Influence of FOXP3 rs2280883 and rs3761548 Variants on IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels and Plaque Psoriasis Risk in the Mexican Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of Study Groups
2.2. Frequencies of the rs2280883 and rs3761548 FOXP3 Variants
2.3. IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels in PP Patients and CSs
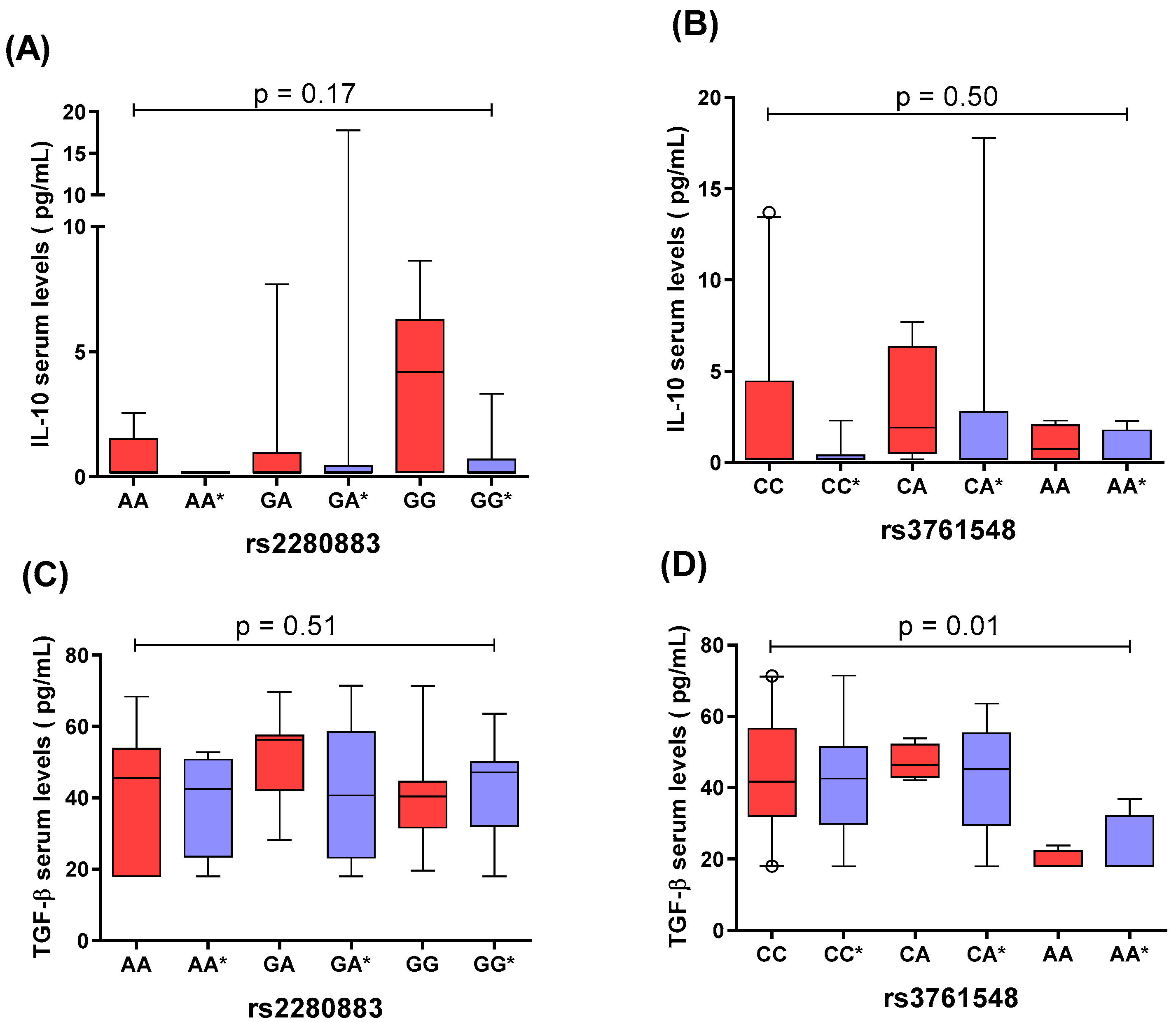
2.4. Comparison of IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels by rs2280883 and rs3761548 FOXP3 Genotypes
2.5. Linkage Disequilibrium Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. FOXP3 Variants Genotyping
4.3. Quantification of IL-10 and TGF-β Serum Levels
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; He, M.; Jiang, J.; Duan, X.; Chai, B.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Q.; Chen, H. Triggers for the Onset and Recurrence of Psoriasis: A Review and Update. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkini, M.-A.; Nakamura, M.; Alexis, A.F.; Londoño-Garcia, A.; van de Kerkhof, P.C.M.; Doss, N.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Kaufman, B.; Kleyn, C.E.; Lebwohl, M.; et al. Psoriasis in People With Skin of Color: An Evidence-Based Update. Int. J. Dermatol. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, R.; Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Kontopantelis, E.; Augustin, M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. Global Psoriasis Atlas National, Regional, and Worldwide Epidemiology of Psoriasis: Systematic Analysis and Modelling Study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.W.; Mehta, M.D.; Schupp, C.W.; Gondo, G.C.; Bell, S.J.; Griffiths, C.E.M. Psoriasis Prevalence in Adults in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Thatiparthi, A.; Martin, A.; Egeberg, A.; Wu, J.J. Prevalence of Psoriasis among Adults in the US 2009-2010 and 2013-2014 National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitropoulos, E.; Romiti, R.; Haro, J.M.; Brnabic, A.; Gómez-Martín, D.; Firmino Goncalves, L.; Burge, R. Burden of Disease for Psoriasis in Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, and Mexico. Value Health Reg. Issues 2021, 26, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, Z.; Bong, Y.B.; Tan, L.L.; Lim, S.X.; Yong, A.S.W.; Ch’ng, C.C.; Tan, M.P.; Ismail, R. Determinants of Quality of Life and Psychological Status in Adults with Psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leikin, J.B. Biologics for the Primary Care Physician: Review and Treatment of Psoriasis. Dis. Mon. 2019, 65, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-Z.; Liu, S.-R. Koebner Phenomenon Leading to the Formation of New Psoriatic Lesions: Evidences and Mechanisms. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20193266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vata, D.; Tarcau, B.M.; Popescu, I.A.; Halip, I.A.; Patrascu, A.I.; Gheuca Solovastru, D.-F.; Mocanu, M.; Chiriac, P.C.; Gheuca Solovastru, L. Update on Obesity in Psoriasis Patients. Life 2023, 13, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yao, Z. Roles of Infection in Psoriasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, L.; Halioua, B. Stress and Psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 1165–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balak, D.M.; Hajdarbegovic, E. Drug-Induced Psoriasis: Clinical Perspectives. Psoriasis 2017, 7, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehncke, W.-H.; Schön, M.P. Psoriasis. Lancet 2015, 386, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, N.; Sakaguchi, S. Transcriptional and Epigenetic Basis of Treg Cell Development and Function: Its Genetic Anomalies or Variations in Autoimmune Diseases. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, S.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Control of Regulatory T Cell Development by the Transcription Factor Foxp3. Science 2003, 299, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Rudensky, A.Y. Foxp3 in Control of the Regulatory T Cell Lineage. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogulska, A.; Borowiec, M.; Polakowska, E.; Dynowski, J.; Młynarski, W.; Wasowska-Królikowska, K. FOXP3, IL-10, and TGF-β Genes Expression in Children with IgE-Dependent Food Allergy. J. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 31, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiri, A.M.; Fard-Aghaie, M.; Bedke, T.; Papazoglou, E.D.; Sabihi, M.; Zazara, D.E.; Zhang, S.; Lücke, J.; Seeger, P.; Evers, M.; et al. Foxp3 + Treg-Derived IL-10 Promotes Colorectal Cancer-Derived Lung Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, E.H.; Wang, X.; Balaji, S.; Butte, M.J.; Bollyky, P.L.; Keswani, S.G. The Role of the Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Interleukin-10 in Tissue Fibrosis. Adv. Wound Care 2020, 9, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Hu, M.; Skarratt, K.; Lee, C.H.; Stormon, M.; Wong, M.; Fuller, S.J.; Nanan, R. IL-10 Potentiates Differentiation of Human Induced Regulatory T Cells via STAT3 and Foxo1. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3665–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, J.M.M.; Hirata, B.K.B.; Guembarovski, R.L.; Watanabe, M.A.E. Genetic Polymorphism in FOXP3 Gene: Imbalance in Regulatory T-Cell Role and Development of Human Diseases. J. Genet. 2013, 92, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; He, F.; Chen, A.; Yang, H.; Pi, B. Meta-Analysis of FOXP3 Gene Rs3761548 and Rs2232365 Polymorphism and Multiple Sclerosis Susceptibility. Medicine 2019, 98, e17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsohafy, M.A.; Elghzaly, A.A.; Abdelsalam, H.M.; Gaballah, M.A. Assessment of the Possible Role of FOXP3 Gene (Rs3761548) Polymorphism in Psoriasis Vulgaris Susceptibility and Pathogenesis: Egyptian Study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 10, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddini, R.; Somi, M.H.; Taghikhani, M.; Moaddab, S.-Y.; Masnadi Shirazi, K.; Shirmohammadi, M.; Eftekharsadat, A.T.; Sadighi Moghaddam, B.; Salek Farrokhi, A. Association of Foxp3 Rs3761548 Polymorphism with Cytokines Concentration in Gastric Adenocarcinoma Patients. Cytokine 2021, 138, 155351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flauzino, T.; Alfieri, D.F.; de Carvalho Jennings Pereira, W.L.; Oliveira, S.R.; Kallaur, A.P.; Lozovoy, M.A.B.; Kaimen-Maciel, D.R.; de Oliveira, K.B.; Simão, A.N.C.; Reiche, E.M.V. The Rs3761548 FOXP3 Variant Is Associated with Multiple Sclerosis and Transforming Growth Factor Β1 Levels in Female Patients. Inflamm. Res. 2019, 68, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Li, K.; Li, F.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, T.; Liu, Y. Polymorphisms in the FOXP3 Gene in Han Chinese Psoriasis Patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2010, 57, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, P.; Cheruvu, R.; Tippisetty, S.; Komaravalli, P.L.; Valluri, V.; Ishaq, M. Association of FOXP3 (Rs3761548) Promoter Polymorphism with Nondermatomal Vitiligo: A Study from India. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2013, 69, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, F.; Skarmoutsou, E.; Marchini, M.; Malaponte, G.; Caronni, M.; Scorza, R.; Mazzarino, M.C. Genetic Polymorphisms of FOXP3 in Italian Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Immunol. Lett. 2013, 152, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Jurkowska, M.; Felis-Giemza, A.; Romanowska-Próchnicka, K.; Manczak, M.; Maslinski, S.; Olesinska, M. Genetic Polymorphisms of Foxp3 in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Zheng, G.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, X. Association of Genetic Variations in FoxP3 Gene with Graves’ Disease in a Southwest Chinese Han Population. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2023, 11, e1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarinejad, P.; Gholijani, N.; Habibagahi, Z.; Malekmakan, M.R.; Amirghofran, Z. FOXP3 Gene Variants in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Association with Disease Susceptibility in Men and Relationship with Abortion in Women. Iran. J. Immunol. 2022, 19, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.F.; Guembarovski, R.L.; Guembarovski, A.L.; Kishima, M.O.; Campos, C.Z.; Oda, J.M.M.; Ariza, C.B.; de Oliveira, K.B.; Borelli, S.D.; Watanabe, M.A.E. FOXP3 Transcription Factor: A Candidate Marker for Susceptibility and Prognosis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 341654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indhumathi, S.; Rajappa, M.; Chandrashekar, L.; Ananthanarayanan, P.H.; Thappa, D.M.; Negi, V.S. T Helper-2 Cytokine/Regulatory T-Cell Gene Polymorphisms and Their Relation with Risk of Psoriasis in a South Indian Tamil Cohort. Hum. Immunol. 2017, 78, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.-Y.; Hsu, L.-H.; Chien, C.-H.; Chiang, B.-L. Novel Foxp3− IL-10− Regulatory T-Cells Induced by B-Cells Alleviate Intestinal Inflammation in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Kitani, A.; Strober, W. Molecular Mechanisms Regulating TGF-β-Induced Foxp3 Expression. Mucosal Immunol. 2010, 3, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Robaee, A.A.; Al-Zolibani, A.A.; Al-Shobili, H.A.; Kazamel, A.; Settin, A. IL-10 Implications in Psoriasis. Int. J. Health Sci. 2008, 2, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Williams, C.A.; Salter, K.; Garl, P.J.; Li, A.G.; Wang, X.-J. A Role for TGFβ Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadullah, K.; Sabat, R.; Friedrich, M.; Volk, H.D.; Sterry, W. Interleukin-10: An Important Immunoregulatory Cytokine with Major Impact on Psoriasis. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2004, 3, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traupe, H. Psoriasis and the Interleukin-10 Family: Evidence for a Protective Genetic Effect, but Not an Easy Target as a Drug. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1438–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutwin, M.; Migdalska-Sęk, M.; Brzeziańska-Lasota, E.; Zelga, P.; Woźniacka, A. An Analysis of IL-10, IL-17A, IL-17RA, IL-23A and IL-23R Expression and Their Correlation with Clinical Course in Patients with Psoriasis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, K.; Blaschke, V.; Maurer, C.; Lippert, U.; Neumann, C.; Garbe, C.; Middel, P.; Westphal, G. Response of Psoriasis to Interleukin-10 Is Associated with Suppression of Cutaneous Type 1 Inflammation, Downregulation of the Epidermal Interleukin-8/CXCR2 Pathway and Normalization of Keratinocyte Maturation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A Simple Salting out Procedure for Extracting DNA from Human Nucleated Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Mirfakhraie, R.; Pirjani, R.; Taheripanah, R.; Bayat, S.; Daryabari, S.A.; Noori, M.; Ghaderian, S.M.H. Association Study of FOXP3 Gene and the Risk of 0020 Pre-Eclampsia. Clin. Exp. Hypertens 2018, 40, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.Y.; He, L. SHEsis, a Powerful Software Platform for Analyses of Linkage Disequilibrium, Haplotype Construction, and Genetic Association at Polymorphism Loci. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 97–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


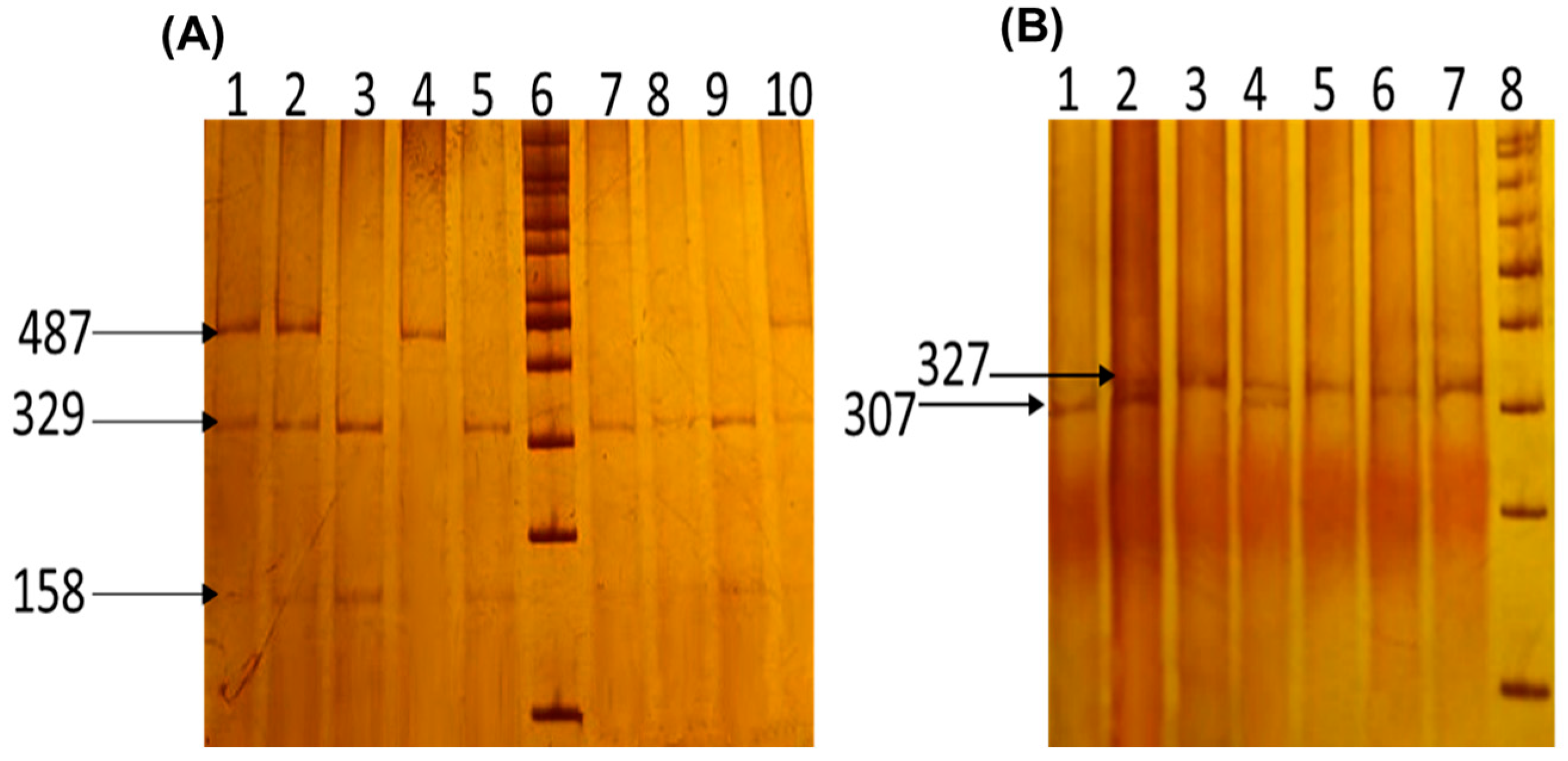
| Characteristics | PP (n = 101) | CS (n = 106) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age a | 46 (35–57) | 45 (32–51) | 0.11 |
| Gender, n (%) | |||
| Female | 49 (49) | 60 (57) | 0.24 |
| Male | 52 (51) | 46 (43) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) b | 29.5 ± 4.8 | 28.7 ± 5.2 | 0.53 |
| Time of evolution of the disease (years) b | 9 ± 0.98 | ||
| PASIb | 10.9 ± 8.5 | ||
| Mild (<10), n (%) | 40 (40) | ||
| Moderate to severe (≥10), n (%) | 61 (60) | ||
| Treatment, n (%) | |||
| Topical exfoliants (30% Urea + Dimeticone) | 34 (33) | ||
| MTX | 11 (11) | ||
| Topical steroids | 5 (5) | ||
| Topical exfoliants + MTX | 8 (8) | ||
| MTX + Topical steroids | 5 (5) | ||
| Topical exfoliants + MTX + Topical steroids | 5 (5) | ||
| None | 33 (33) |
| Variants | PP n = 101% (n) | CS n = 106% (n) | OR (CI 95%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2280883 | ||||
| Genotypes | ||||
| GG a | 56 (57) | 63 (67) | 1 | - |
| GA | 23 (23) | 36 (38) | 0.71 (0.38–1.33) | 0.28 |
| AA | 21 (21) | 1 (1) | 24.68 (3.22–189.25) | <0.0001 |
| Alleles | ||||
| G a | 68 (137) | 81 (172) | 1 | - |
| A | 32 (65) | 19 (40) | 2.04 (1.29–3.21) | 0.001 |
| Genetic models | ||||
| Dominant | ||||
| GG a | 56 (57) | 63 (67) | 1 | - |
| GA+AA | 44 (44) | 37 (39) | 1.32 (0.76–2.31) | 0.32 |
| Recessive | ||||
| GG+GA a | 79 (80) | 99 (105) | 1 | - |
| AA | 21 (21) | 1 (1) | 27.56 (3.63–209.24) | <0.0001 |
| rs3761548 | ||||
| Genotypes | ||||
| CC a | 59 (60) | 58 (61) | 1 | - |
| CA | 30 (30) | 34 (36) | 0.85 (0.46–1.56) | 0.60 |
| AA | 11 (11) | 8 (9) | 1.32 (0.49–3.54) | 0.56 |
| Alleles | ||||
| C a | 74 (150) | 75 (158) | 1 | - |
| A | 26 (52) | 25 (54) | 1.04 (0.66–1.63) | 0.86 |
| Genetic models | ||||
| Dominant | ||||
| CC a | 59 (60) | 58 (61) | 1 | - |
| CA+AA | 41 (41) | 42 (45) | 0.94 (0.53–1.65) | 0.83 |
| Recessive | ||||
| CC+CA a | 89 (90) | 92 (97) | 1 | - |
| AA | 11 (11) | 8 (9) | 1.40 (0.54–3.65) | 0.48 |
| FOXP3 Variant | Primers | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|
| rs3761548 | 5′GCCCTTGTCTACTCCACGCCTCT3′ (sense) 5′ CAGCCTTCGCCAATACAGAGCC 3′ (antisense) | 487 bp [44] |
| rs2280883 | 5′ TACACCCCCAACTGGGCAGC 3′ (sense) 5′ TGGGGTTCGGTGTGGAGTGA 3′ (antisense) (mismatch is underlined) | 327 bp [27] |
| Reagents | Final Concentration | PCR Amplification Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| rs3761548 | ||
| Buffer 10× | 1× | Initial denaturing: 95 °C, 5 min 35 cycles: Denaturing: 30 s at 94 °C Annealing: 35 s at 58 °C Extension: 40 s at 72 °C, Final extension: 5 min at 72 °C |
| MgCl2 | 2.5 mM | |
| dNTPs | 0.4 mM | |
| Primers sense and antisense | 0.15 µM | |
| Taq DNA polymerase | 1.15 U/µL | |
| DNA | 100 ng | |
| Water | (up to 15 µL) | |
| rs2280883 | ||
| Buffer 10× | 1× | Initial denaturing: 95 °C, 5 min 40 cycles: Denaturing: 30 s, 94 °C Annealing: 35 s, 60 °C Extension: 30 s, 72 °C, Final extension: 10 min, 72 °C |
| MgCl2 | 2.5 mM | |
| dNTPs | 0.4 mM | |
| Primer sense and antisense | 0.15 µM | |
| Taq DNA polymerase | 1.15 U/µL | |
| DNA | 100 ng | |
| Water | (up to 15 µL) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Bello, J.; Preciado-Aguiar, M.S.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F.; Baños-Hernández, C.J.; García-Arellano, S.; Alvarado-Navarro, A. Influence of FOXP3 rs2280883 and rs3761548 Variants on IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels and Plaque Psoriasis Risk in the Mexican Population. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051789
Hernández-Bello J, Preciado-Aguiar MS, Muñoz-Valle JF, Baños-Hernández CJ, García-Arellano S, Alvarado-Navarro A. Influence of FOXP3 rs2280883 and rs3761548 Variants on IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels and Plaque Psoriasis Risk in the Mexican Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051789
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Bello, Jorge, Miriam Sarahi Preciado-Aguiar, José Francisco Muñoz-Valle, Christian Johana Baños-Hernández, Samuel García-Arellano, and Anabell Alvarado-Navarro. 2025. "Influence of FOXP3 rs2280883 and rs3761548 Variants on IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels and Plaque Psoriasis Risk in the Mexican Population" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051789
APA StyleHernández-Bello, J., Preciado-Aguiar, M. S., Muñoz-Valle, J. F., Baños-Hernández, C. J., García-Arellano, S., & Alvarado-Navarro, A. (2025). Influence of FOXP3 rs2280883 and rs3761548 Variants on IL-10 and TGF-β1 Serum Levels and Plaque Psoriasis Risk in the Mexican Population. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 1789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051789









