Transcriptional Activity of Genes Related to the Biotransformation Process in the Development of Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Histopathological Confirmation
2.2. Quality Confirmation
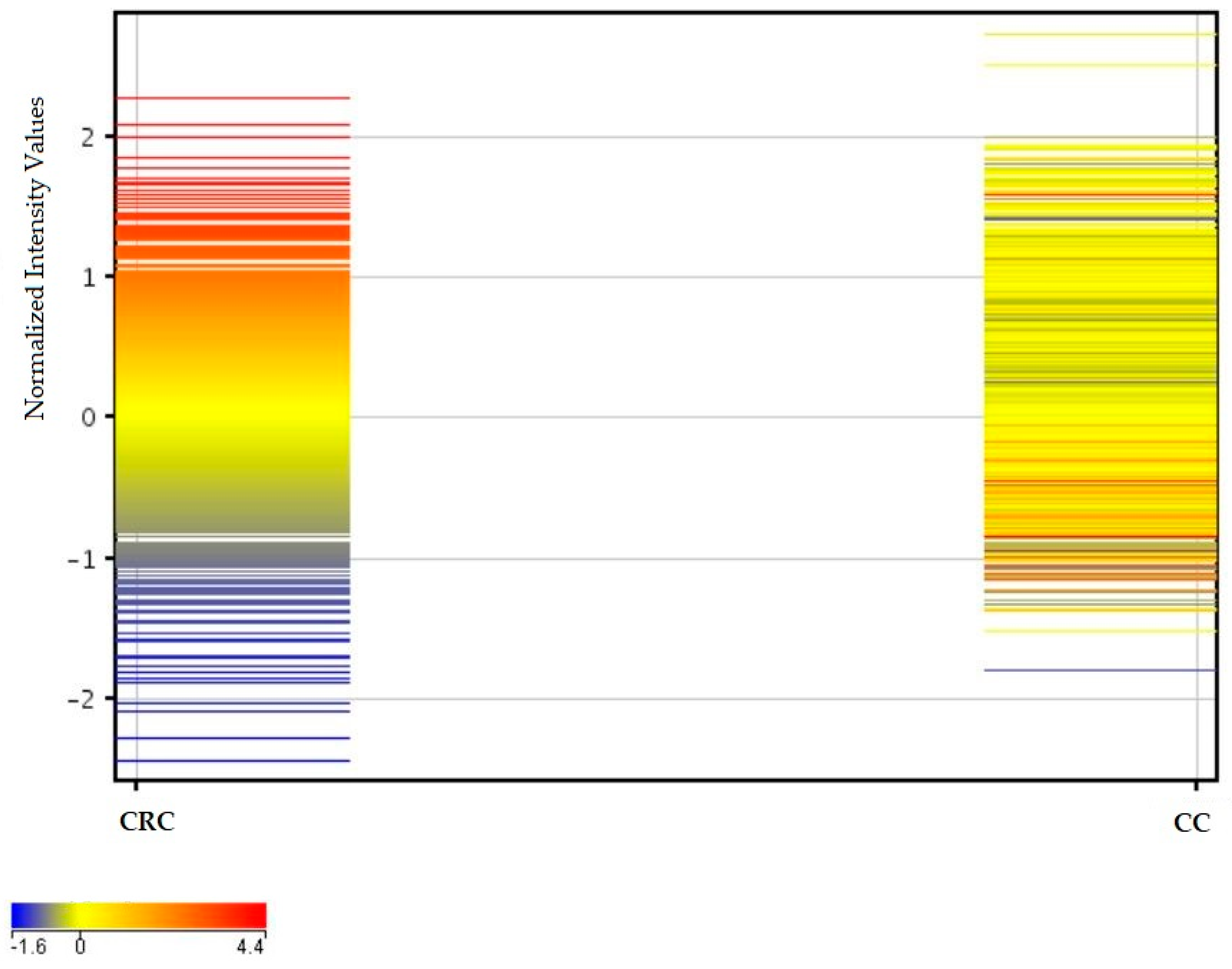
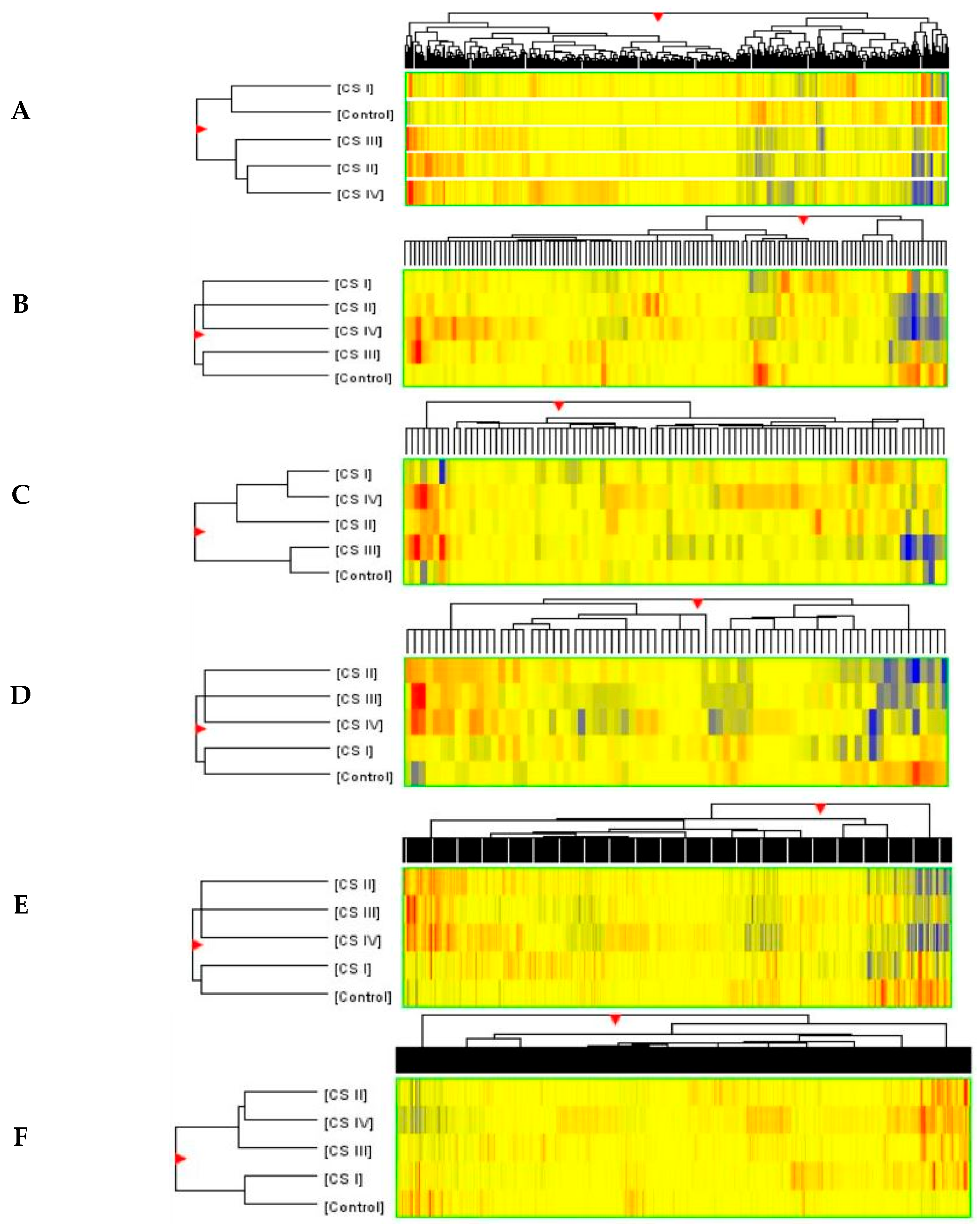
2.3. Similarities and Differences in Fluorescence Signals of mRNAs
2.4. Analysis of Variance and Post Hoc Test
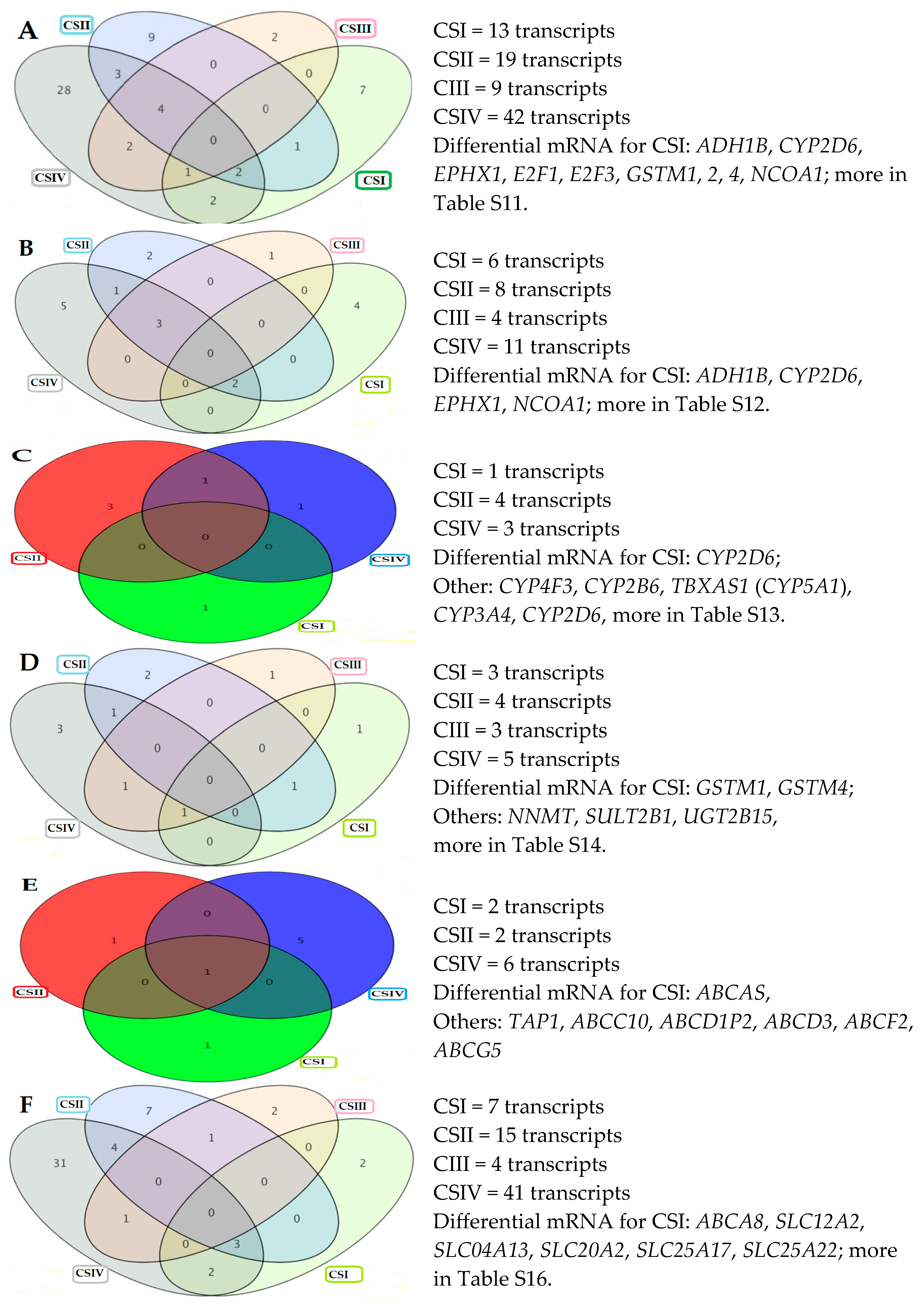
2.5. Differentially Expressed Genes
2.6. Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
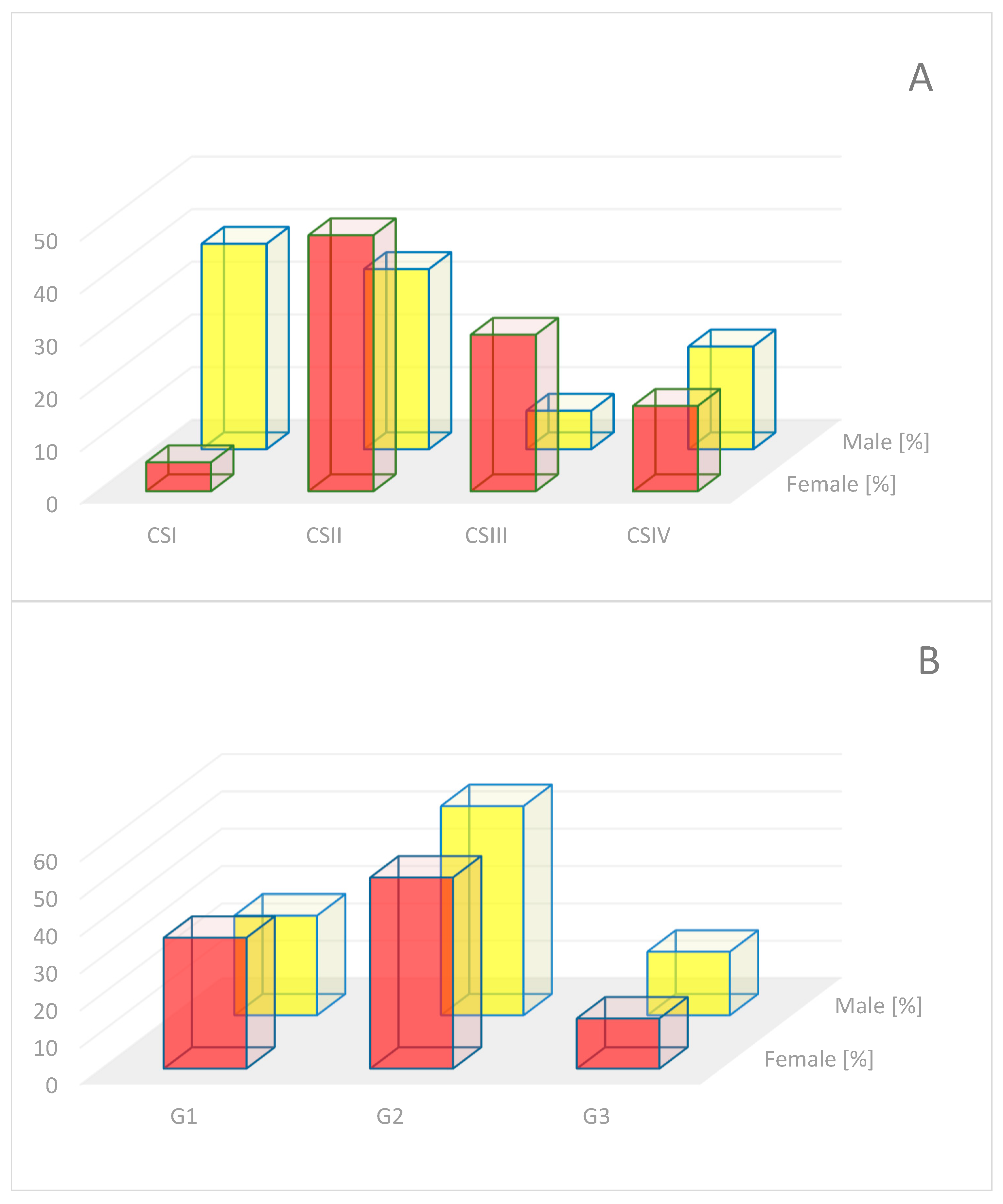
4.1. Material for Analysis
4.2. Histopathological Procedure
4.3. Material Grouping
4.4. RNA Extraction
4.5. Microarray Analysis
4.6. Selecting Gene Panels for Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette |
| AC | Adenocarcinoma |
| ADH | Alcohol dehydrogenase |
| ALDH | Aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BaP | Benzo(a)pyrene |
| B-H | Benjamini–Hochberg correction of p-value |
| BRAF | B-rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma |
| CA 19-9 | Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 |
| CAR T | Chimeric antigen receptor T cells |
| CC | Control colon |
| CEA | Carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| CS | Clinical stage |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| down | downregulation |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERBB2 | Erythroblastic oncogene B |
| FC | Fold Change |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
| FMO | Flavin-containing monooxidase |
| G1 | Grade 1 |
| G2 | Grade 2 |
| G3 | Grade 3 |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| HSD | High Significant Difference |
| ID | Identified number of transcript probes in Affymetrix microarrays |
| KRAS | Kirsten Rat sarcoma |
| MAOA | Monoamine oxidase |
| MEK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
| NRAS | Neuroblastoma RAS |
| p-value | Probability value |
| r | Correlation coefficient |
| RAS | Rat Sarcoma |
| S | Supplemental |
| SLC | Solute Carrier transporter |
| TCDD | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin |
| TNM | Tumor Node Metastasis |
| UGT | Uridine diphospho-glucuronosyl ransferase |
| up | upregulation |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| Names of genes used in the text are explained in Table S18. |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Statistics. Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/colorectal-cancer (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. Systematic review of blood diagnostic markers in colorectal cancer. Tech. Coloproctol. 2018, 22, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Cave, D. Advances in Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Colorectal Cancer: A New Era of Precision Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarlou, V.; Jafarlou, M. Current Approaches, Challenges, and Future Perspectives in Colorectal Cancer Therapeutics and Integrated Care. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Care 2025, 10, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowska, U.; Didkowska, J.; Barańska, K.; Miklewska, M.; Michałek, I.; Olasek, P.; Jawołowska, A. Cancer in Poland in 2022. In Polish National Cancer Registry; Maria Curie-Sklodowska National Institute of Oncology: Warsaw, Poland, 2024; Available online: https://onkologia.org.pl/sites/default/files/publications/2025-02/Nowotwory_2022.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2025).
- Dosunmu, G.T.; Shergill, A. Colorectal Cancer: Genetic Underpinning and Molecular Therapeutics for Precision Medicine. Genes 2024, 15, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Gundín, J.; Fernández-Carballido, A.M.; Martínez-Valdivieso, L.; Barreda-Hernández, D.; Torres-Suárez, A.I. New Trends in the Therapeutic Approach to Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 15, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steup, C.; Kennel, K.B.; Neurath, M.F.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Greten, F.R. Current and emerging concepts for systemic treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2025, 74, 2070–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapanotti, M.C.; Cenci, T.; Scioli, M.G.; Cugini, E.; Anzillotti, S.; Savino, L.; Coletta, D.; Di Raimondo, C.; Campione, E.; Roselli, M.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells: Origin, Role, Current Applications, and Future Perspectives for Personalized Medicine. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeanolue, I.R.; Ezeanolue, C.F.; Plastina, P.; Stefanello, F.M.; Giacomelli Tavares, R.; Spanevello, R.M. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory and Anticancer Potential of Pecan Nut (Carya illinoinensis) Kernel Extracts: Modulation of Cell Signaling Pathways-A Scoping Review. Molecules 2025, 30, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudaev, P.; Tupikov, A.; Chistyakov, E. Organocyclophosphazenes and Materials Based on Them for Pharmaceuticals and Biomedicine. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.B.D.; Pianovski, M.A.D.; Carvalho Filho, N.P. Environmental pollution and cancer. J. Pediatr. 2025, 101, S18–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T. Xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes involved in activation and detoxification of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2006, 21, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang-Lyn, S.; Llerena, V.A. Biochemistry, Biotransformation; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. ABC Family Transporters. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1141, 13–100. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Zhao, Q.; Sharma, V.; Nguyen, L.P.; Lee, Y.N.; Pham, K.L.; Edderkaoui, M.; Pandol, S.J.; Park, W.; Habtezion, A. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligands in Cigarette Smoke Induce Production of Interleukin-22 to Promote Pancreatic Fibrosis in Models of Chronic Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, A.; Busch, D.; Lapczuk, J.; Ostrowski, M.; Drozdzik, M.; Oswald, S. Expression of clinically relevant drug-metabolizing enzymes along the human intestine and their correlation to drug transporters and nuclear receptors: An intra-subject analysis. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan Sridhar, V.; Ambinathan, J.P.N.; Kretzler, M.; Pyle, L.L.; Bjornstad, P.; Eddy, S.; Cherney, D.Z.; Reich, H.N. European Renal cDNA Bank (ERCB): Nephrotic Syndrome Study Network (NEPTUNE). Renal SGLT mRNA expression in human health and disease: A study in two cohorts. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2019, 317, F1224–F1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.C.; Chien, W.C.; Hu, J.M.; Tzeng, N.S.; Chung, C.H.; Pu, T.W.; Hsiao, C.W.; Chen, C.Y. Risk of colorectal cancer in patients with alcoholism: A nationwide, population-based nested case-control study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botteri, E.; Borroni, E.; Sloan, E.K.; Bagnardi, V.; Bosetti, C.; Peveri, G.; Santucci, C.; Specchia, C.; van den Brandt, P.; Gallus, S.; et al. Smoking and Colorectal Cancer Risk, Overall and by Molecular Subtypes: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavarini, M.; Bertarelli, G.; Minelli, L.; Fabiani, R. Dietary Intake of Meat Cooking-Related Mutagens (HCAs) and Risk of Colorectal Adenoma and Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yang, H.; Li, W.; Liu, J.Y.; Ren, L.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Ge, B.B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Fu, W.Q.; Zheng, X.J.; et al. ADH1C inhibits progression of colorectal cancer through the ADH1C/PHGDH /PSAT1/serine metabolic pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2709–2722, Erratum in Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 2450–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropotova, E.S.; Zinovieva, O.L.; Zyryanova, A.F.; Dybovaya, V.I.; Prasolov, V.S.; Beresten, S.F.; Oparina, N.Y.; Mashkova, T.D. Altered expression of multiple genes involved in retinoic acid biosynthesis in human colorectal cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 707–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, S.; Regan, N.; West, M.B.; Kumar, V.P.; Thai, J.; Li, P.K.; Cook, P.F.; Hanigan, M.H. Divergent effects of compounds on the hydrolysis and transpeptidation reactions of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2012, 27, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yardim-Akaydin, S.; Deviren, C.; Miser-Salihoglu, E.; Caliskan-Can, E.; Atalay, M.C. mRNA Expressions of Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase Genes in Different Types of Cancer. FABAD J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 42, 21–28. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Sun, Q.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, W.; Zhou, D.; Lin, J.; Wang, W. Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) expression in colorectal cancer tissues from patients with liver metastasis. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, N.W.; Yang, L.; Rogan, E.G.; Cavalieri, E.L. Evidence for NQO2-mediated reduction of the carcinogenic estrogen ortho-quinones. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Wang, Z.; Hamby, C.V.; Wu, J.M. Inhibition of melanoma cell proliferation by resveratrol is correlated with upregulation of quinone reductase 2 and p53. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 334, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Q.; Zhu, S.Y.; He, Y.; Yu, K.D. Association Between a Tri-allelic Polymorphism in the Estrogen Metabolism Oxidoreductase NRH:Quinone Oxidoreductase 2 Gene and Risk of Breast Cancer by Molecular Subtype. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 658285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.J.; Hong, W.F.; Liu, M.L.; Guo, X.; Yu, Y.Y.; Cui, Y.H.; Liu, T.S.; Liang, L. An integrated bioinformatic investigation of mitochondrial solute carrier family 25 (SLC25) in colon cancer followed by preliminary validation of member 5 (SLC25A5) in tumourigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, D.; Yang, X.; Qian, C.; Liu, Z. Cancer Therapeutic Potential and Prognostic Value of the SLC25 Mitochondrial Carrier Family: A Review. Cancer Control 2024, 31, 10732748241287905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, H.H.; Paeng, J.C.; Park, Y.J.; Oh, S.W.; Chai, Y.J.; Kim, Y.A.; Cheon, G.J.; Kang, K.W.; et al. Adenine nucleotide translocase 2 as an enzyme related to [(18)F] FDG accumulation in various cancers. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yan, D.; Teng, M.; Tang, H.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Qiu, G.; Peng, Z. Digital transcript profile analysis with aRNA-LongSAGE validates FERMT1 as a potential novel prognostic marker for colon cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 2908–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Voorde, J.; Steven, R.T.; Najumudeen, A.K.; Ford, C.A.; Dexter, A.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, A.; Nikula, C.J.; Xiang, Y.; Ford, L.; Stavrakaki, S.M.; et al. Metabolic profiling stratifies colorectal cancer and reveals adenosylhomocysteinase as a therapeutic target. Nat. Metab. 2023, 5, 1303–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.Q.; Wu, Q.M.; Yang, C.H.; Yan, Q.D.; Cao, P.J.; Chen, F.L. Four Low Expression LncRNAs are Associated with Prognosis of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Lab. 2020, 66, 200211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandfellner, H.M.; Ruparel, S.B.; Gelfond, J.A.; Hargreaves, K.M. Major blunt trauma evokes selective upregulation of oxidative enzymes in circulating leukocytes. Shock 2013, 40, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Aldrees, M.; Arif, M.; Li, X.; Mardinoglu, A.; Aziz, M.A. Elucidating the Reprograming of Colorectal Cancer Metabolism Using Genome-Scale Metabolic Modeling. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenach, P.A.; Soeth, E.; Röder, C.; Klöppel, G.; Tepel, J.; Kalthoff, H.; Sipos, B. Dipeptidase 1 (DPEP1) is a marker for the transition from low-grade to high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and an adverse prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebag, S.C.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, Q.; Li, M.; Zhu, Z.; Harata, M.; Li, W.; Zingman, L.V.; Liu, L.; Lira, V.A.; et al. ADH5-mediated NO bioactivity maintains metabolic homeostasis in brown adipose tissue. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelski, W.; Zalewski, B.; Chrostek, L.; Szmitkowski, M. The activity of class I, II, III, and IV alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzymes and aldehyde dehydrogenase in colorectal cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2004, 49, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Li, H.; Qian, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.; Wang, B.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, X. Loss of AKR1B10 promotes colorectal cancer cells proliferation and migration via regulating FGF1-dependent pathway. Aging 2020, 12, 13059–13075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andress Huacachino, A.; Joo, J.; Narayanan, N.; Tehim, A.; Himes, B.E.; Penning, T.M. Aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily website and database: An update. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2024, 398, 111111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wang, T.; Ge, W.; Ren, C.; Ko, B.C.; Zeng, X.; Cao, D. Role of AKR1B10 in inflammatory diseases. Scand. J. Immunol. 2024, 100, e13390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakase, H.; Mizuguchi, H.; Nakajima, M. Quantitative Analysis of mRNA and Protein Expression Levels of Aldo-Keto Reductase and Short-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase Isoforms in the Human Intestine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2023, 51, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, R.C.; Johnston, S.M.; Watson, D.G.; McGarvie, G.; Ellis, E.M. Synthesis and catabolism of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells: Role of the aldo-keto reductase AKR7A2. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 25986–25992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Waals, L.M.; Borel Rinkes, I.H.M.; Kranenburg, O. ALDH1A1 expression is associated with poor differentiation, ‘right-sidedness’ and poor survival in human colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.L.; Zeng, D.Z.; Dong, W.G.; Ding, Y.Q.; Rao, J.; Duan, J.J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhan, N.; Liu, Y.; et al. Distinct patterns of ALDH1A1 expression predict metastasis and poor outcome of colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2976–2986. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Ba, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H. The prognostic significance of epoxide hydrolases in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2025, 41, 101912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, T.; Yin, J. The role of soluble epoxide hydrolase in the intestine. Cell Biol. Int. 2024, 48, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikula, M.; Rubel, T.; Karczmarski, J.; Goryca, K.; Dadlez, M.; Ostrowski, J. Integrating proteomic and transcriptomic high-throughput surveys for search of new biomarkers of colon tumours. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2010, 11, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybaczyk, L.A.; Bashaw, M.J.; Pathak, D.R.; Huang, K. An indicator of cancer: Downregulation of monoamine oxidase-A in multiple organs and species. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, J.C. Monoamine oxidase isoenzymes: Genes, functions and targets for behavior and cancer therapy. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Frampton, G.; Rao, A.; Zhang, K.S.; Chen, W.; Lai, J.M.; Yin, X.Y.; Walker, K.; Culbreath, B.; Leyva-Illades, D.; et al. Monoamine oxidase A expression is suppressed in human cholangiocarcinoma via coordinated epigenetic and IL-6-driven events. Lab. Investig. 2012, 92, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, F.A. Cyclooxygenase enzymes: Regulation and function. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekeye, A.; Agarwal, D.; Nayak, A.; Tchou, J. PTGES3 is a Putative Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2022, 271, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Ruan, N.; Ma, L.; Han, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Screening and Identification of Key Biomarkers for Bladder Cancer: A Study Based on TCGA and GEO Data. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 8283401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.M.; Harris, R.E. Cyclooxygenase and Lipoxygenase Gene Expression in the Inflammogenesis of Colorectal Cancer: Correlated Expression of EGFR, JAK STAT and Src Genes, and a Natural Antisense Transcript, RP11-C67.2.2. Cancers 2023, 15, 2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerle, J.; Holowatyj, A.N.; Haffa, M.; Frei, E.; Gigic, B.; Schrotz-King, P.; Boehm, J.; Habermann, N.; Stiborova, M.; Scherer, D.; et al. Expression Patterns of Xenobiotic-Metabolizing Enzymes in Tumour and Adjacent Normal Mucosa Tissues among Patients with Colorectal Cancer: The ColoCare Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2020, 29, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, W.H.; Nagengast, F.M.; Wobbes, T. Glutathione S-transferases in normal and cancerous human colon tissue. Carcinogenesis 1989, 10, 2371–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, M.; Rollinger, W.; Palme, S.; Hagmann, M.L.; Berndt, P.; Engel, A.M.; Schneidinger, B.; Pfeffer, M.; Andres, H.; Karl, J.; et al. Identification of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase as a novel serum tumour marker for colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 6550–6557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.M.; Long, H. Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase as a potential marker for cancer. Neoplasma 2018, 65, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jancova, P.; Anzenbacher, P.; Anzenbacherova, E. Phase II drug metabolizing enzymes. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc Czech Repub. 2010, 154, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pissios, P. Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase: More Than a Vitamin B3 Clearance Enzyme. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, E.; Wei, H.; Liao, X.; Wu, L.; Zeng, X. Clinical significance and biological mechanisms of glutathione S-transferase mu gene family in colon adenocarcinoma. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ge, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, H.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zao, X.; et al. Downregulation of UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase predicts adverse outcomes in patients with colorectal cancer and promotes tumourigenesis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, B.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, J. A five-gene based risk score with high prognostic value in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6724–6734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Goel, A.; Chung, D.C. Pathways of Colorectal Carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, S.; Park, Y.K.; Franklin, J.L.; Halberg, R.B.; Yu, M.; Jessen, W.J.; Freudenberg, J.; Chen, X.; Haigis, K.; Jegga, A.G.; et al. Transcriptional recapitulation and subversion of embryonic colon development by mouse colon tumour models and human colon cancer. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburg, C.P.; Nguyen, N.; Manns, M.P.; Tukey, R.H. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity in human liver and colon. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; et al. Identification of genes involved in the four stages of colorectal cancer: Gene expression profiling. Mol. Cell Probes 2018, 37, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.N.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Li, J.P.; Li, A.Y. Comprehensive pan-cancer analysis: Essential role of ABCB family genes in cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 1642–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Martin, P.M.; Miyauchi, S.; Ananth, S.; Herdman, A.V.; Martindale, R.G.; Podolsky, R.; Ganapathy, V. Down-regulation of BCRP/ABCG2 in colorectal and cervical cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Huang, Y.; Shi, M.; Qian, X.; Li, H.; Peng, C.; Kong, B.; Zou, X.; Shen, S. Protective role of ABCG2 against oxidative stress in colorectal cancer and its potential underlying mechanism. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 2137–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violante, S.; Achetib, N.; van Roermund, C.W.T.; Hagen, J.; Dodatko, T.; Vaz, F.M.; Waterham, H.R.; Chen, H.; Baes, M.; Yu, C.; et al. Peroxisomes can oxidize medium- and long-chain fatty acids through a pathway involving ABCD3 and HSD17B4. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4355–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Majdoub, Z.M.; Achour, B.; Couto, N.; Howard, M.; Elmorsi, Y.; Scotcher, D.; Alrubia, S.; El-Khateeb, E.; Vasilogianni, A.M.; Alohali, N.; et al. Mass spectrometry-based abundance atlas of ABC transporters in human liver, gut, kidney, brain and skin. FEBS Lett. 2020, 594, 4134–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, G. Abnormal expression of ABCD3 is an independent prognostic factor for colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3567–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J.; Deng, Q.; He, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z. Tumour suppressor ABCA8 inhibits malignant progression of colorectal cancer via Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, J.; Song, R.; Wang, J.; Yin, D.; et al. ABCA8 is regulated by miR-374b-5p and inhibits proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the ERK/ZEB1 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Jung, S.; Park, W.S.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, R.; Heo, S.C.; Choe, E.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.; Chai, Y.J. Upregulation of SLC2A3 gene and prognosis in colorectal carcinoma: Analysis of TCGA data. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Nie, H.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Qiu, P.S.; Wang, F.; Peng, Y.N.; Xu, F.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, M. Comprehensive analyses of solute carrier family members identify SLC12A2 as a novel therapy target for colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.F.; Cai, Y.C.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R.H.; Qiu, H.J.; Xia, L.P.; Jiang, W.Q.; Hu, P.L.; Chen, X.X.; Zhou, F.F.; et al. Overexpression of SGLT1 and EGFR in colorectal cancer showing a correlation with the prognosis. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, S197–S203. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Miyauchi, S.; Martindale, R.G.; Herdman, A.V.; Podolsky, R.; Miyake, K.; Mager, S.; Prasad, P.D.; Ganapathy, M.E.; Ganapathy, V. Upregulation of the amino acid transporter ATB0,+ (SLC6A14) in colorectal cancer and metastasis in humans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1741, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaziri-Moghadam, A.; Foroughmand-Araabi, M.H. Integrating machine learning and bioinformatics approaches for identifying novel diagnostic gene biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashemi, M.; Tahmasebi-Birgani, M.; Talaiezadeh, A.; Saberi, A. Upregulation of SLC25A32 in Tumourous Tissues of Patients with Non-Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Pilot Study. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2025, 40, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Belkhiri, A.; Lockhart, A.C.; Merchant, N.; Glaeser, H.; Harris, E.I.; Washington, M.K.; Brunt, E.M.; Zaika, A.; Kim, R.B.; et al. Overexpression of OATP1B3 confers apoptotic resistance in colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 10315–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, M.J.; Ji, S.H.; Lee, C.K.; Bae, S.B.; Kim, H.J.; Ahn, T.S.; Lee, M.S.; Baek, M.J.; Jeong, D. Solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 4A1 (SLCO4A1) as a prognosis marker of colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.Y.; Wei, P.L.; Lee, C.C.; Zumbi, C.N.; Prince, G.M.S.H.; Batzorig, U.; Huang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.J. Solute Carrier Family 35 A2 (SLC35A2) Promotes Tumour Progression through MYC-Mediated Pathways in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 22, 1992–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.; Wang, D.; Ping, Y.; Sang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Duan, X.; Tao, Z.; Liu, W. Integrated profiling identifies SLC5A6 and MFAP2 as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in gastric cancer patients. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zuo, T.; Zhu, X.; Ahuja, N.; Fu, T. Differential expression of hENT1 and hENT2 in colon cancer cell lines. Genet. Mol. Res. 2017, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, I.A.; Patterson, A.D.; Perdew, G.H. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: Friend and foe. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safe, S.; Lee, S.O.; Jin, U.H. Role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in carcinogenesis and potential as a drug target. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 135, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlowe, J.L.; Fan, Y.; Chang, X.; Peng, L.; Knudsen, E.S.; Xia, Y.; Puga, A. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor binds to E2F1 and inhibits E2F1-induced apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3263–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschopp, J.; Schroder, K. NLRP3 inflammasome activation: The convergence of multiple signalling pathways on ROS production? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.G.; Marri, S.; McKinnon, R.A.; Mackenzie, P.I.; Meech, R. Deregulation of the Genes that Are Involved in Drug Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1471–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobin, L.H.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wittekind, C.H. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours; Wiley-Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]





| Phase | Panel | Number of mRNAs Dependent on p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| all | p < 0.05 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.001 | ||
| I | Biotransformation | 366 | 98 | 57 | 19 |
| Functionalization | 121 | 29 | 19 | 6 | |
| CYPs | 91 | 9 | 1 | 0 | |
| II | Conjugation | 75 | 14 | 11 | 7 |
| III | ATP-binding cassette | 69 | 11 | 4 | 1 |
| Transporters | 456 | 63 | 22 | 11 | |
| Phase | Probe Set ID | Gene Symbol | FDR p-Value B-H Corrected | CSI vs. CC | CSII vs. CC | CSIII vs. CC | CSIV vs. CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | ||||
| 200903_s_at | AHCY | 3.5 × 10−4 | 1.55 | up | 2.77 | up | 1.08 | up | 1.61 | up | |
| I | 206754_s_at | CYP2B7P1 | 0.003 | 1.09 | up | 2.26 | up | 2.19 | up | 4.45 | up |
| 205983_at | DPEP1 | 0.004 | 3.03 | up | 2.30 | up | 2.34 | up | 3.69 | up | |
| 206262_at | ADH1C | 0009 | 1.07 | up | −4.73 | down | −2.64 | down | −4.78 | down | |
| 205582_s_at | GGT5 | 3.3 × 10−4 | −1.16 | down | 1.35 | up | 2.01 | up | 2.05 | up | |
| 208847-s-at | ADH5 | 0.0002 | −1.17 | down | −1.43 | down | −1.72 | down | −2.44 | down | |
| 208848_at | ADH5 | 0.005 | −1.95 | down | −1.78 | down | −1.57 | down | −4.63 | down | |
| 206561_s_at | AKR1B10 | 0.03415 | −1.27 | down | −4.76 | down | −4.01 | down | −6.33 | down | |
| 202139__at | AKR7A2 | 0.005 | −1.18 | down | −1.39 | down | −1.05 | down | −2.42 | down | |
| 212224_at | ALDH1A1 | 1.50 × 10−4 | −3.67 | down | −7.04 | down | −3.21 | down | −6.74 | down | |
| 202017_at | EPHX1 | 0.005 | −2.87 | down | −1.39 | down | −1.17 | down | −2.05 | down | |
| 209368_at | EPHX2 | 0.0002 | −1.68 | down | −2.03 | down | −1.84 | down | −2.24 | down | |
| 212741_at | MAOA | 3.61 × 10−6 | −1.51 | down | −3.38 | down | −2.55 | down | −4.78 | down | |
| 204389_at | MAOA | 8.57 × 10−8 | −1.61 | down | −4.02 | down | −2.61 | down | −5.01 | down | |
| 204388_s_at | MAOA | 1.65 × 10−7 | −1.62 | down | −3.27 | down | −2.71 | down | −4.19 | down | |
| 205127_at | PTGS1 | 0.007 | −4.44 | down | −3.14 | down | −2.18 | down | −4.43 | down | |
| 205128_x_at | PTGS1 | 0.008 | −3.45 | down | −2.55 | down | −1.79 | down | −3.10 | down | |
| 215813_s_at | PTGS1 | 0.006 | −4.03 | down | −2.99 | down | −1.73 | down | −4.30 | down | |
| II | 200824_at | GSTP1 | 0.004 | 1.49 | up | 2.19 | up | 1.42 | up | 1.65 | up |
| 202237_at | NNMT | 4.6 × 10−4 | 1.95 | up | 2.8 | up | 5.5 | up | 4.51 | up | |
| 202238_s_at | NNMT | 5.99 × 10−4 | 1.75 | up | 2.4 | up | 5.4 | up | 3.19 | up | |
| 203814_s_at | NQO2 | 0.004 | −1.01 | down | 2.16 | up | 1.22 | up | 1.19 | up | |
| 204550_x_at | GSTM1 | 0.0008 | −2.03 | down | −1.77 | down | −1.49 | down | −1.34 | down | |
| 204418_at | GSTM2 | 0.0005 | −2.31 | down | −1.79 | down | −1.44 | down | −1.33 | down | |
| 204419_s_at | GSTM4 | 2.6 × 10−5 | −1.95 | down | −1.87 | down | −2.48 | down | −2.36 | down | |
| 203343_at | UGDH | 0.013 | −1.24 | down | −2.14 | down | −1.74 | down | −2.68 | down | |
| 205480_s_at | UGP2 | 4.2 × 10−6 | −1.96 | down | −2.99 | down | −2.37 | down | −5.14 | down | |
| 221305_s_at | UGT1A9 | 0.013 | −1.72 | down | −2.68 | down | −2.46 | down | −1.55 | down | |
| 207245_at | UGT2B17 | 0.01184 | −2.44 | down | −8.52 | down | −3.62 | down | −5.93 | down | |
| Probe Set ID | Gene Symbol | FDR p-Value B-H Corrected | CSI vs. CC | CSII vs. CC | CSIII vs. CC | CSIV vs. CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | |||
| 202307_s_at | ABCB2 | 0.0068 | 2.93 | up | 1.79 | up | 1.37 | up | 1.27 | up |
| 202497_x_at | SLC2A3 | 0.015 | 1.32 | up | 1.18 | up | 2.00 | up | 2.84 | up |
| 202498_s_at | SLC2A3 | 0.022 | 1.06 | up | 1.06 | up | 1.47 | up | 1.37 | up |
| 202499_s_at | SLC2A3 | 0.015 | 1.44 | up | 1.08 | up | 2.70 | up | 3.82 | up |
| 206628_at | SLC5A1 | 0.020 | 1.54 | up | 2.84 | up | 1.02 | up | 1.32 | up |
| 204087_s_at | SLC5A6 | 3.2 × 10−4 | 1.63 | up | 2.81 | up | 1.55 | up | 2.34 | up |
| 219795_at | SLC6A14 | 0.043 | 2.60 | up | 2.84 | up | 1.46 | up | 1.05 | up |
| 201195_s_at | SLC7A5 | 3.0 × 10−5 | 2.01 | up | 4.00 | up | 2.54 | up | 3.91 | up |
| 204404_at | SLC12A2 | 0.011 | 3.90 | up | 1.99 | up | 1.29 | up | 2.15 | up |
| 218653_at | SLC25A15 | 0.014 | 1.83 | up | 2.30 | up | 1.22 | up | 1.59 | up |
| 221020_s_at | SLC25A32 | 0.024 | 1.43 | up | 2.04 | up | 1.50 | up | 1.13 | up |
| 204717_s_at | SLC29A2 | 0.034 | 2.05 | up | 1.53 | up | 1.41 | up | 1.90 | up |
| 206354_at | SLCO1B3 | 0.026 | 1.40 | up | 1.86 | up | 1.07 | up | 2.41 | up |
| 219911_s_at | SLCO4A1 | 9.2 × 10−6 | 3.28 | up | 4.68 | up | 1.81 | up | 2.53 | up |
| 200657_at | SLC25A5 | 9.2 × 10−4 | 1.02 | up | 1.02 | up | −1.65 | down | −2.15 | down |
| 204719_at | ABCA8 | 4.6 × 10−8 | −4.65 | down | −7.15 | down | −1.44 | down | −8.08 | down |
| 202850_at | ABCD3 | 0.0315 | −1.19 | down | −1.36 | down | −1.30 | down | −2.99 | down |
| 209735_at | ABCG2 | 0.010 | −3.20 | down | −4.71 | down | −3.78 | down | −4.73 | down |
| 202825_at | SLC25A4 | 0.004 | −2.00 | down | −1.86 | down | −1.81 | down | −3.07 | down |
| 203306_s_at | SLC35A1 | 0.043 | −1.17 | down | −1.99 | down | −1.49 | down | −3.10 | down |
| Probe Set ID | Gene Symbol | FDR p-Value B-H Corrected | CSI vs. CC | CSII vs. CC | CSIII vs. CC | CSIV vs. CC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | FC | Regulation | |||
| 202820_at | AHR | 0.014 | 1.21 | up | 1.15 | up | 1.51 | up | 1.30 | up |
| 206651_s_at | CPB2 | 7.4 × 10−4 | 1.11 | up | 1.06 | up | 1.09 | up | 1.30 | up |
| 2028_s_at | E2F1 | 0.032 | 1.03 | up | 1.24 | up | 1.05 | up | 1.27 | up |
| 204947_at | E2F1 | 0.001 | 1.40 | up | 1.09 | up | 1.04 | up | 1.54 | up |
| 203957_at | E2F6 | 2.0 × 10−4 | 1.29 | up | 1.61 | up | 1.05 | up | 1.13 | up |
| 206998_x_at | PRB3 | 0.0012 | 1.26 | up | 1.12 | up | 1.09 | up | 1.61 | up |
| CC vs. CC | CC vs. AC | AC vs. AC | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p | Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p | Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p |
| ADH1C | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | 0.68 | 0.002 | AHCY | ↔ | ADH5 | −0.52 | 0.028 | DEPEP1 | ↔ | AHR | −0.49 | 0.040 |
| GGT5 | ↔ | AHCY | 0.46 | 0.046 | DPEP1 | ↔ | AHCY | 0.48 | 0.044 | GGT5 | ↔ | ADH1C | −0.61 | 0.007 |
| GGT5 | ↔ | DPEP1 | 0.50 | 0.030 | ADH1C | ↔ | AHR | −0.56 | 0.016 | ADH5 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | −0.47 | 0.047 |
| ADH5 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | −0.58 | 0.010 | ADH5 | ↔ | EPHX1 | 0.48 | 0.045 | ADH5 | ↔ | DEPEP1 | −0.59 | 0.010 |
| ADH5 | ↔ | ADH1C | −0.74 | 0.000 | AKRB10 | ↔ | AHR | −0.50 | 0.035 | AKRB10 | ↔ | ADH1C | 0.77 | 0.000 |
| ADH5 | ↔ | GGT5 | −0.50 | 0.029 | EPHX1 | ↔ | GGT5 | 0.54 | 0.022 | AKRB10 | ↔ | GGT5 | −0.62 | 0.006 |
| AKRB10 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | 0.67 | 0.002 | EPHX1 | ↔ | MAOA | −0.69 | 0.002 | EPHX1 | ↔ | GGT5 | 0.56 | 0.016 |
| AKRB10 | ↔ | ADH1C | 0.95 | 0.000 | MAOA | ↔ | MAOA | 0.54 | 0.022 | EPHX1 | ↔ | AKR7A | 0.47 | 0.048 |
| AKRB10 | ↔ | ADH5 | −0.82 | 0.000 | PTGS1 | ↔ | MAOA | −0.60 | 0.008 | EPHX2 | ↔ | ADH1C | 0.58 | 0.011 |
| AKR7A2 | ↔ | AHCY | 0.54 | 0.017 | MAOA | ↔ | ADH1C | 0.85 | 0.000 | |||||
| AKR7A2 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | 0.53 | 0.020 | MAOA | ↔ | GGT5 | −0.70 | 0.001 | |||||
| ALDH1A1 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | −0.56 | 0.012 | MAOA | ↔ | ADH5 | 0.50 | 0.035 | |||||
| ALDH1A1 | ↔ | ADH1C | −0.72 | 0.001 | MAOA | ↔ | AKRB10 | 0.71 | 0.001 | |||||
| ALDH1A1 | ↔ | GGT5 | −0.48 | 0.036 | PTGS1 | ↔ | EPHX1 | 0.52 | 0.027 | |||||
| ALDH1A1 | ↔ | ADH5 | 0.92 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| ALDH1A1 | ↔ | AKRB10 | −0.82 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | 0.66 | 0.002 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | ADH1C | 0.63 | 0.004 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | GGT5 | 0.46 | 0.035 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | ADH5 | −0.70 | 0.001 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | AKRB10 | 0.74 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | AKR7A2 | 0.52 | 0.023 | ||||||||||
| EPHX2 | ↔ | ALDH1A1 | −0.82 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| MAOA | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | 0.54 | 0.016 | ||||||||||
| MAOA | ↔ | ADH1C | 0.54 | 0.018 | ||||||||||
| MAOA | ↔ | AKRB10 | 0.53 | 0.020 | ||||||||||
| MAOA | ↔ | EPHX2 | 0.50 | 0.031 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | CYP2B7P1 | −0.58 | 0.010 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | ADH1C | −0.82 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | ADH5 | 0.76 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | AKRB10 | −0.86 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | ALDH1A1 | 0.81 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | EPHX2 | −0.75 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| PTGS1 | ↔ | MAOA | −0.76 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| CC vs. CC | CC vs. AC | AC vs. AC | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p | Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p | Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p |
| NQO2 | ↔ | GSTM1 | 0.46 | 0.049 | GSTP1 | ↔ | NQO2 | −0.55 | 0.017 | GSTP1 | ↔ | UGP2 | −0.60 | 0.008 |
| NQO2 | ↔ | GSTM2 | 0.50 | 0.028 | NNMT | ↔ | UGT2B17 | 0.48 | 0.046 | NQO2 | ↔ | UGT1A9 | −0.53 | 0.023 |
| GSTM1 | ↔ | GSTM2 | 0.94 | 0.000 | NQO2 | ↔ | NNMT | 0.51 | 0.032 | GSTM1 | ↔ | GSTM2 | 0.96 | 0.000 |
| NQO2 | ↔ | GSTM4 | 0.58 | 0.009 | GSTM2 | ↔ | NNMT | 0.47 | 0.048 | UGDH | ↔ | UGP2 | 0.54 | 0.021 |
| GSTM1 | ↔ | UGDH | −0.56 | 0.012 | GSTM4 | ↔ | GSTM4 | 0.58 | 0.013 | |||||
| GSTM2 | ↔ | UGDH | −0.67 | 0.002 | UGDH | ↔ | UGDH | 0.58 | 0.013 | |||||
| NNMT | ↔ | UGP2 | −0.62 | 0.005 | UGP2 | ↔ | UGDH | 0.53 | 0.027 | |||||
| GSTM2 | ↔ | UGP2 | −0.48 | 0.036 | UGT1A9 | ↔ | NQO2 | −0.54 | 0.020 | |||||
| UGDH | ↔ | UGP2 | 0.78 | 0.000 | UGT2B17 | ↔ | UGT2B17 | 0.52 | 0.027 | |||||
| GSTM1 | ↔ | UGT1A9 | −0.57 | 0.011 | ||||||||||
| GSTM2 | ↔ | UGT1A9 | −0.66 | 0.002 | ||||||||||
| UGDH | ↔ | UGT1A9 | 0.78 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| GSTM1 | ↔ | UGT2B17 | 0.59 | 0.008 | ||||||||||
| GSTM2 | ↔ | UGT2B17 | −0.64 | 0.003 | ||||||||||
| UGDH | ↔ | UGT2B17 | 0.79 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| UGT1A9 | ↔ | UGT2B17 | 0.77 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| CC vs. CC | CC vs. AC | AC vs. AC | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p | Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p | Gene | vs. | Gene | r | p |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC5A1 | 0.88 | 0.000 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.52 | 0.028 | ABCB2 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.49 | 0.039 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC5A6 | 0.70 | 0.001 | SLC6A14 | ↔ | SLC6A14 | 0.55 | 0.018 | SLC2A3 | ↔ | SLC5A1 | −0.56 | 0.016 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC12A2 | 0.65 | 0.004 | SLC6A14 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.49 | 0.037 | SLC2A3 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.82 | 0.000 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | 0.72 | 0.001 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLC2A3 | 0.47 | 0.048 | SLC2A3 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | −0.52 | 0.028 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.78 | 0.000 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLC5A1 | −0.53 | 0.023 | SLC2A3 | ↔ | ABCA8 | −0.61 | 0.008 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.77 | 0.000 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | ABCA8 | −0.55 | 0.019 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC6A14 | 0.61 | 0.008 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.37 | 0.014 | SLC12A2 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.52 | 0.026 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | 0.55 | 0.017 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.60 | 0.009 | SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLCO1B3 | −0.63 | 0.005 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.66 | 0.003 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.73 | 0.001 | SLC25A15 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.55 | 0.019 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A32 | 0.48 | 0.045 |
| ABCB2 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.73 | 0.001 | SLC29A2 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.47 | 0.049 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.66 | 0.003 |
| SLC2A3 | ↔ | SLC7A5 | 0.57 | 0.013 | SLC29A2 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.50 | 0.036 | SLC5A1 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.47 | 0.048 |
| SLC2A3 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | 0.47 | 0.050 | SLCO1B3 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.57 | 0.014 | SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC7A5 | 0.73 | 0.001 |
| SLC2A3 | ↔ | ABCD3 | −0.49 | 0.040 | SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.62 | 0.006 | SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.65 | 0.004 |
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC5A6 | 0.78 | 0.000 | ABCA8 | ↔ | SLC2A3 | −0.48 | 0.043 | SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.78 | 0.000 |
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC12A2 | 0.73 | 0.001 | ABCD3 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.52 | 0.026 | SLC6A14 | ↔ | SLC25A32 | 0.49 | 0.037 |
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | 0.79 | 0.000 | ABCG2 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | −0.59 | 0.010 | SLC6A14 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.57 | 0.013 |
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.87 | 0.000 | SLC25A4 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | −0.59 | 0.010 | SLC6A14 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.48 | 0.045 |
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.83 | 0.000 | SLC35A1 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.51 | 0.031 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.61 | 0.007 |
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.56 | 0.015 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.47 | 0.048 | |||||
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.58 | 0.012 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.66 | 0.003 | |||||
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.65 | 0.003 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.58 | 0.011 | |||||
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.82 | 0.000 | SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.58 | 0.011 | |||||
| SLC5A1 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.82 | 0.000 | SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.54 | 0.020 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC12A2 | 0.59 | 0.010 | SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.58 | 0.012 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | 0.58 | 0.013 | SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.50 | 0.033 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.79 | 0.000 | SLC25A5 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.63 | 0.005 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.77 | 0.000 | SLC25A15 | ↔ | SLC25A32 | 0.56 | 0.017 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.61 | 0.007 | SLC29A2 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.67 | 0.002 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.47 | 0.047 | SLC29A2 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.51 | 0.030 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.66 | 0.003 | SLC29A2 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.51 | 0.030 | |||||
| SLC5A6 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.66 | 0.003 | SLCO4A1 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.60 | 0.009 | |||||
| SLC6A14 | ↔ | SLCO1B3 | 0.62 | 0.006 | SLC25A5 | ↔ | ABCG2 | 0.55 | 0.018 | |||||
| SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.67 | 0.003 | SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | 0.55 | 0.018 | |||||
| SLC7A5 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.69 | 0.002 | ABCA8 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.60 | 0.008 | |||||
| SLC7A5 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | −0.70 | 0.001 | ABCA8 | ↔ | ABCG2 | 0.52 | 0.027 | |||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | 0.66 | 0.003 | ABCA8 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | 0.52 | 0.027 | |||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.83 | 0.000 | ABCA8 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.78 | 0.000 | |||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.74 | 0.000 | ABCD3 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.51 | 0.032 | |||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.64 | 0.004 | ABCG2 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.56 | 0.016 | |||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.61 | 0.007 | SLC35A1 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.56 | 0.016 | |||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.81 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.81 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC12A2 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.73 | 0.001 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLC25A15 | 0.73 | 0.001 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.72 | 0.001 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLC25A5 | −0.53 | 0.024 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.47 | 0.048 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.73 | 0.001 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.68 | 0.002 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A5 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.68 | 0.002 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | SLC29A2 | 0.86 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | SLCO4A1 | 0.52 | 0.026 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.48 | 0.044 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.59 | 0.010 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.77 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.77 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A15 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.54 | 0.021 | ||||||||||
| SLC29A2 | ↔ | ABCA8 | 0.61 | 0.008 | ||||||||||
| SLC29A2 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.80 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC29A2 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.90 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC29A2 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.90 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| SLC29A2 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.63 | 0.005 | ||||||||||
| ABCA8 | ↔ | ABCD3 | 0.78 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| ABCA8 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.66 | 0.003 | ||||||||||
| ABCA8 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.66 | 0.003 | ||||||||||
| ABCA8 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.90 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| ABCD3 | ↔ | ABCG2 | −0.81 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| ABCD3 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | −0.81 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| ABCD3 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | 0.68 | 0.002 | ||||||||||
| ABCG2 | ↔ | SLC25A4 | 1.00 | 0.000 | ||||||||||
| ABCG2 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | −0.63 | 0.005 | ||||||||||
| SLC25A4 | ↔ | SLC35A1 | −0.63 | 0.005 | ||||||||||
| Clinical Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| CSI | The cancer cells invade the submucosal muscular layer of the colon. They have not spread into nearby tissues or lymph nodes (T1 or T2, N0, M0). |
| CSII | The cancer has grown through the layers of the muscle to the lining of the abdomen and has grown into the visceral peritoneum. It has not spread to the nearby lymph nodes or elsewhere (T4, N0, M0). |
| CSIII | The cancer has grown through the bowel wall or to surrounding organs and into lymph nodes or to a nodule of tumor in tissues around the colon or rectum that do not appear to be lymph nodes. The cancer has grown through the bowel wall or to the pericolorectal tissue or directly to the surrounding organs and into lymph nodes. The cancer has not spread to distant organs (T1 or T2, N1 or N1c, M0; or T1, N2a, M0T3 or T4a, N1 or N1c, M0; T2 or T3, N2a, M0; or T1 or T2, N2b, M0; T4a, N2a, M0; T3 or T4a, N2b, M0; or T4b, N1 or N2, M0). |
| CSIV | The cancer has spread to a distant part of the body, such as the liver and more than 1 part of the body or to the peritoneum (any T, any N, M1x a b c). |
| Parameters | Indication or Range |
|---|---|
| Age | 39–89 years |
| Male {%] | 55% |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 22.1–24.6 |
| Systolic blood pressure [mmHg] | 115–145 |
| Diastolic blood pressure [mmHg] | 80–90 |
| Hemoglobin [g/dL] | 8–11 |
| WBC × 103/µL | 5–10.8 |
| Cholesterol [mg/dL] | 180–240 |
| Fasting glycemia [mg/dL] | 75–120 |
| CRP [mg/dL] | 1–6 |
| Regular exercise | None |
| Socioeconomic status | Good |
| Health | Early stage (CSI and CSII) of CRC—flatulency, gastrointestinal pricking; late stage (CSIII and CSIV) of CRC—general weakness |
| Alcohol consumption | Occasionally |
| Smoking | Smoking stopped at least 5–15 years earlier |
| Diet | Often meat |
| Eating grilled food | Occasionally |
| Sedentary lifestyle | Often, all work and watch TV |
| Exposure to other carcinogens | Environmental, connected to living from birth in highly industrialized areas (steel mills, mines, cars; exceeding air pollution standards) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janikowska, G.; Janikowski, T.; Kuźbińska, A.; Opiłka, M.; Mazurek, U.; Lorenc, Z. Transcriptional Activity of Genes Related to the Biotransformation Process in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 12116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412116
Janikowska G, Janikowski T, Kuźbińska A, Opiłka M, Mazurek U, Lorenc Z. Transcriptional Activity of Genes Related to the Biotransformation Process in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):12116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412116
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanikowska, Grażyna, Tomasz Janikowski, Aleksandra Kuźbińska, Mieszko Opiłka, Urszula Mazurek, and Zbigniew Lorenc. 2025. "Transcriptional Activity of Genes Related to the Biotransformation Process in the Development of Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 12116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412116
APA StyleJanikowska, G., Janikowski, T., Kuźbińska, A., Opiłka, M., Mazurek, U., & Lorenc, Z. (2025). Transcriptional Activity of Genes Related to the Biotransformation Process in the Development of Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 12116. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412116






