Therapeutic Effects of Pharmacological Modulation of Serotonin Brain System in Human Patients and Animal Models of Fragile X Syndrome
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Physiological Role of Serotonin
1.2. Serotonin Receptors
1.3. Fragile X Syndrome
2. Serotonin Dysregulation in Fragile X Patients and Therapeutic Effects of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
| Pharmacological Category | Drug | Experimental Model | Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI) | Sertraline (2.5 mg/day) Sertraline (20 mg/day) | Fragile X patients, one boy (3 years old) one girl (7 years old). | Improvement of speech ability. Reduced anxiety | [59] |
| SSRI | Sertraline (2.5–5 mg/day) | Fragile X patients (2–6 years old, 48 males and 9 females). | Improvement of language, visual perception and fine motor skills. | [60] |
| 5-HT1A agonist | FPT (mixed agonist of 5-HT1, 5-HT2C and 5-HT7 receptors), 5.6 mg/kg. | Fmr1 KO mice, (males and females) | Prevention of audiogenic seizures; increase of social interaction; anxiolytic effects. | [63] |
| 5-HT1A agonist | FPT (5.6 mg/kg) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Rescue of electroencephalogram activity | [64] |
| 5-HT1A agonist | NLX-101 (1.2–2.4 mg/Kg) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Reduction of audiogenic seizures | [65] |
| 5-HT1A agonist | NLX-112 (1.0–2.5 mg/Kg) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Prevention of audiogenic seizures | [66] |
| 5-HT1A agonist | Eltoprazine (1 mM for 30 min) | FXS Drosophila model (sex not indicated) | Rescue of abnormal mitochondrial function; rescue of locomotor activity | [67] |
| 5-HT2A antagonist | MDL11939 (1 μM for electrophysiology; 1 mg/Kg for behavioral tests) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Rescue of synaptic plasticity (GluA1 synaptic delivery); partial rescue of learning deficits | [68] |
| 5-HT2B agonist | BW723C86 (1 μM for electrophysiology; 5 mg/Kg for behavioral tests) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Rescue of synaptic plasticity (GluA1 synaptic delivery); partial rescue of learning deficits | [68] |
| 5-HT5A antagonist | ASP5736 (0.01–0.1 mg/kg) | Fmr1 KO rats (males) | Correction of hyperactivity, abnormal sensory motor gating and learning deficits | [69] |
| 5-HT7 agonist | 5-HT (10 μM); 8-OH-DPAT (100 nM); LP-211 (10 nM); BA-10 (10 nM) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Rescue of synaptic plasticity (mGluR-LTD) | [70,71] |
| 5-HT7 agonist | LP-211 (10 nM) | Fmr1 KO mice (males and females) | Rescue of synaptic plasticity, learning and stereotyped behavior. | [72] |
| 5-HT7 agonist | LP-211 (3 mg/Kg) | Fmr1 KO mice (males) | Rescue of stereotyped behavior | [73] |
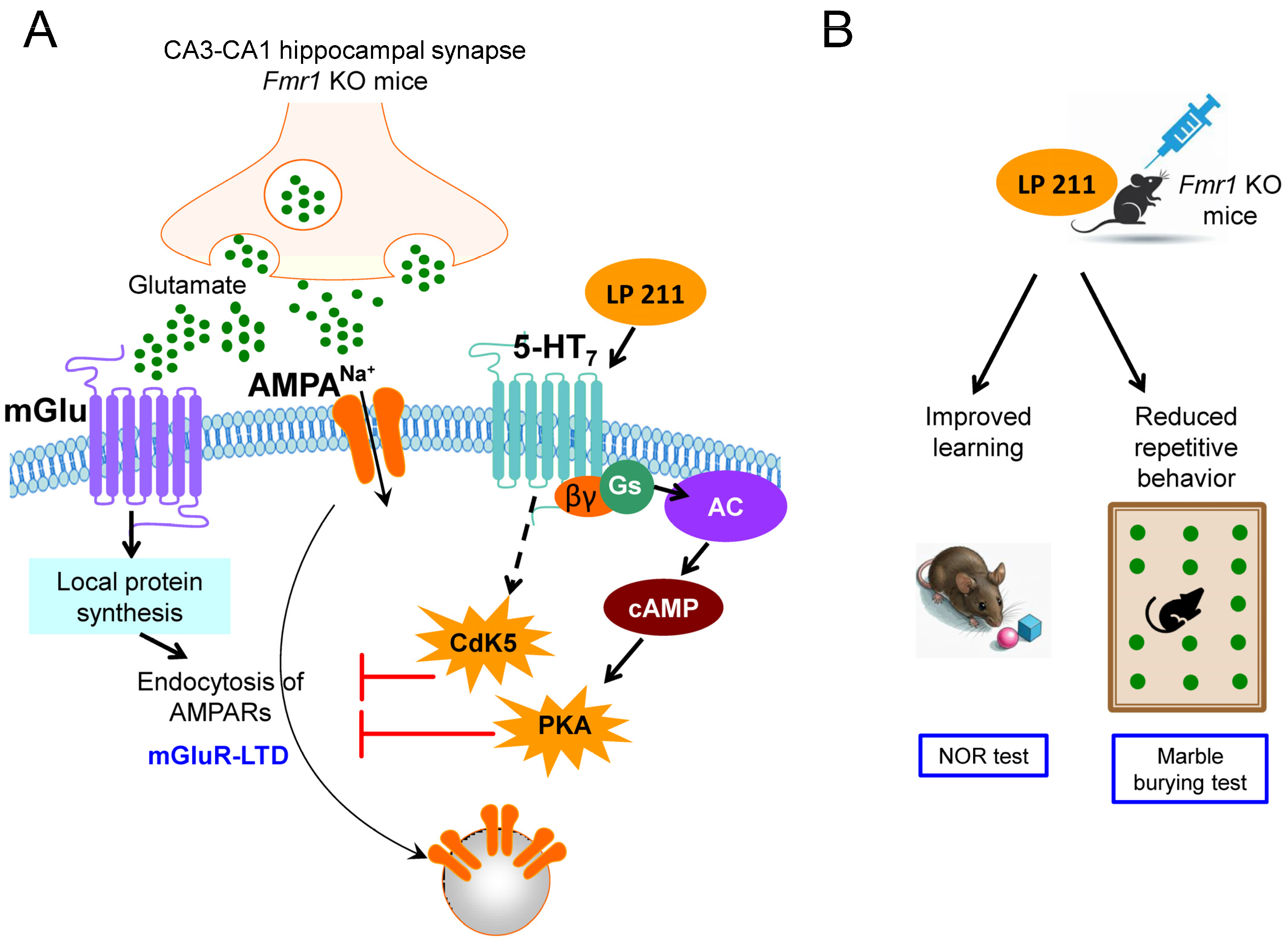
3. Selective Agonists of 5-HT7 Receptors Rescued Synaptic Plasticity, Learning Deficits and Autistic Behavior in Fmr1 KO Mice
4. Drugs Acting on Distinct 5-HT2 Receptor Subtypes Rescued Synaptic Plasticity and Learning in Fmr1 KO Mice
5. Activation of 5-HT1A Receptors Corrected Abnormal Phenotypes in Mouse and Drosophila Models of Fragile X Syndrome
6. The Blockade of 5-HT5A Receptors Improved Behavior and Memory in a Rat Model of Fragile X Syndrome
7. Conclusions
8. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sodhi, M.S.; Sanders-Bush, E. Serotonin and brain development. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2004, 59, 111–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wirth, A.; Holst, K.; Ponimaskin, E. How serotonin receptors regulate morphogenic signalling in neurons. Prog. Neurobiol. 2017, 151, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chugani, D.C. Role of altered brain serotonin mechanisms in autism. Mol. Psychiatry 2002, 7 (Suppl. 2), S16–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannon, J.; Hoyer, D. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Behav. Brain Res. 2008, 195, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Cao, D.Q.; Xu, H.Y.; Sun, M.; Huang, Z.L.; Yung, W.H.; Lu, N.; Huang, Y. 5-HT3A receptors are required in long-term depression and AMPA receptor internalization. Neuroscience 2014, 278, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staubli, U.; Xu, F.B. Effects of 5-HT3 receptor antagonism on hippocampal theta rhythm, memory, and LTP induction in the freely moving rat. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15 Pt 2, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockaert, J.; Sebben, M.; Dumuis, A. Pharmacological characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine4(5-HT4) receptors positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in adult guinea pig hippocampal membranes: Effect of substituted benzamide derivatives. Mol. Pharmacol. 1990, 37, 408–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumuis, A.; Sebben, M.; Bockaert, J. BRL 24924: A potent agonist at a non-classical 5-HT receptor positively coupled with adenylate cyclase in colliculi neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 162, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restivo, L.; Roman, F.; Dumuis, A.; Bockaert, J.; Marchetti, E.; Ammassari-Teule, M. The promnesic effect of G-protein-coupled 5-HT4 receptors activation is mediated by a potentiation of learning-induced spine growth in the mouse hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 2427–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, E.; Chaillan, F.A.; Dumuis, A.; Bockaert, J.; Soumireu-Mourat, B.; Roman, F.S. Modulation of memory processes and cellular excitability in the dentate gyrus of freely moving rats by a 5-HT4 receptors partial agonist, and an antagonist. Neuropharmacology 2004, 47, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.R. 5-ht5A receptors as a therapeutic target. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marazziti, D.; Baroni, S.; Borsini, F.; Picchetti, M.; Vatteroni, E.; Falaschi, V.; Catena-Dell’Osso, M. Serotonin receptors of type 6 (5-HT6): From neuroscience to clinical pharmacology. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Ruat, M.; Traiffort, E.; Leurs, R.; Tardivel-Lacombe, J.; Diaz, J.; Arrang, J.M.; Schwartz, J.C. Molecular cloning, characterization, and localization of a high-affinity serotonin receptor (5-HT7) activating cAMP formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8547–8551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsma, F.J., Jr.; Shen, Y.; Ward, R.P.; Hamblin, M.W.; Sibley, D.R. Cloning and expression of a novel serotonin receptor with high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 43, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovenberg, T.W.; Baron, B.M.; de Lecea, L.; Miller, J.D.; Prosser, R.A.; Rea, M.A.; Foye, P.E.; Racke, M.; Slone, A.L.; Siegel, B.W.; et al. A novel adenylyl cyclase-activating serotonin receptor (5-HT7) implicated in the regulation of mammalian circadian rhythms. Neuron 1993, 11, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P.B.; Sutcliffe, J.G. Functional, molecular and pharmacological advances in 5-HT7 receptor research. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 25, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Cora, F.J.; Pazos, A. Autoradiographic distribution of 5-HT7 receptors in the human brain using [3H]mesulergine: Comparison to other mammalian species. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnas, K.; Thomas, D.R.; Tupala, E.; Tiihonen, J.; Hall, H. Distribution of 5-HT7 receptors in the human brain: A preliminary autoradiographic study using [3H]SB-269970. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 367, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, J.A.; Zgombick, J.; Adham, N.; Vaysse, P.; Branchek, T.A.; Weinshank, R.L. Cloning of a novel human serotonin receptor (5-HT7) positively linked to adenylate cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23422–23426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norum, J.H.; Hart, K.; Levy, F.O. Ras-dependent ERK activation by the human G(s)-coupled serotonin receptors 5-HT4(b) and 5-HT7(a). J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3098–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.L.; Johnson-Farley, N.N.; Lubinsky, D.R.; Cowen, D.S. Coupling of neuronal 5-HT7 receptors to activation of extracellular-regulated kinase through a protein kinase A-independent pathway that can utilize Epac. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errico, M.; Crozier, R.A.; Plummer, M.R.; Cowen, D.S. 5-HT(7) receptors activate the mitogen activated protein kinase extracellular signal related kinase in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 2001, 102, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.S.; Mitchell, G.S. Spinal 5-HT7 receptor activation induces long-lasting phrenic motor facilitation. J. Physiol. 2011, 589 Pt 6, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Farley, N.N.; Kertesy, S.B.; Dubyak, G.R.; Cowen, D.S. Enhanced activation of Akt and extracellular-regulated kinase pathways by simultaneous occupancy of Gq-coupled 5-HT2A receptors and Gs-coupled 5-HT7A receptors in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 2005, 92, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvachnina, E.; Liu, G.; Dityatev, A.; Renner, U.; Dumuis, A.; Richter, D.W.; Dityateva, G.; Schachner, M.; Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.A.; Ponimaskin, E.G. 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to G alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G12-protein to regulate gene transcription and neuronal morphology. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 7821–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A. G proteins and small GTPases: Distant relatives keep in touch. Science 1998, 280, 2074–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthys, A.; Haegeman, G.; Van Craenenbroeck, K.; Vanhoenacker, P. Role of the 5-HT7 receptor in the central nervous system: From current status to future perspectives. Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 43, 228–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe, F.; Guseva, D.; Jensen, T.P.; Wirth, A.; Renner, U.; Hess, D.; Muller, M.; Medrihan, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; et al. 5-HT7R/G12 signaling regulates neuronal morphology and function in an age-dependent manner. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 2915–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speranza, L.; Giuliano, T.; Volpicelli, F.; De Stefano, M.E.; Lombardi, L.; Chambery, A.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Bellenchi, G.C.; di Porzio, U.; et al. Activation of 5-HT7 receptor stimulates neurite elongation through mTOR, Cdc42 and actin filaments dynamics. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneses, A.; Perez-Garcia, G.; Liy-Salmeron, G.; Ponce-Lopez, T.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M. 5-HT7 receptor activation: Procognitive and antiamnesic effects. Psychopharmacology 2015, 232, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, T.M.; Holst, S.; Stan, T.L.; Hager, T.; Sjogren, B.; Ogren, S.O.; Svenningsson, P.; Stiedl, O. 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptor crosstalk in the regulation of emotional memory: Implications for effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciranna, L.; Catania, M.V. 5-HT7 receptors as modulators of neuronal excitability, synaptic transmission and plasticity: Physiological role and possible implications in autism spectrum disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerman, P.J.; Hagerman, R. Fragile X syndrome. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R273–R275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijetunge, L.S.; Chattarji, S.; Wyllie, D.J.; Kind, P.C. Fragile X syndrome: From targets to treatments. Neuropharmacology 2013, 68, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, I.J.; Irwin, S.A.; Klintsova, A.Y.; Spencer, C.M.; Brazelton, A.D.; Miyashiro, K.; Comery, T.A.; Patel, B.; Eberwine, J.; Greenough, W.T. Fragile X mental retardation protein is translated near synapses in response to neurotransmitter activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5395–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, B.E.; Huber, K.M. The State of Synapses in Fragile X Syndrome. Neuroscientist 2009. [CrossRef]
- Bardoni, B.; Davidovic, L.; Bensaid, M.; Khandjian, E.W. The fragile X syndrome: Exploring its molecular basis and seeking a treatment. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2006, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, S.A.; Patel, B.; Idupulapati, M.; Harris, J.B.; Crisostomo, R.A.; Larsen, B.P.; Kooy, F.; Willems, P.J.; Cras, P.; Kozlowski, P.B.; et al. Abnormal dendritic spine characteristics in the temporal and visual cortices of patients with fragile-X syndrome: A quantitative examination. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 98, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comery, T.A.; Harris, J.B.; Willems, P.J.; Oostra, B.A.; Irwin, S.A.; Weiler, I.J.; Greenough, W.T. Abnormal dendritic spines in fragile X knockout mice: Maturation and pruning deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5401–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.M.; Gallagher, S.M.; Warren, S.T.; Bear, M.F. Altered synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of fragile X mental retardation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7746–7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bear, M.F.; Huber, K.M.; Warren, S.T. The mGluR theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci. 2004, 27, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, R.; Musumeci, S.; D’Antoni, S.; Bonaccorso, C.M.; Giuffrida-Stella, A.M.; Oostra, B.A.; Catania, M.V. A reduced number of metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors are associated with constitutive homer proteins in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 8908–8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloisi, E.; Le Corf, K.; Dupuis, J.; Zhang, P.; Ginger, M.; Labrousse, V.; Spatuzza, M.; Georg Haberl, M.; Costa, L.; Shigemoto, R.; et al. Altered surface mGluR5 dynamics provoke synaptic NMDAR dysfunction and cognitive defects in Fmr1 knockout mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, S.H.; Trommer, B.L. Fragile X mice: Reduced long-term potentiation and N-Methyl-D-Aspartate receptor-mediated neurotransmission in dentate gyrus. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gocel, J.; Larson, J. Synaptic NMDA receptor-mediated currents in anterior piriform cortex are reduced in the adult fragile X mouse. Neuroscience 2012, 221, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, C.A.; Majaess, N.M.; Morch, K.; White, E.; Eadie, B.D.; Christie, B.R. Rescue of NMDAR-Dependent Synaptic Plasticity in Fmr1 Knock-Out Mice. Cereb. Cortex 2015, 25, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunova, G.; Hollander, E.; Shepherd, J. The role of ionotropic glutamate receptors in childhood neurodevelopmental disorders: Autism spectrum disorders and fragile x syndrome. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 71–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Hulst, C.; De Geest, N.; Reeve, S.P.; Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P.P.; Hassan, B.A.; Kooy, R.F. Decreased expression of the GABAA receptor in fragile X syndrome. Brain Res. 2006, 1121, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curia, G.; Papouin, T.; Seguela, P.; Avoli, M. Downregulation of tonic GABAergic inhibition in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braat, S.; Kooy, R.F. Insights into GABAAergic system deficits in fragile X syndrome lead to clinical trials. Neuropharmacology 2015, 88, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.S.; Corbin, J.G.; Huntsman, M.M. Deficient tonic GABAergic conductance and synaptic balance in the fragile X syndrome amygdala. J. Neurophysiol. 2014, 112, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, K.B.; Visootsak, J.; Warren, S.T. Fragile X syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardet, M.; Crusio, W.E. Fmr1 KO mice as a possible model of autistic features. Sci. World J. 2006, 6, 1164–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, A.C.; Hagerman, R.J. Serotonin dysregulation in Fragile X Syndrome: Implications for treatment. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2014, 3, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hessl, D.; Tassone, F.; Cordeiro, L.; Koldewyn, K.; McCormick, C.; Green, C.; Wegelin, J.; Yuhas, J.; Hagerman, R.J. Brief report: Aggression and stereotypic behavior in males with fragile X syndrome--moderating secondary genes in a “single gene” disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2008, 38, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.M.; Vied, C.; Trupiano, M.X.; Canekeratne, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Schatschneider, C.; Bhide, P.G. Behavioral, neurotransmitter and transcriptomic analyses in male and female Fmr1 KO mice. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1458502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uutela, M.; Lindholm, J.; Rantamaki, T.; Umemori, J.; Hunter, K.; Voikar, V.; Castren, M.L. Distinctive behavioral and cellular responses to fluoxetine in the mouse model for Fragile X syndrome. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quinlan, M.A.; Robson, M.J.; Ye, R.; Rose, K.L.; Schey, K.L.; Blakely, R.D. Ex vivo Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Serotonin Transporter Interactome: Network Impact of the SERT Ala56 Coding Variant. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarni, T.I.; Schneider, A.; Borodyanskara, M.; Hagerman, R.J. Early intervention combined with targeted treatment promotes cognitive and behavioral improvements in young children with fragile x syndrome. Case Rep. Genet. 2012, 2012, 280813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiss Hess, L.; Fitzpatrick, S.E.; Nguyen, D.V.; Chen, Y.; Gaul, K.N.; Schneider, A.; Lemons Chitwood, K.; Eldeeb, M.A.; Polussa, J.; Hessl, D.; et al. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Low-Dose Sertraline in Young Children With Fragile X Syndrome. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2016, 37, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaratnam, A.; Potter, L.A.; Biag, H.M.B.; Schneider, A.; Petrasic, I.C.; Hagerman, R.J. Review of Autism Profiles and Response to Sertraline in Fragile X Syndrome-Associated Autism vs. Non-syndromic Autism; Next Steps for Targeted Treatment. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 581429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlOlaby, R.R.; Sweha, S.R.; Silva, M.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Yrigollen, C.M.; Pretto, D.; Hagerman, R.J.; Tassone, F. Molecular biomarkers predictive of sertraline treatment response in young children with fragile X syndrome. Brain Dev. 2017, 39, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, J.L.; Casey, A.B.; Saraf, T.S.; Mukherjee, M.; Booth, R.G.; Canal, C.E. (S)-5-(2′-Fluorophenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-amine, a Serotonin Receptor Modulator, Possesses Anticonvulsant, Prosocial, and Anxiolytic-like Properties in an Fmr1 Knockout Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorder. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saraf, T.S.; McGlynn, R.P.; Bhatavdekar, O.M.; Booth, R.G.; Canal, C.E. FPT, a 2-Aminotetralin, Is a Potent Serotonin 5-HT(1A), 5-HT(1B), and 5-HT(1D) Receptor Agonist That Modulates Cortical Electroencephalogram Activity in Adult Fmr1 Knockout Mice. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 3629–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Newman-Tancredi, A.; Varney, M.A.; Razak, K.A. Acute and Repeated Administration of NLX-101, a Selective Serotonin-1A Receptor Biased Agonist, Reduces Audiogenic Seizures in Developing Fmr1 Knockout Mice. Neuroscience 2023, 509, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraf, T.S.; Chen, Y.; Tyagi, R.; Canal, C.E. Altered brain serotonin 5-HT(1A) receptor expression and function in juvenile Fmr1 knockout mice. Neuropharmacology 2024, 245, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannelli, A.; Mariano, V.; Bagni, C.; Kanellopoulos, A.K. Activation of the 5-HT1A Receptor by Eltoprazine Restores Mitochondrial and Motor Deficits in a Drosophila Model of Fragile X Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Hoang, E.T.; Viar, K.E.; Stornetta, R.L.; Scott, M.M.; Zhu, J.J. Pharmacological rescue of Ras signaling, GluA1-dependent synaptic plasticity, and learning deficits in a fragile X model. Genes. Dev. 2014, 28, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Arai, T.; Yarimizu, J.; Matsumoto, M. 5-HT5A Receptor Antagonist ASP5736 Ameliorates Several Abnormal Behaviors in an Fmr1-Targeted Transgenic Male Rat Model of Fragile X Syndrome. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 25, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Spatuzza, M.; D’Antoni, S.; Bonaccorso, C.M.; Trovato, C.; Musumeci, S.A.; Leopoldo, M.; Lacivita, E.; Catania, M.V.; Ciranna, L. Activation of 5-HT7 serotonin receptors reverses metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated synaptic plasticity in wild-type and Fmr1 knockout mice, a model of Fragile X syndrome. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Sardone, L.M.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Ciranna, L. Novel agonists for serotonin 5-HT7 receptors reverse metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated long-term depression in the hippocampus of wild-type and Fmr1 KO mice, a model of Fragile X Syndrome. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Sardone, L.M.; Bonaccorso, C.M.; D’Antoni, S.; Spatuzza, M.; Gulisano, W.; Tropea, M.R.; Puzzo, D.; Leopoldo, M.; Lacivita, E.; et al. Activation of Serotonin 5-HT7 Receptors Modulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity by Stimulation of Adenylate Cyclases and Rescues Learning and Behavior in a Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharghi, S.; Flunkert, S.; Daurer, M.; Rabl, R.; Chagnaud, B.P.; Leopoldo, M.; Lacivita, E.; Hutter-Paier, B.; Prokesch, M. Evaluating the effect of R-Baclofen and LP-211 on autistic behavior of the BTBR and Fmr1-KO mouse models. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1087788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, J.J.; Price, G.W.; Jeffrey, P.; Deeks, N.J.; Stean, T.; Piper, D.; Smith, M.I.; Upton, N.; Medhurst, A.D.; Middlemiss, D.N.; et al. Characterization of SB-269970-A, a selective 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, L.; Trovato, C.; Musumeci, S.A.; Catania, M.V.; Ciranna, L. 5-HT(1A) and 5-HT(7) receptors differently modulate AMPA receptor-mediated hippocampal synaptic transmission. Hippocampus 2012, 22, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry-Kravis, E.; Sklena, P. Demonstration of abnormal cyclic AMP production in platelets from patients with fragile X syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1993, 45, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry-Kravis, E.; Huttenlocher, P.R. Cyclic AMP metabolism in fragile X syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 31, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.J.; Davidson, R.J.; Elliott, J.L.; Lahvis, G.P.; Yin, J.C.; Bhattacharyya, A. The cyclic AMP cascade is altered in the fragile X nervous system. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, T.; Lebrigand, K.; Castagnola, S.; Paquet, A.; Jarjat, M.; Popa, A.; Grossi, M.; Rage, F.; Bardoni, B. HITS-CLIP in various brain areas reveals new targets and new modalities of RNA binding by fragile X mental retardation protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 6344–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurin, T.; Melancia, F.; Jarjat, M.; Castro, L.; Costa, L.; Delhaye, S.; Khayachi, A.; Castagnola, S.; Mota, E.; Di Giorgio, A.; et al. Involvement of Phosphodiesterase 2A Activity in the Pathophysiology of Fragile X Syndrome. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.; Tempio, A.; Lacivita, E.; Leopoldo, M.; Ciranna, L. Serotonin 5-HT7 receptors require cyclin-dependent kinase 5 to rescue hippocampal synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Fragile X Syndrome. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 54, 4124–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, P.C.; Tsai, L.H. Three decades of Cdk5. J. Biomed. Sci. 2021, 28, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, C.; Li, C.; Chen, J.; Tan, J.; Zeng, L. The role of Cdk5 in neurological disorders. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 951202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Xiao, D.; Lu, T.; Qin, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, T.; Han, X. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs and their target genes in the hippocampal tissues of Fmr1 knockout mice. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 813–824. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Hu, X.; Hong, W.; Pan, T.; Wang, Z.; Wang, E.; Wu, G. A novel animal model of spontaneous epilepsy: Cdk5 knockout in pericyte-specific mice. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1474231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, G.; Krapacher, F.; Ferreras, S.; Quassollo, G.; Mari, M.M.; Pisano, M.V.; Montemerlo, A.; Rubianes, M.D.; Bregonzio, C.; Arias, C.; et al. Lack of Cdk5 activity is involved on Dopamine Transporter expression and function: Evidences from an animal model of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 346, 113866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, P.B.; Leopoldo, M.; Caccia, S.; Sarkisyan, G.; Fracasso, C.; Martelli, G.; Lacivita, E.; Berardi, F.; Perrone, R. LP-211 is a brain penetrant selective agonist for the serotonin 5-HT(7) receptor. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 481, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Edagawa, Y.; Saito, H.; Abe, K. The serotonin 5-HT2 receptor-phospholipase C system inhibits the induction of long-term potentiation in the rat visual cortex. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.H.; Yang, Q.; Ma, L.; Liu, S.B.; Chen, G.S.; Wu, Y.M.; Li, X.Q.; Liu, G.; Zhao, M.G. Deficits in LTP induction by 5-HT2A receptor antagonist in a mouse model for fragile X syndrome. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edagawa, Y.; Saito, H.; Abe, K. Stimulation of the 5-HT1A receptor selectively suppresses NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic excitation in the rat visual cortex. Brain Res. 1999, 827, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edagawa, Y.; Saito, H.; Abe, K. Serotonin inhibits the induction of long-term potentiation in rat primary visual cortex. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 22, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canal, C.E.; Felsing, D.E.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Wood, J.T.; Perry, C.K.; Vemula, R.; Booth, R.G. An Orally Active Phenylaminotetralin-Chemotype Serotonin 5-HT7 and 5-HT1A Receptor Partial Agonist that Corrects Motor Stereotypy in Mouse Models. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Napoli, E.; Wong, S.; Hagerman, R.; Liu, S.; Tassone, F.; Giulivi, C. Altered redox mitochondrial biology in the neurodegenerative disorder fragile X-tremor/ataxia syndrome: Use of antioxidants in precision medicine. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.; Wang, F.; Li, M.; Sah, N.; Stockton, M.E.; Tidei, J.J.; Gao, Y.; Korabelnikov, T.; Kannan, S.; Vevea, J.D.; et al. Reduced mitochondrial fusion and Huntingtin levels contribute to impaired dendritic maturation and behavioral deficits in Fmr1-mutant mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Antoni, S.; de Bari, L.; Valenti, D.; Borro, M.; Bonaccorso, C.M.; Simmaco, M.; Vacca, R.A.; Catania, M.V. Aberrant mitochondrial bioenergetics in the cerebral cortex of the Fmr1 knockout mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.K.; Wang, A.; Wang, L.; Tracey, M.; Kleiner, G.; Quinzii, C.M.; Sun, L.; Yang, G.; Perez-Zoghbi, J.F.; Licznerski, P.; et al. Inefficient thermogenic mitochondrial respiration due to futile proton leak in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 7404–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Okabe, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yarimizu, J.; Harada, K. Novel 5-HT5A receptor antagonists ameliorate scopolamine-induced working memory deficit in mice and reference memory impairment in aged rats. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 127, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yarimizu, J.; Okabe, M.; Moriyama, A.; Furutani, M.; Marcus, M.M.; Svensson, T.H.; Harada, K. Functional mechanism of ASP5736, a selective serotonin 5-HT(5A) receptor antagonist with potential utility for the treatment of cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 28, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, M.; Harada, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Yarimizu, J.; Okabe, M.; Shimada, T.; Ni, K.; Matsuoka, N. ASP5736, a novel 5-HT5A receptor antagonist, ameliorates positive symptoms and cognitive impairment in animal models of schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1698–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, E.A.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Czech, C.; Hagerman, R.J.; Hessl, D.; Wong, C.Y.; Rabbia, M.; Deptula, D.; John, A.; Kinch, R.; et al. Effect of the mGluR5-NAM Basimglurant on Behavior in Adolescents and Adults with Fragile X Syndrome in a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial: FragXis Phase 2 Results. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerman, R.; Jacquemont, S.; Berry-Kravis, E.; Des Portes, V.; Stanfield, A.; Koumaras, B.; Rosenkranz, G.; Murgia, A.; Wolf, C.; Apostol, G.; et al. Mavoglurant in Fragile X Syndrome: Results of two open-label, extension trials in adults and adolescents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry-Kravis, E.; Des Portes, V.; Hagerman, R.; Jacquemont, S.; Charles, P.; Visootsak, J.; Brinkman, M.; Rerat, K.; Koumaras, B.; Zhu, L.; et al. Mavoglurant in fragile X syndrome: Results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 321ra325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligsay, A.; Van Dijck, A.; Nguyen, D.V.; Lozano, R.; Chen, Y.; Bickel, E.S.; Hessl, D.; Schneider, A.; Angkustsiri, K.; Tassone, F.; et al. A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ganaxolone in children and adolescents with fragile X syndrome. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2017, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry-Kravis, E.; Hagerman, R.; Visootsak, J.; Budimirovic, D.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Cherubini, M.; Zarevics, P.; Walton-Bowen, K.; Wang, P.; Bear, M.F.; et al. Arbaclofen in fragile X syndrome: Results of phase 3 trials. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2017, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry-Kravis, E.M.; Harnett, M.D.; Reines, S.A.; Reese, M.A.; Ethridge, L.E.; Outterson, A.H.; Michalak, C.; Furman, J.; Gurney, M.E. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase-4D in adults with fragile X syndrome: A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 clinical trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Parent, F.; Champigny, C.; Cote, S.; Mohamad, T.; Hasani, S.A.; Caku, A.; Corbin, F.; Lepage, J.F. Neurophysiological effects of a combined treatment of lovastatin and minocycline in patients with fragile X syndrome: Ancillary results of the LOVAMIX randomized clinical trial. Autism Res. 2024, 17, 1944–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proteau-Lemieux, M.; Lacroix, A.; Galarneau, L.; Corbin, F.; Lepage, J.F.; Caku, A. The safety and efficacy of metformin in fragile X syndrome: An open-label study. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 110, 110307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, P.; Montanaro, F.A.M.; Biag, H.M.B.; Salcedo-Arellano, M.J.; Kim, K.; Ponzini, M.D.; Tassone, F.; Schneider, A.; Abbeduto, L.; Thurman, A.J.; et al. Longitudinal follow-up of metformin treatment in Fragile X Syndrome. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1305597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loane, C.; Politis, M. Buspirone: What is it all about? Brain Res. 2012, 1461, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, A.B.; Canal, C.E. Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Aripiprazole. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, E.M.; Dominick, K.C.; Pedapati, E.V.; Wink, L.K.; Shaffer, R.C.; Andrews, H.; Choo, T.H.; Chen, C.; Kaufmann, W.E.; Tartaglia, N.; et al. Pharmacologic Interventions for Irritability, Aggression, Agitation and Self-Injurious Behavior in Fragile X Syndrome: An Initial Cross-Sectional Analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 4595–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, M.; Sleem, A.; Elsayed, O.H.; Good, M.E.; El-Mallakh, R.S. New Antipsychotic Medications in the Last Decade. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2021, 23, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacivita, E.; Niso, M.; Stama, M.L.; Arzuaga, A.; Altamura, C.; Costa, L.; Desaphy, J.F.; Ragozzino, M.E.; Ciranna, L.; Leopoldo, M. Privileged scaffold-based design to identify a novel drug-like 5-HT7 receptor-preferring agonist to target Fragile X syndrome. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 199, 112395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacivita, E.; Niso, M.; Mastromarino, M.; Garcia Silva, A.; Resch, C.; Zeug, A.; Loza, M.I.; Castro, M.; Ponimaskin, E.; Leopoldo, M. Knowledge-Based Design of Long-Chain Arylpiperazine Derivatives Targeting Multiple Serotonin Receptors as Potential Candidates for Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorder. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2021, 12, 1313–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Receptor | Brain Localization (Rodent; Human) | Transduction Mechanism | Agonists | Antagonists | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | Limbic areas; hippocampus; raphe nuclei | Inhibition of adenylate cyclase | 8-OH DPAT | WAY100635 | [4] |
| 5-HT2A | Cerebral cortex; olfactory bulb; brainstem nuclei | Stimulation of phospholipase C | DOI | Ketanserin MDL100907 | [4] |
| 5-HT2B | Cerebellum; lateral septum; hypothalamus; amygdala | Stimulation of phospholipase C | BW723C86 | SB200646 SB204741 | [4] |
| 5-HT5A | Hippocampus; frontal cortex; raphe nuclei | Inhibition of adenylate cyclase | 5-CT 8-OH DPAT | ASP5736 | [11] [69] |
| 5-HT7 | Thalamus; hypothalamus; hippocampus | Stimulation of adenylate cyclase | 5-CT 8-OH DPAT LP-211 | SB269970 SB656104 | [16]; [87] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciranna, L.; Costa, L. Therapeutic Effects of Pharmacological Modulation of Serotonin Brain System in Human Patients and Animal Models of Fragile X Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062495
Ciranna L, Costa L. Therapeutic Effects of Pharmacological Modulation of Serotonin Brain System in Human Patients and Animal Models of Fragile X Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062495
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiranna, Lucia, and Lara Costa. 2025. "Therapeutic Effects of Pharmacological Modulation of Serotonin Brain System in Human Patients and Animal Models of Fragile X Syndrome" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062495
APA StyleCiranna, L., & Costa, L. (2025). Therapeutic Effects of Pharmacological Modulation of Serotonin Brain System in Human Patients and Animal Models of Fragile X Syndrome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062495







