Association Between Active DNA Demethylation and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Global Demethylation
2.1.1. Demethylation Intermediates in Relation to MASLD
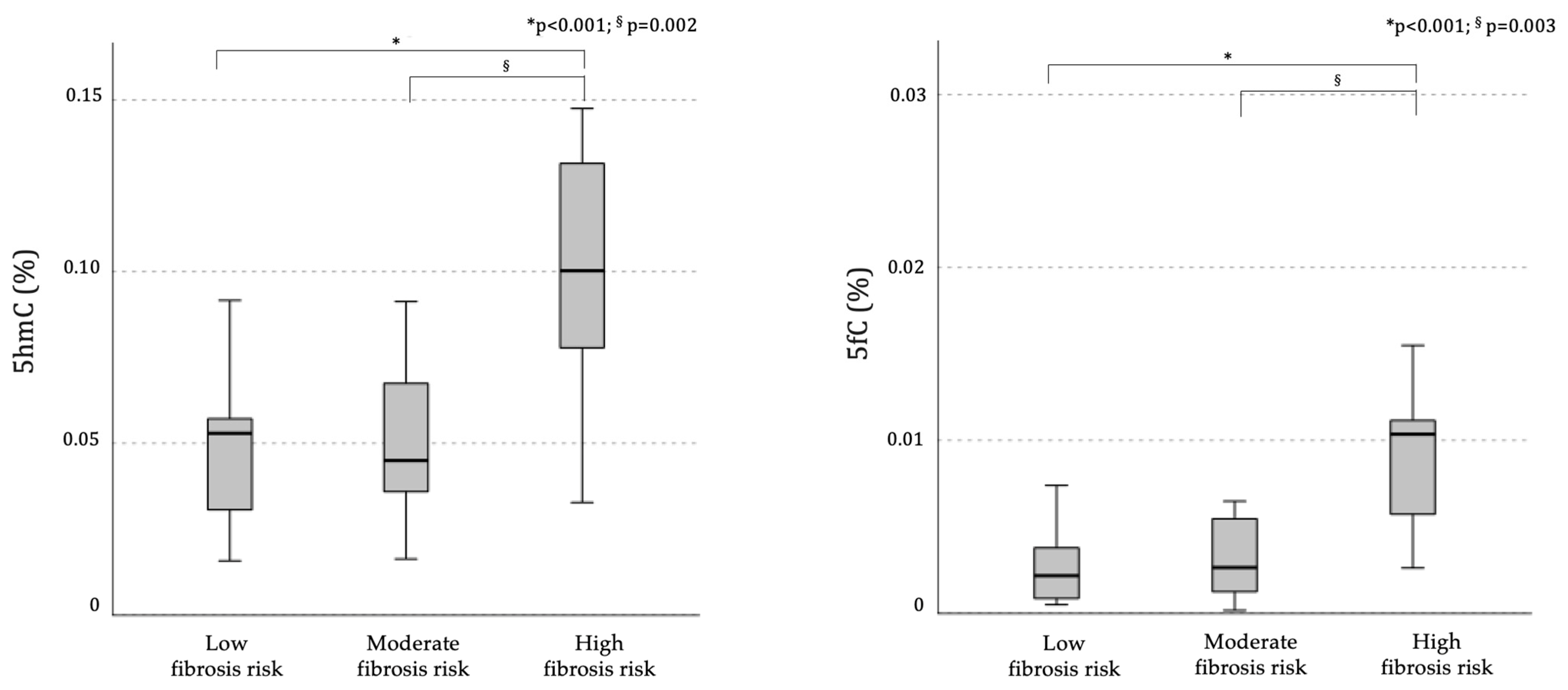
2.1.2. Demethylation Intermediates and Liver Fibrosis
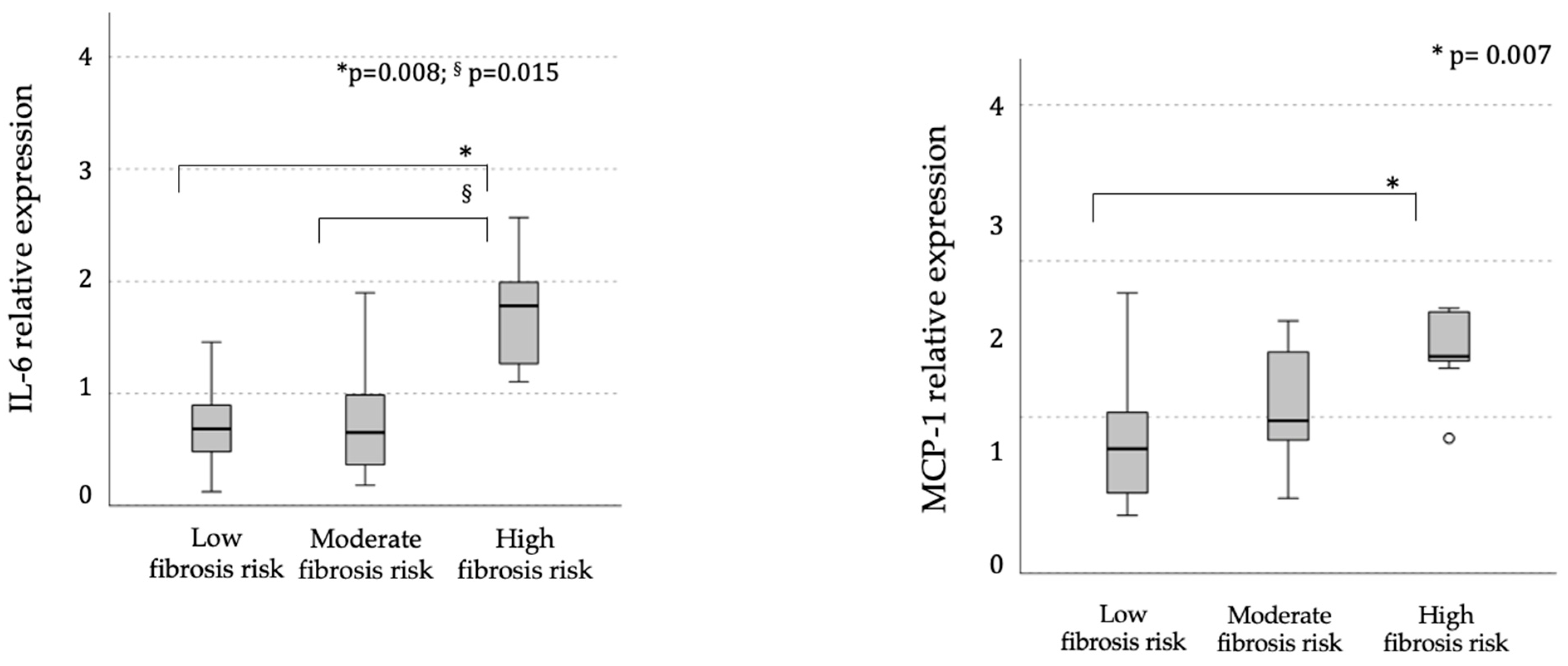
2.2. Gene-Specific Methylation and Associated mRNA Expression Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Isolation
4.3. Extraction of Total DNA and Quantification of Global 5mC, 5hmC, and 5fC Levels
4.4. DNA Methylation Analysis of SREBF1, SOCS3, and TXNIP Gene Regions Using the EpiTYPER Assay
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis by Reverse Transcription–Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.6. Statistical Analysis and Sample Size Calculation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, M.L.; Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Chan, K.E.; Tan, D.J.; Lim, W.H.; Yang, J.D.; Tan, E.; Muthiah, M.D. Global incidence and prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S32–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a nexus of metabolic and hepatic diseases. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1542–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tilg, H. MASLD: A Systemic Metabolic Disorder with Cardiovascular and Malignant Complications. Gut 2024, 73, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H.; Shang, Y.; Hegmar, H.; Nasr, P. Natural History and Progression of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 944–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Rönn, T. Epigenetics in Human Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1028–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stols-Gonçalves, D.; Meijnikman, A.S.; Tristão, L.S.; Santos, C.L.D.; Denswil, N.P.; Verheij, J.; Bernardo, W.M.; Nieuwdorp, M. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease: Liver DNA Methylation Analysis-A Systematic Review. Cells 2024, 13, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Fan, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Dai, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, T. Association between advanced fibrosis and epigenetic age acceleration among individuals with MASLD. J. Gastroenterol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiger, N.; Veed, J.K.; Chinya Nataraj, P.; Mukhopadhyay, A. DNA methylation and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Clin. Epigenetics 2024, 16, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, Y.; Zeng, C.; Yang, K.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, Q.; He, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, S.M. Genome-wide Analysis Reflects Novel 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines Implicated in Diabetic Nephropathy and the Biomarker Potential. Extracell. Vesicles Circ. Nucl. Acids 2022, 3, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, M.; Bacalini, M.G.; Barchetta, I.; Scalea, S.; Cimini, F.A.; Bertoccini, L.; Tagliatesta, S.; De Matteis, G.; Zardo, G.; Cavallo, M.G.; et al. Increased PARylation impacts the DNA methylation process in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dhliwayo, N.; Sarras, M.P., Jr.; Luczkowski, E.; Mason, S.M.; Intine, R.V. Parp inhibition prevents ten-eleven translocase enzyme activation and hyperglycemia-induced DNA demethylation. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3069–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carow, B.; Rottenberg, M.E. SOCS3, a Major Regulator of Infection and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, H.; Chinen, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kinjyo, I.; Takaesu, G.; Shiraishi, H.; Iida, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshimura, A. Loss of SOCS3 in the Liver Promotes Fibrosis by Enhancing STAT3-Mediated TGF-β1 Production. Oncogene 2006, 25, 2520–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.P.; Kim, D.Y.; Im, S.S.; Jeon, T.I. Impairment of ULK1 Sulfhydration-Mediated Lipophagy by SREBF1/SREBP-1c in Hepatic Steatosis. Autophagy 2021, 17, 4489–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, I.N.; Li, L.; Ismael, S.; Ishrat, T.; El-Remessy, A.B. Thioredoxin Interacting Protein, a Key Molecular Switch Between Oxidative Stress and Sterile Inflammation in Cellular Response. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 1979–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dees, C.; Pötter, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bergmann, C.; Zhou, X.; Luber, M.; Wohlfahrt, T.; Karouzakis, E.; Ramming, A.; Gelse, K.; et al. TGF-β-induced epigenetic deregulation of SOCS3 facilitates STAT3 signaling to promote fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2347–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yuan, Q.; Tang, B.; Zhang, C. Signaling pathways of chronic kidney diseases, implications for therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Deng, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D. Role and mechanism of TXNIP in ageing-related renal fibrosis. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 196, 111475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayeh, T.; Tuomi, T.; Almgren, P.; Perfilyev, A.; Jansson, P.A.; de Mello, V.D.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Vaag, A.; Groop, L.; Nilsson, E.; et al. DNA methylation of loci within ABCG1 and PHOSPHO1 in blood DNA is associated with future type 2 diabetes risk. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, J.C.; Loh, M.; Lehne, B.; Drong, A.; Kriebel, J.; Motta, V.; Wahl, S.; Elliott, H.R.; Rota, F.; Scott, W.R.; et al. Epigenome-wide association of DNA methylation markers in peripheral blood from Indian Asians and Europeans with incident type 2 diabetes: A nested case-control study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabre, N.; Luciano-Mateo, F.; Chapski, D.J.; Baiges-Gaya, G.; Fernandez-Arroyo, S.; Hernandez-Aguilera, A.; Castane, H.; Rodriguez-Tomas, E.; Paris, M.; Sabench, F.; et al. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy in Patients with Severe Obesity Restores Adaptive Responses Leading to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.D.; Wu, X.; Still, C.D.; Chu, X.; Petrick, A.T.; Gerhard, G.S.; Conneely, K.N.; DiStefano, J.K. Differential DNA Methylation and Changing Cell-Type Proportions as Fibrotic Stage Progresses in NAFLD. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mello, V.D.; Matte, A.; Perfilyev, A.; Mannisto, V.; Ronn, T.; Nilsson, E.; Kakela, P.; Ling, C.; Pihlajamaki, J. Human Liver Epigenetic Alterations in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Are Related to Insulin Action. Epigenetics 2017, 12, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.K.; Yang, H.; Moylan, C.A.; Pang, H.; Dellinger, A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Garrett, M.E.; Ashley-Koch, A.; Suzuki, A.; Tillmann, H.L.; et al. Relationship Between Methylome and Transcriptome in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulinski, A.; Vance, D.E.; Vance, J.E. A Choline-Deficient Diet in Mice Inhibits Neither the CDP-Choline Pathway for Phosphatidylcholine Synthesis in Hepatocytes Nor Apolipoprotein B Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 23916–23924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, J.M.; Martínez-Chantar, M.L.; Lu, S.C. S-Adenosylmethionine Metabolism and Liver Disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2013, 12, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.; Paoli, P.; Moran Salvador, E.; White, S.; French, J.; Mann, J. Hepatic Stellate Cell Transdifferentiation Involves Genome-Wide Remodeling of the DNA Methylation Landscape. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyall, M.J.; Cartier, J.; Thomson, J.P.; Cameron, K.; Meseguer-Ripolles, J.; O’Duibhir, E.; Szkolnicka, D.; Villarin, B.L.; Wang, Y.; Blanco, G.R.; et al. Modelling Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Human Hepatocyte-Like Cells. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2018, 373, 20170362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyall, M.J.; Thomson, J.P.; Cartier, J.; Ottaviano, R.; Kendall, T.J.; Meehan, R.R.; Drake, A.J. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Is Associated with Dynamic Changes in DNA Hydroxymethylation. Epigenetics 2020, 15, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, C.; Wong, K.; Chen, X.; Pu, L.; Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Association of Hepatic Global DNA Methylation and Serum One-Carbon Metabolites with Histological Severity in Patients with NAFLD. Obesity 2020, 28, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; et al. GCSF Deficiency Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Regulating GCSFR-SOCS3-JAK-STAT3 Pathway and Immune Cells Infiltration. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G531–G542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, C.J.; Scian, R.; Gianotti, T.F.; Dopazo, H.; Rohr, C.; Martino, J.S.; Castaño, G.O.; Sookoian, S. Epigenetic Modifications in the Biology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Role of DNA Hydroxymethylation and TET Proteins. Medicine 2015, 94, e1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pogribny, I.P.; Tryndyak, V.P.; Bagnyukova, T.V.; Melnyk, S.; Montgomery, B.; Ross, S.A.; Latendresse, J.R.; Rusyn, I.; Beland, F.A. Hepatic epigenetic phenotype predetermines individual susceptibility to hepatic steatosis in mice fed a lipogenic methyl-deficient diet. J. Hepatol. 2009, 51, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, N.; Liu, Z.; Shi, B.; Sun, H. Association of Circulating TXNIP Levels with Fatty Liver in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, S.H.; Sung, M.W.; et al. Hepatic Steatosis Index: A Simple Screening Tool Reflecting Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavaglione, F.; Jamialahmadi, O.; De Vincentis, A.; Qadri, S.; Mowlaei, M.E.; Mancina, R.M.; Ciociola, E.; Carotti, S.; Perrone, G.; Bruni, V.; et al. Development and Validation of a Score for Fibrotic Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 1523–1532.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosner, B. Fundamentals of Biostatistics, 7th ed.; Brooks/Cole: Boston, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]

| MASLD (HSI > 36) n = 56 | Non-MASLD (HSI < 36) n = 33 | p-Value Student’s t-Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.92 ± 10.95 | 61.30 ± 9.73 | 0.49 |
| Sex (M%) | 30% | 46% | 0.16 * |
| BMI (kg/m²) | 31.28 ± 4.30 | 23.91 ± 1.75 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 111.63 ± 10.50 | 94.80 ± 5.89 | 0.003 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 136.96 ± 19.56 | 129.07 ± 12.94 | 0.04 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 82.33 ± 9.81 | 78.89 ± 8.92 | 0.13 |
| FBG (mg/dL) | 131.08 ± 47.04 | 107.43 ± 38.27 | 0.02 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.12 ± 1.62 | 6.26 ± 1.57 | 0.02 |
| AST (IU/L) | 21.40 ± 8.70 | 19.17 ± 5.22 | 0.15 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 25.22 ± 12.99 | 15.80 ± 5.14 | <0.001 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 27.55 ± 21.39 | 17.30 ± 8.57 | 0.019 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.59 ± 0.26 | 0.59 ± 0.29 | 0.97 |
| Direct bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.21 ± 0.07 | 0.25 ± 0.11 | 0.19 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 192.19 ± 42.34 | 200.36 ± 36.81 | 0.41 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 47.71 ± 15.61 | 62.40 ± 11.66 | <0.001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 107.77 ± 41.89 | 102.44 ± 46.92 | 0.61 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 169.12 ± 87.62 | 112.69 ± 54.62 | 0.004 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 7.63 ± 10.29 | 4.63 ± 0.12 | 0.21 |
| T2DM diagnosis (%) | 70% | 37% | 0.004 * |
| Lipid-lowering treatments (%) | 21% | 14% | 0.44 * |
| HSI | 43.61 ± 5.75 | 33.07 ± 1.88 | <0.001 |
| FNI | 0.23 ± 0.22 | 0.07 ± 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Low Fibrosis Risk (FNI < 0.10) n = 50 | Moderate Fibrosis Risk (0.10 ≤ FNI < 0.33) n = 27 | High Fibrosis Risk (FNI ≥ 0.33) n = 12 | p-Value ANOVA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60 ± 9.9 | 64.9 ± 10.5 | 62.6 ± 12 | 0.13 |
| Sex (M%) | 50% | 79% | 64% | 0.07 * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.6 ±4.2 | 28.7 ± 4.8 | 33.7 ± 5.1 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 99.8 ±16.4 | 105.4 ± 11.4 | 113 ± 10.5 | 0.26 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 132 ± 15.7 | 137.6 ± 20.4 | 137.1 ± 19.4 | 0.42 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 80.9 ± 9.4 | 81.1 ± 10.2 | 80.9 ± 10.2 | 0.99 |
| FBG (mg/dL) | 102.9 ± 34 | 137.6 ± 38.5 | 160.3 ± 11.6 | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.1 ± 9.3 | 7.2 ± 1.2 | 9.3 ± 1.4 | 0.60 |
| AST (IU/L) | 18.1 ±5.3 | 20.2 ± 5.3 | 27.8 ± 12.2 | <0.001 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 18.4 ± 8.8 | 21 ± 8.9 | 34.8 ± 15.8 | <0.001 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 17.4 ± 6.3 | 26.8 ± 15.5 | 47.3 ± 34.3 | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.50 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.64 ± 0.26 | 0.30 |
| Direct bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.20 ± 0.08 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | 0.23 ± 0.08 | 0.58 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 204.6 ± 35.8 | 182 ± 38.4 | 176 ± 49.2 | 0.02 |
| HDL (mg/dL) | 61.3 ± 13.9 | 43.4 ± 7.7 | 44 ± 12.3 | <0.001 |
| LDL (mg/dL) | 120.6 ± 29.8 | 107.4 ± 38.7 | 97.2 ± 42.2 | 0.09 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 123.7 ± 62.4 | 168 ± 90.2 | 181 ± 83.5 | 0.018 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5.5 ± 1.3 | 8.3 ± 11.9 | 4.9 ± 1.5 | 0.56 |
| T2DM diagnosis (%) | 38% | 93% | 100% | <0.001 * |
| Lipid-lowering treatments (%) | 12% | 22% | 25% | 0.44 |
| FNI | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.18 ± 0.06 | 0.52 ± 0.17 | <0.001 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barchetta, I.; Zampieri, M.; Cimini, F.A.; Dule, S.; Sentinelli, F.; Passarella, G.; Oldani, A.; Karpach, K.; Bacalini, M.G.; Baroni, M.G.; et al. Association Between Active DNA Demethylation and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031271
Barchetta I, Zampieri M, Cimini FA, Dule S, Sentinelli F, Passarella G, Oldani A, Karpach K, Bacalini MG, Baroni MG, et al. Association Between Active DNA Demethylation and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031271
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarchetta, Ilaria, Michele Zampieri, Flavia Agata Cimini, Sara Dule, Federica Sentinelli, Giulia Passarella, Alessandro Oldani, Katsiaryna Karpach, Maria Giulia Bacalini, Marco Giorgio Baroni, and et al. 2025. "Association Between Active DNA Demethylation and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031271
APA StyleBarchetta, I., Zampieri, M., Cimini, F. A., Dule, S., Sentinelli, F., Passarella, G., Oldani, A., Karpach, K., Bacalini, M. G., Baroni, M. G., Reale, A., & Cavallo, M. G. (2025). Association Between Active DNA Demethylation and Liver Fibrosis in Individuals with Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031271








