Comparison of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Human Clinical Cases and Cat Carriers Regarding Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
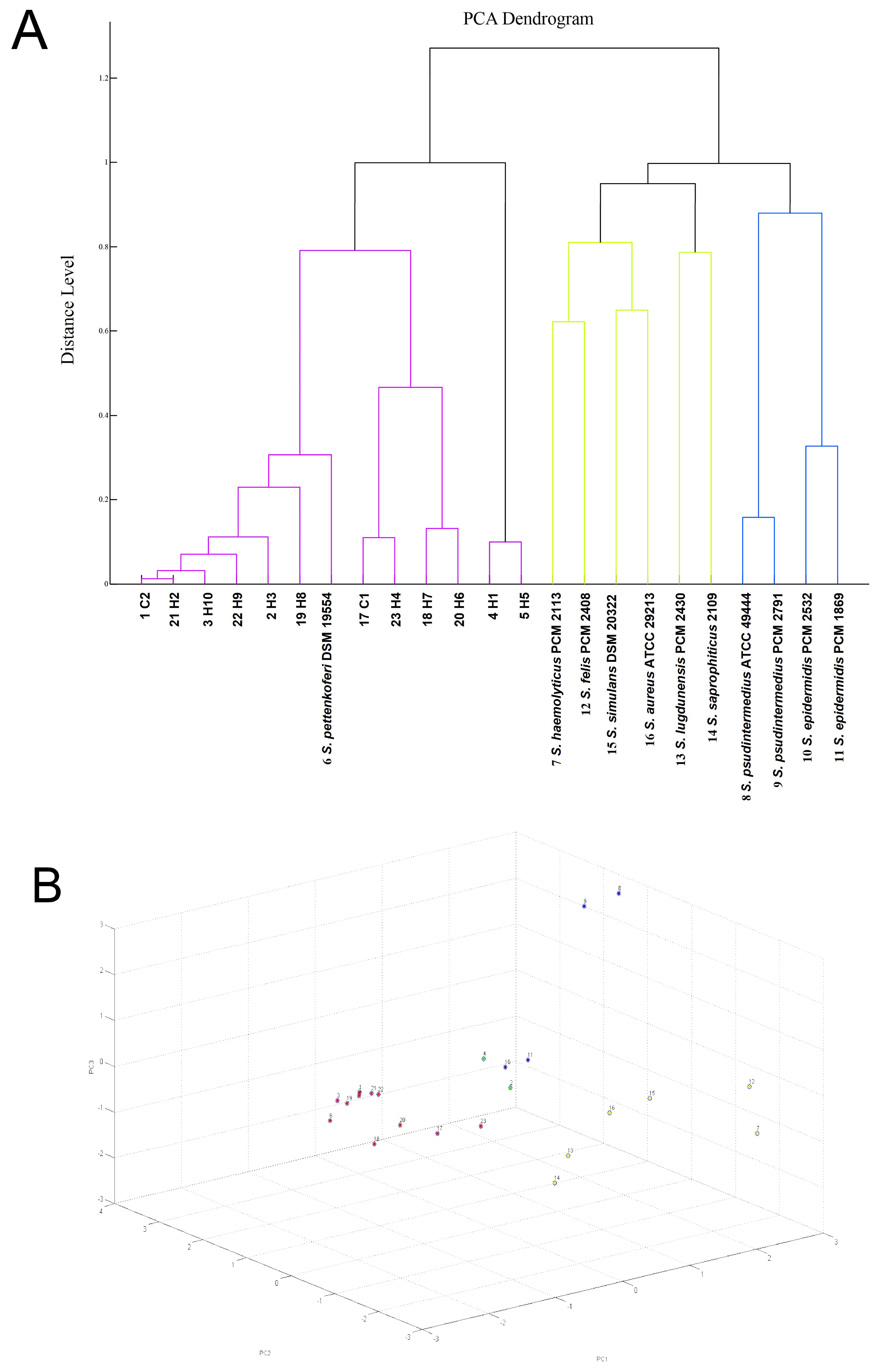
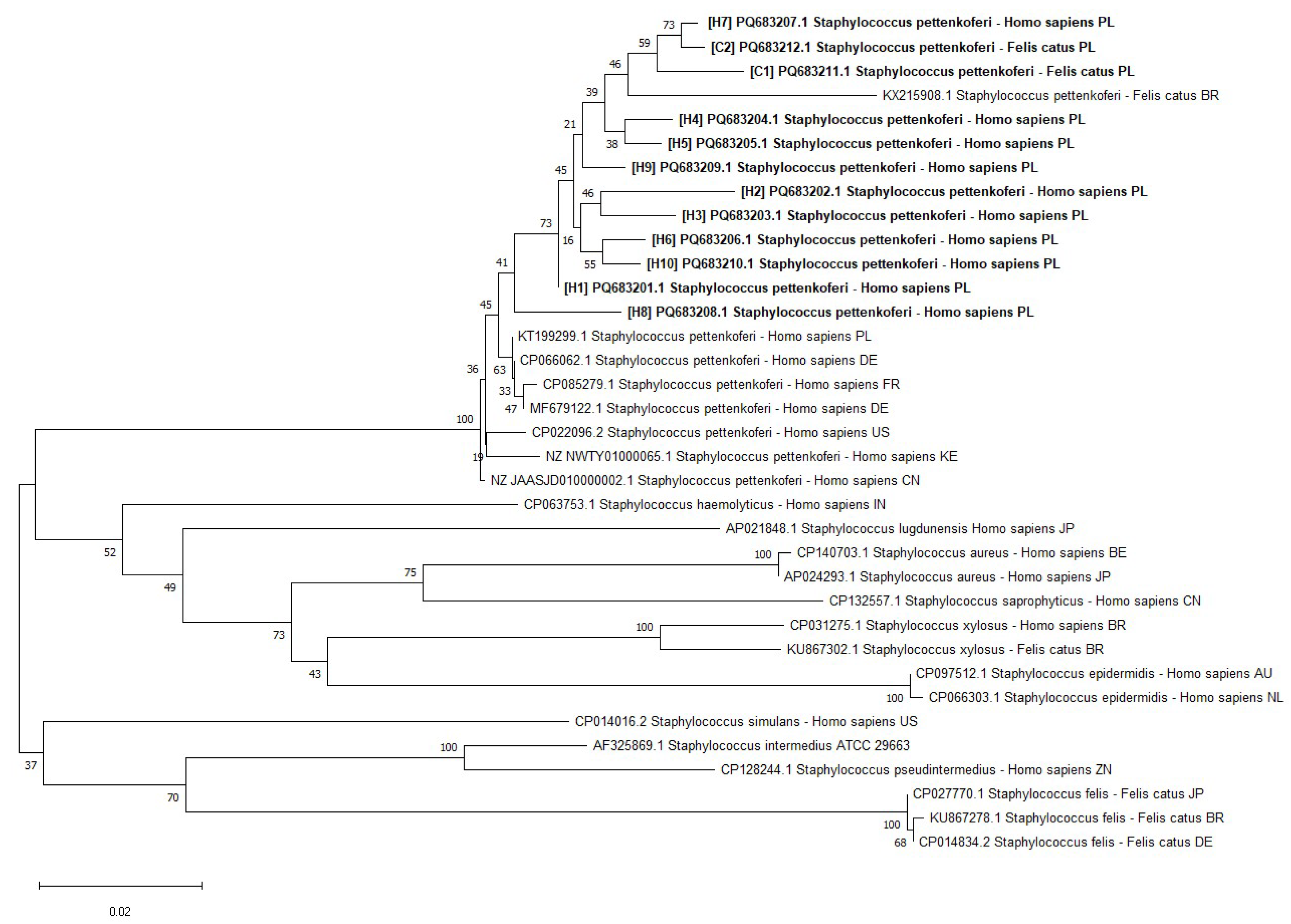
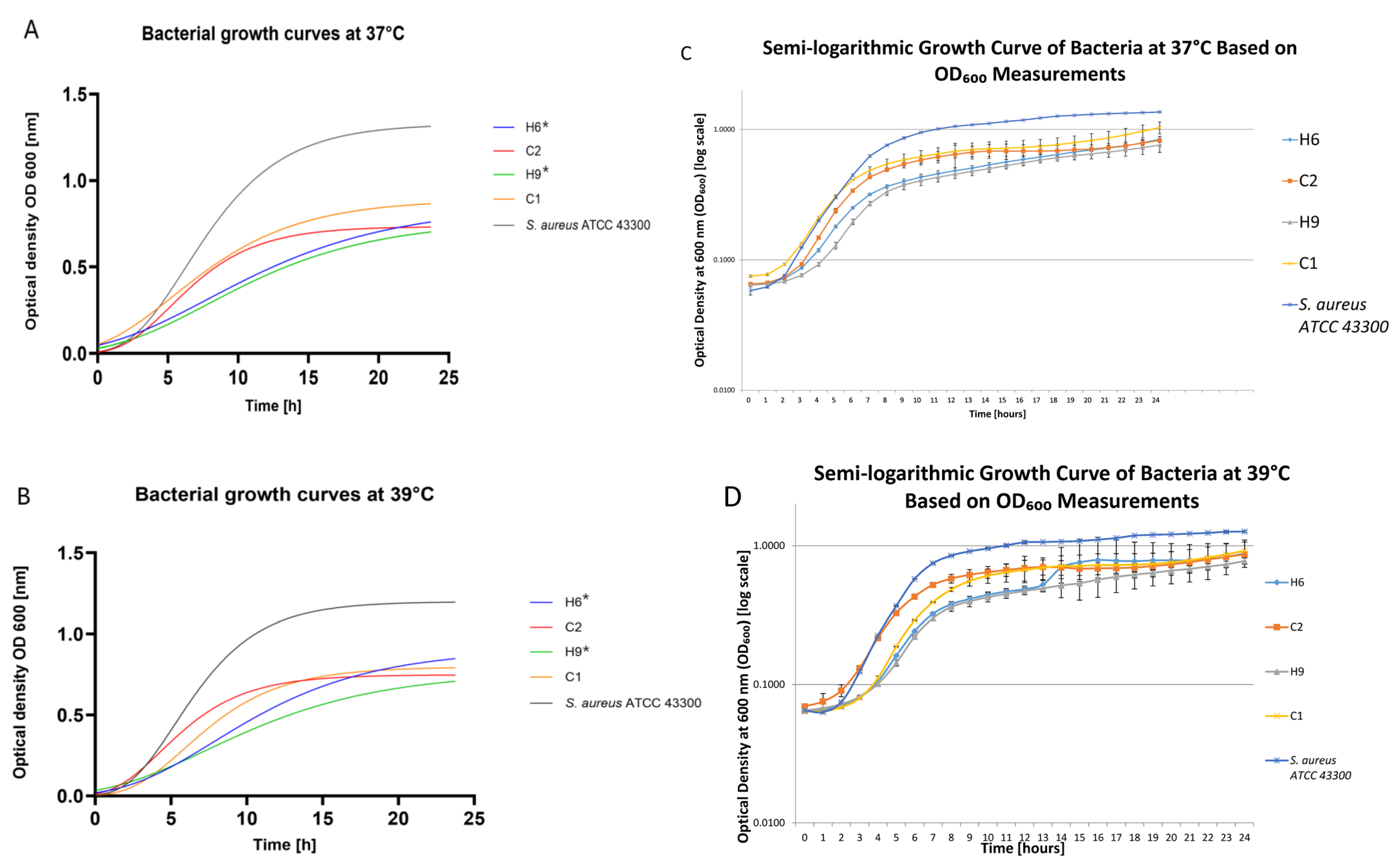
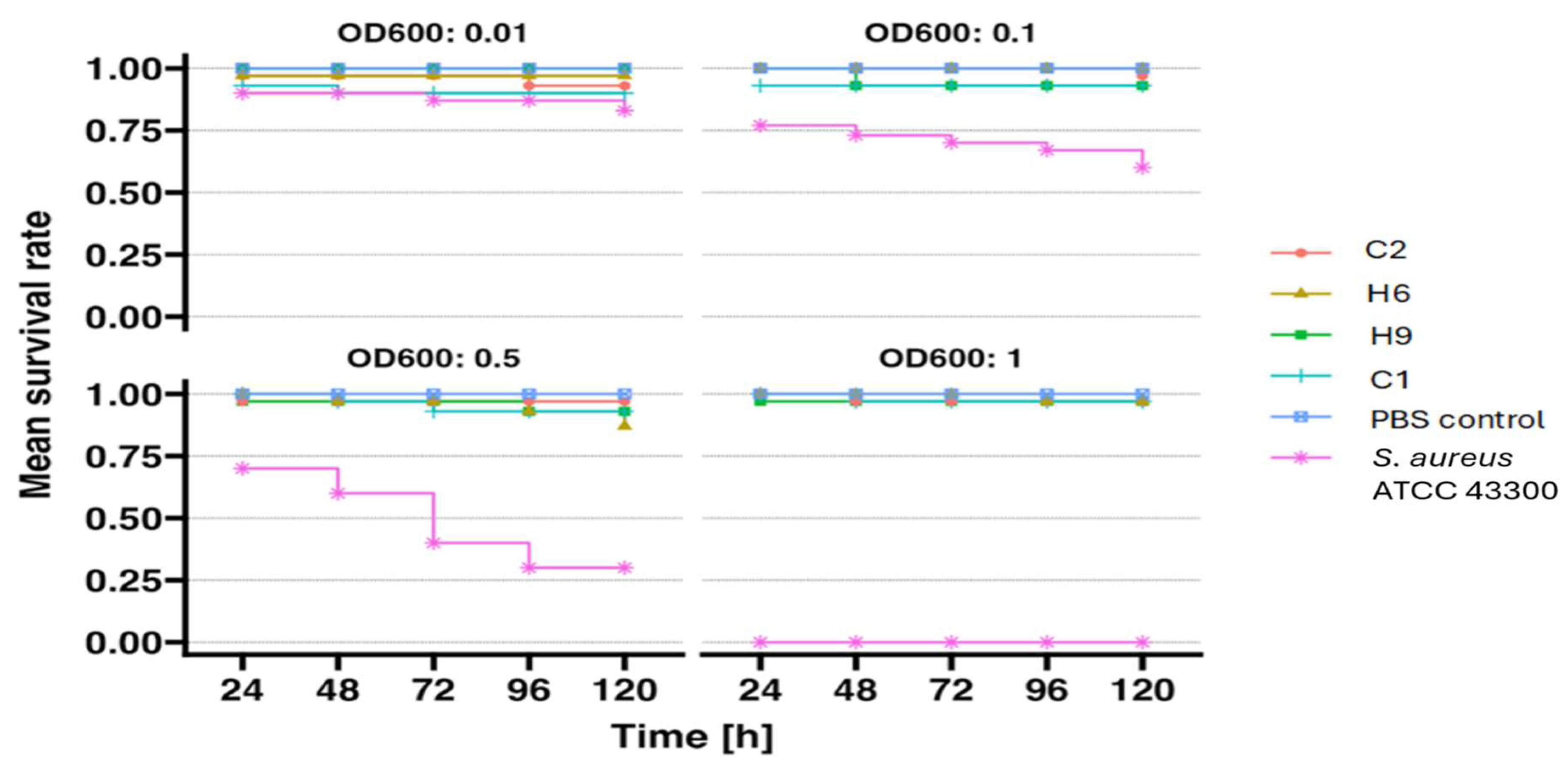
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. S. pettenkoferi Origin and Identification
4.2. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Factors of S. pettenkoferi
4.3. Growth Curves’ Evaluation and Biofilm Formation
4.4. Pathogenicity Tests on Larvae Model
4.4.1. Preparation of Bacterial Suspension
4.4.2. Larval Selection and Injection
4.4.3. Analysis of the Results
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trülzsch, K.; Rinder, H.; Trček, J.; Bader, L.; Wilhelm, U.; Heesemann, J. Staphylococcus pettenkoferi, a novel staphylococcal species isolated from clinical specimens. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2002, 43, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammina, C.; Bonura, C.; Verde, M.S.; Fasciana, T.; Palma, D.M. A Fatal Bloodstream Infection by Staphylococcus pettenkoferi in an Intensive Care Unit Patient. Case Rep. Crit. Care. 2011, 2011, 612732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashi, A.A.; Delport, J.A.; Elsayed, S.; Silverman, M.S. Staphylococcus pettenkoferi bacteremia: A case report and review of the literature. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, C.; Cosiano, M.; Cabezas, M.; Barwatt, J.W.; Tillekeratne, L.G. Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Bacteremia in an American Intensive Care Unit. Case Rep. Infect. Dis. 2021, 29, 5235691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisriel, S.D.; Jacobs, J.W. The first reported case of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi prosthetic joint infection. Microbes Infect. 2022, 24, 104978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugaban, K.B.; She, R.C. The clinical significance of staphylococcus pettenkoferi: A retrospective review at a tertiary care medical center. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 102, 115592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kierzkowska, M.; Markowska, K.; Majewska, A. Knowledge, Attitude and Practice Regarding Staphylococcus pettenkoferi. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2022, 14, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.; Kadlec, K.; Fessler, A.T.; Schwarz, S. Identification and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Staphylococcus pettenkoferi from a small animal clinic. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, U.; von Lützau, A.; Schlattmann, A.; Roesler, U.; Köck, R.; Becker, K. Zoonotic multidrug-resistant microorganisms among small companion animals in Germany. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierowiec, K.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Wzorek, A.; Rypuła, K.; Gamian, A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus Species Colonization in Healthy and Sick Cats. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 20, 4360525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, T.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Das, M.; Mandakini, R.; Vanrahmlimphuii Roychoudhury, P.; Ghorai, S.; Behera, S.K. Multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus pettenkoferi isolated from cat in India. Vet. World. 2018, 11, 1380–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Chung, H.S.; Lee, M. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of six Staphylococcus pettenkoferi isolates from blood samples. Ann. Lab. Med. 2015, 35, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnan, C.; Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Pouget, C.; Morsli, M.; Huc-Brandt, S.; Pantel, A.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Sotto, A.; Molle, V.; Lavigne, J.P. Phenotypic and Genotypic Virulence Characterisation of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Strains Isolated from Human Bloodstream and Diabetic Foot Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, A.; Khairnar, K. Overview of the risks of Staphylococcus aureus infections and their control by bacteriophages and bacteriophage-encoded products. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 2031–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S.A.; Helbig, K.J. The Complex Diseases of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius in Canines: Where to Next? Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.T.; Andam, C.P. Extensive Horizontal Gene Transfer within and between Species of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carretto, E.; Barbarini, D.; Couto, I.; De Vitis, D.; Marone, P.; Verhoef, J.; De Lencastre, H.; Brisse, S. Identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci other than Staphylococcus epidermidis by automated ribotyping. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2005, 11, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Månsson, E.; Hellmark, B.; Stegger, M.; Skytt Andersen, P.; Sundqvist, M.; Söderquist, B. Genomic relatedness of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi isolates of different origins. J. Med. Microbiol. 2017, 66, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argemi, X.; Riegel, P.; Lavigne, T.; Lefebvre, N.; Grandpré, N.; Hansmann, Y.; Jaulhac, B.; Prévost, G.; Schramm, F. Implementation of Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry in Routine Clinical Laboratories Improves Identification of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and Reveals the Pathogenic Role of Staphylococcus lugdunensis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative Staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Ryoo, N. Identification of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Blood Culture. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 22, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, D.; Kurane, K.; Koshu, K.; Shinjoh, M.; Tanaka, D.; Yamagishi1, H.; Kimura, Y.; Nakazato, E.; Yamagata, T. Clinical picture of bacteremia with Staphylococcus pettenkoferi in children. J. Clin. Images Med. Case Rep. 2023, 4, 2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miszczak, M.; Korzeniowska-Kowal, A.; Wzorek, A.; Gamian, A.; Rypuła, K.; Bierowiec, K. Colonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus species in healthy and sick pets: Prevalence and risk factors. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska, J.; Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W. Biofilm Formation Ability and Presence of Adhesion Genes among Coagulase-Negative and Coagulase-Positive Staphylococci Isolates from Raw Cow’s Milk. Pathogens 2020, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Seng, R.; Kitti, T.; Thummeepak, R.; Kongthai, P.; Leungtongkam, U.; Wannalerdsakun, S.; Sitthisak, S. Biofilm formation of methicillin-resistant coagulase negative staphylococci (MR-CoNS) isolated from community and hospital environments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Plumet, L.; Huc-Brandt, S.; Magnan, C.; Yahiaoui-Martinez, A.; Kissa, K.; Pantel, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Molle, V. Investigating Pathogenicity and Virulence of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi: An Emerging Pathogen. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loïez, C.; Wallet, F.; Pischedda, P.; Renaux, E.; Senneville, E.; Mehdi, N.; Courcol, R.J. Case of Osteomyelitis Caused by “Staphylococcus pettenkoferi”. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 1069–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, K.; Sheehan, G. The Use of Galleria Mellonella Larvae to Identify Novel Antimicrobial Agents against Fungal Species of Medical Interest. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, G.; Rouillon, A.; Ghukasyan, G.; Emily, M.; Felden, B.; Donnio, P.Y. Galleria mellonella Larvae as an Infection Model to Investigate sRNA-Mediated Pathogenesis in Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 631710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaskatepe, B.; Ozturk, S. Assessment of synergistic activity of rhamnolipid and linezolid against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in-vitro and in-vivo with Galleria mellonella larvae model. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 174, 105945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryhill, B.A.; Gil-Gil, T.; Witzany, C.; Goldberg, D.A.; Vega, N.M.; Regoes, R.R.; Levin, B.R. The dynamics of Staphylococcal infection and their treatment with antibiotics and bacteriophage in the Galleria mellonella model system. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, G.; Dixon, A.; Kavanagh, K. Utilization of Galleria mellonella larvae to characterize the development of Staphylococcus aureus infection. Microbiology. 2019, 165, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramarao, N.; Nielsen-Leroux, C.; Lereclus, D. The Insect Galleria mellonella as a Powerful Infection Model to Investigate Bacterial Pathogenesis. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 70, e4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Samad, R.; Al Disi, Z.; Mohammad Ashfaq, M.Y.; Wahib, S.M.; Zouari, N. The use of principle component analysis and MALDI-TOF MS for the differentiation of mineral forming Virgibacillus and Bacillus species isolated from sabkhas. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 14606–14616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA Sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Drancourt, M.; Raoult, D. RpoB gene sequence-based identification of Staphylococcus species. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Document M07-A9; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically. CLSI—Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2012.
- CLSI Supplement VET01S; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals. CLSI—Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020.
- CLSI Supplement M100; Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. CLSI—Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2023.
- Coutinho, V.d.L.S.; Paiva, R.M.; Reiter, K.C.; de-Paris, F.; Barth, A.L.; Machado, A.B. Distribution of erm genes and low prevalence of inducible resistance to clindamycin among staphylococci isolates. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wright, R.C.T.; Wood, A.J.; Bottery, M.J.; Muddiman, K.J.; Paterson, S.; Harrison, E.; Brockhurst, M.A.; Hall, J.P.J. A chromosomal mutation is superior to a plasmid-encoded mutation for plasmid fitness cost compensation. PLoS Biol. 2024, 22, e3002926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Płoneczka-Janeczko, K.; Lis, P.; Bierowiec, K.; Rypuła, K.; Chorbiński, P. Identification of bap and icaA genes involved in biofilm formation in coagulase negative staphylococci isolated from feline conjunctiva. Vet. Res. Commun. 2014, 38, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, B.; Tymińska, J.; Szymczyk-Ziółkowska, P.; Chodaczek, G.; Migdał, P.; Czajkowska, J.; Junka, A. In Vitro Activity of Octenidine Dihydrochloride-Containing Lozenges against Biofilm-Forming Pathogens of Oral Cavity and Throat. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saganuwan, A.S. Application of median lethal concentration (LC50) of pathogenic microorganisms and their antigens in vaccine development. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdiyoun, S.M.; Kazemian, H.; Ahanjan, M.; Houri, H.; Goudarzi, M. Frequency of Aminoglycoside-Resistance Genes in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolates from Hospitalized Patients. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2016, 9, e35052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierowiec, K.; Płoneczka-Janeczko, K.; Rypuła, K. Diversity of antimicrobial-resistant pheno- and genotypes of Staphylococcus aureus from clinically healthy cats kept in city households. Berl. Und Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2017, 130, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, E.E.; Boswihi, S.S.; Mathew, B.; Noronha, B.; Verghese, T. Resurgence of Chloramphenicol Resistance in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Due to the Acquisition of a Variant Florfenicol Exporter (fexAv)-Mediated Chloramphenicol Resistance in Kuwait Hospitals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strommenger, B.; Kettlitz, C.; Werner, G.; Witte, W. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, F.; Picard, F.J.; Ke, D.; Paradis, S.; Roy, P.H.; Ouellette, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Development of a PCR assay for identification of staphylococci at genus and species levels. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.J.; Blevins, J.S.; Beenken, K.; Wibowo, N.; Ojha, N.; Smeltzer, M.S. Multiplex PCR protocol for the diagnosis of staphylococcal infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 3332–3338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Fox, L.K.; Seo, K.S.; McGuire, M.A.; Park, Y.H.; Rurangirwa, F.R.; Sischo, W.M.; Bohach, G.A. Detection of classical and newly described staphylococcal superantigen genes in coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from bovine intramammary infections. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Roth, R.; Peters, G. Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: Use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2548–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monday, S.R.; Bohach, G.A. Use of multiplex PCR to detect classical and newly described pyrogenic toxin genes in staphylococcal isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 3411–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.A.; Harnett, G.B.; Hodge, M.M.; Cattell, J.A.; Speers, D.J. Real-time PCR assay for detection of blaZ genes in Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1259–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.H.; Yoon, E.J.; Choi, E.C.; Choi, S.S. Development of TaqMan probe-based real-time PCR method for erm(A),erm(B), and erm(C), rapid detection of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B resistance genes, from clinical isolates. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, K.; Cosman, A.; Belgrader, P.; Chapman, B.; Sullivan, D.C. Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by a duplex droplet digital PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2033–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Peak, N.; Knapp, C.W.; Yang, R.K.; Hanfelt, M.M.; Smith, M.S.; Aga, D.S.; Graham, D.W. Abundance of six tetracycline resistance genes in wastewater lagoons at cattle feedlots with different antibiotic use strategies. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ID | Phenotypic Antimicrobial Profile | Genotypic Antimicrobial Profile |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | P, OX, C | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), ermA, vanA, aph3-IIIa |
| C2 | P, OX | blaZ, mecA, ermA, vanA |
| H1 | P, OX, AMP, AMC, CIP, MAR, E, CL, SMX | mecA, tet(L), ermA |
| H2 | P, OX | blaZ, mecA, ermA, aph3-IIIa |
| H3 | P, OX, AMP, AMC, CIP, MAR, E, CL, SMX | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), ter(M), ermA, aph3-IIIa |
| H4 | P, OX, AMC, TET | blaZ, mecA, tet(M), ermA, fusB, aph3-IIIa |
| H5 | P, OX, AMP, AMC, CIP, MAR, E, CL, SMX, TMP, FD | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), tet(M), ermA, mupA, fusB, aph3-IIIa |
| H6 | P, OX, AMP, AMC, CIP, MAR, E, CL, SMX, TMP, FD, MUP | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), ermA, mupA, fusB, aph3-IIIa |
| H7 | P, CIP, E, CL, SMX | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), ermA, vanA |
| H8 | P, OX, TET, SMX | mecA, tet(L), ermA |
| H9 | P, OX, AMP, AMC, CIP, MAR, E, CL, SMX, TMP, FD, MUP | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), ermA |
| H10 | P, OX, AMC, E, CL, SMX | blaZ, mecA, tet(L), ermA |
| ID | Biofilm Production at 37 °C | Biofilm Production at 39 °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| After 24 h | After 48 h | After 24 h | After 48 h | |
| C1 | weak | medium | medium | strong |
| C2 | weak | strong | medium | strong |
| H1 | weak | medium | weak | strong |
| H2 | weak | weak | weak | medium |
| H3 | weak | weak | weak | medium |
| H4 | weak | weak | weak | strong |
| H5 | weak | weak | weak | medium |
| H6 | weak | medium | weak | strong |
| H7 | weak | weak | weak | medium |
| H8 | weak | medium | weak | medium |
| H9 | not present | medium | weak | strong |
| H10 | weak | medium | weak | strong |
| S. pettenkoferi DSM 19554 | weak | medium | weak | medium |
| S. aureus ATCC 43300 | medium | strong | medium | strong |
| S. aureus ATCC 6532 | strong | strong | strong | strong |
| S. aureus ATCC 11632 | weak | medium | medium | strong |
| S. pseudintermedius PCM 2791 | strong | strong | strong | strong |
| S. pseudintermedius ATCC 49444 | strong | strong | strong | strong |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bierowiec, K.; Delmar, A.; Karwańska, M.; Siedlecka, M.; Kumala-Ćwikła, A.; Książczyk, M.; Kapczyńska, K. Comparison of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Human Clinical Cases and Cat Carriers Regarding Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051948
Bierowiec K, Delmar A, Karwańska M, Siedlecka M, Kumala-Ćwikła A, Książczyk M, Kapczyńska K. Comparison of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Human Clinical Cases and Cat Carriers Regarding Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051948
Chicago/Turabian StyleBierowiec, Karolina, Ashley Delmar, Magdalena Karwańska, Magdalena Siedlecka, Aleksandra Kumala-Ćwikła, Marta Książczyk, and Katarzyna Kapczyńska. 2025. "Comparison of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Human Clinical Cases and Cat Carriers Regarding Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Production" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051948
APA StyleBierowiec, K., Delmar, A., Karwańska, M., Siedlecka, M., Kumala-Ćwikła, A., Książczyk, M., & Kapczyńska, K. (2025). Comparison of Staphylococcus pettenkoferi Isolated from Human Clinical Cases and Cat Carriers Regarding Antibiotic Susceptibility and Biofilm Production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051948









