Application of mRNA-Seq and Metagenomic Sequencing to Study Salmonella pullorum Infections in Chickens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Different Expression of Genes in Cecal Tissues of Positive Group (P) and Negative Group (N) of Salmonella pullorum Infection
2.2. Differentially Expressed Alternative Splicings of Cecal Tissue in Positive (P) and Negative (N) Groups of Salmonella pullorum Infection
2.3. Combined DEGs and DEASs Analysis of Cecal Tissue from Positive (P) and Negative (N) Groups Infected with Salmonella pullorum
2.4. The Metagenomic Sequencing of Cecal Tissue Was Conducted in the Positive (P) and Negative (N) Groups Infected with Salmonella pullorum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animal Management
4.2. Serum Plate Agglutination Test
4.3. PCR Experiment
4.4. mRNA-Seq of Cecal Tissues and Alternative Splicing Analysis
4.5. DNA Extraction and Metagenomic Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DEASs | Differentially expressed alternative splicings |
| P group | positive group |
| N group | negative group |
| AS | Alternative splicing |
References
- Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Bao, H. Identification of candidate genes associated with slaughter traits in F2 chicken population using genome-wide association study. Anim. Genet. 2021, 52, 532–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, S.L.; Johnson, T.J.; Ricke, S.C.; Nayak, R.; Danzeisen, J. Salmonella pathogenicity and host adaptation in chicken-associated serovars. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 582–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Nie, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lv, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Jia, Y.; Ban, L.; et al. A genome-wide association study explores the genetic determinism of host resistance to Salmonella pullorum infection in chickens. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2019, 51, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Hu, X.; Mi, J.; Hu, H.; Wang, H.; Qi, X.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Ligilactobacillus salivarius XP132 with antibacterial and immunomodulatory activities inhibits horizontal and vertical transmission of Salmonella pullorum in chickens. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qiang, B.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Jiao, X. Loss and Gain in the Evolution of the Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Biovar Pullorum Genome. mSphere 2019, 4, e00627-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabeta, T.; Tolosa, T.; Duchateau, L.; Van Immerseel, F.; Antonissen, G. Prevalence and serotype of poultry salmonellosis in Africa: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Avian Pathol. 2024, 53, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivaprasad, H.L.; Timoney, J.F.; Morales, S.; Lucio, B.; Baker, R.C. Pathogenesis of Salmonella enteritidis infection in laying chickens. I. Studies on egg transmission, clinical signs, fecal shedding, and serologic responses. Avian Dis. 1990, 34, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Wang, X.; Qi, X.; Cao, C.; Yang, K.; Gu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Q. Identification of the gut microbiota affecting Salmonella pullorum and their relationship with reproductive performance in hens. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, S.; Jiao, X.; Barrow, P.; Pan, Z.; Chen, X. Virulence determinants of Salmonella Gallinarum biovar Pullorum identified by PCR signature-tagged mutagenesis and the spiC mutant as a candidate live attenuated vaccine. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.C.; Bounous, D.I.; Lee, M.D. Early events in the pathogenesis of avian salmonellosis. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, L.; Kaiser, P.; Barrow, P.; Jones, M.A.; Johnston, C.; Wigley, P. The immunobiology of avian systemic salmonellosis. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 128, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Nie, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shao, P.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Jiao, W.; et al. Evaluation of genetic resistance to Salmonella pullorum in three chicken lines. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Q.; Wang, F.; Jin, J.; Zhou, Y.G.; Ran, J.S.; Feng, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.P. MyD88 Polymorphisms and Association with Susceptibility to Salmonella pullorum. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 692973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setta, A.; Barrow, P.A.; Kaiser, P.; Jones, M.A. Immune dynamics following infection of avian macrophages and epithelial cells with typhoidal and non-typhoidal Salmonella enterica serovars; bacterial invasion and persistence, nitric oxide and oxygen production, differential host gene expression, NF-kappaB signalling and cell cytotoxicity. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 146, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikom, D.; Zheng, S. Alternative splicing in neurodegenerative disease and the promise of RNA therapies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 24, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, P.; He, B.; Peng, X.; Tu, G.; Peng, W.; Wang, L.; Yu, F.; Wang, X. N6-Methyladenosine RNA Methylation Regulator-Related Alternative Splicing (AS) Gene Signature Predicts Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Prognosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 657087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, E.N.D.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Wong, Z.; Raja Ali, R.A. Colonic Mucosal Transcriptomic Changes in Patients with Long-Duration Ulcerative Colitis Revealed Colitis-Associated Cancer Pathways. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, J.; Li, N.; Li, M.; Zhu, C.; Xie, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Analysis of SLC genes alternative splicing identifies the SLC7A6 RI isoform as a therapeutic target for colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2024, 116, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, K.; de Vries Reilingh, G.; Kemp, B.; Lammers, A. Development of ileal cytokine and immunoglobulin expression levels in response to early feeding in broilers and layers. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigley, P. Salmonella enterica in the Chicken: How it has Helped Our Understanding of Immunology in a Non-Biomedical Model Species. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhai, Z.; Zhao, W.; Ding, J.; Dai, R.; Sun, T.; Meng, H. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection Induced the Unbalance of Gut Microbiota in Piglets. Curr. Microbiol. 2015, 71, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science 2012, 336, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dheer, R.; Davies, J.M.; Quintero, M.A.; Damas, O.M.; Deshpande, A.R.; Kerman, D.H.; Sawyer, W.P.; Pignac-Kobinger, J.; Ban, Y.; Fernandez, I.; et al. Microbial Signatures and Innate Immune Gene Expression in Lamina Propria Phagocytes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 9, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducatelle, R.; Goossens, E.; De Meyer, F.; Eeckhaut, V.; Antonissen, G.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F. Biomarkers for monitoring intestinal health in poultry: Present status and future perspectives. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, M.H.; Arsenault, R.J. Editorial: Gut Health: The New Paradigm in Food Animal Production. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Kumar, S.; Oakley, B.; Kim, W.K. Chicken Gut Microbiota: Importance and Detection Technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Jia, H.J.; Zhang, H.J.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.Y.; Wu, S.G.; Qi, G.H. Supplemental Plant Extracts From Flos lonicerae in Combination With Baikal skullcap Attenuate Intestinal Disruption and Modulate Gut Microbiota in Laying Hens Challenged by Salmonella pullorum. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Q.; Dore, J.; Emmanuel, A.; Guarner, F.; Quigley, E.M. Gut microbiota and gastrointestinal health: Current concepts and future directions. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, X.; Yang, Y.; Meng, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Geng, S.; Jiao, X.; Pan, Z. Safety and protective efficacy of Salmonella pullorum spiC and rfaH deletion rough mutant as a live attenuated DIVA vaccine candidate. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Priyamvada, S.; Ge, Y.; Jayawardena, D.; Singhal, M.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Chatterjee, I.; Dayal, A.; Patel, M.; Zadeh, K.; et al. A Novel Role of SLC26A3 in the Maintenance of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Integrity. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1240–1255.e1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, M.; Jiang, M.; Salari, A.; Xiu, R.; Alper, S.L.; Seidler, U.E. Reduced surface pH and upregulated AE2 anion exchange in SLC26A3-deleted polarized intestinal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2024, 326, C829–C842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawardena, D.; Priyamvada, S.; Kageyama, T.; White, Z.; Kumar, A.; Griggs, T.F.; Majumder, A.; Akram, R.; Anbazhagan, A.N.; Sano, T.; et al. Loss of SLC26A3 Results in Colonic Mucosal Immune Dysregulation via Epithelial-Immune Cell Crosstalk. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 903–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, A.; Singh, A.K.; Riederer, B.; Yang, I.; Tan, X.; di Stefano, G.; Tan, Q.; Xiao, F.; Xia, W.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Slc26a3 deletion alters pH-microclimate, mucin biosynthesis, microbiome composition and increases the TNFalpha expression in murine colon. Acta Physiol. 2020, 230, e13498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Zhu, S.; An, Z.; You, B.; Li, Z.; Yao, Y.; Nair, V.; Liao, M. Dissection of key factors correlating with H5N1 avian influenza virus driven inflammatory lung injury of chicken identified by single-cell analysis. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Hou, M.; Jiang, H.; Shen, X.; Xue, M.; Shao, Y.; Wang, L.; He, Q.; Zheng, L.; Tu, J.; et al. Hcp2a of type VI secretion system contributes to IL8 and IL1beta expression of chicken tracheal epithelium by affecting APEC colonization. Res. Vet. Sci. 2020, 132, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, T.H.; Hong, Y.; Truong, A.D.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Song, K.D.; Cha, J.; Dang, H.V.; Tran, H.T.T.; Lillehoj, H.S.; et al. Cytokine-cytokine receptor interactions in the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus-infected lungs of genetically disparate Ri chicken lines. Anim. Biosci. 2022, 35, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckmann, L.; Kagnoff, M.F. Cytokines in host defense against Salmonella. Microbes Infect. 2001, 3, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaggerty, C.L.; Kogut, M.H.; Ferro, P.J.; Rothwell, L.; Pevzner, I.Y.; Kaiser, P. Differential cytokine mRNA expression in heterophils isolated from Salmonella-resistant and -susceptible chickens. Immunology 2004, 113, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vad, O.B.; Angeli, E.; Liss, M.; Ahlberg, G.; Andreasen, L.; Christophersen, I.E.; Hansen, C.C.; Moller, S.; Hellsten, Y.; Haunsoe, S.; et al. Loss of Cardiac Splicing Regulator RBM20 Is Associated With Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation. JACC Basic. Transl. Sci. 2024, 9, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denkena, J.; Zaisser, A.; Merz, B.; Klinger, B.; Kuhl, D.; Bluthgen, N.; Hermey, G. Neuronal activity regulates alternative exon usage. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lee, G.C.; Nakagaki-Silva, E.; Huang, Y.; Peacey, M.; Partridge, R.; Gooding, C.; Smith, C.W.J. Cell-type specific regulator RBPMS switches alternative splicing via higher-order oligomerization and heterotypic interactions with other splicing regulators. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 9961–9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardina, P.J.; Clark, T.A.; Shimada, B.; Staples, M.K.; Yang, Q.; Veitch, J.; Schweitzer, A.; Awad, T.; Sugnet, C.; Dee, S.; et al. Alternative splicing and differential gene expression in colon cancer detected by a whole genome exon array. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawley, T.D.; Bouley, D.M.; Hoy, Y.E.; Gerke, C.; Relman, D.A.; Monack, D.M. Host transmission of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is controlled by virulence factors and indigenous intestinal microbiota. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, B.; Robbiani, R.; Walker, A.W.; Westendorf, A.M.; Barthel, M.; Kremer, M.; Chaffron, S.; Macpherson, A.J.; Buer, J.; Parkhill, J.; et al. Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium exploits inflammation to compete with the intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, 2177–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiennimitr, P.; Winter, S.E.; Baumler, A.J. Salmonella, the host and its microbiota. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Liang, L.; Cui, K.; Li, P.; Hao, G.; Sun, S. Salmonella phage CKT1 significantly relieves the body weight loss of chicks by normalizing the abnormal intestinal microbiome caused by hypervirulent Salmonella pullorum. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhou, H.; Luo, L.; Xiao, L.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, K.; He, C.; Han, C.; et al. Heritable Gut Microbiome Associated with Salmonella enterica Serovar Pullorum Infection in Chickens. mSystems 2021, 6, e01192-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Mao, X.; Cai, T.; Luo, J.; Wei, L. KOBAS server: A web-based platform for automated annotation and pathway identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W720–W724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
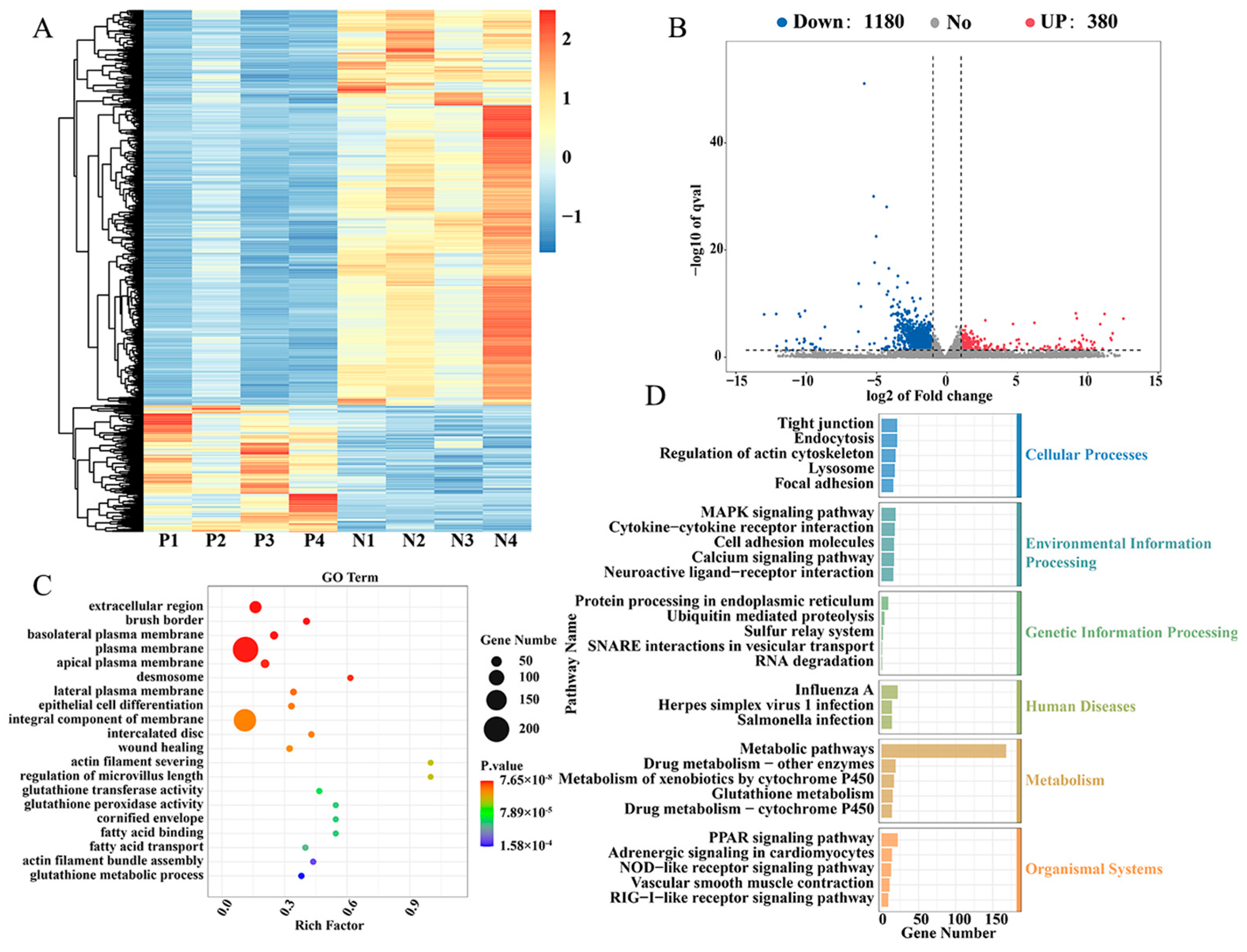
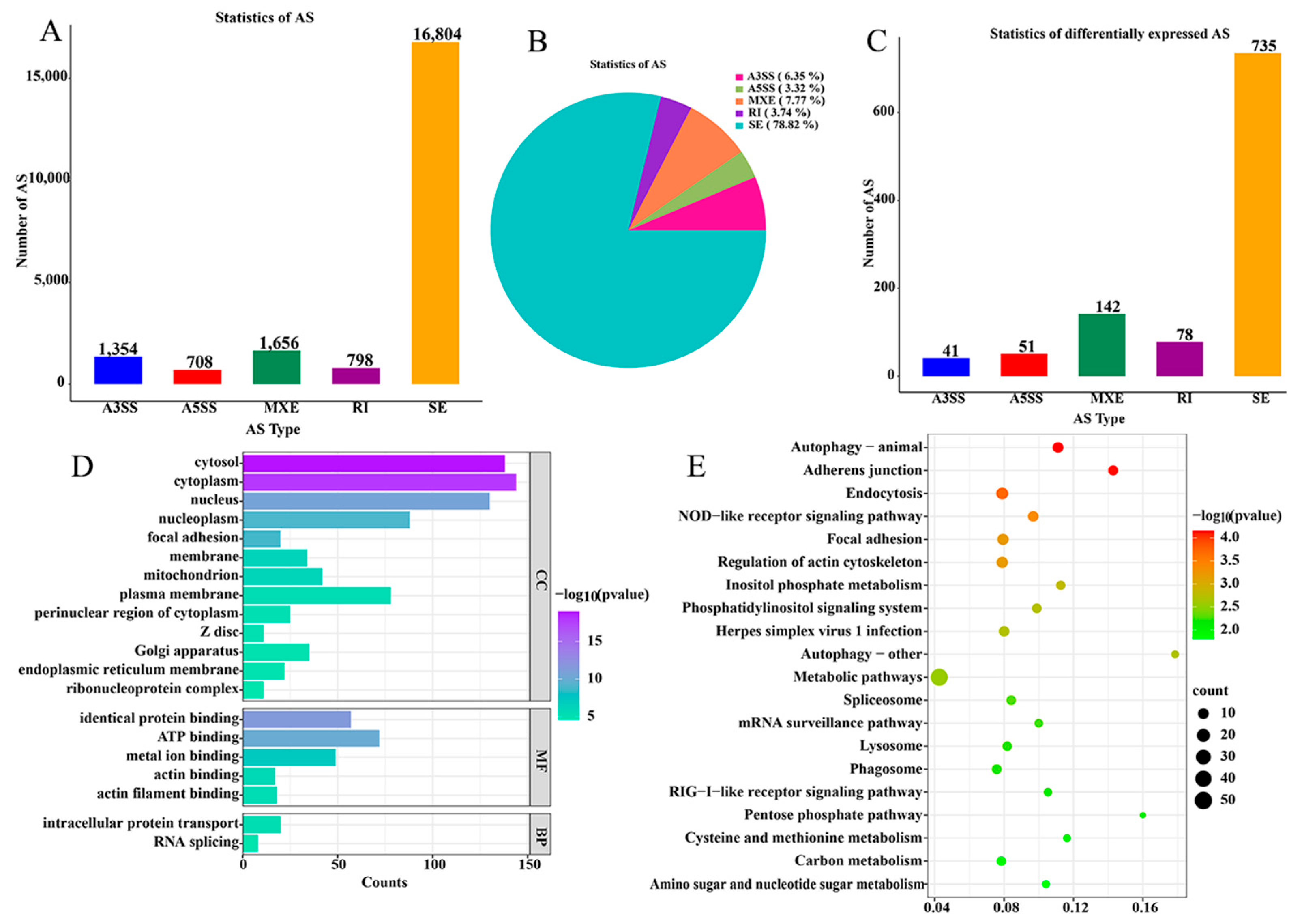
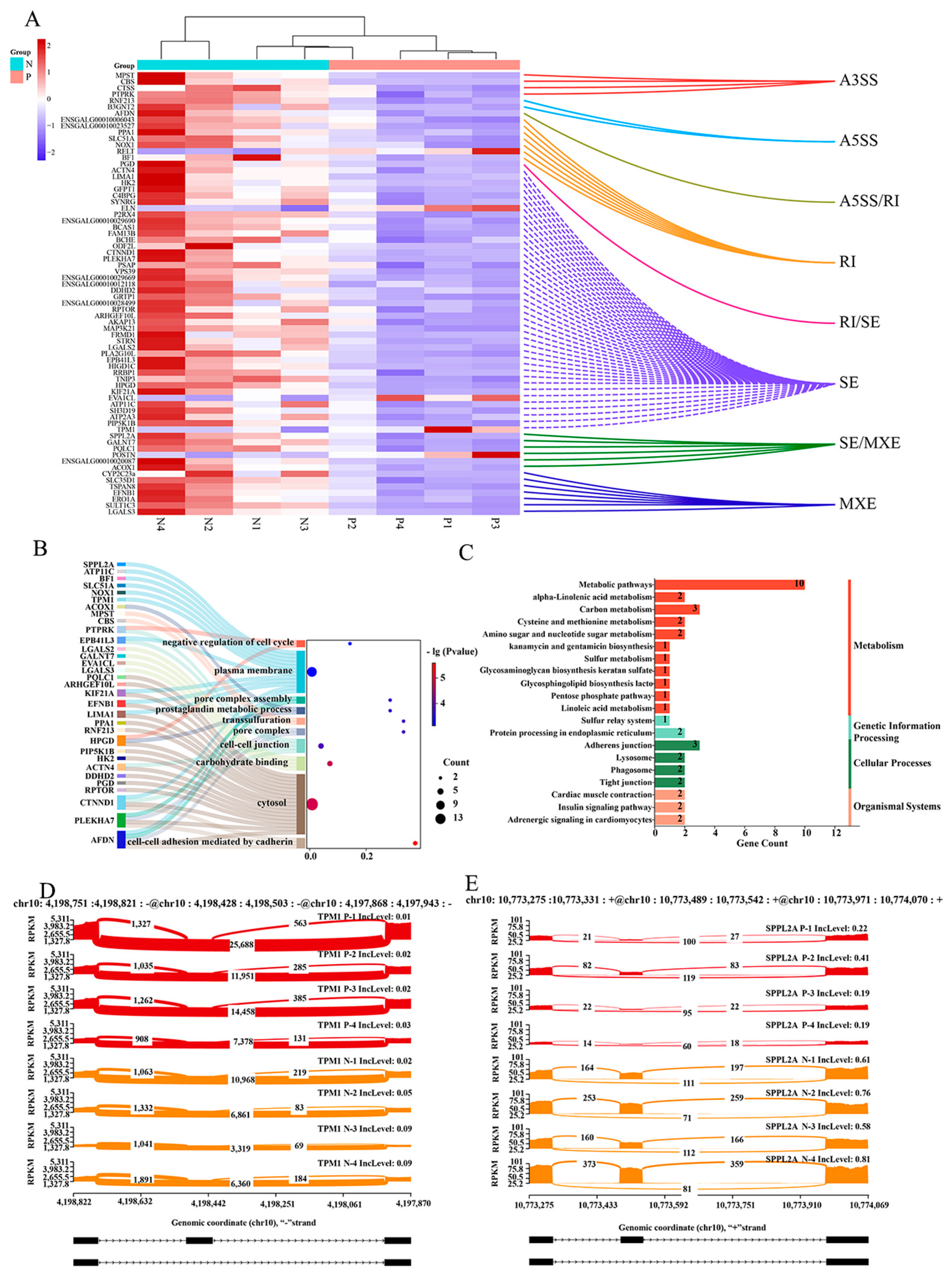

| Gene Name | N Expression | P Expression | log2(FC) (N/P) | Up Down |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQP8 | 8631 | 146.75 | −5.875936928 | down |
| ENSGALG00010017812 | 10,723.5 | 298 | −5.212645245 | down |
| RSAD2 | 2291.75 | 118 | −4.288236383 | down |
| ENSGALG00010001707 | 45,105.25 | 1414.75 | −5.028950395 | down |
| CBS | 94,320.75 | 2736.25 | −5.147365626 | down |
| ENSGALG00010021763 | 4732.75 | 269 | −4.133430962 | down |
| ENSGALG00010005012 | 2873.25 | 257.5 | −3.485079358 | down |
| SCNN1A | 4646.25 | 674.25 | −2.809438512 | down |
| DDX60 | 5710 | 206 | −4.830147732 | down |
| ENSGALG00010017719 | 517 | 7.5 | −6.278950066 | down |
| ANPEP | 20,453.25 | 1817.75 | −3.531739751 | down |
| SLC26A3 | 1882 | 104.75 | −4.179327946 | down |
| IFI6 | 18,342 | 986.5 | −4.269812813 | down |
| EDN2 | 532.75 | 98 | −2.453229646 | down |
| COBL | 1703.5 | 463.5 | −1.897709004 | down |
| SLC30A10 | 1501.25 | 111.75 | −3.790121129 | down |
| EPSTI1 | 2068 | 406.25 | −2.365929024 | down |
| SERPINB1 | 3981.75 | 401.5 | −3.35058651 | down |
| LAMC2 | 1558.75 | 138 | −3.512285305 | down |
| KRT40 | 22,899.5 | 1603 | −3.858303875 | down |
| Sample | Original Data (G) | Valid Data (G) | Valid Data Ratio (%) | Q20% | Q30% | GC% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 6.53 | 5.45 | 89.52 | 98.56 | 95.52 | 52.21 |
| P2 | 6.35 | 5.32 | 90.04 | 98.50 | 95.43 | 51.18 |
| P3 | 6.48 | 5.29 | 88.33 | 98.49 | 95.43 | 50.28 |
| P4 | 6.34 | 5.16 | 88.02 | 98.51 | 95.49 | 52.07 |
| N1 | 5.31 | 4.26 | 87.14 | 98.64 | 95.81 | 52.06 |
| N2 | 6.21 | 4.72 | 83.50 | 98.59 | 95.70 | 51.47 |
| N3 | 6.44 | 5.05 | 85.86 | 98.58 | 95.71 | 51.62 |
| N4 | 6.49 | 5.11 | 85.72 | 98.69 | 95.88 | 51.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chao, X.; Fan, Z.; Wu, J.; Ye, C.; Wang, X.; Li, R.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.; Fang, C.; Luo, Q. Application of mRNA-Seq and Metagenomic Sequencing to Study Salmonella pullorum Infections in Chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041448
Chao X, Fan Z, Wu J, Ye C, Wang X, Li R, Chen S, Zhang X, Fang C, Luo Q. Application of mRNA-Seq and Metagenomic Sequencing to Study Salmonella pullorum Infections in Chickens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(4):1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041448
Chicago/Turabian StyleChao, Xiaohuan, Zhexia Fan, Jiongwen Wu, Chutian Ye, Xiaomeng Wang, Ruina Li, Shuya Chen, Xiquan Zhang, Cheng Fang, and Qingbin Luo. 2025. "Application of mRNA-Seq and Metagenomic Sequencing to Study Salmonella pullorum Infections in Chickens" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 4: 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041448
APA StyleChao, X., Fan, Z., Wu, J., Ye, C., Wang, X., Li, R., Chen, S., Zhang, X., Fang, C., & Luo, Q. (2025). Application of mRNA-Seq and Metagenomic Sequencing to Study Salmonella pullorum Infections in Chickens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(4), 1448. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26041448







