Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Exposure on Intestinal Microbial Community, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Lesions in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Response of Intestinal Flora to PFOS Exposure
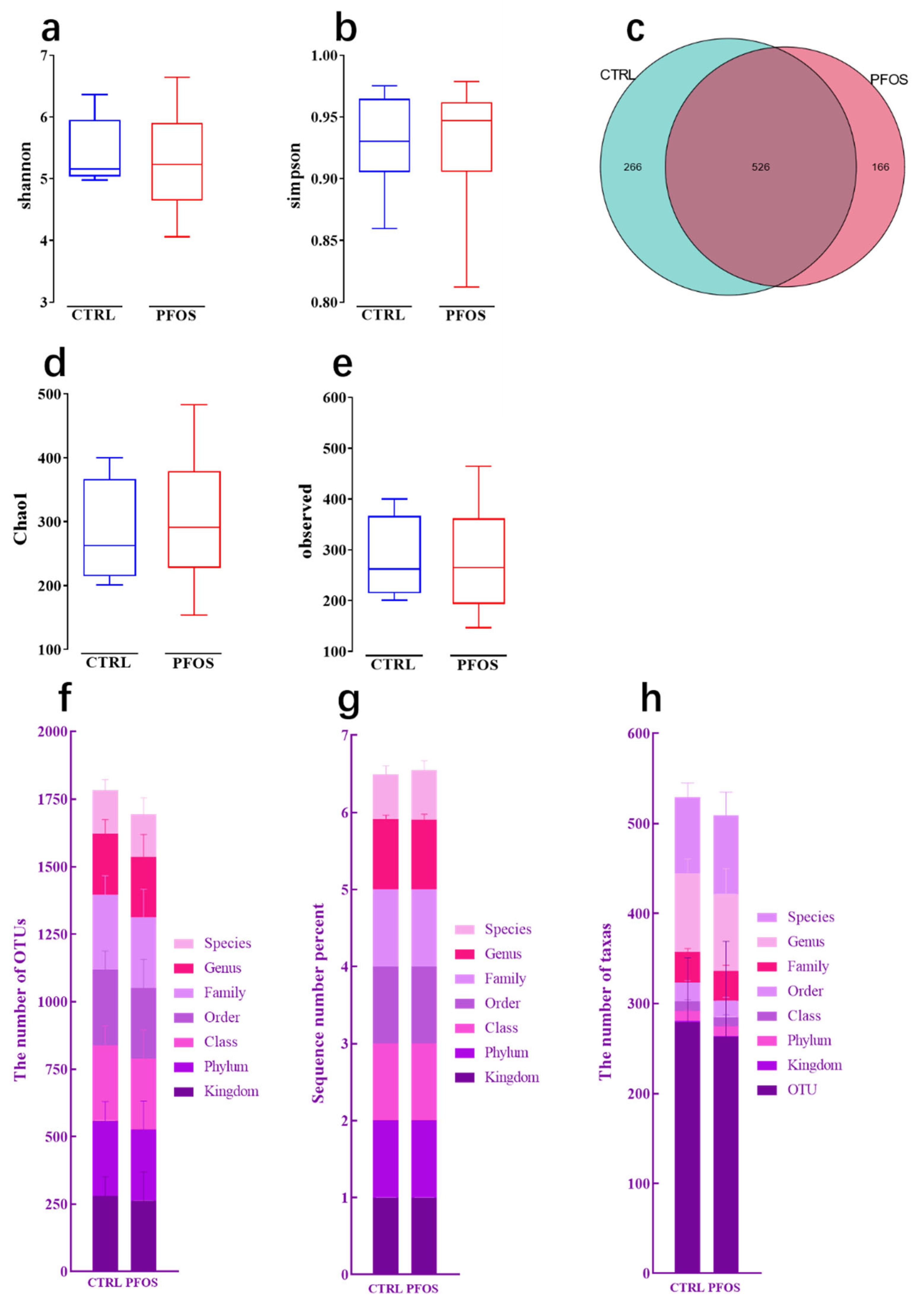
2.1.1. Alpha Diversity Analysis
2.1.2. Composition at Various Taxonomic Levels
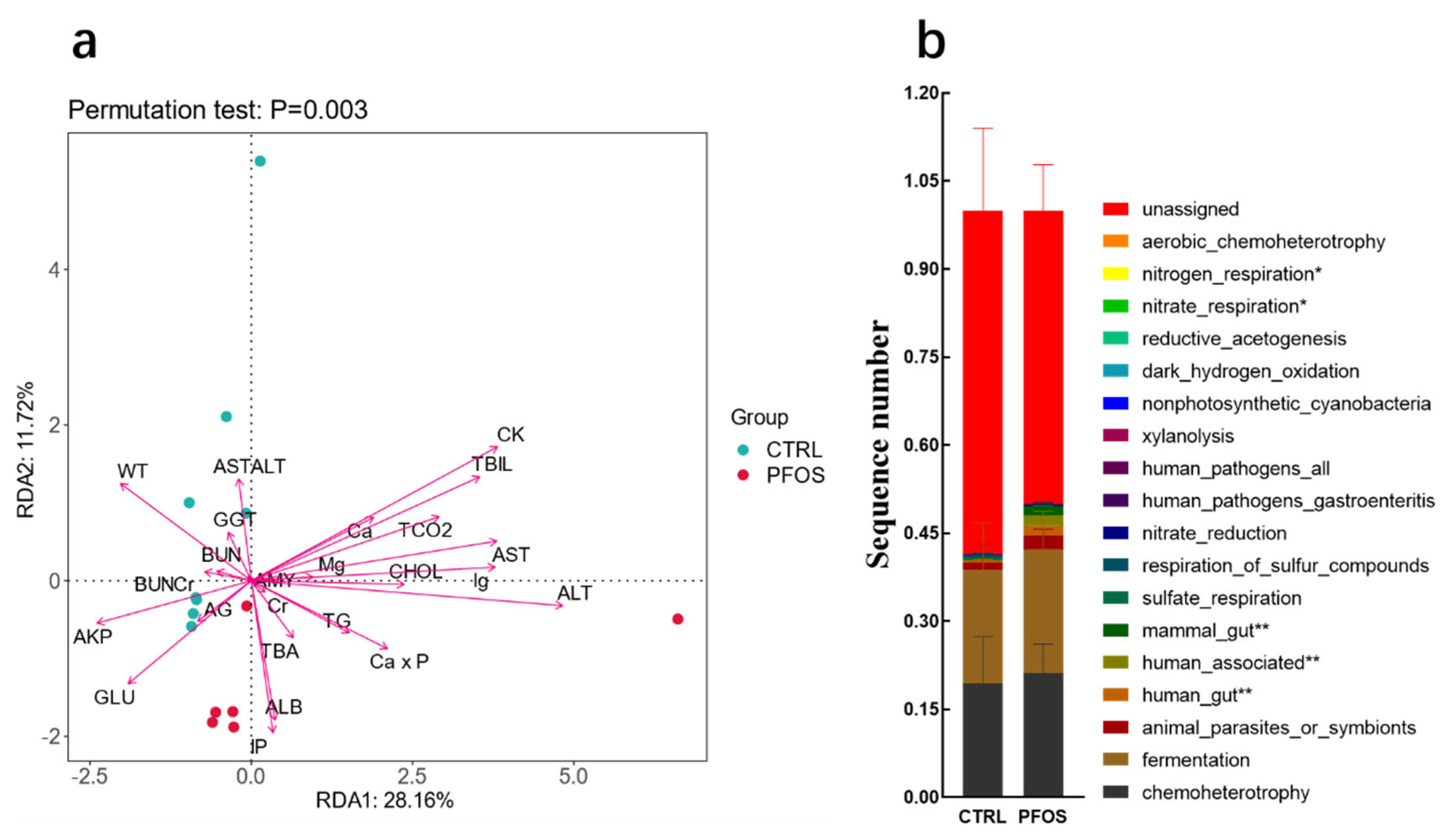
2.1.3. Beta Diversity Analysis
2.1.4. Analysis and Functional Statistics of RDA
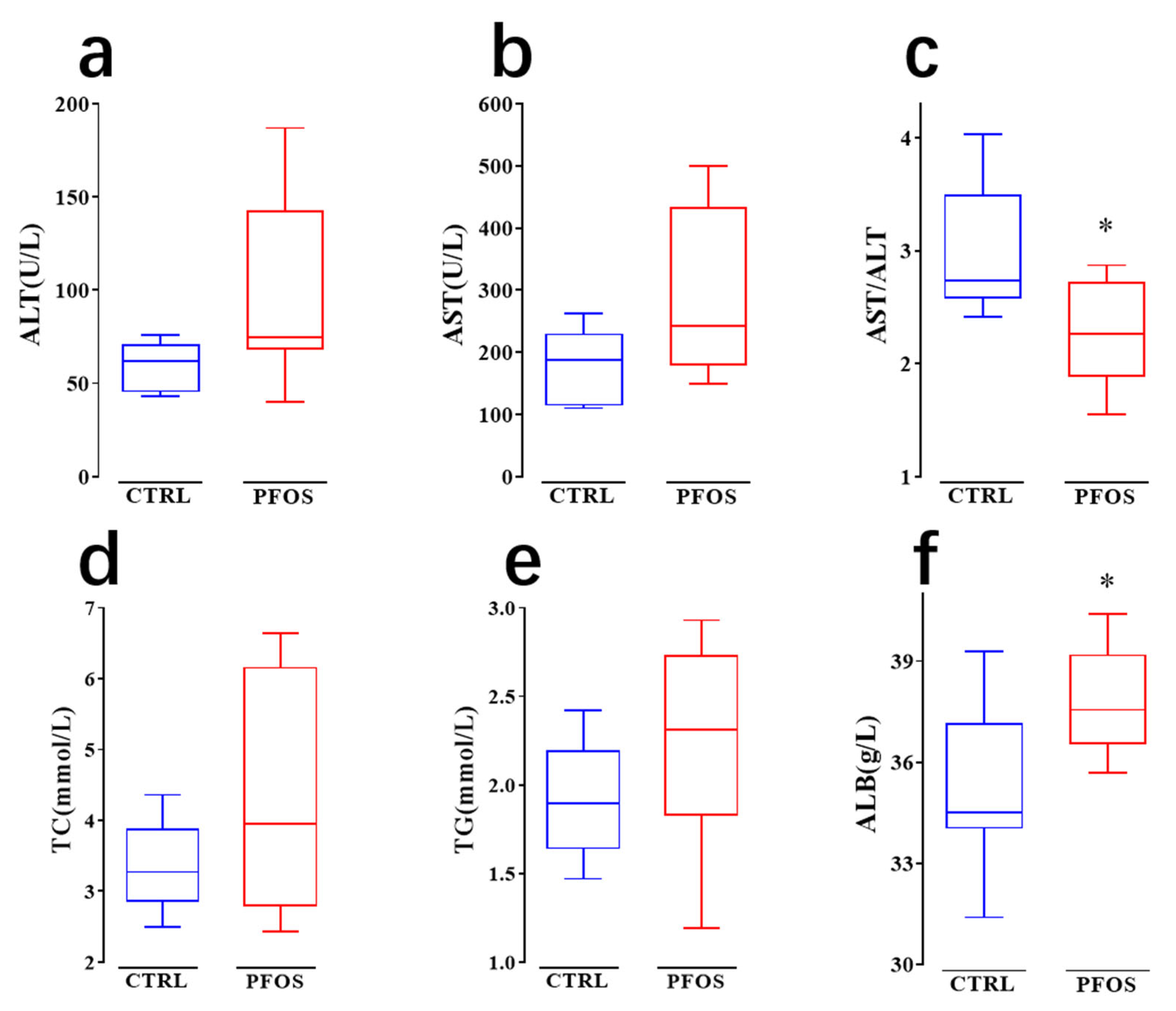
2.2. PFOS Causes Dyslipidemia in Mice
2.3. PFOS Causes Steatosis and Inflammation in Mouse Hepatocytes
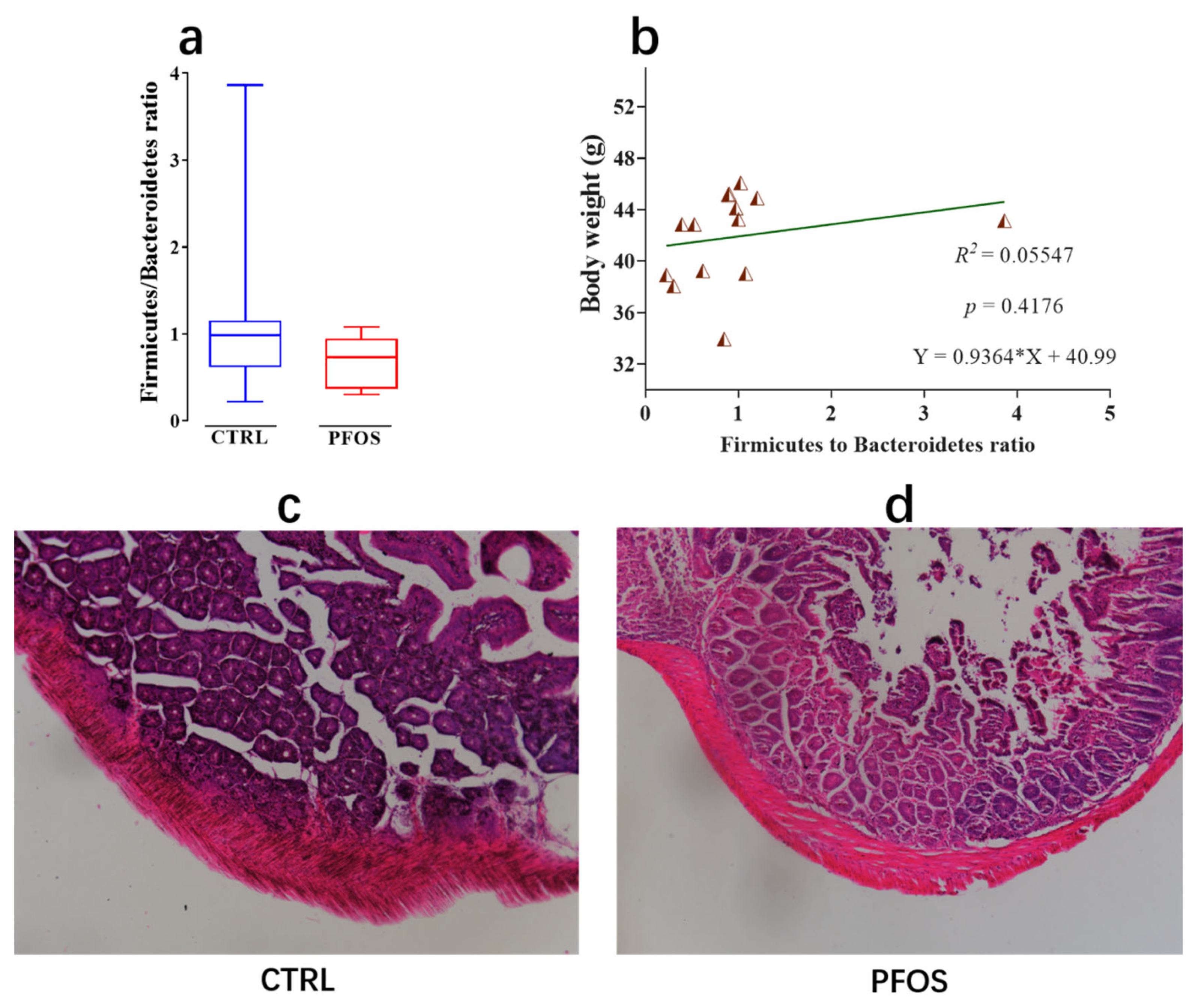
2.4. Effect of PFOS Exposure on Intestinal Lesions
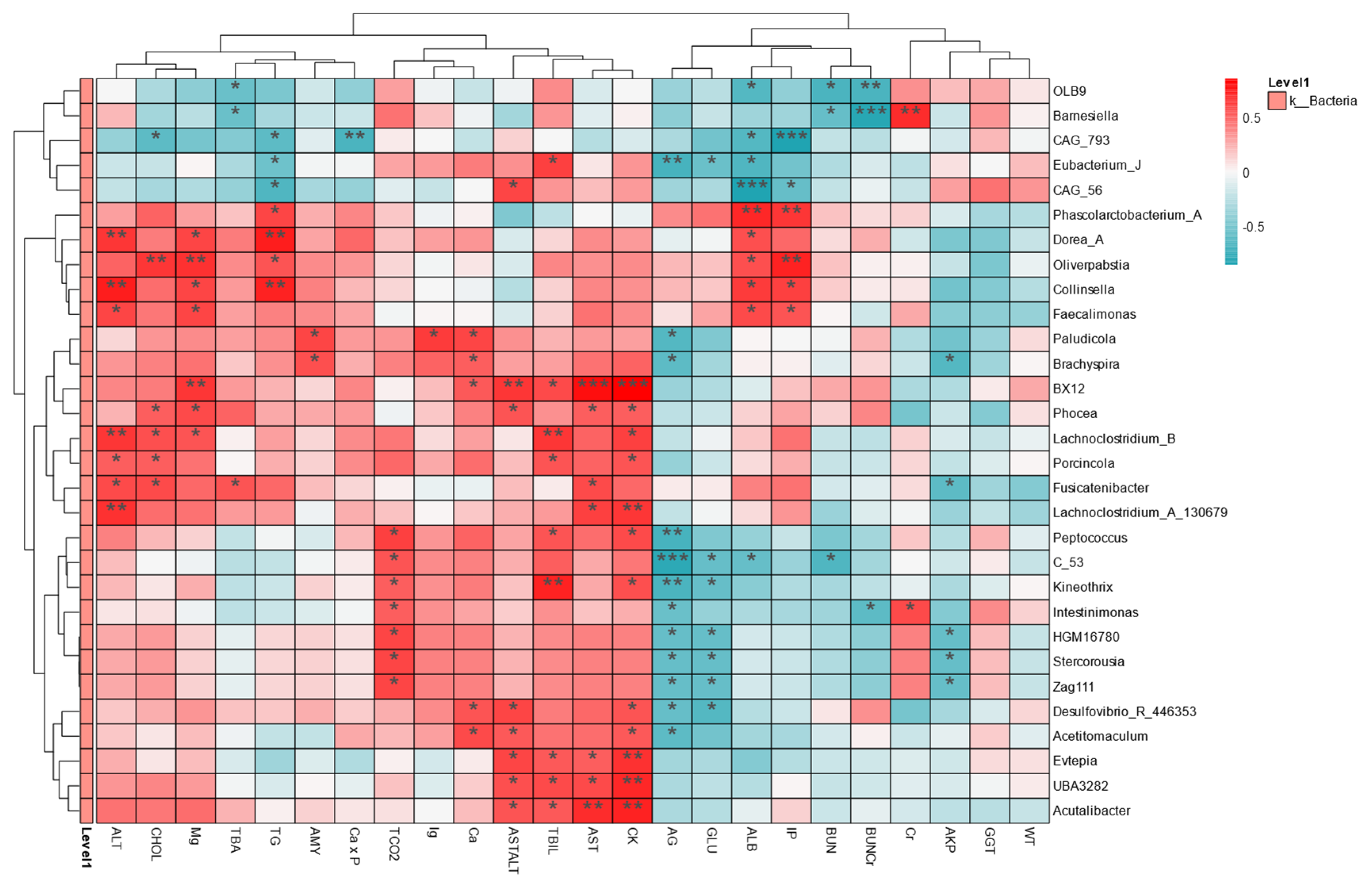
2.5. Intestinal Flora Is Associated with Health Indicators
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animal Experiments
3.2. Sample Collection and Processing
3.3. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
3.4. Generated Library and Sequencing
3.5. Analysis of Gene Expression
3.6. Serum Biochemical Analysis
3.7. Correlation Analysis
3.8. Histology
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Grandjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; et al. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; DeWitt, J.C.; Higgins, C.P.; Cousins, I.T. A Never-Ending Story of Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs)? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 2508–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunderland, E.M.; Hu, X.C.; Dassuncao, C.; Tokranov, A.K.; Wagner, C.C.; Allen, J.G. A review of the pathways of human exposure to poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) and present understanding of health effects. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 29, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, D.W.; Palekar, A.I.; Conley, H.E.; Ferrero, G.; Driggers, J.H.; Linder, K.E.; Kullman, S.W.; Reif, D.M.; Sheats, M.K.; DeWitt, J.C.; et al. Legacy and emerging per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances suppress the neutrophil respiratory burst. J. Immunotoxicol. 2023, 20, 2176953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudzanova, B.; Vlaanderen, J.; Kalina, J.; Piler, P.; Zvonar, M.; Klanova, J.; Blaha, L.; Adamovsky, O. Impact of PFAS exposure on prevalence of immune-mediated diseases in adults in the Czech Republic. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, G.; Zhang, R.; Feng, L.; Zhang, J. Early life exposure to low-dose perfluorooctane sulfonate disturbs gut barrier homeostasis and increases the risk of intestinal inflammation in offspring. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 329, 121708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Porta, M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Vandenberg, L.N. Chlorinated persistent organic pollutants, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 557–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myre, M.; Imbeault, P. Persistent organic pollutants meet adipose tissue hypoxia: Does cross-talk contribute to inflammation during obesity? Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sun, S.; Wu, X.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Intestinal environmental disorders associate with the tissue damages induced by perfluorooctane sulfonate Exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; Wu, G.D.; Albenberg, L.; Tomov, V.T. Gut microbiota and IBD: Causation or correlation? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, R.B.; Wu, G.D. Roles for Intestinal Bacteria, Viruses, and Fungi in Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Therapeutic Approaches. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, T.; Ng, S.C. The Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qazi, M.R.; Abedi, M.R.; Nelson, B.D.; DePierre, J.W.; Abedi-Valugerdi, M. Dietary exposure to perfluorooctanoate or perfluorooctane sulfonate induces hypertrophy in centrilobular hepatocytes and alters the hepatic immune status in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seacat, A.M.; Thomford, P.J.; Hansen, K.J.; Clemen, L.A.; Eldridge, S.R.; Elcombe, C.R.; Butenhoff, J.L. Sub-chronic dietary toxicity of potassium perfluorooctanesulfonate in rats. Toxicology 2002, 183, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.T.; Zhao, Y.G.; Wei, X.; Hui, K.Y.; Giesy, J.P.; Wong, C.K. PFOS-induced hepatic steatosis, the mechanistic actions on β-oxidation and lipid transport. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albillos, A.; de Gottardi, A.; Rescigno, M. The gut-liver axis in liver disease: Patho physiological basis for therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 558–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Dubinkina, V.; Ahmad, S.; Maslov, S.; Irudayaraj, J.M.K. Gut Microbiome-Host Metabolome Homeostasis upon Exposure to PFOS and GenX in Male Mice. Toxics 2023, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Ng, A.H.-M.; Wan, H.T.; Wong, A.Y.-M.; Leung, C.C.-T.; Li, R.; Wong, C.K.-C. Dietary Exposure to the Environmental Chemical, PFOS on the Diversity of Gut Microbiota, Associated With the Development of Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, L.S.; Huber, S.; Becher, G.; Thomsen, C. Characterisation of human exposure pathways to perfluorinated compounds–comparing exposure estimates with Biomarkers of exposure. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boursier, J.; Mueller, O.; Barret, M.; Machado, M.; Fizanne, L.; Araujo-Perez, F.; Guy, C.D.; Seed, P.C.; Rawls, J.F.; David, L.A.; et al. The severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with gut dysbiosis and shift in the metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Hepatology 2016, 63, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Xin, L.; Jiang, F. Maternal PFOS exposure in mice induces hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammation in adult female offspring: Involvement of microbiome-gut-liver axis and autophagy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobet, A.; Quince, C.; Ramette, A. Multivariate Cutoff Level Analysis (MultiCoLA) of large community data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, N.; Tan, Z. Gut microbiota characteristics in mice with antibiotic-associated diarrhea. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, C.; Jun, G.; Naj, A.; Rajbhandary, R.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Wang, L.S.; Valladares, O.; Lin, C.F.; Larson, E.B.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; et al. Variants in the ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter (AB CA7), Apolipoprotein E ϵ4, and the Risk of Late-Onset Alzheimer Disease in African Americans. Jama 2013, 309, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierangeli, G.M.F.; Domingues, M.R.; Choueri, R.B.; Hanisch, W.S.; Gregoracci, G.B.; Benassi, R.F. Spatial Variation and Environmental Parameters Affecting the Abundant and Rare Communities of Bacteria and Archaea in the Sediments of Tropical Urban Reservoirs. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 86, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, X.; Lu, J.; Ge, X.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.; Tian, C.; Ge, Z.; Yu, C.; et al. Association between exposure to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance and liver injury in American adults. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 38, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraulob, J.C.; Ogg-Diamantino, R.; Fernandes-Santos, C.; Aguila, M.B.; Mandarim-De-Lacerda, C.A. A Mouse Model of Metabolic Syndrome: Insulin Resistance, Fatty Liver and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Pancreas Disease (NAFPD) in C57BL/6 Mice Fed a High Fat Diet. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2010, 46, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashitani, M.; Mizuno, A.; Kimura, T.; Shimbo, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Tokioka, S.; Kobayashi, D. Low Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)/Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) Ratio Associated with Increased Cardiovascular Disease and its Risk Factors in Healthy Japanese Population. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2022, 31, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, K.T.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Lipworth, L.; Tjønneland, A.; Overvad, K.; Sørensen, M. Association between plasma PFOA and PFOS levels and total cholesterol in a middle-aged Danish population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, G.W.; Burris, J.M.; Burlew, M.M.; Mandel, J.H. Epidemiologic assessment of worker serum perfluorooctanesulfonate (PFOS) and perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) concentrations and medical surveillance examinations. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2003, 45, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Tinker, S.; Frisbee, S.; Ducatman, A.; Vaccarino, V. Association of Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate with Serum Lipids Among Adults Living Near a Chemical Plant. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2009, 170, 1268–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsthuber, M.; Kaiser, A.M.; Granitzer, S.; Hassl, I.; Hengstschlager, M.; Stangl, H.; Gundacker, C. Albumin is the major carrier protein for PFOS, PFOA, PFHxS, PFNA and P FDA in human plasma. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.-H.; Son, M.-H.; Choi, S.-D.; Lee, D.-H.; Chang, Y.-S. Influence of exposure to perfluoroalkyl substances (PFASs) on the Korean general population: 10-year trend and health effects. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.; Pfohl, M.; Auclair, A.; Jamwal, R.; Barlock, B.J.; Sammoura, F.M.; Goedken, M.; Akhlaghi, F.; Slitt, A.L. Perfluorooctanesulfonic acid (PFOS) administration shifts the hepatic proteome an d augments dietary Outcomes related to hepatic steatosis in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 408, 115250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhang, J.; Yin, H.; Li, S.; Xu, S.; Li, S. Cannabidiol alleviates perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced macrophage extracellular trap mediate inflammation and fibrosis in mice liver. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Wu, W.; Ge, S.; Jia, R.; Lin, T.; Yuan, Y.; Kuang, H.; Yang, B.; Wu, L.; Wei, J.; et al. Naringin protects against perfluorooctane sulfonate-induced liver injury by modulating NRF2 and NF-κB in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lala, V.; Zubair, M.; Minter, D.A. Liver Function Tests. In StatPearls; Treasure Isl and (FL) ineligible companies. Disclosure: Muhammad Zubair declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: David Minter declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Strukelj, B. The Influence of Probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio in the Treatment of Obesity and Inflammatory Bowel diseases. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Yang, M.; Zeng, C.; Wu, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y. Perfluorooctane sulfonate exerts inflammatory bowel disease-like intestinal injury in rats. PeerJ 2021, 9, e10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, P.; Minacapelli, C.D.; Rustgi, V. The Microbiome and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2020, 26, 1316–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L. Role and Mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 625913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comino, I.; Real, A.; de Lorenzo, L.; Cornell, H.; López-Casado, M.Á.; Barro, F.; Lorite, P.; Torres, M.I.; Cebolla, Á.; Sousa, C. Diversity in oat potential immunogenicity: Basis for the selection of oat varieties with no toxicity in coeliac disease. Gut 2011, 60, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahe, L.K.; Le Chatelier, E.; Prifti, E.; Pons, N.; Kennedy, S.; Hansen, T.; Pedersen, O.; Astrup, A.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Larsen, L.H. Specific gut microbiota features and metabolic markers in postmenopausal women with obesity. Nutr. Diabetes 2015, 5, e159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Chi, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ma, N.; Min, L.; Ji, S. Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Exposure on Intestinal Microbial Community, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Lesions in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062648
Chen Q, Chi Y, Zhu Q, Ma N, Min L, Ji S. Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Exposure on Intestinal Microbial Community, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Lesions in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062648
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qianfeng, Yulang Chi, Qingyu Zhu, Nana Ma, Lingli Min, and Shouping Ji. 2025. "Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Exposure on Intestinal Microbial Community, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Lesions in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062648
APA StyleChen, Q., Chi, Y., Zhu, Q., Ma, N., Min, L., & Ji, S. (2025). Effects of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid Exposure on Intestinal Microbial Community, Lipid Metabolism, and Liver Lesions in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062648





