B-Cell Receptor-Associated Protein 31 Deficiency Aggravates Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis and Liver Injury via Attenuating Fatty Acid Oxidation and Glycogen Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
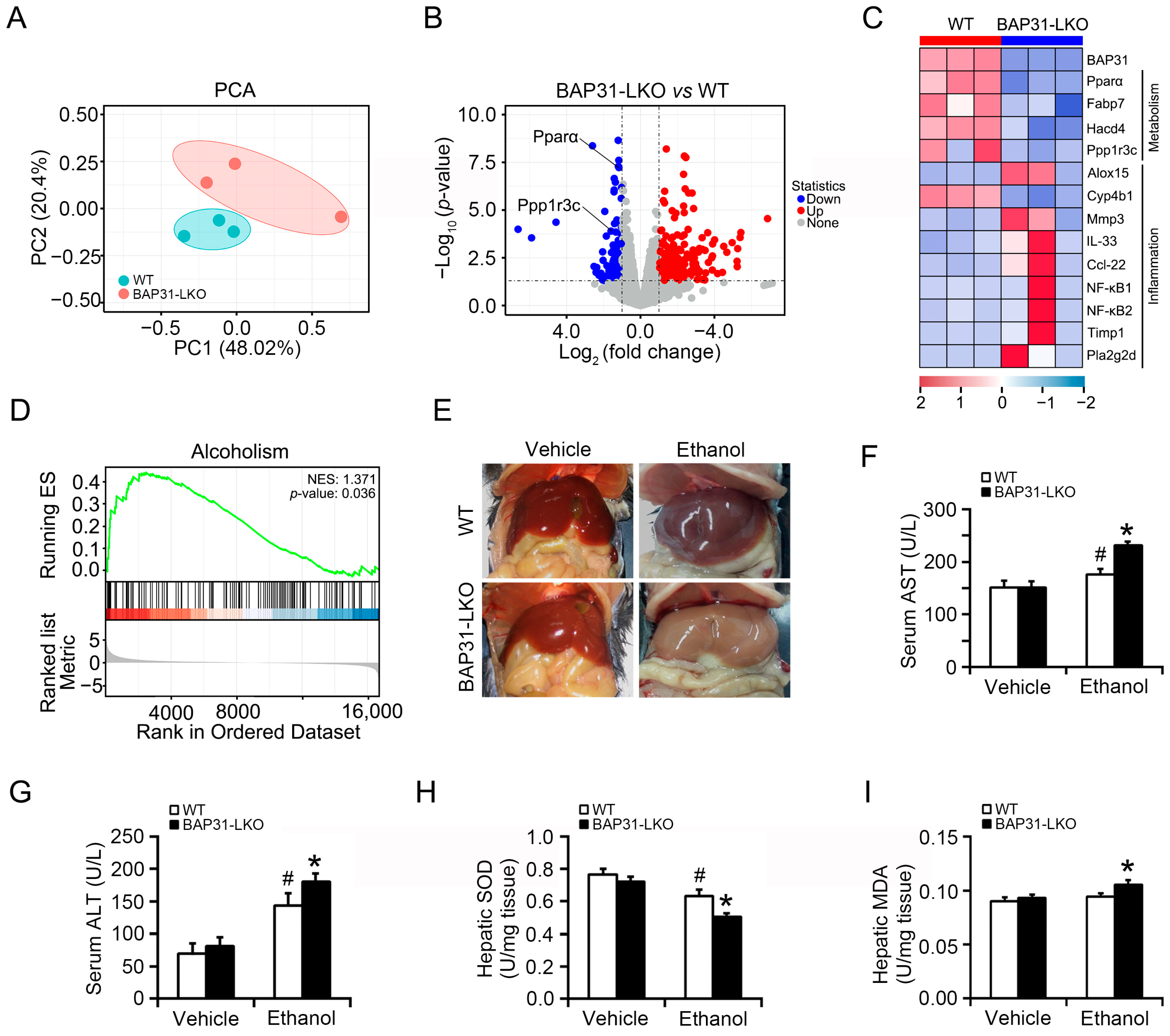
2.1. BAP31 Deficiency Aggravated Ethanol-Induced Liver Injury in Mice
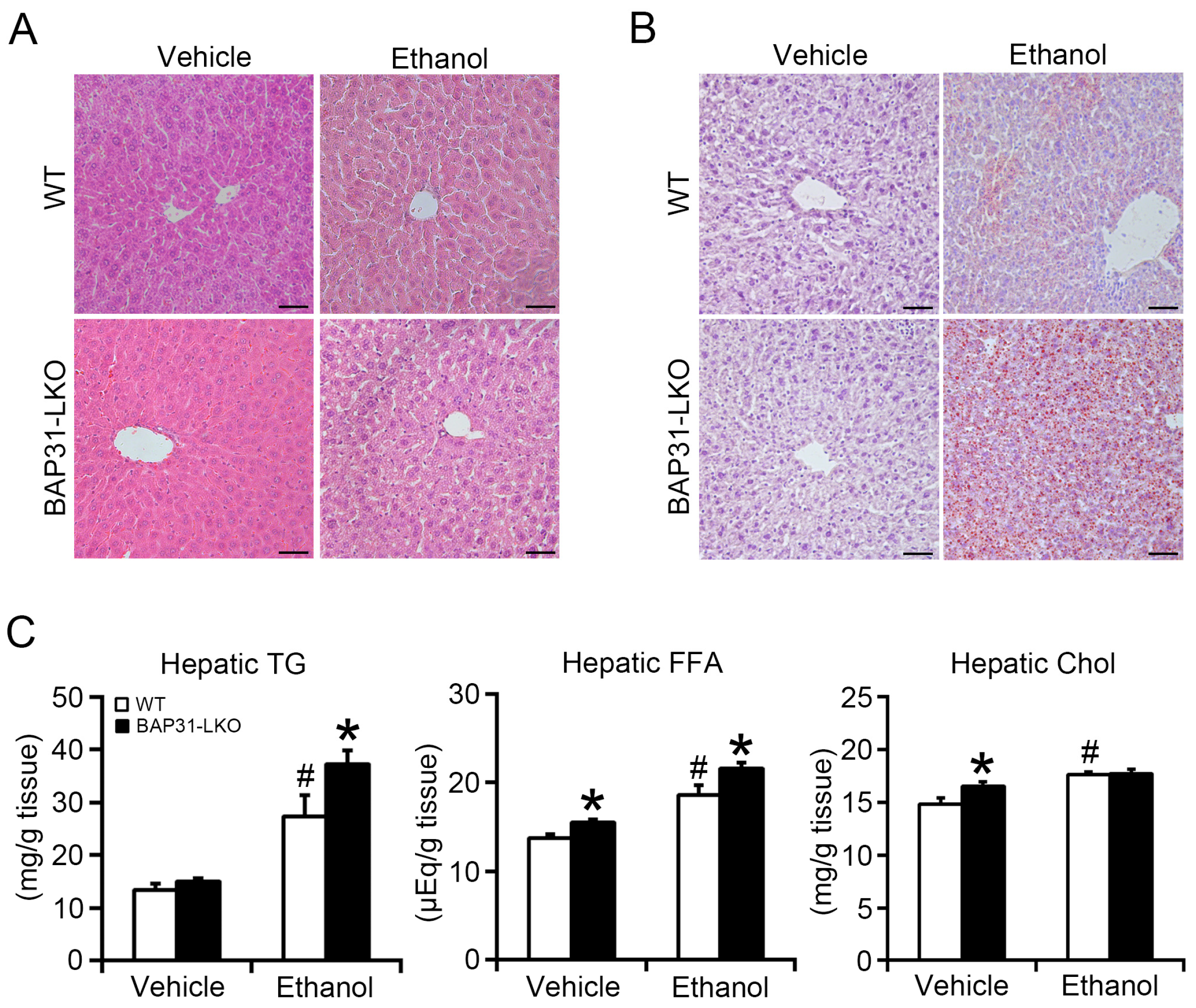
2.2. BAP31 Deficiency Promoted Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis in Mice
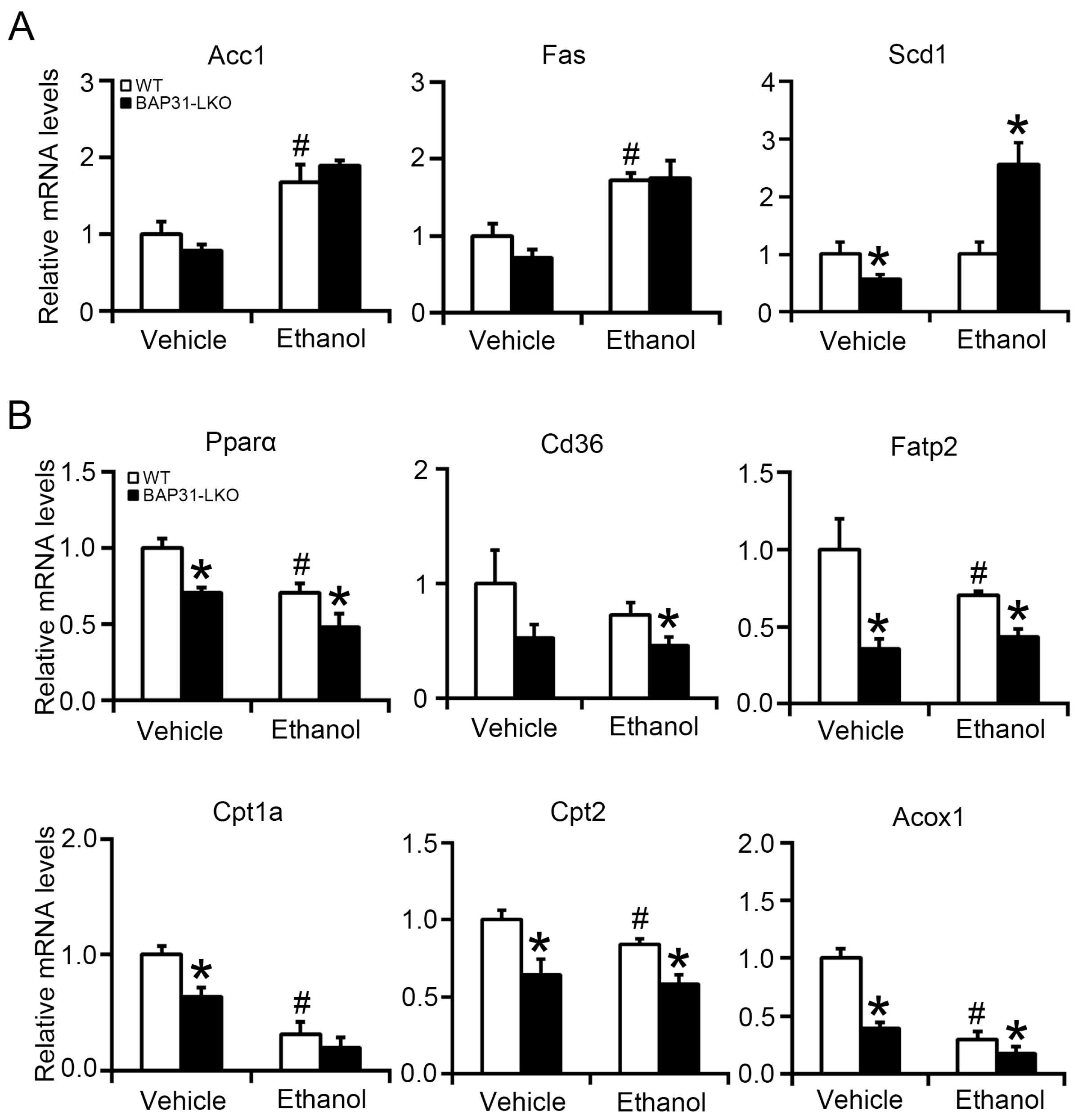
2.3. BAP31 Deficiency Decreased Fatty Acid Oxidation-Related Gene Expression
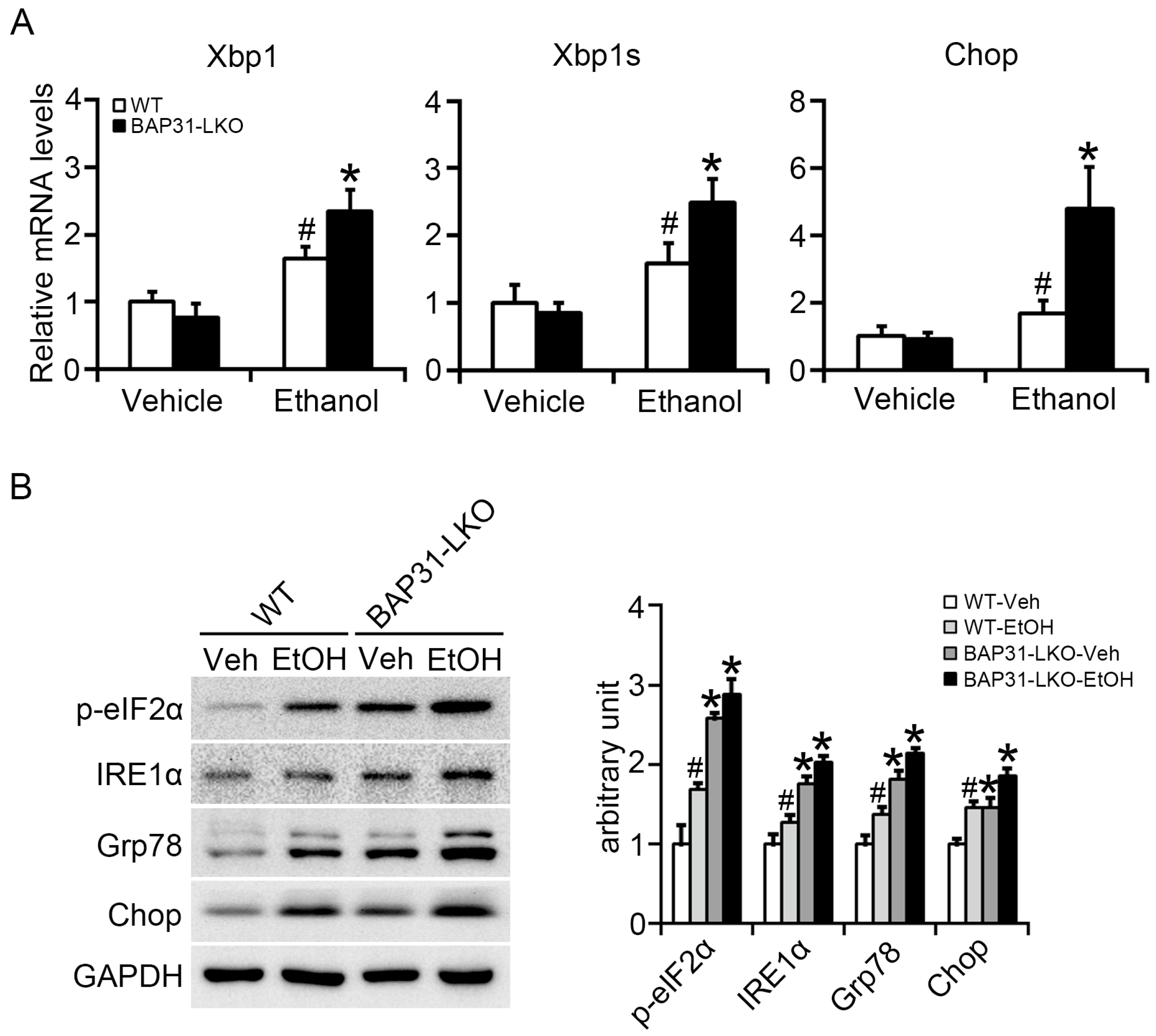
2.4. BAP31 Deficiency Increased Ethanol-Induced ER Stress in Mice Livers
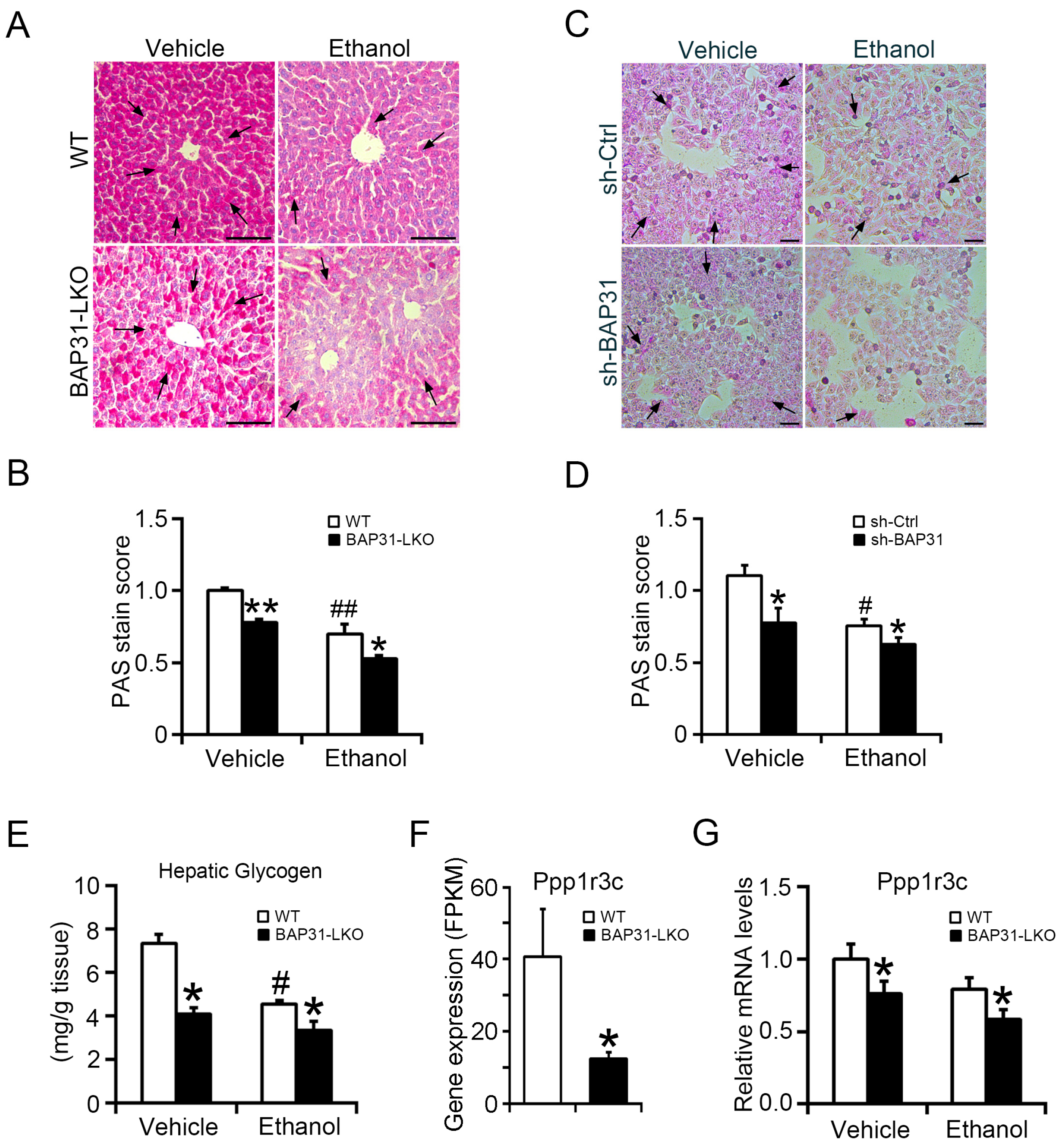
2.5. BAP31 Deficiency Reduced Glycogen Storage and Inhibited Glycogen Synthesis in Liver Cells
2.6. BAP31 Deficiency Increased Ethanol-Induced Lipid Accumulation, ER Stress and Inflammatory Response in HepG2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiment
4.2. Measurement of Serum Metabolites and Liver Extracts
4.3. Measurement of Hepatic Lipids
4.4. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining, Periodic Acid-Schiff Staining, and Oil Red O Staining
4.5. Cell Culture
4.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
4.7. Transcriptome Sequencing
4.8. Immunoblotting Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCD1 | ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily D Member 1 |
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase |
| ACOX1 | Peroxisomal Acyl-coenzyme A Oxidase 1 |
| ADH | Alcohol Dehydrogenase |
| AKT | Protein Kinase B |
| ALD | Alcoholic Liver Disease |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| ATF4 | Activating Transcription Factor 4 |
| ATF6 | Activating Transcription Factor 6 |
| BAP31 | B-cell Receptor-Associated Protein 31 |
| BCL-2 | B-cell Lymphoma-2 |
| BCL-XL | B-cell Lymphoma-extra Large |
| CD36 | Cluster of Differentiation 36 |
| CHOL | Cholesterol |
| CHOP | C/EBP Homologous Protein |
| CPT1α | Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 1 Alpha |
| CPT2 | Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase 2 |
| EIF2α | Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 2 Alpha |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| FAS | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| FATP2 | Fatty Acid Transport Protein 2 |
| FFA | Free Fatty Acid |
| FPKM | Fragments per Kilobase of Transcript per Million Mapped Reads |
| GRP78 | Glucose Regulated Protein 78 |
| GSK3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| HDL-C | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IRE1α | Inositol Requiring Kinase Enzyme 1 Alpha |
| LDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NF-κB1 | Nuclear Factor Kappa B Subunit 1 |
| NF-κB2 | Nuclear Factor Kappa B Subunit 2 |
| PERK | Protein Kinase RNA–like Endoplasmic Reticulum Kinase |
| PPARα | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Alpha |
| PPP1R3A | Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 3A |
| PPP1R3C | Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 3C |
| PPP1R3G | Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 3G |
| SCD1 | Stearoyl Coenzyme A Desaturase 1 |
| SIRT1 | Silent Information Regulator 1 |
| SIRT2 | Silent Information Regulator 2 |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| SREBP1C | Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Protein-1c |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
| XBP1 | X-Box Binding Protein 1 |
| XBP1S | Spliced X-Box Binding Protein 1 |
References
- Goldman, M.R.; Molina-Castro, M.; Etkins, J.C.; Koide, T.L.; Ramchandani, V.A.; Plawecki, M.H.; Mennella, J.A.; Pepino, M.Y. Recent advances in alcohol metabolism: From the gut to the brain. Physiol. Rev. 2025, 105, 2501–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Hu, W.; Tu, J.; Li, J.; Liang, Q.; Han, S. Pathogenic mechanisms and regulatory factors involved in alcoholic liver disease. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhao, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. The Preparation of Black Goji Berry Enzyme and Its Therapeutic Effect on Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice. Foods 2025, 14, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, C.; Ding, W.; Kong, D. Liver Organoid and Liver-On-A-Chip Platforms for Modeling Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Comparative Review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, e03273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.Y. Liver Failure from Alcohol Takes on Several Forms: Decompensated Cirrhosis, Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure, and Alcohol-Related Hepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2026, 30, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddur, H.; Flamm, S. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease: Novel Insights into Mechanism. Clin. Liver Dis. 2026, 30, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, V.L.; Arteel, G.E. Acute alcohol-induced liver injury. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, R.; Farías, C.; Muñoz, Y.; Zúñiga-Hernández, J.; Videla, L.A. Interrelationship between alcohol consumption, overnutrition, and pharmacotherapy for liver steatosis: Considerations and proposals. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2026, 611, 112676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Carr, R. Alcohol effects on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Mehta, K.J. Betaine in ameliorating alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listenberger, L.; Townsend, E.; Rickertsen, C.; Hains, A.; Brown, E.; Inwards, E.G.; Stoeckman, A.K.; Matis, M.P.; Sampathkumar, R.S.; Osna, N.A.; et al. Decreasing Phosphatidylcholine on the Surface of the Lipid Droplet Correlates with Altered Protein Binding and Steatosis. Cells 2018, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; George, J. Interaction between fatty acid oxidation and ethanol metabolism in liver. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2024, 326, G483–G494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoudam, T.; Gao, H.; Jiang, Y.; Huda, N.; Yang, Z.; Ma, J.; Liangpunsakul, S. Mitochondrial quality control in alcohol-associated liver disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H.K.; Moreira, B.; Neuman, M.G. Pathogenesis of Alcoholic Fatty Liver a Narrative Review. Life 2023, 13, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, S.; Santarsiero, A.; Convertini, P.; De Stefano, G.; Gilio, M.; Iacobazzi, V.; Infantino, V. PPAR Alpha as a Metabolic Modulator of the Liver: Role in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Biology 2022, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Jia, Y.; Fu, T.; Viswakarma, N.; Bai, L.; Rao, M.S.; Zhu, Y.; Borensztajn, J.; Reddy, J.K. Sustained activation of PPARα by endogenous ligands increases hepatic fatty acid oxidation and prevents obesity in ob/ob mice. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2012, 26, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalloyer, F.; Staels, B. Fibrates, glitazones, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kong, L.; Xu, S.; Wang, C.; Gu, J.; Luo, H.; Meng, Q. FXR overexpression prevents hepatic steatosis through inhibiting AIM2 inflammasome activation in alcoholic liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 188–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scoditti, E.; Sabatini, S.; Carli, F.; Gastaldelli, A. Hepatic glucose metabolism in the steatotic liver. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cao, P.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis is modulated by glycogen level in the liver. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udoh, U.S.; Swain, T.M.; Filiano, A.N.; Gamble, K.L.; Young, M.E.; Bailey, S.M. Chronic ethanol consumption disrupts diurnal rhythms of hepatic glycogen metabolism in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 308, G964–G974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quistgaard, E.M. BAP31: Physiological functions and roles in disease. Biochimie 2021, 186, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, M.; Yamagata, T.; Mizuguchi, M.; Itoh, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Hironaka, M.; Honda, A.; Momoi, M.Y.; Shimozawa, N. Contiguous ABCD1 DXS1357E deletion syndrome: Report of an autopsy case. Neuropathol. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Neuropathol. 2013, 33, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L.; Li, L.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, Y.Q.; Shan, M.; Sun, S.Z.; Yu, Y.; Wang, B. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of BAP31 promotes SREBP1C activation, promotes hepatic lipid accumulation, and worsens IR in mice. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, F.; Jiang, S.; Sun, X.; Xu, J. Induction of Liver Steatosis in BAP31-Deficient Mice Burdened with Tunicamycin-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Shan, W.; Li, G.; Yan, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, J.; Zhang, N. Deacetylation of BAP31 by sirtuin 2 attenuates apoptosis of hepatocytes induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress, in chronic alcoholic liver injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 180, 5023–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, Q.H.; Lu, Y.J.; Ren, K.; Yi, G.H. Involvement of the IRE1alpha-XBP1 pathway and XBP1s-dependent transcriptional reprogramming in metabolic diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wazir, N.U.; Khwaja, T.M.; Khaliq, H.; Hayat, W.; Shehzad, K.; Faisal, M.S. Preserving Hepatic Glycogen Stores: Investigating the Therapeutic Influence of Vitamin E in Alcoholic Liver Injury-Induced Intracellular Carbohydrate Depletion. Ann. Punjab Med. Coll. 2024, 18, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.L.; Shen, Y.H.; Song, Y.J.; Xu, Y.; Xu, H.X. Prunella vulgaris L. attenuates gut dysbiosis and endotoxin leakage against alcoholic liver disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foufelle, F.; Ferré, P. New perspectives in the regulation of hepatic glycolytic and lipogenic genes by insulin and glucose: A role for the transcription factor sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c. Biochem. J. 2002, 366, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Chan, C.; Kaplowitz, N. Predominant role of sterol response element binding proteins (SREBP) lipogenic pathways in hepatic steatosis in the murine intragastric ethanol feeding model. J. Hepatol. 2006, 45, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolková, K.; Gotvaldová, K. Fatty Acid Trafficking Between Lipid Droplets and Mitochondria: An Emerging Perspective. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 1863–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, D.; Liu, Y.; Lin, X.; Luo, M.; Deng, C.; Li, J.; Liang, P.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, B. Rewiring Lipid Metabolism: The Central Role of CPT1 in Metabolic Dysfunction. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2025, 199, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Chen, X.; Tan, M.; Chen, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhang, X.; Dean, J.M.; Razani, B.; Lodhi, I.J. Acetyl-CoA Derived from Hepatic Peroxisomal β-Oxidation Inhibits Autophagy and Promotes Steatosis via mTORC1 Activation. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 30–42.e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Kamijo, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Sugiyama, E.; Tanaka, E.; Kiyosawa, K.; Fukushima, Y.; Peters, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Aoyama, T. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha protects against alcohol-induced liver damage. Hepatology 2004, 40, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; George, J.; Ozaki, K.; Tsuchishima, M.; Tsutsumi, M. Pemafibrate modulates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and prevents alcohol-associated liver disease in rats. Mol. Med. 2025, 31, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Denning, K.L.; Lu, Y. PPARα agonist WY-14,643 induces the PLA2/COX-2/ACOX1 pathway to enhance peroxisomal lipid metabolism and ameliorate alcoholic fatty liver in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 613, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, R.; Chen, G.Y.; Xie, G.; Hao, L.; Guo, W.; Sun, X.; Jia, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Zhong, W. Activation of PPARalpha-catalase pathway reverses alcoholic liver injury via upregulating NAD synthesis and accelerating alcohol clearance. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 174, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Huo, Y.; Hu, X.; Lu, J.; Pi, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Yao, Y.; et al. BAP31 depletion inhibited adipogenesis, repressed lipolysis and promoted lipid droplets abnormal growth via attenuating Perilipin1 proteasomal degradation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 1713–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakhshandehroo, M.; Knoch, B.; Muller, M.; Kersten, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha target genes. PPAR Res. 2010, 2010, 612089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhong, W.; Xu, W. Alcohol and the mechanisms of liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 38, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.; de la Monte, S.; Wands, J.R. Acute ethanol exposure inhibits insulin signaling in the liver. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, C.-L.; Zhao, N.; Guan, M.-J.; Xiao, M.; Yang, R.; Zhao, X.-L.; Yu, L.-H.; Zhu, Z.-P.; Xie, K.-Q. Impairment of Akt activity by CYP2E1 mediated oxidative stress is involved in chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Shimada, E.; Guardino, N.; Miyamoto, R.; Puviindran, V.; Peairs, E.; Matarangas, A.; Ishikawa, K.; Nguyen, T.; Browne, M.; et al. Protein Phosphatase 1 Regulatory Subunit 3C integrates cholesterol metabolism and isocitrate dehydrogenase in chondrocytes and neoplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2501519122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Chua, B.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, P. The Protein Phosphatase 1 Complex Is a Direct Target of AKT that Links Insulin Signaling to Hepatic Glycogen Deposition. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3406–3422.e3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.-M.; Zhang, F.-L.; Liu, X.-L.; Zhang, J.-W. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-mediated regulation of PPP1R3C promotes glycogen accumulation in human MCF-7 cells under hypoxia. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 4366–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Cheng, K.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zeng, S.; Qi, X.; Yu, L. Regulation mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum stress on metabolic enzymes in liver diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 207, 107332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stem, A.D.; Tieghi, R.S.; Chatzi, V.L.; Kleinstreuer, N.; Valvi, D.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. Synergistic toxicity in alcohol-associated liver disease and PFAS exposure. Toxicol. Sci. 2025, 208, 9–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, J.; Xia, T.; Liu, B.; Guo, Y.; Deng, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Guo, F. Liver-specific Gene Inactivation of the Transcription Factor ATF4 Alleviates Alcoholic Liver Steatosis in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 18536–18546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chi, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yao, J. BAP31 represses endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and alleviates neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2025, 16, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machihara, K.; Namba, T. BAP31 Inhibits Cell Adaptation to ER Stress Conditions, Negatively Regulating Autophagy Induction by Interaction with STX17. Cells 2019, 8, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, T. BAP31 regulates mitochondrial function via interaction with Tom40 within ER-mitochondria contact sites. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Iwakiri, Y.; Szabo, G.; Wang, H. Immunological mechanisms and emerging therapeutic targets in alcohol-associated liver disease. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2025, 22, 1190–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Cao, J.N.; Li, X.D.; Jin, L. Key Transcription Factors: Avenue for Treating Alcoholic Liver Disease. Curr. Med. Sci. 2025, 45, 841–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blainey, P.; Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Points of significance: Replication. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 879–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaux, D.L.; Fidler, F.; Cumming, G. Replicates and repeats—What is the difference and is it significant? A brief discussion of statistics and experimental design. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- eBioMedicine. The 3Rs of Animal Research. eBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P. Men and mice: Relating their ages. Life Sci. 2016, 152, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Baumgartner, J.; Malan, L.; Smuts, C.M. Determining sample size adequacy for animal model studies in nutrition research: Limits and ethical challenges of ordinary power calculation procedures. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, T.L.; Kiersgaard, M.K.; Sørensen, D.B.; Mikkelsen, L.F. Fasting of mice: A review. Lab. Anim. 2013, 47, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.M.; Du, K.; You, M.; Ding, W.X. Critical role of FoxO3a in alcohol-induced autophagy and hepatotoxicity. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Chao, X.; Ni, H.M.; Ding, W.X. An Update on Animal Models of Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Donepudi, A.C.; More, V.R.; Slitt, A.L. Enhanced Nrf2 activity worsens insulin resistance, impairs lipid accumulation in adipose tissue, and increases hepatic steatosis in leptin-deficient mice. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3208–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Luo, H.; Jin, Y.; Shu, Y.; Wen, C.; Qin, T.; Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; You, Y.; et al. Asperosaponin VI protects alcohol-induced hepatic steatosis and injury via regulating lipid metabolism and ER stress. Phytomedicine 2023, 121, 155080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, A.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Yao, Y.; Guo, J. Understanding the effect of anthocyanin extracted from Lonicera caerulea L. on alcoholic hepatosteatosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, H.D.; Xu, J.J.; Li, J.J.; Cheng, M.; Meng, X.M.; Huang, C.; Li, J. Advancements in the Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease Model. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Control | Ethanol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | WT | BAP31-LKO | WT | BAP31-LKO | |
| Glucose | mg/dL | 48.71 ± 5.34 | 49.79 ± 3.63 | 68.00 ± 4.88 | 52.75 ± 4.47 * |
| TG | mg/dL | 44.42 ± 5.44 | 41.06 ± 2.45 | 53.77 ± 5.11 | 47.94 ± 5.49 |
| FFA | mEq/L | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 0.36 ± 0.05 | 0.26 ± 0.04 | 0.50 ± 0.06 * |
| Cholesterol | mg/dL | 100.21 ± 3.17 | 92.69 ± 3.63 | 84.31 ± 3.98 | 87.47 ± 5.83 |
| HDL-C | mg/dL | 41.98 ± 2.05 | 38.92 ± 1.65 | 32.98 ± 2.25 | 31.17 ± 2.92 |
| LDL-C | mg/dL | 50.82 ± 2.24 | 46.96 ± 3.18 | 43.65 ± 6.41 | 37.48 ± 2.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, C.; Han, X.; Feng, X.; Li, L.; Ma, H.; Xu, J. B-Cell Receptor-Associated Protein 31 Deficiency Aggravates Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis and Liver Injury via Attenuating Fatty Acid Oxidation and Glycogen Synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412173
Yu S, Xia Y, Zhang C, Han X, Feng X, Li L, Ma H, Xu J. B-Cell Receptor-Associated Protein 31 Deficiency Aggravates Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis and Liver Injury via Attenuating Fatty Acid Oxidation and Glycogen Synthesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412173
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shubin, Yaodong Xia, Chunyan Zhang, Xiangyue Han, Xiaoyue Feng, Liya Li, Hang Ma, and Jialin Xu. 2025. "B-Cell Receptor-Associated Protein 31 Deficiency Aggravates Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis and Liver Injury via Attenuating Fatty Acid Oxidation and Glycogen Synthesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412173
APA StyleYu, S., Xia, Y., Zhang, C., Han, X., Feng, X., Li, L., Ma, H., & Xu, J. (2025). B-Cell Receptor-Associated Protein 31 Deficiency Aggravates Ethanol-Induced Liver Steatosis and Liver Injury via Attenuating Fatty Acid Oxidation and Glycogen Synthesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 12173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412173






