Phylogenetic Relationship and Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Cuckoo Species Clamator coromandus (Aves: Cuculidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Genome Content and Organization
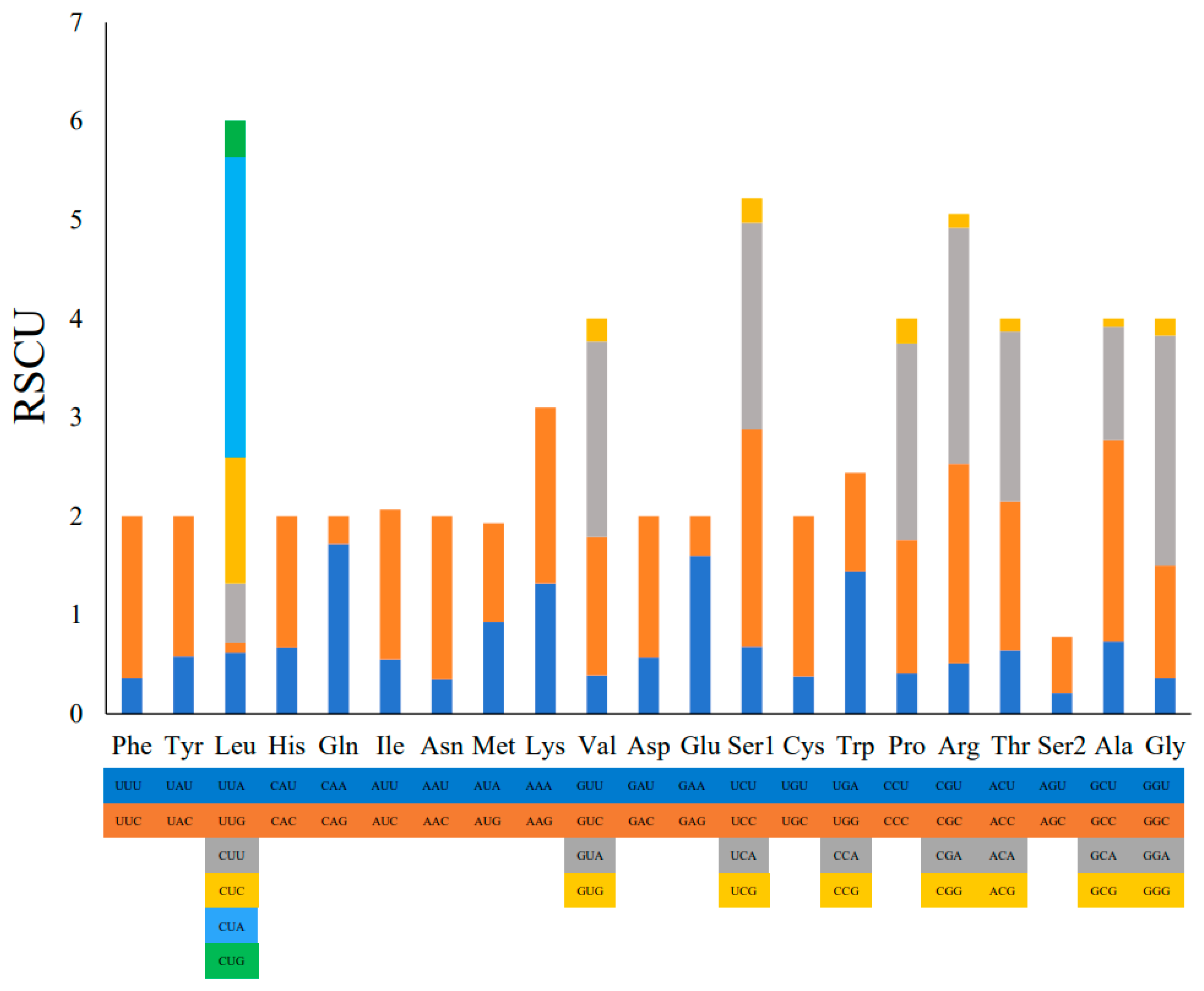
2.2. Protein-Coding Genes and Codon Usage Patterns
2.3. Transfer and Ribosomal RNA Genes
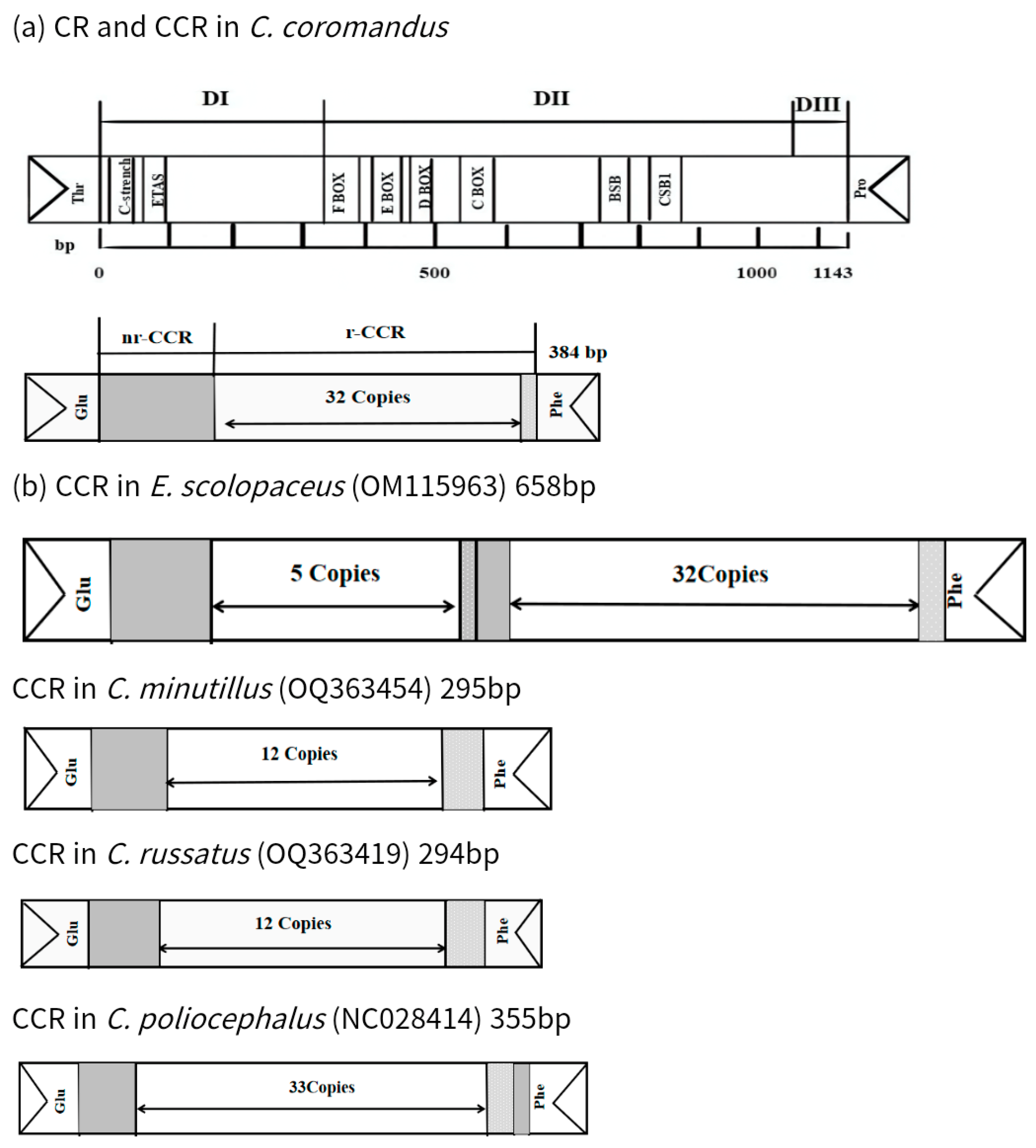
2.4. Noncoding Regions
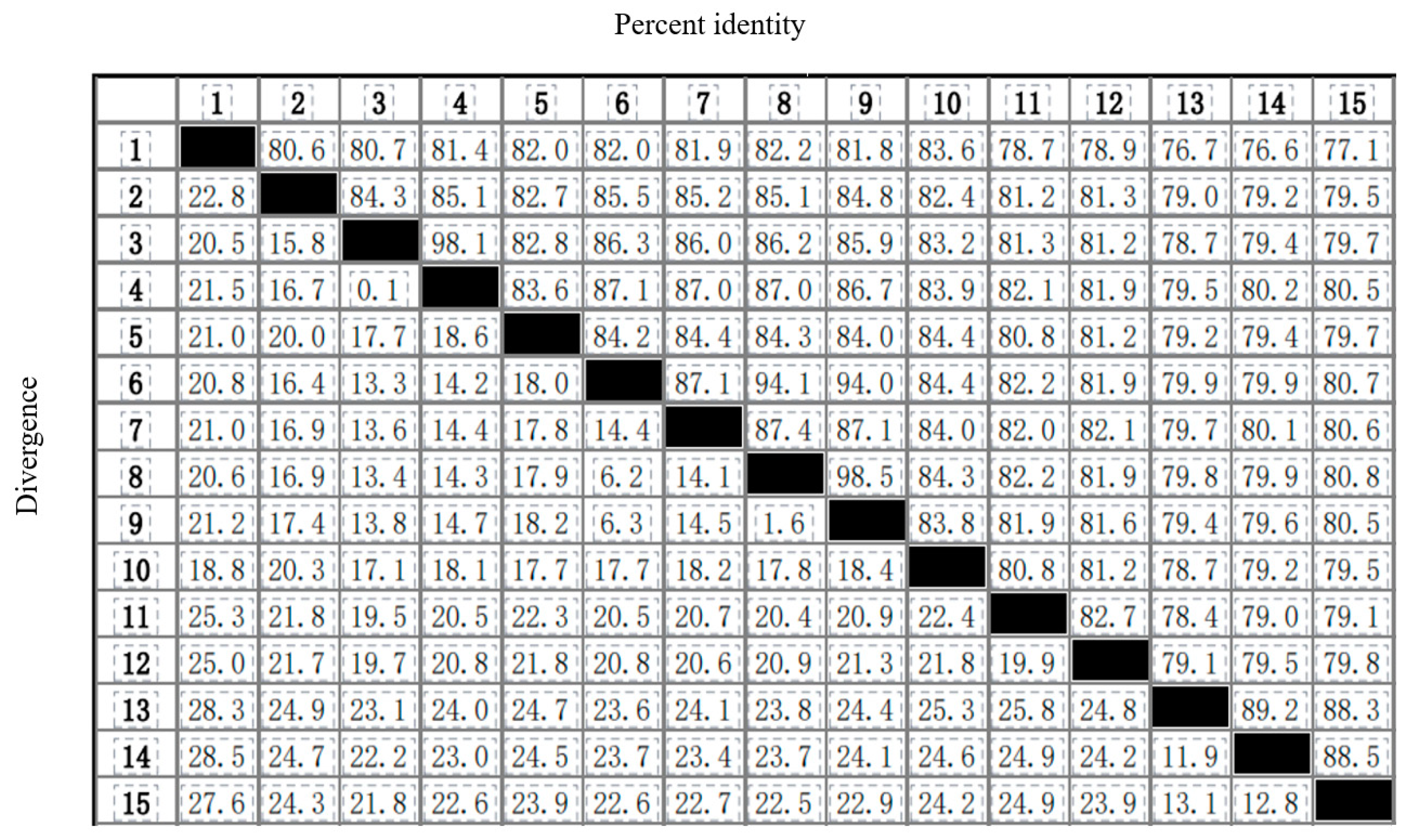
2.5. Phylogenetic Relationships
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Genomic DNA Extraction
4.2. Mitochondrial DNA Amplification and Sequencing
4.3. Assembly, Annotation, and Analysis of the Mitochondrial Genome
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Billerman, S.M.; Keeney, B.K.; Rodewald, P.G.; Schulenberg, T.S. Birds of the World; Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2022; Database. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Shan, C.; Chen, D.; Hu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, B.; Liang, W. “Isolation by Gentes with Asymmetric Migration” shapes the genetic structure of the common cuckoo in China. Integr. Zool. 2025, 20, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Arai, E. Differential visual ornamentation between brood parasitic and parental cuckoos. J. Evol. Biol. 2018, 31, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erritzøe, J.; Mann, C.F.; Brammer, F.; Fuller, R.A. Cuckoos of the World; Christopher Helm: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- del Hoyo, J.; Elliott, A.; Christie, D. Handbook of the Birds of the World, Vol. 10: Cuckoo-Shrikes to Thrushes; Dickinson, E.C., Dekker, R., Eds.; Lynx Edicions: Barcelona, Spain, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Liang, W.; Antonov, A.; Cai, Y.; Stokke, B.G.; Fossøy, F.; Moksnes, A.; Røskaft, E. Diversity of parasitic cuckoos and their hosts in China. Chin. Birds 2012, 3, 9–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.M. A Checklist on the Classification and Distribution of the Birds of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y. Attribution index for changes in migratory bird distributions: The role of climate change over the past 50 years in China. Ecol. Inform. 2016, 31, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Cheong, E.; Park, J.Y.; Hur, W.-H.; Choi, Y.-S.; Nam, H.-K.; Kim, D.-W. Complete mitochondrial genome of Asian koel Eudynamys scolopaceus (Aves: Cuculiformes) from South Korea. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2022, 7, 1893–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Manfredi, G.; Hirano, M.; Schon, E.A. Maintenance of human rearranged mitochondrial DNAs in long-term cultured transmitochondrial cell lines. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 2349–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, S.; Tang, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Hamasaki, N.; Schon, E.A.; Kang, D. Both heavy strand replication origins are active in partially duplicated human mitochondrial DNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Xu, Y. Evolutionary progression of mitochondrial gene rearrangements and phylogenetic relationships in Strigidae (Strigiformes). Gene 2018, 674, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, J.R.; Wright, T.F. Rearrangement and evolution of mitochondrial genomes in parrots. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 94, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liang, B.; Huo, J.; Liang, W. Complete mitochondrial genome and the phylogenetic position of the Lesser Cuckoo, Cuculus poliocephalus (Aves: Cuculiformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2015, 27, 4409–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Liu, H.; Cai, Y.-S.; Hou, W.; Dou, L.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Li, J. Complete mitochondrial genome and the phylogenetic position of the common cuckoo, Cuculus canorus bakeri (Aves: Cuculiformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 2802–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindell, D.P.; Sorenson, M.D.; Dimcheff, D.E. Multiple independent origins of mitochondrial gene order in birds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 10693–10697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhard, J.R.; Wright, T.F.; Bermingham, E. Duplication and concerted evolution of the mitochondrial control region in the parrot genus Amazona. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, C.L.; Double, M.C.; Trueman, J.W.; Robinson, A.; Cockburn, A. An unusual source of apparent mitochondrial heteroplasmy: Duplicate mitochondrial control regions in Thalassarche albatrosses. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 3605–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skujina, I.; McMahon, R.; Lenis, V.P.E.; Gkoutos, G.V.; Hegarty, M. Duplication of the mitochondrial control region is associated with increased longevity in birds. Aging 2016, 8, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, F.K.; Benesh, M.K.; Vandergon, A.J.; Lanyon, S.M. Contrasting evolutionary dynamics and information content of the avian mitochondrial control region and ND2 gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, G.C.; Kardailsky, O.; Kimball, R.T.; Braun, E.L.; Penny, D. Mitochondrial genomes and avian phylogeny: Complex characters and resolvability without explosive radiations. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, A.; Léger, N.; Deutsch, J. Evidence for multiple reversals of asymmetric mutational constraints during the evolution of the mitochondrial genome of Metazoa, and consequences for phylogenetic inferences. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Tang, C.; Li, J.; Huang, Q.; Nong, J.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Q. Complete mitogenome of the Common Koel Eudynamys scolopaceus Linnaeus 1758 (Aves: Cuculidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2022, 7, 831–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xu, J.; Dou, L.; Zheng, A.; Qiao, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Indian Cuckoo Cuculus micropterus (Aves: Cuculiformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2021, 6, 2556–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curole, J.P.; Kocher, T.D. Mitogenomics: Digging deeper with complete mitochondrial genomes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1999, 14, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathy, S.T.; Udayasuriyan, V.; Bhadana, V. Codon usage bias. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-F.; Nie, L.-W.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.-L. The complete mitochondrial genome of the large-headed frog, Limnonectes bannaensis (Amphibia: Anura), and a novel gene organization in the vertebrate mtDNA. Gene 2009, 442, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, D.R. Animal Mitochondrial DNA: Structure and evolution. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1992, 141, 173–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.L. Mitochondrial genome organization and vertebrate phylogenetics. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2000, 23, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, S.; Cedergren, R. Structural compensation in atypical mitochondrial tRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 1994, 1, 507–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrov, D.V.; Brown, W.M.; Boore, J.L. A novel type of RNA editing occurs in the mitochondrial tRNAs of the centipede Lithobius forficatus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13738–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutell, R.R.; Lee, J.C.; Cannone, J.J. The accuracy of ribosomal RNA comparative structure models. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2002, 12, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boore, J.L. Animal mitochondrial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1767–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruokonen, M.; Kvist, L. Structure and evolution of the avian mitochondrial control region. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2002, 23, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.J.; Marshall, H.D. Mitochondrial control region sequences as tools for understanding evolution. Avian Mol. Evol. S. 1997, 51–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccone, C.; Pesole, G.; Sbisá, E. The main regulatory region of mammalian mitochondrial DNA: Structure-function model and evolutionary pattern. J. Mol. Evol. 1991, 33, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.S.; Lee, S.E.; Jeong, H.W.; Ha, J.H. The complete nucleotide sequence of the domestic dog (Canis familiaris) mitochondrial genome. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 1998, 10, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dou, H.; Yang, X.; Zhao, C.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the Sparrowhawk (Accipiter nisus). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2014, 27, 1648–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, R.B. Bird Families of the World: Cuckoos; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Morelli, F.; Benedetti, Y.; Møller, A.P.; Liang, W.; Carrascal, L.M. Cuckoos host range is associated positively with distribution range and negatively with evolutionary uniqueness. J. Anim. Ecol. 2018, 87, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, N.D.; Feldstein, T.; Shenkar, N.; Botero-Castro, F.; Griggio, F.; Mastrototaro, F.; Delsuc, F.; Douzery, E.J.P.; Gissi, C.; Huchon, D. Deep sequencing of mixed total DNA without barcodes allows efficient assembly of highly plastic ascidian mitochondrial genomes. Genome Eiol. Evol. 2013, 5, 1185–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, L.V.; Lubkovskaia, R.S.; Bulyuk, V.N. Migration Routes and Wintering Grounds of Common Cuckoos (Cuculus canorus, Cuculiformes, Cuculidae) from the Southeastern Part of the Baltic Region (Based on Satellite Telemetry). Biol. Bull. 2022, 49, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemoes, M.; Strandberg, R.; Klaassen, R.H.G.; Tøttrup, A.P.; Vardanis, Y.; Howey, P.W.; Thorup, K.; Wikelski, M.; Alerstam, T. Narrow-front loop migration in a population of the common cuckoo Cuculus canorus, as revealed by satellite telemetry. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwin, C. On the Origins of Species by Means of Natural Selection; Murray: London, UK, 1859; Volume 247. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, R.B.; Kirwan, G.M. Chestnut-winged Cuckoo (Clamator coromandus), Version 1.0. In Birds of the World; del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D.A., de Juana, E., Eds.; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Shi, R.; Li, W.; Li, G. Grazing pressure affects offspring sex ratio in a socially monogamous passerine on the Tibet Plateau. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, jav-01660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, T.G. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Bioinform. Methods Protoc. 1999, 132, 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumazawa, Y.; Nishida, M. Sequence evolution of mitochondrial tRNA genes and deep-branch animal phylogenetics. J. Mol. Evol. 1993, 37, 380–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothard, P.; Wishart, D.S. Circular genome visualization and exploration using CGView. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, N.T.; Kocher, T.D. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 41, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, H.D.; Baker, A.J. Structural conservation and variation in the mitochondrial control region of fringilline finches (Fringilla spp.) and the greenfinch (Carduelis chloris). Mol. Biol. Evol. 1997, 14, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randi, E.; Lucchini, V. Organization and evolution of the mitochondrial DNA control region in the avian genus Alectoris. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 47, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wu, X.; Yan, P.; Su, X.; Yang, B. Complete mitochondrial genome of Otis tarda (Gruiformes: Otididae) and phylogeny of Gruiformes inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 37, 3057–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, J.; Cong, J.; Guo, C.; Hou, J.; Zhen, J.; Shi, B. Complete mitochondrial genome of the greater Coucal, Centropus sinensis (Aves: Cuculiformes). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2015, 28, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmore, N.E.; Grealy, A.; Noh, H.-J.; Medina, I.; Skeels, A.; Grant, J.; Murray, K.D.; Kilner, R.M.; Holleley, C.E. Coevolution with hosts underpins speciation in brood-parasitic cuckoos. Science 2024, 384, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetz, W.; Thomas, G.H.; Joy, J.B.; Hartmann, K.; Mooers, A.O. The global diversity of birds in space and time. Nature 2012, 491, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubolini, D.; Liker, A.; Garamszegi, L.Z.; Møller, A.P.; Saino, N. Using the BirdTree.org website to obtain robust phylogenies for avian comparative studies: A primer. Curr. Zool. 2015, 61, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimin, A.; Zimin, S.V.; Grismer, L.L.; Bauer, A.M.; Chapple, D.G.; Dembitzer, J.; Roll, U.; Meiri, S. Microhabitat and adhesive toepads shape gecko limb morphology. Integr. Zool. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, O.; Davies, N.B. The evolution of cuckoo parasitism: A comparative analysis. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R Version 4.3.3 (Angel Food Cake); R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2024; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Revell, L.J. Phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2011, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


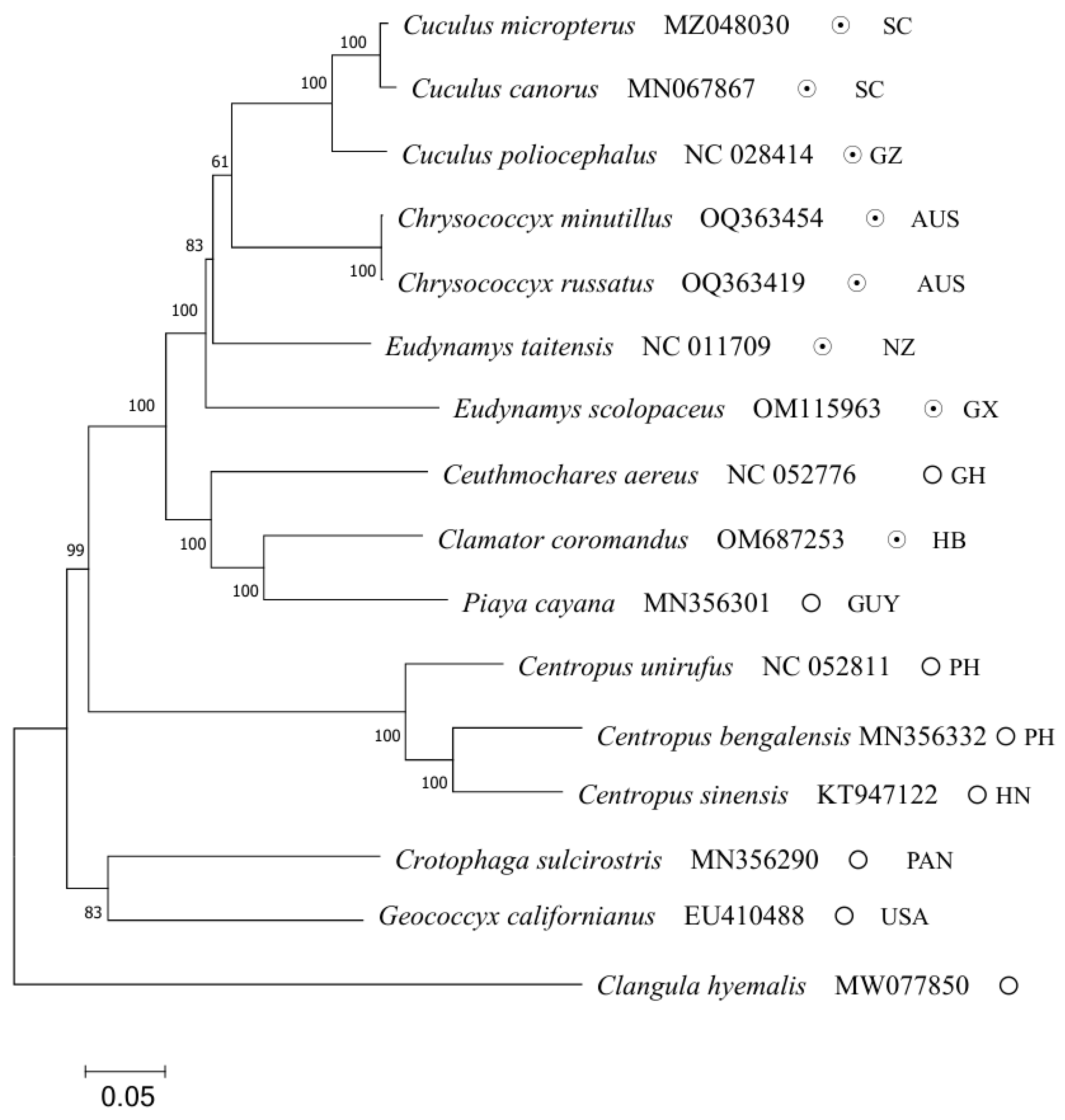


| Species Number | Scientific Name | GenBank Number | Reproductive Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Clamator coromandus | OM687253 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 2 | Eudynamys scolopaceus | OM115963 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 3 | Chrysococcyx minutillus | OQ363454 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 4 | Chrysococcyx russatus | OQ363419 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 5 | Ceuthmochares aereus | NC052776 | parental care |
| 6 | Cuculus poliocephalus | NC028414 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 7 | Eudynamys taitensis | NC011709 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 8 | Cuculus micropterus | MZ048030 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 9 | Cuculus canorus | MN067867 | interspecific brood parasitism |
| 10 | Piaya cayana | MN356301 | parental care |
| 11 | Crotophaga sulcirostris * | MN356290 | parental care |
| 12 | Geococcyx californianus | EU410488 | parental care |
| 13 | Centropus bengalensis | MN356332 | parental care |
| 14 | Centropus sinensis | KT947122 | parental care |
| 15 | Centropus unirufus | NC052811 | parental care |
| Gene | Position | Sizes | Codon | Intergenic Nucleotide b | Strand c | A + T% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From | To | Nucleotide (bp) | Start | Stop a | ||||
| tRNA-Phe | 1 | 70 | 70 | H | 45.7 | |||
| 12S rRNA | 70 | 1044 | 975 | −1 | H | 53.1 | ||
| tRNA-Val | 1044 | 1115 | 72 | −1 | H | 58.3 | ||
| 16S rRNA | 1115 | 2710 | 1596 | −1 | H | 56.5 | ||
| tRNA-Leu | 2710 | 2783 | 74 | −1 | H | 48.7 | ||
| ND1 | 2795 | 3772 | 978 | ATG | AGA | 11 | H | 54.8 |
| tRNA-Ile | 3788 | 3858 | 71 | 15 | H | 57.8 | ||
| tRNA-Gln | 3871 | 3941 | 71 | 12 | L | 67.6 | ||
| tRNA-Met | 3941 | 4009 | 69 | −1 | H | 53.6 | ||
| ND2 | 4010 | 5050 | 1041 | ATG | TAG | 0 | H | 57.5 |
| tRNA-Trp | 5049 | 5118 | 70 | −2 | H | 62.9 | ||
| tRNA-Ala | 5120 | 5188 | 69 | 1 | L | 56.5 | ||
| tRNA-Asn | 5192 | 5264 | 73 | 3 | L | 46.6 | ||
| tRNA-Cys | 5269 | 5333 | 65 | 4 | L | 56.9 | ||
| tRNA-Tyr | 5334 | 5403 | 70 | 0 | L | 52.9 | ||
| COXⅠ | 5405 | 6955 | 1551 | ATG | AGG | 1 | H | 52.9 |
| tRNA-Ser | 6947 | 7020 | 74 | −9 | L | 54.1 | ||
| tRNA-Asp | 7023 | 7091 | 69 | 2 | H | 59.4 | ||
| COXⅡ | 7093 | 7776 | 684 | ATG | TAA | 1 | H | 53.1 |
| tRNA-Lys | 7781 | 7848 | 68 | 4 | H | 60.3 | ||
| ATP8 | 7850 | 8017 | 168 | ATG | TAA | 1 | H | 58.9 |
| ATP6 | 8008 | 8691 | 684 | ATG | TAA | −10 | H | 54.8 |
| COXⅢ | 8691 | 9474 | 784 | ATG | T- | −1 | H | 54.2 |
| tRNA-Gly | 9475 | 9543 | 69 | 0 | H | 62.3 | ||
| ND3 | 9544 | 9895 | 352 | ATT | TAA | 0 | H | 56.0 |
| tRNA-Arg | 9900 | 9968 | 69 | 4 | H | 65.2 | ||
| ND4L | 9970 | 10,266 | 297 | ATG | TAA | 1 | H | 53.2 |
| ND4 | 10,260 | 11,637 | 1378 | ATG | T- | −7 | H | 55.5 |
| tRNA-His | 11,638 | 11,707 | 70 | 0 | H | 65.7 | ||
| tRNA-Ser | 11,708 | 11,773 | 66 | 0 | H | 51.5 | ||
| tRNA-Leu | 11,773 | 11,843 | 71 | −1 | H | 59.2 | ||
| ND5 | 11,844 | 13,652 | 1809 | ATG | AGA | 0 | H | 56.7 |
| Cytb | 13,661 | 14,803 | 1143 | ATG | TAA | 8 | H | 55.0 |
| tRNA-Thr | 14,807 | 14,876 | 70 | 3 | H | 62.9 | ||
| Control region | 14,877 | 16,019 | 1143 | 0 | H | 59.8 | ||
| tRNA-Pro | 16,020 | 16,089 | 70 | 0 | L | 64.3 | ||
| ND6 | 16,101 | 16,622 | 522 | CTA | T- | 11 | L | 54.0 |
| tRNA-Glu | 16,627 | 16,698 | 72 | 4 | L | 56.9 | ||
| Pseudo-control region | 16,699 | 17,082 | 384 | 0 | H | 67.5 | ||
| M (QL, QU) | Z | P | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13PCGs | AT-skews | interspecific brood parasitism | 0.100 (0.090~0.123) | −2.639 | 0.008 |
| parental care | 0.070 (0.050~0.080) | ||||
| GC-skews | interspecific brood parasitism | −0.405 (−0.425~−0.400) | −0.945 | 0.344 | |
| parental care | −0.400 (−0.420~−0.370) | ||||
| overall | AT-skews | interspecific brood parasitism | 0.160 (0.150~0.175) | −2.598 | 0.009 |
| parental care | 0.140 (0.110~0.140) | ||||
| GC-skews | interspecific brood parasitism | −0.400 (−0.410~−0.393) | −1.413 | 0.158 | |
| parental care | −0.390 (−0.410~−0.370) |
| Codon | Count | RSCU | % | Codon | Count | RSCU | % | Codon | Count | RSCU | % | Codon | Count | RSCU | % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UUU (F) | 34.0 | 0.36 | 0.92 | UCU (S) | 36.0 | 0.68 | 0.97 | UAU (Y) | 44.0 | 0.58 | 1.19 | UGU (C) | 5.0 | 0.38 | 0.14 |
| UUC (F) | 155.0 | 1.64 | 4.19 | UCC (S) | 116.0 | 2.20 | 3.14 | UAC (Y) | 107.0 | 1.42 | 2.90 | UGC (C) | 21.0 | 1.62 | 0.57 |
| UUA (L) | 55.0 | 0.62 | 1.49 | UCA (S) | 110.0 | 2.09 | 2.98 | UAA (*) | 56.0 | 0.99 | 1.52 | UGA (W) | 81.0 | 1.44 | 2.19 |
| UUG (L) | 9.0 | 0.10 | 0.24 | UCG (S) | 13.0 | 0.25 | 0.35 | UAG (*) | 32.0 | 0.57 | 0.87 | UGG (W) | 11.0 | 1.00 | 0.30 |
| CUU (L) | 53.0 | 0.60 | 1.43 | CCU (P) | 30.0 | 0.41 | 0.81 | CAU (H) | 52.0 | 0.67 | 1.41 | CGU (R) | 7.0 | 0.51 | 0.19 |
| CUC (L) | 114.0 | 1.28 | 3.08 | CCC (P) | 98.0 | 1.35 | 2.65 | CAC (H) | 103.0 | 1.33 | 2.79 | CGC (R) | 28.0 | 2.02 | 0.76 |
| CUA (L) | 270.0 | 3.03 | 7.31 | CCA (P) | 145.0 | 1.99 | 3.92 | CAA (Q) | 119.0 | 1.72 | 3.22 | CGA (R) | 33.0 | 2.39 | 0.89 |
| CUG (L) | 33.0 | 0.37 | 0.89 | CCG (P) | 18.0 | 0.25 | 0.49 | CAG (Q) | 19.0 | 0.28 | 0.51 | CGG (R) | 2.0 | 0.14 | 0.05 |
| AUU (I) | 72.0 | 0.55 | 1.95 | ACU (T) | 54.0 | 0.64 | 1.46 | AAU (N) | 29.0 | 0.35 | 0.78 | AGU (S) | 11.0 | 0.21 | 0.30 |
| AUC (I) | 199.0 | 1.52 | 5.38 | ACC (T) | 128.0 | 1.51 | 3.46 | AAC (N) | 135.0 | 1.65 | 3.65 | AGC (S) | 30.0 | 0.57 | 0.81 |
| AUA (M) | 122.0 | 0.93 | 3.30 | ACA (T) | 146.0 | 1.72 | 3.95 | AAA (K) | 99.0 | 1.78 | 2.68 | AGA (*) | 10.0 | 0.72 | 0.27 |
| AUG (M) | 24.0 | 1.00 | 0.65 | ACG (T) | 11.0 | 0.13 | 0.30 | AAG (K) | 12.0 | 0.22 | 0.32 | AGG (*) | 3.0 | 0.22 | 0.08 |
| GUU (V) | 12.0 | 0.39 | 0.32 | GCU (A) | 46.0 | 0.73 | 1.24 | GAU (D) | 19.0 | 0.57 | 0.51 | GGU (G) | 15.0 | 0.36 | 0.41 |
| GUC (V) | 43.0 | 1.40 | 1.16 | GCC (A) | 129.0 | 2.04 | 3.49 | GAC (D) | 48.0 | 1.43 | 1.30 | GGC (G) | 47.0 | 1.14 | 1.27 |
| GUA (V) | 61.0 | 1.98 | 1.65 | GCA (A) | 73.0 | 1.15 | 1.98 | GAA (E) | 76.0 | 1.60 | 2.06 | GGA (G) | 96.0 | 2.33 | 2.60 |
| GUG (V) | 7.0 | 0.23 | 0.19 | GCG (A) | 5.0 | 0.08 | 0.14 | GAG (E) | 19.0 | 0.40 | 0.51 | GGG (G) | 7.0 | 0.17 | 0.19 |
| Scientific Name | Accession Number | Genome Length (bp) | CCR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types | Tandem Repeats | Single Repeat Unit | |||
| C. coromandus | OM687253 | 17,082 | 1 | 32.6 × (7) | CAAACAA |
| E. scolopaceus | OM115963 | 17,610 | 2 | 5.1 × (66) | CACCACCACCCTCCCCGCTGAAATTACATTAACAAATTACATCATATCACCCATAATTTTATATTT |
| 23.1 × (7) | AAACAAC | ||||
| C. minutillus | OQ363454 | 17,190 | 1 | 12.8 × (12) | AAAACAAACAAC |
| C. russatus | OQ363419 | 17,211 | 1 | 12.8 × (12) | AAAACAAACAAC |
| C. aereus | NC052776 | 17,187 | - | - | - |
| C. poliocephalus | NC028414 | 17,508 | 1 | 33.4 × (7) | CAACAAA |
| E. taitensis | NC011709 | 17,559 | 1 | 16.9 × (7) | AAACAAC |
| C. micropterus | MZ048030 | 17,541 | - | - | - |
| C. canorus | MN067867 | 17,457 | - | - | - |
| P. cayana | MN356301 | 17,007 | - | - | - |
| C. sulcirostris | MN356290 | 16,933 | - | - | - |
| G. californianus | EU410488 | 17,091 | 1 | 31.7 × (7) | CAAACAA |
| C. bengalensis | MN356332 | 17,107 | - | - | - |
| C. sinensis | KT947122 | 17,159 | - | - | - |
| C. unirufus | NC052811 | 17,089 | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhang, F.; Xia, C.; Li, G.; Li, S. Phylogenetic Relationship and Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Cuckoo Species Clamator coromandus (Aves: Cuculidae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030869
Zhang Y, Gao H, Zhang F, Xia C, Li G, Li S. Phylogenetic Relationship and Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Cuckoo Species Clamator coromandus (Aves: Cuculidae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030869
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Hao Gao, Fan Zhang, Chengxing Xia, Guopan Li, and Shaobin Li. 2025. "Phylogenetic Relationship and Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Cuckoo Species Clamator coromandus (Aves: Cuculidae)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030869
APA StyleZhang, Y., Gao, H., Zhang, F., Xia, C., Li, G., & Li, S. (2025). Phylogenetic Relationship and Characterization of the Complete Mitochondrial Genome of the Cuckoo Species Clamator coromandus (Aves: Cuculidae). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030869






