bonder, M.J.; Deelen, P.; Zeng, B.; Kirsten, H.; Saha, A.; Kreuzhuber, R.; Yazar, S.; et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1300–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, A.; Spracklen, C.N.; Zhang, W.; Ng, M.Y.; Petty, L.E.; Kitajima, H.; Yu, G.Z.; Rüeger, S.; Speidel, L.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. Multi-ancestry genetic study of type 2 diabetes highlights the power of diverse populations for discovery and translation. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yengo, L.; Sidorenko, J.; Kemper, K.E.; Zheng, Z.; Wood, A.R.; Weedon, M.N.; Frayling, T.M.; Hirschhorn, J.; Yang, J.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in ∼700000 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3641–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demontis, D.; Walters, G.B.; Athanasiadis, G.; Walters, R.; Therrien, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Farajzadeh, L.; Voloudakis, G.; Bendl, J.; Zeng, B.; et al. Genome-wide analyses of ADHD identify 27 risk loci, refine the genetic architecture and implicate several cognitive domains. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, M.I.; Karjalainen, J.; Palta, P.; Sipilä, T.P.; Kristiansson, K.; Donner, K.M.; Reeve, M.P.; Laivuori, H.; Aavikko, M.; Kaunisto, M.A.; et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature 2023, 613, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.J.; Yilmaz, Z.; Thornton, L.M.; Hübel, C.; Coleman, J.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; Bryois, J.; Hinney, A.; Leppä, V.M.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight risk loci and implicates metabo-psychiatric origins for anorexia nervosa. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otowa, T.; Hek, K.; Lee, M.; Byrne, E.M.; Mirza, S.S.; Nivard, M.G.; Bigdeli, T.; Aggen, S.H.; Adkins, D.; Wolen, A.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of anxiety disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.; Ripke, S.; Als, T.D.; Mattheisen, M.; Walters, R.K.; Won, H.; Pallesen, J.; Agerbo, E.; Andreassen, O.A.; Anney, R.; et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, N.; Forstner, A.J.; O’Connell, K.S.; Coombes, B.; Coleman, J.I.; Qiao, Z.; Als, T.D.; Bigdeli, T.B.; Børte, S.; Bryois, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.-K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis of depression identifies 102 independent variants and highlights the importance of the prefrontal brain regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievergelt, C.M.; Maihofer, A.X.; Klengel, T.; Atkinson, E.G.; Chen, C.-Y.; Choi, K.W.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Dalvie, S.; Duncan, L.E.; Gelernter, J.; et al. International meta-analysis of PTSD genome-wide association studies identifies sex- and ancestry-specific genetic risk loci. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature 2014, 511, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.C.; Demontis, D.; Thorgeirsson, T.E.; Walters, R.K.; Polimanti, R.; Hatoum, A.S.; Sanchez-Roige, S.; Paul, S.E.; Wendt, F.R.; Clarke, T.-K.; et al. A large-scale genome-wide association study meta-analysis of cannabis use disorder. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Roige, S.; Palmer, A.A.; Fontanillas, P.; Elson, S.L.; 23andMe Research Team; Substance Use Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium; Adams, M.J.; Howard, D.M.; Edenberg, H.J.; Davies, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Meta-Analysis of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) in Two Population-Based Cohorts. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945–D954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosoff, D.B.; Bell, A.S.; Jung, J.; Wagner, J.; Mavromatis, L.A.; Lohoff, F.W. Mendelian Randomization Study of PCSK9 and HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibition and Cognitive Function. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 80, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Liu, L.; Tzoulaki, I.; Fan, J.; Targher, G.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, J. Genetic Evidence for GLP-1 and GIP Receptors as Targets for Treatment and Prevention of MASLD/MASH. Liver Int. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J.; Holst, J.J. The expanding incretin universe: From basic biology to clinical translation. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1765–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Davey Smith, G.; Davies, N.M.; Dudbridge, F.; Gill, D.; Glymour, M.M.; Hartwig, F.P.; Kutalik, Z.; Holmes, M.V.; Minelli, C.; et al. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: Update for summer 2023. Wellcome Open Res. 2023, 4, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, S.; Butterworth, A.; Thompson, S.G. Mendelian randomization analysis with multiple genetic variants using summarized data. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Del Greco, M.F.; Minelli, C.; Zhao, Q.; Lawlor, D.A.; Sheehan, N.A.; Thompson, J.; Davey Smith, G. Improving the accuracy of two-sample summary-data Mendelian randomization: Moving beyond the NOME assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 48, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.R.; Sanderson, E.; Hammerton, G.; Richmond, R.C.; Davey Smith, G.; Heron, J.; Taylor, A.E.; Davies, N.M.; Howe, L.D. Mendelian randomisation for mediation analysis: Current methods and challenges for implementation. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 36, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Borges, M.C.; Hemani, G.; Lawlor, D.A. The role of glycaemic and lipid risk factors in mediating the effect of BMI on coronary heart disease: A two-step, two-sample Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 2210–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Pärna, K.; van Zon, S.R.; Snieder, H.; Thio, C.L. Mediators of the association between educational attainment and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A two-step multivariable Mendelian randomisation study. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1364–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, J.G., Jr.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: Myths and Truths about Mediation Analysis. J. Consum. Res. 2010, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Phenotypes | Source | Sample Size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| eQTL for GLP1R | eQTLGen consortium | 31,684 | [57] |
| T2D | DIAMANTE consortium 1 | 681,275 | [58] |
| BMI | GIANT consortium 2 | 933,970 | [59] |
| ADHD | PGC 3 | 38,691/225,534 | [60] |
| Finngen | 4452/490,708 | [61] | |
| AN | PGC | 16,992/72,517 | [62] |
| Finngen | 546/499,802 | [61] | |
| ANX | PGC | 7016/21,761 | [63] |
| Finngen | 35,875/444,414 | [61] | |
| ASD | PGC | 18,381/46,350 | [64] |
| Finngen | 888/362,304 | [61] | |
| BD | PGC | 41,917/413,466 | [65] |
| Finngen | 8946/434,831 | [61] | |
| MDD | PGC | 43,204/138,884 | [66] |
| Finngen | 59,333/434,831 | [61] | |
| PTSD | PGC | 32,428/206,655 | [67] |
| Finngen | 3444/444,414 | [61] | |
| SZ | PGC | 30,989/113,075 | [68] |
| Finngen | 7234/484,776 | [61] | |
| CUD | PGC | 20,916/363,116 | [69] |
| Finngen | 1168/491,508 | [61] | |
| AUD | PGC | 141,932 | [70] |
| Finngen | 20,597/479,751 | [61] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, L.; Peng, Y. Impact of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Mental Illness: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062741
Xiang L, Peng Y. Impact of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Mental Illness: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062741
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Longgang, and Ying Peng. 2025. "Impact of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Mental Illness: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062741
APA StyleXiang, L., & Peng, Y. (2025). Impact of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Mental Illness: Evidence from a Mendelian Randomization Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062741






