Mechanisms of mepA Overexpression and Membrane Potential Reduction Leading to Ciprofloxacin Heteroresistance in a Staphylococcus aureus Isolate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
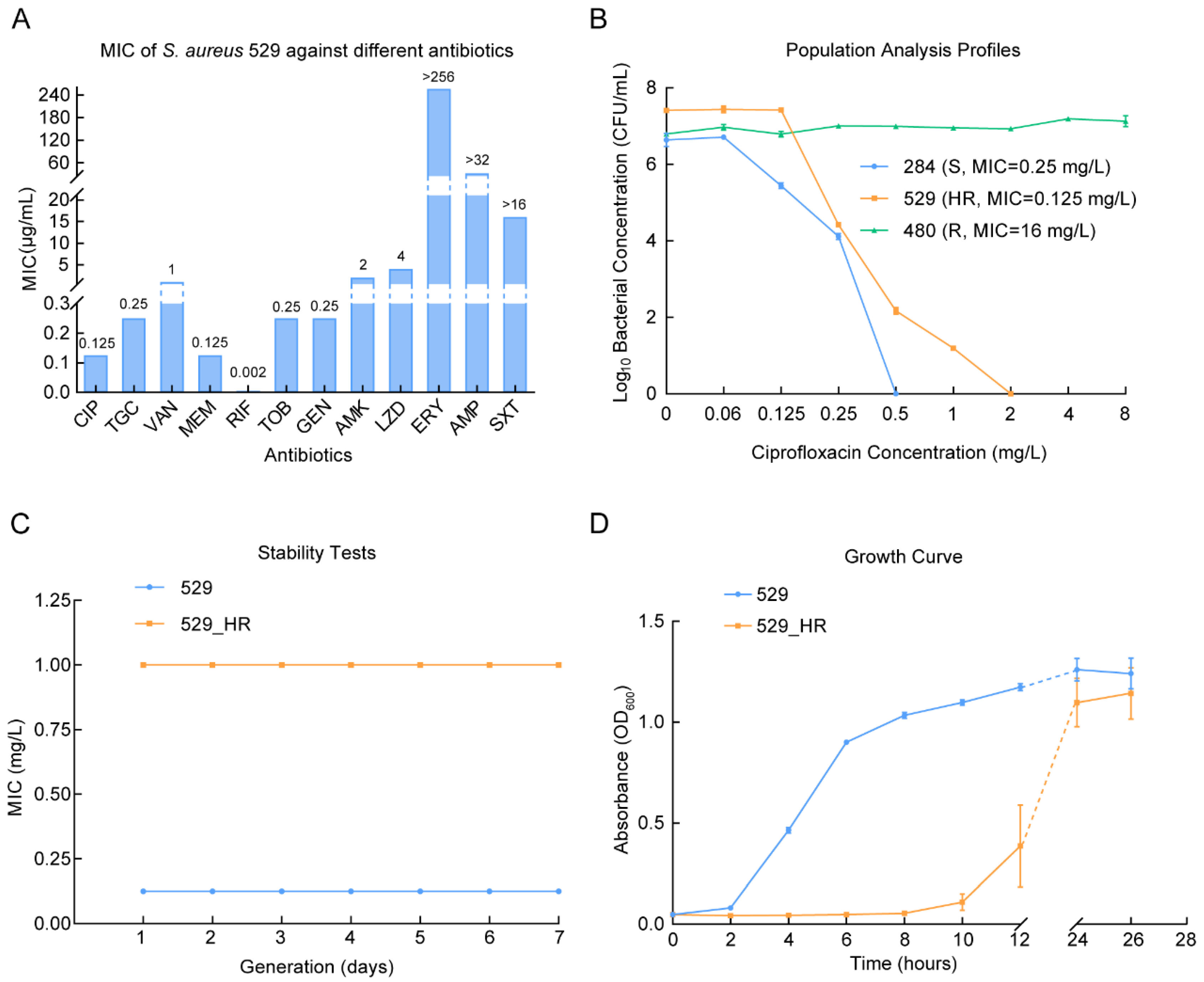
2.1. The Ciprofloxacin Heteroresistance of Staphylococcus aureus 529
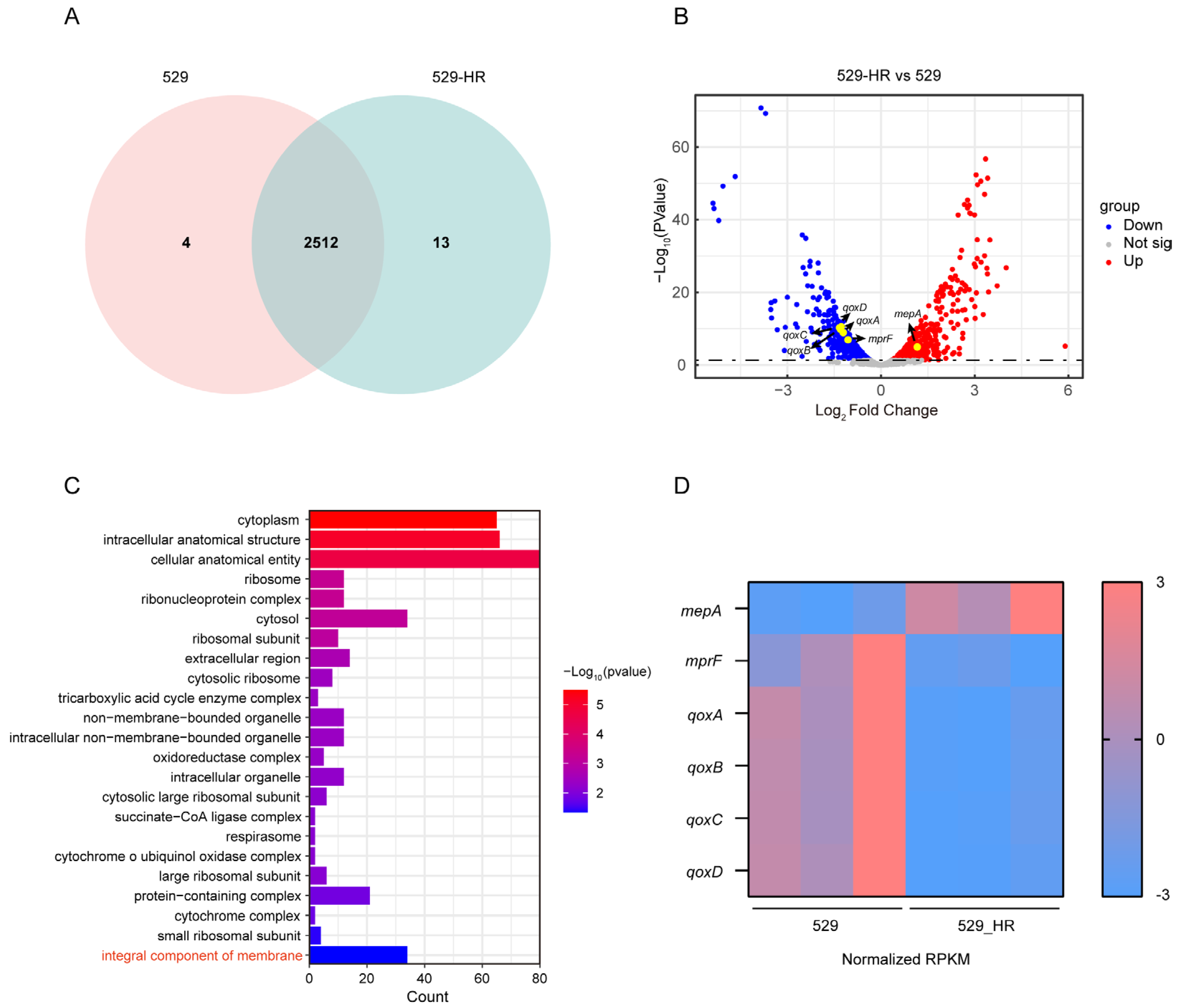
2.2. Genomic Characteristics Between 529 and 529_HR
2.3. Transcriptional Regulation of the Heteroresistant Subclone 529_HR
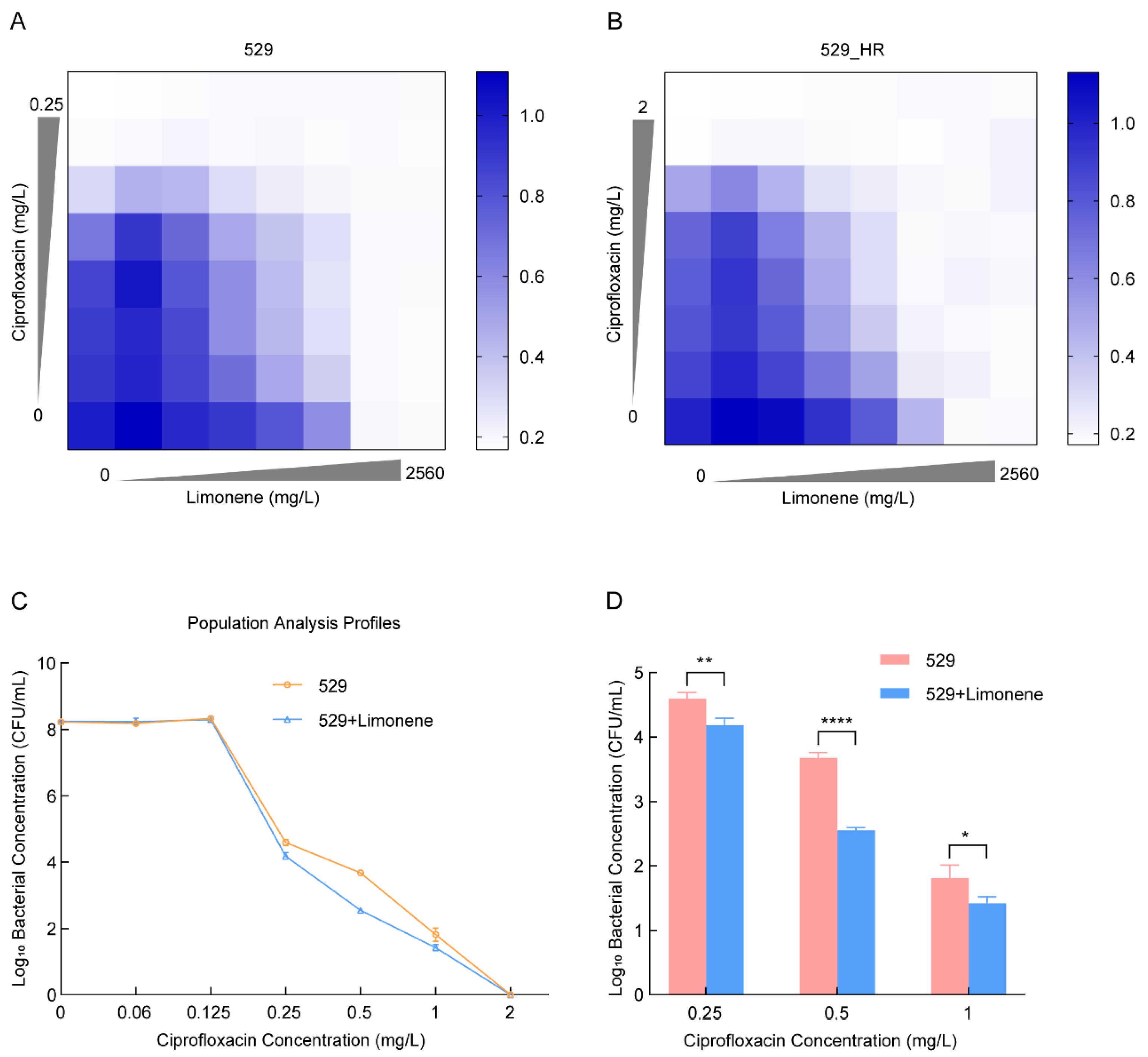
2.4. Limonene Changes the Heteroresistance Phenotype of 529
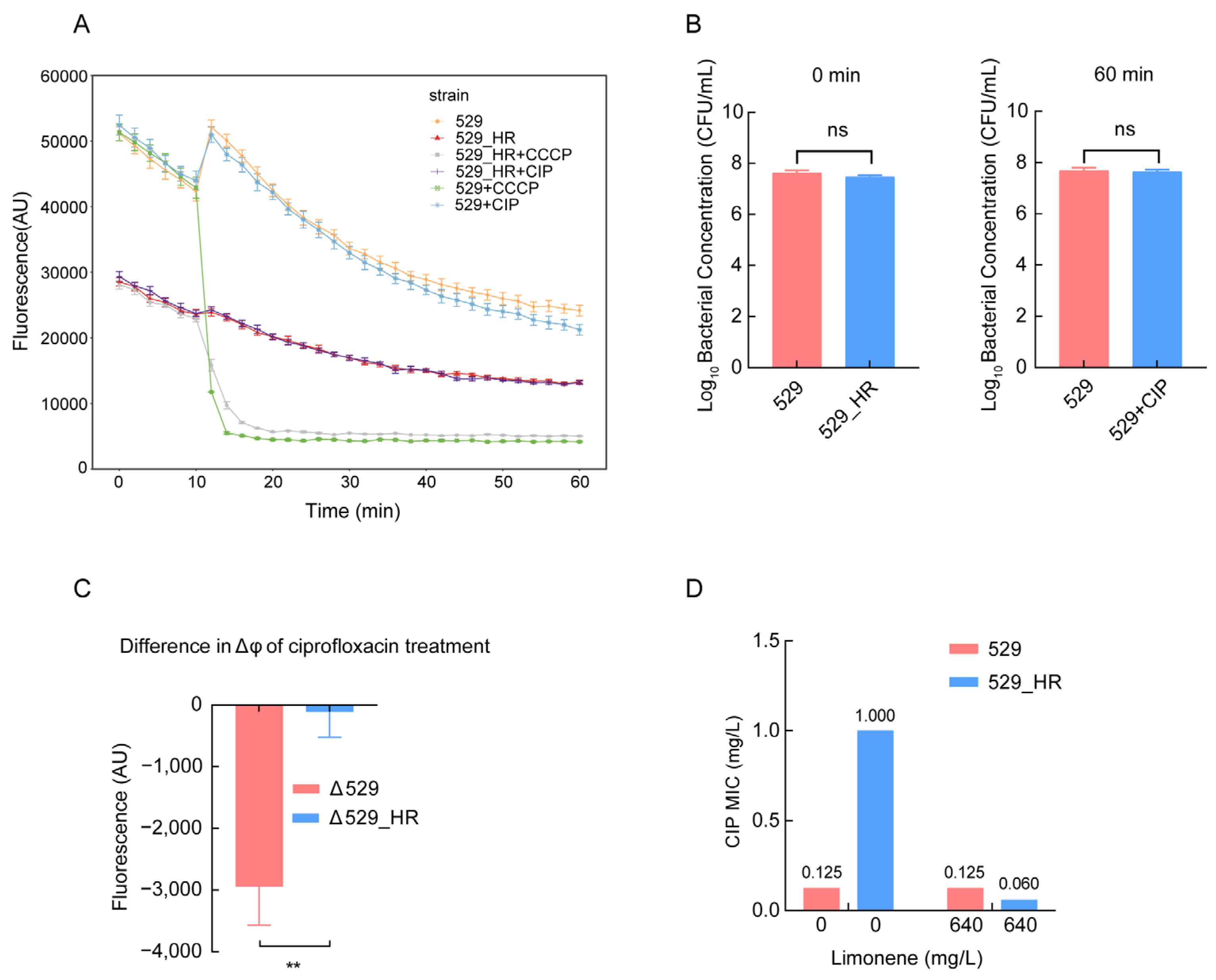
2.5. Reduced Membrane Potential Led to Heteroresistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.3. Population Analysis Profiling
4.4. Stability Evaluations and Growth Curve
4.5. Whole-Genome Sequence and Sequence Analysis
4.6. RNA-seq and Transcriptomic Analysis
4.7. Determination of Limonene Inhibitory Effectiveness
4.8. DiOC2(3) Membrane Potential Measurement
4.9. RT-qPCR
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Buist, G.; van Dijl, J.M. Staphylococcus aureus cell wall maintenance—The multifaceted roles of peptidoglycan hydrolases in bacterial growth, fitness, and virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2022, 46, fuac025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-T.; Chen, E.-Z.; Yang, L.; Peng, C.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, D.-Q. Emerging resistance mechanisms for 4 types of common anti-MRSA antibiotics in Staphylococcus aureus: A comprehensive review. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 156, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Bessa, L.J.; Sousa, C.F.; Eaton, P.; Bongiorno, D.; Stefani, S.; Campanile, F.; Gameiro, P. Fluoroquinolone metalloantibiotics: A promising approach against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaie, A.; Peirovi, N.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Moghtaderi, M.; Heidari, F.; Yeganeh, F.E.; Noorbazargan, H.; Mirzazadeh, S.; Bakhtiari, R. Preparation and optimization of ciprofloxacin encapsulated niosomes: A new approach for enhanced antibacterial activity, biofilm inhibition and reduced antibiotic resistance in ciprofloxacin-resistant methicillin-resistance Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 103, 104231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.-L. Ciprofloxacin derivatives and their antibacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayumi, T.; Tong, W.; Yoshikuni, O.; Yoko, U.; Kenichi, S. Mechanism of quinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Chemother. 2000, 6, 131–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, Y.G.; Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Bin Kim, H.; Song, K.H.; Kim, E.S.; Hooper, D.C. Association of norB overexpression and fluoroquinolone resistance in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus from Korea. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 2766–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAleese, F.; Petersen, P.; Ruzin, A.; Dunman, P.M.; Murphy, E.; Projan, S.J.; Bradford, P.A. A novel MATE family efflux pump contributes to the reduced susceptibility of laboratory-derived Staphylococcus aureus mutants to tigecycline. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 1865–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips-Jones, M.K.; Harding, S.E. Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) nanomachines-mechanisms for fluoroquinolone and glycopeptide recognition, efflux and/or deactivation. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, P.R.; de Araújo, A.C.J.; dos Santos Barbosa, C.R.; Muniz, D.F.; de Almeida, R.S.; de Menezes, I.R.A.; da Costa, J.G.M.; Rodrigues, F.F.G.; Rocha, J.E.; Pereira-Junior, F.N.; et al. Inhibition of the MepA efflux pump by limonene demonstrated by in vitro and in silico methods. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 67, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Nicoloff, H.; Hjort, K. Mechanisms and clinical relevance of bacterial heteroresistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.M.; Hsueh, P.R.; Liu, C.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Chiueh, T.S.; Shyr, J.M.; Tsao, S.M.; Chuang, Y.C.; Yan, J.J.; Wang, L.S.; et al. Prevalence and accessory gene regulator (agr) analysis of vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus among methicillin-resistant isolates in Taiwan—SMART program, 2003. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2010, 29, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Chiu, S.-K.; Fung, C.-P.; Lu, P.-L.; Wang, L.-S.; Wu, T.-L.; Wang, J.-T. Prevalence of vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus (VISA) and heterogeneous VISA among methicillin-resistant S. aureus with high vancomycin minimal inhibitory concentrations in Taiwan: A multicenter surveillance study, 2012–2013. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Wei, X.; Jiang, S.; Ji, S. In-host evolution of daptomycin resistance and heteroresistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from three endocarditis patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221 (Suppl. 2), S243–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Lin, Z.; Pu, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.; Sun, X.; Zheng, J.; Li, P.; Deng, Q.; et al. In vitro activity and heteroresistance of omadacycline against clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates from China reveal the impact of omadacycline susceptibility by branched-chain amino acid transport system II carrier protein, Na/Pi cotransporter family protein, and fibronectin-binding protein. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Bai, B.; Xu, G.; Li, P.; Yu, Z.; Deng, Q.; Shang, Y.; Zheng, J. Eravacycline susceptibility was impacted by genetic mutation of 30S ribosome subunits, and branched-chain amino acid transport system II carrier protein, Na/Pi cotransporter family protein in Staphylococcus aureus. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roch, M.; Sierra, R.; Andrey, D.O. Antibiotic heteroresistance in ESKAPE pathogens, from bench to bedside. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2023, 29, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shen, P.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J. Spatial transcriptome uncovers rich coordination of metabolism in E. coli K12 biofilm. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2023, 19, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S.; Franklin, M.J. Physiological heterogeneity in biofilms. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benarroch, J.M.; Asally, M. The microbiologist’s guide to membrane potential dynamics. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Tian, T.; Tseng, C.K.; Luo, X.; Chen, X.; Lo, C.J.; Leake, M.C.; Bai, F. Sensitive bacterial V(m) sensors revealed the excitability of bacterial V(m) and its role in antibiotic tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2208348120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-y.D.; Galera-Laporta, L.; Bialecka-Fornal, M.; Moon, E.C.; Shen, Z.; Briggs, S.P.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Süel, G.M. Magnesium flux modulates ribosomes to increase bacterial survival. Cell 2019, 177, 352–360.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, N.; Knapen, W.J.; Kint, C.I.; Liebens, V.; Van den Bergh, B.; Dewachter, L.; Michiels, J.E.; Fu, Q.; David, C.C.; Fierro, A.C.; et al. Obg and membrane depolarization are part of a microbial bet-hedging strategy that leads to antibiotic tolerance. Mol. Cell 2015, 59, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damper, P.D.; Epstein, W. Role of the membrane potential in bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 20, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, V.I.; Weiss, D.S. Heteroresistance to beta-lactam antibiotics may often be a stage in the progression to antibiotic resistance. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.-M.; Lin, X.-L.; Lian, X.-L.; Trampari, E.; Thomson, N.M.; Ding, H.-Z.; Webber, M.A.; Jiang, H.-X. Emergence of ciprofloxacin heteroresistance in foodborne Salmonella enterica serovar Agona. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 2773–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.H.; Traglia, G.; Bastias, N.; Pandolfo, C.; Bruni, G.; Nastro, M.; Barrios, R.; Bavastro, E.M.; Rey, M.C.; Marques, I.A.; et al. Discrepancies in susceptibility testing to colistin in Acinetobacter baumannii: The influence of slow growth and heteroresistance. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 587–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidarian, S.; Guliaev, A.; Nicoloff, H.; Hjort, K.; Andersson, D.I. High prevalence of heteroresistance in Staphylococcus aureus is caused by a multitude of mutations in core genes. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okado, J.B.; Avaca-Crusca, J.S.; Oliveira, A.L.; Dabul, A.N.G.; Camargo, I.L.B.d.C. Daptomycin and vancomycin heteroresistance revealed among CC5-SCCmecII MRSA clone and in vitro evaluation of treatment alternatives. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 14, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong-Bolduc, Q.C.; Wang, Y.; Reedy, J.L.; Vyas, J.M.; Hooper, D.C. Staphylococcus aureus efflux pumps and tolerance to ciprofloxacin and chlorhexidine following induction by mupirocin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2022, 66, e0184521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanzadeh, S.; Mashhadi, R.; Yousefi, M.; Askari, E.; Saniei, M.; Pourmand, M.R. Frequency of efflux pump genes mediating ciprofloxacin and antiseptic resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Araújo, A.C.J.; Freitas, P.R.; Dos Santos Barbosa, C.R.; Muniz, D.F.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Tintino, S.R.; Júnior, J.P.S.; Filho, J.M.B.; de Sousa, G.R.; Coutinho, H.D.M. Modulation of drug resistance by limonene: Inhibition of efflux pumps in Staphylococcus aureus strains RN-4220 and IS-58. Curr. Drug Metab. 2021, 22, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino de Araújo, A.C.; Freitas, P.R.; Rodrigues Dos Santos Barbosa, C.; Muniz, D.F.; Rocha, J.E.; Albuquerque da Silva, A.C.; Datiane de Morais Oliveira-Tintino, C.; Ribeiro-Filho, J.; Everson da Silva, L.; Confortin, C.; et al. GC-MS-FID characterization and antibacterial activity of the Mikania cordifolia essential oil and limonene against MDR strains. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 111023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Tong, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Bacterial proton motive force as an unprecedented target to control antimicrobial resistance. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 1068–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Nøhr-Meldgaard, K.; Ingmer, H. Multiple pathways towards reduced membrane potential and concomitant reduction in aminoglycoside susceptibility in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters, Version 9.0; 2019. EUCAST. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/Breakpoint_tables/v_9.0_Breakpoint_Tables.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). EUCAST Reading Guide for Broth Microdilution; 2021. EUCAST. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/MIC_testing/Reading_guide_BMD_v_3.0_2021.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Routine and Extended Internal Quality Control for MIC Determination and Disk Diffusion as Recommended by EUCAST, Version 13.2; 2023. EUCAST. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/fileadmin/src/media/PDFs/EUCAST_files/QC/v_13.2_EUCAST_QC_tables_routine_and_extended_QC.pdf (accessed on 19 December 2023).
- Dao, T.H.; Alsallaq, R.; Parsons, J.B.; Ferrolino, J.; Hayden, R.T.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Rafiqullah, I.M.; Robinson, D.A.; Margolis, E.B.; Rosch, J.W.; et al. Vancomycin heteroresistance and clinical outcomes in bloodstream infections caused by coagulase-negative Staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 64, e00944-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wen, L.; Chen, J.; Van Tyne, D. Combined effect of polymyxin B and tigecycline to overcome heteroresistance in carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00152-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Yan, C.; Shi, C.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, C.; Peng, X.; Xia, X. Inhibitory Effect of Coenzyme Q0 on the Growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2019, 16, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurevich, A.; Saveliev, V.; Vyahhi, N.; Tesler, G. QUAST: Quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Founou, L.L.; Founou, R.C.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Essack, S.Y. Genome analysis of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from pigs. Pathogens 2022, 11, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.-L.; Mai, Z.-B.; Lian, X.-L.; Zhong, J.-Y.; Jin, J.-j.; He, Q.-Y.; Zhang, G. FANSe2: A robust and cost-efficient alignment tool for quantitative next-generation sequencing applications. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellio, P.; Fagnani, L.; Nazzicone, L.; Celenza, G. New and simplified method for drug combination studies by checkerboard assay. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhoff, C.; Cypionka, H. Boosted membrane potential as bioenergetic response to anoxia in Dinoroseobacter shibae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzola, S.; Cocconcelli, P.S. Vancomycin heteroresistance and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis from food. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3224–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Type | Gene | Substrate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance genes | Beta-lactams | blaZ | Methicillin |
| Macrolides | erm(A) | Erythromycin | |
| Aminoglycosides | spc | Spectinomycin | |
| Rifamycins | rpoB | Rifampicin | |
| Multidrug resistant efflux pumps | MFS family | norA, norB, norG | Ciprofloxacin |
| sdrM | Norfloxacin Acriflavine Ethidium bromide | ||
| MATE family | mepA | Ciprofloxacin Norfloxacin Tigecycline |
| SNP Position | Gene | SNPs |
|---|---|---|
| 188,068 | ggt | p.Val549Ser |
| 294,112 | essG_6 | p.Leu7Gln |
| 390,715 | ssl3 | p.Ile157Thr |
| 390,730 | p.ThrAspMetThr162LysGluIleAsn | |
| 798,468 | ssp | p.Gln200_Ser201dup |
| 1,043,951 | isdB | p.Glu71_Thr72delinsValAlaLysProValAla |
| 1,338,822 | asd | p.Asp242Glu |
| 1,378,171 | ebh | p.Asp8843Gly |
| 1,684,208 | lysP_2 | p.Glu375Gln |
| 1,684,220 | p.Lys371Glu | |
| 2,246,711 | farB_1 | p.Thr253Ser |
| 2,723,613 | clfB | p.Asp663Glu |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, M.; Jian, Q.; Ye, X.; Jing, M.; Wu, J.; Wu, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Long, X.; Zhang, R.; Ren, H.; et al. Mechanisms of mepA Overexpression and Membrane Potential Reduction Leading to Ciprofloxacin Heteroresistance in a Staphylococcus aureus Isolate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052372
Li M, Jian Q, Ye X, Jing M, Wu J, Wu Z, Ruan Y, Long X, Zhang R, Ren H, et al. Mechanisms of mepA Overexpression and Membrane Potential Reduction Leading to Ciprofloxacin Heteroresistance in a Staphylococcus aureus Isolate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052372
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Mengyuan, Qianting Jian, Xinyi Ye, Mou Jing, Jia’en Wu, Zhihong Wu, Yali Ruan, Xiaoling Long, Rongmin Zhang, Hao Ren, and et al. 2025. "Mechanisms of mepA Overexpression and Membrane Potential Reduction Leading to Ciprofloxacin Heteroresistance in a Staphylococcus aureus Isolate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052372
APA StyleLi, M., Jian, Q., Ye, X., Jing, M., Wu, J., Wu, Z., Ruan, Y., Long, X., Zhang, R., Ren, H., Sun, J., Liu, Y., Liao, X., & Lian, X. (2025). Mechanisms of mepA Overexpression and Membrane Potential Reduction Leading to Ciprofloxacin Heteroresistance in a Staphylococcus aureus Isolate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2372. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052372






