Structural and Functional Analysis of ASFV pI73R Reveals GNB1 Binding and Host Gene Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. pI73R Protein Feature Analysis
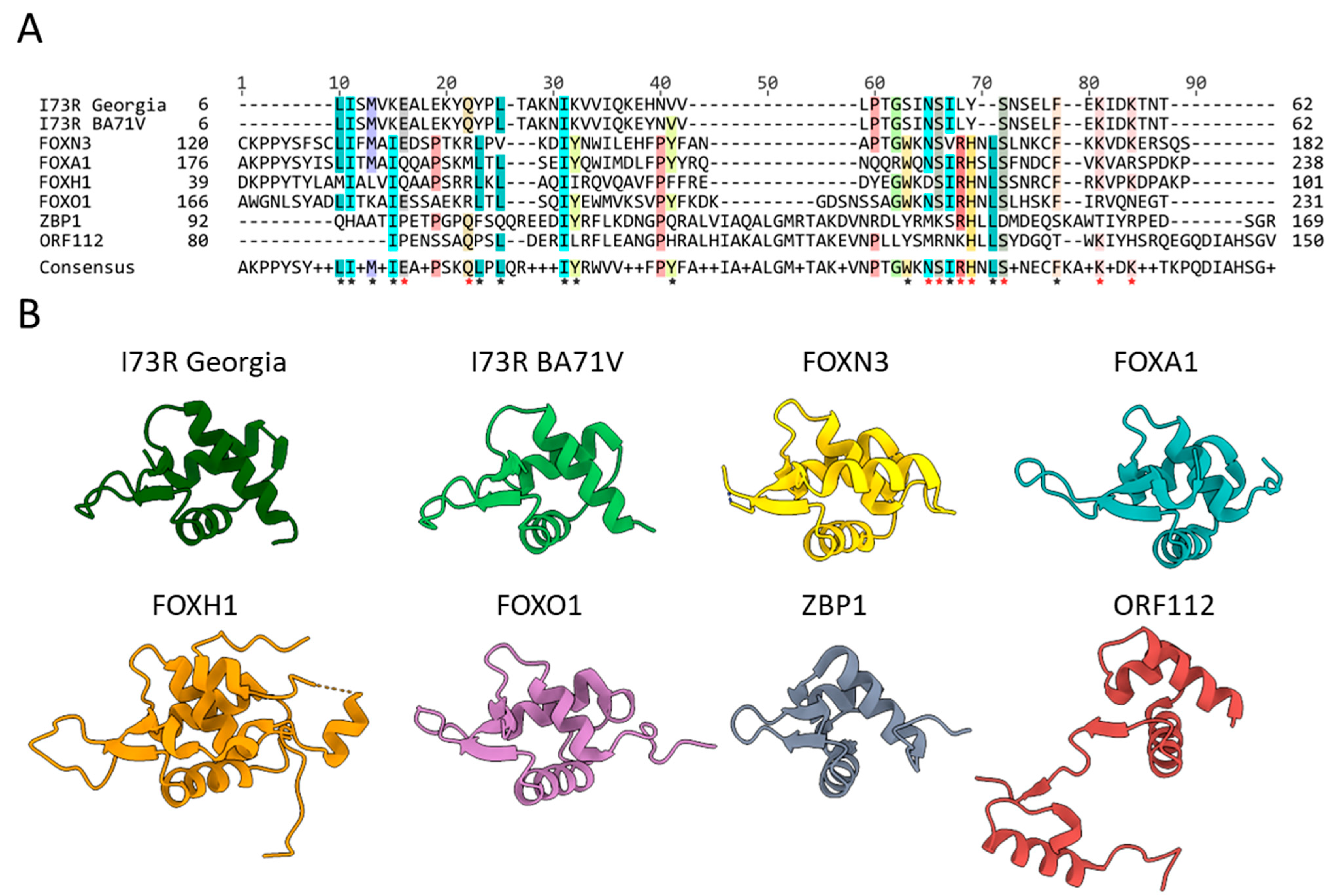
2.2. pI73R Homology with FOX and Z-DNA-Binding Proteins
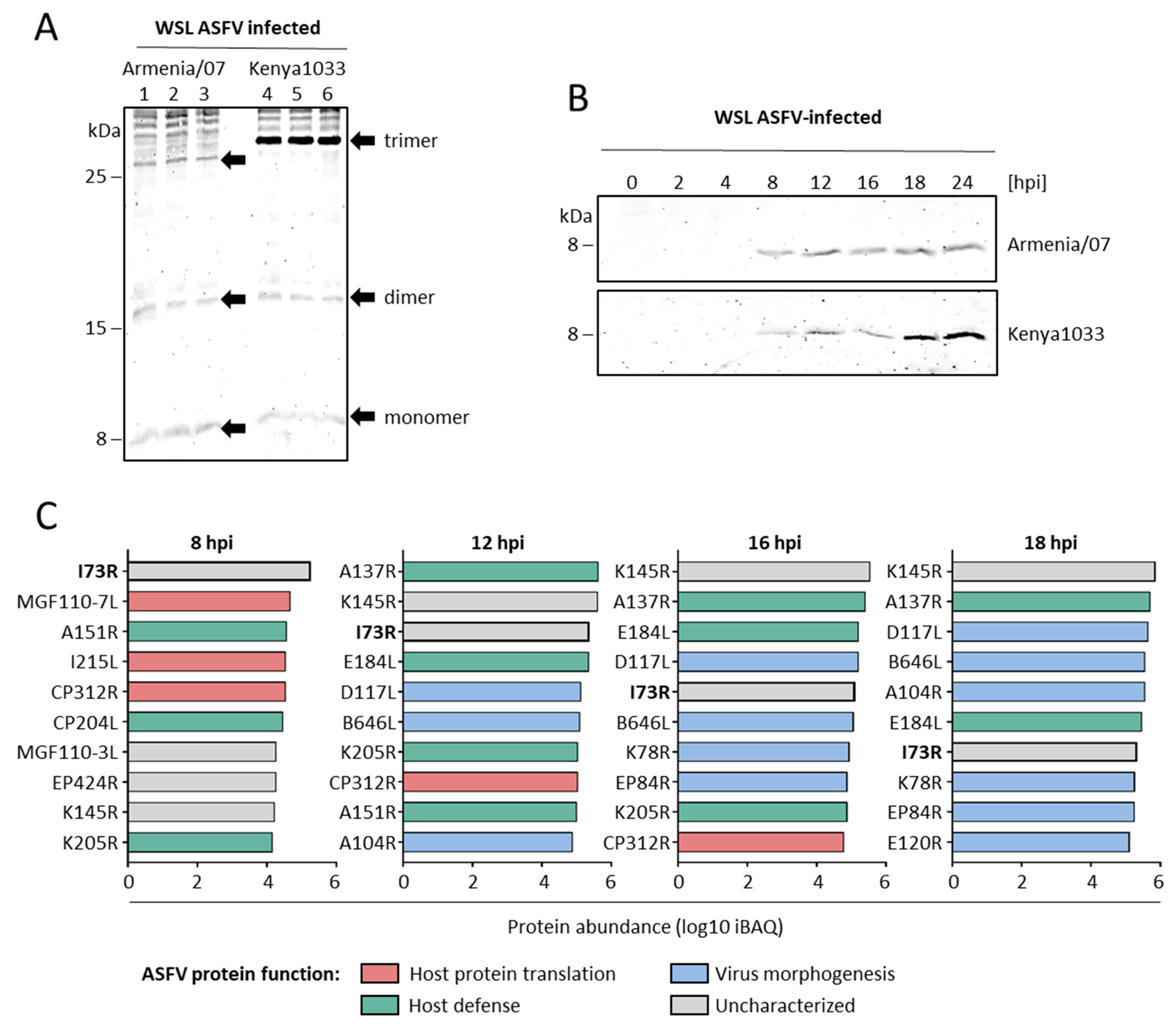
2.3. pI73R Is a Highly Abundant Early ASFV Protein with Genotype II-Specific Amino Acid Variation
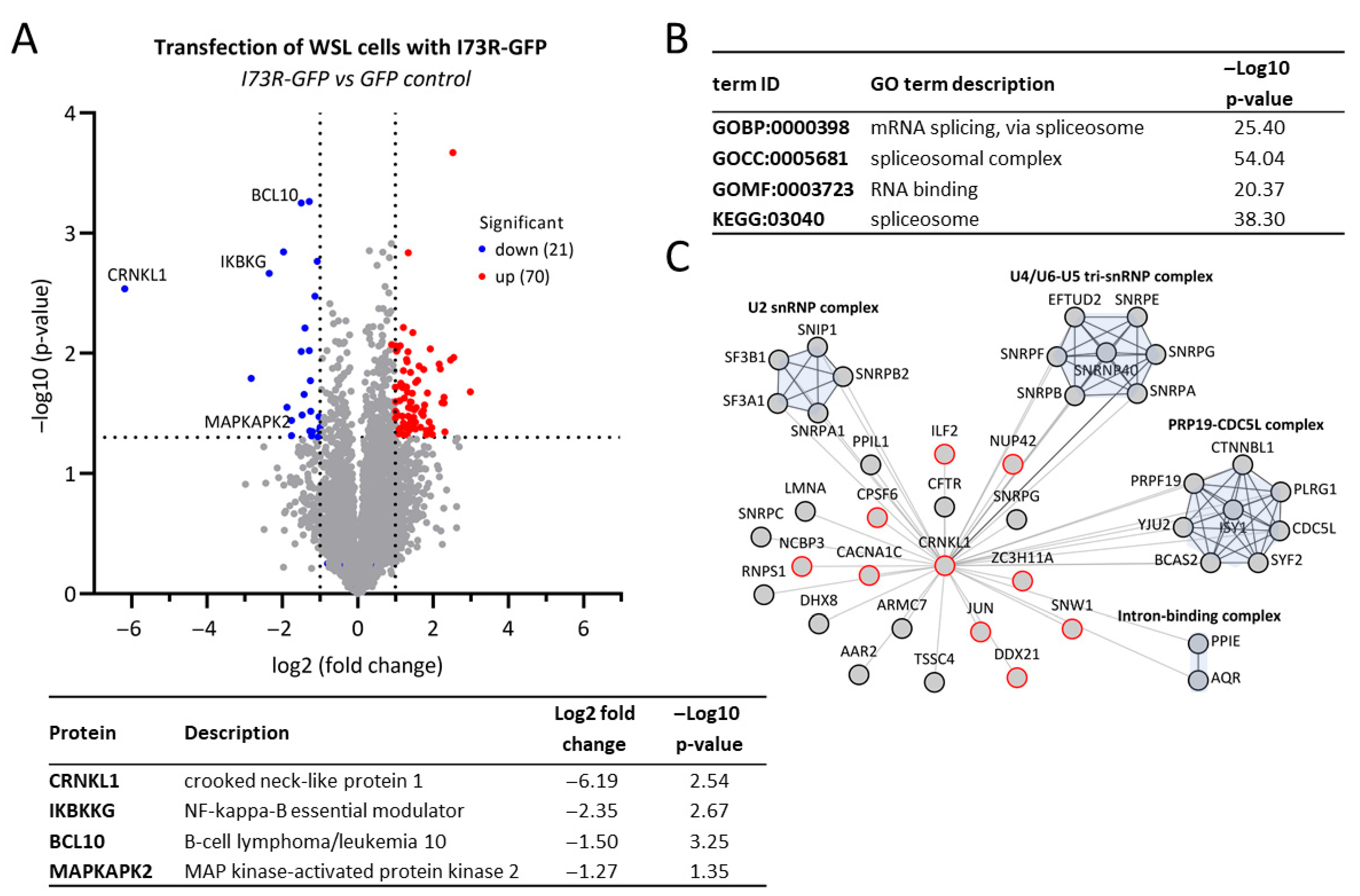
2.4. pI73R Overexpression Induces CRNKL1 Downregulation
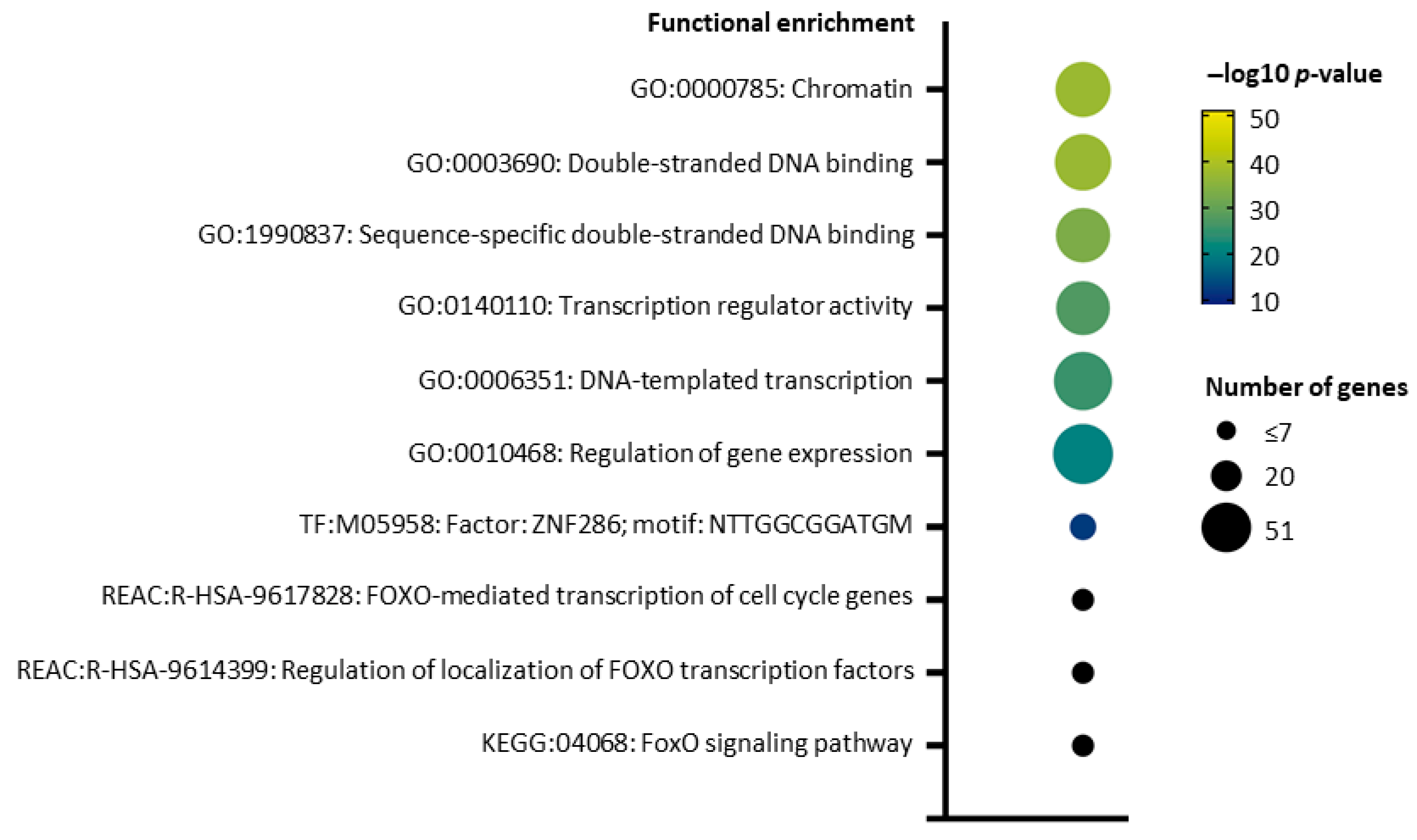
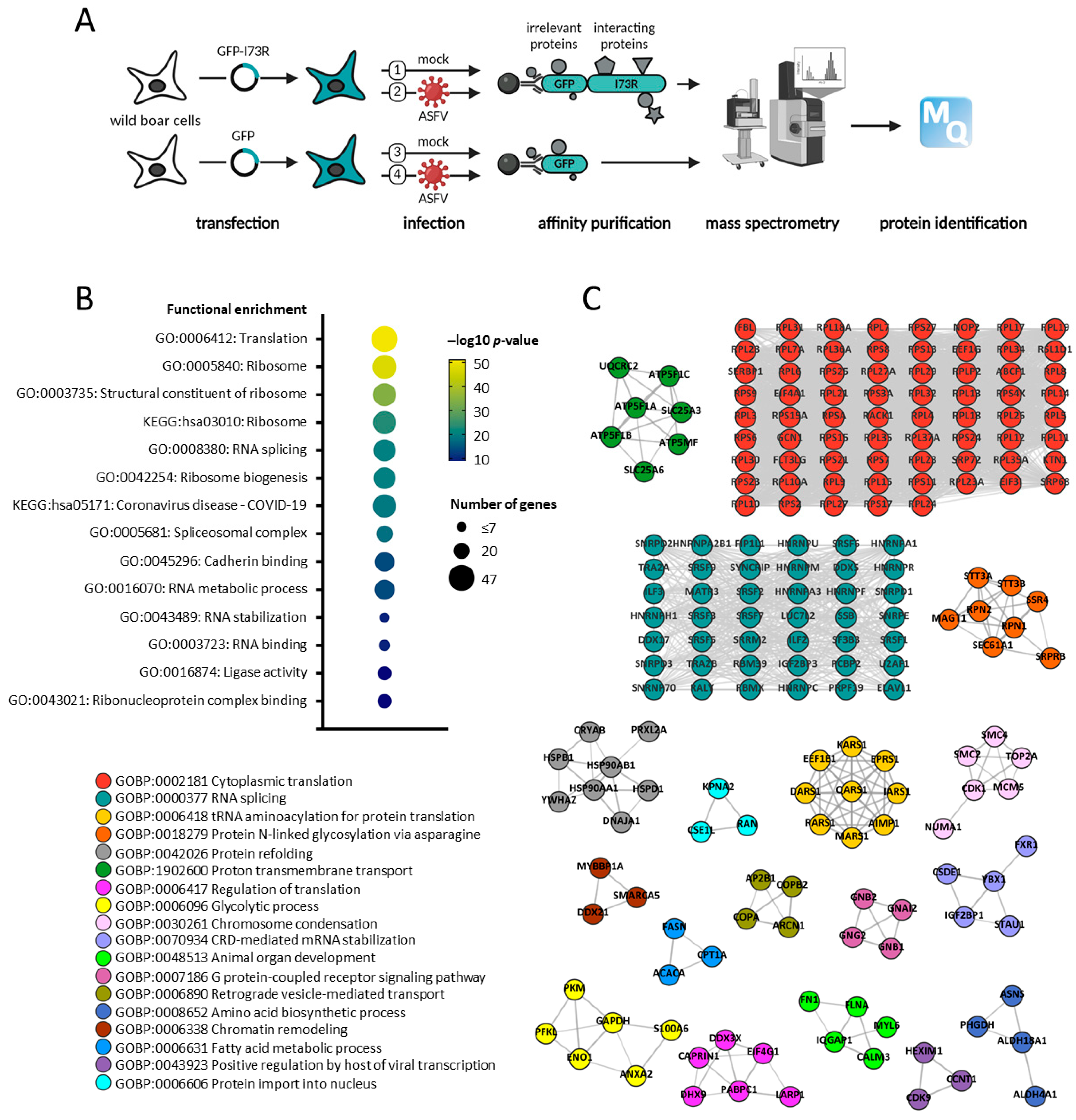
2.5. pI73R Protein Interaction Network
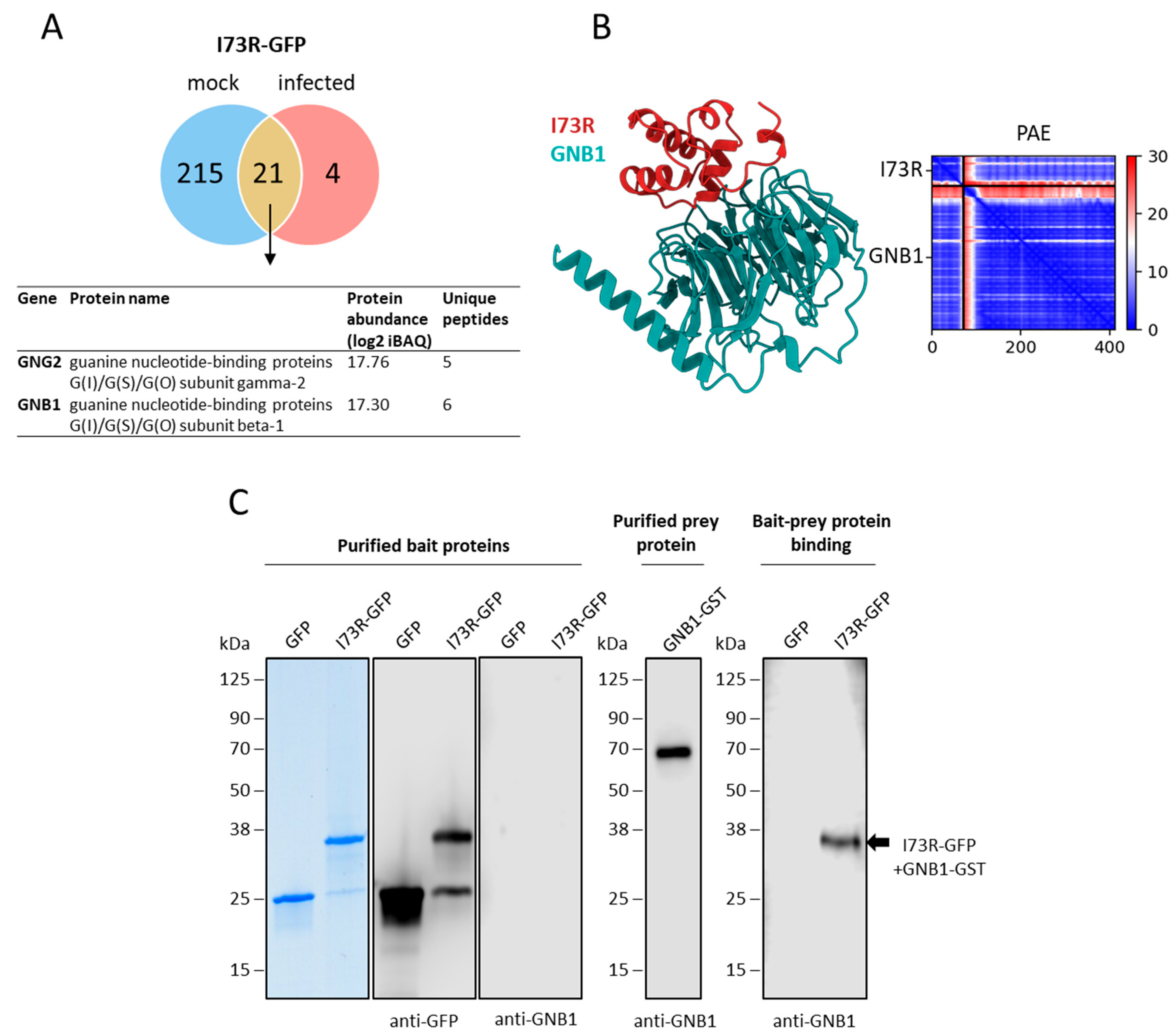
2.6. pI73R Interacts with GNB1 Protein in ASFV-Infected Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cells and Viruses
4.2. Plasmids and DNA Transfection
4.3. ASFV Infection
4.4. Antibodies and Recombinant Proteins
4.5. Generation of Polyclonal Antiserum Against pI73R
4.6. Purification of pI73R-GFP and GFP for Western Blotting
4.7. Generation and Analysis of MS-Sample
4.7.1. Affinity Purification
4.7.2. On-Bead Digestion
4.7.3. Lysate Sample Preparation
4.7.4. MS Data Acquisition and Analysis
4.8. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.8.1. Term Enrichment Analysis
4.8.2. Protein–Protein Interaction Networks
4.8.3. Computational Modeling of Proteins and Protein Complexes
4.8.4. Structure Analysis
4.8.5. Multi Sequence Alignment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP-MS | Affinity purification-mass spectrometry |
| Armenia/07 | ASFV strain Armenia from 2007 |
| ASF | African swine fever |
| ASFV | African swine fever virus |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| CRNKL1 | Crooked neck-like protein 1 |
| FASP | Filter-aided sample preparation |
| FOX | Forkhead box |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| GNB1 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-like protein 1 |
| GPCR | G protein-coupled receptor |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| Kenya1033 | ASFV strain Kenya1033-ΔCD2v-dsRed |
| MCL | Markov clustering |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| MSA | Multi sequence alignment |
| WSL | Wild boar lung-derived cells |
| TM-score | Template modeling score |
| PAE | Predicted aligned error |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank at www.rcsb.org |
| pLDDT | predicted local distance difference test |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline with 0.25% Tween 20 |
References
- Dixon, L.K.; Sun, H.; Roberts, H. African swine fever. Antivir. Res. 2019, 165, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Villamandos, J.C.; Hervás, J.; Méndez, A.; Carrasco, L.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. Ultrastructural study of the renal tubular system in acute experimental African swine fever: Virus replication in glomerular mesangial cells and in the collecting ducts. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiboeker, S.B.; Scoles, G.A.; Burrage, T.G.; Sur, J. African swine fever virus replication in the midgut epithelium is required for infection of Ornithodoros ticks. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 8587–8598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eustace Montgomery, R. On A Form of Swine Fever Occurring in British East Africa (Kenya Colony). J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 1921, 34, 159–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Liu, T.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Dong, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wei, X.; Shi, B. African swine fever outbreaks in China led to gross domestic product and economic losses. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Z.; Shan, H.; Cai, X. Vaccines for African swine fever: An update. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1139494, Correction in Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1529175. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2024.1529175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.H.; Le, T.T.P.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Do, T.T.; van Nguyen, D.; Gay, C.G.; Borca, M.V.; Gladue, D.P. African swine fever virus vaccine candidate ASFV-G-ΔI177L efficiently protects European and native pig breeds against circulating Vietnamese field strain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e497–e504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, X.H.; Le Phuong, T.T.; Huy, N.Q.; Thuy, D.T.; van Nguyen, D.; Quang, P.H.; Ngôn, Q.V.; Rai, A.; Gay, C.G.; Gladue, D.P.; et al. Evaluation of the Safety Profile of the ASFV Vaccine Candidate ASFV-G-ΔI177L. Viruses 2022, 14, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Dong, P.; Zhang, H.; Wu, L.; Jiang, M.; Chen, L.; Yang, W.; et al. Structural insight into African swine fever virus I73R protein reveals it as a Z-DNA binding protein. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1923–e1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Zheng, X.; Park, C.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.K.; Won, H.; Choi, J.; Kim, Y.-G.; Choi, H.-J. Dual conformational recognition by Z-DNA binding protein is important for the B-Z transition process. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 12957–12971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Xie, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Liang, R.; Gong, L.; Di, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; et al. African swine fever virus I73R is a critical virulence-related gene: A potential target for attenuation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2210808120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Ao, Q.; Lv, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Hu, R.; Chen, H.; et al. A novel function of African Swine Fever Virus pE66L in inhibition of host translation by the PKR/eIF2α pathway. J. Virol. 2021, 95, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.C.; Chaudhari, J.; Vu, H.L.X. African swine fever virus early protein pI73R suppresses the type-I IFN promoter activities. Virus Res. 2024, 343, 199342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillitoe, I.; Bordin, N.; Dawson, N.; Waman, V.P.; Ashford, P.; Scholes, H.M.; Pang, C.S.M.; Woodridge, L.; Rauer, C.; Sen, N.; et al. CATH: Increased structural coverage of functional space. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D266–D273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, M.; Andreeva, A.; Florentino, L.C.; Chuguransky, S.R.; Grego, T.; Hobbs, E.; Pinto, B.L.; Orr, A.; Paysan-Lafosse, T.; Ponamareva, I.; et al. InterPro: The protein sequence classification resource in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D444–D456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajiwala, K.S.; Burley, S.K. Winged helix proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. g:Profiler-interoperable web service for functional enrichment analysis and gene identifier mapping (2023 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W207–W212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milacic, M.; Beavers, D.; Conley, P.; Gong, C.; Gillespie, M.; Griss, J.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase 2024. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D672–D678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matys, V.; Fricke, E.; Geffers, R.; Gössling, E.; Haubrock, M.; Hehl, R.; Hornischer, K.; Karas, D.; Kel, A.E.; Kel-Margoulis, O.V.; et al. TRANSFAC: Transcriptional regulation, from patterns to profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kempen, M.; Kim, S.S.; Tumescheit, C.; Mirdita, M.; Lee, J.; Gilchrist, C.L.M.; Söding, J.; Steinegger, M. Fast and accurate protein structure search with Foldseek. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. TM-align: A protein structure alignment algorithm based on the TM-score. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Toro, N.; Shrivastava, A.; Ragueneau, E.; Meldal, B.; Combe, C.; Barrera, E.; Perfetto, L.; How, K.; Ratan, P.; Shirodkar, G.; et al. The IntAct database: Efficient access to fine-grained molecular interaction data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D648–D653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolata, K.M.; Fuchs, W.; Caignard, G.; Dupré, J.; Pannhorst, K.; Blome, S.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Karger, A. CP204L Is a Multifunctional Protein of African Swine Fever Virus That Interacts with the VPS39 Subunit of the Homotypic Fusion and Vacuole Protein Sorting Complex and Promotes Lysosome Clustering. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0194322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, L.M.; Balaji, S.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. Evolutionary genomics of nucleo-cytoplasmic large DNA viruses. Virus Res. 2006, 117, 156–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, G.; García-Beato, R.; Viñuela, E.; Salas, M.L.; Salas, J. Replication of African swine fever virus DNA in infected cells. Virology 1999, 257, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, W.; Wang, H.; Ye, M.; Hu, D.; Wu, J.; Qu, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; et al. Revisiting the early event of African swine fever virus DNA replication. J. Virol. 2025, 99, e0058425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Beato, R.; Salas, M.L.; Viñuela, E.; Salas, J. Role of the host cell nucleus in the replication of African swine fever virus DNA. Virology 1992, 188, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulálio, A.; Nunes-Correia, I.; Salas, J.; Salas, M.L.; Simões, S.; Pedroso de Lima, M.C. African swine fever virus p37 structural protein is localized in nuclear foci containing the viral DNA at early post-infection times. Virus Res. 2007, 130, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortin, J.; Vińuela, E. Requirement of cell nucleus for African swine fever virus replication in Vero cells. J. Virol. 1977, 21, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.; Martins, C.; Ferreira, F. Early intranuclear replication of African swine fever virus genome modifies the landscape of the host cell nucleus. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballester, M.; Rodríguez-Cariño, C.; Pérez, M.; Gallardo, C.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Salas, M.L.; Rodriguez, F. Disruption of Nuclear Organization during the Initial Phase of African Swine Fever Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8263–8269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.; Rino, J.; Pinheiro, I.; Martins, C.; Ferreira, F. Alterations of Nuclear Architecture and Epigenetic Signatures during African Swine Fever Virus Infection. Viruses 2015, 7, 4978–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejo, A.; Matamoros, T.; Guerra, M.; Andrés, G. A Proteomic Atlas of the African Swine Fever Virus Particle. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cackett, G.; Matelska, D.; Sýkora, M.; Portugal, R.; Malecki, M.; Bähler, J.; Dixon, L.; Werner, F. The African Swine Fever Virus Transcriptome. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Becanovic, K.; Desplats, P.A.; Spencer, B.; Hill, A.M.; Connolly, C.; Masliah, E.; Leavitt, B.R.; Thomas, E.A. Forkhead box protein p1 is a transcriptional repressor of immune signaling in the CNS: Implications for transcriptional dysregulation in Huntington disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 3097–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, F. Role of Forkhead box O3a transcription factor in autoimmune diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, M.; Hollander, P.d.; Mani, S.A. Forkhead Box Transcription Factors: Double-Edged Swords in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 2057–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothan, H.A.; Arora, K.; Natekar, J.P.; Strate, P.G.; Brinton, M.A.; Kumar, M. Z-DNA-Binding Protein 1 Is Critical for Controlling Virus Replication and Survival in West Nile Virus Encephalitis. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenburg, S.; Deigendesch, N.; Dittmar, K.; Koch-Nolte, F.; Haag, F.; Lowenhaupt, K.; Rich, A. A PKR-like eukaryotic initiation factor 2alpha kinase from zebrafish contains Z-DNA binding domains instead of dsRNA binding domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1602–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, N.; Samuel, C.E. RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR and the Z-DNA binding orthologue PKZ differ in their capacity to mediate initiation factor eIF2α-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis and virus-induced stress granule formation. Virology 2013, 443, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.R.; Puig, M.; Darnell, M.E.R.; Mihalik, K.; Feinstone, S.M. New antiviral pathway that mediates hepatitis C virus replicon interferon sensitivity through ADAR1. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6291–6298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomé, A.R.; Kuś, K.; Correia, S.; Paulo, L.M.; Zacarias, S.; de Rosa, M.; Figueiredo, D.; Parkhouse, R.M.E.; Athanasiadis, A. Crystal structure of a poxvirus-like zalpha domain from cyprinid herpesvirus 3. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3998–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.D.; Jacobs, B.L. The amino terminus of the vaccinia virus E3 protein is necessary to inhibit the interferon response. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5895–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Zhou, Z.; Huddleston, K.A.; Harrison, D.A.; Reed, R.; Coleman, T.A.; Rymond, B.C. Crooked neck is a component of the human spliceosome and implicated in the splicing process. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1576, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanarat, S.; Sträßer, K. Splicing and beyond: The many faces of the Prp19 complex. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 2126–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhai, B.; Yin, S.; Gygi, S.; Reed, R. Evidence that a consensus element found in naturally intronless mRNAs promotes mRNA export. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammani, K.; Cook, W.B.; Barkan, A. RNA binding and RNA remodeling activities of the half-a-tetratricopeptide (HAT) protein HCF107 underlie its effects on gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5651–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wyler, E.; Milek, M.; Grewe, B.; Kirchner, P.; Ekici, A.; Silva, A.B.O.V.; Jungnickl, D.; Full, F.; Thomas, M.; et al. CRNKL1 Is a Highly Selective Regulator of Intron-Retaining HIV-1 and Cellular mRNAs. mBio 2021, 12, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torma, G.; Tombácz, D.; Csabai, Z.; Moldován, N.; Mészáros, I.; Zádori, Z.; Boldogkői, Z. Combined Short and Long-Read Sequencing Reveals a Complex Transcriptomic Architecture of African Swine Fever Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wöhnke, E.; Klupp, B.G.; Blome, S.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Karger, A. Mass-Spectrometric Evaluation of the African Swine Fever Virus-Induced Host Shutoff Using Dynamic Stable Isotope Labeling with Amino Acids in Cell Culture (SILAC). Viruses 2023, 15, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keßler, C.; Forth, J.H.; Keil, G.M.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Blome, S.; Karger, A. The intracellular proteome of African swine fever virus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhnke, E.; Fuchs, W.; Hartmann, L.; Blohm, U.; Blome, S.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Karger, A. Comparison of the Proteomes of Porcine Macrophages and a Stable Porcine Cell Line after Infection with African Swine Fever Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Fan, S.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, D.; Han, S.; Wan, B.; Zhang, G. African Swine Fever Virus MGF110-7L Induces Host Cell Translation Suppression and Stress Granule Formation by Activating the PERK/PKR-eIF2α Pathway. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0328222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrado-Gil, L.; Del Puerto, A.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Galindo, I.; Cuesta-Geijo, M.Á.; Urquiza, J.; Nistal-Villán, E.; Maluquer de Motes, C.; Alonso, C. African Swine Fever Virus Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme Interacts With Host Translation Machinery to Regulate the Host Protein Synthesis. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 622907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagoss, Y.T.; Shen, D.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Sun, E.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, J.; Guo, Y.; Bu, Z.; et al. African swine fever virus pCP312R interacts with host RPS27A to shut off host protein translation and promotes viral replication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 134213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballin, J.D.; Prevas, J.P.; Ross, C.R.; Toth, E.A.; Wilson, G.M.; Record, M.T. Contributions of the histidine side chain and the N-terminal alpha-amino group to the binding thermodynamics of oligopeptides to nucleic acids as a function of pH. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 2018–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freissmuth, M.; Casey, P.J.; Gilman, A.G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Ma, L.; Gui, R.; Lin, X.; Ke, X.; Jian, X.; Ye, C.; Chen, Q. G Protein Subunit β1 Facilitates Influenza A Virus Replication by Promoting the Nuclear Import of PB2. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0049422, Erratum in J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0054623. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00546-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Pu, J.; et al. H9N2 virus-derived M1 protein promotes H5N6 virus release in mammalian cells: Mechanism of avian influenza virus inter-species infection in humans. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keil, G.M.; Giesow, K.; Portugal, R. A novel bromodeoxyuridine-resistant wild boar lung cell line facilitates generation of African swine fever virus recombinants. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 2421–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, A.; Petersen, B.; Keil, G.M.; Niemann, H.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Fuchs, W. Efficient inhibition of African swine fever virus replication by CRISPR/Cas9 targeting of the viral p30 gene (CP204L). Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Donovan, W.P.; Shikapwashya-Hasser, O.; Ye, X.; Cole, R.H. Hot Fusion: An efficient method to clone multiple DNA fragments as well as inverted repeats without ligase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towbin, H.; Staehelin, T.; Gordon, J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 4350–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewski, J.R.; Zougman, A.; Nagaraj, N.; Mann, M. Universal sample preparation method for proteome analysis. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 359–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aken, B.L.; Achuthan, P.; Akanni, W.; Amode, M.R.; Bernsdorff, F.; Bhai, J.; Billis, K.; Carvalho-Silva, D.; Cummins, C.; Clapham, P.; et al. Ensembl 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D635–D642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Sinitcyn, P.; Carlson, A.; Hein, M.Y.; Geiger, T.; Mann, M.; Cox, J. The Perseus computational platform for comprehensive analysis of (prote)omics data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. gprofiler2—an R package for gene list functional enrichment analysis and namespace conversion toolset g:Profiler. F1000Research 2020, 9, ELIXIR-709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayols, S. rrvgo. Bioconductor. 2020. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/rrvgo.html (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, J.H.; Apeltsin, L.; Newman, A.M.; Baumbach, J.; Wittkop, T.; Su, G.; Bader, G.D.; Ferrin, T.E. clusterMaker: A multi-algorithm clustering plugin for Cytoscape. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.; O’Neill, M.; Pritzel, A.; Antropova, N.; Senior, A.; Green, T.; Žídek, A.; Bates, R.; Blackwell, S.; Yim, J.; et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D384–D388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, N.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdős, G.; Pajkos, M.; Dosztányi, Z. IUPred3: Prediction of protein disorder enhanced with unambiguous experimental annotation and visualization of evolutionary conservation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W297–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallgren, J.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Pedersen, M.D.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Marcatili, P.; Nielsen, H.; Krogh, A.; Winther, O. DeepTMHMM predicts alpha and beta transmembrane proteins using deep neural networks. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, W.; Gou, Y.; Xu, D.; Wei, Y.; Liu, D.; Han, C.; Huang, X.; Li, C.; Ning, W.; et al. GPS 6.0: An updated server for prediction of kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W243–W250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, D.; Yuchi, J.; He, F.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, J.; Xu, D. MusiteDeep: A deep-learning based webserver for protein post-translational modification site prediction and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W140–W146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Rozewicki, J.; Yamada, K.D. MAFFT online service: Multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foust, D.J.; Godin, A.G.; Ustione, A.; Wiseman, P.W.; Piston, D.W. Two-Color Spatial Cumulant Analysis Detects Heteromeric Interactions between Membrane Proteins. Biophys. J. 2019, 117, 1764–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcaíno, J.A.; Deutsch, E.W.; Wang, R.; Csordas, A.; Reisinger, F.; Ríos, D.; Dianes, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Farrah, T.; Bandeira, N.; et al. ProteomeXchange provides globally coordinated proteomics data submission and dissemination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

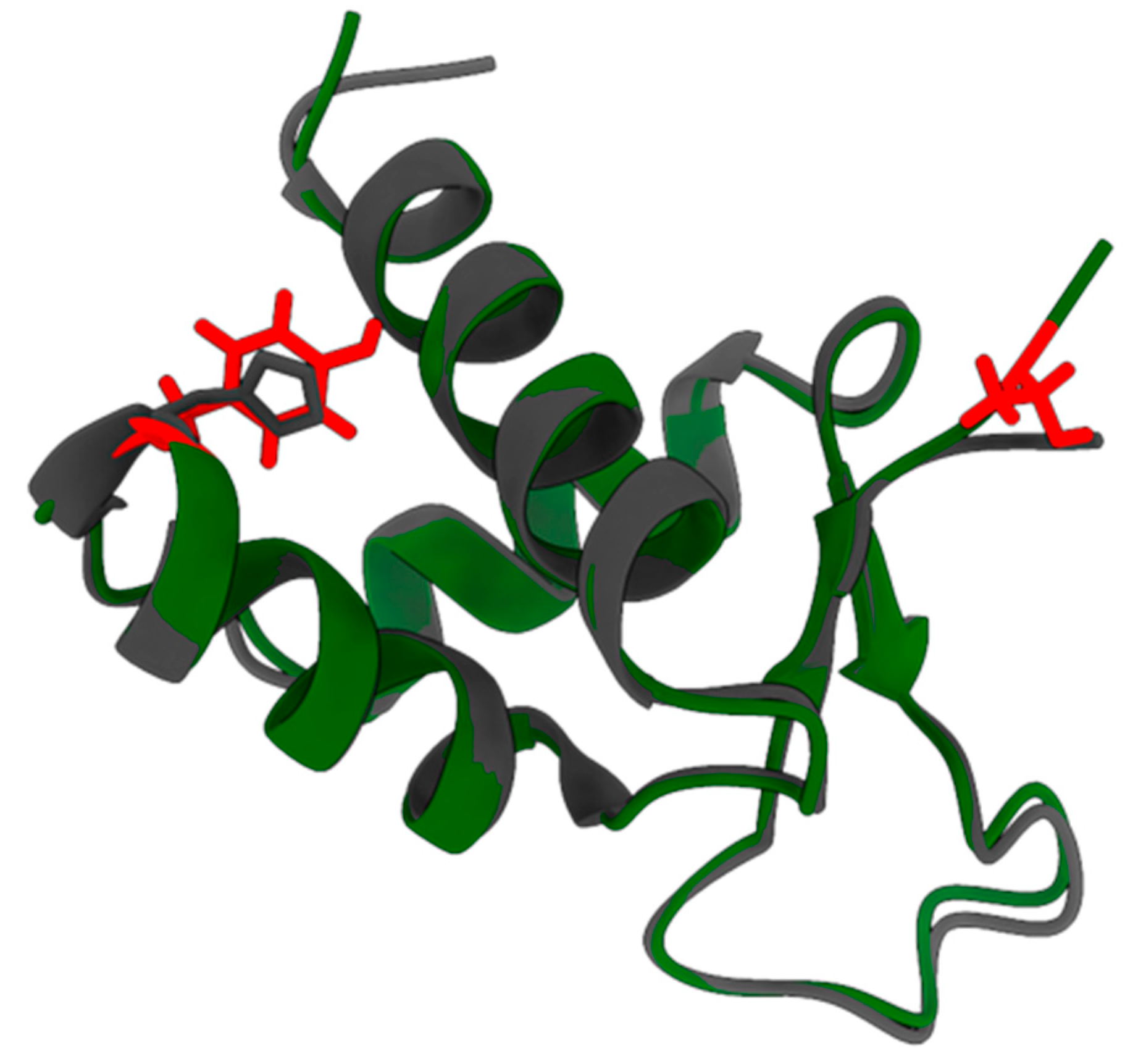
| Reference Protein | Reference PDB ID | Protein Family | TM-Score 1 | RMSD (Å) 2 | Aligned Length 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOXA1 | 7VOX | FOX family | 0.73098 | 2.16 | 66 |
| FOXA2 | 7YZF | FOX family | 0.73680 | 2.30 | 67 |
| FOXG1 | 7CBY | FOX family | 0.73435 | 2.36 | 67 |
| FOXH1 | 7YZB | FOX family | 0.73821 | 2.74 | 71 |
| FOXM1 | 3G73 | FOX family | 0.72205 | 2.24 | 66 |
| FOXK2 | 2C6Y | FOX family | 0.72879 | 2.01 | 65 |
| FOXN1 | 6EL8 | FOX family | 0.74521 | 2.39 | 67 |
| FOXN3 | 6NCM | FOX family | 0.73821 | 2.04 | 65 |
| FOXO1 | 3CO7 | FOX family | 0.73043 | 2.50 | 68 |
| FOXO4 | 3L2C | FOX family | 0.71315 | 2.45 | 66 |
| ZBP1 | 3EYI | Z-DNA binding | 0.64462 | 1.91 | 58 |
| ADAR1 | 1QBJ | Z-DNA binding | 0.72164 | 1.31 | 61 |
| PKZ | 4KMF | Z-DNA binding | 0.71986 | 1.28 | 60 |
| DLM1 | 1J75 | Z-DNA binding | 0.65001 | 1.37 | 55 |
| ORF112 | 4HOB | Z-DNA binding | 0.62616 | 2.15 | 55 |
| E3L | 1SFU | Z-DNA binding | 0.66341 | 1.83 | 62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dolata, K.M.; Bettin, B.; Küchler, R.; Pannhorst, K.; Ushakov, D.S.; Fuchs, W.; Karger, A. Structural and Functional Analysis of ASFV pI73R Reveals GNB1 Binding and Host Gene Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411768
Dolata KM, Bettin B, Küchler R, Pannhorst K, Ushakov DS, Fuchs W, Karger A. Structural and Functional Analysis of ASFV pI73R Reveals GNB1 Binding and Host Gene Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):11768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411768
Chicago/Turabian StyleDolata, Katarzyna Magdalena, Barbara Bettin, Richard Küchler, Katrin Pannhorst, Dmitry S. Ushakov, Walter Fuchs, and Axel Karger. 2025. "Structural and Functional Analysis of ASFV pI73R Reveals GNB1 Binding and Host Gene Modulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 11768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411768
APA StyleDolata, K. M., Bettin, B., Küchler, R., Pannhorst, K., Ushakov, D. S., Fuchs, W., & Karger, A. (2025). Structural and Functional Analysis of ASFV pI73R Reveals GNB1 Binding and Host Gene Modulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 11768. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411768





