Early Anti-Drug Antibodies Predict Adalimumab Response in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
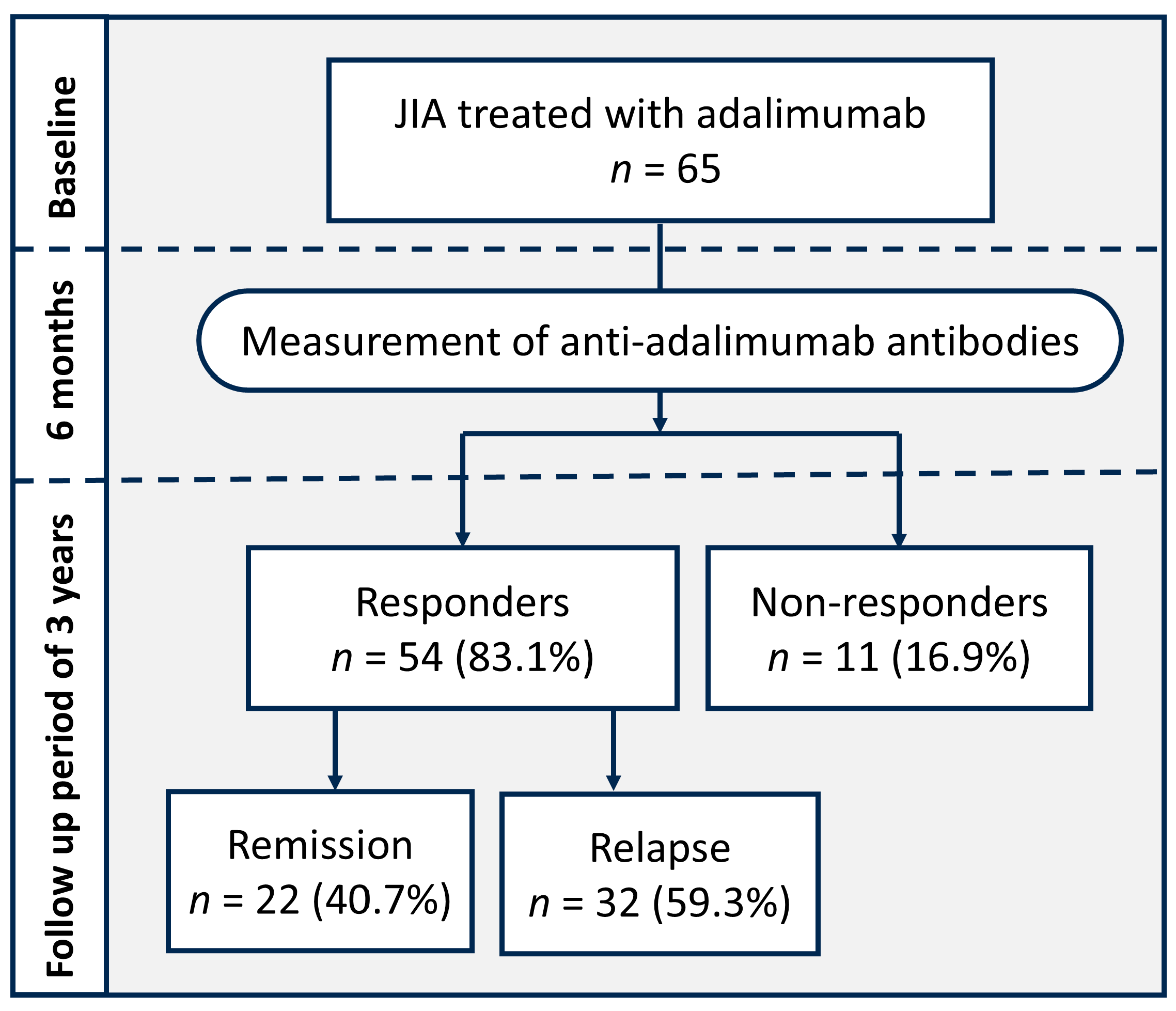
2. Results
2.1. Patients’ Characteristics
2.2. Comparison Between the Response and Non-Response Groups
2.3. Role of Anti-Drug Antibodies in Adalimumab Treatment Response Prediction
2.4. Factors Related to Immunogenicity
2.5. Role of Anti-Drug Antibodies in Predicting Disease Relapse
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects
4.2. Ethics
4.3. Treatment Response
4.4. Anti-Adalimumab Antibodies
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANA | Antinuclear antibody |
| AUC | Area under curve |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| DMARDs | Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs |
| ERA | Enthesitis-related arthritis |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| HLA-B27 | Human leukocyte antigen B27 |
| JIA | Juvenile idiopathic arthritis |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| RF | Rheumatoid factor |
| SI | Sacroiliac |
| TMJ | Temporomandibular joint |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
References
- Petty, R.E.; Southwood, T.R.; Manners, P.; Baum, J.; Glass, D.N.; Goldenberg, J.; He, X.; Maldonado-Cocco, J.; Orozco-Alcala, J.; Prieur, A.M.; et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 390–392. [Google Scholar]
- Prakken, B.; Albani, S.; Martini, A. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet 2011, 377, 2138–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haverman, L.; Verhoof, E.J.; Maurice-Stam, H.; Heymans, H.S.; Gerlag, D.M.; van Rossum, M.A.; Grootenhuis, M.A. Health-related quality of life and psychosocial developmental trajectory in young female beneficiaries with JIA. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, J.E.; Woreta, F.; Kedhar, S.R.; Dunn, J.P.; Jabs, D.A. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis: Incidence of ocular complications and visual acuity loss. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giancane, G.; Muratore, V.; Marzetti, V.; Quilis, N.; Benavente, B.S.; Bagnasco, F.; Alongi, A.; Civino, A.; Quartulli, L.; Consolaro, A.; et al. Disease activity and damage in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Methotrexate era versus biologic era. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, A.V.; Dick, A.D.; Jones, A.P.; McKay, A.; Williamson, P.R.; Compeyrot-Lacassagne, S.; Hardwick, B.; Hickey, H.; Hughes, D.; Woo, P.; et al. Adalimumab plus Methotrexate for Uveitis in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minden, K.; Niewerth, M.; Zink, A.; Seipelt, E.; Foeldvari, I.; Girschick, H.; Ganser, G.; Horneff, G. Long-term outcome of patients with JIA treated with etanercept, results of the biologic register JuMBO. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ringold, S.; Angeles-Han, S.T.; Beukelman, T.; Lovell, D.; Cuello, C.A.; Becker, M.L.; Colbert, R.A.; Feldman, B.M.; Ferguson, P.J.; Gewanter, H.; et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Therapeutic Approaches for Non-Systemic Polyarthritis, Sacroiliitis, and Enthesitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 846–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onel, K.B.; Horton, D.B.; Lovell, D.J.; Shenoi, S.; Cuello, C.A.; Angeles-Han, S.T.; Becker, M.L.; Cron, R.Q.; Feldman, B.M.; Ferguson, P.J.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Therapeutic Approaches for Oligoarthritis, Temporomandibular Joint Arthritis, and Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2022, 74, 521–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, D.J.; Ruperto, N.; Goodman, S.; Reiff, A.; Jung, L.; Jarosova, K.; Nemcova, D.; Mouy, R.; Sandborg, C.; Bohnsack, J.; et al. Adalimumab with or without methotrexate in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovell, D.J.; Brunner, H.I.; Reiff, A.O.; Jung, L.; Jarosova, K.; Nemcova, D.; Mouy, R.; Sandborg, C.; Bohnsack, J.F.; Elewaut, D.; et al. Long-term outcomes in patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis receiving adalimumab with or without methotrexate. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horneff, G.; Klein, A.; Klotsche, J.; Minden, K.; Huppertz, H.I.; Weller-Heinemann, F.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.; Haas, J.P.; Hospach, A. Comparison of treatment response, remission rate and drug adherence in polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients treated with etanercept, adalimumab or tocilizumab. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takei, S.; Iwata, N.; Kobayashi, I.; Igarashi, T.; Yoshinaga, Y.; Matsubara, N.; Sunaga, N.; Ito, A.; Yokota, S. Safety and effectiveness of adalimumab in Japanese patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Results from a real-world postmarketing study. Mod. Rheumatol. 2021, 31, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, C.Y.; Chang, C.L.; Chiang, B.L. Enthesitis-related arthritis is the most common category of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Taiwan and presents persistent active disease. Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2019, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glerup, M.; Rypdal, V.; Arnstad, E.D.; Ekelund, M.; Peltoniemi, S.; Aalto, K.; Rygg, M.; Toftedal, P.; Nielsen, S.; Fasth, A.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Eighteen Years of Follow-Up in the Population-Based Nordic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Cohort. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrabl-Baumgartner, A.; Erwa, W.; Muntean, W.; Jahnel, J. Anti-adalimumab antibodies in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Frequent association with loss of response. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, A.; Real-Fernandez, F.; Rovero, P.; Giani, T.; Pagnini, I.; Cimaz, R.; Simonini, G. Anti-adalimumab antibodies in a cohort of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Incidence and clinical correlations. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doeleman, M.J.H.; de Roock, S.; El Amrani, M.; van Maarseveen, E.M.; Wulffraat, N.M.; Swart, J.F. Association of adalimumab trough concentrations and treatment response in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology 2021, 61, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, M.C.; Alfano, R.; Cuomo, G.; Romano, C.; Gravina, A.G.; Romano, M.; Galdiero, M.; Montemurro, M.V.; Giordano, A.; D’Amico, M. Comparison of Timing to Develop Anti-Drug Antibodies to Infliximab and Adalimumab Between Adult and Pediatric Age Groups, Males and Females. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 27, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrabl-Baumgartner, A.; Seidel, G.; Langner-Wegscheider, B.; Schlagenhauf, A.; Jahnel, J. Drug monitoring in long-term treatment with adalimumab for juvenile idiopathic arthritis-associated uveitis. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar-Sheikh Rashid, A.; Schonenberg-Meinema, D.; Bergkamp, S.C.; Bakhlakh, S.; de Vries, A.; Rispens, T.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Wolbink, G.; van den Berg, J.M. Therapeutic drug monitoring of anti-TNF drugs: An overview of applicability in daily clinical practice in the era of treatment with biologics in juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). Pediatr. Rheumatol. Online J. 2021, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, J.B.; Silva, C.A.; Pasoto, S.G.; Saa, C.G.S.; Kozu, K.T.; Goldenstein-Schainberg, C.; Leon, E.P.; Vendramini, M.B.G.; Fontoura, N.; Bonfa, E.; et al. Anti-adalimumab antibodies kinetics: An early guide for juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) switching. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doeleman, M.J.H.; van Maarseveen, E.M.; Swart, J.F. Immunogenicity of biologic agents in juvenile idiopathic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1839–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, F.; Klein, A.; Klotsche, J.; Windschall, D.; Dressler, F.; Kuemmerle-Deschner, J.; Minden, K.; Foeldvari, I.; Foell, D.; Mrusek, S.; et al. Biologics with or without methotrexate in treatment of polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Effectiveness, safety and drug survival. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, A.; Becker, I.; Minden, K.; Foeldvari, I.; Haas, J.P.; Horneff, G. Adalimumab versus adalimumab and methotrexate for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Long-term data from the German BIKER registry. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2019, 48, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, R.L.; Zelinkova, Z.; Wolbink, G.J.; Kuipers, E.J.; Stokkers, P.C.; van der Woude, C.J. Immunogenicity negatively influences the outcome of adalimumab treatment in Crohn’s disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 28, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos-Vargas, R.; Tse, S.M.; Horneff, G.; Pangan, A.L.; Kalabic, J.; Goss, S.; Unnebrink, K.; Anderson, J.K. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multicenter Study of Adalimumab in Pediatric Patients with Enthesitis-Related Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2015, 67, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagawa, T.; Takei, S.; Umebayashi, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Itoh, Y.; Kawai, T.; Iwata, N.; Murata, T.; Okafuji, I.; Miyoshi, M.; et al. Efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and safety of adalimumab in pediatric patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Japan. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murias, S.; Alcobendas, R.; Pascual-Salcedo, D.; Remesal, A.; Peralta, J.; Merino, R. Anti-adalimumab antibodies in paediatric rheumatology patients: A pilot experience. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 2124–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leinonen, S.T.; Aalto, K.; Kotaniemi, K.M.; Kivela, T.T. Anti-adalimumab antibodies in juvenile idiopathic arthritis-related uveitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.C.; Yeh, K.W.; Ou, L.S.; Yao, T.C.; Chen, L.C.; Huang, J.L. Clinical features of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis using the ILAR classification criteria: A community-based cohort study in Taiwan. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, P.F.; Beukelman, T.; Schanberg, L.E.; Kimura, Y.; Colbert, R.A. Enthesitis-related arthritis is associated with higher pain intensity and poorer health status in comparison with other categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: The Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance Registry. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 2341–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipa, M.R.; Heyer, N.; Mansoor, R.; Deakin, C.T.; Madenidou, A.V.; Bouraioui, A.; Fisher, C.; Leandro, M.; Ciurtin, C.; Sen, D. Adalimumab or etanercept as first line biologic therapy in enthesitis related arthritis (ERA)—A drug-survival single centre study spanning 10 years. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2022, 55, 152038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostik, M.M.; Gaidar, E.V.; Sorokina, L.S.; Avrusin, I.S.; Nikitina, T.N.; Isupova, E.A.; Chikova, I.A.; Korin, Y.Y.; Orlova, E.D.; Snegireva, L.S.; et al. Uveitis Is a Risk Factor for Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis’ Significant Flare in Patients Treated with Biologics. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 849940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artamonov, A.K.; Kaneva, M.A.; Gordeeva, N.A.; Sorokina, L.S.; Kostik, M.M. Temporomandibular Joint Involvement in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: The Results from a Retrospective Cohort Tertial Center Study. Life 2023, 13, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.H.; Chiang, B.L.; Yang, Y.H. Tapering of Biological Agents in Juvenile ERA Patients in Daily Clinical Practice. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 665170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, D.B.; Onel, K.B.; Beukelman, T.; Ringold, S. Attitudes and Approaches for Withdrawing Drugs for Children with Clinically Inactive Nonsystemic JIA: A Survey of the Childhood Arthritis and Rheumatology Research Alliance. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judit Szántó, K.; Madácsy, T.; Kata, D.; Ferenci, T.; Rutka, M.; Bálint, A.; Bor, R.; Fábián, A.; Milassin, Á.; Jójárt, B.; et al. Advances in the optimization of therapeutic drug monitoring using serum, tissue and faecal anti-tumour necrosis factor concentration in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with TNF-α antagonists. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, C.A.; Ruperto, N.; Giannini, E.; Childhood, A.; Rheumatology Research, A.; Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials, O.; Pediatric Rheumatology Collaborative Study, G. Preliminary criteria for clinical remission for select categories of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 2290–2294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sam, M.J.; Connor, S.J.; Ng, W.W.; Toong, C.M. Comparative Evaluation of 4 Commercially Available ELISA Kits for Measuring Adalimumab and Anti-adalimumab Antibodies. Ther. Drug Monit. 2020, 42, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kui, R.; Gál, B.; Gaál, M.; Kiss, M.; Kemény, L.; Gyulai, R. Presence of antidrug antibodies correlates inversely with the plasma tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α level and the efficacy of TNF-inhibitor therapy in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| n = 65 | |
|---|---|
| Male subjects, n (%) | 40 (61.5) |
| Age at diagnosis, mean ± SD, years | 10.47 ± 3.90 |
| Disease duration, mean ± SD, years | 7.97 ± 5.53 |
| Duration between diagnosis and adalimumab initiation, mean ± SD, years | 3.28 ± 4.97 |
| Duration of adalimumab use, mean ± SD, years | 2.64 ± 0.56 |
| JIA subtypes, n (%) | |
| Oligoarthritis | 1 (1.5) |
| Seronegative polyarthritis | 16 (24.6) |
| Seropositive polyarthritis | 5 (7.7) |
| Enthesitis related arthritis | 42 (64.6) |
| Undifferentiated arthritis | 1 (1.5) |
| Laboratory parameters, n (%) | |
| ANA positive (≥1:80) * | 4 (6.6) |
| RF † | 5 (7.9) |
| HLA-B27 ‡ | 40 (65.6) |
| Previous Medications, n (%) | |
| NSAIDs | 62 (95.4) |
| Systemic steroids | 55 (84.6) |
| Intra-articular glucocorticoid | 25 (38.5) |
| Methotrexate | 56 (86.2) |
| Sulfasalazine | 30 (46.2) |
| Other TNF-α (Etanercept) | 4 (6.2) |
| Response Group n = 54 | Non-Response Group n = 11 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male subjects, n (%) | 34 (63.0) | 6 (54.5) | 0.601 |
| Age at diagnosis, mean ± SD, years | 10.53 ± 3.98 | 10.08 ± 3.62 | 0.791 |
| Duration between diagnosis and adalimumab initiation, mean ± SD, years | 2.71 ± 3.65 | 6.52 ± 9.27 | 0.183 |
| Duration of adalimumab use, mean ± SD, years | 2.61 ± 5.82 | 2.76 ± 0.46 | 0.972 |
| JIA subtypes, n (%) | 0.187 | ||
| Oligoarthritis | 1 (1.9) | 0 | |
| Seronegative polyarthritis | 13 (24.1) | 3 (27.3) | |
| Seropositive polyarthritis | 5 (9.3) | 0 | |
| ERA | 35 (64.8) | 7 (63.6) | |
| Undifferentiated arthritis | 0 | 1 (9.1) | |
| ERA/non-ERA | 35/19 | 7/4 | 1.000 |
| Laboratory parameters, n (%) | |||
| ANA positive (≥1:80) $ | 4 (8.1) | 0 | 1.000 |
| RF † | 4 (7.7) | 1 (9.1) | 1.000 |
| HLA-B27 ‡ | 32 (64.0) | 8 (72.7) | 0.581 |
| CRP, mean ± SD, mg/L | 35.68 ± 24.35 | 35.50 ± 27.27 | 0.340 |
| ESR, mean ± SD, mm/h | 29.37 ± 17.86 | 31.45 ± 25.15 | 0.971 |
| Concomitant medications used, n (%) | |||
| NSAIDs | 13 (24.1) | 3 (27.3) | 1.000 |
| Systemic steroids | 5 (9.3) | 3 (27.3) | 0.126 |
| Methotrexate | 51 (94.4) | 11 (100) | 1.000 |
| Sulfasalazine | 8 (14.8) | 4 (36.4) | 0.194 |
| Initial joint involvement, n | |||
| TMJs | 5 | 4 | 0.038 * |
| SI joints | 8 | 3 | 0.379 |
| Enthesitis, n (%) | 7 | 0 | 0.592 |
| Uveitis, n (%) | 4 | 0 | 1.000 |
| Anti-adalimumab antibodies | |||
| Detectable, n (%) | 17 (31.5) | 8 (73.7) | 0.023 * |
| Concentrations, mean ± SD, ng/mL | 48.89 ± 200.15 | 287.59 ± 444.48 | 0.002 * |
| Antibodies ≥ 7.426 ng/mL n = 17 | Antibodies < 7.426 ng/mL n = 33 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male subjects, n (%) | 8 (47.1) | 23 (69.7) | 0.118 |
| Age at diagnosis, mean ± SD, years | 10.50 ± 3.14 | 10.36 ± 4.14 | 0.900 |
| Duration between diagnosis and adalimumab initiation, mean ± SD, years | 4.43 ± 7.54 | 2.63 ± 3.46 | 0.493 |
| Duration of adalimumab use, mean ± SD, years | 2.61 ± 0.53 | 2.59 ± 0.64 | 0.935 |
| JIA subtypes, n (%) | 0.111 | ||
| Oligoarthritis | 0 | 1 (3.0) | |
| Seronegative polyarthritis | 6 (35.3) | 9 (27.3) | |
| Seropositive polyarthritis | 2 (11.8) | 0 | |
| ERA | 8 (47.1) | 23 (69.7) | |
| Undifferentiated arthritis | 1 (5.9) | 0 | |
| ERA/non-ERA | 8/9 | 23/10 | 0.118 |
| Laboratory parameters, n (%) | |||
| ANA positive $ (≥1:80) | 2 (12.5) | 2 (6.7) | 0.602 |
| RF † | 2 (12.5) | 0 | 0.106 |
| HLA-B27 ‡ | 8 (50.0) | 22 (73.3) | 0.114 |
| CRP, mean ± SD, mg/L | 36.45 ± 31.01 | 35.14 ± 20.24 | 0.095 |
| ESR, mean ± SD, mm/h | 24.00 ± 17.31 | 30.71 ± 17.89 | 0.129 |
| Concomitant medications between 0–6 month, n (%) | |||
| NSAIDs | 15 (88.2) | 32 (97.0) | 0.264 |
| Oral Steroids | 14 (82.4) | 26 (78.8) | 1.000 |
| Methotrexate | 17 (100) | 31 (93.9) | 0.542 |
| Sulfasalazine | 7 (41.2) | 15 (45.5) | 0.703 |
| Initial joint involvement, n | |||
| TMJs | 3 | 3 | 0.396 |
| SI joints | 2 | 7 | 0.699 |
| Enthesitis, n (%) | 0 | 7 (21.2) | 0.080 |
| Uveitis, n (%) | 1 (5.9) | 3 (9.1) | 1.000 |
| Remission n = 22 | Relapse n = 32 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male subjects, n (%) | 16 (72.7) | 18 (56.3) | 0.218 |
| Age at diagnosis, mean ± SD, years | 10.36 ± 3.79 | 10.66 ± 4.17 | 0.753 |
| Duration between diagnosis and adalimumab initiation, mean ± SD, years | 2.74 ± 3.58 | 2.70 ± 3.77 | 0.677 |
| Duration of adalimumab use, mean ± SD, years | 2.50 ± 0.55 | 2.79 ± 0.44 | 0.000 * |
| JIA subtypes, n (%) | 0.854 | ||
| Oligoarthritis | 0 | 1 (3.1) | |
| Seronegative polyarthritis | 5 (22.7) | 8 (25.0) | |
| Seropositive polyarthritis | 2 (9.1) | 3 (9.4) | |
| ERA | 15 (68.2) | 20 (62.5) | |
| Undifferentiated arthritis | 0 | 0 | |
| ERA/non-ERA | 15/7 | 20/12 | 0.667 |
| Laboratory parameters, n (%) | |||
| ANA positive (≥1:80) $ | 0 (0.0) | 4 (14.3) | 0.125 |
| RF † | 2 (9.1) | 2 (6.7) | 1.000 |
| HLA-B27 ‡ | 14 (66.7) | 18 (62.1) | 0.774 |
| CRP, mean ± SD, mg/L | 30.42 ± 18.78 | 39.68 ± 27.55 | 0.224 |
| ESR, mean ± SD, mm/h | 26.48 ± 13.98 | 31.40 ± 20.11 | 0.559 |
| Concomitant medications used, n (%) | |||
| NSAIDs | 2 (9.1) | 11 (34.4) | 0.051 |
| Systemic steroids | 0 | 5 (15.6) | 0.072 |
| Methotrexate | 19 (86.4) | 32 (100) | 0.062 |
| Sulfasalazine | 2 (9.1) | 6 (18.8) | 0.449 |
| Initial joint involvement, n | |||
| TMJs | 4 | 1 | 0.146 |
| SI joints | 2 | 6 | 0.449 |
| Enthesitis, n (%) | 2 (9.1) | 5 (15.6) | 0.687 |
| Uveitis, n (%) | 2 (9.1) | 2 (6.3) | 1.000 |
| Anti-adalimumab antibodies | |||
| Antibodies ≥ 7.426 ng/mL, n (%) | 2/17 (11.8) | 8/24 (33.3) | 0.152 |
| Concentrations, mean ± SD, ng/mL | 5.10 ± 16.72 | 79.92 ± 258.95 | 0.032 * |
| Adalimumab schedule, n | |||
| Every other week | 13 | 10 | 0.042 * |
| Prolonged interval (>2 weeks) | 9 | 22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, B.-H.; Hsu, J.-L.; Huang, H.-Y.; Huang, J.-L.; Yeh, K.-W.; Chen, L.-C.; Lee, W.-I.; Yao, T.-C.; Ou, L.-S.; Lin, S.-J.; et al. Early Anti-Drug Antibodies Predict Adalimumab Response in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031189
Huang B-H, Hsu J-L, Huang H-Y, Huang J-L, Yeh K-W, Chen L-C, Lee W-I, Yao T-C, Ou L-S, Lin S-J, et al. Early Anti-Drug Antibodies Predict Adalimumab Response in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031189
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Bo-Han, Jr-Lin Hsu, Hsin-Yi Huang, Jing-Long Huang, Kuo-Wei Yeh, Li-Chen Chen, Wen-I Lee, Tsung-Chieh Yao, Liang-Shiou Ou, Syh-Jae Lin, and et al. 2025. "Early Anti-Drug Antibodies Predict Adalimumab Response in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031189
APA StyleHuang, B.-H., Hsu, J.-L., Huang, H.-Y., Huang, J.-L., Yeh, K.-W., Chen, L.-C., Lee, W.-I., Yao, T.-C., Ou, L.-S., Lin, S.-J., Su, K.-W., & Wu, C.-Y. (2025). Early Anti-Drug Antibodies Predict Adalimumab Response in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031189





