Effects of Topography and Extracellular Matrix Composition on Focal Adhesion Patterning in Human Corneal Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Deposition of Aligned and Random Collagen Fibrils on PDMS-Coated Glass Coverslips
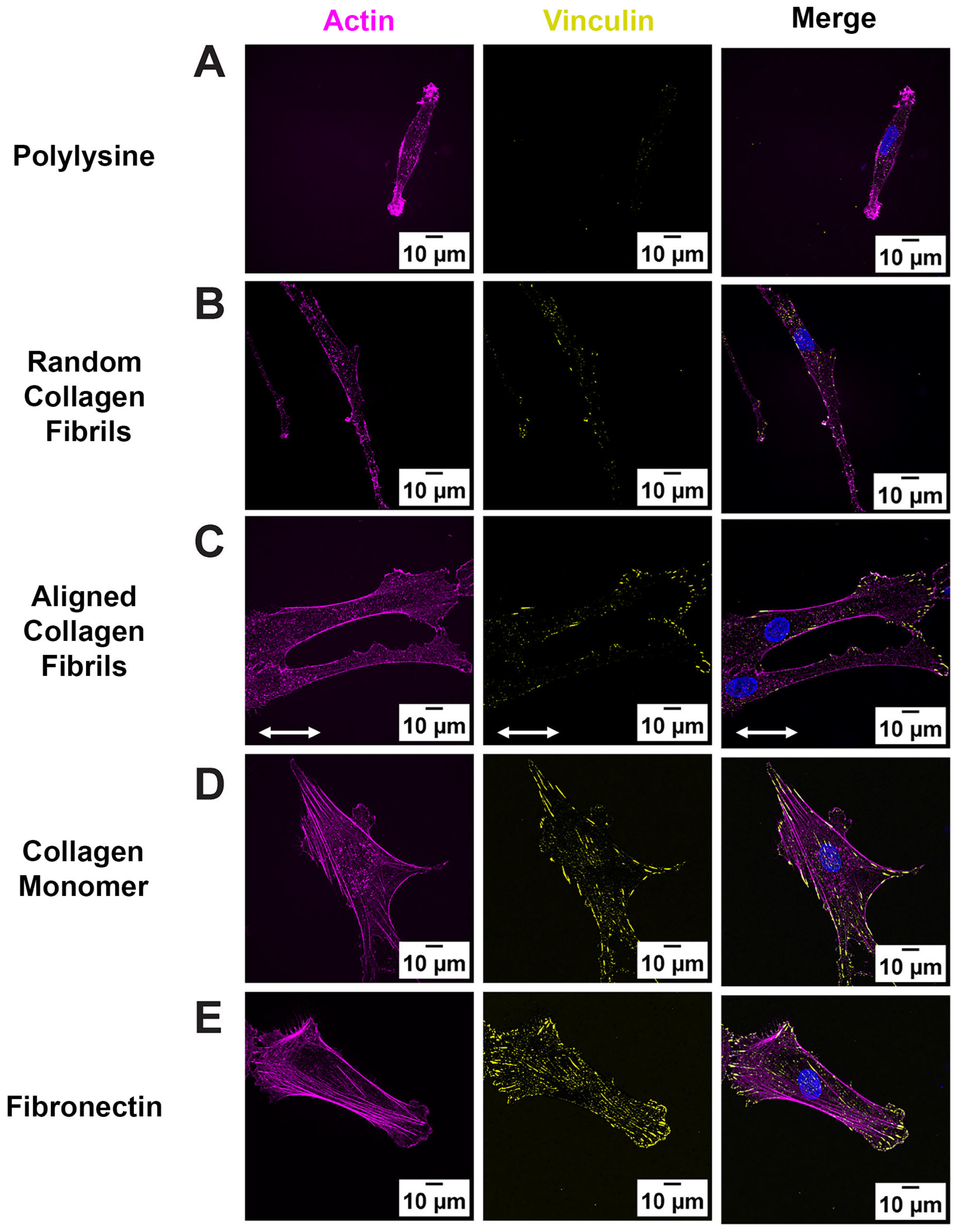
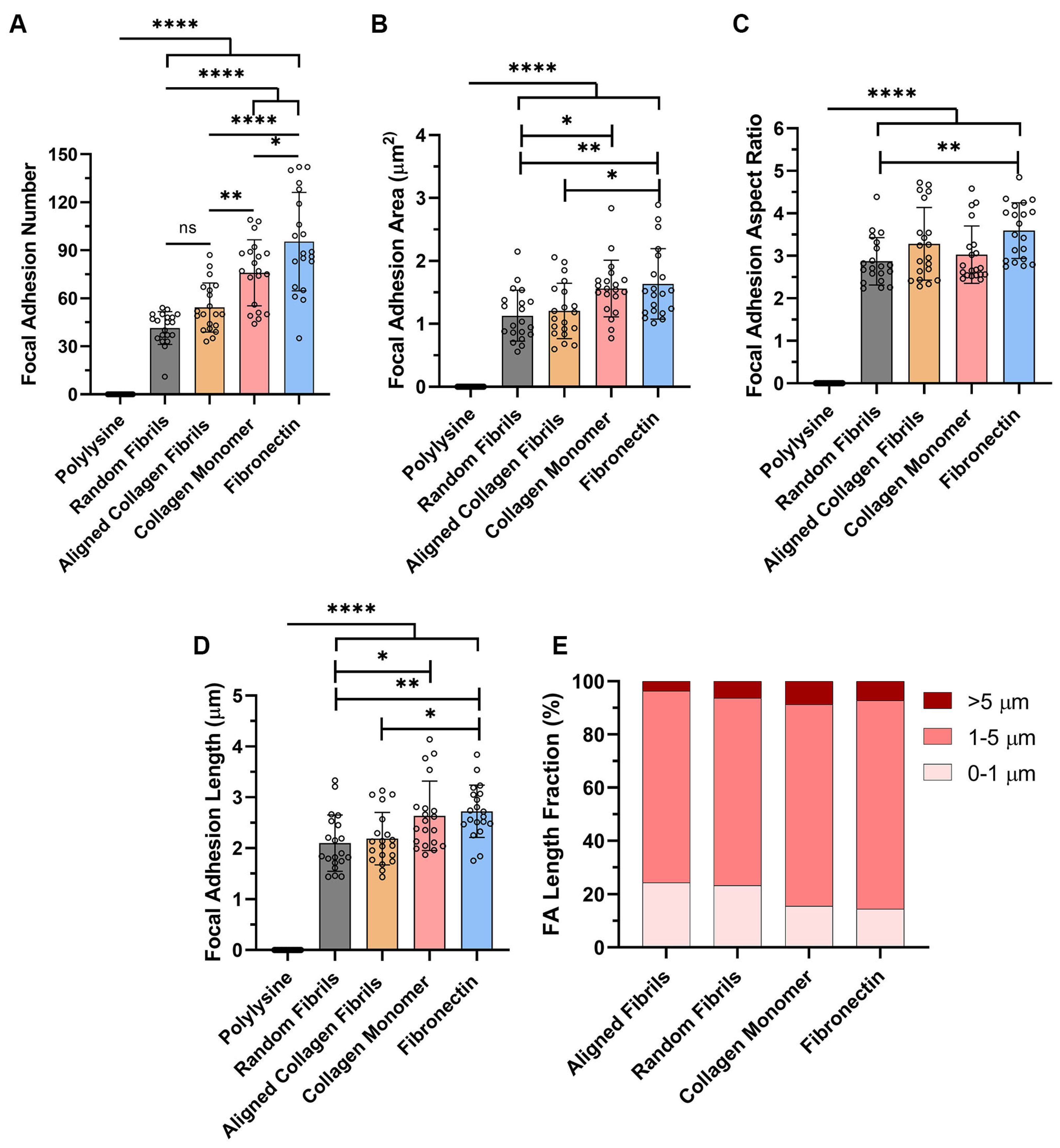
2.2. ECM Composition and Alignment Modulate Focal Adhesion Patterning
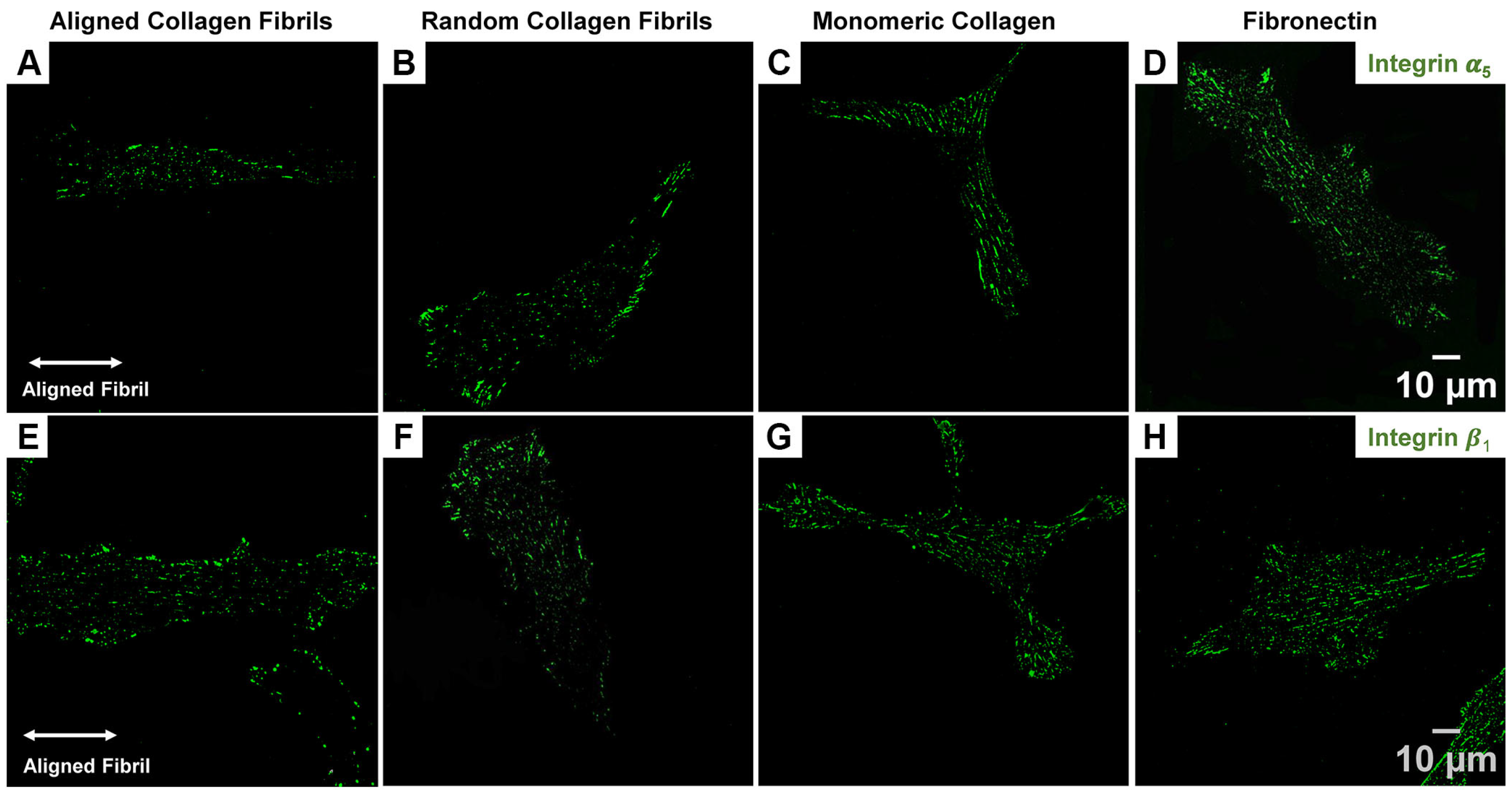
2.3. Corneal Fibroblasts Expression of Integrin α5 and β1 on Different ECM Coatings
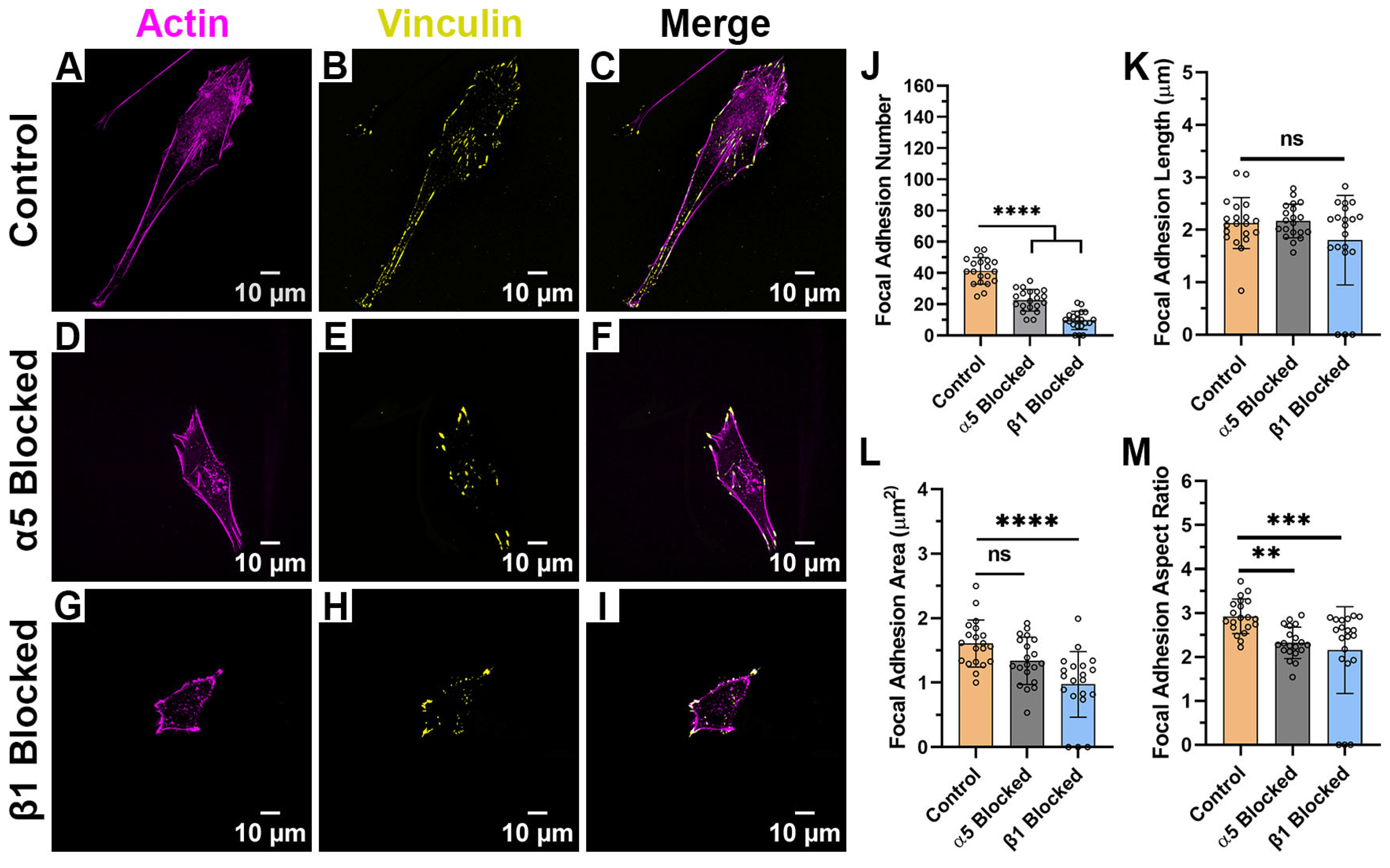
2.4. Focal Adhesion Patterning Is Regulated by Integrin Subunits and ECM Composition
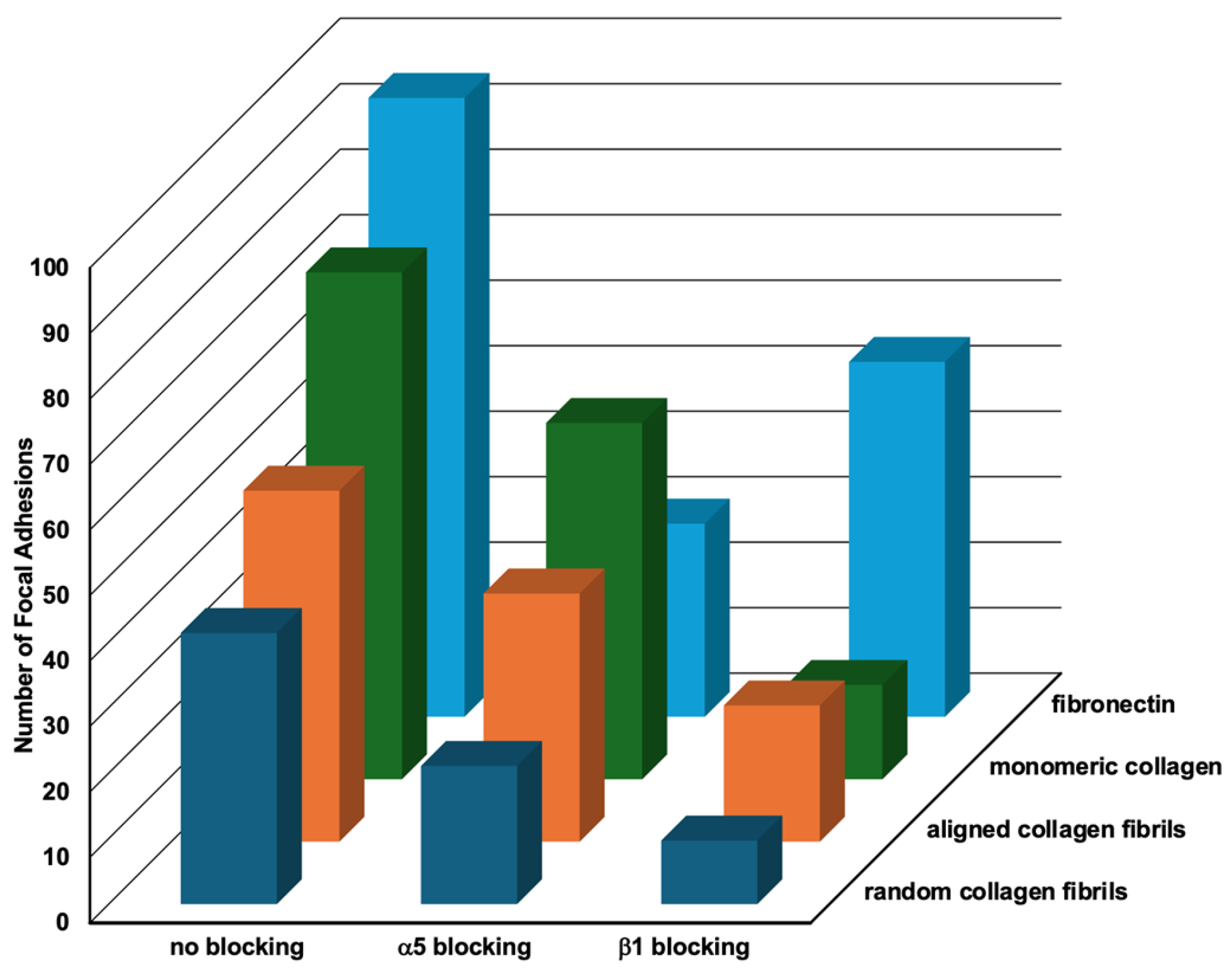
2.5. Relative Importance of Topography and ECM Composition on Focal Adhesion Formation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of Microfluidic Devices and PDMS-Coated Glass Coverslips
3.2. Patterning of Aligned and Random Collagen Fibrils on PDMS Glass Coverslips
3.3. DTAF Staining and Imaging of Aligned and Random Collagen Fibrils
3.4. Preparation of Other ECM Coatings
3.5. Cell Culture
3.6. Antibody Blocking Experiments
3.7. Immunofluorescence Imaging
3.8. Quantitative Analysis of Focal Adhesions
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hynes, R. Integrins: Versatility, Modulation, and Signaling in Cell Adhesion. Cell 1992, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kechagia, J.Z.; Ivaska, J.; Roca-Cusachs, P. Integrins as Biomechanical Sensors of the Microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.; Lee, O.; Win, Z.; Edwards, R.M.; Alford, P.W.; Kim, D.H.; Provenzano, P.P. Anisotropic Forces from Spatially Constrained Focal Adhesions Mediate Contact Guidance Directed Cell Migration. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubow, K.E.; Conrad, S.K.; Horwitz, A.R. Matrix Microarchitecture and Myosin II Determine Adhesion in 3D Matrices. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.W.; Tong, W.Y.; Shen, W.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Lam, Y.W. Stringent Requirement for Spatial Arrangement of Extracellular Matrix in Supporting Cell Morphogenesis and Differentiation. BMC Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, K.M.; Leonard, D.W. Ultrastructure of the Corneal Stroma: A Comparative Study. Biophys. J. 1993, 64, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, K.M. Corneal Collagen-Its Role in Maintaining Corneal Shape and Transparency. Biophys. Rev. 2009, 1, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riching, K.M.; Cox, B.L.; Salick, M.R.; Pehlke, C.; Riching, A.S.; Ponik, S.M.; Bass, B.R.; Crone, W.C.; Jiang, Y.; Weaver, A.M.; et al. 3D Collagen Alignment Limits Protrusions to Enhance Breast Cancer Cell Persistence. Biophys. J. 2015, 107, 2546–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, J.L.; Ledet, T.; Hager, H.; Josephsen, K.; Ehlers, N. The Influence of Corneal Stromal Matrix Proteins on the Migration of Human Corneal Fibroblasts. Exp. Eye Res. 2000, 71, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidinger, G.; Hanselmayer, G.; Pieh, S.; Lackner, B.; Kaminski, S.; Ruhswurm, I.; Skorpik, C. Effect of Tenascin and Fibronectin on the Migration of Human Corneal Fibroblasts. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2003, 29, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjahjono, N.S.; Subramanian, D.; Shihabeddin, T.Z.; Hicks, H.D.; Varner, V.D.; Petroll, W.M.; Schmidtke, D.W. Effect of Decorin and Aligned Collagen Fibril Topography on TGF-Β1 Activation of Corneal Keratocytes. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, E.S.; Park, S.H.; Marchant, J.; Omenetto, F.; Kaplan, D.L. Response of Human Corneal Fibroblasts on Silk Film Surface Patterns. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 664–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Shi, W.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, D.; Zhao, L.; Yang, L.; Liu, T.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, L. Decellularized Porcine Cornea-Derived Hydrogels for the Regeneration of Epithelium and Stroma in Focal Corneal Defects. Ocul. Surf. 2020, 18, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, A.I.; Nealey, P.F.; Murphy, C.J. Responses of Human Keratocytes to Micro- and Nanostructured Substrates. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2004, 71, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pot, S.A.; Liliensiek, S.J.; Myrna, K.E.; Bentley, E.; Jester, J.V.; Nealey, P.F.; Murphy, C.J. Nanoscale Topography-Induced Modulation of Fundamental Cell Behaviors of Rabbit Corneal Keratocytes, Fibroblasts, and Myofibroblasts. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrna, K.E.; Mendonsa, R.; Russell, P.; Pot, S.A.; Liliensiek, S.J.; Jester, J.V.; Nealey, P.F.; Brown, D.; Murphy, C.J. Substratum Topography Modulates Corneal Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Transformation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.; Shihabeddin, T.Z.; Awkal, J.A.; Najjar, A.M.; Miron-Mendoza, M.; Maruri, D.P.; Varner, V.D.; Petroll, W.M.; Schmidtke, D.W. Effects of Topography and PDGF on the Response of Corneal Keratocytes to Fibronectin-Coated Surfaces. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, S.A.; Ting, Y.H.; Mallon, K.S.; Wendt, A.E.; Murphy, C.J.; Nealey, P.F. Sub-Micron and Nanoscale Feature Depth Modulates Alignment of Stromal Fibroblasts and Corneal Epithelial Cells in Serum-Rich and Serum-Free Media. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 86, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhurenkov, K.E.; Lobov, A.A.; Bildyug, N.B.; Alexander-Sinclair, E.I.; Darvish, D.M.; Lomert, E.V.; Kriger, D.V.; Zainullina, B.R.; Chabina, A.S.; Khorolskaya, J.I.; et al. Focal Adhesion Maturation Responsible for Behavioral Changes in Human Corneal Stromal Fibroblasts on Fibrillar Substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Cavanagh, B.L.; Ahearne, M. Influence of Micropatterned Substrates on Keratocyte Phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Cavanagh, B.L.; Ahearne, M. Effect of Substrate Topography on the Regulation of Human Corneal Stromal Cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreier, B.; Raghunathan, V.K.; Russell, P.; Murphy, C.J. Focal Adhesion Kinase Knockdown Modulates the Response of Human Corneal Epithelial Cells to Topographic Cues. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, D.; Tjahjono, N.S.; Hernandez, P.A.; Varner, V.D.; Petroll, W.M.; Schmidtke, D.W. Fabrication of Micropatterns of Aligned Collagen Fibrils. Langmuir 2024, 40, 2551–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, D.; Tjahjono, N.S.; Nammi, S.; Miron-Mendoza, M.; Varner, V.D.; Petroll, W.M.; Schmidtke, D.W. Effects of Cell Seeding Density, Extracellular Matrix Composition, and Geometry on Yes-Associated Protein Translocation in Corneal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Wirtz, D. Predicting How Cells Spread and Migrate: Focal Adhesion Size Does Matter. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Wirtz, D. Focal Adhesion Size Uniquely Predicts Cell Migration. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dede Eren, A.; Lucassen, A.W.A.; Tuvshindorj, U.; Truckenmüller, R.; Giselbrecht, S.; Eren, E.D.; Tas, M.O.; Sudarsanam, P.; de Boer, J. Cells Dynamically Adapt to Surface Geometry by Remodeling Their Focal Adhesions and Actin Cytoskeleton. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 863721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, N.D. Cell Adhesion Strengthening: Contributions of Adhesive Area, Integrin Binding, and Focal Adhesion Assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 4329–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elineni, K.K.; Gallant, N.D. Regulation of Cell Adhesion Strength by Peripheral Focal Adhesion Distribution. Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2903–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardone, G.; Oliver-De La Cruz, J.; Vrbsky, J.; Martini, C.; Pribyl, J.; Skládal, P.; Pešl, M.; Caluori, G.; Pagliari, S.; Martino, F.; et al. YAP Regulates Cell Mechanics by Controlling Focal Adhesion Assembly. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Downey, G.P.; McCulloch, C.A. Focal Adhesions and Ras Are Functionally and Spatially Integrated to Mediate IL-1 Activation of ERK. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3448–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berrier, A.; Yamada, K.M. Cell-Matrix Adhesion. J. Cell. Physiol. 2006, 213, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, M.J.P.; Richards, R.G.; Gadegaard, N.; McMurray, R.J.; Affrossman, S.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Dalby, M.J. Interactions with Nanoscale Topography: Adhesion Quantification and Signal Transduction in Cells of Osteogenic and Multipotent Lineage. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 91, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, J.W.; Roberts, J.N.; Smith, C.A.; Robertson, M.; White, K.; Biggs, M.J.; Oreffo, R.O.C.; Dalby, M.J. Osteogenic Lineage Restriction by Osteoprogenitors Cultured on Nanometric Grooved Surfaces: The Role of Focal Adhesion Maturation. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masur, S.K.; Cheung, J.K.H.; Antohi, S. Identification of Integrins in Cultured Corneal Fibroblasts and in Isolated Keratocytes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1993, 34, 2690–2698. [Google Scholar]
- Jester, J.V.; Barry, P.A.; Lind, G.J.; Petroll, W.M.; Garana, R.; Cavanagh, H.D. Corneal Keratocytes: In Situ and in Vitro Organization of Cytoskeletal Contractile Proteins. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 730–743. [Google Scholar]
- Stepp, M.A. Corneal Integrins and Their Functions. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xing, M.; Wang, L.; Guan, G. Effects of Aligned Electrospun Fibers with Different Diameters on Hemocompatibility, Cell Behaviors and Inflammation in Vitro. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Yao, D.; Jiang, J.; Guo, X.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Shen, C. Effects of Aligned and Random Fibers with Different Diameter on Cell Behaviors. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 171, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, J.Y.; Ramamurthy, E.; Young, A.D.; Redman, T.P.; Leonard, C.E.; Das, S.K.; Fisher, P.B.; Lemmon, C.A.; Hwang, P.Y. Leader Cells Mechanically Respond to Aligned Collagen Architecture to Direct Collective Migration. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, C.P.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Foss, M.; Chevallier, J.; Fink, T.; Zachar, V.; Besenbacher, F.; Yoshida, K. Nanoscale Topography Reduces Fibroblast Growth, Focal Adhesion Size and Migration-Related Gene Expression on Platinum Surfaces. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, C.H.; Furukawa, K.; Montagne, K.; Jeong, H.; Ushida, T. The Effect of Substrate Microtopography on Focal Adhesion Maturation and Actin Organization via the RhoA/ROCK Pathway. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9568–9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.I.; Abrams, G.A.; Bertics, P.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Nealey, P.F. Epithelial Contact Guidance on Well-Defined Micro- and Nanostructured Substrates. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116 Pt 10, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, A.; Ende, K.; Diemer, J.; Kyvik, A.R.; Veciana, J.; Ratera, I.; Kemkemer, R.; Spatz, J.P.; Guasch, J. Cell Type-Dependent Integrin Distribution in Adhesion and Migration Responses on Protein-Coated Microgrooved Substrates. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, K.H.; Kivanany, P.B.; Grose, K.; Yonet-Tanyeri, N.; Alsmadi, N.; Varner, V.D.; Petroll, W.M.; Schmidtke, D.W. A High-Throughput Microfluidic Method for Fabricating Aligned Collagen Fibrils to Study Keratocyte Behavior. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jester, J.V.; Huang, J.; Fisher, S.; Spiekerman, J.; Chang, J.H.; Wright, W.E.; Shay, J.W. Myofibroblast Differentiation of Normal Human Keratocytes and HTERT, Extended-Life. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruri, D.P.; Iyer, K.S.; Schmidtke, D.W.; Petroll, W.M.; Varner, V.D. Signaling Downstream of Focal Adhesions Regulates Stiffness-Dependent Differences in the TGF-Β1-Mediated Myofibroblast Differentiation of Corneal Keratocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 886759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, D. Investigating the Role of Extracellular Matrix Topography, Geometry and Composition of Corneal Fibroblast Behavior. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Texas at Dallas, Richardson, TX, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]

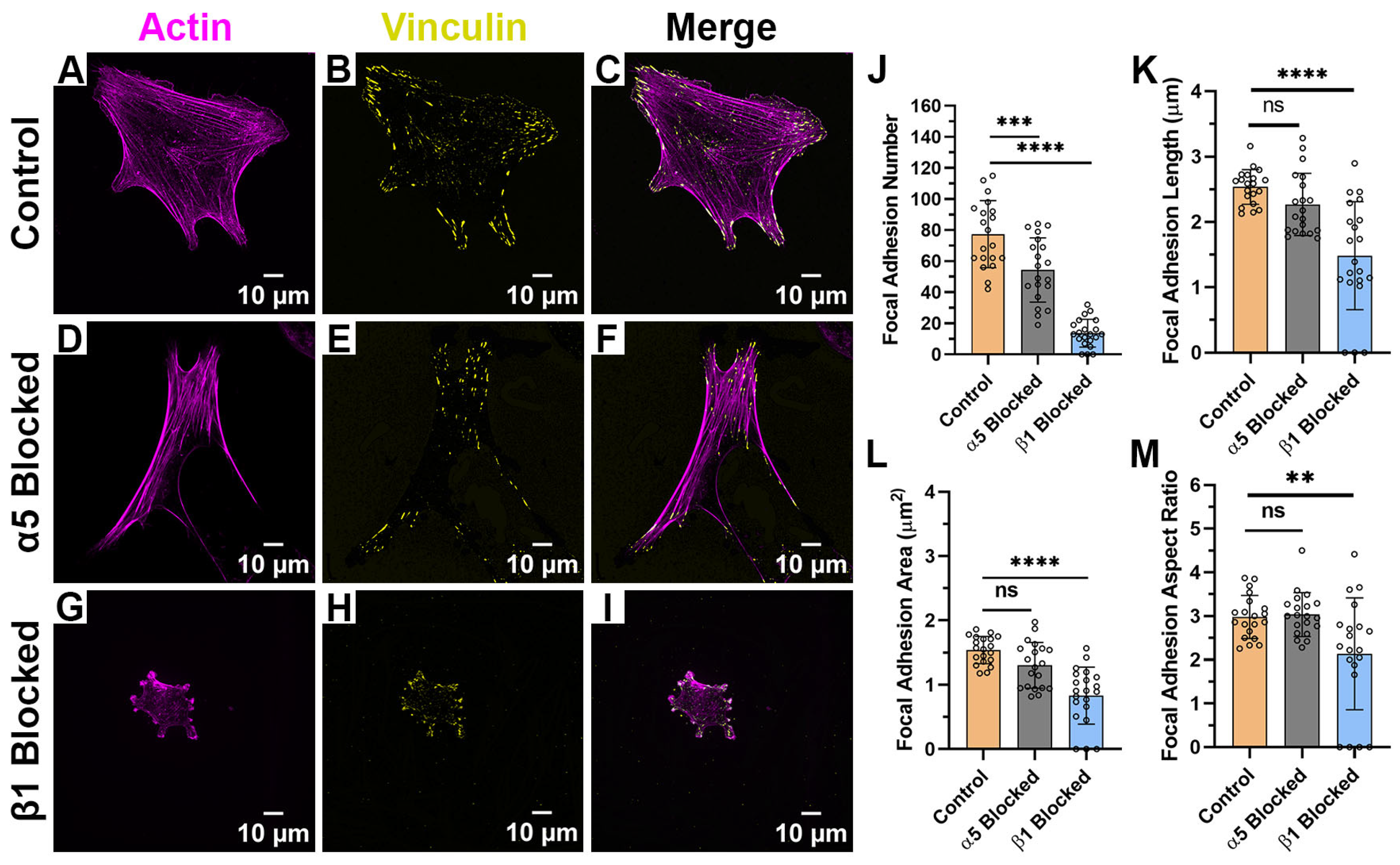
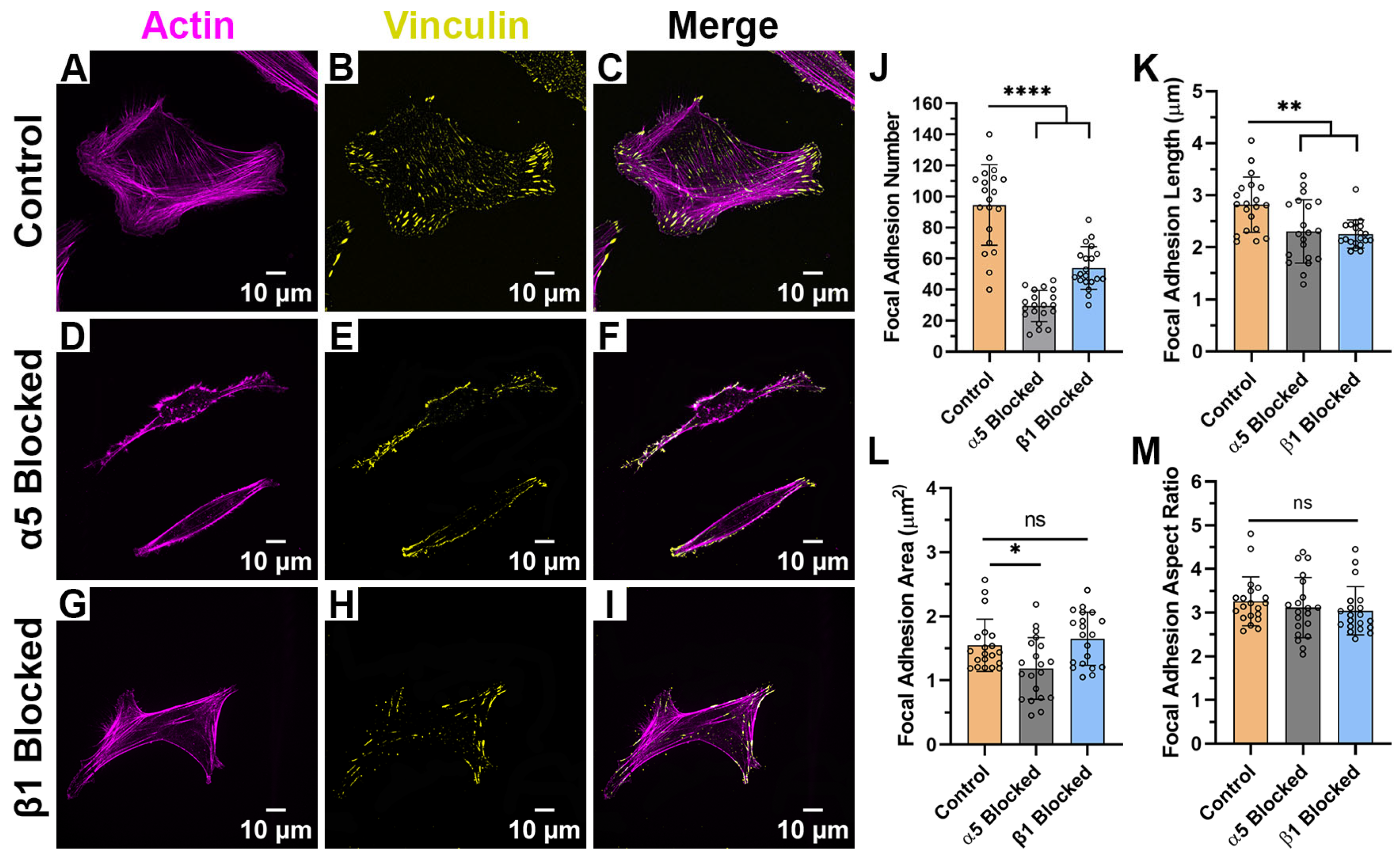
| Focal Adhesion Morphology | Control (Average ± SD) | α5 Blocked (Average ± SD) | β1 Blocked (Average ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA Number | |||
| FA Area | |||
| FA Length | |||
| FA Aspect Ratio |
| Focal Adhesion Morphology | Control (Average ± SD) | α5 Blocked (Average ± SD) | β1 Blocked (Average ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA Number | |||
| FA Area | |||
| FA Length | |||
| FA Aspect Ratio |
| Focal Adhesion Morphology | Control (Average ± SD) | α5 Blocked (Average ± SD) | β1 Blocked (Average ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA Number | |||
| FA Area | |||
| FA Length | |||
| FA Aspect Ratio |
| Focal Adhesion Morphology | Control (Average ± SD) | α5 Blocked (Average ± SD) | β1 Blocked (Average ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FA Number | |||
| FA Area | |||
| FA Length | |||
| FA Aspect Ratio |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Subramanian, D.; Tjahjono, N.S.; Shihabeddin, T.Z.; Nammi, S.; Miron-Mendoza, M.; Varner, V.D.; Petroll, W.M.; Schmidtke, D.W. Effects of Topography and Extracellular Matrix Composition on Focal Adhesion Patterning in Human Corneal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411935
Subramanian D, Tjahjono NS, Shihabeddin TZ, Nammi S, Miron-Mendoza M, Varner VD, Petroll WM, Schmidtke DW. Effects of Topography and Extracellular Matrix Composition on Focal Adhesion Patterning in Human Corneal Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):11935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411935
Chicago/Turabian StyleSubramanian, Divya, Nathaniel S. Tjahjono, Tarik Z. Shihabeddin, Satweka Nammi, Miguel Miron-Mendoza, Victor D. Varner, W. Matthew Petroll, and David W. Schmidtke. 2025. "Effects of Topography and Extracellular Matrix Composition on Focal Adhesion Patterning in Human Corneal Fibroblasts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 11935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411935
APA StyleSubramanian, D., Tjahjono, N. S., Shihabeddin, T. Z., Nammi, S., Miron-Mendoza, M., Varner, V. D., Petroll, W. M., & Schmidtke, D. W. (2025). Effects of Topography and Extracellular Matrix Composition on Focal Adhesion Patterning in Human Corneal Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 11935. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411935







