Evaluation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Effects and Its Receptors During Bovine Embryo Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
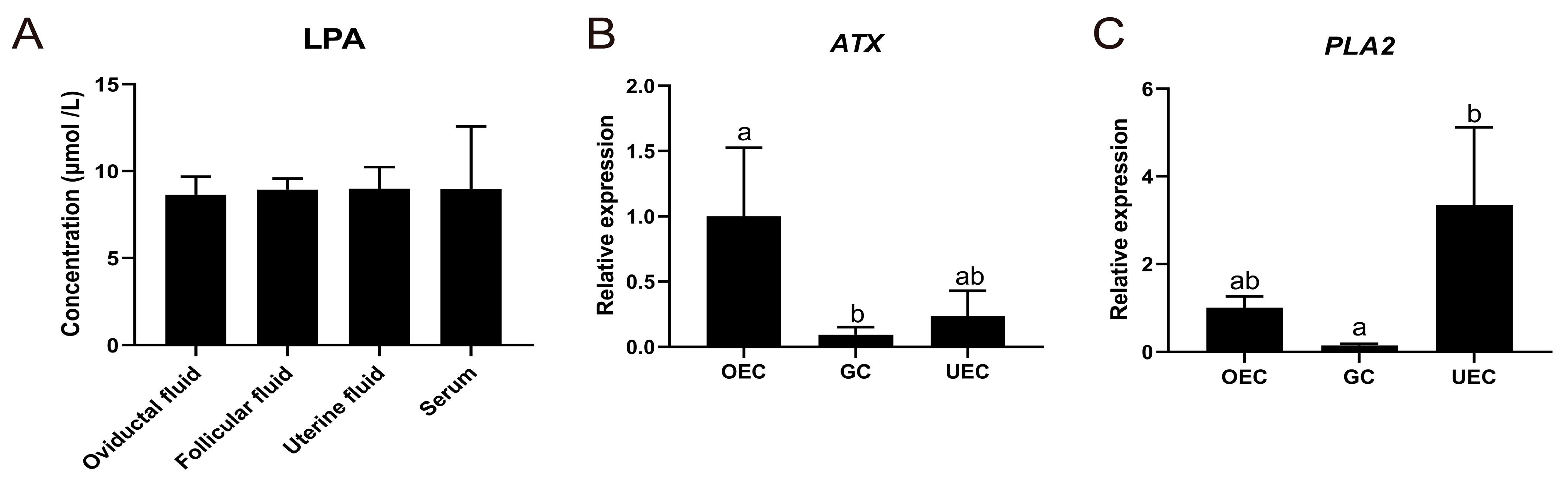
2.1. Presence of LPA in Oviductal Fluid
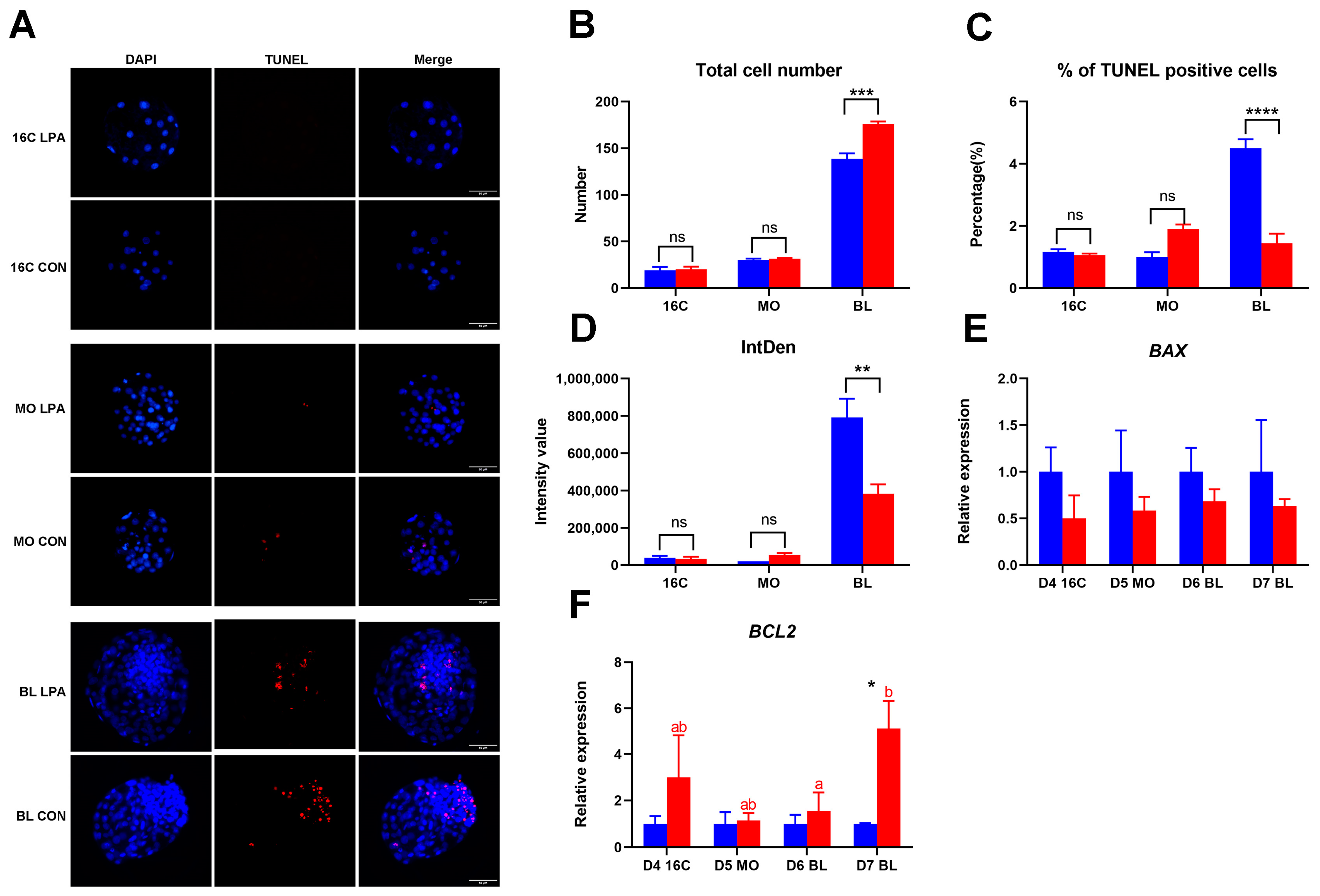
2.2. The Level of Apoptosis in Embryos After LPA Stimulation
2.3. Molecular Docking Between LPA and LPARs
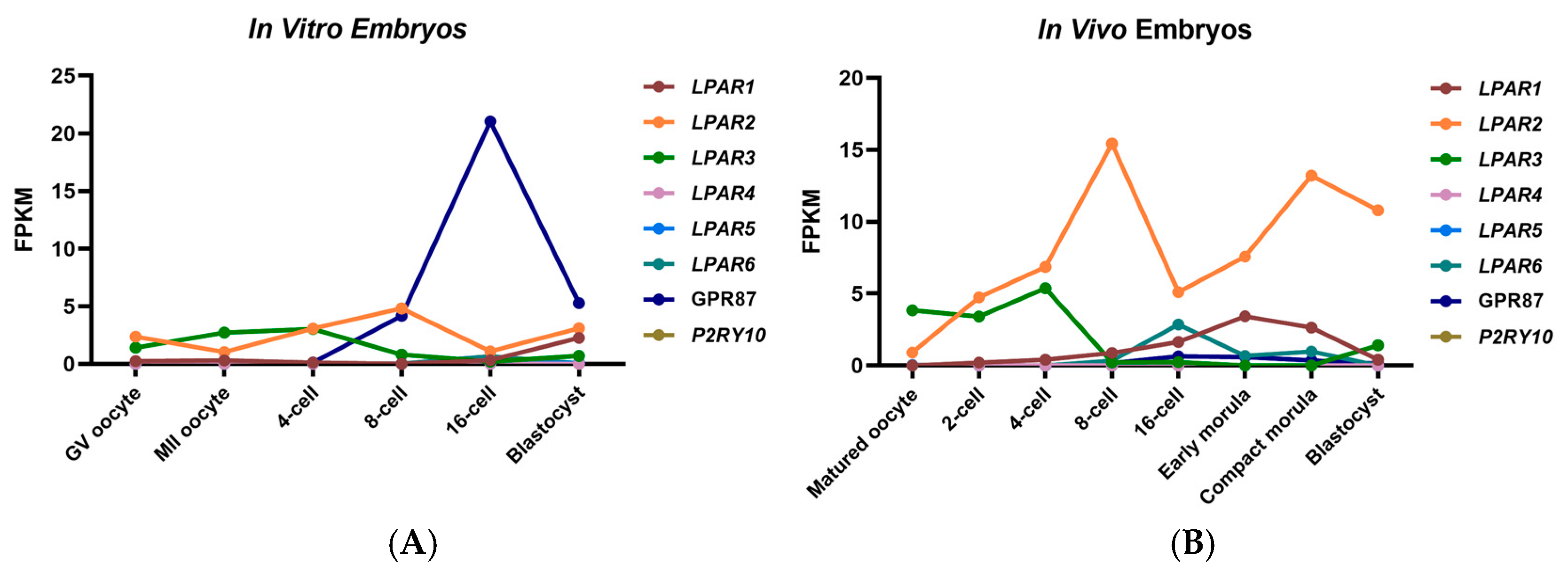
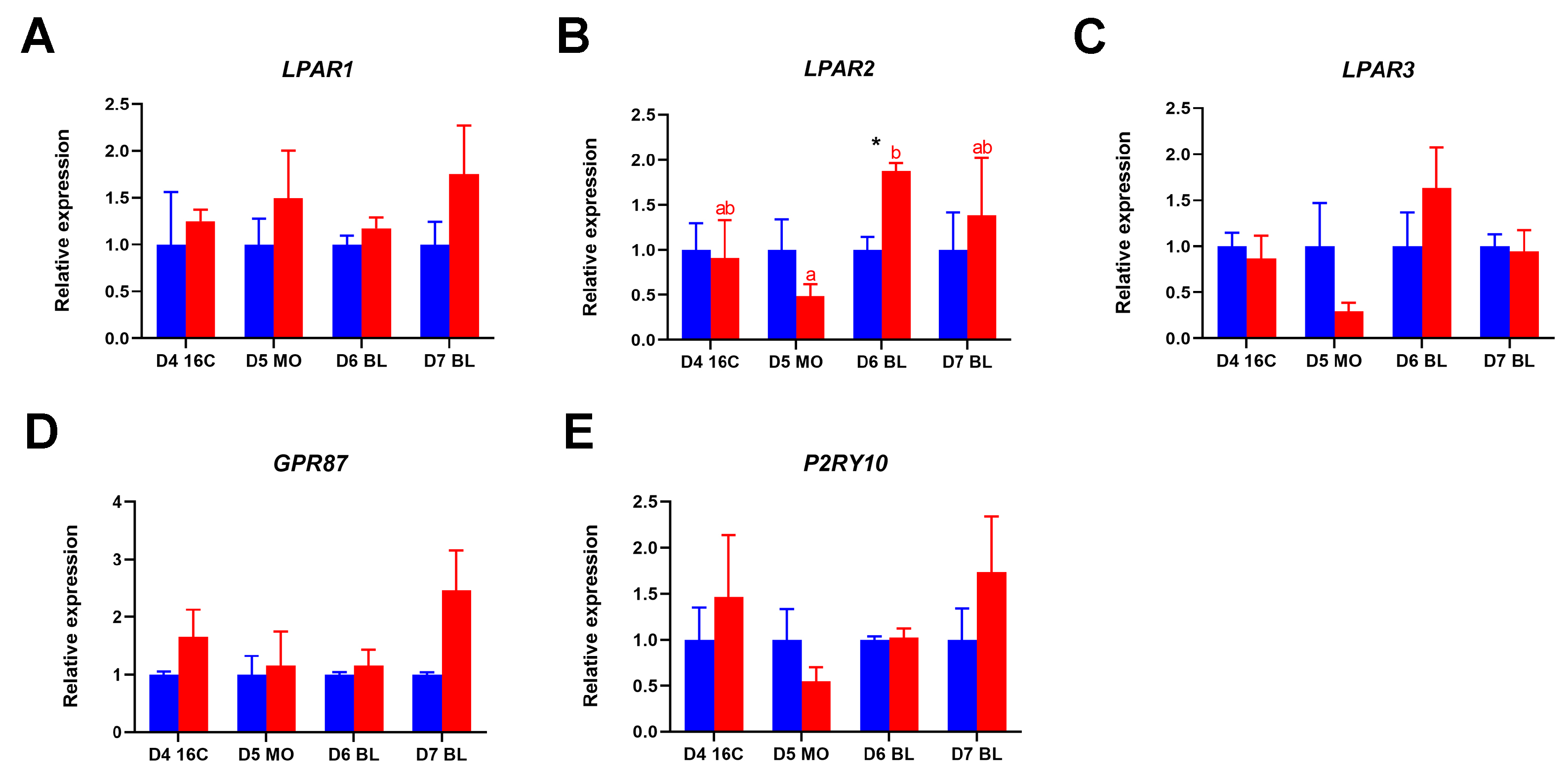
2.4. Expression of LPARs During In Vivo and In Vitro Preimplantation Embryo Development
2.5. Expression of LPARs in In Vitro Embryo After LPA Treatment
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vitro Embryo Production and LPA Treatment
4.2. Sample Collection
4.3. TUNEL Assay
4.4. LPA Concentration Detection
4.5. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR
4.6. Molecular Docking
4.7. RNA-Seq Data Processing
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LPA | Lysophosphatidic acid |
| CON | Control |
| IVP | In vitro embryo production |
| AXT | Autotaxin |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A |
| BL | Blastocyst |
| EDG | Endothelial differentiation gene |
| 16C | 16-cell stage embryo |
| MO | Morula |
| D | Day |
| LPAR | Lysophosphatidic acid receptor |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| RNA-seq | RNA sequencing |
| COCs | Cumulus–oocyte complexes |
References
- Geraldo, L.H.M.; Spohr, T.; Amaral, R.F.D.; Fonseca, A.; Garcia, C.; Mendes, F.A.; Freitas, C.; dosSantos, M.F.; Lima, F.R.S. Role of lysophosphatidic acid and its receptors in health and disease: Novel therapeutic strategies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasaka, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sano, F.K.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Shihoya, W.; Nureki, O. Structure of the active G(i)-coupled human lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 complexed with a potent agonist. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matas-Rico, E.; Moolenaar, W.H. Tumor immune escape by autotaxin: Keeping eosinophils at bay. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, J.; Inoue, A.; Okudaira, S. Two pathways for lysophosphatidic acid production. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1781, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnik, L.T.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K. Lysophosphatidic acid and its role in reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2002, 66, 859–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkrioti, C.; Kaffe, E.; Aidinis, V. The Role of Autotaxin and LPA Signaling in Embryonic Development, Pathophysiology and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Qian, J.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xie, C.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y. Lysophosphatidic Acid Improves Human Sperm Motility by Enhancing Glycolysis and Activating L-Type Calcium Channels. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 896558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Kimura, T.; Terashima, R.; Sugiyama, M.; Kizaki, K.; Kawaminami, M.; Kurusu, S. Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates rat uterine contraction in vitro. J. Reprod. Dev. 2023, 69, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza-Fabjan, J.M.G.; Leal, G.R.; Monteiro, C.A.S.; Batista, R.; Barbosa, N.O.; Freitas, V.J.F. In vitro embryo production in small ruminants: What is still missing? Anim. Reprod. 2023, 20, e20230055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferré, L.B.; Kjelland, M.E.; Strøbech, L.B.; Hyttel, P.; Mermillod, P.; Ross, P.J. Review: Recent advances in bovine in vitro embryo production: Reproductive biotechnology history and methods. Anim. Int. J. Anim. Biosci. 2020, 14, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetrio, D.G.B.; Benedetti, E.; Demetrio, C.G.B.; Fonseca, J.; Oliveira, M.; Magalhaes, A.; Dos Santos, R.M. How can we improve embryo production and pregnancy outcomes of Holstein embryos produced in vitro? (12 years of practical results at a California dairy farm). Anim. Reprod. 2020, 17, e20200053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Chun, J. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling in vertebrate reproduction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Huang, X.-H.; Wang, J.; Xing, Y.; Liu, F.; Xiang, J.-Z.; Wang, H.-N.; Yue, Y.-L.; Li, X.-L. Effects of LPA on the development of sheep in vitro fertilized embryos and attempt to establish sheep embryonic stem cells. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, T.; Kang, J.W.; Lee, J.E.; Jin, D.I. Lysophosphatidic acid improves porcine oocyte maturation and embryo development in vitro. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2015, 82, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; van Tol, H.T.A.; Oei, C.H.Y.; Stout, T.A.E.; Roelen, B.A.J. Lysophosphatidic Acid Accelerates Bovine In Vitro-Produced Blastocyst Formation through the Hippo/YAP Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasaka, H.; Sano, F.K.; Shihoya, W.; Nureki, O. Structural mechanisms of potent lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 activation by nonlipid basic agonists. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Herr, D.R.; Noguchi, K.; Yung, Y.C.; Lee, C.W.; Mutoh, T.; Lin, M.E.; Teo, S.T.; Park, K.E.; Mosley, A.N.; et al. LPA receptors: Subtypes and biological actions. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 157–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Lu, Y.; Shao, M.; Wu, T. Lysophosphatidic Acid Receptors: Biochemical and Clinical Implications in Different Diseases. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3519–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadam, A.; Parida, S.; Padol, A.R.; Verma, A.D.; Baba, N.A.; Khuman, W.M.; Srivastava, V.; Panigrahi, M.; Singh, T.U.; Sarkar, S.N. Study of lysophosphatidic acid receptors (LPARs) in buffalo uterus demonstrated upregulation of LPAR1 and LPAR6 in early pregnancy. Theriogenology 2017, 99, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Hama, K.; Contos, J.J.; Anliker, B.; Inoue, A.; Skinner, M.K.; Suzuki, H.; Amano, T.; Kennedy, G.; Arai, H.; et al. LPA3-mediated lysophosphatidic acid signalling in embryo implantation and spacing. Nature 2005, 435, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewska, E.; Reinaud, P.; Billon-Denis, E.; Dubois, O.; Robin, P.; Charpigny, G. Lysophosphatidic acid signaling during embryo development in sheep: Involvement in prostaglandin synthesis. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.C.; Boruszewska, D.; Batista, M.; Kowalczyk-Zieba, I.; Diniz, P.; Sinderewicz, E.; Saulnier-Blache, J.S.; Woclawek-Potocka, I.; Lopes-da-Costa, L. Lysophosphatidic acid signaling in late cleavage and blastocyst stage bovine embryos. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 678968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Armant, D.R. Lysophosphatidic acid regulates murine blastocyst development by transactivation of receptors for heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 296, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, A.; Krebs, S.; Zakhartchenko, V.; Schwalb, B.; Blum, H.; Wolf, E. Fine mapping of genome activation in bovine embryos by RNA sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4139–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Sun, J.; Dong, H.; Luo, O.; Zheng, X.; Obergfell, C.; Tang, Y.; Bi, J.; O’Neill, R.; Ruan, Y.; et al. Transcriptional profiles of bovine in vivo pre-implantation development. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Salle, S. Growing fast or slow: What makes the best embryo? Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegel, R.E.; Rubini, E.; Rousian, M.; Schoenmakers, S.; Laven, J.S.E.; Willemsen, S.P.; Baart, E.B.; Steegers-Theunissen, R.P.M. Human oocyte area is associated with preimplantation embryo usage and early embryo development: The Rotterdam Periconception Cohort. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2023, 40, 1495–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H. Development speed of sibling embryo positively reflects live birth rate after fresh day 3 embryo transfer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, P.C.; Afiukwa, C.A.; Orji, O.U.; Ezeh, E.M.; Ofoke, I.H.; Ogbu, C.O.; Ugwuja, E.I.; Aja, P.M. Molecular docking as a tool for the discovery of molecular targets of nutraceuticals in diseases management. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondaparla, S.; Debnath, U.; Soni, A.; Dola, V.R.; Sinha, M.; Srivastava, K.; Puri, S.K.; Katti, S.B. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling Studies of Chiral Chloroquine Analogues as Antimalarial Agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02347-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnashi, M.H.; Koganole, P.; Ashgar, S.S.; Shaikh, I.A.; Joshi, S.D.; Alqahtani, A.S. Synthesis, Molecular Docking Study, and Biological Evaluation of New 4-(2,5-Dimethyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)-N’-(2-(substituted)acetyl)benzohydrazides as Dual Enoyl ACP Reductase and DHFR Enzyme Inhibitors. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
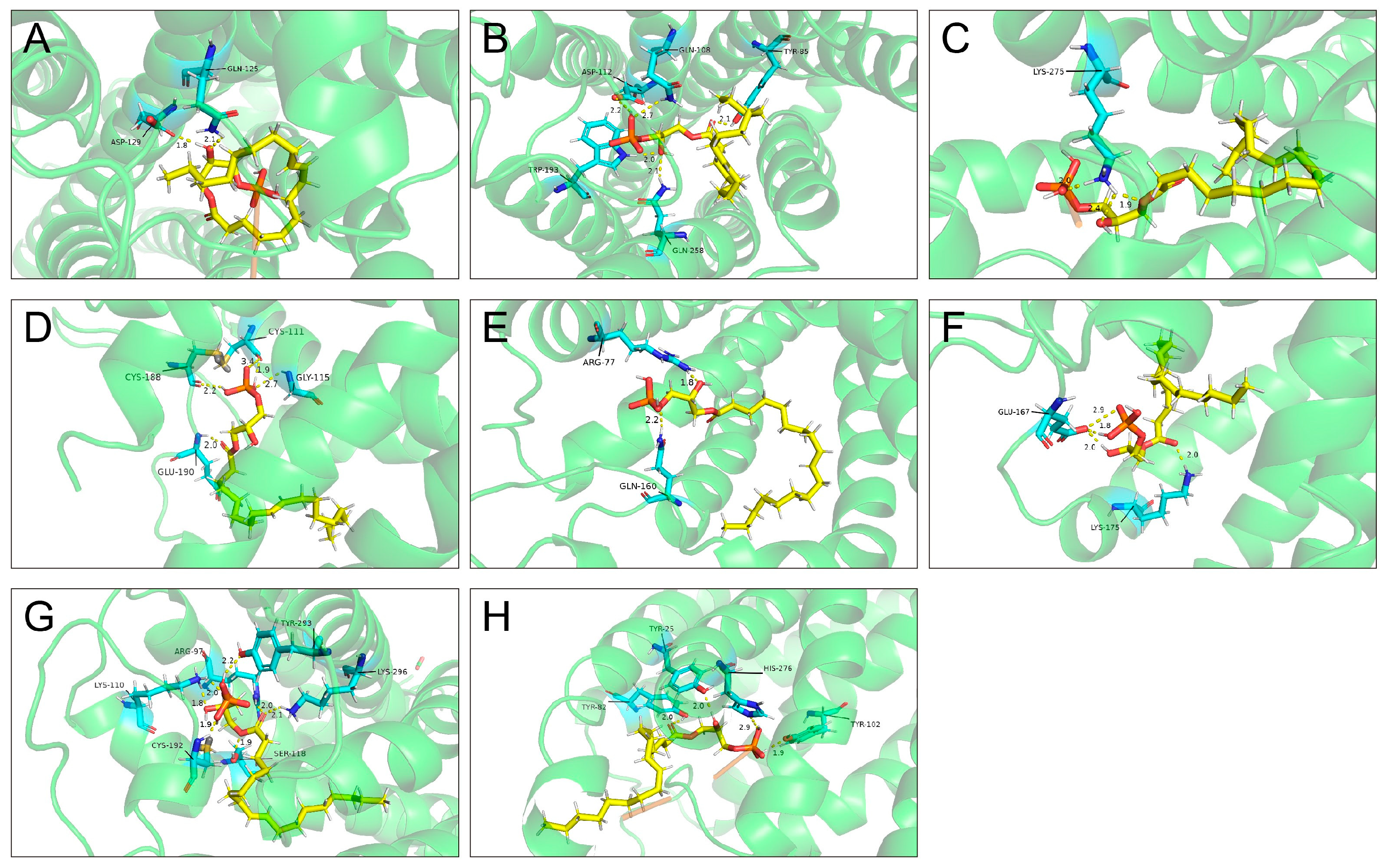
| Molecules | Total Score | Crash Score | Polar Score | Binding Sites |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPAR1 | 9.9848 | −6.4532 | 1.8122 | GLN-125, ASP-129 |
| LPAR2 | 11.4654 | −2.3193 | 4.2882 | TYR-85, GLN-108, ASP-112, TRP-193, GLN-258 |
| LPAR3 | 7.1863 | −6.5855 | 2.1880 | LYS-275 |
| LPAR4 | 9.4880 | −1.1479 | 2.9762 | CYS-111, GLY-115, CYS-188, GLU-190 |
| LPAR5 | 8.6331 | −3.3448 | 2.7064 | ARG-77, GLN-160 |
| LPAR6 | 6.8475 | −3.0658 | 3.9243 | GLU-167, LYS-175 |
| GPR87 | 13.2981 | −5.6552 | 5.9959 | ARG-97, LYS-110, SER-118, CYS-192, TYR-293, LYS-296 |
| P2RY10 | 10.0559 | −2.2346 | 4.5339 | TYR-25, TYR-82, TYR-102, HIS-276 |
| Gene Name | Accession | Direction | Sequence | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPAR1 | NM_174047.2 | Forward Reverse | GTTCAACACAGGGCCCAATACT AACCGTCAGGCTGGTGTCA | 60 | 85 |
| LPAR2 | NM_001192235.1 | Forward Reverse | ATCGCCGCTTCCACCAACCCAT GCCGTCAGGCTCGTGTCCAACA | 63.1 | 172 |
| LPAR3 | NC_007305.3 | Forward Reverse | TCAAGTAAAGCACGGGCAGAA CGGGTGAGAACGCATTGTG | 60 | 90 |
| LPAR4 | NM_001098105.1 | Forward Reverse | ATCACCAATCTGGCCCTCTCT CAGTGGCGGTTGAAATTGTAAAA | 60 | 80 |
| LPAR5 | NM_001034304.2 | Forward Reverse | AGAAGCCAGCTCGGGAGA CCAGAGCAAACGGAGGTTCA | 60 | 161 |
| LPAR6 | NM_001101284.1 | Forward Reverse | TGCTCAGCAGCAATAGCAGT CCCAGTAAAGTCCTGGCGTT | 60 | 284 |
| GPR87 | NM_001205451.1 | Forward Reverse | CCAGCAGGCAATTCATAAGCCAGTC TCGGATGCTTTCGCTCCTCGTTC | 58.9 | 311 |
| P2RY10 | NM_001075699.2 | Forward Reverse | ACCAACTCCCTGCAAAGAAAC GTGGTTGCGTAGAGAGGGTAA | 60 | 171 |
| BAX | NM_173894.1 | Forward Reverse | GCAGAGGATGATCGCAGCTG CCAATGTCCAGCCCATGATG | 62 | 197 |
| BCL2 | XM_005224105.5 | Forward Reverse | CTTCGCCGAGATGTCCAGTC CACCACCGTGGCGAAGC | 58 | 70 |
| ATX | NM_001080293.1 | Forward Reverse | ACCCCCTGATTGTCGATGTG TCTCCGCATCTGTCCTTGGT | 60 | 120 |
| PLA2 | NM_001075864.1 | Forward Reverse | CCATTATTCCCACAAGTTCACAGTA TGTCAAGCATGTCACCAAAGGT | 60 | 80 |
| YWHAZ | XM_025001430.1 | Forward Reverse | GCATCCCACAGACTATTTCC GCAAAGACAATGACAGACCA | 58 | 120 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, B.; Dai, S.; Cheng, L.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Chen, H. Evaluation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Effects and Its Receptors During Bovine Embryo Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062596
Yu B, Dai S, Cheng L, Lu Q, Liu Q, Chen H. Evaluation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Effects and Its Receptors During Bovine Embryo Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062596
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Bo, Shuying Dai, Lei Cheng, Qirong Lu, Qing Liu, and Hongbo Chen. 2025. "Evaluation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Effects and Its Receptors During Bovine Embryo Development" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062596
APA StyleYu, B., Dai, S., Cheng, L., Lu, Q., Liu, Q., & Chen, H. (2025). Evaluation of Lysophosphatidic Acid Effects and Its Receptors During Bovine Embryo Development. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2596. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062596







