Innate Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis: Varied Effects of CFTR Modulator Therapy on Cell-to-Cell Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Cystic Fibrosis and CFTR
1.2. Chronic Infection and Inflammation in CF Airways
1.3. Key Soluble Factors and EVs Modulating Innste Immunity in CF
1.3.1. Immune Mediators and Growth Factors
1.3.2. Proteases
1.3.3. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
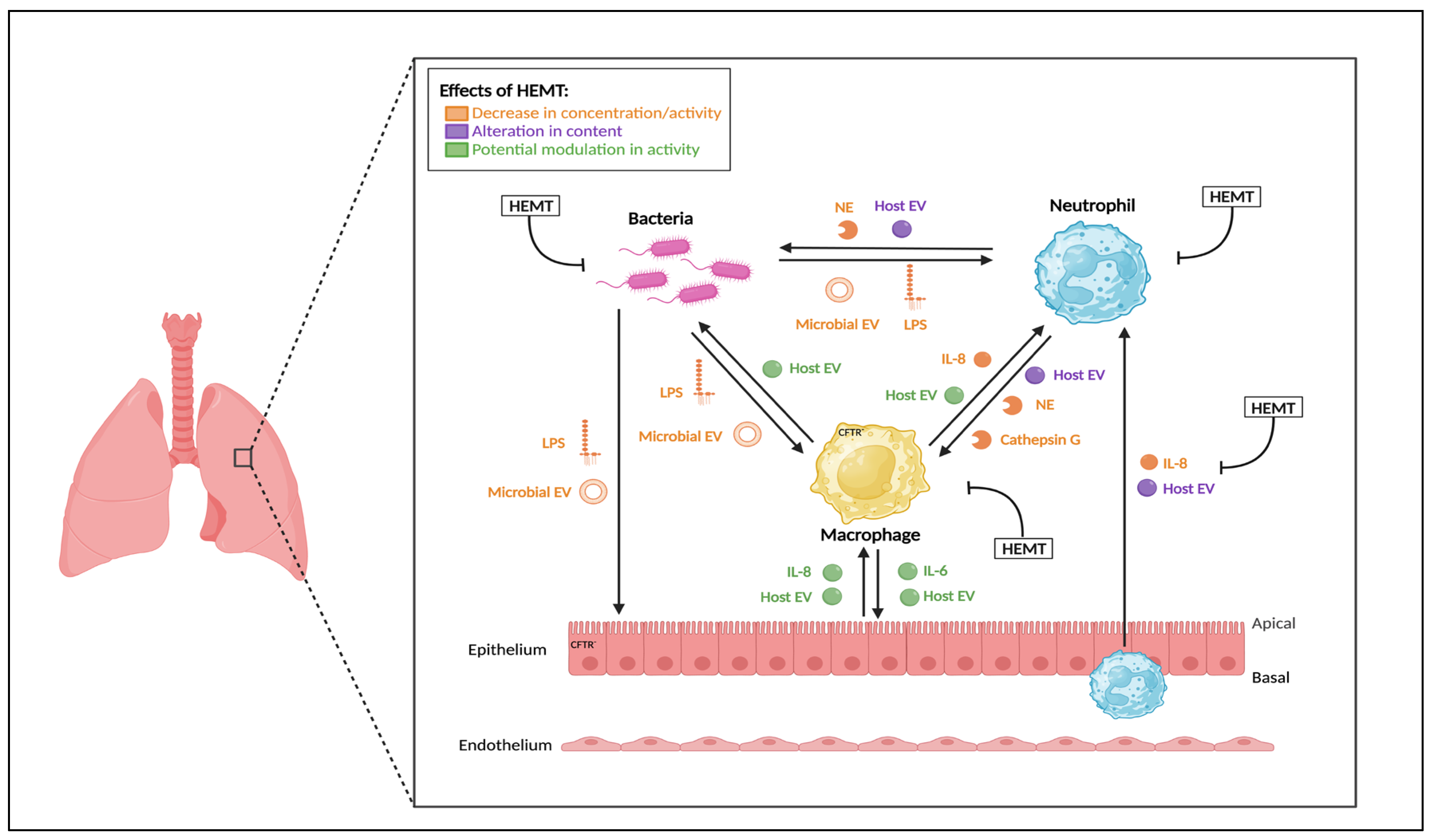
2. Highly Effective CFTR Modulators (HEMT)
2.1. HEMT Classification
2.2. Effects of Monotherapy
2.3. Effect of Dual Therapy
2.4. Effect of Triple Therapy
| Modulator | Sample | Effect of Modulator on Inflammation | Outcome | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monotherapy (Ivacaftor only) | Sputum | No significant changes in levels of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., NE, IL-8, IL-1β) in sputum | Clinical improvements in FEV1 and SCC. | [82] |
| BAL | No significant changes in NE positivity, IL-8, or absolute neutrophil count in BAL | Retrospective but clinical improvements in lung function previously reported for these cohorts | [83] | |
| Sputum | ↓ levels of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., NE, IL-8, IL-1β) in sputum | Clinical improvements in FEV1 and mucus plugging, as well as reduced bacterial concentrations in sputum | [85] | |
| Blood | ↓ levels of a pro-inflammatory mediator (HMGB-1) and neutrophilic inflammatory markers (calprotectin and G-CSF) in circulation | Clinical improvements in FEV1, weight, BMI, and SCC | [87] | |
| Sputum | No changes in sputum inflammatory markers including NE | Clinical improvement in FEV1 and MCC | [100] | |
| Nasal lavage | ↓ levels of IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8 in nasal lavage | Significant clinical improvements in FEV1 and SCC | [101] | |
| Dual Therapy | Lung cells | IVA/LUM significantly ↓ CXCL8, CXCL1 and CXCL2 transcripts in response to P. aeruginosa exposure in primary HBE cells | Potential ↓ lung inflammation but no clinical parameters measured | [88] |
| Blood | ↓ in IL-18 with IVA/LUM and IVA/TEZ in CF monocytes/serum/PBMCs, but ↓ in IL-1β levels only found with IVA/TEZ | No significant changes in clinical parameters, consistent with stability in disease, rather than decline in health | [89] | |
| Sputum | ↓ levels of IL-1β in sputum with IVA/LUM, but no change in other inflammatory mediators, e.g., IL-6, IL-8, TNFα, and NE activity | No change in FEV1, but improvements in LCI, MRI morphology, perfusion score and total bacterial load | [90] | |
| Blood | ↓ in IL-1β, IL-8 and TNFα levels in plasma with IVA/LUM | Clinical improvement in FEV1 and SCC | [91] | |
| Blood | ↓ in WBC counts and serum CRP levels with IVA/LUM | Improvements in FEV1, SCC and BMI | [102] | |
| Triple Therapy (ETI) | Sputum Blood | ↓ in levels of inflammatory cytokines (e.g., NE, IL-8, IL-1β) in sputum in parallel to CRP and PMN count in blood, indicating blunted neutrophil-derived inflammation | Clinical improvements in FEV1 and body weight, with some patients also presenting with decreased SCC | [94] |
| Sputum | ↓ reduction in neutrophil-derived proteins (eg. S100-A8) but not proteases (eg. NE) in sputum, but overall improved balance of harmful/beneficial proteins | Clinical improvements in FEV1 | [95] | |
| Sputum | ↓ in expression of protease inhibitor alpha 1 antitrypsin in sputum EVs | Clinical improvements in lung function and FEV1 | [96] | |
| Sputum | ↓ IL-8 at 3 months and free NE at all timepoints (1, 3, 1 2 months) in sputum | Improvements in FEV1 and relative abundance of P. aeruginosa, | [97] | |
| Sputum Blood | ↓ activity of NE, proteinase 3 and cathepsin G, and ↓ concentrations of IL−1β and IL-8 in sputum. Also restoration of secretory leukoprotease inhibitor levels. | Improvements in FEV1, irrespective of the degree of pre-ETI airflow obstruction, sustained at 1 year. | [98] | |
| Plasma | ↓ levels of MIP-3α, GROα and IL-8 (not significant) in plasma | Improvements in FEV1 and SCC | [103] | |
| Blood | No change in cytokine (e.g., IL-1β, IL-8) secretion in monocyte-derived macrophages from either CF or non-CF individuals. | No clinical parameters measured | [104] |
3. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis |
| CFTR | Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator |
| EV | Extracellular Vesicle |
| HEMT | Highly Effective Modulator Therapy |
| MCC | Mucociliary Clearance |
| FEV1 | Forced Expiratory Volume in 1 s |
| PwCF | Persons with Cystic Fibrosis |
| ASL | Airway Surface Liquid |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| GRIM | Primary Granule Release, Immunomodulatory Activity, and Metabolic Licensing |
| NE | Neutrophil Elastase |
| TNF-α | Tumour Necrosis Factor alpha |
| PAMP | Pathogen-Associated Molecular Pattern |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid |
| MMP | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| ETI | Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor (Trikafta/Kaftrio) |
| SCC | Sweat Chloride Concentration |
References
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, D.P.; Chmiel, J.F. Inflammation and Its Genesis in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2015, 50 (Suppl. S40), S39–S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regamey, N.; Jeffery, P.K.; Alton, E.W.F.W.; Bush, A.; Davies, J.C. Airway Remodelling and Its Relationship to Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis. Thorax 2011, 66, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagel, S.D.; Sontag, M.K.; Wagener, J.S.; Kapsner, R.K.; Osberg, I.; Accurso, F.J. Induced Sputum Inflammatory Measures Correlate with Lung Function in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Pediatr. 2002, 141, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, C.J.; Alkhatib, A.; Einarsson, G.G.; Tunney, M.M.; Taggart, C.C.; Downey, D.G. Diminished Airway Host Innate Response in People with Cystic Fibrosis Who Experience Frequent Pulmonary Exacerbations. Eur. Respir. J. 2024, 63, 2301228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clary-Meinesz, C.; Mouroux, J.; Cosson, J.; Huitorel, P.; Blaive, B. Influence of External pH on Ciliary Beat Frequency in Human Bronchi and Bronchioles. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 11, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ali, Z.S.; Sweezey, N.; Grasemann, H.; Palaniyar, N. Progression of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease from Childhood to Adulthood: Neutrophils, Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET) Formation, and NET Degradation. Genes 2019, 10, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sun, L.; Kato, T.; Okuda, K.; Martino, M.B.; Abzhanova, A.; Lin, J.M.; Gilmore, R.C.; Batson, B.D.; O’Neal, Y.K.; et al. IL-1β Dominates the Promucin Secretory Cytokine Profile in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4433–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birket, S.E.; Rowe, S.M. Revealing the Molecular Signaling Pathways of Mucus Stasis in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4089–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutts, M.J.; Knowles, M.R.; Gatzy, J.T.; Boucher, R.C. Oxygen Consumption and Ouabain Binding Sites in Cystic Fibrosis Nasal Epithelium. Pediatr. Res. 1986, 20, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzsching, B.; Zhou-Suckow, Z.; Trojanek, J.B.; Schubert, S.C.; Schatterny, J.; Hirtz, S.; Agrawal, R.; Muley, T.; Kahn, N.; Sticht, C.; et al. Hypoxic Epithelial Necrosis Triggers Neutrophilic Inflammation via IL-1 Receptor Signaling in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirouvanziam, R.; Khazaal, I.; Péault, B. Primary Inflammation in Human Cystic Fibrosis Small Airways. Am. J. Phys-Lung Cell Mol. Phys. 2002, 283, L445–L451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiddens, H.A.W.M.; Donaldson, S.H.; Rosenfeld, M.; Paré, P.D. Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease Starts in the Small Airways: Can We Treat It More Effectively? Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaroli, C.; Tirouvanziam, R. Neutrophil Plasticity Enables the Development of Pathological Microenvironments: Implications for Cystic Fibrosis Airway Disease. Mol. Cell Pediatr. 2016, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, B.J.; Ooi, C.Y.; Strachan, R.E.; Hameed, S.; Ebrahimkhani, S.; Waters, S.A.; Verge, C.F.; Widger, J. Early Glucose Abnormalities Are Associated with Pulmonary Inflammation in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, S.A.; Lozano, C.; Moustafa, A.M.; Liimatta, K.; Tomlinson, K.L.; Britto, C.; Khanal, S.; Gill, S.K.; Narechania, A.; Azcona-Gutiérrez, J.M.; et al. CFTR-PTEN–Dependent Mitochondrial Metabolic Dysfunction Promotes Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Airway Infection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luly, F.R.; Lévêque, M.; Licursi, V.; Cimino, G.; Martin-Chouly, C.; Théret, N.; Negri, R.; Cavinato, L.; Ascenzioni, F.; Del Porto, P. MiR-146a Is over-Expressed and Controls IL-6 Production in Cystic Fibrosis Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Reyna, S.; Scambler, T.; Holbrook, J.; Wong, C.; Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Martinon, F.; Savic, S.; Peckham, D.; McDermott, M.F. Metabolic Reprograming of Cystic Fibrosis Macrophages via the IRE1α Arm of the Unfolded Protein Response Results in Exacerbated Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazi, M.F.; Dakhlallah, D.A.; Caution, K.; Gerber, M.M.; Chang, S.-W.; Khalil, H.; Kopp, B.T.; Ahmed, A.E.; Krause, K.; Davis, I.; et al. Elevated Mirc1/Mir17-92 Cluster Expression Negatively Regulates Autophagy and CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) Function in CF Macrophages. Autophagy 2016, 12, 2026–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Yu, M.A.; Lefrançais, E.; Mallavia, B.; Valet, C.; Tian, J.J.; Ranucci, S.; Wang, K.M.; Liu, Z.; Kwaan, N.; et al. Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Dysfunction in Platelets Drives Lung Hyperinflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2041–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, R.G.; Marrero, L.; Lombard, G.A.; Valentine, V.G.; Nauseef, W.M.; Wang, G. CFTR-Mediated Halide Transport in Phagosomes of Human Neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 87, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, A.; Brown, M.E.; Deriy, L.V.; Li, C.; Szeto, F.L.; Chen, Y.; Huang, P.; Tong, J.; Naren, A.P.; Bindokas, V.; et al. CFTR Regulates Phagosome Acidification in Macrophages and Alters Bactericidal Activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venaille, T.J.; Ryan, G.; Robinson, B.W. Epithelial Cell Damage Is Induced by Neutrophil-Derived, Not Pseudomonas-Derived, Proteases in Cystic Fibrosis Sputum. Respir. Med. 1998, 92, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M.; Kappler, M.; Gaggar, A.; Hartl, D. Inhibition of Airway Proteases in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Eur. Resp. J. 2008, 32, 783–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sly, P.D.; Gangell, C.L.; Chen, L.; Ware, R.S.; Ranganathan, S.; Mott, L.S.; Murray, C.P.; Stick, S.M.; AREST CF Investigators. Risk Factors for Bronchiectasis in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1963–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, K.; Hayes, E.; Keenan, J.; Henry, M.; Meleady, P.; Molloy, K.; Jundi, B.; Bergin, D.A.; McCarthy, C.; McElvaney, O.J.; et al. A Neutrophil Intrinsic Impairment Affecting Rab27a and Degranulation in Cystic Fibrosis Is Corrected by CFTR Potentiator Therapy. Blood 2014, 124, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandivier, R.W.; Henson, P.M.; Douglas, I.S. Burying the Dead: The Impact of Failed Apoptotic Cell Removal (Efferocytosis) on Chronic Inflammatory Lung Disease. Chest 2006, 129, 1673–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makam, M.; Diaz, D.; Laval, J.; Gernez, Y.; Conrad, C.K.; Dunn, C.E.; Davies, Z.A.; Moss, R.B.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A.; et al. Activation of Critical, Host-Induced, Metabolic and Stress Pathways Marks Neutrophil Entry into Cystic Fibrosis Lungs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5779–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirouvanziam, R.; Gernez, Y.; Conrad, C.K.; Moss, R.B.; Schrijver, I.; Dunn, C.E.; Davies, Z.A.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A. Profound Functional and Signaling Changes in Viable Inflammatory Neutrophils Homing to Cystic Fibrosis Airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4335–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laval, J.; Touhami, J.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Conrad, C.; Taylor, N.; Battini, J.-L.; Sitbon, M.; Tirouvanziam, R. Metabolic Adaptation of Neutrophils in Cystic Fibrosis Airways Involves Distinct Shifts in Nutrient Transporter Expression. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6043–6050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Kummarapurugu, A.B.; Hawkridge, A.; Ghosh, S.; Zheng, S.; Voynow, J.A. Neutrophil Elastase-Regulated Macrophage Sheddome/Secretome and Phagocytic Failure. Am. J. Phy-Lung Cell Mol. Phys. 2021, 321, L555–L565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaroli, C.; Horati, H.; Garratt, L.W.; Giacalone, V.D.; Schofield, C.; Dittrich, A.S.; Rosenow, T.; Dobosh, B.S.; Lim, H.S.; Frey, D.L.; et al. Macrophage PD-1 Associates with Neutrophilia and Reduced Bacterial Killing in Early Cystic Fibrosis Airway Disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingersoll, S.A.; Laval, J.; Forrest, O.A.; Preininger, M.; Brown, M.R.; Arafat, D.; Gibson, G.; Tangpricha, V.; Tirouvanziam, R. Mature Cystic Fibrosis Airway Neutrophils Suppress T Cell Function: Evidence for a Role of Arginase 1 but Not Programmed Death-Ligand 1. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5520–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaroli, C.; Moncada-Giraldo, D.; Gulick, D.A.; Dobosh, B.; Giacalone, V.D.; Forrest, O.A.; Sun, F.; Gu, C.; Gaggar, A.; Kissick, H.; et al. Transcriptional Firing Represses Bactericidal Activity in Cystic Fibrosis Airway Neutrophils. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öz, H.H.; Cheng, E.-C.; Di Pietro, C.; Tebaldi, T.; Biancon, G.; Zeiss, C.; Zhang, P.-X.; Huang, P.H.; Esquibies, S.S.; Britto, C.J.; et al. Recruited Monocytes/Macrophages Drive Pulmonary Neutrophilic Inflammation and Irreversible Lung Tissue Remodeling in Cystic Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, T.L.; Hodges, C.A.; Cotton, C.U.; Drumm, M.L. Absence of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator (Cftr) from Myeloid-Derived Cells Slows Resolution of Inflammation and Infection. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruscia, E.M.; Bonfield, T.L. Cystic Fibrosis Lung Immunity: The Role of the Macrophage. J. Innate Immun. 2016, 8, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiringer, K.; Treis, A.; Fucik, P.; Gona, M.; Gruber, S.; Renner, S.; Dehlink, E.; Nachbaur, E.; Horak, F.; Jaksch, P.; et al. A Th17- and Th2-Skewed Cytokine Profile in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs Represents a Potential Risk Factor for Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, A.; Schäfer, H.; Pöschel, S.; Fischer, A.; Fritzsching, B.; Ralhan, A.; Carevic, M.; Öz, H.; Zundel, S.; Hogardt, M.; et al. Regulatory T-Cell Impairment in Cystic Fibrosis Patients with Chronic Pseudomonas Infection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 191, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rose, V.; Molloy, K.; Gohy, S.; Pilette, C.; Greene, C.M. Airway Epithelium Dysfunction in Cystic Fibrosis and COPD. Mediators Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 1309746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kinter, M.; Shank, S.; Cotton, C.; Kelley, T.J.; Ziady, A.G. Dysfunction of Nrf-2 in CF Epithelia Leads to Excess Intracellular H2O2 and Inflammatory Cytokine Production. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, D.; Gaggar, A.; Bruscia, E.; Hector, A.; Marcos, V.; Jung, A.; Greene, C.; McElvaney, G.; Mall, M.; Döring, G. Innate Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2012, 11, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richman-Eisenstat, J.B.; Jorens, P.G.; Hebert, C.A.; Ueki, I.; Nadel, J.A. Interleukin-8: An Important Chemoattractant in Sputum of Patients with Chronic Inflammatory Airway Diseases. Am. J. Phys-Lung Cell Mol. Phys. 1993, 264, L413–L418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimessi, A.; Bezzerri, V.; Patergnani, S.; Marchi, S.; Cabrini, G.; Pinton, P. Mitochondrial Ca2+-Dependent NLRP3 Activation Exacerbates the Pseudomonas Aeruginosa-Driven Inflammatory Response in Cystic Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, A.J.; Mathie, S.A.; Gregory, L.G.; Lloyd, C.M. Pulmonary Macrophages: Key Players in the Innate Defence of the Airways. Thorax 2015, 70, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfield, T.L.; Panuska, J.R.; Konstan, M.W.; Hilliard, K.A.; Hilliard, J.B.; Ghnaim, H.; Berger, M. Inflammatory Cytokines in Cystic Fibrosis Lungs. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1995, 152 Pt 1, 2111–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickmeier, O.; Fussbroich, D.; Mueller, K.; Serve, F.; Smaczny, C.; Zielen, S.; Schubert, R. Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediator Resolvin D1 Serves as a Marker of Lung Disease in Cystic Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, N.; Wartelle, J.; Malleret, L.; Todorov, A.A.; Devouassoux, G.; Pacheco, Y.; Jenne, D.E.; Belaaouaj, A. Unopposed Cathepsin G, Neutrophil Elastase, and Proteinase 3 Cause Severe Lung Damage and Emphysema. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, L.W.; Sutanto, E.N.; Ling, K.-M.; Looi, K.; Iosifidis, T.; Martinovich, K.M.; Shaw, N.C.; Kicic-Starcevich, E.; Knight, D.A.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Matrix Metalloproteinase Activation by Free Neutrophil Elastase Contributes to Bronchiectasis Progression in Early Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, S.; McNally, P.; McElvaney, N.G.; Elborn, J.S.; McAuley, D.F.; Wartelle, J.; Belaaouaj, A.; Levine, R.L.; Taggart, C.C. Decreased Levels of Secretory Leucoprotease Inhibitor in the Pseudomonas-Infected Cystic Fibrosis Lung Are Due to Neutrophil Elastase Degradation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 8148–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, N.; Butler, M.W.; McNally, P.; Weldon, S.; Greene, C.M.; Levine, R.L.; O’Neill, S.J.; Taggart, C.C.; McElvaney, N.G. Elafin, an Elastase-Specific Inhibitor, Is Cleaved by Its Cognate Enzyme Neutrophil Elastase in Sputum from Individuals with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32377–32385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, D.M.; Zani, M.-L.; Quinn, D.J.; Dallet-Choisy, S.; Glasgow, A.M.; O’Kane, C.; McAuley, D.F.; McNally, P.; Weldon, S.; Moreau, T.; et al. A Functional Variant of Elafin With Improved Anti-Inflammatory Activity for Pulmonary Inflammation. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camper, N.; Glasgow, A.M.A.; Osbourn, M.; Quinn, D.J.; Small, D.M.; McLean, D.T.; Lundy, F.T.; Elborn, J.S.; McNally, P.; Ingram, R.J.; et al. A Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor Variant with Improved Activity against Lung Infection. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, D.; Latzin, P.; Hordijk, P.; Marcos, V.; Rudolph, C.; Woischnik, M.; Krauss-Etschmann, S.; Koller, B.; Reinhardt, D.; Roscher, A.A.; et al. Cleavage of CXCR1 on Neutrophils Disables Bacterial Killing in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1423–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Barillec, K.; Si-Tahar, M.; Balloy, V.; Chignard, M. Proteolysis of Monocyte CD14 by Human Leukocyte Elastase Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Mediated Cell Activation. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosi, M.F.; Zakem, H. Surface Expression of Fc Gamma Receptor III (CD16) on Chemoattractant-Stimulated Neutrophils Is Determined by Both Surface Shedding and Translocation from Intracellular Storage Compartments. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, W.C.; Shapiro, S.D. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Lung Biology. Respir. Res. 2000, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratjen, F.; Hartog, C.-M.; Paul, K.; Wermelt, J.; Braun, J. Matrix Metalloproteases in BAL Fluid of Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and Their Modulation by Treatment with Dornase Alpha. Thorax 2002, 57, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggar, A.; Li, Y.; Weathington, N.; Winkler, M.; Kong, M.; Jackson, P.; Blalock, J.E.; Clancy, J.P. Matrix Metalloprotease-9 Dysregulation in Lower Airway Secretions of Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2007, 293, L96–L104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagel, S.D.; Kapsner, R.K.; Osberg, I. Induced Sputum Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Correlates with Lung Function and Airway Inflammation in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2005, 39, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderfeld, M.; Rath, T.; Schulz, R.; Seeger, W.; Tschuschner, A.; Graf, J.; Roeb, E. Serum Matrix Metalloproteinases in Adult CF Patients: Relation to Pulmonary Exacerbation. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2009, 8, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devereux, G.; Steele, S.; Jagelman, T.; Fielding, S.; Muirhead, R.; Brady, J.; Grierson, C.; Brooker, R.; Winter, J.; Fardon, T.; et al. An Observational Study of Matrix Metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2014, 13, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, C.C.; Greene, C.M.; Smith, S.G.; Levine, R.L.; McCray, P.B.; O’Neill, S.; McElvaney, N.G. Inactivation of Human Beta-Defensins 2 and 3 by Elastolytic Cathepsins. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogan, M.P.; Taggart, C.C.; Greene, C.M.; Murphy, P.G.; O’Neill, S.J.; McElvaney, N.G. Loss of Microbicidal Activity and Increased Formation of Biofilm Due to Decreased Lactoferrin Activity in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 190, 1245–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, M.A.; Schultz, C. A New Player in the Game: Epithelial Cathepsin S in Early Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, A.; Donnelly, S.C.; McNally, P.; Coppinger, J.A. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Chronic Lung Disease. Thorax 2021, 76, 1047–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Useckaite, Z.; Ward, M.P.; Trappe, A.; Reilly, R.; Lennon, J.; Davage, H.; Matallanas, D.; Cassidy, H.; Dillon, E.T.; Brennan, K.; et al. Increased Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Inflammatory Signalling in Cystic Fibrosis. Thorax 2020, 75, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, O.A.; Dobosh, B.; Ingersoll, S.A.; Rao, S.; Rojas, A.; Laval, J.; Alvarez, J.A.; Brown, M.R.; Tangpricha, V.; Tirouvanziam, R. Neutrophil-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Feed-Forward Inflammasome Signaling in Cystic Fibrosis Airways. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 112, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.F.; Avner, B.S.; Greenlee-Wacker, M.C.; Horswill, A.R.; Nauseef, W.M. Neutrophil-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate the Phenotype of Naïve Human Neutrophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 110, 917–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppen, K.; Nymon, A.; Barnaby, R.; Li, Z.; Hampton, T.H.; Ashare, A.; Stanton, B.A. CF Monocyte-Derived Macrophages Have an Attenuated Response to Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Phys-Lung Cell Mol. Phys. 2021, 320, L530–L544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitse, J.; Devreese, B. The Contribution of Membrane Vesicles to Bacterial Pathogenicity in Cystic Fibrosis Infections and Healthcare Associated Pneumonia. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafeeq, M.M.; Murad, H.A.S. Cystic Fibrosis: Current Therapeutic Targets and Future Approaches. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsey, B.W.; Davies, J.; McElvaney, N.G.; Tullis, E.; Bell, S.C.; Dřevínek, P.; Griese, M.; McKone, E.F.; Wainwright, C.E.; Konstan, M.W.; et al. A CFTR Potentiator in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and the G551D Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1663–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.C.; Wainwright, C.E.; Canny, G.J.; Chilvers, M.A.; Howenstine, M.S.; Munck, A.; Mainz, J.G.; Rodriguez, S.; Li, H.; Yen, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Ivacaftor in Patients Aged 6 to 11 Years with Cystic Fibrosis with a G551D Mutation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, J.P.; Rowe, S.M.; Accurso, F.J.; Aitken, M.L.; Amin, R.S.; Ashlock, M.A.; Ballmann, M.; Boyle, M.P.; Bronsveld, I.; Campbell, P.W.; et al. Results of a Phase IIa Study of VX-809, an Investigational CFTR Corrector Compound, in Subjects with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for the F508del-CFTR Mutation. Thorax 2012, 67, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, C.E.; Elborn, J.S.; Ramsey, B.W.; Marigowda, G.; Huang, X.; Cipolli, M.; Colombo, C.; Davies, J.C.; Boeck, K.D.; Flume, P.A.; et al. Lumacaftor–Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for Phe508del CFTR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, J.C.; Moskowitz, S.M.; Brown, C.; Horsley, A.; Mall, M.A.; McKone, E.F.; Plant, B.J.; Prais, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; et al. VX-659-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and One or Two Phe508del Alleles. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, S.C.; Mall, M.A.; Gutierrez, H.; Macek, M.; Madge, S.; Davies, J.C.; Burgel, P.-R.; Tullis, E.; Castaños, C.; Castellani, C.; et al. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine Commission on the Future of Care of Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 65–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijerman, H.G.M.; McKone, E.F.; Downey, D.G.; Van Braeckel, E.; Rowe, S.M.; Tullis, E.; Mall, M.A.; Welter, J.J.; Ramsey, B.W.; McKee, C.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the Elexacaftor plus Tezacaftor plus Ivacaftor Combination Regimen in People with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for the F508del Mutation: A Double-Blind, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluer, A.Z.; MacGregor, G.; Azevedo, P.; Indihar, V.; Keating, C.; Mall, M.A.; McKone, E.F.; Ramsey, B.W.; Rowe, S.M.; Rubenstein, R.C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Vanzacaftor–Tezacaftor–Deutivacaftor in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: Randomised, Double-Blind, Controlled, Phase 2 Trials. Lancet Resp. Med. 2023, 11, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gushue, C.; Eisner, M.; Bai, S.; Johnson, T.; Holtzlander, M.; McCoy, K.; Sheikh, S. Impact of Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor on Lung Disease in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 2308–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.K.; Wagner, B.D.; Zemanick, E.T.; Robertson, C.E.; Stevens, M.J.; Heltshe, S.L.; Rowe, S.M.; Sagel, S.D. Changes in Airway Microbiome and Inflammation with Ivacaftor Treatment in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and the G551D Mutation. Ann. ATS 2020, 17, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, P.; Butler, D.; Karpievitch, Y.V.; Linnane, B.; Ranganathan, S.; Stick, S.M.; Hall, G.L.; Schultz, A. Ivacaftor and Airway Inflammation in Preschool Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durfey, S.L.; Pipavath, S.; Li, A.; Vo, A.T.; Ratjen, A.; Carter, S.; Morgan, S.J.; Radey, M.C.; Grogan, B.; Salipante, S.J.; et al. Combining Ivacaftor and Intensive Antibiotics Achieves Limited Clearance of Cystic Fibrosis Infections. mBio 2021, 12, e03148-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisert, K.B.; Heltshe, S.L.; Pope, C.; Jorth, P.; Wu, X.; Edwards, R.M.; Radey, M.; Accurso, F.J.; Wolter, D.J.; Cooke, G.; et al. Restoring Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Function Reduces Airway Bacteria and Inflammation in People with Cystic Fibrosis and Chronic Lung Infections. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, F.J.; Nazareth, D.S.; Charman, S.C.; Winstanley, C.; Walshaw, M.J. Ivacaftor Is Associated with Reduced Lung Infection by Key Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens. A Cohort Study Using National Registry Data. Ann. ATS 2019, 16, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, J.E.; Wagner, B.D.; Kirk Harris, J.; Rowe, S.M.; Heltshe, S.L.; DeBoer, E.M.; Sagel, S.D. Effects of Ivacaftor on Systemic Inflammation and the Plasma Proteome in People with CF and G551D. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffin, M.; Roussel, L.; Maillé, É.; Rousseau, S.; Brochiero, E. Vx-809/Vx-770 Treatment Reduces Inflammatory Response to Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Primary Differentiated Cystic Fibrosis Bronchial Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Phys-Lung Cell Mol. Phys. 2018, 314, L635–L641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarosz-Griffiths, H.H.; Scambler, T.; Wong, C.H.; Lara-Reyna, S.; Holbrook, J.; Martinon, F.; Savic, S.; Whitaker, P.; Etherington, C.; Spoletini, G.; et al. Different CFTR Modulator Combinations Downregulate Inflammation Differently in Cystic Fibrosis. eLife 2020, 9, e54556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, S.Y.; Boutin, S.; Wielpütz, M.O.; Joachim, C.; Frey, D.L.; Wege, S.; Sommerburg, O.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Stahl, M.; Dalpke, A.H.; et al. Effects of Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor on Lung Clearance Index, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Airway Microbiome in Phe508del Homozygous Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2021, 18, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arooj, P.; Morrissy, D.V.; McCarthy, Y.; Vagg, T.; McCarthy, M.; Fleming, C.; Daly, M.; Eustace, J.A.; Murphy, D.M.; Plant, B.J. ROCK STUDY in CF: Sustained Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lumacaftor–Ivacaftor in Sputum and Peripheral Blood Samples of Adult Patients with Cystic Fibrosis—An Observational Study. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2023, 10, e001590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, P.; Linnane, B.; Williamson, M.; Elnazir, B.; Short, C.; Saunders, C.; Kirwan, L.; David, R.; Kemner-Van de Corput, M.P.C.; Tiddens, H.A.W.M.; et al. The Clinical Impact of Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor on Structural Lung Disease and Lung Function in Children Aged 6–11 with Cystic Fibrosis in a Real-World Setting. Respir. Res. 2023, 24, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enaud, R.; Lussac-Sorton, F.; Charpentier, E.; Velo-Suárez, L.; Guiraud, J.; Bui, S.; Fayon, M.; Schaeverbeke, T.; Nikolski, M.; LumIvaBiota Study Group; et al. Effects of Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor on Airway Microbiota-Mycobiota and Inflammation in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Appear To Be Linked to Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Chronic Colonization. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0225122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepissier, A.; Bonnel, A.S.; Wizla, N.; Weiss, L.; Mittaine, M.; Bessaci, K.; Kerem, E.; Houdouin, V.; Reix, P.; Marguet, C.; et al. Moving the Dial on Airway Inflammation in Response to Trikafta in Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 792–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, R.E.; Barry, P.J.; Emmott, E.; Jones, A.M.; Lin, L.; McNamara, P.S.; Smith, J.A.; Lord, R.W. Influence of Highly Effective Modulator Therapy on the Sputum Proteome in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2024, 23, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, A.; Lakkappa, N.; Carter, S.; Dillon, E.; Wynne, K.; McKone, E.; McNally, P.; Coppinger, J.A. Investigating Serum Extracellular Vesicles in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaupp, L.; Addante, A.; Völler, M.; Fentker, K.; Kuppe, A.; Bardua, M.; Duerr, J.; Piehler, L.; Röhmel, J.; Thee, S.; et al. Longitudinal Effects of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor on Sputum Viscoelastic Properties, Airway Infection and Inflammation in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 62, 2202153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, M.; Gabillard-Lefort, C.; McElvaney, O.F.; McElvaney, O.J.; Carroll, T.; Heeney, R.C.; Gunaratnam, C.; Reeves, E.P.; Murphy, M.P.; McElvaney, N.G. Effect of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor on Airway and Systemic Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis. Thorax 2023, 78, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, A.-M.; Sieber, S.; Naehrlich, L.; Burkhart, M.; Hafkemeyer, S.; Tümmler, B. Use of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor Leads to Changes in Detection Frequencies of Staphylococcus Aureus and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Dependent on Age and Lung Function in People with Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 139, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, S.M.; Heltshe, S.L.; Gonska, T.; Donaldson, S.H.; Borowitz, D.; Gelfond, D.; Sagel, S.D.; Khan, U.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Van Dalfsen, J.M.; et al. Clinical Mechanism of the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Potentiator Ivacaftor in G551D-Mediated Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainz, J.G.; Arnold, C.; Wittstock, K.; Hipler, U.-C.; Lehmann, T.; Zagoya, C.; Duckstein, F.; Ellemunter, H.; Hentschel, J. Ivacaftor Reduces Inflammatory Mediators in Upper Airway Lining Fluid From Cystic Fibrosis Patients With a G551D Mutation: Serial Non-Invasive Home-Based Collection of Upper Airway Lining Fluid. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favia, M.; Gallo, C.; Guerra, L.; De Venuto, D.; Diana, A.; Polizzi, A.M.; Montemurro, P.; Mariggiò, M.A.; Leonetti, G.; Manca, A.; et al. Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis Patients Homozygous for F508del with Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor (Orkambi®) Restores Defective CFTR Channel Function in Circulating Mononuclear Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westhölter, D.; Pipping, J.; Raspe, J.; Schmitz, M.; Sutharsan, S.; Straßburg, S.; Welsner, M.; Taube, C.; Reuter, S. Plasma Levels of Chemokines Decrease during Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor Therapy in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e23428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aridgides, D.S.; Mellinger, D.L.; Gwilt, L.L.; Hampton, T.H.; Mould, D.L.; Hogan, D.A.; Ashare, A. Comparative Effects of CFTR Modulators on Phagocytic, Metabolic and Inflammatory Profiles of CF and nonCF Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shrestha, C.L.; Robledo-Avila, F.; Jaganathan, D.; Wisniewski, B.L.; Brown, N.; Pham, H.; Carey, K.; Amer, A.O.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; et al. Cystic Fibrosis Macrophage Function and Clinical Outcomes after Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, G.R.; Reis, M.; Gheinani, A.H.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, A.; Taglauer, E.S.; Yeung, V.; Liu, X.; Ericsson, M.; Haas, E.; Mitsialis, S.A.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Protect the Neonatal Lung from Hyperoxic Injury through the Epigenetic and Transcriptomic Reprogramming of Myeloid Cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1418–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahida, R.Y.; Matthay, M.A. Myeloid Extracellular Vesicles: New Players in Indirect Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 68, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Ros, J.; Mas-Bargues, C.; Romero-García, N.; Huete-Acevedo, J.; Dromant, M.; Borrás, C. Extracellular Vesicles as Therapeutic Resources in the Clinical Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, C.; Xu, Z.; Bardin, P.; Corvol, H.; Touqui, L.; Tabary, O. Novel Anti-Inflammatory Approaches for Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease: Identification of Molecular Targets and Design of Innovative Therapies. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hynes, J.; Taggart, C.C.; Tirouvanziam, R.; Coppinger, J.A. Innate Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis: Varied Effects of CFTR Modulator Therapy on Cell-to-Cell Communication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062636
Hynes J, Taggart CC, Tirouvanziam R, Coppinger JA. Innate Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis: Varied Effects of CFTR Modulator Therapy on Cell-to-Cell Communication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062636
Chicago/Turabian StyleHynes, Jennifer, Clifford C. Taggart, Rabindra Tirouvanziam, and Judith A. Coppinger. 2025. "Innate Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis: Varied Effects of CFTR Modulator Therapy on Cell-to-Cell Communication" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062636
APA StyleHynes, J., Taggart, C. C., Tirouvanziam, R., & Coppinger, J. A. (2025). Innate Immunity in Cystic Fibrosis: Varied Effects of CFTR Modulator Therapy on Cell-to-Cell Communication. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2636. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062636







