Activin A Inhibitory Peptides Suppress Fibrotic Pathways by Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transformation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
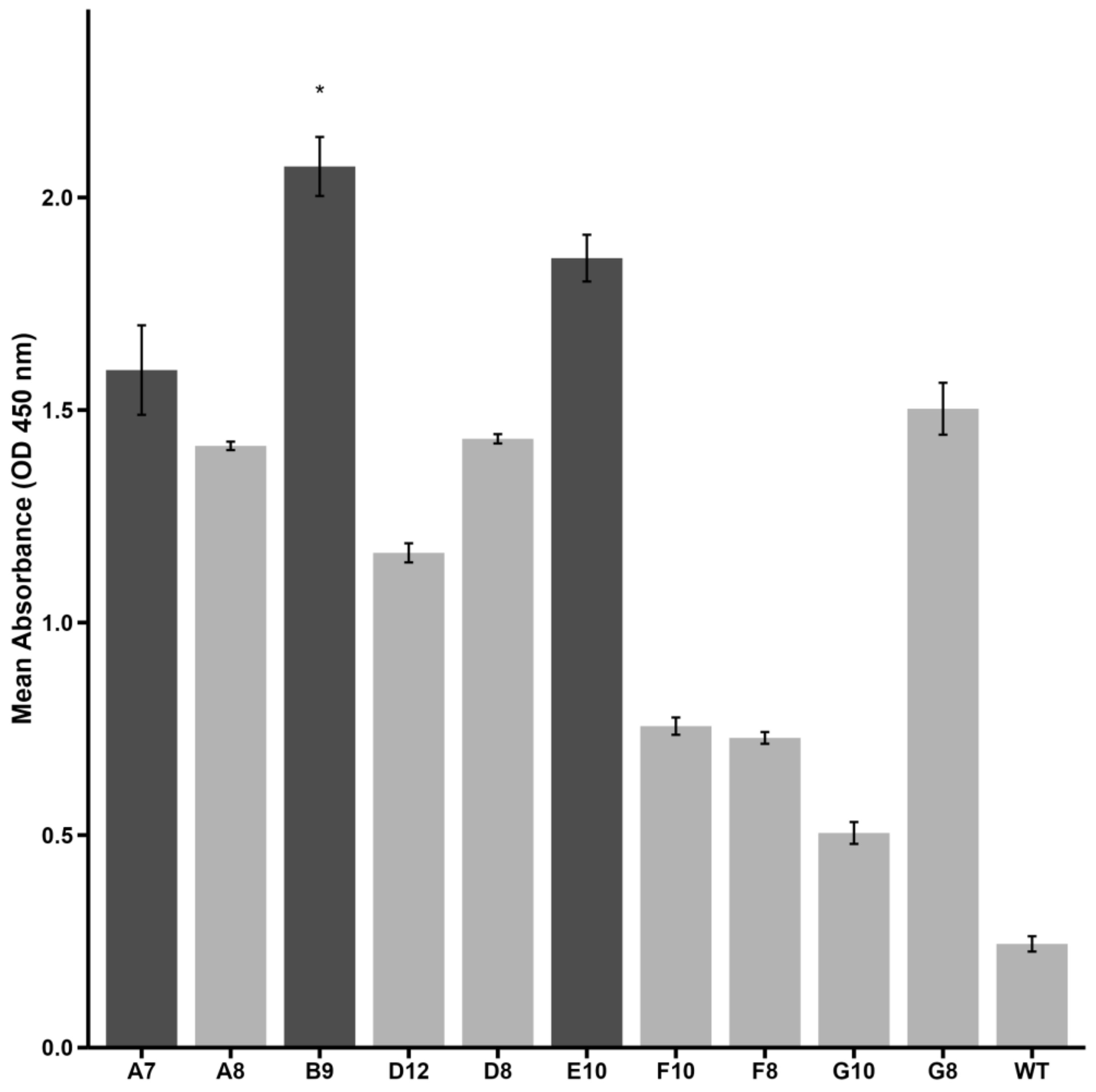
2.1. Peptide Selection by Phage Display
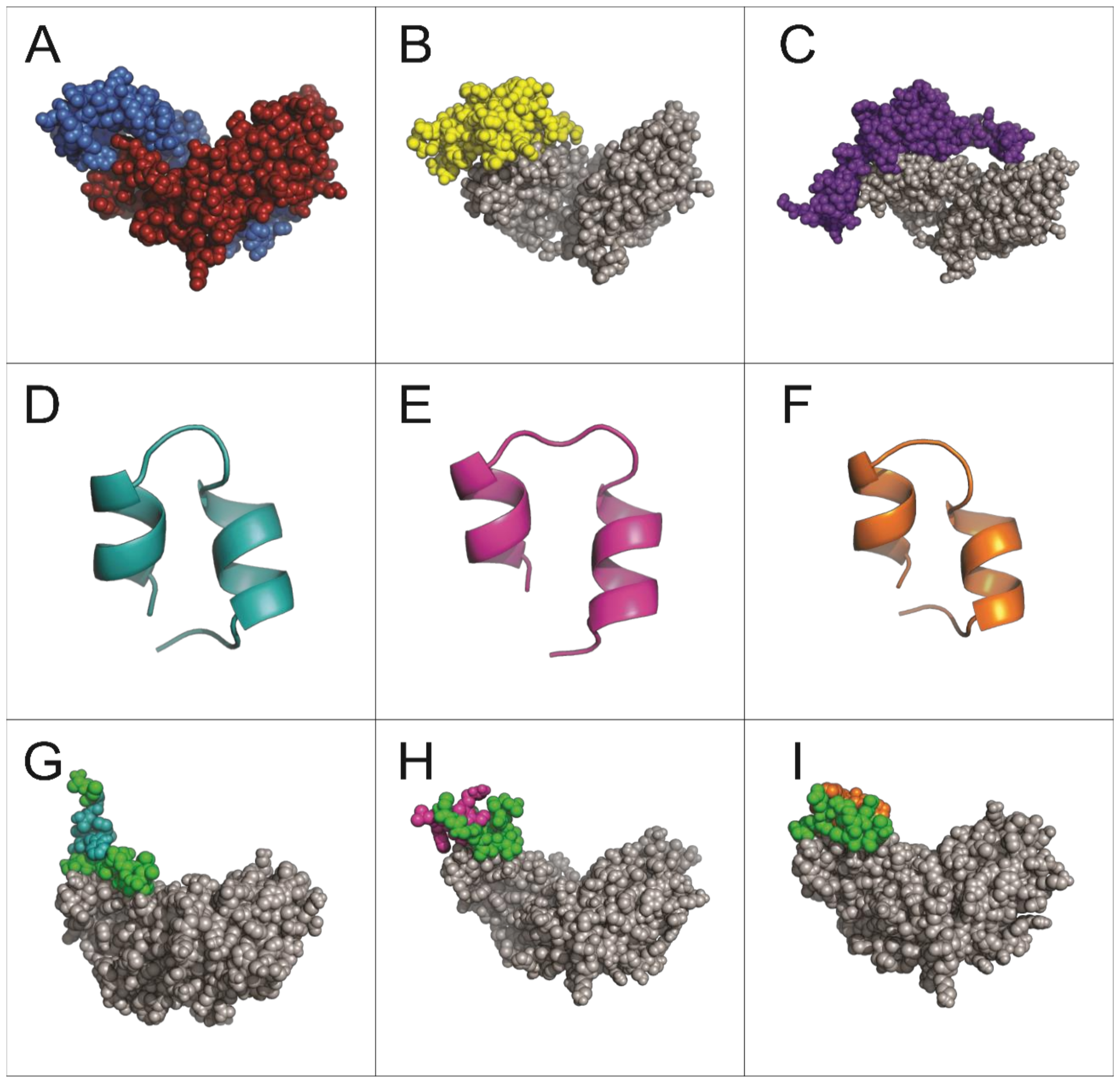
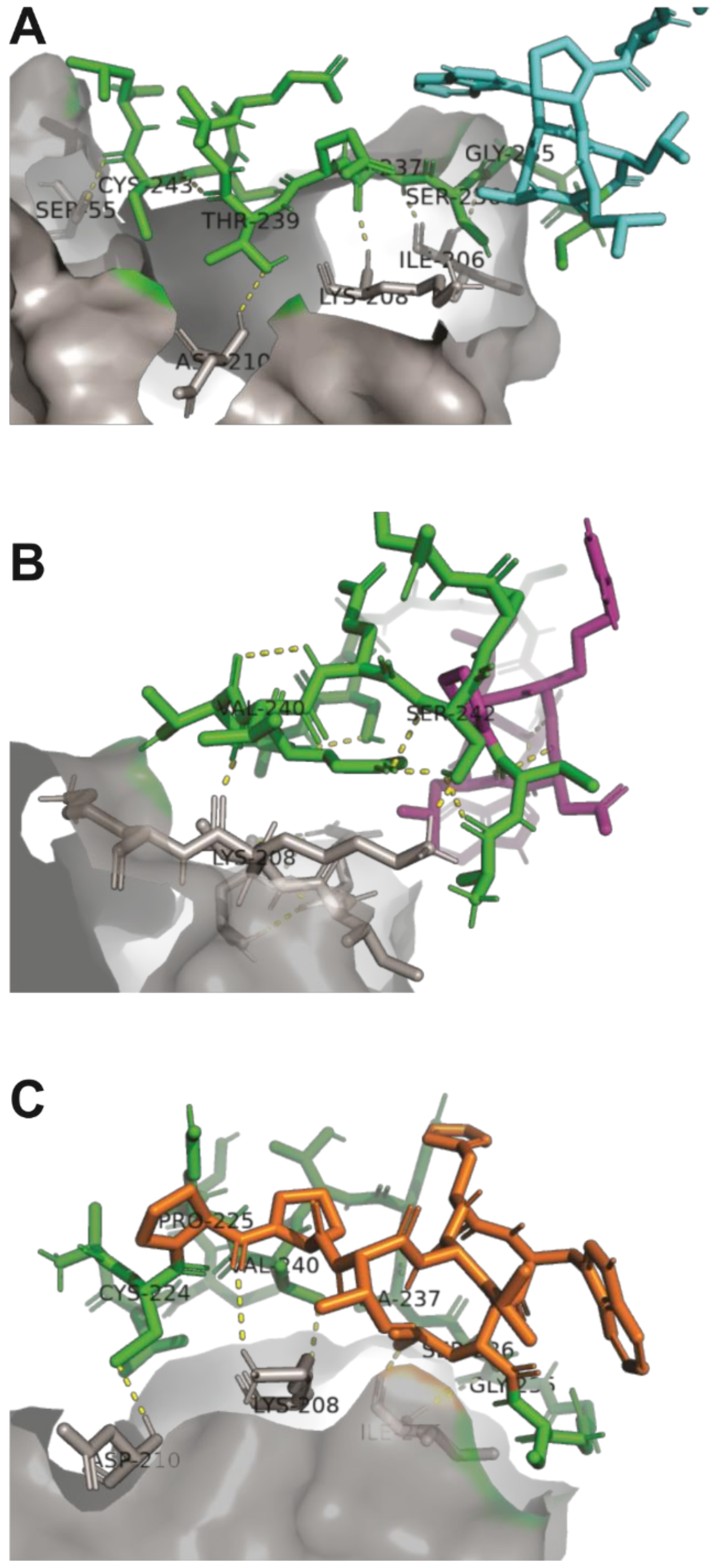
2.2. Structural Analysis and Interaction of Selected Peptides with Activin A
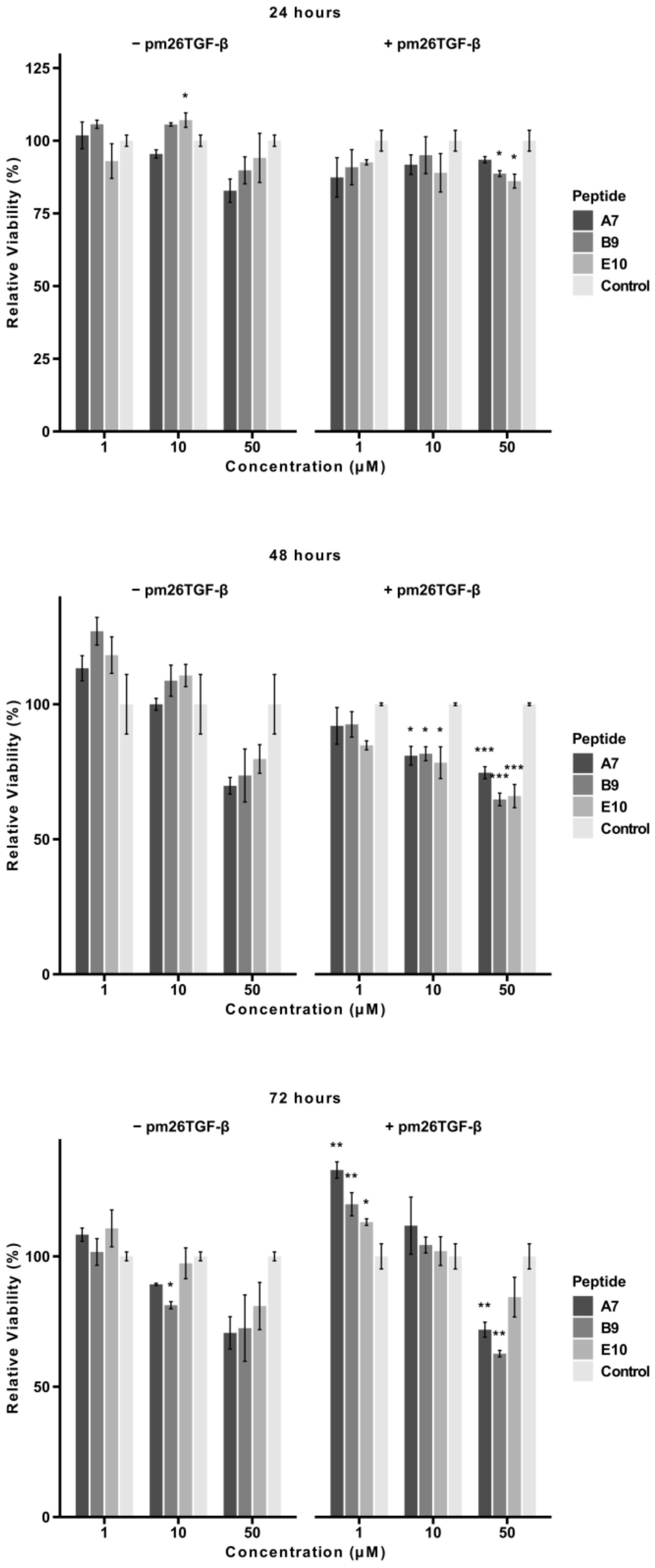
2.3. Cytotoxicity of Selected Peptides
2.4. Cellular Migration
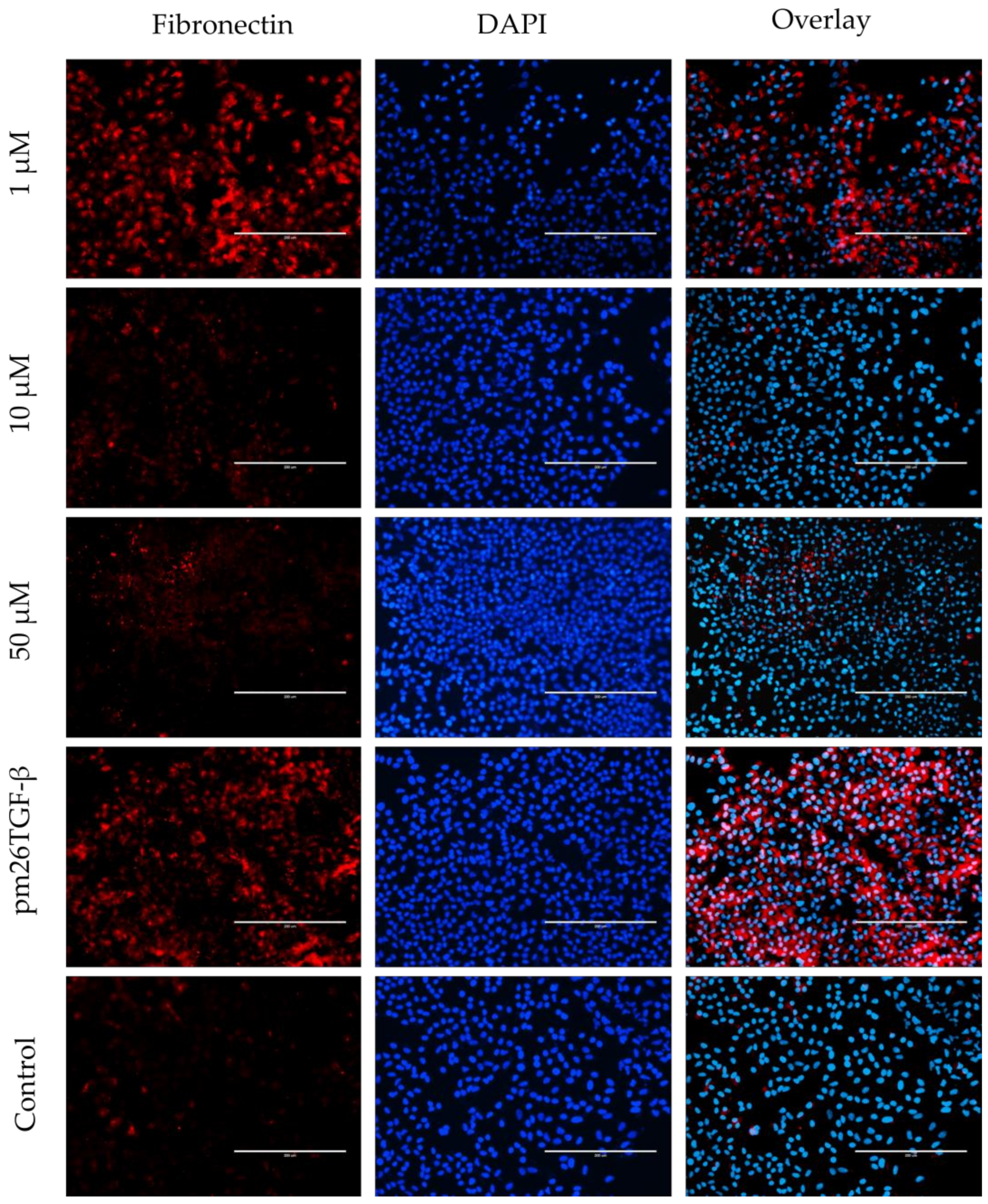
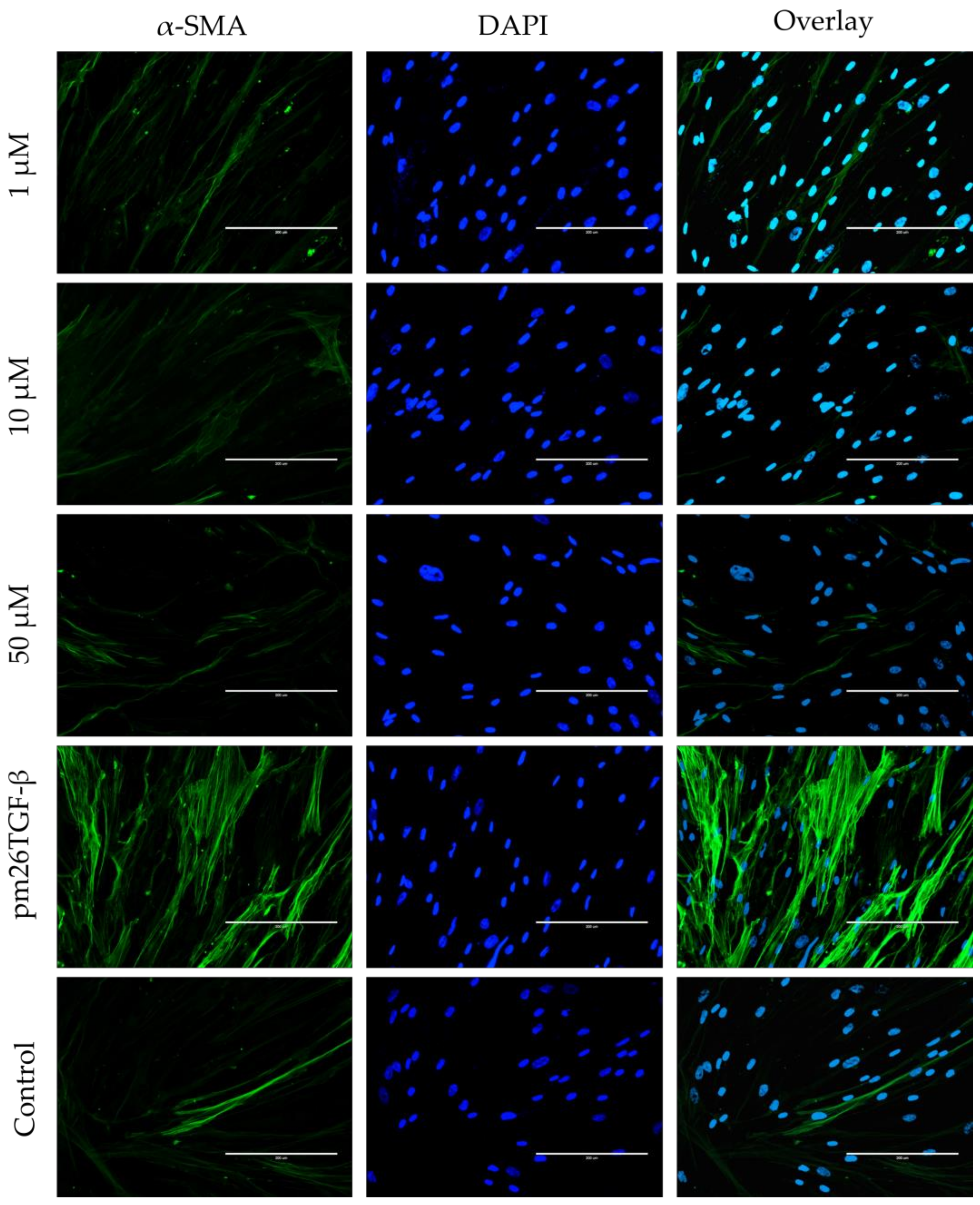
2.5. EMT and FMT Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
Cell Lines and Primary Culture
4.2. Phage Display Screening
4.3. Phage DNA Sequencing
4.4. In Silico Analysis
4.5. Peptide Synthesis
4.6. Cell Culture Assays
4.6.1. Cytotoxicity Assay by MTT
4.6.2. Cellular Migration
4.6.3. Fibroblast-to-Myofibroblast Transition (FMT) Assay
4.6.4. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Assay
4.6.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Urteaga, M.B.; Ruz, J.R.; González, M.S. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Radiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 64, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, P.; Kropski, J.A.; Jones, M.G.; Lee, J.S.; Rossi, G.; Karampitsakos, T.; Maher, T.M.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Ryerson, C.J. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Disease Mechanisms and Drug Development. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 222, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.M.; Spagnolo, P.; Kreuter, M.; Altinisik, G.; Bonifazi, M.; Martinez, F.J.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Renzoni, E.A.; Richeldi, L.; Tomassetti, S.; et al. Progressive Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease: Clinical Uncertainties, Consensus Recommendations, and Research Priorities. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudstaal, T.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Presse Medicale 2023, 52, 104166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, D.S.; Grossfeld, D.; Renna, H.A.; Agarwala, P.; Spiegler, P.; DeLeon, J.; Reiss, A.B. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Current and Future Treatment. Clin. Respir. J. 2022, 16, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolanczuk, A.J.; Thomson, C.C.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Martinez, F.J.; Kolb, M.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: State of the Art for 2023. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 61, 2200957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.; Fabiano, A.; Mota, P.C.; Rodrigues, I.; Carvalho, D.; Melo, N.; Novais-Bastos, H.; Alexandre, A.T.; Moura, C.S.; Guimarães, S.; et al. The Impact of Nintedanib and Pirfenidone on Lung Function and Survival in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in Real-Life Setting. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 83, 102261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Hong, Y.; Luo, F. Bibliometric Analysis of the Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Interstitial Lung Diseases. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morianos, I.; Papadopoulou, G.; Semitekolou, M.; Xanthou, G. Activin-A in the Regulation of Immunity in Health and Disease. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 104, 102314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, Y. Exacerbation of Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Acute Lung Injury via Activin-A Production by Recruited Alveolar Macrophages. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 7709–7728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, C.; Hense, G.; Martin, C.; Epstein, M.; Rückert, B.; Mantel, P.-Y.; Menz, G.; Uhlig, S.; Blaser, K.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B. Activin A Is an Acute Allergen-Responsive Cytokine and Provides a Link to TGF-β–Mediated Airway Remodeling in Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 117, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundra, S.; Kaur, R.; Pasricha, C.; Kumari, P.; Singh, T.G.; Singh, R. Pathological Insights into Activin A: Molecular Underpinnings and Therapeutic Prospects in Various Diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.L.; de Kretser, D.M.; Patella, S.; Phillips, D.J. Activin A and Follistatin in Systemic Inflammation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 225, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Han, L.; Chen, Y.; Wu, H. Progranulin and Activin A Concentrations Are Elevated in Serum from Patients with Acute Exacerbations of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 2021, 199, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Suo, L.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L.; Wan, G.; Han, X. Activin a Promotes Myofibroblast Differentiation of Endometrial Mesenchymal Stem Cells via STAT3-Dependent Smad/CTGF Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younesi, F.S.; Miller, A.E.; Barker, T.H.; Rossi, F.M.V.; Hinz, B. Fibroblast and Myofibroblast Activation in Normal Tissue Repair and Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 617–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, C.L.; King, S.J.; Mifsud, N.A.; Hedger, M.P.; Phillips, D.J.; Mackay, F.; de Kretser, D.M.; Wilson, J.W.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E. The Activin A Antagonist Follistatin Inhibits Cystic Fibrosis-like Lung Inflammation and Pathology. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietecha, M.S.; Pensalfini, M.; Cangkrama, M.; Müller, B.; Jin, J.; Brinckmann, J.; Mazza, E.; Werner, S. Activin-Mediated Alterations of the Fibroblast Transcriptome and Matrisome Control the Biomechanical Properties of Skin Wounds. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, I.; Takei, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Okada, M.; Maeshima, A. The Activin-Follistatin System: Key Regulator of Kidney Development, Regeneration, Inflammation, and Fibrosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 81, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, A.E.; Morris-Triggs, S.A.; Ruotolo, B.T.; Robinson, C.V.; Ohnuma, S.; Hyvönen, M. Structural Basis for the Inhibition of Activin Signalling by Follistatin. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamper, A.M.; Fleming, R.H.; Ladd, K.M.; Lee, A.S.Y. A Phosphorylation-Regulated EIF3d Translation Switch Mediates Cellular Adaptation to Metabolic Stress. Science 2020, 370, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozans, S.J.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Wu, Y.; Atanasoff, K.; Nino, L.; Dunne, K.; Pashuck, E.T. Quantifying and Controlling the Proteolytic Degradation of Cell Adhesion Peptides. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 10, 4916–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozans, S.J.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Pashuck, E.T. A Streamlined High-Throughput LC-MS Assay for Quantifying Peptide Degradation in Cell Culture. bioRxiv 2024, 113, e37864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonella, F.; Spagnolo, P.; Ryerson, C. Current and Future Treatment Landscape for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Drugs 2023, 83, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zeng, Y. Progress in Understanding and Treating Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Recent Insights and Emerging Therapies. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1205948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, M.; Screm, G.; Salton, F.; Confalonieri, P.; Trotta, L.; Barbieri, M.; Ruggero, L.; Mari, M.; Reccardini, N.; Geri, P.; et al. Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Lights and Shadows. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, M.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, B.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wei, W. Real-World Safety and Effectiveness of Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 1445–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Wairkar, S. Revolutionizing the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: From Conventional Therapies to Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Molina, M. The Future of Pharmacological Treatment in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Arch. Bronconeumol. (Engl. Ed.) 2019, 55, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libra, A.; Sciacca, E.; Muscato, G.; Sambataro, G.; Spicuzza, L.; Vancheri, C. Highlights on Future Treatments of IPF: Clues and Pitfalls. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, I.; Afzal, M.; Islam, A.; Sohal, S.S.; Hassan, M.I. Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pathophysiology, Cellular Signaling, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Accel. Drug Discov. 2023, 20, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namwanje, M.; Brown, C.W. Activins and Inhibins: Roles in Development, Physiology, and Disease. CSH Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a021881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Schneyer, A.L. The Biology of Activin: Recent Advances in Structure, Regulation and Function. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 202, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, H.; Sin, T.K.; Zhang, G. Activin A Induces Leiomyoma Cell Proliferation, Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Accumulation and Myofibroblastic Transformation of Myometrial Cells via P38 MAPK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Ni, L.; Wu, X. Activin A Activation Drives Renal Fibrosis through the STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 134, 105950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Z.; Yin, R.; Nie, J.; Fu, Y.; Ying, R. Knockdown of Dual Oxidase 1 Suppresses Activin A-Induced Fibrosis in Cardiomyocytes via the Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Pyroptotic Pathway. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2021, 131, 105902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.-L.; Li, X.-J.; Duan, T.-T.; Li, Z.-H.; Yang, J.-Z.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Zou, L.; Miao, H.; Zhao, Y.-Y. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling: From Tissue Fibrosis to Therapeutic Opportunities. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 369, 110289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, F.; Kurabayashi, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kojima, I. Attenuation of Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Follistatin. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Bhasin, S.; Klickstein, L.; Krishnan, V.; Rooks, D. Challenges and Future Prospects of Targeting Myostatin/Activin A Signaling to Treat Diseases of Muscle Loss and Metabolic Dysfunction. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2023, 78, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaden, B.C.; Wang, Y.X.; Wilson, J.M.; Culver, A.E.; Milner, A.; Datta-Mannan, A.; Shetler, P.; Croy, J.E.; Dai, G.; Krishnan, V. Inhibition of Activin A Ameliorates Skeletal Muscle Injury and Rescues Contractile Properties by Inducing Efficient Remodeling in Female Mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polkey, M.I.; Praestgaard, J.; Berwick, A.; Franssen, F.M.E.; Singh, D.; Steiner, M.C.; Casaburi, R.; Tillmann, H.-C.; Lach-Trifilieff, E.; Roubenoff, R.; et al. Activin Type II Receptor Blockade for Treatment of Muscle Depletion in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 199, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Suragani, R.N.V.S.; Aluri, S.; Shah, N.; Bhagat, T.D.; Alexander, M.J.; Komrokji, R.; Kumar, R. Biological Basis for Efficacy of Activin Receptor Ligand Traps in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Long, Y.; Yu, X.; Tong, Y.; Gong, L. Different Immunoregulation Roles of Activin A Compared With TGF-β. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 921366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossino, G.; Marchese, E.; Galli, G.; Verde, F.; Finizio, M.; Serra, M.; Linciano, P.; Collina, S. Peptides as Therapeutic Agents: Challenges and Opportunities in the Green Transition Era. Molecules 2023, 28, 7165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabri, W.; Cantelmi, P.; Corbisiero, D.; Fantoni, T.; Ferrazzano, L.; Martelli, G.; Mattellone, A.; Tolomelli, A. Therapeutic Peptides Targeting PPI in Clinical Development: Overview, Mechanism of Action and Perspectives. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 697586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karande, S.; Sharma, K.; Kumar, A.; Charan, S.; Patil, C.; Sharma, A. Potential Role of Biopeptides in the Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Health Sci. Rev. 2023, 6, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.J. Functional Analysis of the Cysteine Residues of Activin A. Mol. Endocrinol. 1994, 8, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.A.; Gray, P.C.; Vale, W.W.; Robertson, D.M. Antagonists of Activin Signaling: Mechanisms and Potential Biological Applications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.B.; Woodruff, T.K.; Jardetzky, T.S. Structures of an ActRIIB:Activin A Complex Reveal a Novel Binding Mode for TGF-β Ligand:Receptor Interactions. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, W.; Park, M.; Donaldson, C.; Wiater, E.; Vaughan, J.; Bilezikjian, L.; Vale, W. Residues in the C-Terminal Region of Activin A Determine Specificity for Follistatin and Type II Receptor Binding. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 176, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Chen, J.; Qin, J.; Chen, R.; Yi, Z. TGF-β-Induced α-SMA Expression Is Mediated by C/EBPβ Acetylation in Human Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulivendala, G.; Bale, S.; Godugu, C. Honokiol: A Polyphenol Neolignan Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Inhibiting TGF-β/Smad Signaling, Matrix Proteins and IL-6/CD44/STAT3 Axis Both in vitro and in vivo. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 391, 114913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Hou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, T.; Cui, Y.; Nie, H. MiR-130a-3p Alleviates Inflammatory and Fibrotic Phases of Pulmonary Fibrosis Through Proinflammatory Factor TNF-α and Profibrogenic Receptor TGF-ΒRII. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 863646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, H.; Luan, J.; Gao, S.; Li, S.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, R.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; et al. Fedratinib Attenuates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis via the JAK2/STAT3 and TGF-Β1 Signaling Pathway. Molecules 2021, 26, 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerner, A.M.; Zuraw, B.L. TGF-Β1 Induced Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Is Enhanced by IL-1β but Not Abrogated by Corticosteroids. Respir. Res. 2009, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, H.; Allen, J.T.; Mason, R.M.; Kamimura, T.; Zhang, Z. TGF-Β1 Induces Human Alveolar Epithelial to Mesenchymal Cell Transition (EMT). Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzani, S.; Musso, T. The Yin and Yang of Activin A. Blood 2011, 117, 5013–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Fibroblast—Extracellular Matrix Interactions in Tissue Fibrosis. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2016, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, C.B.; Kilian, K.A. Matrix Mechanics Influence Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transition by Directing the Localization of Histone Deacetylase 4. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2017, 10, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, G.S.; Wood, S.; Ona, V.; Li, D.J.; Lukashev, M.E.; Weinreb, P.H.; Simon, K.J.; Hahm, K.; Allaire, N.E.; Rinaldi, N.J.; et al. Partial Inhibition of Integrin Avβ6 Prevents Pulmonary Fibrosis without Exacerbating Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Geng, B.; Jiang, W.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Hao, B.; Li, N.; Geng, Q. Histone Deacetylase 3 Deletion in Alveolar Type 2 Epithelial Cells Prevents Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Clin. Epigenetics 2023, 15, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, X.; Hua, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhen, L.; Wang, G.; Lü, J.; Luo, A.; Cho, W.C.; et al. YY1 Mediates TGF-Β1-Induced EMT and pro-Fibrogenesis in Alveolar Epithelial Cells. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doolin, M.T.; Smith, I.M.; Stroka, K.M. Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transition Is Enhanced by Increased Cell Density. Mol. Biol. Cell 2021, 32, ar41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, M.; Kurniawan, N.A. Mechanical and Physical Regulation of Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transition: From Cellular Mechanoresponse to Tissue Pathology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 609653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorio, J.D.; Robuffo, I.; Spalletta, S.; Giambuzzi, G.; Iuliis, V.D.; Toniato, E.; Martinotti, S.; Conti, P.; Flati, V. The Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition as a Possible Therapeutic Target in Fibrotic Disorders. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 607483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusama, K.; Fukushima, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Azumi, M.; Yoshie, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Kajihara, T.; Tamura, K. PGE2 and Thrombin Induce Myofibroblast Transdifferentiation via Activin A and CTGF in Endometrial Stromal Cells. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Džepina, P.; Ćorić, M.; Perica, M.K.; Aničić, M.N.; Grizelj, R.; Vuković, J. Expression of Activin A in Liver Tissue and the Outcome of Patients with Biliary Atresia. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1457837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yang, T.; Zhou, J.; Wang, R.; Li, X. A Real-World Study of Antifibrotic Drugs-Related Adverse Events Based on the United States Food and Drug Administration Adverse Event Reporting System and VigiAccess Databases. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1310286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, E.R.; Fujimura, P.T.; Araujo, G.R.; da Silva, C.A.T.; Silva, R.L.; Cunha, T.M.; Lopes-Ferreira, M.; Lima, C.; Ferreira, M.J.; Cunha-Junior, J.P.; et al. A Short Peptide That Mimics the Binding Domain of TGF-Β1 Presents Potent Anti-Inflammatory Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbas, C.F., III; Burton, D.R.; Scott, J.K.; Silverman, G.J. Phage Display: A Laboratory Manua. Q. Rev. Biol. 2001, 76, 487–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The Proteomics Server for in-Depth Protein Knowledge and Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Maupetit, J.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. Improved PEP-FOLD Approach for Peptide and Miniprotein Structure Prediction. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 4745–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thévenet, P.; Shen, Y.; Maupetit, J.; Guyon, F.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. PEP-FOLD: An Updated de Novo Structure Prediction Server for Both Linear and Disulfide Bonded Cyclic Peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W288–W293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamiable, A.; Thévenet, P.; Rey, J.; Vavrusa, M.; Derreumaux, P.; Tufféry, P. PEP-FOLD3: Faster de Novo Structure Prediction for Linear Peptides in Solution and in Complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Heo, L.; Lee, M.S.; Seok, C. GalaxyPepDock: A Protein–Peptide Docking Tool Based on Interaction Similarity and Energy Optimization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W431–W435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bastos, V.A.F.; Fujimura, P.T.; Souza, A.G.d.; Vaz, E.R.; Saito, N.; Sabino-Silva, R.; Goulart, L.R.; Cunha, T.M. Activin A Inhibitory Peptides Suppress Fibrotic Pathways by Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transformation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062705
Bastos VAF, Fujimura PT, Souza AGd, Vaz ER, Saito N, Sabino-Silva R, Goulart LR, Cunha TM. Activin A Inhibitory Peptides Suppress Fibrotic Pathways by Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transformation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062705
Chicago/Turabian StyleBastos, Victor Alexandre F., Patrícia Tiemi Fujimura, Aline Gomes de Souza, Emília Rezende Vaz, Natieli Saito, Robinson Sabino-Silva, Luiz Ricardo Goulart, and Thulio Marquez Cunha. 2025. "Activin A Inhibitory Peptides Suppress Fibrotic Pathways by Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transformation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062705
APA StyleBastos, V. A. F., Fujimura, P. T., Souza, A. G. d., Vaz, E. R., Saito, N., Sabino-Silva, R., Goulart, L. R., & Cunha, T. M. (2025). Activin A Inhibitory Peptides Suppress Fibrotic Pathways by Targeting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Fibroblast–Myofibroblast Transformation in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062705





