Borate–Guanosine Hydrogels and Their Hypothetical Participation in the Prebiological Selection of Ribonucleoside Anomers: A Computational (DFT) Study
Abstract
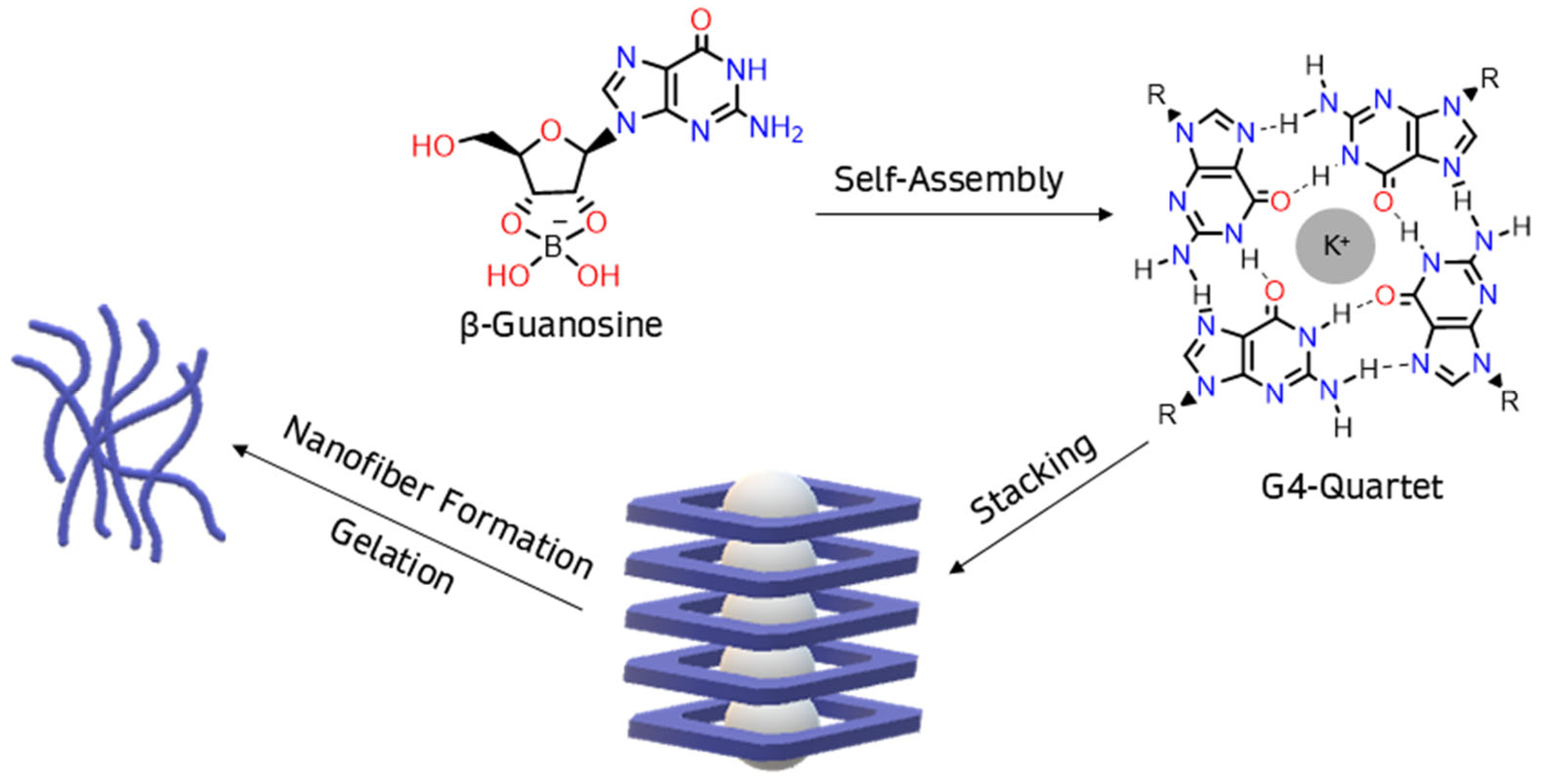
1. Introduction
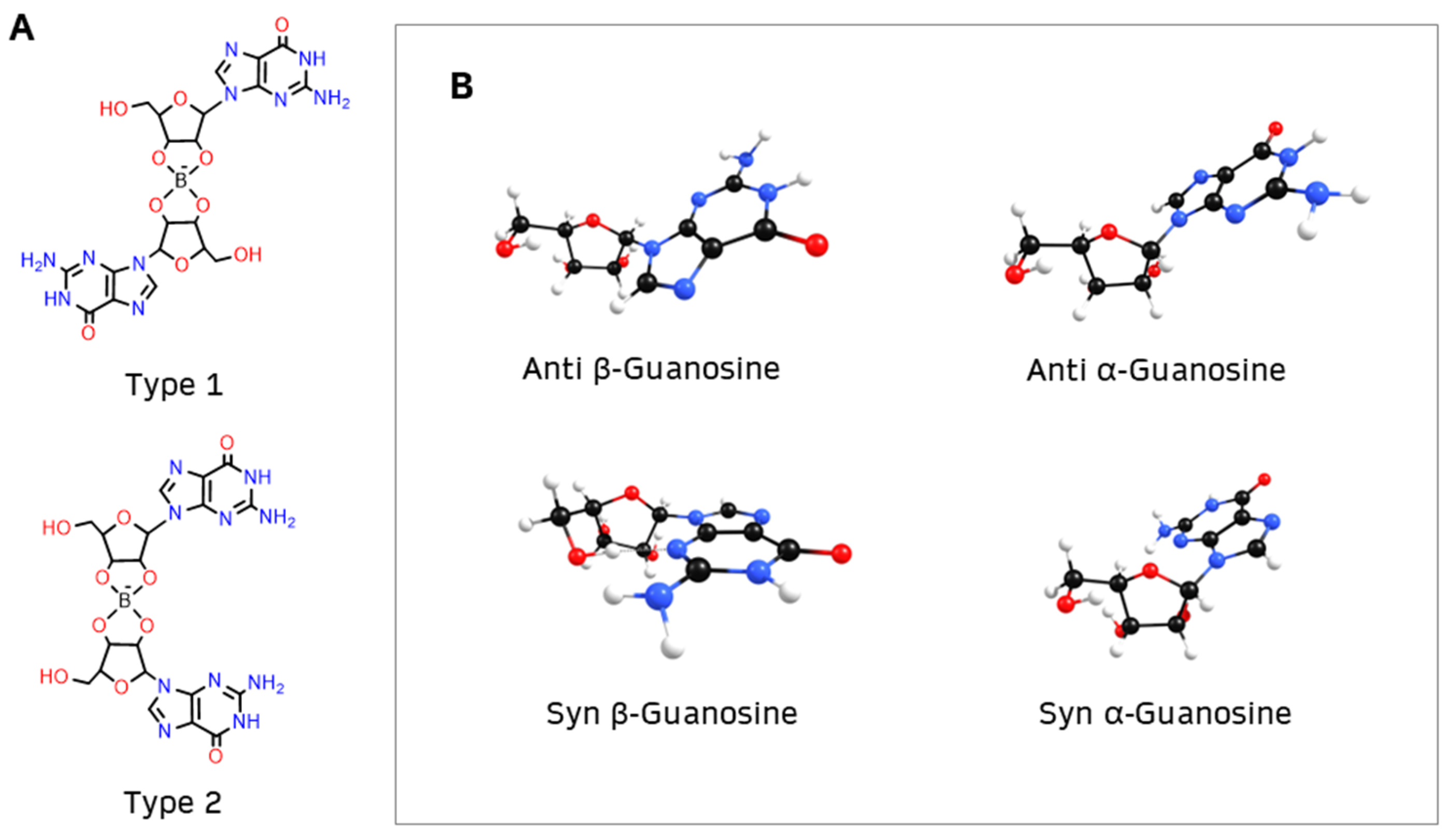
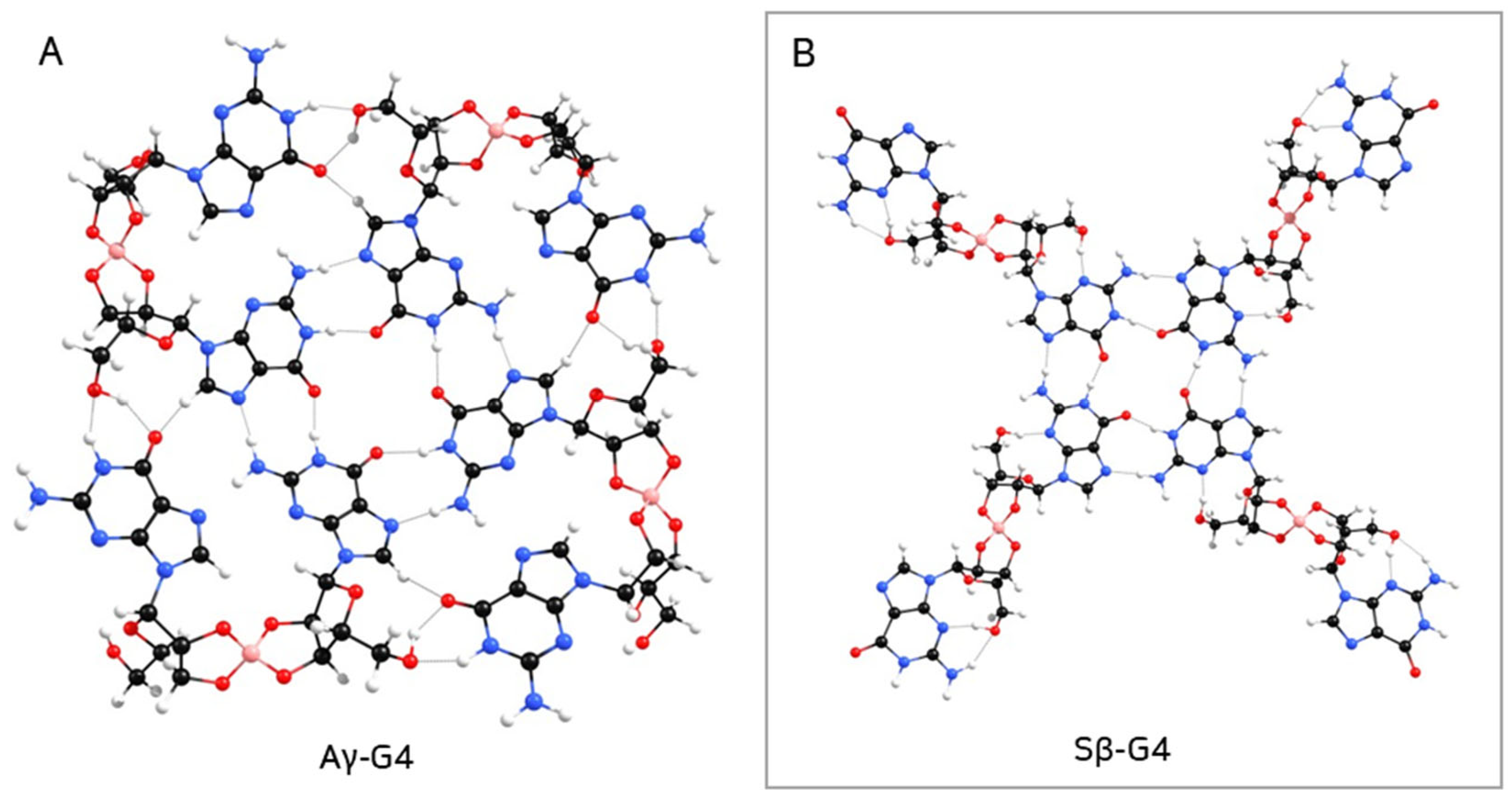
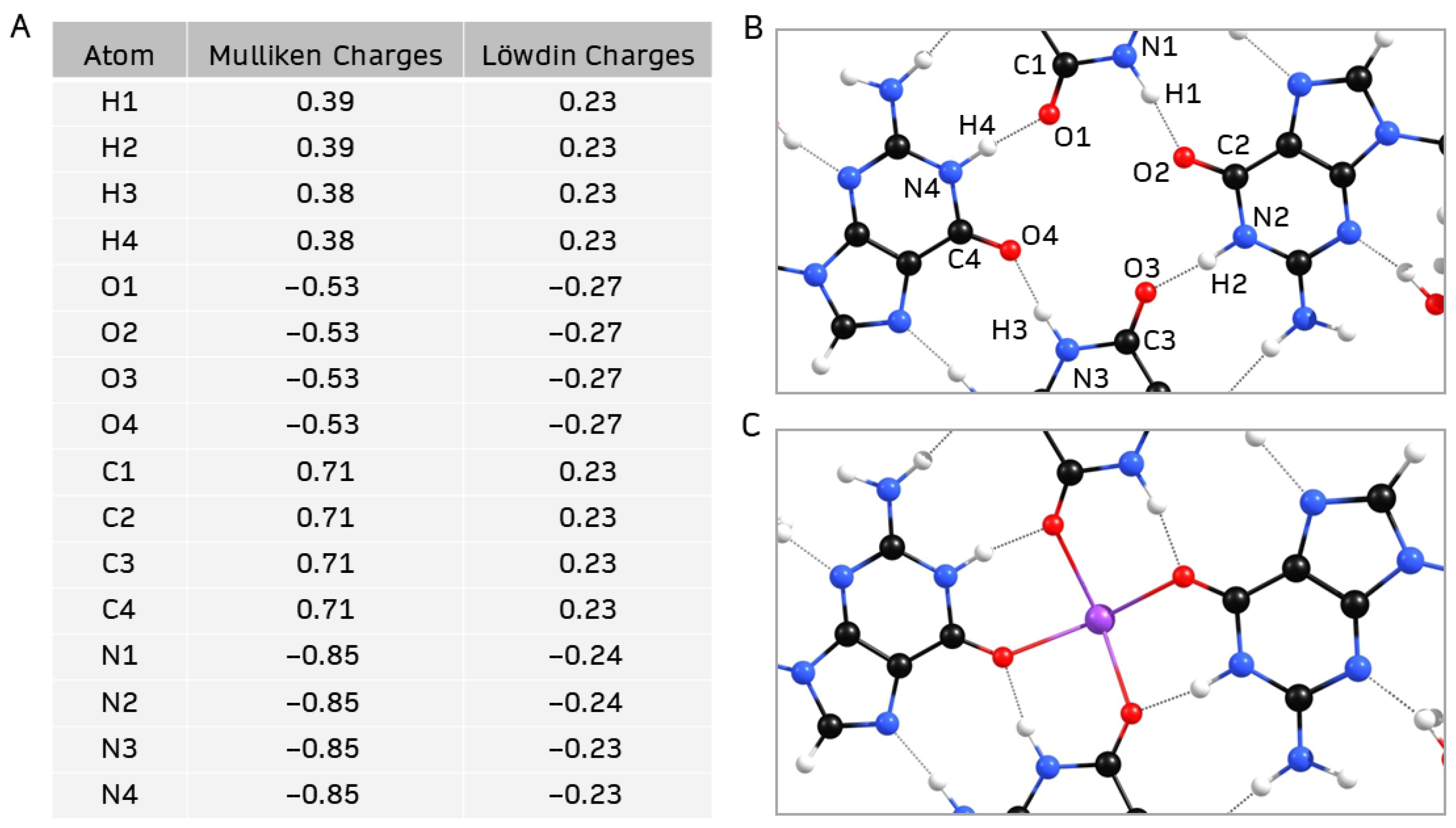
2. Results and Discussion
- (1)
- α diesters, with two α-guanosines (types α1 and α2);
- (2)
- β diesters, with two β-guanosines (types β1 and β2);
- (3)
- γ diesters, with one α-guanosine and one β-guanosine (types γ1 and γ2).
- (1)
- Aα2-G22 + Aα2 −> Aα-G3;
- (2)
- Aβ1-G21 + Aβ1 −> Aβ-G3;
- (3)
- Aγ1-G21 + Aγ1 −> Aγ-G3;
- (4)
- Sα1-G23 + Sα1 −> Sα-G3;
- (5)
- Sβ1-G21 + Sβ1 −> Sβ-G3;
- (6)
- Sγ2-G23 + Sγ2 −> Sγ-G3.
- (1)
- Aα-G3 + Aα2 −> Aα-G4;
- (2)
- Aβ-G3 + Aβ1 −>; Aβ-G4;
- (3)
- Aγ-G3 + Aγ1 −> Aγ-G4;
- (4)
- Sα-G3 + Sα1 −> Sα-G4;
- (5)
- Sβ-G3 + Sβ1 −> Sβ-G4;
- (6)
- Sγ-G3 + Sγ2 −> Sγ-G4.
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OPT | Optimization |
| SPE | Single point energy |
| G2 | Structure formed by two borate–guanosine diesters |
| G3 | Structure formed by three borate–guanosine diesters |
| G4 | Structure formed by four borate–guanosine diesters |
| α | Structure formed by borate-α-guanosine diesters |
| β | Structure formed by borate-β-guanosine diesters |
| γ | Structure formed by borate–guanosine diesters, where each diester has one α-guanosine and one β-guanosine. |
References
- Bhattacharyya, T.; Saha, P.; Dash, J. Guanosine-derived supramolecular hydrogels: Recent developments and future opportunities. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 2230–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, G.M.; Davis, J.T. Supramolecular gels made from nucleobase, nucleoside and nucleotide analogs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3188–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, G.M.; Skala, L.P.; Plank, T.N.; Oh, H.; Reddy, G.N.M.; Marsh, A.; Brown, S.P.; Raghavan, S.R.; Davis, J.T. G4-quartet M+ borate hydrogels. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5819–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, J.S.; de Araujo, D.R.; Sella, F.; Liguori, G.R.; Liguori, T.T.A.; Moreira, L.F.P.; Spinozzi, F.; Mariani, P.; Itri, R. Self-assembled guanosine-hydrogels for drug-delivery application: Structural and mechanical characterization, methylene blue loading and controlled release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 121, 111834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasachary, N.; Lehn, J.M. Gelation-driven component selection in the generation of constitutional dynamic hydrogels based on guanine-quartet formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5938–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasachary, N.; Lehn, J. Structural selection in G-quartet-based hydrogels and controlled release of bioactive molecules. Chem. Asian J. 2007, 3, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchs, B.; Fieber, W.; Vigouroux-Elie, F.; Sreenivasachary, N.; Lehn, J.M.; Herrmann, A. Release of bioactive volatiles from supramolecular hydrogels: Influence of reversible acylhydrazone formation on gel stability and volatile compound evaporation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoussoub, A.; Lehn, J.M. Dynamic sol–gel interconversion by reversible cation binding and release in G-quartet-based supramolecular polymers. Chem. Commun. 2005, 46, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nakamura, D.; DeBoyace, K.; Neisius, A.W.; McGown, L.B. Tunable thermoassociation of binary guanosine gels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 1130–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerkle, L.E.; Li, Z.; Jamieson, A.M.; Rowan, S.J. Tailoring the properties of Guanosine-Based supramolecular hydrogels. Langmuir 2009, 25, 8833–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Buerkle, L.E.; Orseno, M.R.; Streletzky, K.A.; Seifert, S.; Jamieson, A.M.; Rowan, S.J. Structure and gelation mechanism of tunable guanosine-based supramolecular hydrogels. Langmuir 2010, 26, 10093–10101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buerkle, L.E.; Von Recum, H.A.; Rowan, S.J. Toward potential supramolecular tissue engineering scaffolds based on guanosine derivatives. Chem. Sci. 2011, 3, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Shah, A.; Kraatz, H.-B. Self-assembly of guanosine and deoxy-guanosine into hydrogels: Monovalent cation guided modulation of gelation, morphology and self-healing properties. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4802–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, J.; Patil, A.J.; Das, R.N.; Dowdall, F.L.; Mann, S. Supramolecular hydrogels derived from silver ion-mediated self-assembly of 5′-guanosine monophosphate. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Parasar, B.; Bhattacharyya, T.; Dash, J. Chiral carbon dots derived from guanosine 5′-monophosphate form supramolecular hydrogels. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11159–11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.N.; Kumar, Y.P.; Pagoti, S.; Patil, A.J.; Dash, J. Diffusion and birefringence of bioactive dyes in a supramolecular guanosine hydrogel. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 6008–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; da Silva, J.A.L. Boron in prebiological evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 10458–10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Ascenso, J.R.; Ilharco, L.M.; da Silva, J.A.L. Synthesis of ribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleosides under plausible prebiotic conditions within self-assembled supramolecular structures. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 2206–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Gómez, M.; Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Wendner, M.; Mateos-Timoned, M.A.; Gil, F.J.; Perez, R.A. Optimization of guanosine-based hydrogels with boric acid derivatives for enhanced long-term stability and cell survival. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1147943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-G.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.-F.; Wang, B.-C.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y. Transforming sustained release into on-demand release: Self-healing guanosine–borate supramolecular hydrogels with multiple responsiveness for Acyclovir delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 619–6203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, X.; Wang, B.-C.; Xue, W.; Zhou, C.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.-H. TMPyP-bound guanosine-borate supramolecular hydrogel as smart hemoperfusion device with real-time visualized/electrochemical bi-modal monitoring for selective blood lead elimination. Biosens. Bioelectron 2021, 184, 113230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xie, X.-Q.; Peng, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, C.-S. Self-healing mechanism and bioelectrochemical interface properties of core-shell guanosine-borate hydrogels. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; An, Y.; Shi, L. A G-quadruplex hydrogel via multicomponent self-assembly: Formation and zero-order controlled release. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 19, 13056–13067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Lei, S.; Song, S.; Xia, X.; Qi, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H. Guanosine-based hydrogel integrating photothermal effect of PDA-AuNPs through dynamic borate bond for photothermal therapy of cancer. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, S.; Xiang, Q. The use of hydrogel-based materials for radioprotection. Gels 2023, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Li, M.; Gao, J.; Han, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, J. Hydrogel-based strategies for the prevention and treatment of radiation-induced skin injury: Progress and mechanistic insights. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhdar, H.; Alghamdi, S. Radiation shielding evaluation of carbohydrate hydrogel radiotherapy pads containing high-Z fillers: A GEANT4 study. Polymers 2025, 17, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Choi, S.; Sun, J.-Y. Self-healable soft shield for γ-ray radiation based on polyacrylamide hydrogel composites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Hu, X.; Liang, W.; Zheng, S.; Luo, X.; Zhao, H. Dual-functional guanosine-based hydrogel: High-efficiency protection in radiation-induced oral mucositis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2025, 13, 3039–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, J.A.L.; Holm, N.G. Borophosphates and silicophosphates as plausible contributors to the emergence of life. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 431, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanum, R.; Satthiyasilan, N.; Tharumen, N.; Kee, T.P.; Mayer, C.; Menon, P.S.; Jia, T.Z.; Chandru, K. Prebiotic Gels as the cradle of life. ChemSystemsChem 2025, e00038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevors, J.T.; Pollack, G.H. Hypothesis: The origin of life in a hydrogel environment. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2004, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damer, B.; Deamer, D. The Hot Spring hypothesis for an origin of life. Astrobiology 2019, 20, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, A.F.; Marques, M.M.; da Silva, J.A.L.; da Silva, J.J.R.F. Interactions of D-ribose with polyatomic anions, and alkaline and alkaline-earth cations: Possible clues to environmental synthesis conditions in the pre-RNA world. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Ascenso, J.R.; Ilharco, L.; Diogo, H.P.; André, V.; da Silva, J.A.L. Ribose-borate esters as potential components for prebiological evolution. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1184, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, G.; Du, Y.; Tang, F.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; Chen, Q. Review of α-nucleosides: From discovery, synthesis to properties and potential applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14302–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Villa, A.; Pietrucci, F.; Saitta, A.M. Prebiotic chemistry and origins of life research with atomistic computer simulations. Phys. Life Rev. 2018, 34–35, 105–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, V.; Latouche, C.; Skouteris, D.; Vazart, F.; Balucani, N.; Ceccarelli, C.; Lefloch, B. Gas-phase formation of the prebiotic molecule formamide: Insights from new quantum computations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 453, L31–L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spezia, R.; Jeanvoine, Y.; Hase, W.L.; Song, K.; Largo, A. Synthesis of formamide and related organic species in the interstellar medium via chemical dynamic simulations. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snow, J.L.; Orlova, G.; Blagojevic, V.; Bohme, D.K. Gas-phase ionic syntheses of amino acids: β versus α. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 9910–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimola, A.; Ugliengo, P.; Sodupe, M. Formation versus hydrolysis of the peptide bond from a quantum-mechanical viewpoint: The role of mineral surfaces and implications for the origin of life. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 746–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, P.; Sodupe, M. Theoretical study of the adsorption of DNA bases on the acidic external surface of montmorillonite. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 14, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignon, P.; Sodupe, M. Structural behaviors of cytosine into the hydrated interlayer of Na+-montmorillonite clay. An ab initio molecular dynamics study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 26179–26189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šponer, J.E.; Sumpter, B.G.; Leszczynski, J.; Šponer, J.; Fuentes-Cabrera, M. Theoretical study on the factors controlling the stability of the borate complexes of ribose, arabinose, lyxose, and xylose. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 9990–9998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asami, H.; Urashima, S.; Tsukamoto, M.; Motoda, A.; Hayakawa, Y.; Saigusa, H. Controlling glycosyl bond conformation of guanine nucleosides: Stabilization of the anti conformer in 5′-O-ethylguanosine. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Liu, T.; Tang, F.; Jin, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Q.M. Chirality from D-guanosine to L-guanosine shapes a stable gel for three-dimensional cell culture. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12936–12939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo, L.A.M.; Matta, C.F. On the prebiotic selection of nucleotide anomers: A computational study. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2007, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, J.; Weisz, K. Thermodynamic Stability of G-Quadruplexes: Impact of sequence and environment. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 2848–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdagi, S.; Roux, B.; Noskov, S.Y. Potassium-Binding Site Types in Proteins. In Encyclopedia of Metalloproteins, 2013th ed.; Kretsinger, R.H., Uversky, V.N., Permyakov, E.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1809–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, M.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Tukachev, N.; Senn, H.M.; Wynne, K. Low-frequency vibrational modes in G-quadruplexes reveal the mechanical properties of nucleic acids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 13250–13260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemcraft—Graphical Software for Visualization of Quantum Chemistry Computations. Available online: https://www.chemcraftprog.com/ (accessed on 2 December 2025).
- Barca, G.M.J.; Bertoni, C.; Carrington, L.; Datta, D.; de Silva, N.; Deustua, J.E.; Fedorov, D.G.; Gour, J.R.; Gunina, A.O.; Guidez, E.B.; et al. Recent developments in the general atomic and molecular electronic structure system. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 154102-1–154102-26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yang, W.; Parr, R.G. Development of the Colle-Salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafferty, B.J.; Fialho, D.M.; Khanam, J.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Hud, N.V. Spontaneous formation and base pairing of plausible prebiotic nucleotides in water. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokosawa, T.; Enomoto, R.; Uchino, S.; Hirasawa, I.; Umehara, T.; Tamura, K. A step into the RNA world: Conditional analysis of hydrogel formation of adenosine 5′-monophosphate induced by cyanuric acid. Biosyst. 2017, 162, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Plank, T.N.; Zhu, T.; Yu, H.; Ge, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, L.; Davis, J.T.; Pei, H. Self-assembly of metallo-nucleoside hydrogels for injectable materials that promote wound closure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19743–19750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



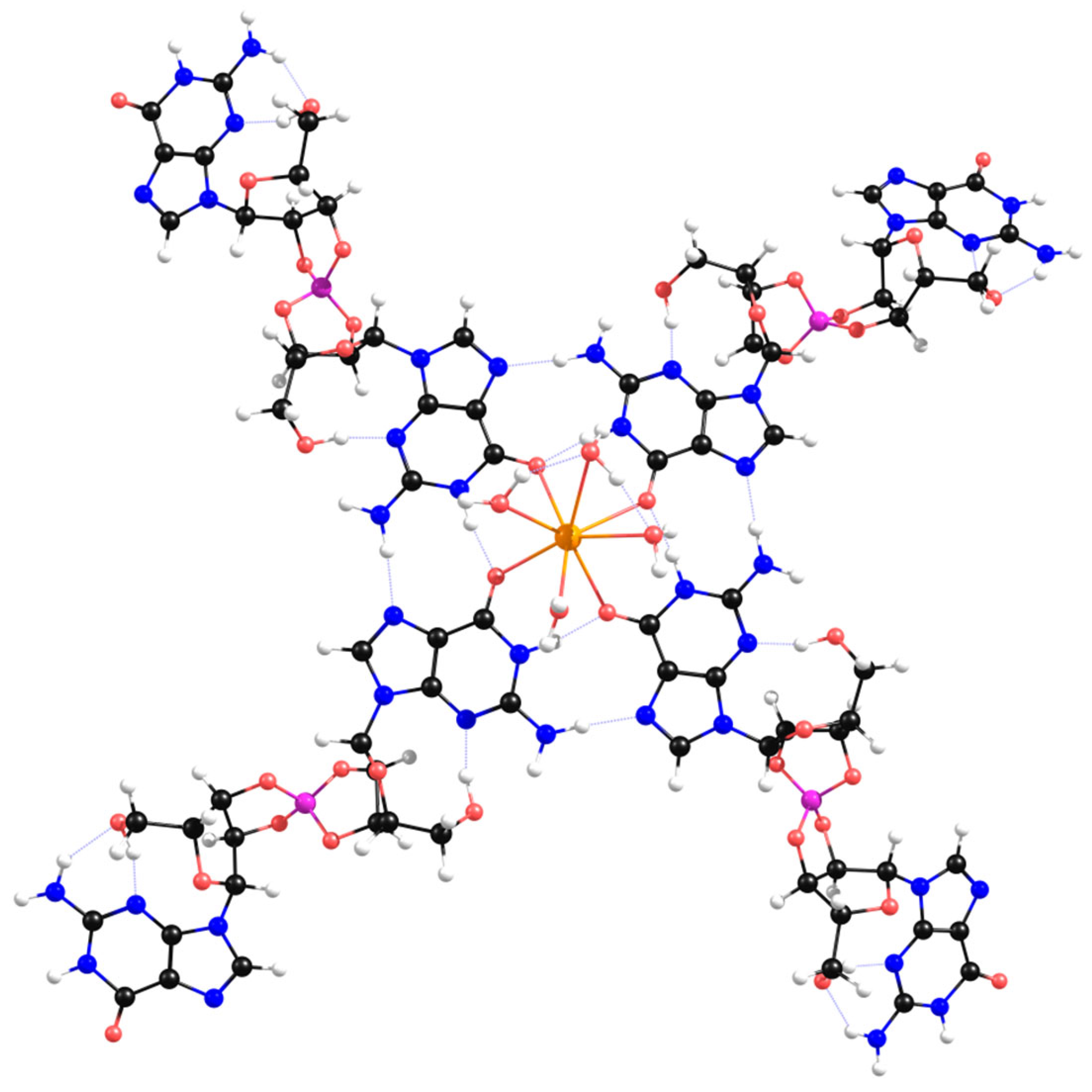
| Anti Conformation | Syn Conformation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diester | ΔE (kcal/mol) | Diester | ΔE (kcal/mol) |
| Aα1 | 7.74 | Sα1 * | 12.90 |
| Aα2 * | 0.00 | Sα2 | 21.13 |
| Aβ1 * | 9.36 | Sβ1 * | 0.00 * |
| Aβ2 | 10.60 | Sβ2 | 1.20 |
| Aγ1 * | 2.11 | Sγ1 | 6.53 |
| Aγ2 | 9.71 | Sγ2 * | 2.91 |
| Anti Conformation ΔE (kcal/mol) | Syn Conformation ΔE (kcal/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2 * | OPT (3-21G) | SPE (6-31G**) | G2 * | OPT (3-21G) | SPE (6-31G**) |
| Aα2-G21 | 9.16 | 7.03 | Sα1-G21 | 27.58 | 19.28 |
| Aα2-G22 ** | 0.00 | 0.00 | Sα1-G22 | 27.55 | 19.16 |
| Aα2-G23 | 0.08 | 0.19 | Sα1-G23 ** | 27.47 | 19.12 |
| Aβ1-G21 ** | 36.36 | 32.06 | Sβ1-G21 ** | 6.57 | 5.63 |
| Aβ1-G22 | 41.85 | 32.26 | Sβ1-G22 | 7.32 | 5.77 |
| Aβ1-G23 | 40.08 | 32.19 | Sβ1-G23 | 8.33 | 6.43 |
| Aγ1-G21 ** | 9.40 | 11.07 | Sγ2-G21 | 0.63 | 6.22 |
| Aγ1-G22 | 19.24 | 14.02 | Sγ2-G22 | 14.79 | 7.16 |
| Aγ1-G23 | 26.05 | 19.15 | Sγ2-G23 ** | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Anti Conformation ΔE (kcal/mol) | Syn Conformation ΔE (kcal/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G3 | OPT (3-21G) | SPE (6-31G**) | G3 | OPT (3-21G) | SPE (6-31G**) |
| Aα-G3 | 2.89 | 9.40 | Sα-G3 | 38.56 | 29.54 |
| Aβ-G3 | 42.76 | 10.91 | Sβ-G3 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Aγ-G3 | 9.77 | 10.91 | Sγ-G3 | 27.62 | 32.23 |
| Anti Conformation ΔE (kcal/mol) | Syn Conformation ΔE (kcal/mol) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G4 | OPT (3-21G) | SPE (6-31G**) | G4 | OPT (3-21G) | SPE (6-31G**) |
| Aα-G4 | 36.26 | 3.42 | Sα-G4 | 64.20 | 59.11 |
| Aβ-G4 | 54.15 | 15.68 | Sβ-G4 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Aγ-G4 | 11.37 | 0.22 | Sγ-4 | 73.44 | 78.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franco, A.; Galvão, A.M.; da Silva, J.A.L. Borate–Guanosine Hydrogels and Their Hypothetical Participation in the Prebiological Selection of Ribonucleoside Anomers: A Computational (DFT) Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 12103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412103
Franco A, Galvão AM, da Silva JAL. Borate–Guanosine Hydrogels and Their Hypothetical Participation in the Prebiological Selection of Ribonucleoside Anomers: A Computational (DFT) Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):12103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412103
Chicago/Turabian StyleFranco, Ana, Adelino M. Galvão, and José A. L. da Silva. 2025. "Borate–Guanosine Hydrogels and Their Hypothetical Participation in the Prebiological Selection of Ribonucleoside Anomers: A Computational (DFT) Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 12103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412103
APA StyleFranco, A., Galvão, A. M., & da Silva, J. A. L. (2025). Borate–Guanosine Hydrogels and Their Hypothetical Participation in the Prebiological Selection of Ribonucleoside Anomers: A Computational (DFT) Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 12103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412103






