Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
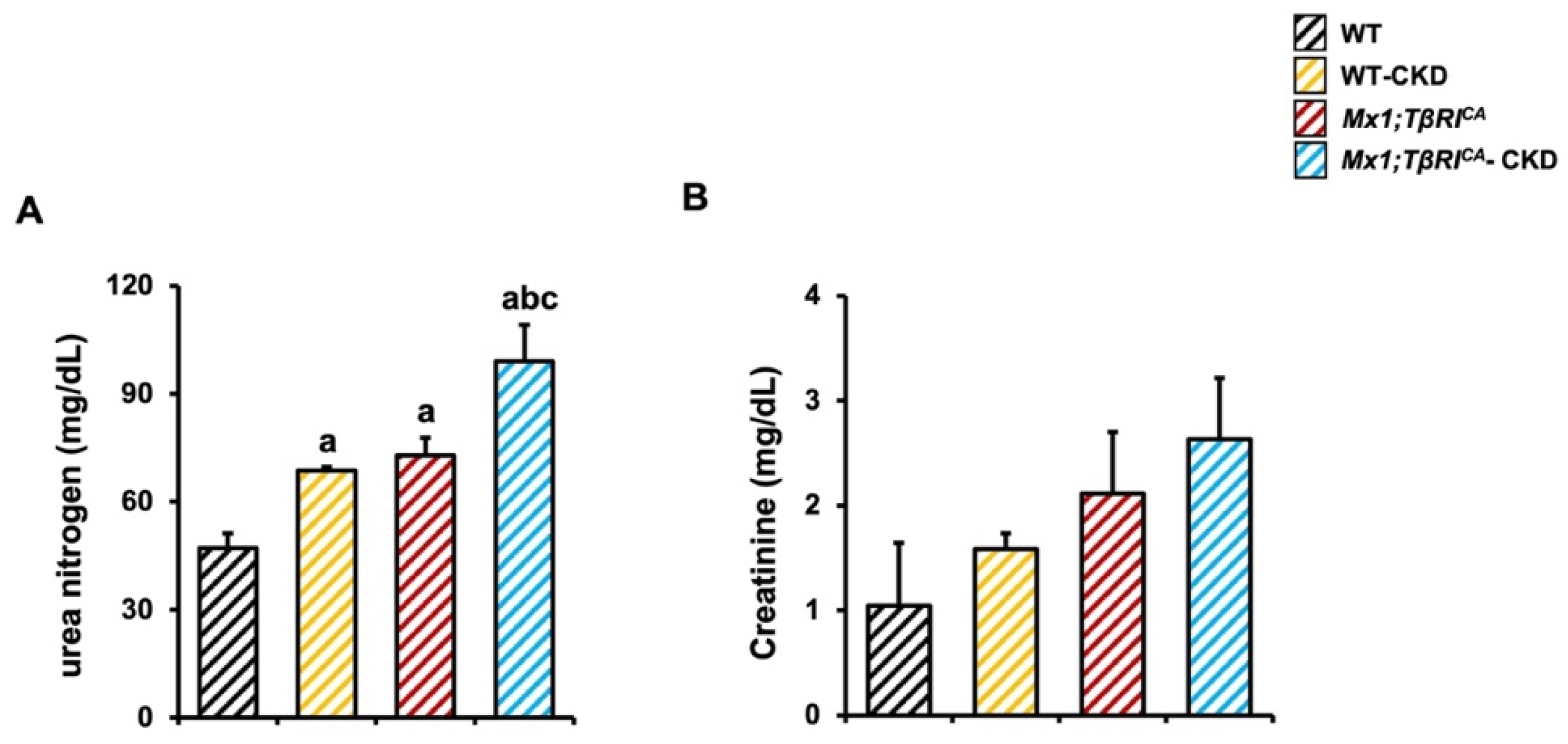
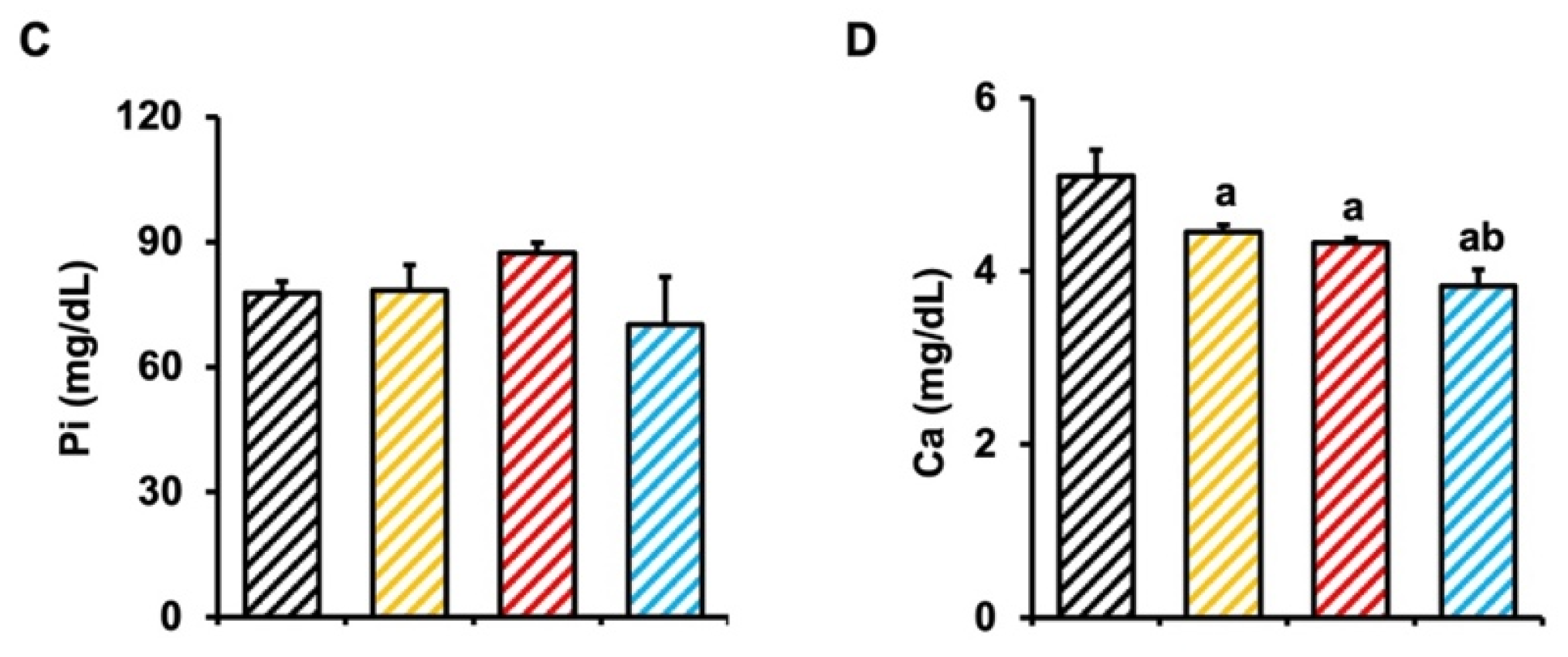
2.1. CKD Mice Display Characteristics of Abnormal Renal Function, and More Severe Characteristics Were Found in Mx1;TβRICA Mice
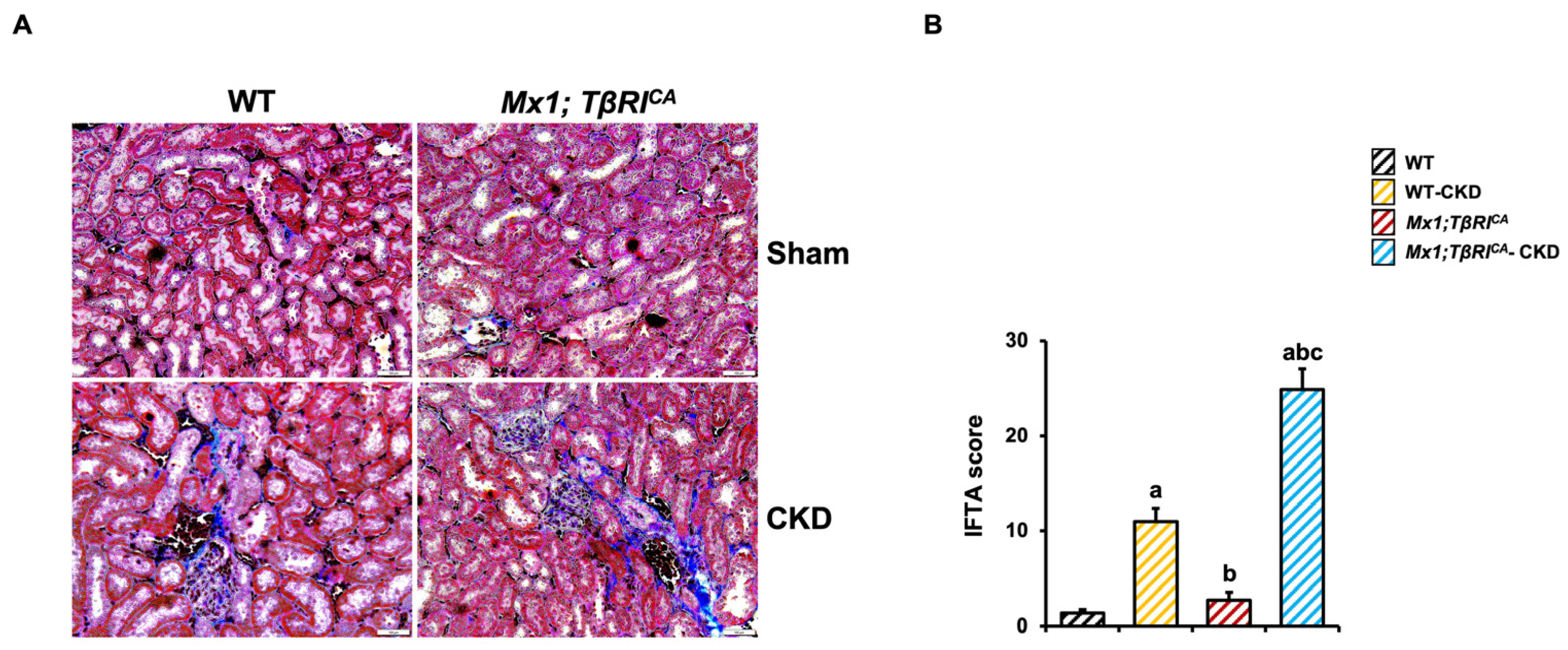
2.2. TβRI Induces Renal Fibrosis During CKD
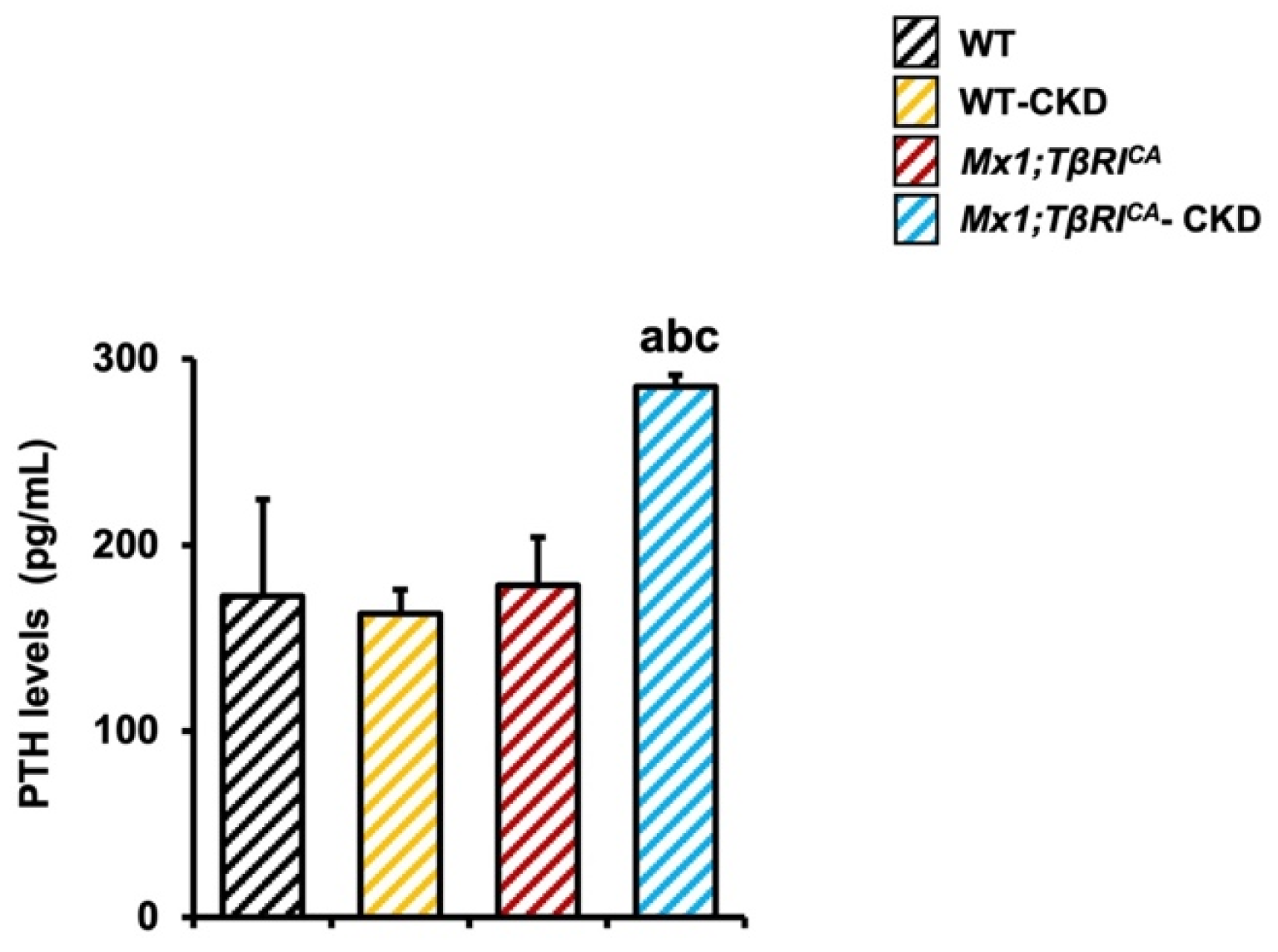
2.3. Mx1;TβRICA-CKD Mice Have Increased Serum PTH Levels
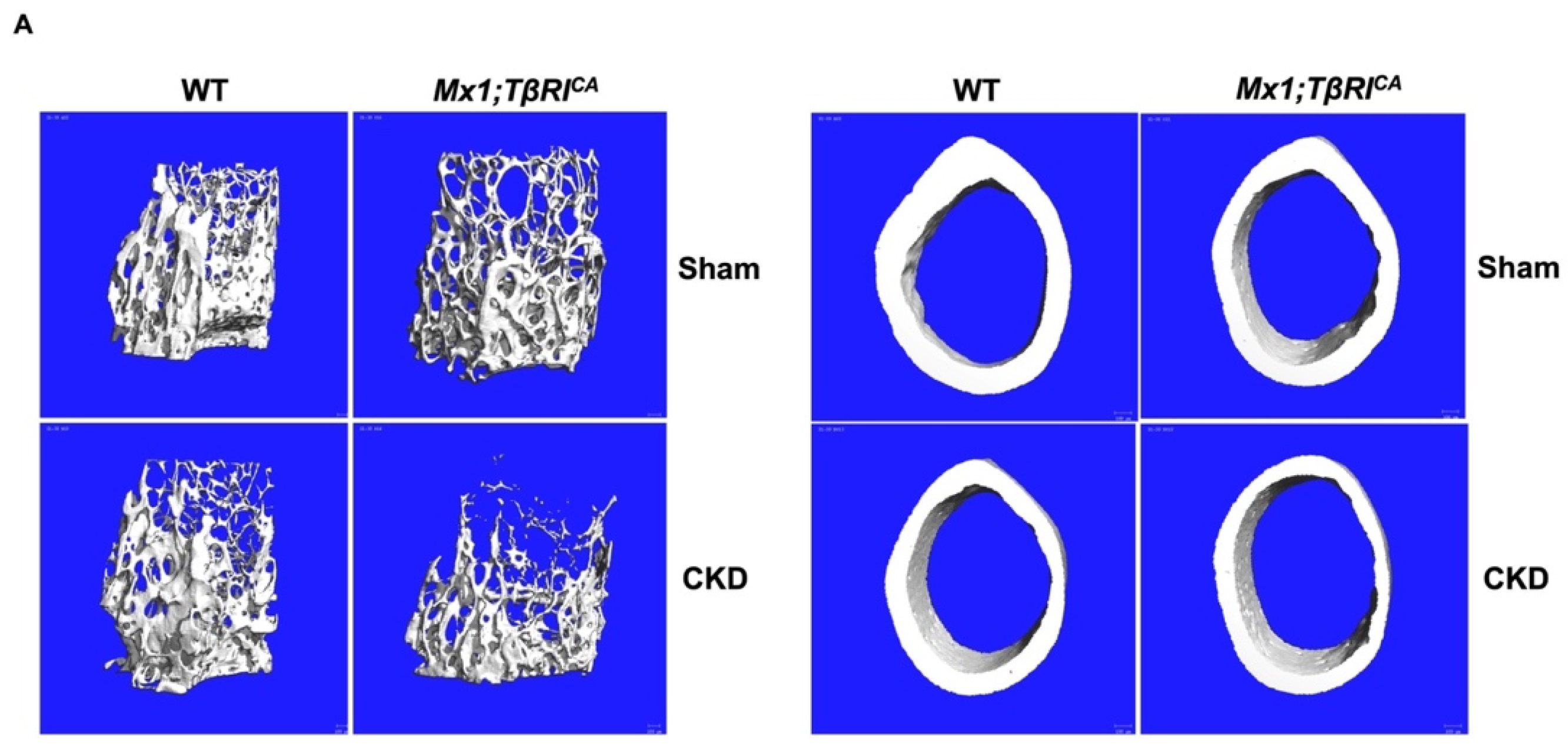
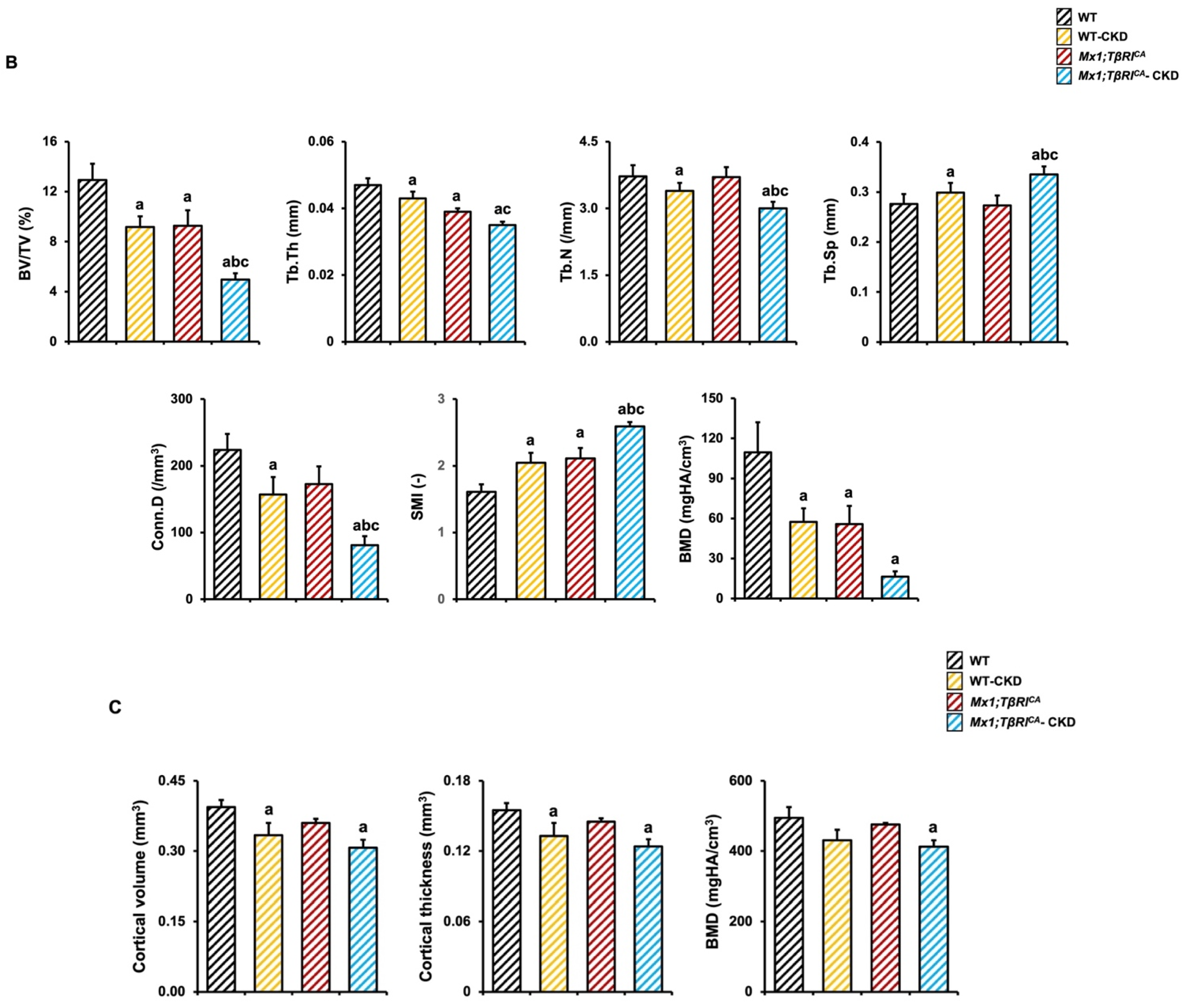
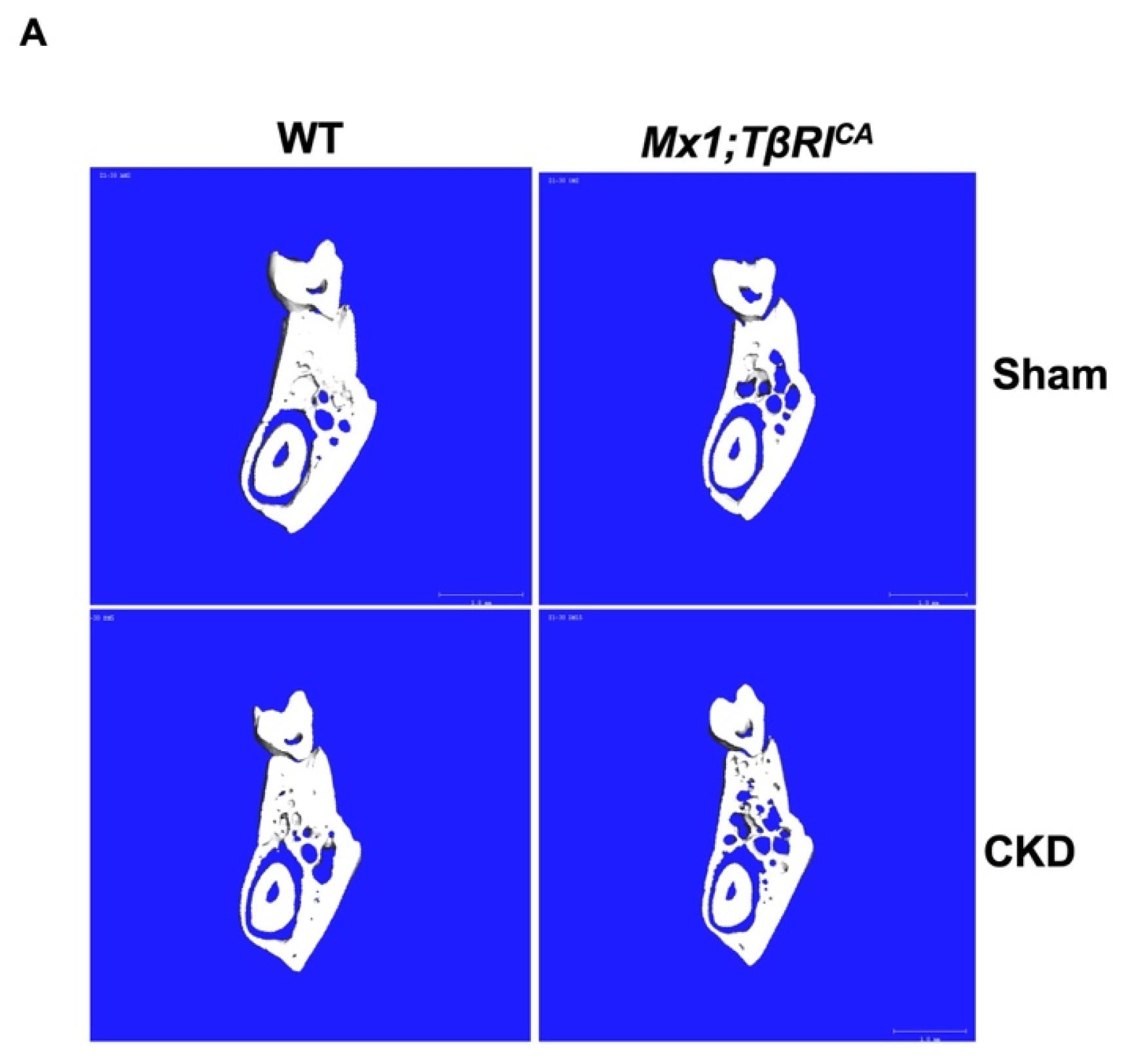
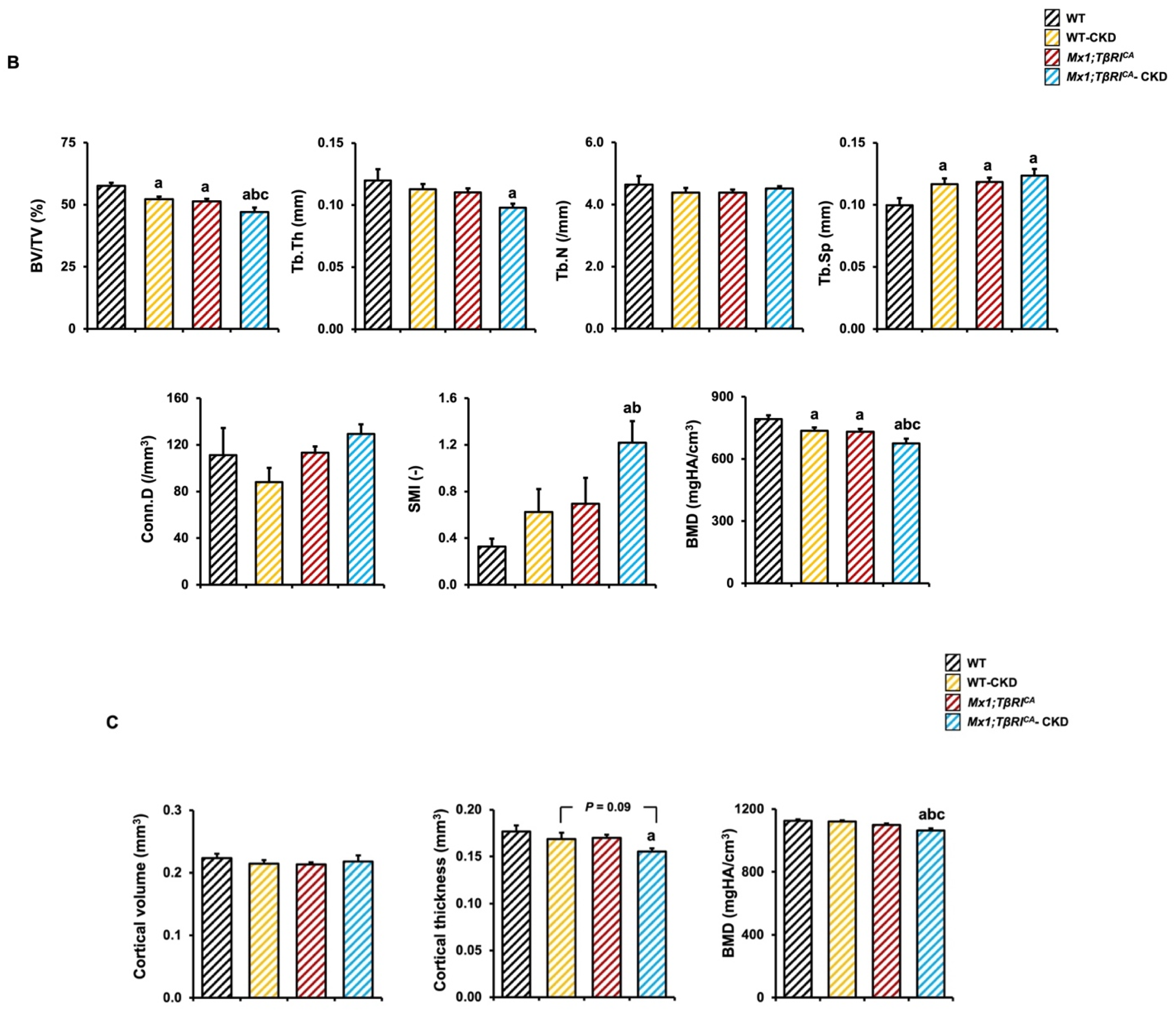
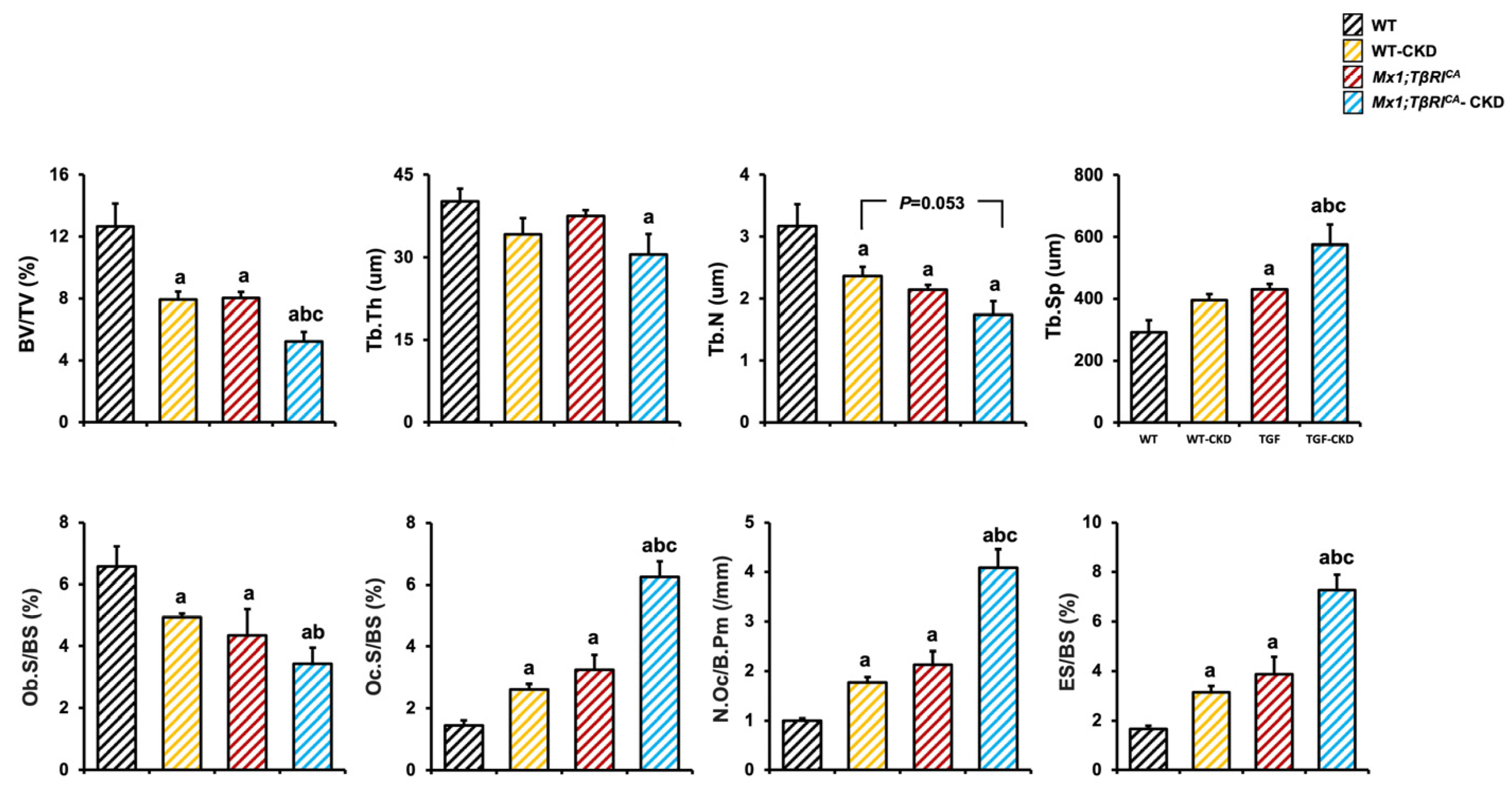
2.4. Mx1;TβRICA-CKD Mice Have Severe Cancellous and Cortical Bone Loss in Femurs and Mandibles
2.5. Mx1;TβRICA-CKD Mice Have Decreased Osteoblasts and Increased Osteoclasts in Tibiae
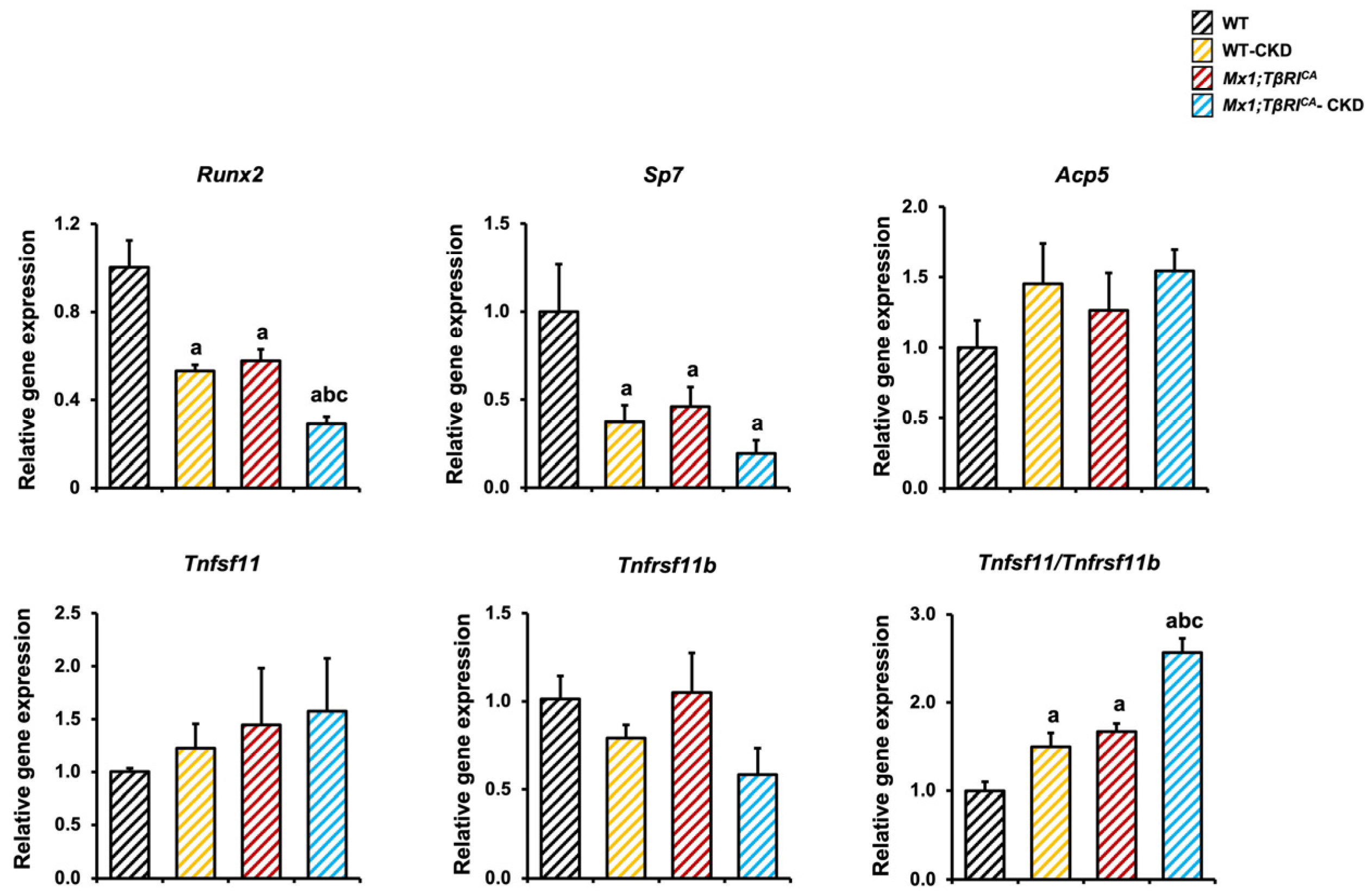
2.6. Mx1;TβRICA Mice Have Decreased Osteoblast and Increased Osteoclast-Related Gene Expression Following CKD
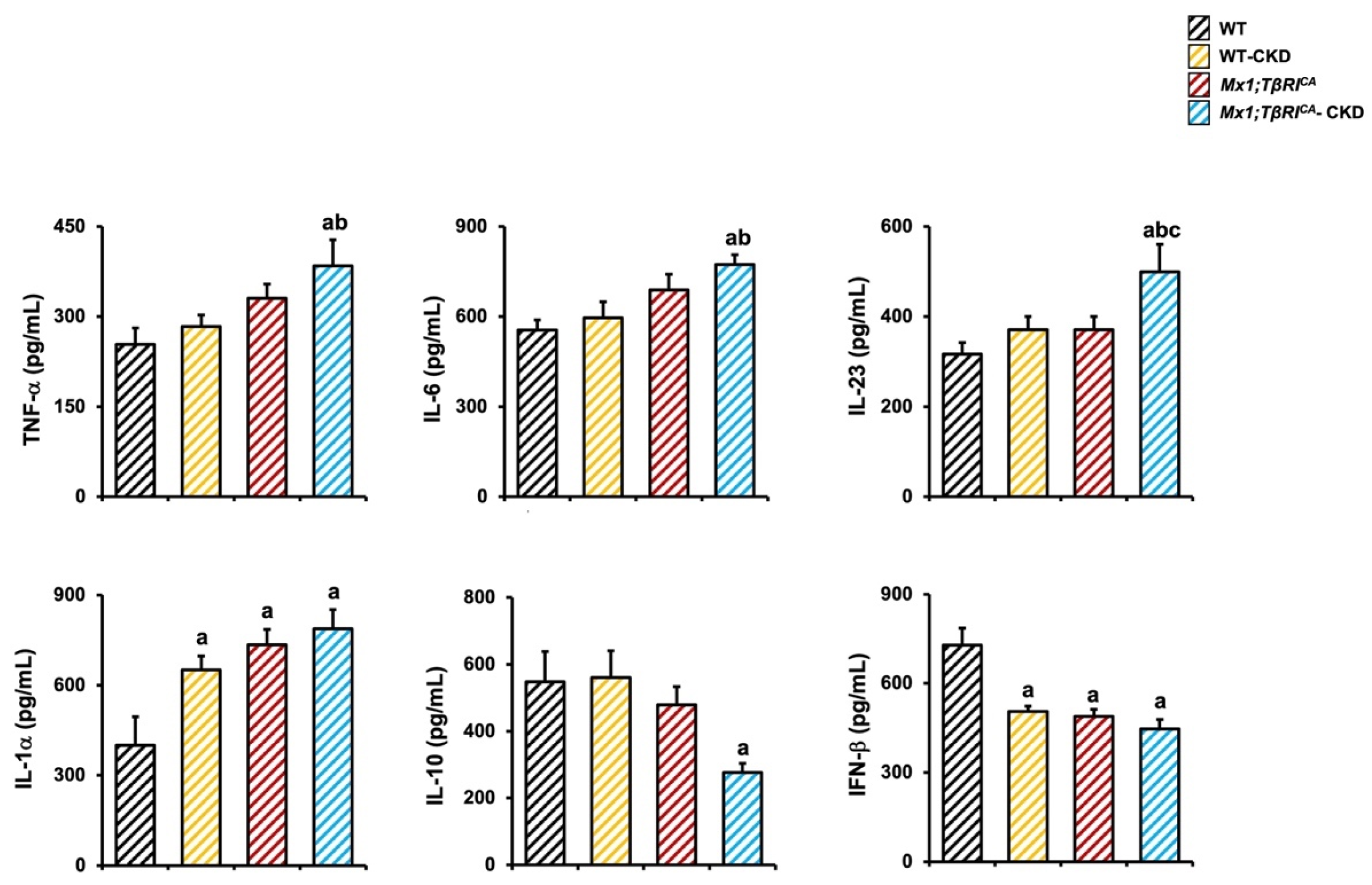
2.7. Mx1;TβRICA-CKD Mice Have Increased Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines and Decreased Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Makers Related Bone Loss
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Generation of Mice Overexpressing TβRI in the Setting of CKD
4.3. μCT
4.4. Histomorphometry
4.5. qPCR Analysis
4.6. Renal Histology
4.7. Serum Chemistry
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janssens, K.; ten Dijke, P.; Janssens, S.; Van Hul, W. Transforming Growth Factor-β1 to the Bone. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 743–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, M.M.; Ormsby, I.; Kier, A.B.; Pawlowski, S.; Diebold, R.J.; Yin, M.; Allen, R.; Sidman, C.; Proetzel, G.; Calvin, D.; et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature 1992, 359, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsdal, M.A.; Larsen, L.; Engsig, M.T.; Lou, H.; Ferreras, M.; Lochter, A.; Delaissé, J.-M.; Foged, N.T. Matrix Metalloproteinase-dependent Activation of Latent Transforming Growth Factor-β Controls the Conversion of Osteoblasts into Osteocytes by Blocking Osteoblast Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 44061–44067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, G.; Wen, C.; Jia, X.; Li, Y.; Crane, J.L.; Mears, S.C.; Askin, F.B.; Frassica, F.J.; Chang, W.; Yao, J.; et al. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, T.; Kadono, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Oshima, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Masuda, H.; Hirose, J.; Omata, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Imamura, T.; et al. Regulation of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by TGF-β through molecular interaction between Smad3 and Traf6. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2011, 26, 1447–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunobu, T.; Torigoe, K.; Ishikawa, M.; de Vega, S.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Iwamoto, Y.; Yamada, Y. Critical roles of the TGF-beta type I receptor ALK5 in perichondrial formation and function, cartilage integrity, and osteoblast differentiation during growth plate development. Dev. Biol. 2009, 332, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Serra, R. Deletion of Tgfbr2 in Prx1-cre expressing mesenchyme results in defects in development of the long bones and joints. Dev. Biol. 2007, 310, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.B.; Wang, Y.; Serra, R. Tgfbr2 is required in osterix expressing cells for postnatal skeletal development. Bone 2017, 97, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toejing, P.; Sakunrangsit, N.; Pho-On, P.; Phetkong, C.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Sridurongrit, S.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Lotinun, S. Accelerated Bone Loss in Transgenic Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGF-β Receptor Type I. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Napoletano, A.; Provenzano, M.; Garofalo, C.; Bini, C.; Comai, G.; La Manna, G. Mineral Bone Disorders in Kidney Disease Patients: The Ever-Current Topic. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzger, C.E.; Swallow, E.A.; Stacy, A.J.; Allen, M.R. Adenine-induced chronic kidney disease induces a similar skeletal phenotype in male and female C57BL/6 mice with more severe deficits in cortical bone properties of male mice. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Kang, N.; Seriwatanachai, D.; Dong, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lin, Y.; Ye, L.; Liang, X.; Yuan, Q. Chronic Kidney Disease Impairs Bone Defect Healing in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.M.; Chu, E.Y.; El-Abbadi, M.M.; Foster, B.L.; Tompkins, K.A.; Giachelli, C.M.; Somerman, M.J. Characterization of Mandibular Bone in a Mouse Model of Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, J.B.; Factor, V.M.; Mozes, M.; Nagy, P.; Sanderson, N.; Böttinger, E.P.; Klotman, P.E.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Transgenic mice with increased plasma levels of TGF-beta 1 develop progressive renal disease. Lab. Investig. 1996, 74, 991–1003. [Google Scholar]
- Koesters, R.; Kaissling, B.; Lehir, M.; Picard, N.; Theilig, F.; Gebhardt, R.; Glick, A.B.; Hähnel, B.; Hosser, H.; Gröne, H.J.; et al. Tubular overexpression of transforming growth factor-beta1 induces autophagy and fibrosis but not mesenchymal transition of renal epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Muragaki, Y.; Saika, S.; Roberts, A.B.; Ooshima, A. Targeted disruption of TGF-beta1/Smad3 signaling protects against renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Koka, V.; Lan, H.Y. Transforming growth factor-β and Smad signalling in kidney diseases. Nephrology 2005, 10, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-M.; Huang, X.R.; Xiao, J.; Chung, A.C.K.; Qin, W.; Chen, H.-y.; Lan, H.Y. Disruption of Smad4 impairs TGF-β/Smad3 and Smad7 transcriptional regulation during renal inflammation and fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.I.; Kwak, J.H.; Zachariah, M.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Choi, M.E. TGF-β-activated kinase 1 and TAK1-binding protein 1 cooperate to mediate TGF-β1-induced MKK3-p38 MAPK activation and stimulation of type I collagen. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F1471–F1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qu, X.; Yao, J.; Caruana, G.; Ricardo, S.D.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Bertram, J.F. Blockade of endothelial-mesenchymal transition by a Smad3 inhibitor delays the early development of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2612–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Border, W.A.; Okuda, S.; Languino, L.R.; Sporn, M.B.; Ruoslahti, E. Suppression of experimental glomerulonephritis by antiserum against transforming growth factor β1. Nature 1990, 346, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Li, X.; Wei, C.; Gou, L.; Dang, Y.; Shan, Z. Transfected miR-1908 inhibits renal fibrosis via targeting transforming growth factor beta 1. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi 2015, 31, 1682–1685, 1689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leelahavanichkul, A.; Yan, Q.; Hu, X.; Eisner, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, R.; Mizel, D.; Zhou, H.; Wright, E.C.; Kopp, J.B.; et al. Angiotensin II overcomes strain-dependent resistance of rapid CKD progression in a new remnant kidney mouse model. Kidney Int. 2010, 78, 1136–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Alpers, C.E.; Yoshimura, A.; Lombardi, D.; Pritzl, P.; Floege, J.; Schwartz, S.M. Renal injury from angiotensin II-mediated hypertension. Hypertension 1992, 19, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagami, S.; Border, W.A.; Miller, D.E.; Noble, N.A. Angiotensin II stimulates extracellular matrix protein synthesis through induction of transforming growth factor-beta expression in rat glomerular mesangial cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2431–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Raman, A.; Daniel, E.; Metcalf, J.; Reif, G.; Pierucci-Alves, F.; Wallace, D.P. Overexpression of TGF-β1 induces renal fibrosis and accelerates the decline in kidney function in polycystic kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 319, F1135–F1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.Z.; Zhong, X.; Li, J.C.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yan, Y.; Liao, Y.; Wen, D.; Diao, H.; Wang, L.; Shen, H.C. An optimized 5/6 nephrectomy mouse model based on unilateral kidney ligation and its application in renal fibrosis research. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, K.; Enoki, Y.; Uchida, S.; Taguchi, K.; Matsumoto, K. A combination of 5/6-nephrectomy and unilateral ureteral obstruction model accelerates progression of remote organ fibrosis in chronic kidney disease. FASEB Bioadv. 2023, 5, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, W.; Yu, X.; Jia, Z. Cilomilast Ameliorates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis by Inhibiting the TGF-β1-Smad2/3 Signaling Pathway. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 626140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakova, T.; Wahl, P.; Vargas, G.S.; Gutiérrez, O.M.; Scialla, J.; Xie, H.; Appleby, D.; Nessel, L.; Bellovich, K.; Chen, J.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 23 is elevated before parathyroid hormone and phosphate in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, W.G.; Quarles, L.D. Development and progression of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease: Lessons from molecular genetics. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, P.K.; Zhu, B.T.; Cooper, C.W. Effect of transforming growth factor β on parathyroid hormone receptor binding and cAMP formation in rat osteosarcoma cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1992, 7, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wu, S.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.-P. The roles and regulatory mechanisms of TGF-β and BMP signaling in bone and cartilage development, homeostasis and disease. Cell Res. 2024, 34, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Alliston, T.; Delston, R.; Derynck, R. Repression of Runx2 function by TGF-beta through recruitment of class II histone deacetylases by Smad3. Embo J. 2005, 24, 2543–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, M.; Leko-Mohr, Z.; Roschger, P.; Kletzmayr, J.; Schwarz, C.; Domenig, C.; Zsontsich, T.; Klaushofer, K.; Delling, G.; Oberbauer, R. Osteoprotegerin and parathyroid hormone as markers of high-turnover osteodystrophy and decreased bone mineralization in hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2002, 39, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.X.; O’Neill, K.D.; Allen, M.R.; Newman, C.L.; Moe, S.M. Low Bone Turnover in Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Decreased VEGF-A Expression and Osteoblast Differentiation. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.L.; Yi, T.; Baek, K.; Kwon, A.; Hwang, H.R.; Qadir, A.S.; Park, H.J.; Woo, K.M.; Ryoo, H.M.; Kim, G.S.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α enhances the transcription of Smad ubiquitination regulatory factor 1 in an activating protein-1- and Runx2-dependent manner. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.-Y.; Wu, H.-K.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-P.; Cheng, M.-T.; Yu, C.-H.; Chen, S.-K. Interleukin-6 transiently promotes proliferation of osteoclast precursors and stimulates the production of inflammatory mediators. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 3927–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Liang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X. Interleukin-6 Knockout Inhibits Senescence of Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells in High-Fat Diet-Induced Bone Loss. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 622950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, H.; Nguyen, C.T.; Gu, R.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Maverakis, E.; Adamopoulos, I.E. Interleukin-23 Regulates Inflammatory Osteoclastogenesis via Activation of CLEC5A(+) Osteoclast Precursors. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1477–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.X.; Kukita, T.; Kukita, A.; Otsuka, T.; Niho, Y.; Iijima, T. Interleukin-10 selectively inhibits osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting differentiation of osteoclast progenitors into preosteoclast-like cells in rat bone marrow culture system. J. Cell. Physiol. 1995, 165, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayanagi, H.; Sato, K.; Takaoka, A.; Taniguchi, T. Interplay between interferon and other cytokine systems in bone metabolism. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 208, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, H.; Yu, S.-J.; Yoo, D.H.; Chae, I.J.; Song, G.G.; Sohn, J. Increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and metalloproteinase-1 by TGF-β1 in synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis and normal individuals. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2002, 127, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapa, S.F.; Di Iorio, B.R.; Campiglia, P.; Heidland, A.; Marzocco, S. Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Kidney Disease-Potential Therapeutic Role of Minerals, Vitamins and Plant-Derived Metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.L.; Dai, C.L.; Quan, J.X.; Zhu, Z.F.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, H.X.; Guo, S.Y.; Guo, G.; Zhang, J.Y.; Qiu, M.C. Parathyroid hormone regulates osterix and Runx2 mRNA expression predominantly through protein kinase A signaling in osteoblast-like cells. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Miyakoshi, N.; Kasukawa, Y.; Nozaka, K.; Tsuchie, H.; Sato, C.; Abe, K.; Shoji, R.; Shimada, Y. Analysis of bone in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease model rats. Osteoporos. Sarcopenia 2021, 7, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Müller, R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro-computed tomography. J. Bone Min. Res. 2010, 25, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, D.W.; Compston, J.E.; Drezner, M.K.; Glorieux, F.H.; Kanis, J.A.; Malluche, H.; Meunier, P.J.; Ott, S.M.; Recker, R.R.; Parfitt, A.M. Standardized nomenclature, symbols, and units for bone histomorphometry: A 2012 update of the report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J. Bone Min. Res. 2013, 28, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toejing, P.; Myint, O.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Sridurongrit, S.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Lotinun, S. Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062704
Toejing P, Myint O, Leelahavanichkul A, Sridurongrit S, Greenblatt MB, Lotinun S. Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062704
Chicago/Turabian StyleToejing, Parichart, Ohnmar Myint, Asada Leelahavanichkul, Somyoth Sridurongrit, Matthew B. Greenblatt, and Sutada Lotinun. 2025. "Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062704
APA StyleToejing, P., Myint, O., Leelahavanichkul, A., Sridurongrit, S., Greenblatt, M. B., & Lotinun, S. (2025). Nephrectomy Induces Severe Bone Loss in Mice Expressing Constitutively Active TGFβ Receptor Type I. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062704






