Determining the Role of OsAGP6P in Anther Development Within the Arabinogalactan Peptide Family of Rice (Oryza sativa)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
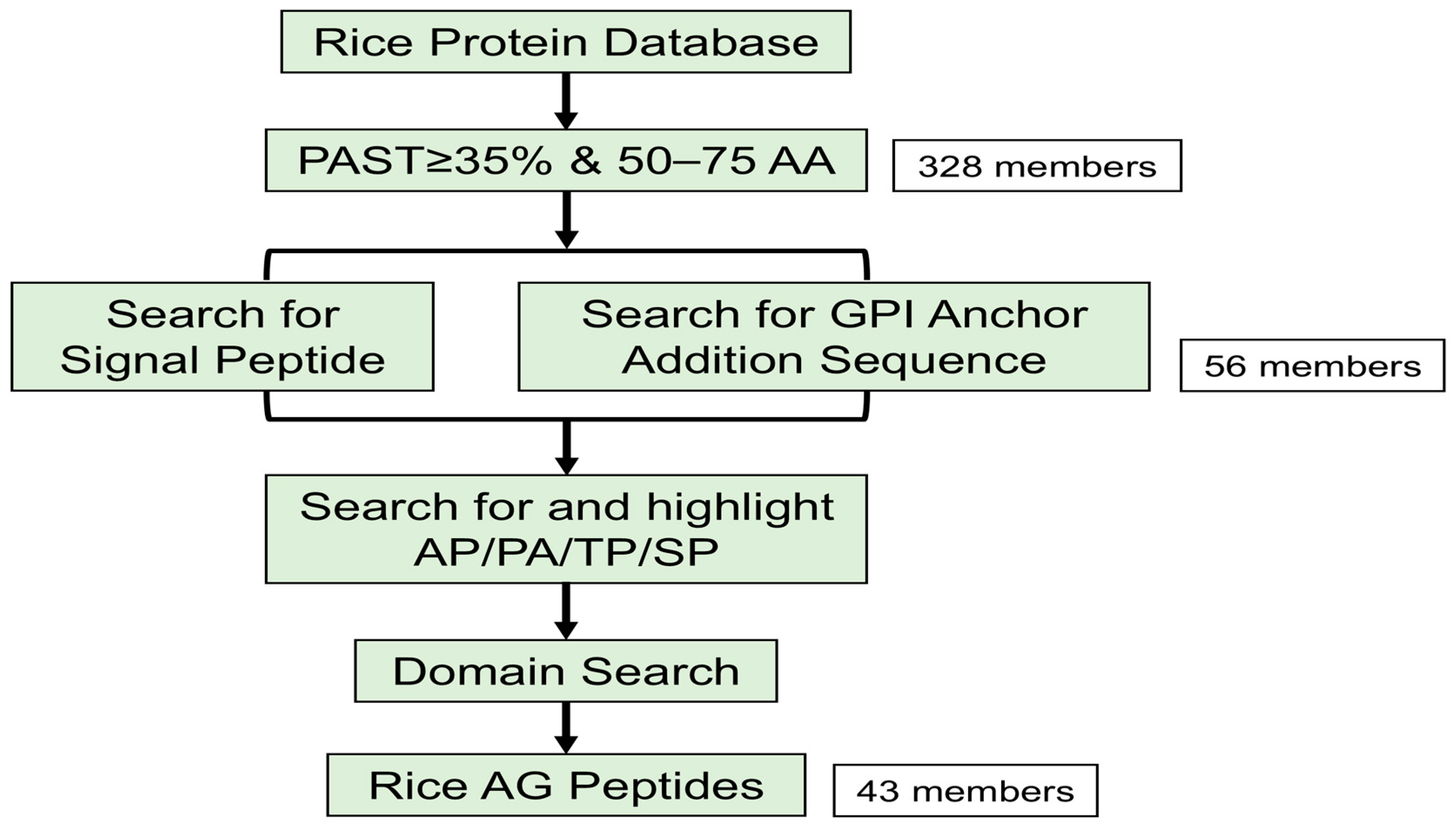
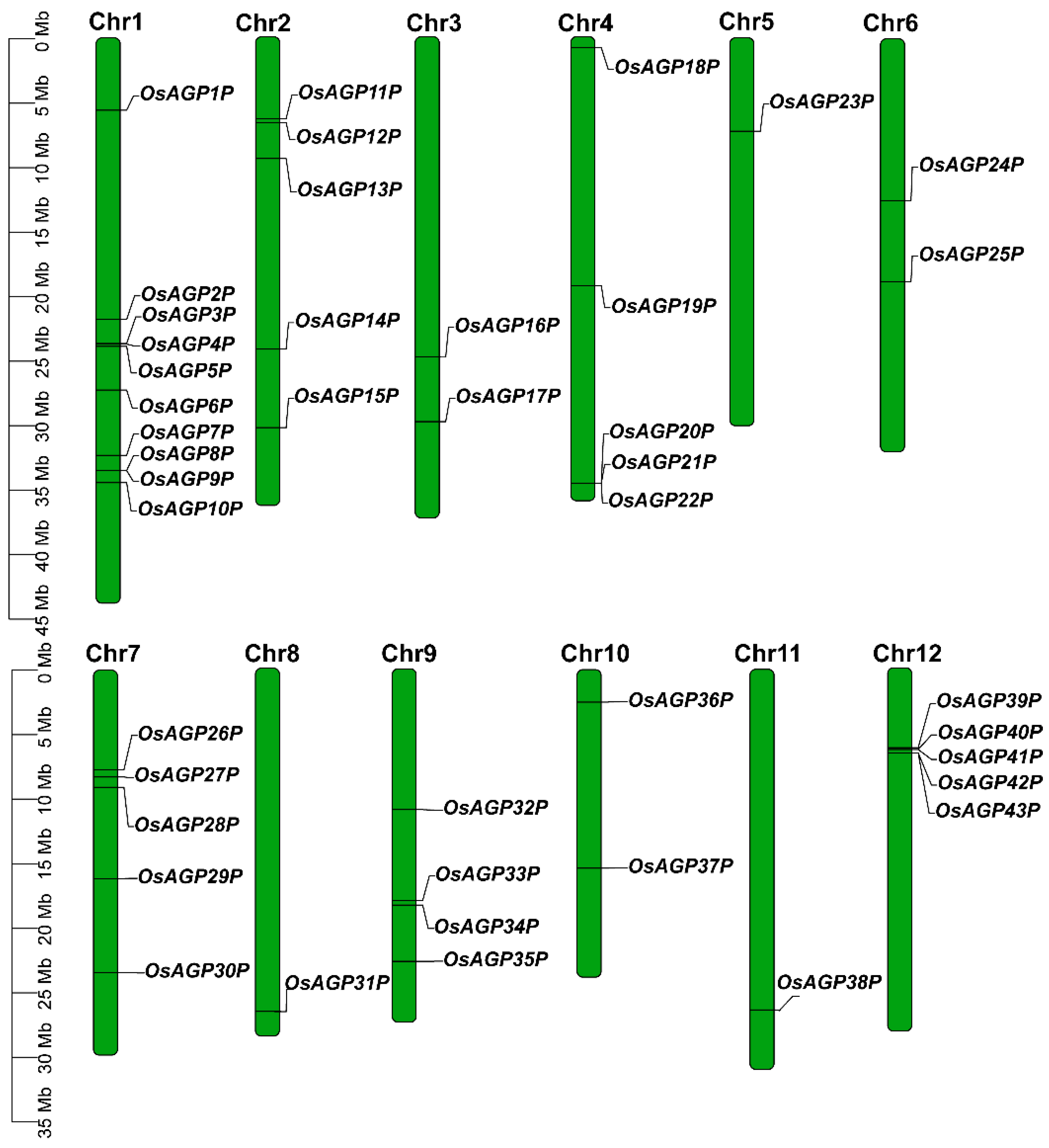
2.1. Identification of AG Peptide Genes in Rice
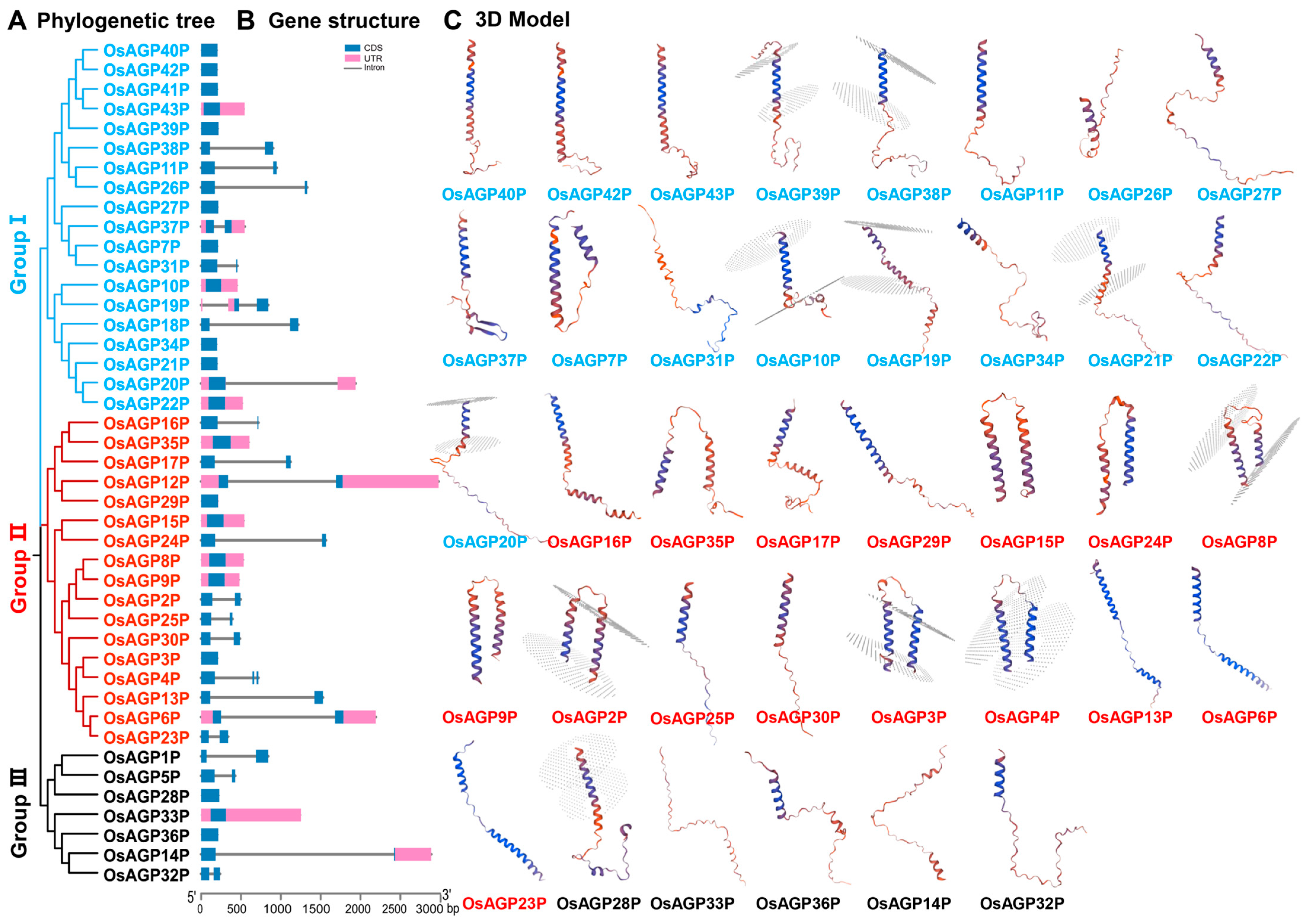
2.2. Phylogenetic and Protein Structure Analyses of AG Peptide Proteins in Rice
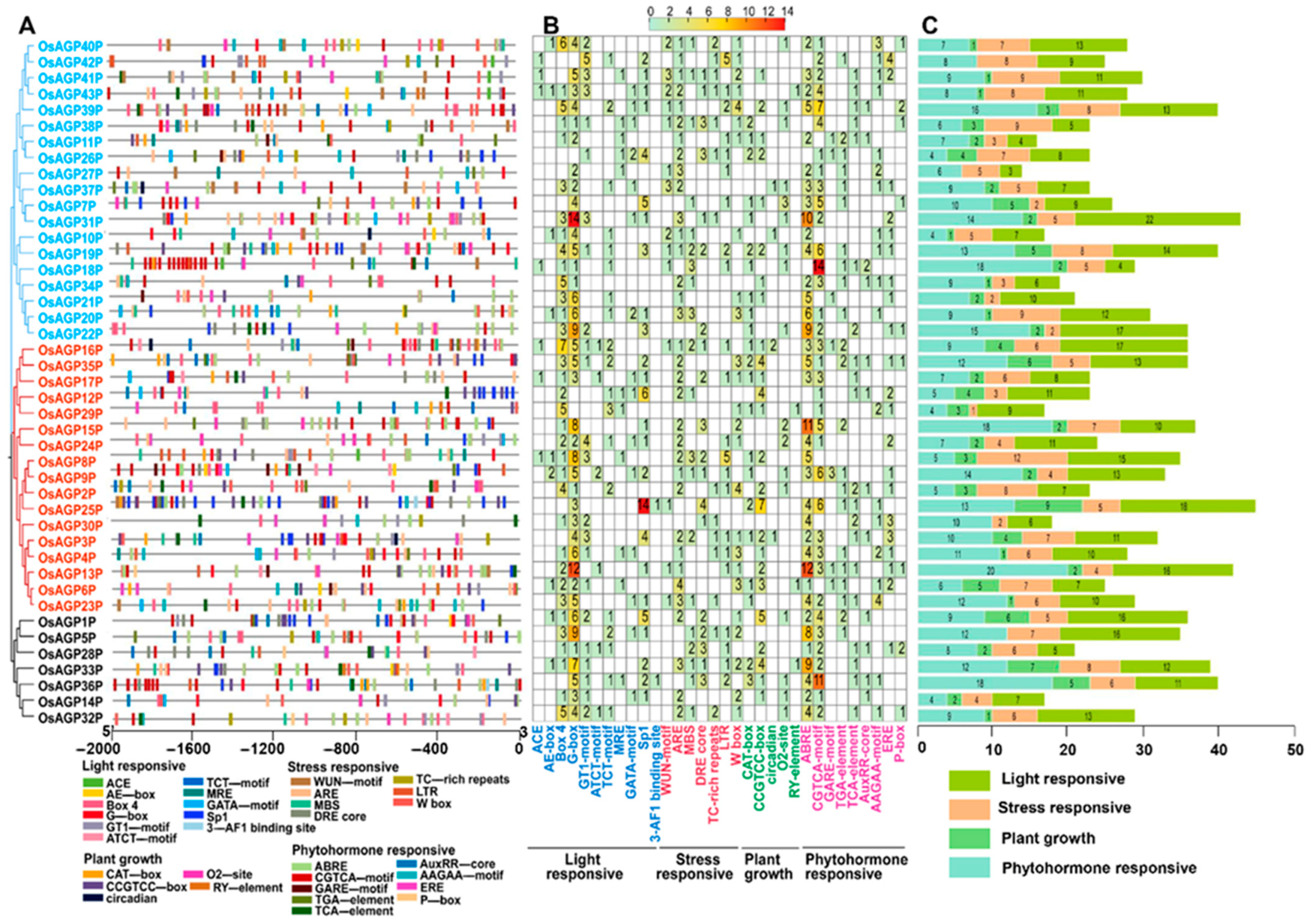
2.3. Identification of Cis-Regulatory Elements Within the Promoters of AG Peptide Genes
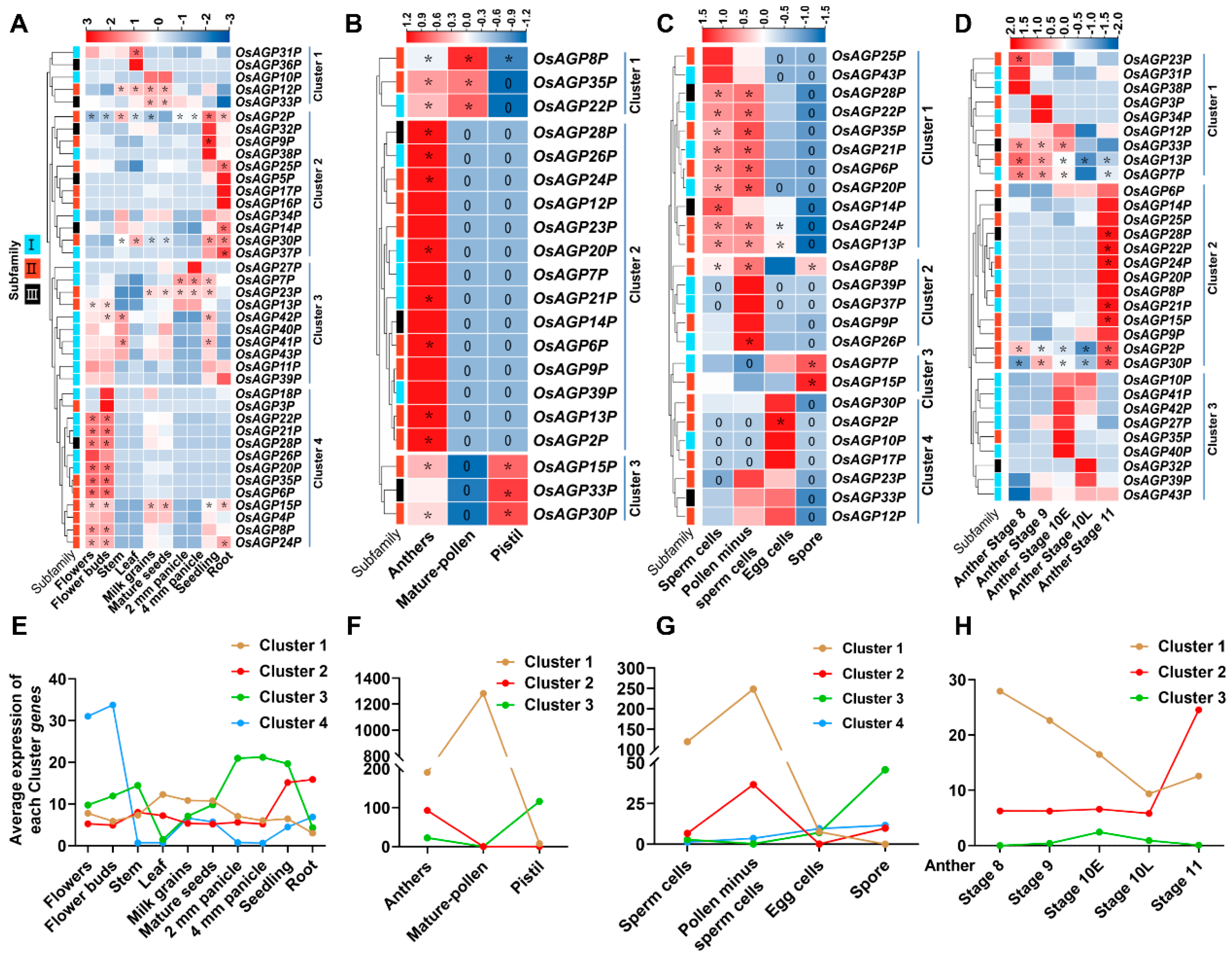
2.4. Expression Patterns of AG Peptide Genes in Multiple Tissues
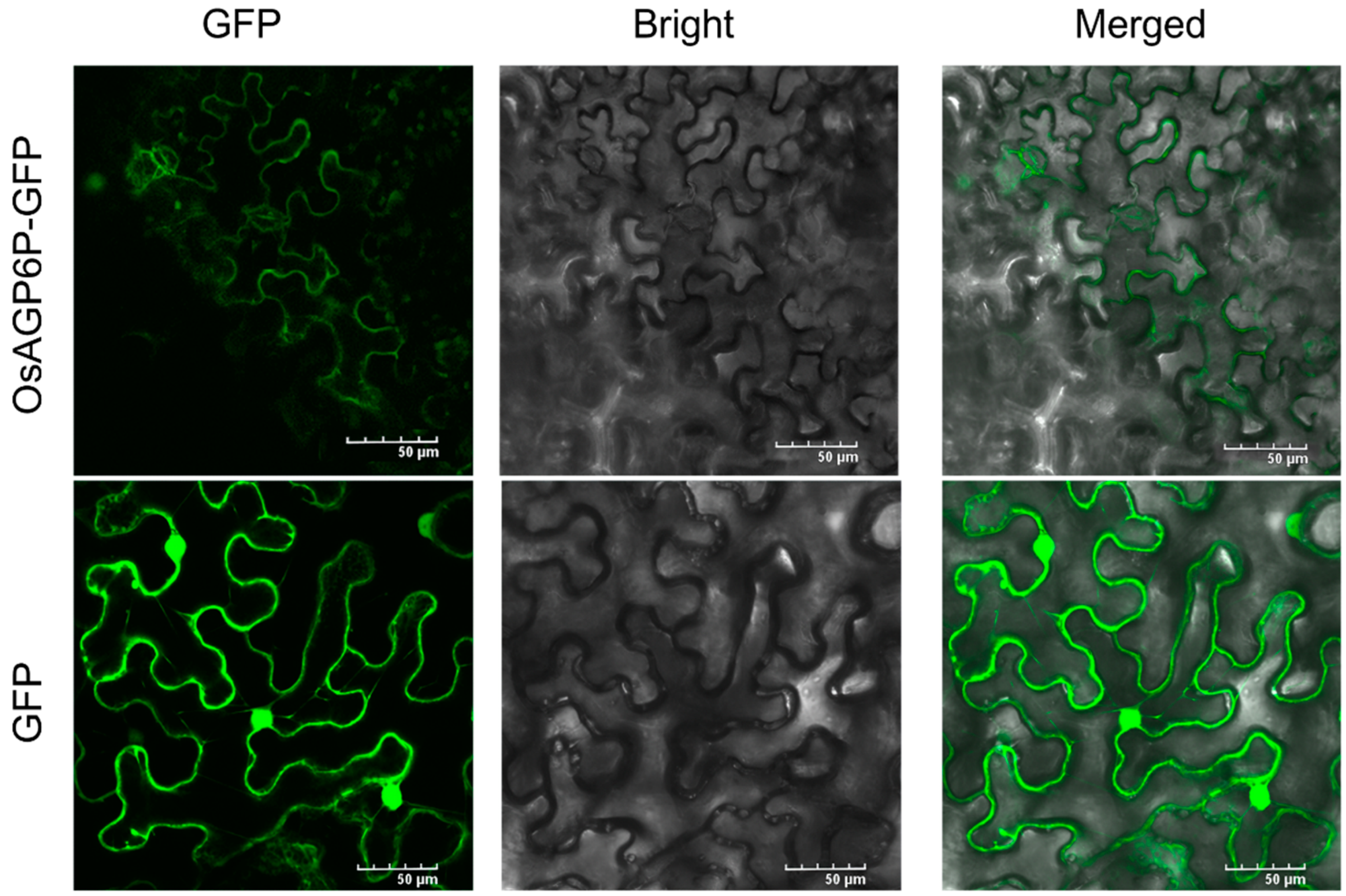
2.5. Subcellular Localization of the OsAGP6P Protein and the GUS Staining of OsAGP6P in Tissues and Organs
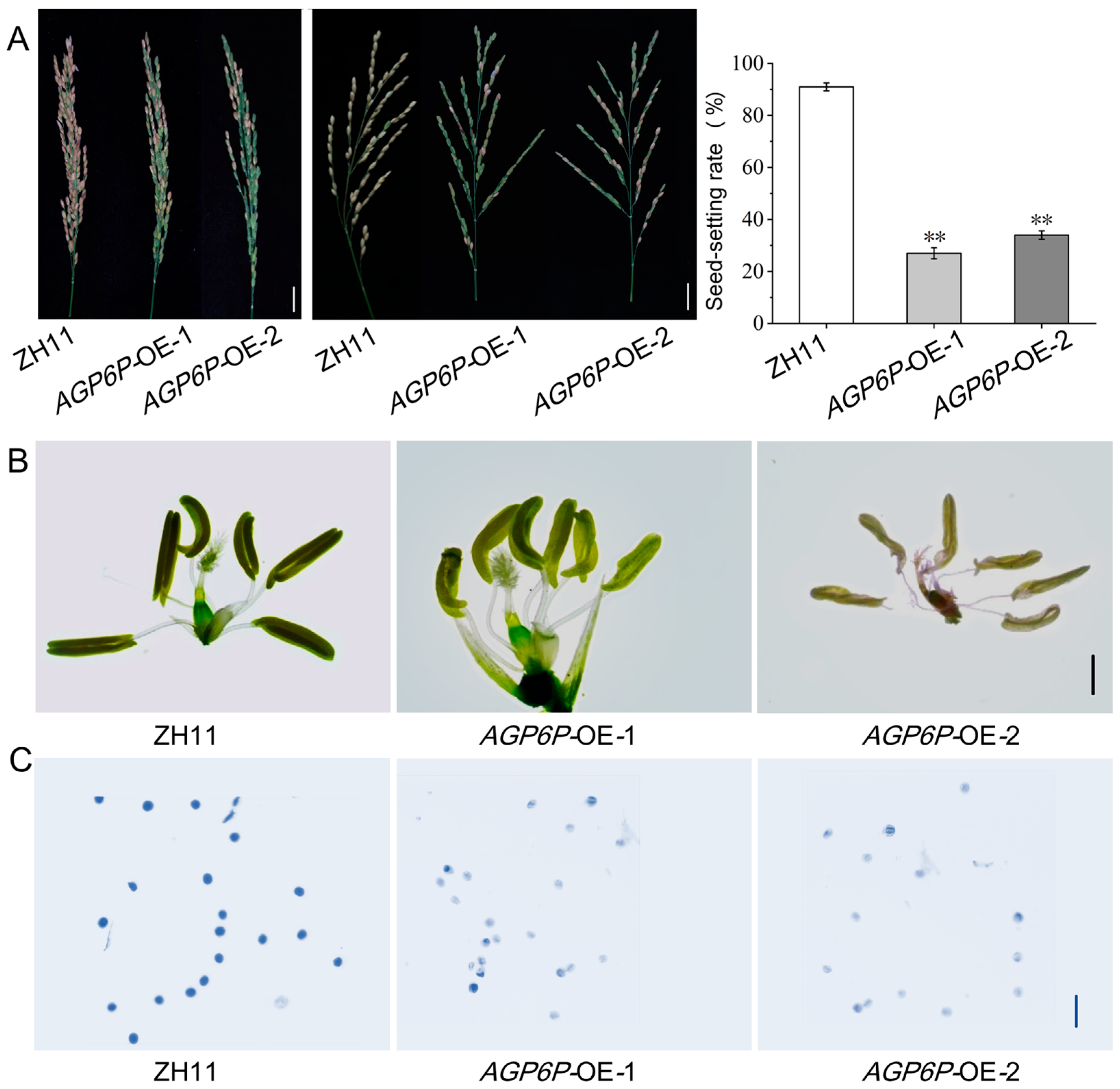
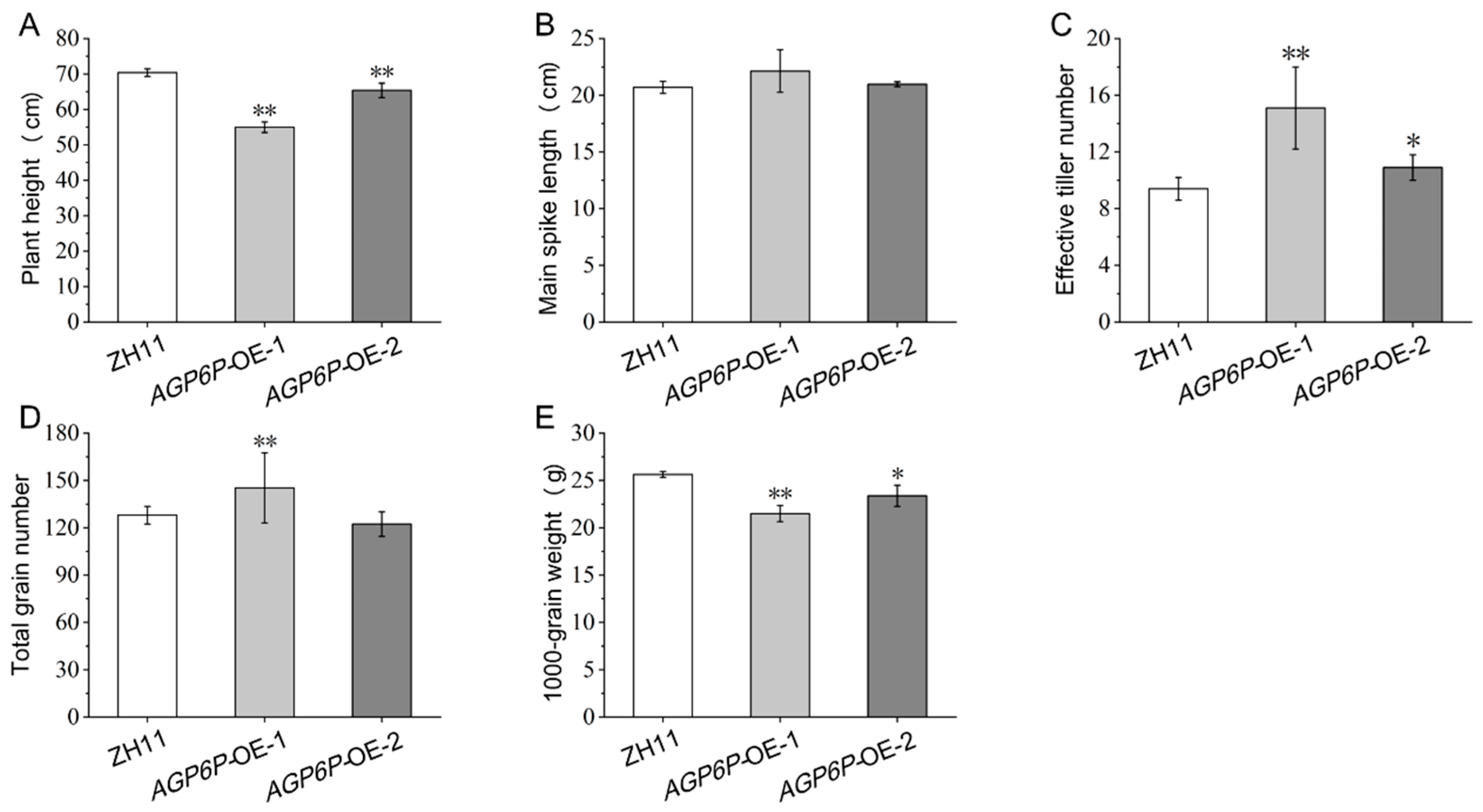
2.6. Phenotypic Observation of OsAGP6P Overexpression Plants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Identification of AG Peptide Proteins in Rice
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis, the Motifs Prediction, and the Three-Dimensional (3D) Structure Models of AG Peptide Proteins
4.3. Chromosomal Mapping, Gene Structure Analysis, and Promoter’s Cis-Element Analysis of AG Peptide Genes
4.4. Expression Pattern Analysis of AG Peptide Genes
4.5. Subcellular Localization Analysis of OsAGP6P Protein
4.6. The Construction and the Transformation of the Recombinant Vector pCAMBIA1381Z-OsAGP6P and GUS Staining of the Tissues from Transgenic Plants
4.7. The Construction and the Investigation of Pollen Sterility of OsAGP6P Overexpression Transgenic Plants
4.8. The Agronomic Traits and Statistical Analysis of OsAGP6P Overexpression Transgenic Plants
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henry, J.S.; Ligrone, R.; Vaughn, K.C.; Lopez, R.A.; Renzaglia, K.S. Cell wall polymers in the Phaeoceros placenta reflect developmental and functional differences across generations. Bryophyt. Divers. Evol. 2021, 43, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Showalter, A.M. Arabinogalactan-proteins: Structure, expression and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2001, 58, 1399–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, M.; Roujol, D.; Nguyen-Kim, H.; del Rocio Cisneros Castillo, L.; Saland, E.; Jamet, E.; Albenne, C. Arabinogalactan protein 31 (AGP31), a putative network-forming protein in Arabidopsis thaliana cell walls? Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Ferraz, R.; Dupree, P.; Showalter, A.M.; Coimbra, S. Three decades of advances in arabinogalactan-protein biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 610377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguema-Ona, E.; Coimbra, S.; Vicré-Gibouin, M.; Mollet, J.C.; Driouich, A. Arabinogalactan proteins in root and pollen-tube cells: Distribution and functional aspects. Ann. Bot. 2012, 110, 383–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromadová, D.; Soukup, A.; Tylová, E. Arabinogalactan proteins in plant roots–an update on possible functions. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 674010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.J.; Johnson, K.L.; Currie, G.; Bacic, A. The classical arabinogalactan protein gene family of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1751–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Dong, H.; Cui, J.; Li, M.; Lin, S.; Cao, J.; Huang, L. Genomic, molecular evolution, and expression analysis of genes encoding putative classical AGPs, lysine-rich AGPs, and AG peptides in Brassica rapa. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Moreira, D.; Coimbra, S.; Showalter, A.M. Hydroxyproline-O-galactosyltransferases synthesizing type ii arabinogalactans are essential for male gametophytic development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 935413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, J. Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of the arabinogalactan protein gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2647–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, C.P.; Taylor, L.; Bi, Y.; Southerton, S.G.; Evans, R.; Spokevicius, A. The fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein family of Eucalyptus grandis contains members that impact wood biology and biomechanics. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J. The phytocyanin gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Genome-wide identification, classification and transcriptional analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Motose, H.; Iwamoto, K.; Fukuda, H. Expression and genome-wide analysis of the xylogen-type gene family. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Yin, T.; Wu, H. Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis of the Fasciclin-like Arabinogalactan Proteins (FLAs) in Salicacea and Identification of Secondary Tissue Development-Related Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Johnson, K. Arabinogalactan proteins–multifunctional glycoproteins of the plant cell wall. Cell Surf. 2023, 9, 100102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, A.M.; Keppler, B.D.; Lichtenberg, J.; Gu, D.; Welch, L.R. A bioinformatics approach to the identification, classification, and analysis of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 485–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Cassin, A.M.; Lonsdale, A.; Wong, G.K.S.; Soltis, D.E.; Miles, N.W.; Melkonian, M.; Melkonian, B.; Deyholos, M.K.; Leebens-Mack, J. Insights into the evolution of hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins from 1000 plant transcriptomes. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 904–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Cassin, A.M.; Lonsdale, A.; Bacic, A.; Doblin, M.S.; Schultz, C.J. Pipeline to identify hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 886–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zeng, W.; Bacic, A.; Johnson, K. AGPs through time and space. Annu. Plant Rev. Online 2018, 1, 767–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shafee, T.; Mudiyanselage, A.M.; Ratcliffe, J.; MacMillan, C.P.; Mansfield, S.D.; Bacic, A.; Johnson, K.L. Distinct functions of FASCICLIN-LIKE ARABINOGALACTAN PROTEINS relate to domain structure. Plant Physiol. 2023, 192, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczuk, A.; Kalaitzis, P.; Kulik, J.; Zdunek, A. Review: Structure and modifications of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs). BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.Q.; Gong, S.Y.; Xu, W.L.; Li, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, C.J.; Li, D.D.; Zheng, Y.; Li, F.G.; Li, X.B. A fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein, GhFLA1, is involved in fiber initiation and elongation of cotton. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Přerovská, T.; Jindřichová, B.; Henke, S.; Yvin, J.C.; Ferrieres, V.; Burketová, L.; Lipovová, P.; Nguema-Ona, E. Arabinogalactan protein-like proteins from Ulva lactuca activate immune responses and plant resistance in an oilseed crop. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 893858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.M.; Pereira, L.G.; Coimbra, S. Arabinogalactan proteins: Rising attention from plant biologists. Plant Reprod. 2015, 28, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Higashiyama, T. Arabinogalactan proteins and their sugar chains: Functions in plant reproduction, research methods, and biosynthesis. Plant Reprod. 2018, 31, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszczuk, A.; Cybulska, J.; Skrzypek, T.; Zdunek, A. Properties of arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs) in apple (Malus × Domestica) fruit at different stages of ripening. Biology 2020, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareri, L.; Romi, M.; Cai, G. Arabinogalactan proteins: Actors or spectators during abiotic and biotic stress in plants? Plant Biosyst.-Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2019, 153, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, C.; Zienkiewicz, A.; Castro, A.J.; Zienkiewicz, K.; Majewska-Sawka, A.; Rodríguez-García, M.I. Cellular localization and levels of pectins and arabinogalactan proteins in olive (Olea europaea L.) pistil tissues during development: Implications for pollen–pistil interaction. Planta 2013, 237, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafińska, K.; Niedojadło, K.; Świdziński, M.; Niedojadło, J.; Bednarska-Kozakiewicz, E. Spatial and temporal distribution of arabinogalactan proteins during Larix decidua Mill. male gametophyte and ovule interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, D.; Wang, W.; Ma, S.; DeBrosse, T.; Poirier, E.; Emch, K.; Soukup, E.; Tian, L.; Showalter, A.M. Two hydroxyproline galactosyltransferases, GALT5 and GALT2, function in arabinogalactan-protein glycosylation, growth and development in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Lopes, A.L.; Silva, J.; Ferreira, M.J.; Pinto, S.C.; Mendes, S.; Pereira, L.G.; Coimbra, S.; Pereira, A.M. New insights on the expression patterns of specific arabinogalactan proteins in reproductive tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1083098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, D.; Held, M.A.; Smith, M.R.; Showalter, A.M. Functional characterization of hydroxyproline-O-galactosyltransferases for Arabidopsis arabinogalactan-protein synthesis. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, K.; Feng, P.; Wang, N. OsFLA1 encodes a fasciclin-like arabinogalactan protein and affects pollen exine development in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foubert-Mendes, S.; Silva, J.; Ferreira, M.J.; Pereira, L.G.; Coimbra, S. A review on the function of arabinogalactan-proteins during pollen grain development. Plant Reprod. 2025, 38, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T. Genome-Wide Analysis of Xylogen-Like Arabinogalactan Protein Gene Family and Biological Function Studies of OsAGP13 in Rice. Ph.D. Dissertation, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Xu, F.; Chen, Z.; Teng, Z.; Sun, K.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, G.; Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Synergistic interplay of ABA and BR signal in regulating plant growth and adaptation. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hengel, A.J.; Roberts, K. AtAGP30, an arabinogalactan-protein in the cell walls of the primary root, plays a role in root regeneration and seed germination. Plant J. 2003, 36, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hengel, A.J.; Barber, C.; Roberts, K. The expression patterns of arabinogalactan-protein AtAGP30 and GLABRA2 reveal a role for abscisic acid in the early stages of root epidermal patterning. Plant J. 2004, 39, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Hernandez, F.; Tryfona, T.; Rizza, A.; Yu, X.L.; Harris, M.O.; Webb, A.A.R.; Kotake, T.; Dupree, P. Calcium binding by arabinogalactan polysaccharides is important for normal plant development. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3346–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Lee, S.; Tanaka, T.; Numa, H.; Kim, J.; Kawahara, Y.; Wakimoto, H.; Yang, C.-C.; Iwamoto, M.; Abe, T.; et al. Rice Annotation Project Database (RAP-DB): An integrative and interactive database for rice genomics. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 54, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, Y.; Bastide, M.D.L.; Hamilton, J.P.; Kanamori, H.; McCombie, W.; Shu, O.; Schwartz, D.; Tanaka, T.; Wu, J.; Zhou, S.; et al. Improvement of the Oryza sativa Nipponbare reference genome using next generation sequence and optical map data. Rice 2013, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; He, W.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, X.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Lv, Y.; et al. A complete assembly of the rice Nipponbare reference genome. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, C.J.; Rumsewicz, M.P.; Johnson, K.L.; Jones, B.J.; Gaspar, Y.M.; Bacic, A. Using genomic resources to guide research directions. The arabinogalactan protein gene family as a test case. Plant Physiol. 2002, 129, 1448–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Leykam, J.F.; Kieliszewski, M.J. Glycosylation motifs that direct arabinogalactan addition to arabinogalactan-proteins. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, Y.; Johnson, K.L.; Mckenna, J.A.; Bacic, A.; Schultz, C.J. The complex structures of arabinogalactan-proteins and the journey towards understanding function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 47, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfson, D.N. Understanding a protein fold: The physics, chemistry, and biology of α-helical coiled coils. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardar, H.S.; Yang, J.; Showalter, A.M. Molecular interactions of arabinogalactan proteins with cortical microtubules and F-actin in Bright Yellow-2 tobacco cultured cells. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Zheng, G. Distribution and Function of Arabinogalactan-proteins in Higher Plant. North. Hortic. 2016, 1, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamport, D.T.; Várnai, P. Periplasmic arabinogalactan glycoproteins act as a calcium capacitor that regulates plant growth and development. New Phytol. 2013, 197, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, E.; García De La Garma, J.; Gomez-Jimenez, M.C.; Fernandez-Garcia, N. Arabinogalactan proteins are involved in salt-adaptation and vesicle trafficking in tobacco by-2 cell cultures. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lease, K.A.; Walker, J.C. The Arabidopsis unannotated secreted peptide database, a resource for plant peptidomics. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plett, J.M.; Yin, H.; Mewalal, R.; Hu, R.; Li, T.; Ranjan, P.; Jawdy, S.; Paoli, H.C.D.; Butler, G.; Burch-Smith, T.M.; et al. Populus trichocarpa encodes small, effector-like secreted proteins that are highly induced during mutualistic symbiosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Lu, H.; Hassan, M.M.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, G.; Abraham, P.E.; Shrestha, H.K.; Solis, M.I.V.; Chen, J.G.; Tschaplinski, T.J. Advances and perspectives in discovery and functional analysis of small secreted proteins in plants. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.; Nobre, M.S.; Becker, J.D.; Masiero, S.; Amorim, M.I.; Pereira, L.G.; Coimbra, S. Expression-based and co-localization detection of arabinogalactan protein 6 and arabinogalactan protein 11 interactors in Arabidopsis pollen and pollen tubes. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Huang, L.; Miao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Peng, R.; Cao, J. Constitutive overexpression of the classical arabinogalactan protein gene BcMF18 in Arabidopsis causes defects in pollen intine morphogenesis. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 88, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Narciso, J.O.; Zeng, W.; van de Meene, A.; Yasutomi, M.; Takemura, S.; Lampugnani, E.R.; Doblin, M.S.; Bacic, A.; Ishiguro, S. KNS4/UPEX1: A type II arabinogalactan β-(1, 3)-galactosyltransferase required for pollen exine development. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaj, J.; Ensikat, H.J.; Baluska, F.; Knox, J.P.; Volkmann, D. Immunogold localization of plant surface arabinogalactan-proteins using glycerol liquid substitution and scanning electron microscopy. J. Microsc. 1999, 193, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.G.; Coimbra, S.; Oliveira, H.; Monteiro, L.; Sottomayor, M. Expression of arabinogalactan protein genes in pollen tubes of Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2006, 223, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.; Costa, M.; Mendes, M.A.; Pereira, A.M.; Pinto, J.; Pereira, L.G. Early germination of Arabidopsis pollen in a double null mutant for the arabinogalactan protein genes AGP6 and AGP11. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2010, 23, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, L.; Mo, A.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Ren, D.; Chen, W.; Long, H.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, T.; Lu, P. Arabidopsis novel microgametophyte defective mutant 1 is required for pollen viability via influencing intine development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 814870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.J.; Ferguson, K.L.; Lahnstein, J.; Bacic, A. Post-translational modifications of arabinogalactan-peptides of Arabidopsis thaliana: Endoplasmic reticulum and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchor signal cleavage sites and hydroxylation of proline. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45503–45511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G. A brief history of protein sorting prediction. Protein J. 2019, 38, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.C.; Shen, H.B. Cell-ploc 2.0: An improved package of web-servers for predicting subcellular localization of proteins in various organisms. Nat. Sci. 2010, 2, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; De Beer, T.A.; Tauriello, G.; Studer, G.; Bordoli, L.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Repository—New features and functionality. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D313–D319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; de Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Long, Y.; Shu, Y.; Zhai, J. PPRD: A comprehensive online database for expression analysis of ~45,000 plant public RNA-Seq libraries. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 806–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkirala, V.R.; Peng, Y.; Abbagani, S.; Zhu, Z.; Umate, P. Subcellular localization of proteins of Oryza sativa L. in the model tobacco and tomato plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Schöffl, F. GUS activity staining in gels: A powerful tool for studying protein interactions in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Report. 1995, 13, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferson, R.A.; Kavanagh, T.A.; Bevan, M.W. GUS fusions: Beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3901–3907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béziat, C.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Feraru, E. Histochemical staining of β-glucuronidase and its spatial quantification. In Plant Hormones; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ji, L.; Liu, S.; Jing, P.; Hu, J.; Jin, D.; Wang, L.; Xie, G. The CaM1-associated CCaMK–MKK1/6 cascade positively affects lateral root growth via auxin signaling under salt stress in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 6611–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| AGIS ID | Locus ID | Gene Name | PAST (%) | SP | GPI | AP/PA/SP/TP Repeats | AA Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGIS_Os01g009100 | LOC_Os01g10550 | OsAGP1P | 35.62 | Yes | No | 0/2/0/0 | 73 |
| AGIS_Os01g032060 | LOC_Os01g37950 | OsAGP2P (OsAGP14) | 51.43 | Yes | No | 4/2/0/0 | 70 |
| AGIS_Os01g034750 | LOC_Os01g40880 | OsAGP3P | 40.00 | Yes | Yes | 0/1/1/0 | 70 |
| AGIS_Os01g034820 | LOC_Os01g40950 | OsAGP4P (OsAGP15) | 40.28 | Yes | No | 3/3/0/0 | 72 |
| AGIS_Os01g035100 | LOC_Os01g41230 | OsAGP5P | 44.93 | Yes | No | 2/1/1/0 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os01g039860 | LOC_Os01g46850 | OsAGP6P (OsAGP6P) | 40.58 | Yes | Yes | 3/2/0/0 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os01g047750 | LOC_Os01g55220 | OsAGP7P (OsAGP17) | 47.14 | Yes | Yes | 4/3/0/0 | 70 |
| AGIS_Os01g049500 | LOC_Os01g57030 | OsAGP8P (OsAGP18) | 58.82 | Yes | Yes | 3/2/0/0 | 68 |
| AGIS_Os01g049510 | LOC_Os01g57040 | OsAGP9P (OsAGP19) | 57.35 | Yes | Yes | 4/3/0/0 | 68 |
| AGIS_Os01g051100 | LOC_Os01g58590 | OsAGP10P | 37.50 | Yes | No | 0/2/0/0 | 64 |
| AGIS_Os02g010250 | LOC_Os02g12150 | OsAGP11P | 42.25 | Yes | No | 0/2/3/0 | 71 |
| AGIS_Os02g010720 | LOC_Os02g12654 | OsAGP12P | 40.91 | Yes | No | 2/0/1/0 | 66 |
| AGIS_Os02g014470 | LOC_Os02g16500 | OsAGP13P (OsAGP20) | 38.36 | Yes | Yes | 4/0/1/0 | 73 |
| AGIS_Os02g035140 | LOC_Os02g39290 | OsAGP14P | 43.75 | Yes | No | 1/1/2/0 | 64 |
| AGIS_Os02g044090 | LOC_Os02g48710 | OsAGP15P (OsAGP21) | 49.28 | Yes | Yes | 2/2/0/0 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os03g036830 | LOC_Os03g42990 | OsAGP6P | 43.84 | Yes | Yes | 0/1/1/0 | 73 |
| AGIS_Os03g043930 | LOC_Os03g50720 | OsAGP17P | 38.67 | Yes | No | 1/0/0/1 | 75 |
| AGIS_Os04g001290 | LOC_Os04g02380 | OsAGP18P | 39.13 | Yes | No | 2/1/0/1 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os04g027720 | None | OsAGP19P | 38.81 | Yes | No | 1/1/1/0 | 67 |
| AGIS_Os04g050800 | LOC_Os04g57260 | OsAGP20P | 62.32 | Yes | No | 4/4/2/0 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os04g050820 | LOC_Os04g57270 | OsAGPp21P | 60.29 | Yes | No | 4/4/2/0 | 68 |
| AGIS_Os04g050830 | LOC_Os04g57280 | OsAGP22P | 57.97 | Yes | No | 4/4/2/0 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os05g010800 | LOC_Os05g12580 | OsAGP23P | 43.28 | Yes | Yes | 2/1/1/0 | 67 |
| AGIS_Os06g019180 | LOC_Os06g21410 | OsAGP24P (OsAGP25) | 45.95 | Yes | No | 3/3/0/0 | 74 |
| AGIS_Os06g027160 | LOC_Os06g30920 | OsAGP25P | 50.94 | Yes | No | 3/4/0/0 | 53 |
| AGIS_Os07g011720 | LOC_Os07g13319 | OsAGP26P | 41.79 | Yes | No | 0/2/0/0 | 67 |
| AGIS_Os07g012700 | LOC_Os07g14360 | OsAGP27P | 43.66 | Yes | No | 1/2/2/0 | 71 |
| AGIS_Os07g013810 | LOC_Os07g15530 | OsAGP28P | 36.00 | Yes | No | 0/1/1/0 | 75 |
| AGIS_Os07g023740 | LOC_Os07g27410 | OsAGP29P | 45.71 | Yes | No | 3/0/3/0 | 70 |
| AGIS_Os07g034440 | LOC_Os07g38630 | OsAGP30P (OsAGP27) | 40.63 | Yes | No | 4/3/0/0 | 64 |
| AGIS_Os08g038920 | LOC_Os08g41860 | OsAGP31P | 41.67 | Yes | No | 0/1/0/1 | 72 |
| AGIS_Os09g019700 | LOC_Os09g11780 | OsAGP32P | 41.67 | Yes | No | 1/1/2/1 | 60 |
| AGIS_Os09g029540 | LOC_Os09g22510 | OsAGP33P | 48.44 | Yes | No | 1/2/0/0 | 64 |
| AGIS_Os09g029970 | LOC_Os09g23430 | OsAGP34P | 37.88 | Yes | No | 2/0/0/1 | 66 |
| AGIS_Os09g036360 | LOC_Os09g30040 | OsAGP35P | 43.24 | Yes | No | 1/0/1/0 | 74 |
| AGIS_Os10g003720 | LOC_Os10g05150 | OsAGP36P | 35.21 | Yes | No | 0/1/1/1 | 71 |
| AGIS_Os10g022660 | LOC_Os10g28299 | OsAGP37P | 37.70 | Yes | No | 2/0/2/0 | 61 |
| AGIS_Os11g035190 | LOC_Os11g40850 | OsAGP38P | 36.62 | Yes | No | 1/1/1/1 | 71 |
| AGIS_Os12g010080 | LOC_Os12g11420 | OsAGP39P | 38.89 | Yes | No | 1/0/2/0 | 72 |
| AGIS_Os12g010260 | LOC_Os12g11610 | OsAGP40P | 42.65 | Yes | No | 1/1/0/1 | 68 |
| AGIS_Os12g010270 | LOC_Os12g11620 | OsAGP41P | 43.48 | Yes | No | 1/0/0/1 | 69 |
| AGIS_Os12g010590 | LOC_Os12g11980 | OsAGP42P | 42.65 | Yes | No | 1/1/0/1 | 68 |
| AGIS_Os12g010600 | LOC_Os12g11990 | OsAGP43P | 44.12 | Yes | No | 1/0/0/1 | 68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Zhou, H.; Wu, S.; Wang, L. Determining the Role of OsAGP6P in Anther Development Within the Arabinogalactan Peptide Family of Rice (Oryza sativa). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062616
Shao S, Wu Y, Zhang L, Zhao Z, Li X, Yang M, Zhou H, Wu S, Wang L. Determining the Role of OsAGP6P in Anther Development Within the Arabinogalactan Peptide Family of Rice (Oryza sativa). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062616
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Shuai, Yuxin Wu, Lijie Zhang, Zhiyuan Zhao, Xianlong Li, Mingchong Yang, Haiyu Zhou, Songguo Wu, and Lingqiang Wang. 2025. "Determining the Role of OsAGP6P in Anther Development Within the Arabinogalactan Peptide Family of Rice (Oryza sativa)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062616
APA StyleShao, S., Wu, Y., Zhang, L., Zhao, Z., Li, X., Yang, M., Zhou, H., Wu, S., & Wang, L. (2025). Determining the Role of OsAGP6P in Anther Development Within the Arabinogalactan Peptide Family of Rice (Oryza sativa). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062616






