Targeting Tumor Microenvironment Interactions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Using Leukotriene Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of CLL Cells Isolated from Patients
2.2. Heterogeneous Stromal Cell Adhesion Activity of Patient-Derived CLL Cells Ex Vivo
2.3. Heterogeneous Effect of 5-LOX Pathway Inhibitors on Stromal Cell Adhesion Activity of Patient-Derived CLL Cells Ex Vivo
2.4. Mutation Status and Lymphocyte Count for CLL Samples Are Associated with the Level of Their Adhesion to Stromal Cells in the Absence and Presence of Small-Molecule Inhibitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Patients Blood Samples and CLL Cell Enrichment
4.3. Cell–Cell Binding Assay and Flow Cytometry
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sylvan, S.E.; Asklid, A.; Johansson, H.; Klintman, J.; Bjellvi, J.; Tolvgård, S.; Kimby, E.; Norin, S.; Andersson, P.O.; Karlsson, C.; et al. First-line therapy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A Swedish nation-wide real-world study on 1053 consecutive patients treated between 2007 and 2013. Haemiatologica 2019, 104, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallek, M.; Cheson, B.D.; Catovsky, D.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Dighiero, G.; Döhner, H.; Hillmen, P.; Keating, M.; Montserrat, E.; Chiorazzi, N.; et al. iwCLL guidelines for diagnosis, indications for treatment, response assessment, and supportive management of CLL. Blood 2018, 131, 2745–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.; Nadeu, F.; Colomer, D.; Campo, E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: From molecular pathogenesis to novel therapeutic strategies. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2205–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montague, A.M.; Pathak, S. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with Variant Genetics; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Brieghel, C.; Galle, V.; Agius, R.; da Cunha-Bang, C.; Andersen, M.A.; Vlummens, P.; Mattsson, M.; Rosenquist, R.; Smedby, K.E.; Herling, C.D.; et al. Identifying patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia without need of treatment: End of endless watch and wait? Eur. J. Haematol. 2022, 108, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, P.; Jain, N.; O’Brien, S. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Diagnosis and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkin, D.; Thomas, A.; Teicher, B.A. Cancer treatments: Past, present, and future. Cancer Genet. 2024, 286–287, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, F.; Dalla-Favera, R. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: From genetics to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, T.J.; Davis, Z.; Gardiner, A.; Oscier, D.G.; Stevenson, F.K. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1999, 94, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Puente, X.S.; Beà, S.; Valdés-Mas, R.; Villamor, N.; Gutiérrez-Abril, J.; Martín-Subero, J.I.; Munar, M.; Rubio-Pérez, C.; Jares, P.; Aymerich, M.; et al. Non-coding recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2015, 526, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, M.; Gatti, R.A. Pathogenesis of ataxia-telangiectasia: The next generation of ATM functions. Blood 2013, 121, 4036–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abruzzo, L.V.; Herling, C.D.; Calin, G.A.; Oakes, C.; Barron, L.L.; Banks, H.E.; Katju, V.; Keating, M.J.; Coombes, K.R. Trisomy 12 chronic lymphocytic leukemia expresses a unique set of activated and targetable pathways. Haematologica 2018, 103, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenz, T.; Kröber, A.; Scherer, K.; Häbe, S.; Bühler, A.; Benner, A.; Denzel, T.; Winkler, D.; Edelmann, J.; Schwänen, C.; et al. Monoallelic TP53 inactivation is associated with poor prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Results from a detailed genetic characterization with long-term follow-up. Blood 2008, 112, 3322–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A. Nurture versus Nature: The Microenvironment in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2011, 2011, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppezzo, P.; Dighiero, G. Role of the B-cell receptor and the microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-κB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayiotidis, P.; Jones, D.; Ganeshaguru, K.; Foroni, L.; Hoffbrand, A.V. Human bone marrow stromal cells prevent apoptosis and support the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells in vitro. Br. J. Haematol. 1996, 92, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Kokhaei, P.; Mulder, T.A.; Ghaderi, A.; Moshfegh, A.; Lundin, J.; Palma, M.; Schultz, J.; Olin, T.; Österborg, A.; et al. A Small Molecule Antagonist of CX3CR1 (KAND567) Inhibited the Tumor Growth-Promoting Effect of Monocytes in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Cancers 2024, 16, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.M.; El-Sharkawy, N.M.; Osman, R.A.; El-Fattah, E.K.A.; El-Noshokaty, E.; El-Hamid, T.A.; Kandeel, E.Z. Adhesion molecules expression in CLL: Potential impact on clinical and hematological parameters. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 28, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagneaux, L.; Delforge, A.; Bron, D.; De Bruyn, C.; Stryckmans, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemic B cells but not normal B cells are rescued from apoptosis by contact with normal bone marrow stromal cells. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 1998, 91, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar]
- E Ryan, C.; Davids, M.S.; Hermann, R.; Shahkarami, M.; Biondo, J.; Abhyankar, S.; Alhasani, H.; Sharman, J.P.; Mato, A.R.; E Roeker, L. MAJIC: A Phase III Trial of Acalabrutinib + Venetoclax versus Venetoclax + Obinutuzumab in Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia or Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 3689–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygmunciak, P.; Robak, T.; Puła, B. Treatment of Double-Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia—An Unmet Clinical Need. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rådmark, O.; Samuelsson, B. 5-Lipoxygenase: Mechanisms of regulation. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S40–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelsson, B.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Lindgren, J.Å.; Rouzer, C.A.; Serhan, C.N. Leukotrienes and Lipoxins: Structures, Biosynthesis, and Biological Effects. Science 1987, 237, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rådmark, O.; Werz, O.; Steinhilber, D.; Samuelsson, B. 5-Lipoxygenase, a key enzyme for leukotriene biosynthesis in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2015, 1851, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, H.; Dahlén, S. Asthma and leukotrienes: Antileukotrienes as novel anti-asthmatic drugs. J. Intern. Med. 1999, 245, 205–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guriec, N.; Corcos, C.L.J.; Simon, B.; Ianotto, J.-C.; Tempescul, A.; Dréano, Y.; Salaün, J.-P.; Berthou, C.; Corcos, L. The arachidonic acid–LTB4–BLT2 pathway enhances human B-CLL aggressiveness. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 2096–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runarsson, G.; Liu, A.; Mahshid, Y.; Feltenmark, S.; Pettersson, A.; Klein, E.; Björkholm, M.; Claesson, H.-E. Leukotriene B4 plays a pivotal role in CD40-dependent activation of chronic B lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2005, 105, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, H.E.; Sjöberg, J.; Xu, D.; Björkholm, M. Expression and putative biological roles of lipoxygenases and leukotriene receptors in leukemia and lymphoma. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2024, 174, 106871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Sadeghi, L.; Strååt, K.; Merrien, M.; Wright, A.P.; Sander, B.; Xu, D.; Österborg, A.; Björkholm, M.; Claesson, H.-E. Intrinsic 5-lipoxygenase activity regulates migration and adherence of mantle cell lymphoma cells. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2021, 156, 106575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonello, P.; Pizzagalli, D.U.; Foglierini, M.; Melgrati, S.; Radice, E.; Thelen, S.; Thelen, M. ACKR3 promotes CXCL12/CXCR4-mediated cell-to-cell-induced lymphoma migration through LTB4 production. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1067885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, X.S.; Jares, P.; Campo, E. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and mantle cell lymphoma: Crossroads of genetic and microenvironment interactions. Blood 2018, 131, 2283–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xie, R.; Dai, Q.; Fang, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, B. Exploring the mechanism underlying hyperuricemia using comprehensive research on multi-omics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Dilger, J.P.; Lin, J. The Role of Transient Receptor Potential Melastatin 7 (TRPM7) in Cell Viability: A Potential Target to Suppress Breast Cancer Cell Cycle. Cancers 2020, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, L.; Arvidsson, G.; Merrien, M.; Wasik, A.M.; Görgens, A.; Smith, C.E.; Sander, B.; Wright, A.P. Differential B-Cell Receptor Signaling Requirement for Adhesion of Mantle Cell Lymphoma Cells to Stromal Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, L.; Wright, A.P.H. GSK-J4 Inhibition of KDM6B Histone Demethylase Blocks Adhesion of Mantle Cell Lymphoma Cells to Stromal Cells by Modulating NF-kappaB Signaling. Cells 2023, 12, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, C.U.; Herman, S.E.; Maric, I.; Gomez-Rodriguez, J.; Biancotto, A.; Chang, B.Y.; Martyr, S.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yuan, C.M.; Calvo, K.R.; et al. Disruption of in vivo Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Tumor-Microenvironment Interactions by Ibrutinib--Findings from an Investigator-Initiated Phase II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1572–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.M.; Smith, S.D.; Roschewski, M.J.; O’Brien, S.M.; Sharman, J.P.; Melear, J.M.; Patel, P.; Calvo, R.; Yang, H.; Spurgeon, S.E. Phase 1/2 study of acalabrutinib and the PI3K delta inhibitor ACP-319 in relapsed/refractory B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, M.; Krstic, A.; Perez, L.P.; Berglöf, A.; Meinke, S.; Wang, Q.; Blomberg, K.E.M.; Kamali-Moghaddam, M.; Shen, Q.; Jaremko, G.; et al. Ibrutinib induces rapid down-regulation of inflammatory markers and altered transcription of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia-related genes in blood and lymph nodes. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 183, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H. Biostatistics 104: Correlational analysis. Singapore Med. J. 2003, 44, 614–619. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Hu, P.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W. Ibrutinib in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Clinical Applications, Drug Resistance, and Prospects. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4877–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guièze, R.; Wu, C.J. Genomic and epigenomic heterogeneity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ten Hacken, E.; Burger, J.A. Microenvironment interactions and B-cell receptor signaling in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Implications for disease pathogenesis and treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Campo, E.; Cymbalista, F.; Ghia, P.; Jäger, U.; Pospisilova, S.; Rosenquist, R.; Schuh, A.; Stilgenbauer, S. TP53 aberrations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An overview of the clinical implications of improved diagnostics. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicker, F.; Herholz, H.; Schnittger, S.; Nakao, A.; Patten, N.; Wu, L.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Haferlach, C. The detection of TP53 mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia independently predicts rapid disease progression and is highly correlated with a complex aberrant karyotype. Leukemia 2008, 23, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastan, M.B.; Onyekwere, O.; Sidransky, D.; Vogelstein, B.; Craig, R.W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 6304–6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F.; Kipps, T.J. Exploring the pathways to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Wenzel, S.; Kamada, A.K. Zileuton: The First 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor for the Treatment of Asthma. Ann. Pharmacother. 1996, 30, 858–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, E.; Cohn, J.; Dubé, L.; Drazen, J.M.; Ratner, P.; Pleskow, W.; DeGraff, A.; Chervinsky, P.; Wasserman, S.; Nelson, H.; et al. Effect of treatment with zileuton, a 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor, in patients with asthma. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 1996, 275, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrien, M.; Wasik, A.M.; Melén, C.M.; Morsy, M.H.A.; Sonnevi, K.; Junlén, H.-R.; Christensson, B.; Wahlin, B.E.; Sander, B. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol Modulates CXCL12-Mediated Chemotaxis in Mantle Cell Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
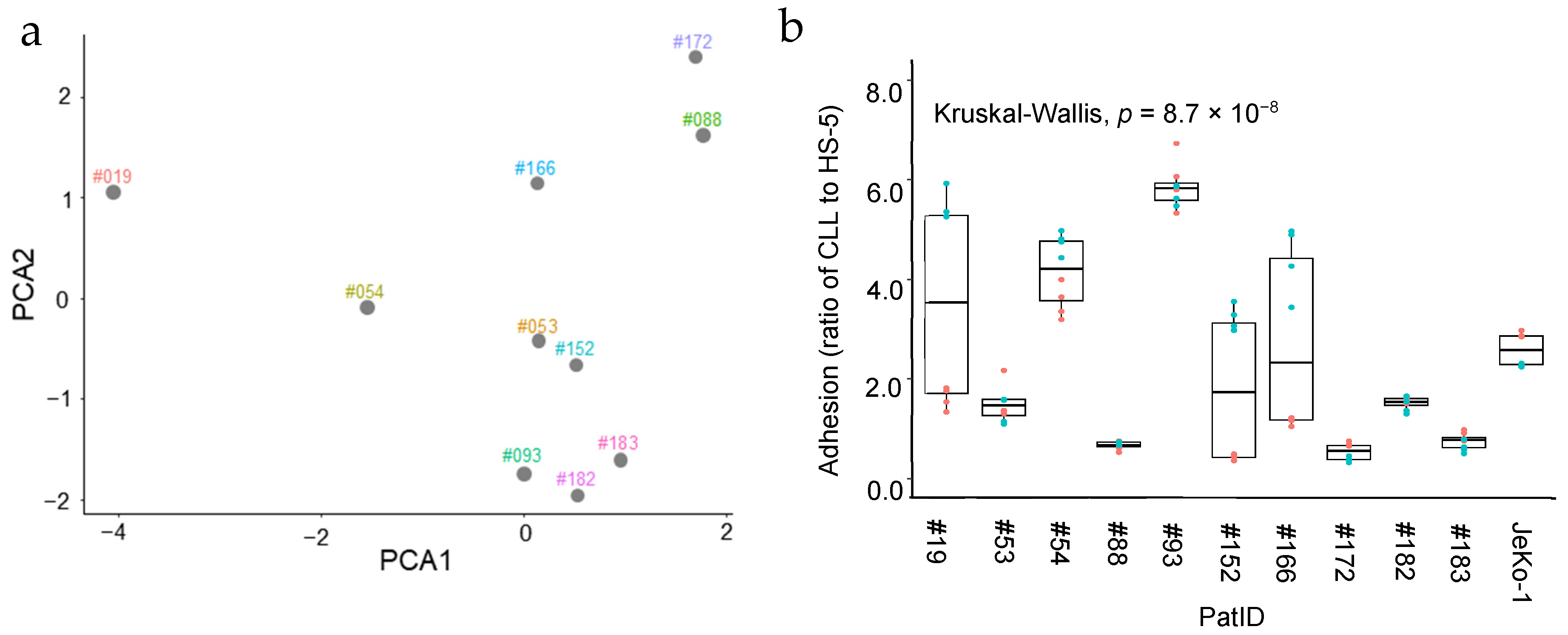

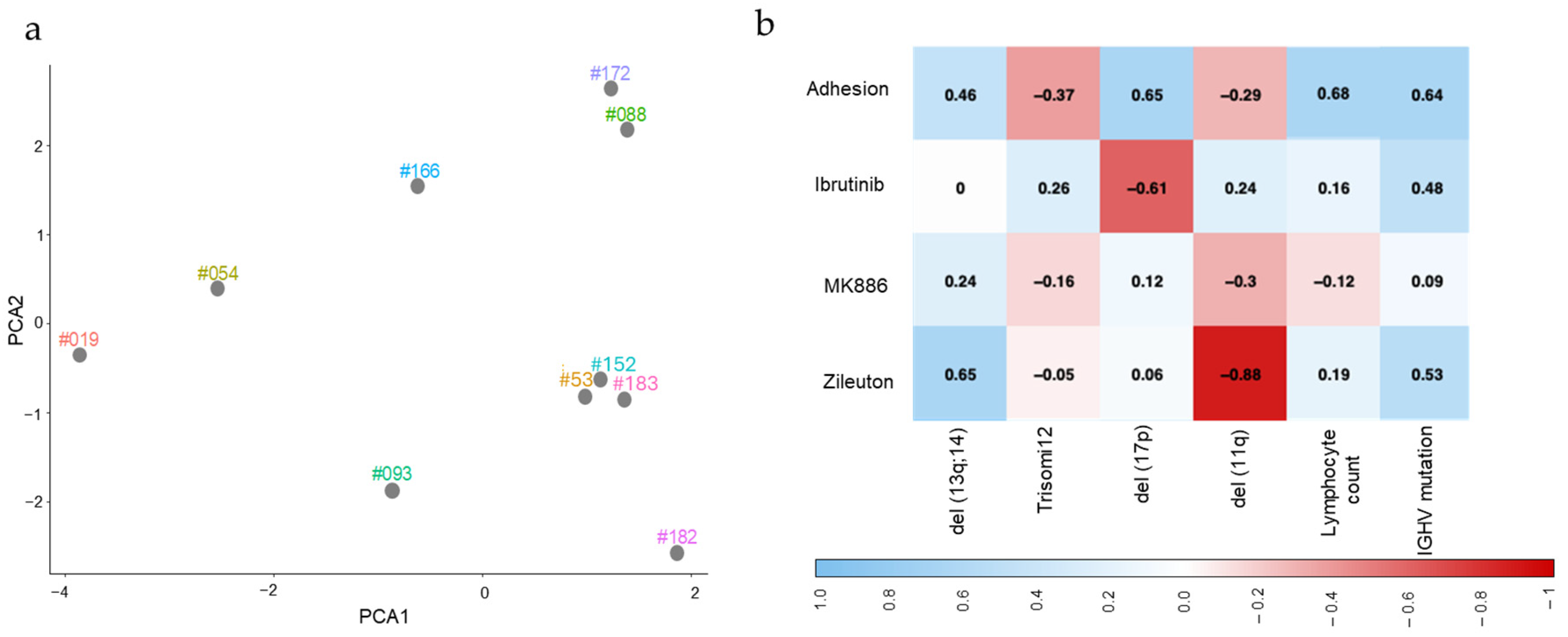
| Patient ID | Sex | Age | Lymphocyte Count (109 /L) | IGHV Mutation Status | del (17p) | del (13q;14) | del (11q) | Trisomy 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #182 | F | 73 | 87.5 | + | − | + | − | − |
| #183 | F | 59 | 66 | + | − | + | − | − |
| #019 | F | 79 | 500 | − | + | − | − | − |
| #053 | F | 58 | 100 | − | − | − | + | − |
| #054 | M | 75 | 286 | − | − | + | − | − |
| #088 | M | 44 | 35 | − | − | − | − | + |
| #093 | F | 78 | 114 | + | − | + | − | − |
| #152 | M | 72 | 70 | − | − | + | − | − |
| #166 | M | 47 | 260 | − | + | + | − | − |
| #172 | M | 34 | 166 | + | − | − | − | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sadeghi, L.; Merrien, M.; Björkholm, M.; Österborg, A.; Sander, B.; Claesson, H.-E.; Wright, A.P.H. Targeting Tumor Microenvironment Interactions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Using Leukotriene Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052209
Sadeghi L, Merrien M, Björkholm M, Österborg A, Sander B, Claesson H-E, Wright APH. Targeting Tumor Microenvironment Interactions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Using Leukotriene Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052209
Chicago/Turabian StyleSadeghi, Laia, Magali Merrien, Magnus Björkholm, Anders Österborg, Birgitta Sander, Hans-Erik Claesson, and Anthony P. H. Wright. 2025. "Targeting Tumor Microenvironment Interactions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Using Leukotriene Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052209
APA StyleSadeghi, L., Merrien, M., Björkholm, M., Österborg, A., Sander, B., Claesson, H.-E., & Wright, A. P. H. (2025). Targeting Tumor Microenvironment Interactions in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Using Leukotriene Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052209






