Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of Children with KD
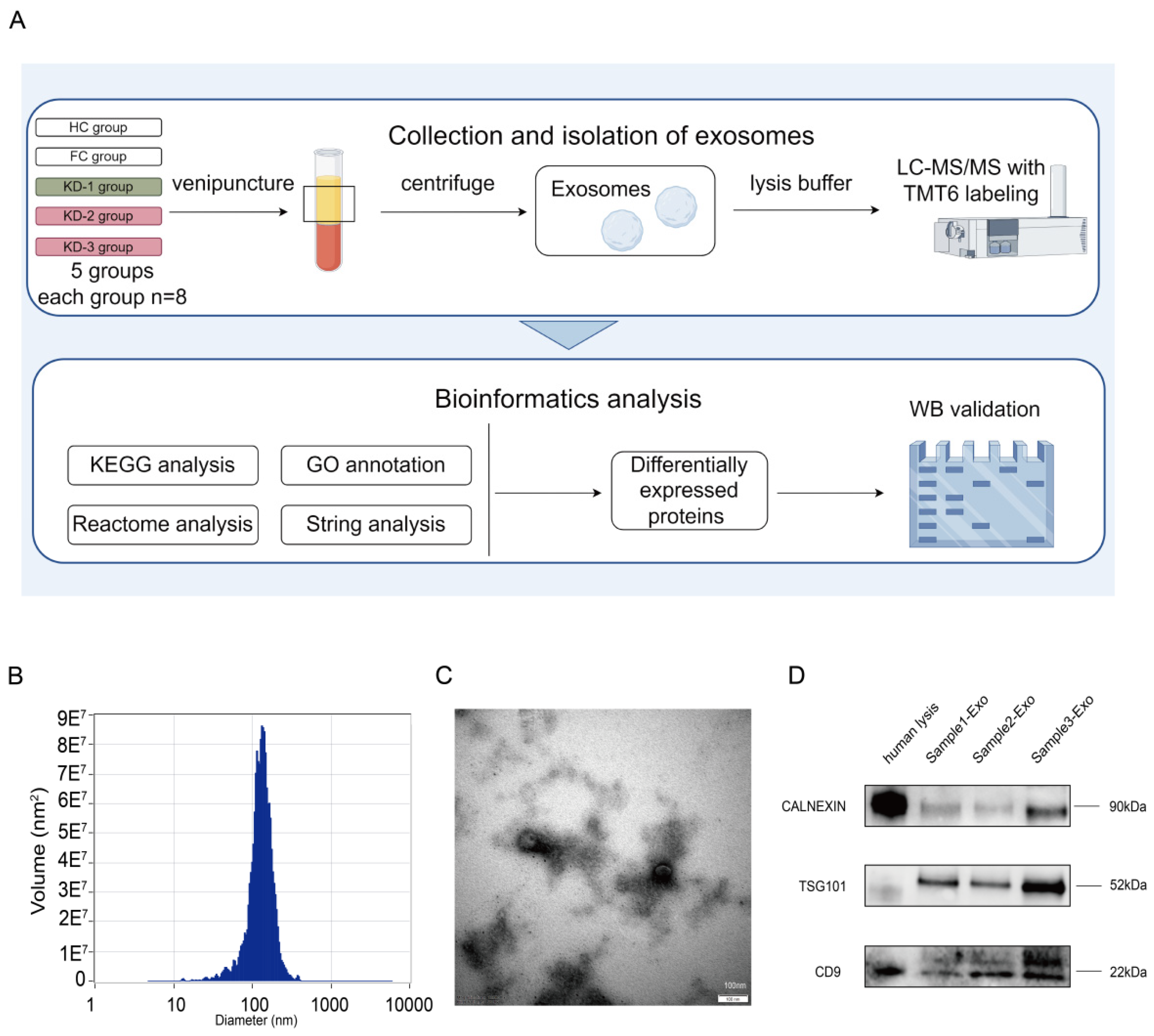
2.2. Isolation and Validation of Plasma Exosomes
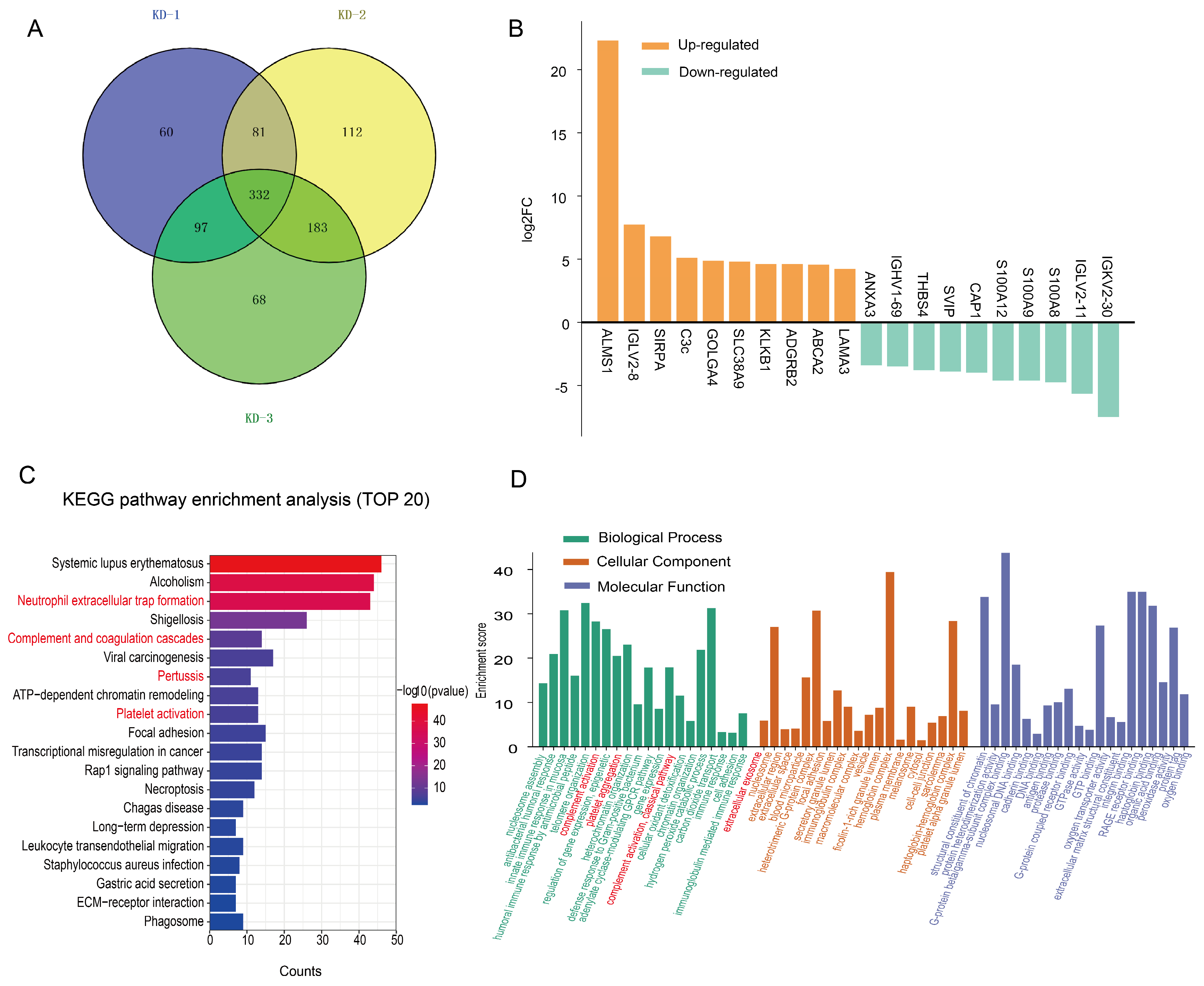
2.3. Expression Patterns of the Exosomal Proteome in KD Patients Compared with the HC Group
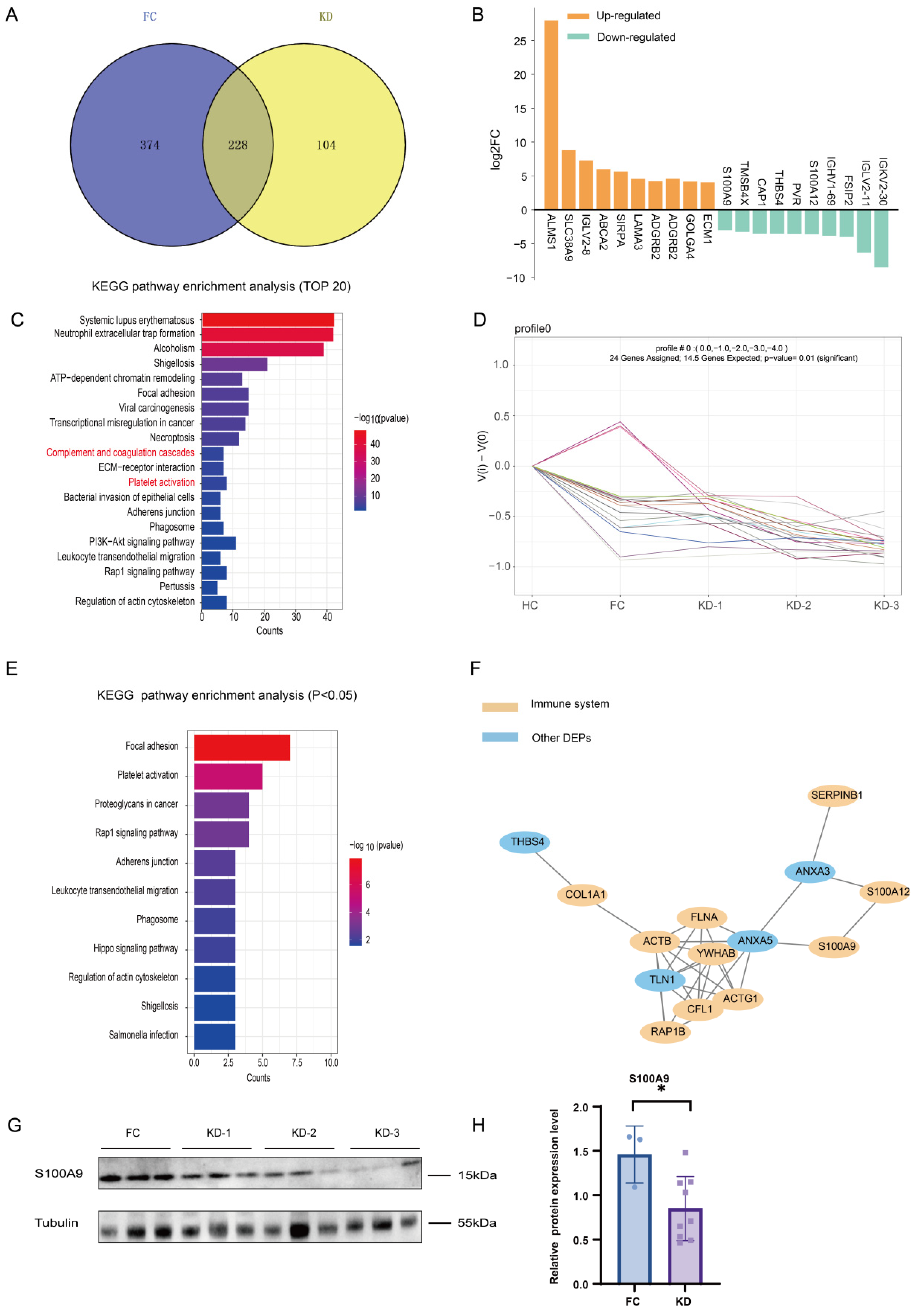
2.4. Expression Patterns of the Exosomal Proteome in KD Patients Compared with the FC Group
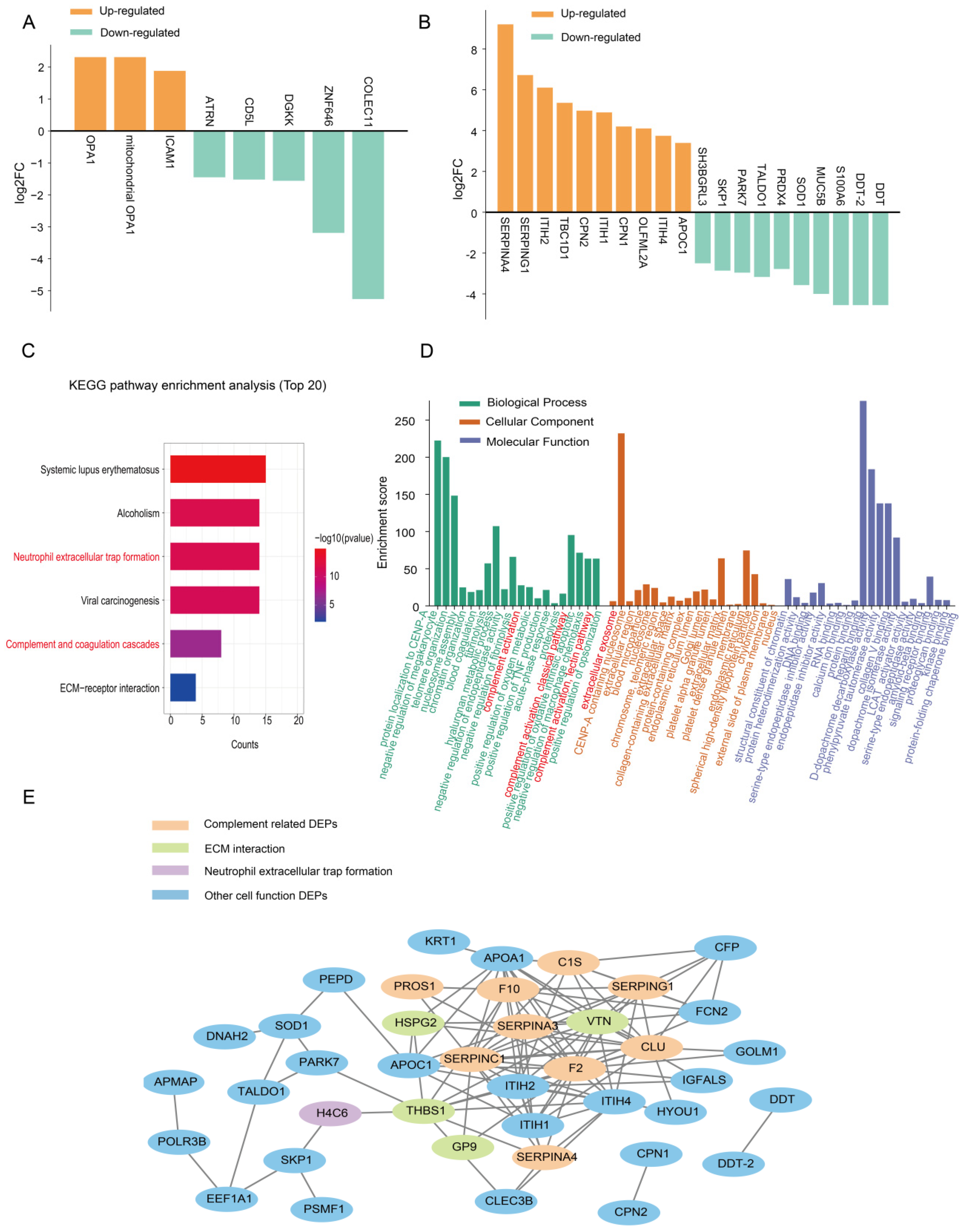
2.5. Expression Patterns of the Exosomal Proteome Expressed in the KD Groups with and Without CAAs
2.6. Expression Patterns of the Exosomal Proteome Expressed in KD Patients with Different Severities of CAAs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Recruited Subjects
4.2. Collection and Isolation of Plasma Exosome Samples
4.3. Preparation of Plasma Tryptic Digests and TMT6 Labeling
4.4. Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- McCrindle, B.W.; Rowley, A.H.; Newburger, J.W.; Burns, J.C.; Bolger, A.F.; Gewitz, M.; Baker, A.L.; Jackson, M.A.; Takahashi, M.; Shah, P.B.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of kawasaki disease: A scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 27, e927–e999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.C.; Glodé, M.P. Kawasaki syndrome. Lancet 2004, 364, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Burns, J.C. Kawasaki Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.R.; Yalcindag, A. An Update on Kawasaki Disease. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2024, 27, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Chen, H.C.; Yeh, S.J.; Lin, M.T.; Huang, S.C.; Huang, S.K. Prevalence and the long-term coronary risks of patients with kawasaki disease in a general population <40 years. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2012, 5, 566–570. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, H.C. Preventing coronary artery lesions in kawasaki disease. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunica, N.; Van Den Helm, S.; McCafferty, C.; Swaney, E.; Cai, T.; Attard, C.; Karlaftis, V.; Monagle, P.; Ignjatovic, V. Proteomics in thrombosis and hemostasis. Thromb. Haemost. 2022, 122, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mund, A.; Brunner, A.D.; Mann, M. Unbiased spatial proteomics with single-cell resolution in tissues. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vistain, L.F.; Tay, S. Single-cell proteomics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldjarn, G.H.; Ferkingstad, E.; Lund, S.H.; Helgason, H.; Magnusson, O.T.; Gunnarsdottir, K.; Olafsdottir, T.A.; Halldorsson, B.V.; Olason, P.I.; Zink, F.; et al. Large-scale plasma proteomics comparisons through genetics and disease associations. Nature 2023, 622, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benincasa, G.; Suades, R.; Padró, T.; Badimon, L.; Napoli, C. Bioinformatic platforms for clinical stratification of natural history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2023, 9, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, C.J.; Kuzmanov, U.; Gramolini, A.O. Multi-omic analyses and network biology in cardiovascular disease. Proteomics 2023, 23, e2200289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Cai, H.; Huang, Y.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, G. (Apo)Lipoprotein Profiling with Multi-Omics Analysis Identified Medium-HDL-Targeting PSRC1 with Therapeutic Potential for Coronary Artery Disease. Adv. Sci. 2025, 22, e2413491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, H.L.; Huang, W.M.; Liu, C.W.; Hua, L.; Liu, T.C.; Mao, L.J.; Xu, Y.F.; Li, W.; Xia, S.L.; et al. Monitoring of the serum proteome in kawasaki disease patients before and after immunoglobulin therapy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 447, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Tang, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, L.; Qian, G.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; et al. Plasma proteomic profiling reveals that serpine1 is a potential biomarker associated with coronary artery lesions in kawasaki disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Yanagimachi, M.; Ino, Y.; Aketagawa, M.; Matsuo, M.; Okayama, A.; Shimizu, H.; Oba, K.; Morioka, I.; Imagawa, T.; et al. Identification of candidate diagnostic serum biomarkers for kawasaki disease using proteomic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.M.; Du, H.W.; Cui, J.W.; Feng, D.Q.; Du, Z.D. New biomarkers of kawasaki disease identified by urine proteomic analysis. FEBS Open Bio. 2018, 9, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentsis, A.; Shulman, A.; Ahmed, S.; Brennan, E.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Lee, Y.H.; Lipsett, S.; Paulo, J.A.; Dedeoglu, F.; Fuhlbrigge, R.; et al. Urine proteomics for discovery of improved diagnostic markers of kawasaki disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Xu, L.; Qin, J.; Huang, H.; Zhu, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Leukocyte proteomics coupled with serum metabolomics identifies novel biomarkers and abnormal amino acid metabolism in kawasaki disease. J. Proteom. 2021, 239, 104183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Zheng, S.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Exosome theranostics: Biology and translational medicine. Theranostics 2018, 8, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Ostrowski, M.; Segura, E. Membrane vesicles as conveyors of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lian, X.L.; Zhong, J.Y.; Su, S.X.; Xu, Y.F.; Xie, X.F.; Wang, Z.P.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Che, D.; et al. Serum exosomal microrna let-7i-3p as candidate diagnostic biomarker for kawasaki disease patients with coronary artery aneurysm. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, G.; Sun, D. Serum exosomal mir-328, mir-575, mir-134 and mir-671-5p as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of kawasaki disease and the prediction of therapeutic outcomes of intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2420–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.L.; Liu, C.W.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.J.; Gao, X.J.; Bai, J.; Xu, Y.F.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, G. Sets of serum exosomal micrornas as candidate diagnostic biomarkers for kawasaki disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cun, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, P. Exosome in crosstalk between inflammation and angiogenesis: A potential therapeutic strategy for stroke. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 7006281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Kang, H. Exosome-based treatment for atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C. Exosome detection via surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy for cancer diagnosis. Acta Biomater. 2022, 144, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, Q.F.; Jin, J.J.; Huang, P.; Wang, Z.P.; Xie, X.F.; Gu, X.Q.; Gao, X.J.; Jia, H.L. Differential protein analysis of serum exosomes post-intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in patients with kawasaki disease. Cardiol. Young 2017, 27, 1786–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Bai, J.; Xu, Y.F.; Li, L.Q.; Hua, L.; Deng, L.; Jia, H.L. Proteomic analysis associated with coronary artery dilatation caused by kawasaki disease using serum exosomes. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2016, 35, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Chu, H.J.; Xu, Y.F.; Hua, L.; Wang, Z.P.; Huang, P.; Jia, H.L.; Zhang, L. Proteomics study of serum exosomes in kawasaki disease patients with coronary artery aneurysms. Cardiol. J. 2019, 26, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinković, G.; Koenis, D.S.; de Camp, L.; Jablonowski, R.; Graber, N.; de Waard, V.; de Vries, C.J.; Goncalves, I.; Nilsson, J.; Jovinge, S.; et al. S100a9 links inflammation and repair in myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, R.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, J. S100a8/a9 in inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averill, M.M.; Kerkhoff, C.; Bornfeldt, K.E. S100a8 and s100a9 in cardiovascular biology and disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Mirsaidi-Madjdabadi, S.; Ramirez, F., Jr.; Simonson, T.S.; Makino, A. Transcriptome meta-analysis of Kawasaki disease in humans and mice. Front. Pediatr. 2024, 12, 1423958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, J.; Jibiki, T.; Noma, S.; Nakajima, T.; Saito, H.; Terai, M. Gene expression profiling of the effect of high-dose intravenous Ig in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5837–5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.C.; Tsai, K.W.; Huang, L.H.; Weng, K.P.; Chien, K.J.; Lin, Y.; Tu, C.Y.; Lin, P.H. Serum proteins may facilitate the identification of Kawasaki disease and promote in vitro neutrophil infiltration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckman, C.; Vandal, K.; Rouleau, P.; Talbot, M.; Tessier, P.A. Proinflammatory activities of S100: Proteins S100A8, S100A9, and S100A8/A9 induce neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polycarpou, A.; Grigoriadou, S.; Klavinskis, L.; Sacks, S. Does the lectin complement pathway link Kawasaki disease and SARS-CoV-2? Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 604512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senent, Y.; Remírez, A.; Repáraz, D.; Llopiz, D.; Celias, D.P.; Sainz, C.; Entrialgo-Cadierno, R.; Suarez, L.; Rouzaut, A.; Alignani, D.; et al. The c5a/c5ar1 axis promotes migration of tolerogenic dendritic cells to lymph nodes, impairing the anticancer immune response. Cancer Immunol Res. 2025, 13, 384–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.Q.; Guan, P.P.; Wang, P. Complement 3a induces the synapse loss via c3ar in mitochondria-dependent nlrp3 activating mechanisms during the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 165, 105868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Y.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, X. Complement molecule c3a exacerbates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage by inducing neuroinflammation through the c3ar-erk-p2x7-nlrp3 inflammasome signaling axis. Inflammation, 2024; ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
- Ekeowa, U.I.; Marciniak, S.J.; Lomas, D.A. A1 -antitrypsin deficiency and inflammation. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 7, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneva, M.K.; Muley, M.M.; Krustev, E.; Reid, A.R.; Souza, P.R.; Dell’Accio, F.; McDougall, J.J.; Perretti, M. Alpha-1-antitrypsin reduces inflammation and exerts chondroprotection in arthritis. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, W.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, G. Proteomic insights into molecular alterations associated with Kawasaki disease in children. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2025, 51, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.R.; Kuo, H.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Wang, L.; Lin, I.C.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, K.D. A unique plasma proteomic profiling with imbalanced fibrinogen cascade in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2009, 20, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.R.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, E.Y.; Liang, C.D.; Hwang, K.P.; Lin, I.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Wang, T.J.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, K.D. Plasma clusterin levels in predicting the occurrence of coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2010, 31, 1151–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, K.; Duraiyarasan, S.; Adefuye, M.; Manjunatha, N.; Ganduri, V. Kawasaki Disease and Coronary Artery Involvement: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e28358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Han, Y.; Xing, J.; Zhai, X.; Wang, S.; Xin, S.; Zhang, J. Kallistatin correlates with inflammation in abdominal aortic aneurysm and suppresses its formation in mice. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 10, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, L.; Peroni, M.; Zanotti, C.; Pini, A.; Bossoni, E.; Giordani, J.; Bargagli, E.; Perger, E.; Ferrarotti, I.; Vizzardi, E.; et al. Investigating the Link between Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency and Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 77, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekdahl, K.N.; Teramura, Y.; Hamad, O.A.; Asif, S.; Duehrkop, C.; Fromell, K.; Gustafson, E.; Hong, J.; Kozarcanin, H.; Magnusson, P.U.; et al. Dangerous liaisons: Complement, coagulation, and kallikrein/kinin cross-talk act as a linchpin in the events leading to thromboinflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 274, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawish, E.; Sauter, M.; Sauter, R.; Nording, H.; Langer, H.F. Complement, inflammation and thrombosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2892–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Liu, X.P.; Xia, H.B.; Cui, L.N.; Lang, X.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Huang, W.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liu, X.; Kuo, H.C.; et al. Complement 3 and the prognostic nutritional index distinguish kawasaki disease from other fever illness with a nomogram. Children 2021, 8, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.B.; Shang, X.P.; Wu, J.G.; Cai, Y.L. The immunologic profiles of Kawasaki disease triggered by mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2023, 42, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, N.; Rasras, A.; Ormenisan, D.M.; Amslinger, S.; Enzmann, V.; Jägle, H.; Pauly, D. Complement factor h-related 3 enhanced inflammation and complement activation in human rpe cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 769242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Qi, L.N.; Zhang, M.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Chai, J.L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.R.; Cao, C. Gαi1/3 mediation of akt-mtor activation is important for rspo3-induced angiogenesis. Protein Cell. 2023, 14, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gurunathan, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Ash-Shaheed, B.; Kelsall, B.L. Primary role for gi protein signaling in the regulation of interleukin 12 production and the induction of t helper cell type 1 responses. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.L.; Luo, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.; Kong, C.; Chen, J.; Lin, Z.; Tang, X.; et al. S-nitrosylation-mediated coupling of g-protein alpha-2 with cxcr5 induces hippo/yap-dependent diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Sun, B.; Gong, T.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Sugawara, A.; Jiang, M.; Yan, J.; Gurary, A.; et al. GNAI1 and GNAI3 Reduce Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis in Mice by Blocking IL6 Signaling and Down-regulating Expression of GNAI2. Gastroenterol. 2019, 156, 2297–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pero, R.S.; Borchers, M.T.; Spicher, K.; Ochkur, S.I.; Sikora, L.; Rao, S.P.; Abdala-Valencia, H.; O'Neill, K.R.; Shen, H.; McGarry, M.P.; et al. Gαi2-mediated signaling events in the endothelium are involved in controlling leukocyte extravasation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 4371–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Deem, T.L.; Burcin, T.L.; Ley, K. Gαi2 is required for chemokine-induced neutrophil arrest. Blood 2007, 110, 3773–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Baskaran, R.; Lee, N.H.; Hsu, H.H.; Ho, T.J.; Tu, C.C.; Lin, Y.M.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y. Cxcl2/cxcr2 axis induces cancer stem cell characteristics in cpt-11-resistant lovo colon cancer cells via gαi-2 and gαq. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 11822–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callow, B.; He, X.; Juriga, N.; Mangum, K.D.; Joshi, A.; Xing, X.; Obi, A.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Milewicz, D.M.; O'Riordan, M.X.; et al. Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle cell PERK/ATF4 ER stress signaling protects against abdominal aortic aneurysms. JCI Insight. 2025, 10, e183959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Yang, X.; Shen, Y.; Yu, F.; et al. Inhibition of aortic CX3CR1+ macrophages mitigates thoracic aortic aneurysm progression in Marfan syndrome in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e178198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Luo, Y. Difference in inflammation, atherosclerosis, and platelet activation between coronary artery aneurysm and coronary artery ectasia. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 5811–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Lu, Z.; Gu, R.; Xuan, X.; Zhang, R.; Hu, J.; Dong, H. Deciphering the Intercellular Communication Between Immune Cells and Altered Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypes in Aortic Aneurysm from Single-Cell Transcriptome Data. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 936287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.B.; Bartoli, M.A.; Ennis, T.L.; Mao, D.; Simmons, P.M.; Thompson, R.W.; Pham, C.T. Critical role of dipeptidyl peptidase I in neutrophil recruitment during the development of experimental abdominal aortic aneurysms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Control Groups | KD Groups | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery Group | Validation Group | Discovery Group | Validation Group | |||||||
| Subgroups | HC | FC | HC | FC | KD-1 | KD-2 | KD-3 | KD-1 | KD-2 | KD-3 |
| No. of participants | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Age (year) | 2.14 ± 1.28 | 1.92 ± 1.04 | 2.25 ± 1.86 | 1.73 ± 1.76 | 2.09 ± 1.37 | 2.45 ± 1.47 | 2.20 ± 1.43 | 2.1 ± 1.62 | 1.82 ± 1.65 | 2.42 ± 1.29 |
| Males/Females, (n) | 4/4 | 4/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 4/4 | 4/4 | 4/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 | 3/4 |
| Z score | / | / | / | / | / | 5.87 ± 2.87 | 13.23 ± 2.63 | / | 6.23 ± 2.85 | 11.96 ± 2.09 |
| WBC, ×109/L | 13.01 ± 4.83 | 12.89 ± 6.78 | 10.83 ± 5.33 | 14.97 ± 2.66 | 13.21 ± 2.60 | 10.76 ± 4.60 | ||||
| NEUT, ×109/L | 8.15 ± 3.02 | 7.49 ± 4.73 | 6.31 ± 5.02 | 9.05 ± 3.15 | 7.29 ± 3.35 | 7.32 ± 3.89 | ||||
| PLT, ×109/L | 339.63 ± 102.75 | 487.00 ± 210.05 | 625.00 ± 267.02 | 513.00 ± 62.80 | 569.75 ± 152.99 | 371.75 ± 171.93 | ||||
| CRP, mg/L | 59.60 ± 32.28 | 55.08 ± 51.67 | 15.50 (1, 38) | 34.64 ± 23.56 | 52.65 ± 51.73 | 93.70 ± 79.29 | ||||
| KD Groups | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovery Group | Validation Group | |||
| Subgroups | KD-1 | KD-2 + KD-3 | KD-1 | KD-2 + KD-3 |
| WBC, ×109/L | 13.01 ± 4.83 | 11.86 ± 5.99 | 14.97 ± 2.66 | 11.98 ± 3.70 |
| NEUT, ×109/L | 8.15 ± 3.02 | 6.90 ± 4.75 | 9.05 ± 3.15 | 7.30 ± 3.36 |
| PLT, ×109/L | 339.63 ± 102.75 | 556.00 ± 210.05 | 513.00 ± 62.80 | 470.75 ± 184.12 |
| CRP, mg/L | 59.60 ± 32.28 | 24.50 (2.83, 65.89) | 34.64 ± 23.56 | 73.18 ± 65.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Bai, B.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X. Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062668
Zheng Y, Bai B, Wei Z, Zhang M, Zhang Q, Li X. Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062668
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yang, Baoling Bai, Zhimiao Wei, Mingming Zhang, Qin Zhang, and Xiaohui Li. 2025. "Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062668
APA StyleZheng, Y., Bai, B., Wei, Z., Zhang, M., Zhang, Q., & Li, X. (2025). Plasma Exosomal-Derived SERPINA1 and GNAI2 Downregulation as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Artery Aneurysms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062668






