Analysis of Molecular Aspects of Periodontitis as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Single-Center 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Participants
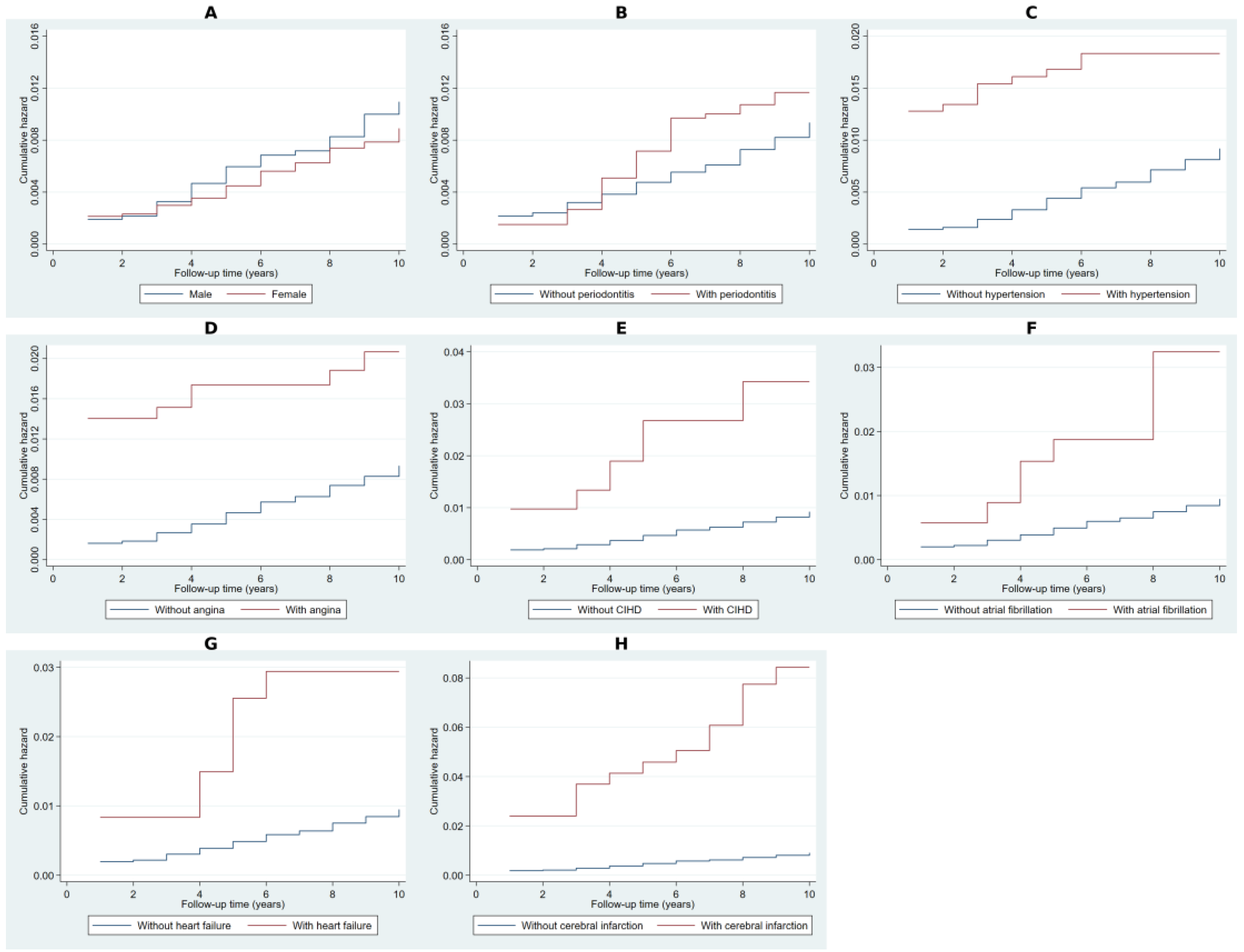
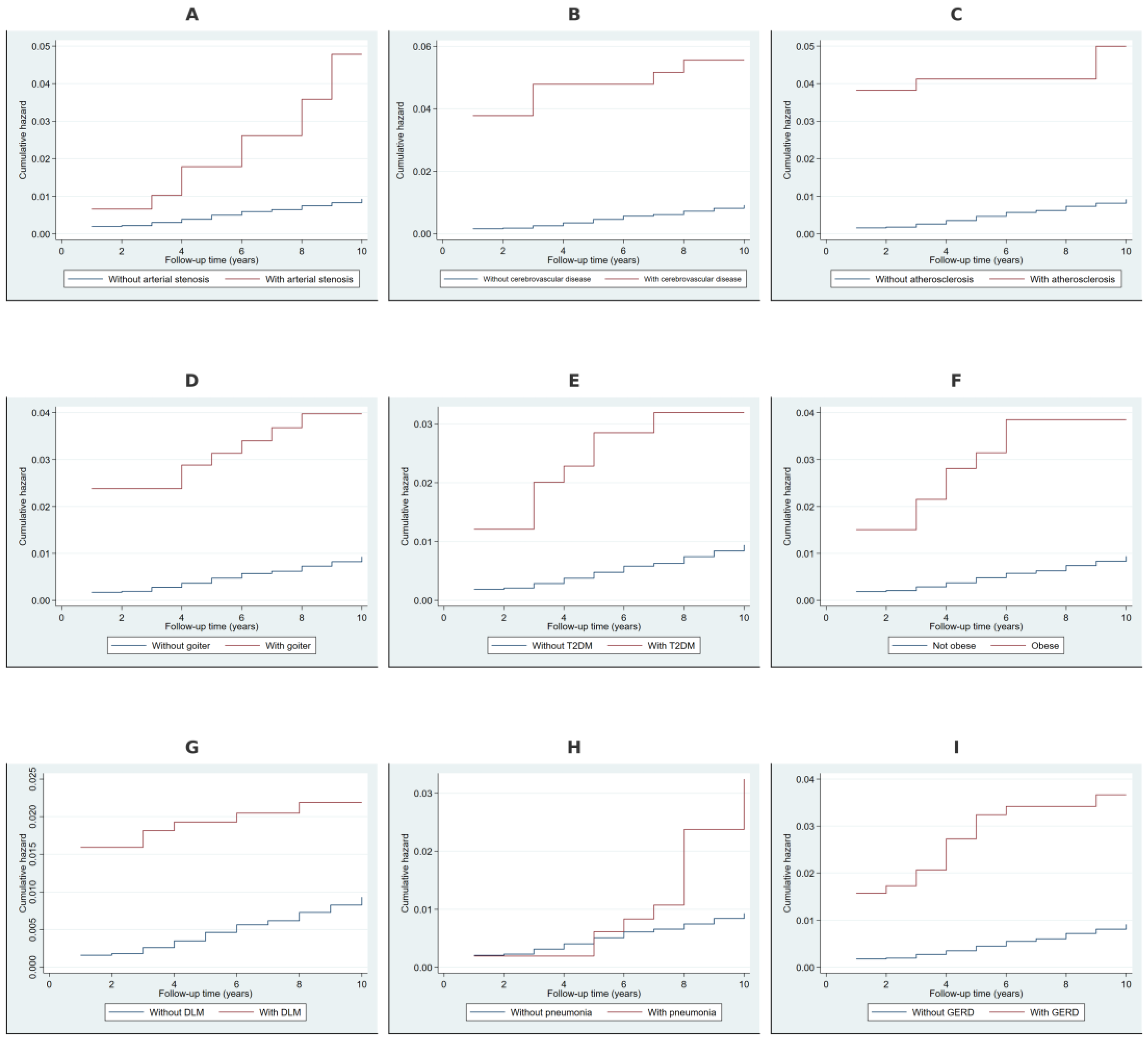
2.2. Cumulative Hazard Analysis Using Nelson–Aalen Estimates
2.3. Cox Regression-Based Likelihood Ratio Tests for Covariates
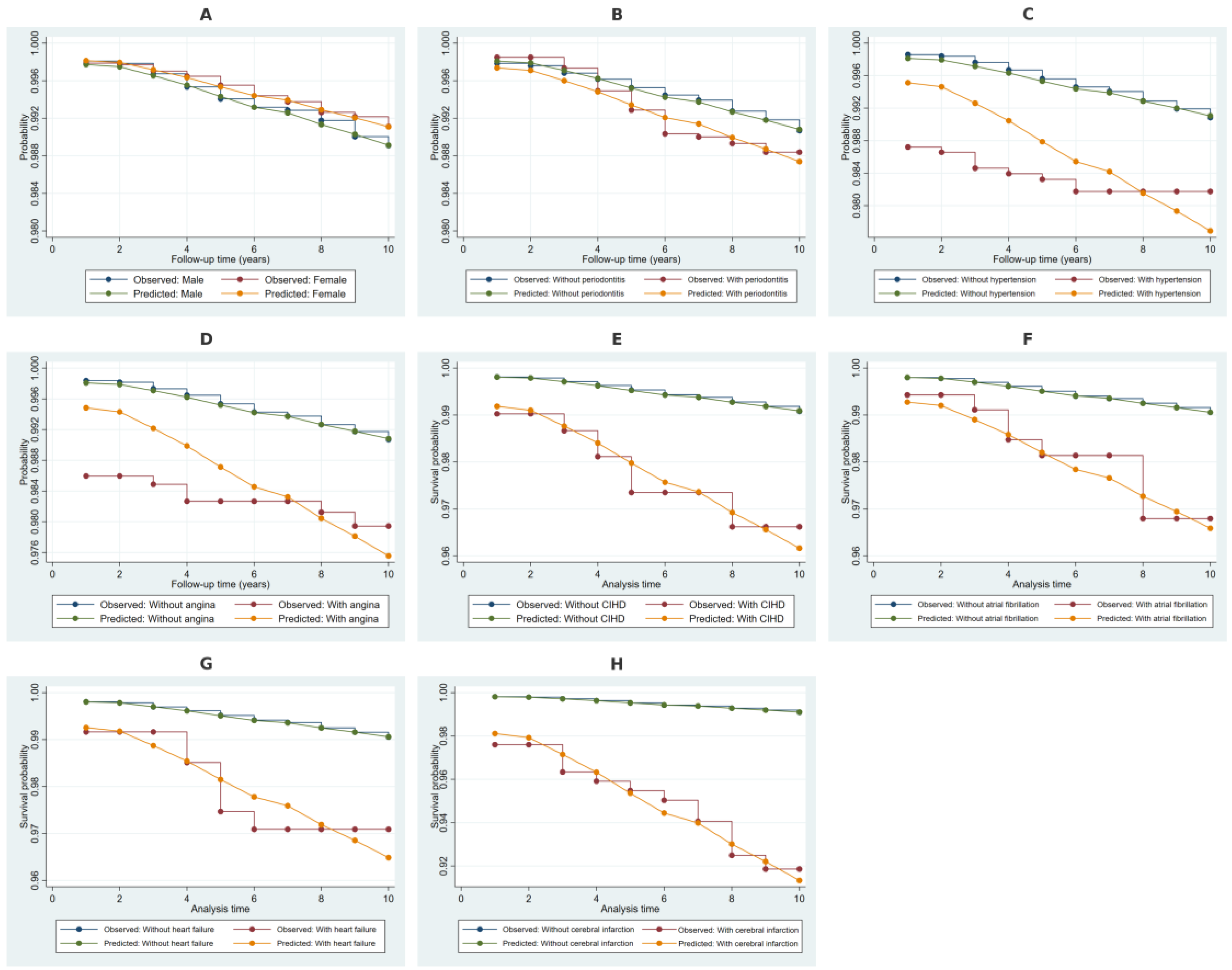
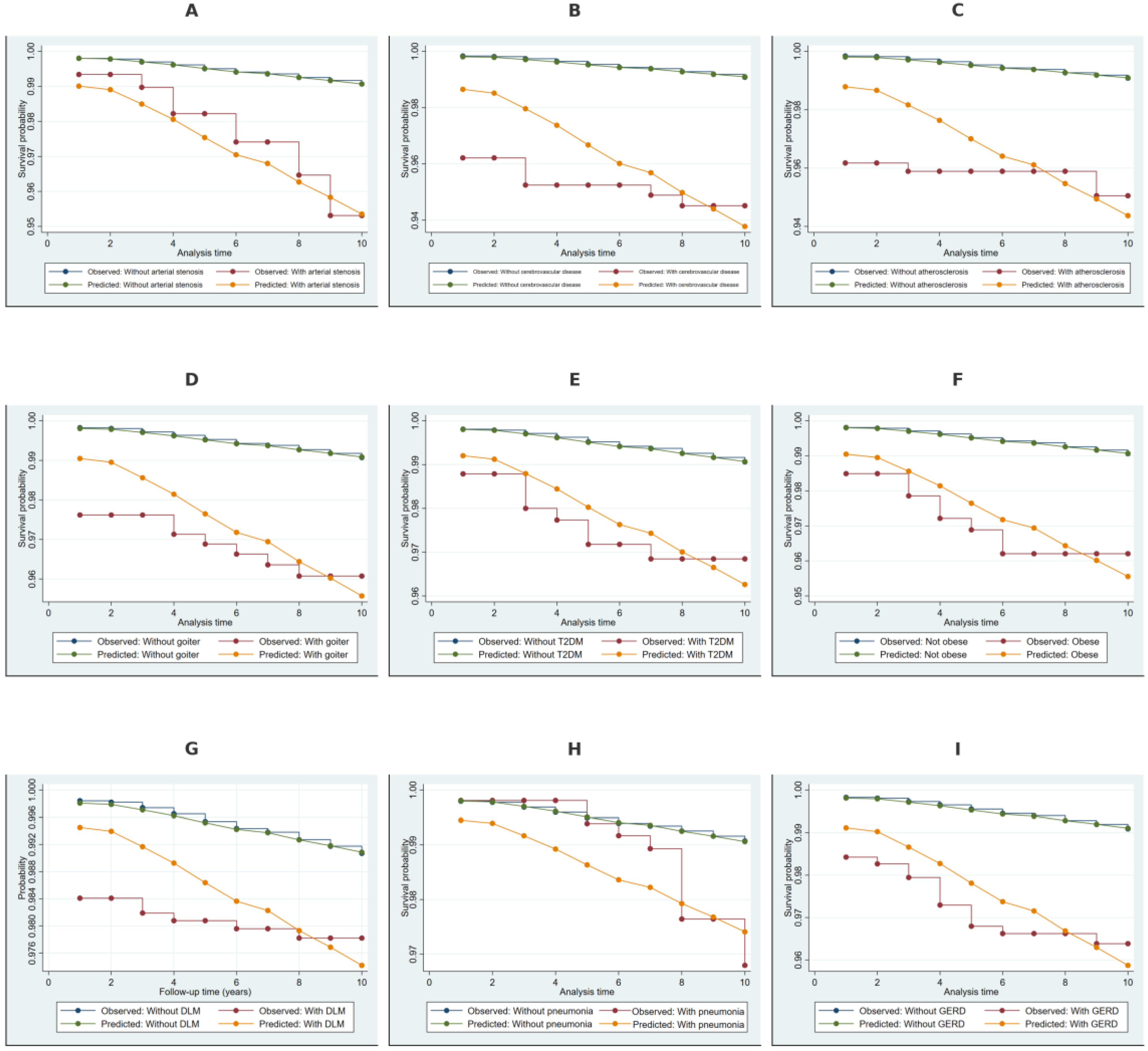
2.4. Kaplan–Meier Survival Estimates Stratified by Covariates
2.5. Weibull Regression Analysis of Risk Factors for NDD
2.6. Discriminative Performance of the Weibull Model
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Database Cleaning and Data Processing
4.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
4.3. Variable Definitions and Covariate Selection
4.4. Statistical Methods
4.4.1. Cumulative Hazard Estimation
4.4.2. Likelihood Ratio Test for Equality of Survival Distributions
- -
- Restricted Model (): A model without the covariate of interest.
- -
- Full Model (): A model including the covariate of interest.
4.4.3. Kaplan–Meier Estimates
- -
- is the estimated survival probability at time ,
- -
- is the number of events (e.g., diagnosis of periodontitis) at time ,
- -
- is the number of participants at risk just before time .
- -
- is the baseline survival function,
- -
- is the vector of estimated regression coefficients,
- -
- is the covariate matrix.
4.4.4. Multivariable Parametric Survival Modeling Using the Weibull Regression Model
- -
- is the hazard function at time given covariates ;
- -
- is the scale parameter;
- -
- is the shape parameter, which determines whether the hazard is increasing (), constant (), or decreasing () over time;
- -
- represents the linear predictor derived from the covariate effects.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Neurodegenerative Diseases. National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. Available online: https://www.niehs.nih.gov/research/supported/health/neurodegenerative (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Feigin, V.L.; Vos, T.; Nichols, E.; O Owolabi, M.; Carroll, W.M.; Dichgans, M.; Deuschl, G.; Parmar, P.; Brainin, M.; Murray, C. The global burden of neurological disorders: Translating evidence into policy. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 19, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics | Parkinson’s Foundation. Available online: https://www.parkinson.org/understanding-parkinsons/statistics (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Dementia. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Alvarenga, M.O.P.; Frazão, D.R.; de Matos, I.G.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Rösing, C.K.; Maia, L.C.; Lima, R.R. Is There Any Association Between Neurodegenerative Diseases and Periodontitis? A Systematic Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 651437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachokova, A.S.; Gjaltema, J.; Hagens, E.R.C.; Hashemi, Z.; Knüppe, T.B.A.; Kootstra, T.J.M.; Visser, A.; Bloem, B.R. Periodontitis: A Plausible Modifiable Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Diseases? A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, P.C.; Castro, M.M.L.; Magno, M.B.; Almeida, A.P.C.P.S.C.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Maia, L.C.; Lima, R.R. Association Between Periodontitis and Cognitive Impairment in Adults: A Systematic Review. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, A.; Paladini, S.; Cossatis, J. Periodontal Disease and Alzheimer’s: Insights from a Systematic Literature Network Analysis. J. Prev. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 11, 1148–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, D.S.; Qazi, D.S.; Baig, D.M.S.; Gul, D.J.; Gull, D.N.; Umair, D.M. Periodontal Disease as a Potential Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Disease. J. Popl. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, 2727–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, J.; Risco, R.; Munive-Degregori, A.; Guerrero, M.E.; Mauricio, F.; Mayta-Tovalino, F. Periodontitis and neuropathic diseases: A literature review. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2024, 14, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesidou, E.; Theotokis, P.; Damianidou, O.; Boziki, M.; Konstantinidou, N.; Taloumtzis, C.; Sintila, S.-A.; Grigoriadis, P.; Evangelopoulos, M.E.; Bakirtzis, C.; et al. CNS Ageing in Health and Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivagurunathan, N.; Calivarathan, L. Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases. In Evidence-Based Functional Foods for Prevention of Age-Related Diseases; Pathak, S., Banerjee, A., Duttaroy, A.K., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, S.; Haque, M.E.; Balakrishnan, R.; Kim, I.-S.; Choi, D.-K. The Ageing Brain: Molecular and Cellular Basis of Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 683459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardenoije, R.; Iatrou, A.; Kenis, G.; Kompotis, K.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Mastroeni, D.; Coleman, P.; Lemere, C.A.; Hof, P.R.; van den Hove, D.L.A.; et al. The epigenetics of aging and neurodegeneration. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 131, 21–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thadathil, N.; Hori, R.; Xiao, J.; Khan, M.M. DNA double-strand breaks: A potential therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases. Chromosome Res. 2019, 27, 345–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D. Oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2013, 8, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasner, N.S.; Schure, R.S. Periodontal Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554590/ (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Brahmbhatt, Y.; Alqaderi, H.; Chinipardaz, Z. Association Between Severe Periodontitis and Cognitive Decline in Older Adults. Life 2024, 14, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liccardo, D.; Marzano, F.; Carraturo, F.; Guida, M.; Femminella, G.D.; Bencivenga, L.; Agrimi, J.; Addonizio, A.; Melino, I.; Valletta, A.; et al. Potential Bidirectional Relationship Between Periodontitis and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendahl, U.; Nilsson, P.; Betsholtz, C. Emerging links between cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative diseases—A special role for pericytes. Embo Rep. 2019, 20, e48070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Kantamneni, S. Editorial: Cerebrovascular and Neurodegenerative Diseases—New Insights Into Molecular Cell Biology and Therapeutic Targets. Front. Neurolec. 2019, 10, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, J.B.; Arnold, S.E.; Raible, K.; Brettschneider, J.; Xie, S.X.; Grossman, M.; Monsell, S.E.; Kukull, W.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Contribution of cerebrovascular disease in autopsy confirmed neurodegenerative disease cases in the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Centre. Brain 2013, 136, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esiri, M.M.; Nagy, Z.; Smith, M.Z.; Barnetson, L.; Smith, A.D. Cerebrovascular disease and threshold for dementia in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 1999, 354, 919–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Kisler, K.; Montagne, A.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. The role of brain vasculature in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1318–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Mäe, M.; Nisancioglu, M.H.; Wallgard, E.; Niaudet, C.; He, L.; Norlin, J.; Lindblom, P.; Strittmatter, K.; et al. Pericytes regulate the blood-brain barrier. Nature 2010, 468, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leijenaar, J.F.; van Maurik, I.S.; Kuijer, J.P.; van der Flier, W.M.; Scheltens, P.; Barkhof, F.; Prins, N.D. Lower cerebral blood flow in subjects with Alzheimer’s dementia, mild cognitive impairment, and subjective cognitive decline using two-dimensional phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 9, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimura, T.; Kimura, T.; Miyakawa, T. Morphological changes of blood vessels in the brain with Alzheimer’s disease. Jpn J. Psychiatry Neurol. 1991, 45, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halliday, M.R.; Rege, S.V.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Z.; A Miller, C.; A Winkler, E.; Zlokovic, B.V. Accelerated pericyte degeneration and blood-brain barrier breakdown in apolipoprotein E4 carriers with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joutel, A.; Rege, S.V.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Z.; A Miller, C.; A Winkler, E.; Zlokovic, B.V. Notch3 mutations in CADASIL, a hereditary adult-onset condition causing stroke and dementia. Nature 1996, 383, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colín-Castelán, D.; Zaina, S. Associations between atherosclerosis and neurological diseases, beyond ischemia-induced cerebral damage. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2019, 20, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdile, G.; Fuller, S.J.; Martins, R.N. The role of type 2 diabetes in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 84, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szablewski, L. Associations Between Diabetes Mellitus and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, A.; Fernandes, A.; Barateiro, A. The complex relationship between obesity and neurodegenerative diseases: An updated review. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1294420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Hu, C.-J.; Tu, Y.-K. Endothelial Dysfunction in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, J.J. Goiter in Adult Patients Aged 55 Years and Older: Etiology and Clinical Features in 634 Patients. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2005, 60, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Xiao, Y.; Mao, J.; Mao, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, G.; Guo, L.; Huang, H.; Mu, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Metabolic syndrome and its components are associated with thyroid volume in adolescents. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondi, B.; Kahaly, G.J. Cardiovascular involvement in patients with different causes of hyperthyroidism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gau, S.-Y.; Lai, J.-N.; Yip, H.-T.; Wu, M.-C.; Wei, J.C.-C. Higher Dementia Risk in People With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Real-World Evidence. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 830729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dawson, T.M.; Kulkarni, S. Neurodegenerative disorders and gut-brain interactions. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ide, K.; Matsuoka, N.; Kawakami, K. Is the Use of Proton-pump Inhibitors a Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease? Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Shae, Z.-Y.; Kao, C.-H. Association between neurodegenerative diseases and pneumonia: A retrospective population-based study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2019, 35, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Yao, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Fan, Q.; Yang, Q.; Xu, J.; Dai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; et al. Neurological disorders after severe pneumonia are associated with translocation of endogenous bacteria from the lung to the brain. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi0699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.A. Cognitive Decline in Pneumonia: A Neglected Consequence. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Definition of Retrospective Cohort Study—NCI Dictionary of Cancer Terms—NCI. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/retrospective-cohort-study (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- World Health Organization. ICD-10: International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems: Tenth Revision; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004; Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/42980 (accessed on 4 February 2025).
- Swallow, D.M.A.; Counsell, C.E. Accuracy of routinely collected hospital administrative discharge data and death certificate ICD-10 diagnostic coding in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal syndrome: A systematic review and validation study. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, W.E.; Sanchez, M.; Wu, J. Feasibility of creating a National ALS Registry using administrative data in the United States. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal. Degener. 2014, 15, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, S.; Afshari, S.; Molaei, S.; Rezaei, N.; Dadkhah, M. The role of genetics and gender specific differences in neurodegenerative disorders: Insights from molecular and immune landscape. J. Neuroimmunol. 2023, 384, 578206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidou, E. The Sex and Gender Intersection in Chronic Periodontitis. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousineau, J.P.; Dawe, A.M.; Alpaugh, M. Investigating the Interplay between Cardiovascular and Neurodegenerative Disease. Biology 2024, 13, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, J.A.; Karthikeyan, M.; Lackey, M.; Villavicencio, D.; Potashkin, J.A. Diabetes: A tipping point in neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 1029–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yuan, Y.-H.; Liu, H.-H.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, B.-W.; Chen, W.; An, Z.-J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Han, B.; et al. Epidemiologic relationship between periodontitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q. Cholesterol Metabolism in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2024, 41, 1051–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitencourt, F.V.; Nascimento, G.G.; Costa, S.A.; Orrico, S.R.P.; Ribeiro, C.C.C.; Leite, F.R.M. The Role of Dyslipidemia in Periodontitis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brock, M.; Bahammam, S.; Sima, C. The Relationships Among Periodontitis, Pneumonia and COVID-19. Front. Oral Health 2022, 2, 801815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.-Q.; Huang, Z.-M.; Zhou, H.-B.; Xie, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.-Z.; Luo, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Z.; Kang, J.-Q.; Cheng, Z.J.; Sun, B. Gastroesophageal reflux disease with 6 neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders: Genetic correlations, causality, and potential molecular mechanisms. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2024, 172, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chaouhan, H.S.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wang, I.-K.; Lin, C.-L.; Shen, T.-C.; Li, C.-Y.; Sun, K.-T. Risk of Periodontitis in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Nationwide Retrospective Cohort Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, W. Hazard Plotting for Incomplete Failure Data. J. Qual. Technol. 1969, 1, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. The Cox Proportional Hazards Model and Its Characteristics. In Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text; Kleinbaum, D.G., Klein, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 97–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. Kaplan-Meier Survival Curves and the Log-Rank Test. In Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text; Kleinbaum, D.G., Klein, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 55–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbaum, D.G.; Klein, M. Evaluating the Proportional Hazards Assumption. In Survival Analysis: A Self-Learning Text; Kleinbaum, D.G., Klein, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 161–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdogan, H. Model selection and Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC): The general theory and its analytical extensions. Psychometrika 1987, 52, 345–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E.; Califf, R.M.; Pryor, D.B.; Lee, K.L.; Rosati, R.A. Evaluating the yield of medical tests. JAMA 1982, 247, 2543–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalbfleisch, J.D.; Prentice, R.L. Inference in Parametric Models and Related Topics. In The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 52–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18; StataCorp LLC: College Station, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- The Matplotlib Development Team. Matplotlib: Visualization with Python; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Category | n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 2218 (45.42%) |
| Female | 2665 (54.58%) | |
| Periodontitis | No | 3851 (78.82%) |
| Yes | 1035 (21.18%) | |
| Hypertension | No | 4274 (87.47%) |
| Yes | 612 (12.53%) | |
| Angina pectoris | No | 4550 (93.12%) |
| Yes | 336 (6.88%) | |
| Chronic ischemic heart disease | No | 4717 (96.54%) |
| Yes | 169 (3.46%) | |
| Atrial fibrillation | No | 4822 (98.69%) |
| Yes | 64 (1.31%) | |
| Heart failure | No | 4824 (98.73%) |
| Yes | 62 (1.27%) | |
| Cerebral infarction | No | 4860 (99.47%) |
| Yes | 26 (0.53%) | |
| Arterial occlusion/stenosis of precerebral arteries | No | 4832 (98.89%) |
| Yes | 54 (1.11%) | |
| Other cerebrovascular disease | No | 4821 (98.67%) |
| Yes | 65 (1.33%) | |
| Atherosclerosis | No | 4791 (98.06%) |
| Yes | 95 (1.94%) | |
| Non-toxic goiter | No | 4772 (97.67%) |
| Yes | 114 (2.33%) | |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | No | 4786 (97.95%) |
| Yes | 100 (2.05%) | |
| Obesity | No | 4768 (97.58%) |
| Yes | 118 (2.42%) | |
| Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism | No | 4590 (93.94%) |
| Yes | 296 (6.06%) | |
| Pneumonia | No | 4818 (98.61%) |
| Yes | 68 (1.39%) | |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | No | 4811 (98.47%) |
| Yes | 75 (1.53%) |
| Variable | Category | Observed Events | Expected Events | Relative Hazard | LR Chi2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 104 | 92.75 | 1.13 | 2.27 | 0.132 |
| Female | 126 | 137.25 | 0.92 | |||
| Periodontitis | No | 185 | 195.42 | 0.95 | 3.44 | 0.064 |
| Yes | 45 | 34.58 | 1.31 | |||
| Hypertension | No | 201 | 217.92 | 0.95 | 18.29 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 29 | 12.08 | 2.47 | |||
| Angina pectoris | No | 211 | 222.53 | 0.97 | 13.02 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 19 | 7.47 | 2.6 | |||
| Chronic ischemic heart disease | No | 212 | 225.52 | 0.97 | 23.88 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 18 | 4.48 | 4.16 | |||
| Atrial fibrillation | No | 221 | 227.48 | 0.99 | 10.12 | 0.002 |
| Yes | 9 | 2.52 | 3.62 | |||
| Heart failure | No | 221 | 227.55 | 0.99 | 10.51 | 0.001 |
| Yes | 9 | 2.45 | 3.73 | |||
| Cerebral infarction | No | 212 | 228.07 | 0.98 | 49.4 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 18 | 1.93 | 9.84 | |||
| Arterial occlusion/stenosis of precerebral arteries | No | 219 | 227.75 | 0.98 | 17.77 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 11 | 2.25 | 5.01 | |||
| Other cerebrovascular disease | No | 213 | 227.43 | 0.98 | 36.32 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 17 | 2.57 | 6.91 | |||
| Atherosclerosis | No | 213 | 227.15 | 0.98 | 33.31 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 17 | 2.85 | 6.22 | |||
| Non-toxic goiter | No | 214 | 226.57 | 0.98 | 24.84 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 16 | 3.43 | 4.82 | |||
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | No | 218 | 226.94 | 0.98 | 15.25 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 12 | 3.06 | 4 | |||
| Obesity | No | 218 | 227.43 | 0.98 | 18.54 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 12 | 2.57 | 4.79 | |||
| Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism | No | 210 | 222.57 | 0.97 | 15.18 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 20 | 7.43 | 2.76 | |||
| Pneumonia | No | 219 | 225.92 | 0.98 | 8.2 | 0.004 |
| Yes | 11 | 4.08 | 2.73 | |||
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | No | 208 | 224.93 | 0.97 | 32.01 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 22 | 5.07 | 4.53 |
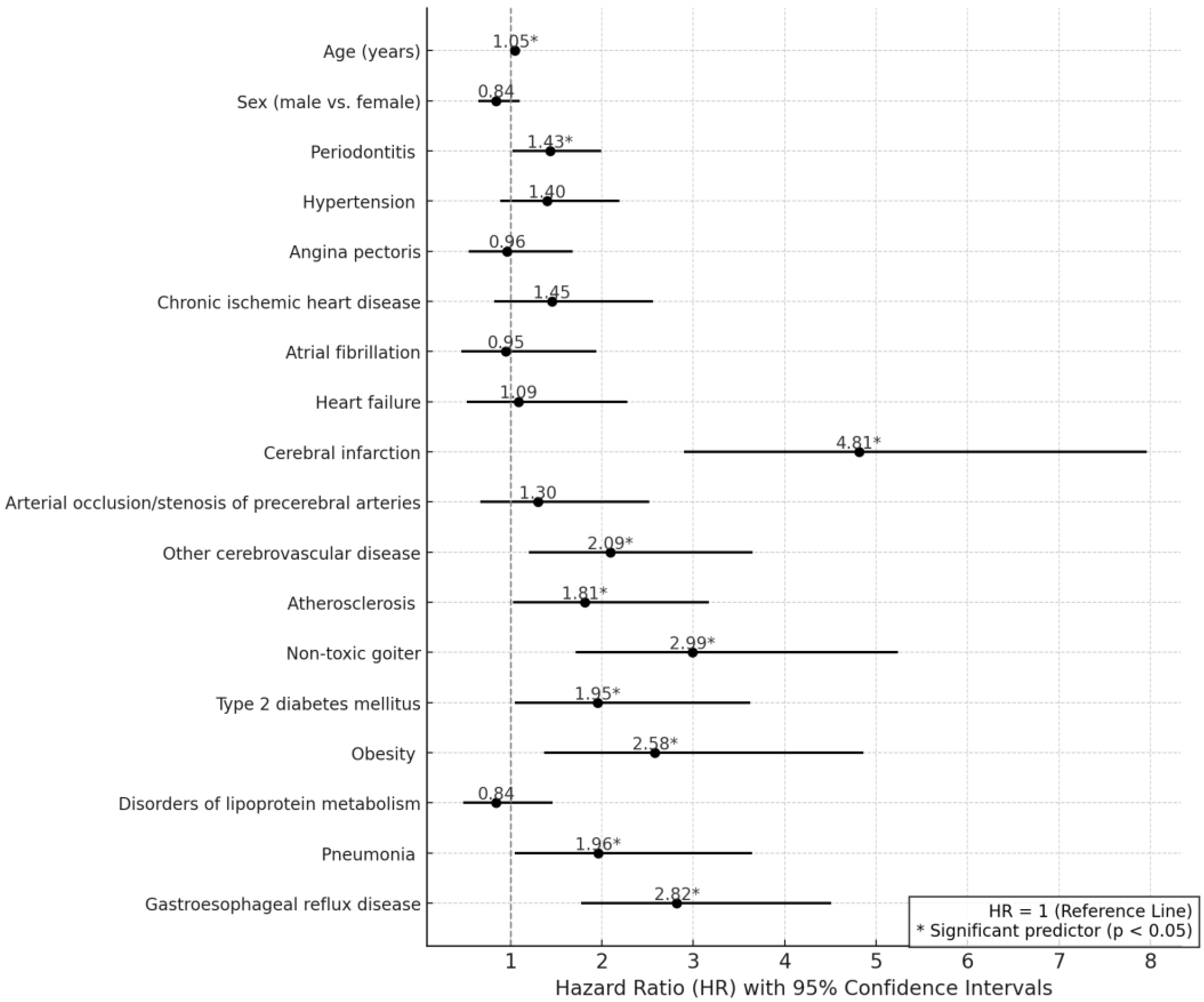
| Variable | Hazard Ratio [95% CI] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1.05 [1.04–1.07] | <0.001 |
| Sex (Male vs. Female) | 0.84 [0.65–1.10] | 0.204 |
| Periodontitis | 1.43 [1.02–1.99] | 0.037 |
| Hypertension | 1.40 [0.89–2.19] | 0.143 |
| Angina pectoris | 0.96 [0.54–1.68] | 0.875 |
| Chronic ischemic heart disease | 1.45 [0.82–2.56] | 0.206 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 0.95 [0.46–1.94] | 0.887 |
| Heart failure | 1.09 [0.52–2.28] | 0.824 |
| Cerebral infarction | 4.81 [2.90–7.96] | <0.001 |
| Arterial occlusion/stenosis of precerebral arteries | 1.30 [0.67–2.52] | 0.435 |
| Other cerebrovascular disease | 2.09 [1.20–3.65] | 0.01 |
| Atherosclerosis | 1.81 [1.03–3.17] | 0.038 |
| Non-toxic goiter | 2.99 [1.71–5.24] | <0.001 |
| Type 2 diabetes mellitus | 1.95 [1.05–3.62] | 0.034 |
| Obesity | 2.58 [1.37–4.86] | 0.003 |
| Disorders of lipoprotein metabolism | 0.84 [0.48–1.46] | 0.534 |
| Pneumonia | 1.96 [1.05–3.64] | 0.035 |
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | 2.82 [1.77–4.51] | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghanem, A.S.; Móré, M.; Nagy, A.C. Analysis of Molecular Aspects of Periodontitis as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Single-Center 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062382
Ghanem AS, Móré M, Nagy AC. Analysis of Molecular Aspects of Periodontitis as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Single-Center 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062382
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhanem, Amr Sayed, Marianna Móré, and Attila Csaba Nagy. 2025. "Analysis of Molecular Aspects of Periodontitis as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Single-Center 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062382
APA StyleGhanem, A. S., Móré, M., & Nagy, A. C. (2025). Analysis of Molecular Aspects of Periodontitis as a Risk Factor for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Single-Center 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062382






