The Complete Chloroplast Genome and the Phylogenetic Analysis of Fimbristylis littoralis (Cyperaceae) Collected in Cherry Blossom Nursery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chloroplast Genome Component
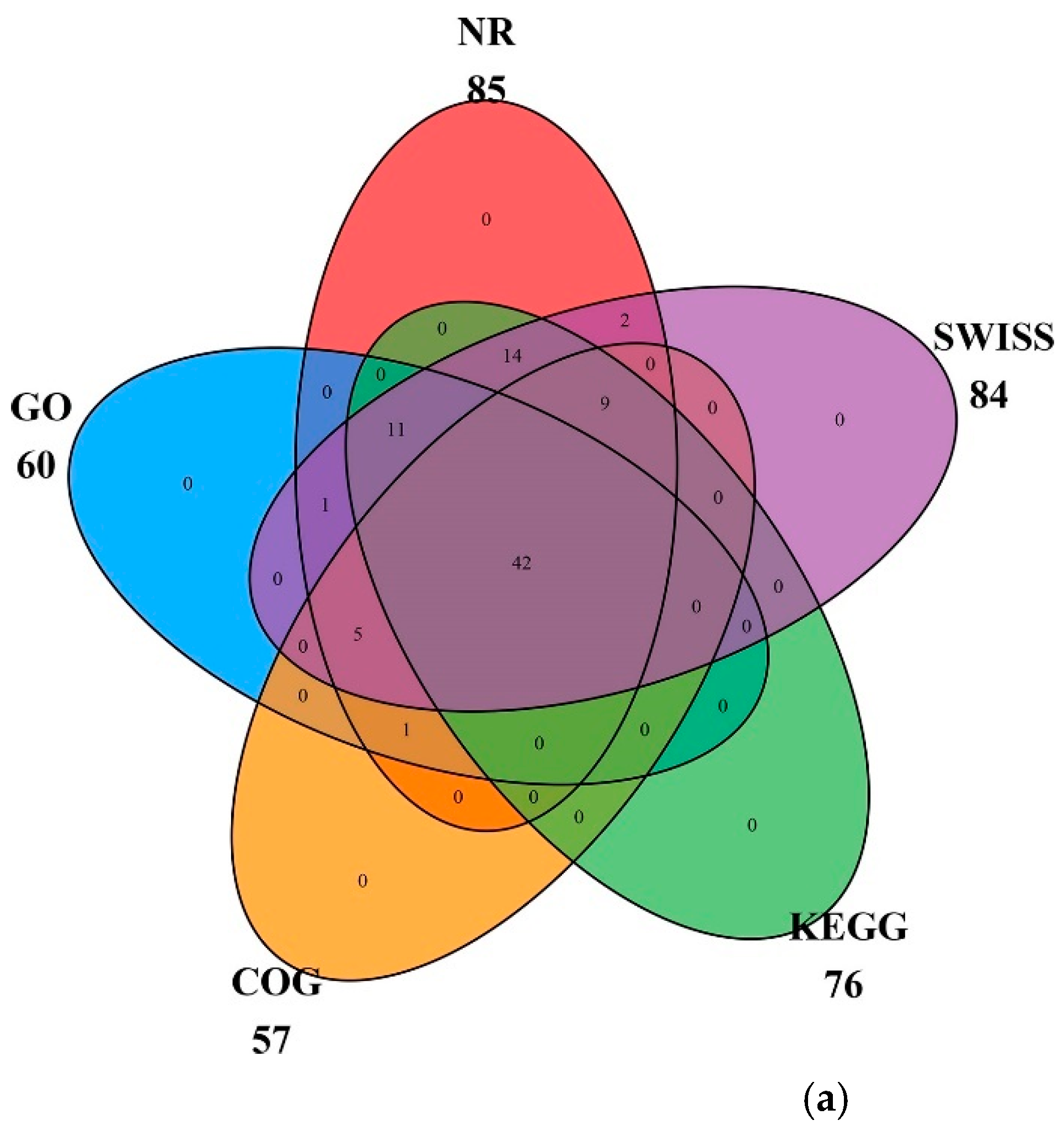
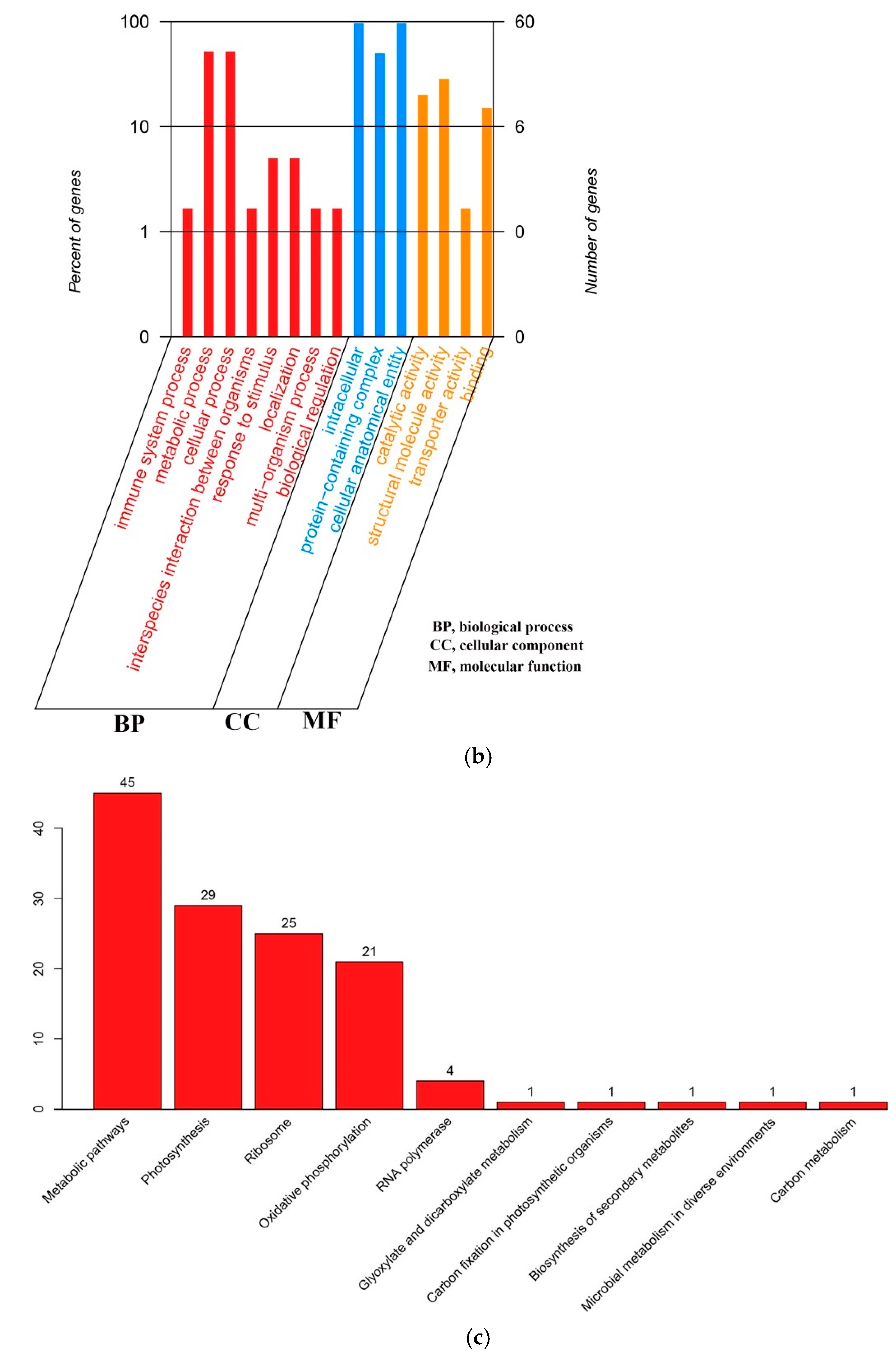
2.2. Gene Function Annotation and Classification
2.3. IR Expansion and Contraction
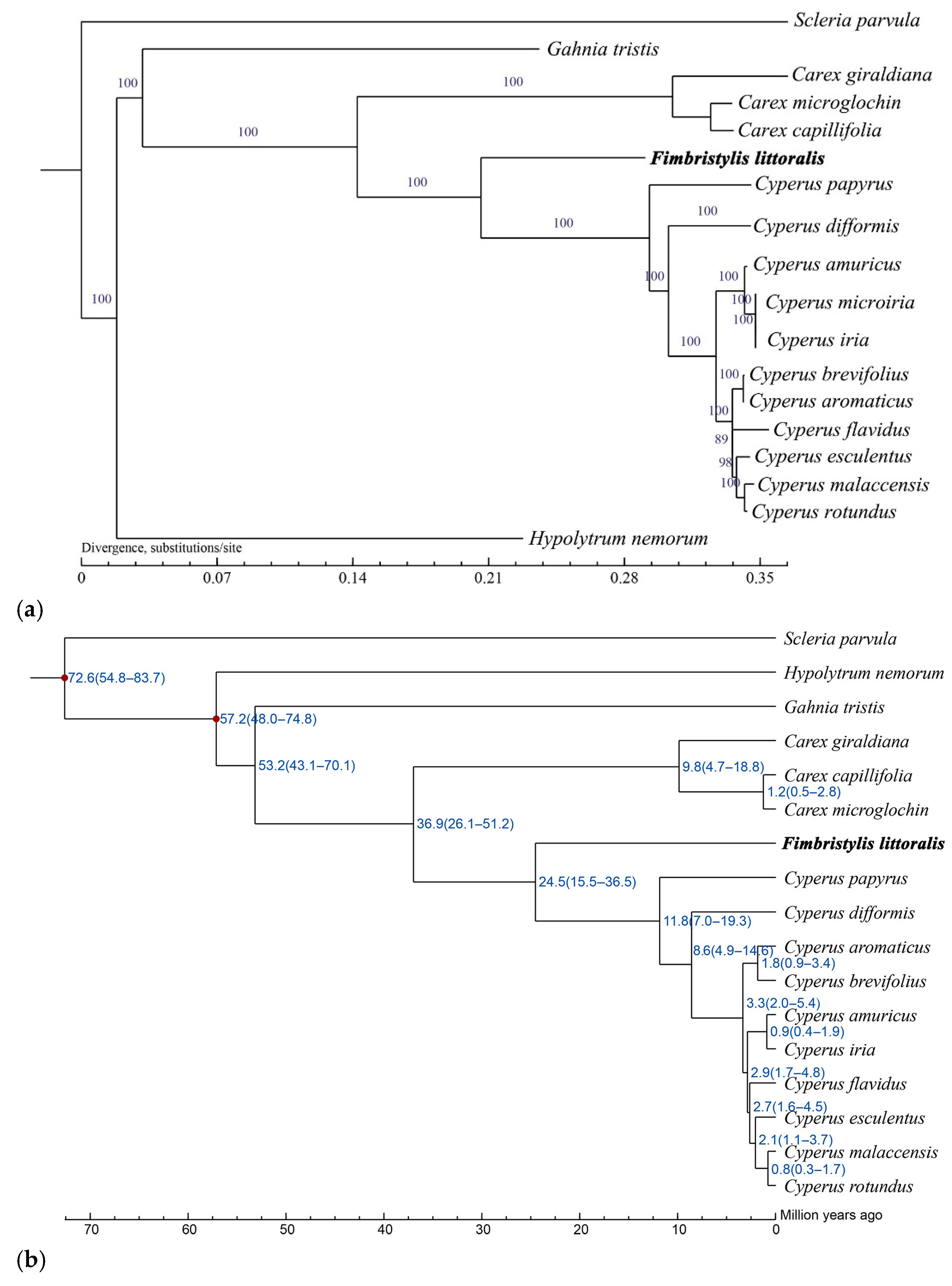
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis and Divergence Time Dating Among Common Sedges
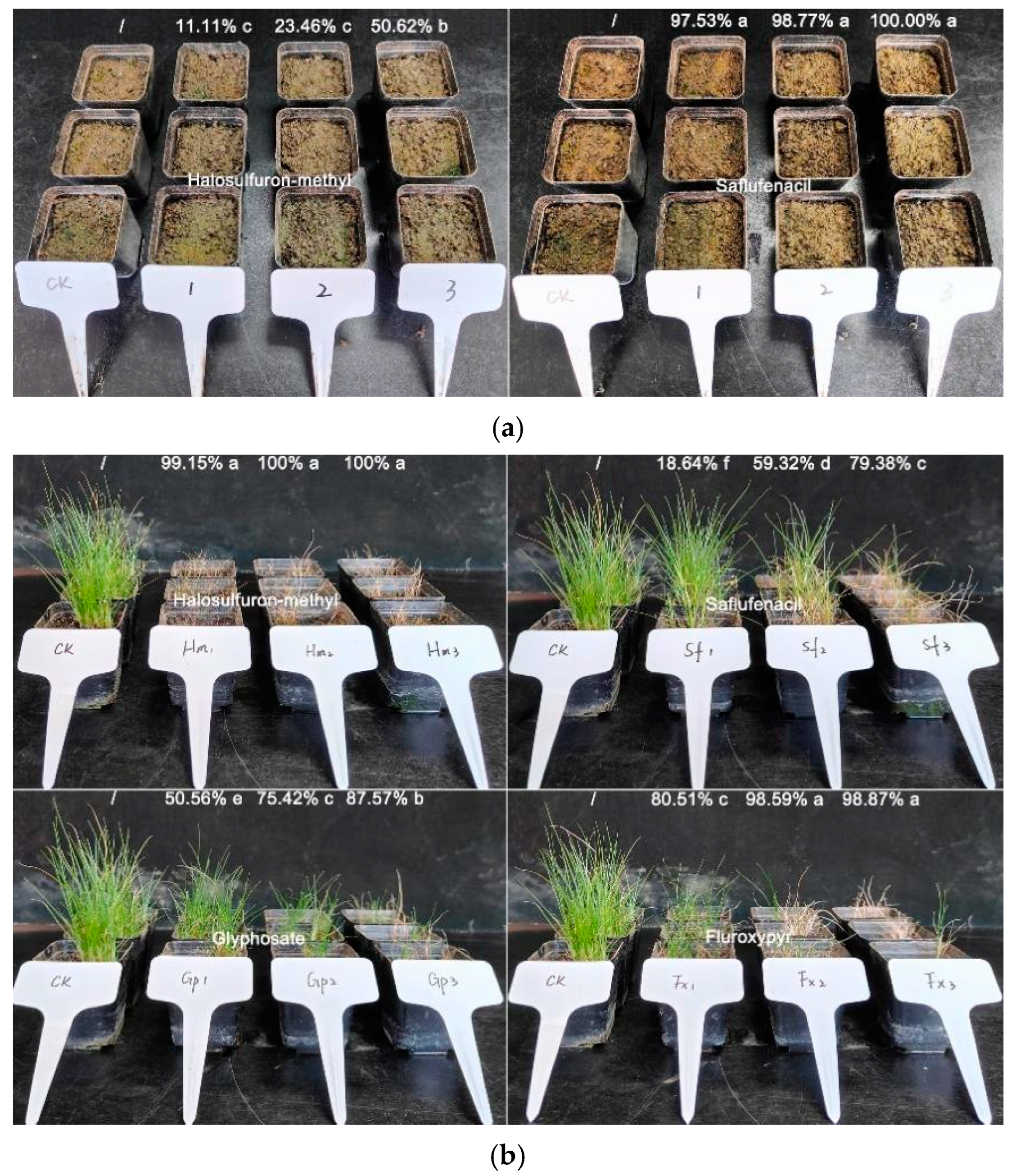
2.5. Chemical Control Method
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.2. Genome Assembly
4.3. Genome Component Analysis
4.4. Gene Function Annotation and Classification Analysis
4.5. Contraction and Expansion Analysis of Inverted Repeats Regions
4.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.7. Divergence Time Dating Analysis
4.8. Detection of Sensitivity to Common Herbicides
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdallah, I.; Garcia, A.; Fischer, A. Rice field bulrush (Schoenoplectus mucronatus (L.) Palla) evolved multiple resistances to propanil and bensulfuron herbicides. J. Biol. Chem. Res. 2014, 31, 788–799. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, B. The life cycle and ecology of Cyperus difformis (rice weed) in temperate Australia: A review. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 1994, 34, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant Science Data Center. Available online: https://www.plantplus.cn/cn (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Larridon, I.; Zuntini, A.R.; Léveillé-Bourret, É.; Barrett, R.L.; Starr, J.R.; Muasya, A.M.; Villaverde, T.; Bauters, K.; Brewer, G.E.; Bruhl, J.J. A new classification of Cyperaceae (Poales) supported by phylogenomic data. J. Syst. Evol. 2021, 59, 852–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W. Weed Species and Population Density. Agric. Res. 1970, 19, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Awan, T.H.; Ahmed, S.; Cruz, P.C.S.; Chauhan, B.S. Ecological studies for plant characteristics of Fimbristylis miliacea under multiple resource limitations in dry-seeded upland ecosystems. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2022, 68, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.; Johnson, D. Ecological studies on Cyperus difformis, Cyperus iria and Fimbristylis miliacea: Three troublesome annual sedge weeds of rice. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2009, 155, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, M.; Juraimi, A.; Azmi, M.; Syed Omar, S.; Rajan, A. Soil seedbank of the Muda rice granary in northwest Peninsular Malaysia invaded by the weed Fimbristylis miliacea (L.) Vahl. Plant Prot. Q. 2008, 23, 157–161. [Google Scholar]
- Begum, M.; Juraimi, A.S.; Amartalingam, R.; Bin Man, A.; Bin Syed Rastans, S.O. The effects of sowing depth and flooding on the emergence, survival, and growth of Fimbristylis miliacea (L.) Vahl. Weed Biol. Manag. 2006, 6, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaedler, C.; Noldin, J.; Agostinetto, D.; Dal Magro, T.; Fontana, L. Germination and growth of Fimbristylis miliacea biotypes resistant and susceptible to acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicides. Planta Daninha 2013, 31, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaedler, C.; Noldin, J.; Eberhardt, D.; Agostinetto, D.; Burgos, N. Globe fringerush (Fimbristylis miliacea) cross resistance to als-inhibitor herbicides under field conditions in irrigated rice in the south of Brazil. Planta Daninha 2013, 31, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.; Siddique, A. Identification of allelochemicals from Fimbristylis miliacea and their allelopathic potential against weed species. Allelopath. J. 2012, 30, 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Daula, A.S.U.; Akter, A.; Sultana, S.; Barek, M.A.; Liya, I.J.; Basher, M.A. Antipyretic and anti-nociceptive effects of methanol extract of leaves of Fimbristylis miliacea in mice model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, C.J.; Barbrook, A.C.; Koumandou, V.L.; Nisbet, R.E.R.; Symington, H.A.; Wightman, T.F. Evolution of the chloroplast genome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 358, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosner, M.E.; Raubeson, L.A.; Jansen, R.K. Chloroplast DNA rearrangements in Campanulaceae: Phylogenetic utility of highly rearranged genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2004, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plunkett, G.M.; Downie, S.R. Expansion and contraction of the chloroplast inverted repeat in Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae. Syst. Bot. 2000, 25, 648–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Müller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Guo, J.; Tembrock, L.R.; Xu, D. Comparative analyses of five complete chloroplast genomes from the genus Pterocarpus (Fabacaeae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.-S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.-X. The complete chloroplast genomes of three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) species: Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.-T.; Jabbour, F.; Barrett, R.L.; Ye, J.-F.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Lu, K.-Q.; Lu, L.-M.; Chen, Z.-D. Combining complete chloroplast genome sequences with target loci data and morphology to resolve species limits in Triplostegia (Caprifoliaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 129, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinard, D.; Myburg, A.A.; Mizrachi, E. The plastid and mitochondrial genomes of Eucalyptus grandis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, M.-F.; Xue, J.; Dong, R.; Du, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.-H. Chloroplast genomic resources for phylogeny and DNA barcoding: A case study on Fritillaria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lu, R.-S.; Xu, W.-Q.; Ohi-Toma, T.; Cai, M.-Q.; Qiu, Y.-X.; Cameron, K.M.; Fu, C.-X. Comparative genomics and phylogenomics of East Asian tulips (Amana, Liliaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-H.; Chan, M.-T.; Liao, D.-C.; Hsu, C.-T.; Lee, Y.-W.; Daniell, H.; Duvall, M.R.; Lin, C.-S. Complete chloroplast genome of Oncidium Gower Ramsey and evaluation of molecular markers for identification and breeding in Oncidiinae. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Liang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wuyun, T.; Tan, X. Five complete chloroplast genome sequences from Diospyros: Genome organization and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maréchal, A.; Brisson, N. Recombination and the maintenance of plant organelle genome stability. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Guo, J.; Xuan, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Yin, Y.; Yang, Y. Comparative chloroplast genomics of the genus Taxodium. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kugita, M.; Kaneko, A.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takeya, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Yoshinaga, K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the hornwort (Anthoceros formosae) chloroplast genome: Insight into the earliest land plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.J. Plant Diversity and Evolution: Genotypic and Phenotypic Variation in Higher Plants; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yamane, K.; Yasui, Y.; Ohnishi, O. Intraspecific cpDNA variations of diploid and tetraploid perennial buckwheat, Fagopyrum cymosum (Polygonaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2003, 90, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, W.; Cai, P.; Huo, D.; Hong, Y. Comparative chloroplast genomes: Insights into the evolution of the chloroplast genome of Camellia sinensis and the phylogeny of Camellia. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shen, G.; Yuan, G.; Tian, Z. Comparative analysis of whole chloroplast genomes of three common species of Echinochloa (Gramineae) in paddy fields. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Yuan, G.; Fang, J.; Shen, G.; Tian, Z. Comparison of Biological and genetic characteristics between two most common broad-leaved weeds in Paddy Fields: Ammannia arenaria and A. multiflora (Lythraceae). Biology 2023, 12, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, M.A.B.; Ismail, B.S. Allelopathic effects of ‘Fimbristylis miliacea’on the physiological activities of five Malaysian rice varieties. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar]
- Ramli, N.; Zain, W.; Ab Wahab, M.; Hamid, N.; Abdullah, N.; Zamanhuri, N. Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant and Antifungal Activity of Methanolic Extract of Fimbristylis dichotoma and Fimbristylis miliacea. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sustainability Agriculture and Biosystem, Online, 24 November 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; Volume 1059, p. 012080. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, R.; Roy, J.; Liya, I.J.; Ahmed, J.; Akter, A.; Basher, M.A. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of methanolic extract of Fimbristylis miliacea (L.) Vahl. Phytomed. Plus 2023, 3, 100449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Ohme, M.; Tanaka, M.; Wakasugi, T.; Hayashida, N.; Matsubayashi, T.; Zaita, N.; Chunwongse, J.; Obokata, J.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: Its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/?term=Cyperaceae+chloroplast+complete+genome (accessed on 8 October 2024).
- Fan, R.; Ma, W.; Liu, S.; Huang, Q. Integrated analysis of three newly sequenced fern chloroplast genomes: Genome structure and comparative analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 4550–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, S. The complete Amomum kravanh chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of the commelinids. Molecules 2017, 22, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Duan, B.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yao, H. Complete chloroplast genomes of Papaver rhoeas and Papaver orientale: Molecular structures, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorduin, L.; Gravendeel, B.; Lammers, Y.; Ariyurek, Y.; Chin-A-Woeng, T.; Vrieling, K. The complete chloroplast genome of 17 individuals of pest species Jacobaea vulgaris: SNPs, microsatellites and barcoding markers for population and phylogenetic studies. DNA Res. 2011, 18, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, Y.; Volis, S.; Li, D.; Yi, T. Genetic diversity and population structure: Implications for conservation of wild soybean (Glycine soja Sieb. et Zucc) based on nuclear and chloroplast microsatellite variation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12608–12628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.L. Polymorphic chloroplast microsatellite loci in Nelumbo (Nelumbonaceae). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, e240–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.H.; Zhang, J.J.; Yao, X.H.; Huang, H.W. Chloroplast microsatellite markers in Liriodendron tulipifera (Magnoliaceae) and cross-species amplification in L. chinense. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, e123–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Xiao, P. Complete chloroplast genome sequences of Schisandra chinensis: Genome structure, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic relationship of basal angiosperms. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1286–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhai, X.; Zhou, H.; Ding, Q.; Ma, L. Assembly and comparative analysis of chloroplast genome of wheat K-CMS line and maintainer line. Preprints 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Chloroplast evolution: Secondary symbiogenesis and multiple losses. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R62–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, T.; Long, J.; Shen, G.; Tian, Z. Complete chloroplast genome and comparison of herbicides toxicity on Aeschynomene indica (Leguminosae) in upland direct-seeding paddy field. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, M.-F.; Li, Y.; Sun, H.-F.; Tang, D.-Y.; Xu, A.-S.; Yin, C.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Zhang, L.-X. Complete chloroplast genome analysis of two important medicinal Alpinia species: Alpinia galanga and Alpinia kwangsiensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 705892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, H.; Maliga, P. The plastid clpP1 protease gene is essential for plant development. Nature 2003, 425, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Messing, J. High-throughput sequencing of three Lemnoideae (duckweeds) chloroplast genomes from total DNA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logacheva, M.D.; Krinitsina, A.A.; Belenikin, M.S.; Khafizov, K.; Konorov, E.A.; Kuptsov, S.V.; Speranskaya, A.S. Comparative analysis of inverted repeats of polypod fern (Polypodiales) plastomes reveals two hypervariable regions. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Raubeson, L.A.; Peery, R.; Chumley, T.W.; Dziubek, C.; Fourcade, H.M.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Comparative chloroplast genomics: Analyses including new sequences from the angiosperms Nuphar advena and Ranunculus macranthus. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, G.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Yun, Q.; Zhao, D.; Al-Mssallem, I.S.; Yu, J. The complete chloroplast genome sequence of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-B.; Yang, S.-X.; Li, H.-T.; Yang, J.; Li, D.-Z. Comparative chloroplast genomes of Camellia species. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-T.; Yi, T.-S.; Gao, L.-M.; Ma, P.-F.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.-B.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Cai, J.; Luo, Y. Origin of angiosperms and the puzzle of the Jurassic gap. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, M.; Guan, Y.; Ma, X. Species identification of Dracaena using the complete chloroplast genome as a super-barcode. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, G.; Aagesen, L.; Seberg, O.; Larsen, I.H. When is enough, enough in phylogenetics? A case in point from Hordeum (Poaceae). Cladistics 2011, 27, 428–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortley, A.H.; Rudall, P.J.; Harris, D.J.; Scotland, R.W. How much data are needed to resolve a difficult phylogeny? Case study in Lamiales. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Wang, J.; Farooq, M.A.; Khan, M.S.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, M.; Muños, S.; Li, Q.X.; Zhou, W. Potential impact of the herbicide 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on human and ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 332–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parven, A.; Meftaul, I.M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Herbicides in modern sustainable agriculture: Environmental fate, ecological implications, and human health concerns. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 1181–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, R.; Li, J.; Pan, L.; Dong, L. Effect of an adjuvant, Jijian, on isoproturon to control fenoxaprop-P-ethyl-resistant Beckmannia syzigachne. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2024, 70, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Fu, R.; Dong, L. ynergism of the adjuvant Silwet 806 on herbicides controlling the Alopecurus japonicus resistant to fenoxaprop-P-ethyl in wheat fields. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. 2019, 42, 842–848. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, R.K.; Raubeson, L.A.; Boore, J.L.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Chumley, T.W.; Haberle, R.C.; Wyman, S.K.; Alverson, A.J.; Peery, R.; Herman, S.J.; et al. Methods for obtaining and analyzing whole chloroplast genome sequences. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 395, 348–384. [Google Scholar]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq–versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D.; Jansen, R.K.; Michaels, H.J.; Chase, M.W.; Manhart, J.R. Chloroplast DNA variation and plant phylogeny. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 1988, 75, 1180–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tembrock, L.R.; Ge, S. Are differences in genomic data sets due to true biological variants or errors in genome assembly: An example from two chloroplast genomes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): A web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Category | Gene Groups | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Subunits_of_photosystem_I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| Subunits_of_photosystem_II | pbf1, psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbT, psbZ | |
| Subunits_of_NADH_dehydrogenase | ndhA, ndhB, ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK | |
| Subunits_of_cytochrome_b/f_complex | petA, petB, petD, petG, petL, petN | |
| Subunits_of_ATP_synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpF, atpH, atpI | |
| Large_subunit_of_Rubisco | rbcL | |
| Self-replication | Large_subunits_of_ribosome | rpl14, rpl16, rpl2, rpl20, rpl22, rpl23, rpl32, rpl33, rpl36 |
| Small_subunits_of_ribosome | rps11, rps12, rps14, rps16, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7, rps8 | |
| DNA-dependent_RNA_polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1, rpoC2 | |
| Ribosomal_RNAs | rrn16, rrn23, rrn4.5, rrn5 | |
| Transfer_RNAs | trnA-UGC, trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU, trnI-GAU, trnK-UUU, trnL-CAA, trnL-UAA, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU, trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG, trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC, trnV-UAC, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU | |
| Other genes | Maturase | matK |
| Protease | clpP1 | |
| Envelope_membrane_protein | cemA | |
| Acetyl-CoA_carboxylase | ||
| C-type_cytochrome_synthesis_gene | ccsA | |
| Translation_initiation_factor | ||
| protochlorophillide_reductase_subunit | ||
| Unknown Genes | Proteins_of_unknown_function | ycf3, ycf4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Long, J.; Wang, B.; Huang, Z.; Gao, Y. The Complete Chloroplast Genome and the Phylogenetic Analysis of Fimbristylis littoralis (Cyperaceae) Collected in Cherry Blossom Nursery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052321
Gao Z, Cai Y, Long J, Wang B, Huang Z, Gao Y. The Complete Chloroplast Genome and the Phylogenetic Analysis of Fimbristylis littoralis (Cyperaceae) Collected in Cherry Blossom Nursery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052321
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Zhaoliang, Yutong Cai, Jiaqi Long, Bo Wang, Zhaofeng Huang, and Yuan Gao. 2025. "The Complete Chloroplast Genome and the Phylogenetic Analysis of Fimbristylis littoralis (Cyperaceae) Collected in Cherry Blossom Nursery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052321
APA StyleGao, Z., Cai, Y., Long, J., Wang, B., Huang, Z., & Gao, Y. (2025). The Complete Chloroplast Genome and the Phylogenetic Analysis of Fimbristylis littoralis (Cyperaceae) Collected in Cherry Blossom Nursery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052321





