Quantitative Modeling of IgG N-Glycosylation Profiles from Population Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
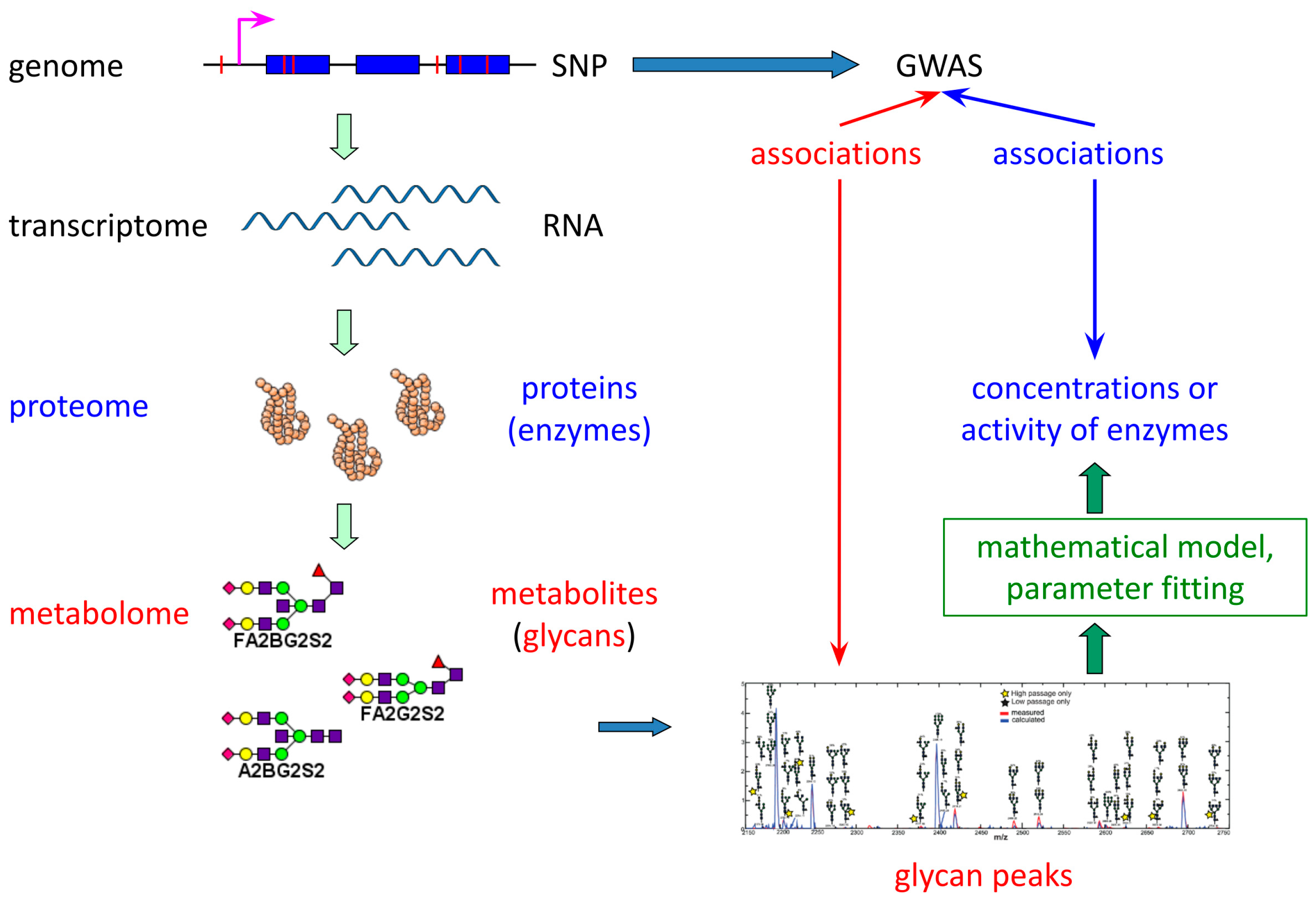
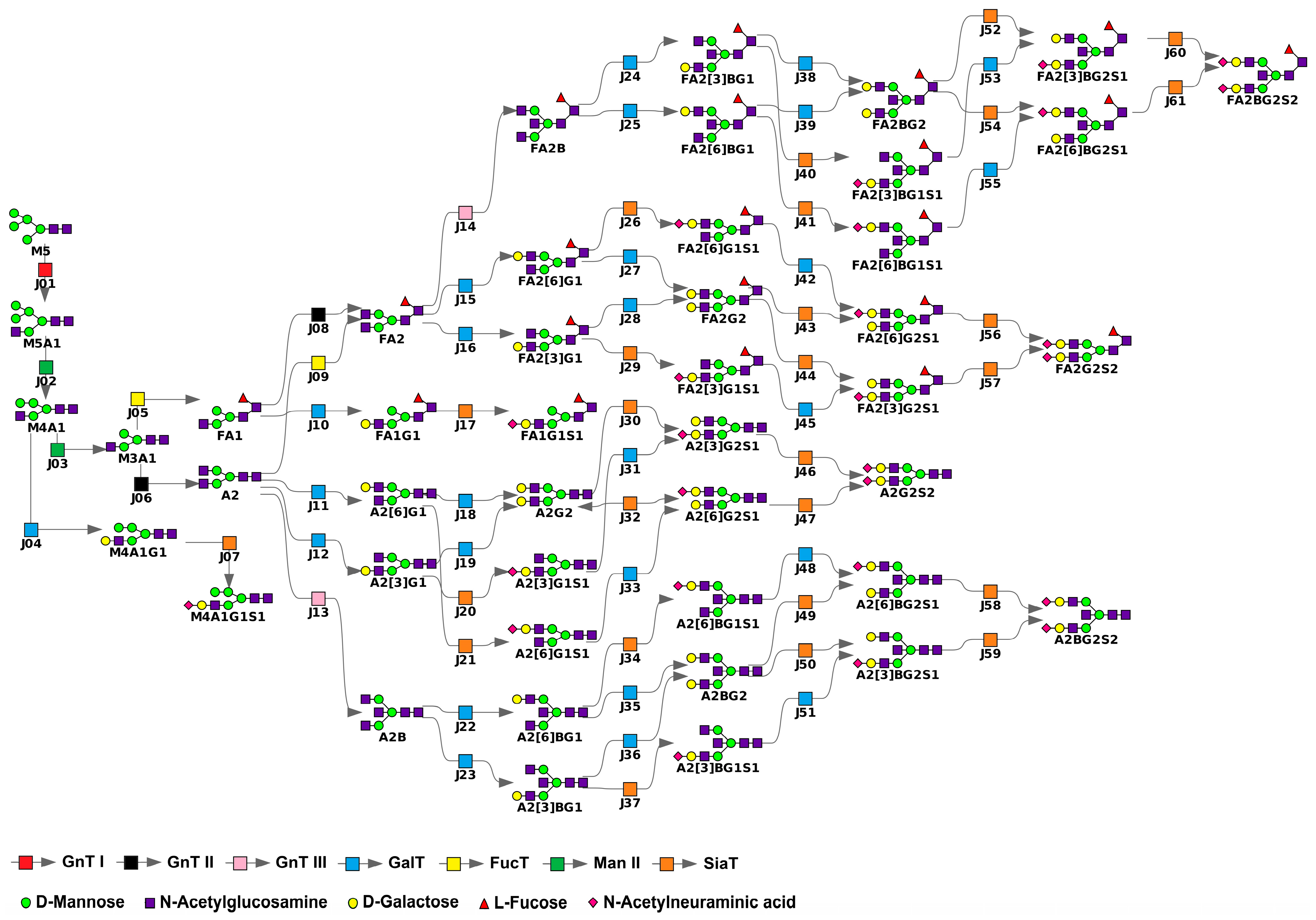
2.1. Model Construction
- GnT I, GnT II, and GnT III mediate the attachment of a single N-acetylglucosamine via β1,2-linkage (GnT I, GnT II) or β1,4-linkage (GnT III) to the α1,3-linked (GnT I), α1,6-linked (GnT II), or β-linked (GnT III) mannose residue.
- Man II catalyzes the cleavage of α1,3- and α1,6-linked mannose residues.
- FucT transfers a fucose residue to the innermost N-acetylglucosamine of N-glycans via α1,6-linkage.
- GalT adds galactose to terminal N-acetylglucosamine through β1,4-linkage.
- SiaT facilitates the attachment of N-acetylneuraminic acid to galactose via α2,3- and α2,6-linkages.
2.2. Model Calibration
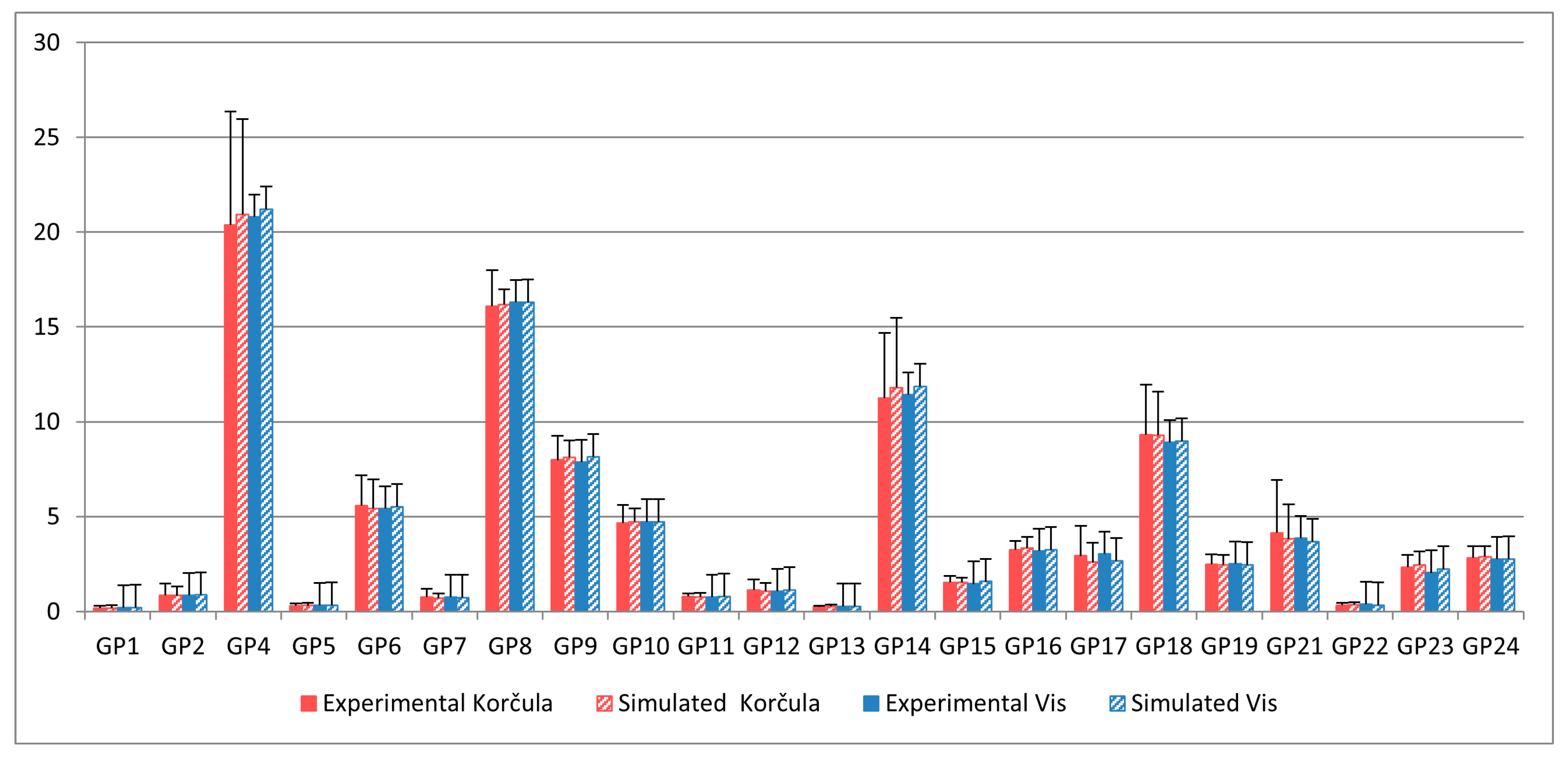
2.3. Model Personalization for the Korčula Cohort
2.4. Identifiability and Sensitivity Analysis of the Model
2.5. Model Validation with Vis Cohort Data
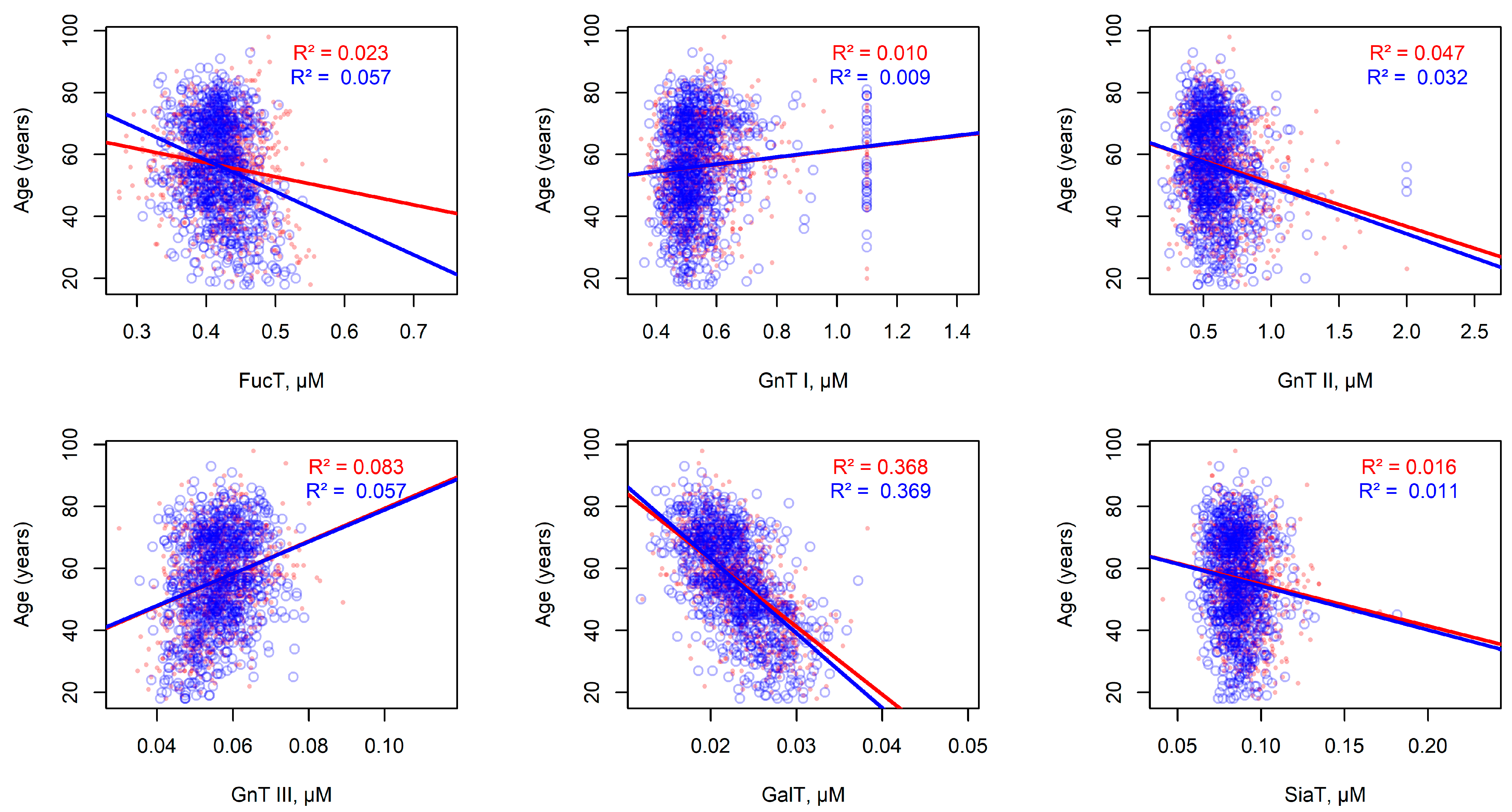
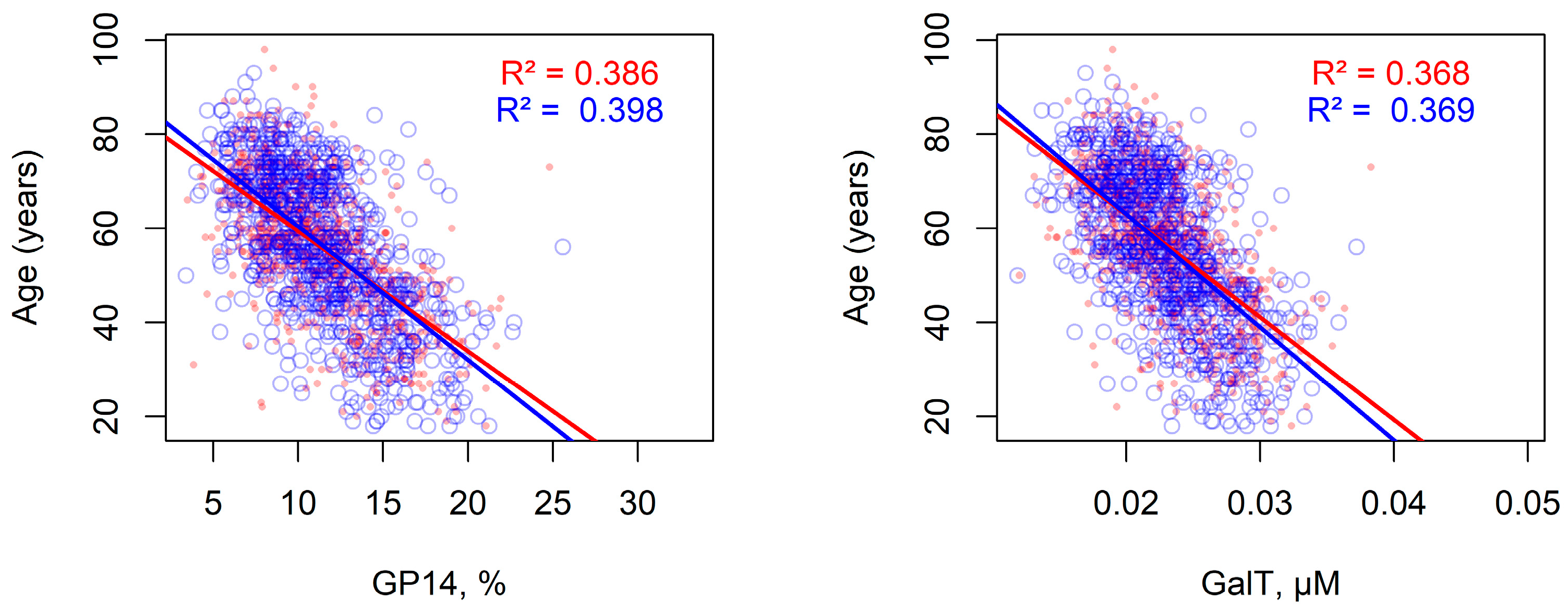
2.6. Statistical Associations Between Modeled Enzyme Concentrations and Individual Experimental Parameters in the Populations
3. Discussion
3.1. Future Perspectives
3.2. Limitations of the Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mathematical Formalism of the Model
4.2. Experimental Data
4.3. Parameter Estimation
4.4. Parameter Identifiability
4.5. Global Sensitivity Analysis
4.6. Local Sensitivity Analysis
4.7. Computational Methods and Software
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Asn | Asparagine |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Glc | Glucose |
| GlcNAc | N-acetylglucosamine |
| GWAS | Genome-wide association studies |
| IgG | Immunoglobulin G |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| Man | Mannose |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| UHPLC | Ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- Schwarz, F.; Aebi, M. Mechanisms and Principles of N-Linked Protein Glycosylation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X. Glycosylation: Mechanisms, Biological Functions and Clinical Implications. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmail, S.; Manolson, M.F. Advances in Understanding N-Glycosylation Structure, Function, and Regulation in Health and Disease. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 100, 151186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, P.; Moremen, K.W.; Lewis, N.E.; Taniguchi, N.; Aebi, M. N-Glycans. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-62182-421-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lefeber, D.J.; Freeze, H.H.; Steet, R.; Kinoshita, T. Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation. In Essentials of Glycobiology; Varki, A., Cummings, R.D., Esko, J.D., Stanley, P., Hart, G.W., Aebi, M., Mohnen, D., Kinoshita, T., Packer, N.H., Prestegard, J.H., et al., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-62182-421-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reily, C.; Stewart, T.J.; Renfrow, M.B.; Novak, J. Publisher Correction: Glycosylation in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2025, 21, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illiano, A.; Pinto, G.; Melchiorre, C.; Carpentieri, A.; Faraco, V.; Amoresano, A. Protein Glycosylation Investigated by Mass Spectrometry: An Overview. Cells 2020, 9, 1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, T.; Kizuka, Y. N-Glycosylation. In The Role of Glycosylation in Health and Disease; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Lauc, G., Trbojević-Akmačić, I., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 1325, pp. 3–24. ISBN 978-3-030-70114-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, V.K.; Sharma, R.; Prajapati, G.K.; Mohanta, T.K.; Mishra, A.K. N-Glycosylation, a Leading Role in Viral Infection and Immunity Development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 8109–8120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodish, H. Molecular Cell Biology, 5th ed.; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-7167-4366-8. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B. (Ed.) Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-8153-4072-0. [Google Scholar]
- Krištić, J.; Lauc, G. The Importance of IgG Glycosylation—What Did We Learn after Analyzing over 100,000 Individuals. Immunol. Rev. 2024, 328, 143–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y. Abberant Immunoglobulin G Glycosylation in Rheumatoid Arthritis by LTQ-ESI-MS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzos, S.; Link-Lenczowski, P.; Sokołowski, G.; Pocheć, E. Changes of IgG N-Glycosylation in Thyroid Autoimmunity: The Modulatory Effect of Methimazole in Graves’ Disease and the Association with the Severity of Inflammation in Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 841710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, D.; Yan, R.; Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; Hu, C. Changes of Serum IgG Glycosylation Patterns in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Proteom. 2023, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Hu, C.; Tian, X. Altered Glycosylation Profiles of Serum IgG in Takayasu Arteritis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslund-Gourley, B.S.; Wigdahl, B.; Comunale, M.A. IgG N-Glycan Signatures as Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovani, B.; Nimmerjahn, F. IgG Glycosylation: Biomarker, Functional Modulator, and Structural Component. J. Immunol. 2024, 213, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krištić, J.; Lauc, G.; Pezer, M. Immunoglobulin G Glycans–Biomarkers and Molecular Effectors of Aging. Clin. Chim. Acta 2022, 535, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapčan, B.; Song, M.; Frkatović-Hodžić, A.; Pribić, T.; Vuk, J.; Beletić, A.; Hanić, M.; Jurić, J.; Tominac, P.; Milas, J.; et al. Glycan Clock of Ageing—Analytical Precision and Time-Dependent Inter- and i-Individual Variability. GeroScience 2024, 46, 5781–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauc, G.; Huffman, J.E.; Pučić, M.; Zgaga, L.; Adamczyk, B.; Mužinić, A.; Novokmet, M.; Polašek, O.; Gornik, O.; Krištić, J.; et al. Loci Associated with N-Glycosylation of Human Immunoglobulin G Show Pleiotropy with Autoimmune Diseases and Haematological Cancers. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Klarić, L.; Sharapov, S.; Mangino, M.; Ning, Z.; Wu, D.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Pučić-Baković, M.; Rudan, I.; Polašek, O.; et al. Multivariate Discovery and Replication of Five Novel Loci Associated with Immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, A.; Van Den Akker, E.; Klaric, L.; Štambuk, J.; Benedetti, E.; Plomp, R.; Razdorov, G.; Trbojević-Akmačić, I.; Deelen, J.; Van Heemst, D.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study on Immunoglobulin G Glycosylation Patterns. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarić, L.; Tsepilov, Y.A.; Stanton, C.M.; Mangino, M.; Sikka, T.T.; Esko, T.; Pakhomov, E.; Salo, P.; Deelen, J.; McGurnaghan, S.J.; et al. Glycosylation of Immunoglobulin G Is Regulated by a Large Network of Genes Pleiotropic with Inflammatory Diseases. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax0301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadrina, A.S.; Zlobin, A.S.; Zaytseva, O.O.; Klarić, L.; Sharapov, S.Z.; Pakhomov, E.D.; Perola, M.; Esko, T.; Hayward, C.; Wilson, J.F.; et al. Multivariate Genome-Wide Analysis of Immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation Identifies New Loci Pleiotropic with Immune Function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frkatović-Hodžić, A.; Mijakovac, A.; Miškec, K.; Nostaeva, A.; Sharapov, S.Z.; Landini, A.; Haller, T.; Akker, E.V.D.; Sharma, S.; Cuadrat, R.R.C.; et al. Mapping of the Gene Network That Regulates Glycan Clock of Ageing. Aging 2023, 15, 14509–14552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pučić, M.; Knežević, A.; Vidič, J.; Adamczyk, B.; Novokmet, M.; Polašek, O.; Gornik, O.; Šupraha-Goreta, S.; Wormald, M.R.; Redžić, I.; et al. High Throughput Isolation and Glycosylation Analysis of IgG–Variability and Heritability of the IgG Glycome in Three Isolated Human Populations. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2011, 10, M111.010090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: Biological Systems Database as a Model of the Real World. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D672–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krambeck, F.J.; Betenbaugh, M.J. A Mathematical Model of N-linked Glycosylation. Biotech. Bioeng. 2005, 92, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krambeck, F.J.; Bennun, S.V.; Narang, S.; Choi, S.; Yarema, K.J.; Betenbaugh, M.J. A Mathematical Model to Derive N-Glycan Structures and Cellular Enzyme Activities from Mass Spectrometric Data. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennun, S.V.; Yarema, K.J.; Betenbaugh, M.J.; Krambeck, F.J. Integration of the Transcriptome and Glycome for Identification of Glycan Cell Signatures. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1002813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banin, E.; Neuberger, Y.; Altshuler, Y.; Halevi, A.; Inbar, O.; Nir, D.; Dukler, A. A Novel Linear Code Nomenclature for Complex Carbohydrates. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 2002, 14, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossler, P.; Mulukutla, B.C.; Hu, W.-S. Systems Analysis of N-Glycan Processing in Mammalian Cells. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krištić, J.; Vučković, F.; Menni, C.; Klarić, L.; Keser, T.; Beceheli, I.; Pučić-Baković, M.; Novokmet, M.; Mangino, M.; Thaqi, K.; et al. Glycans Are a Novel Biomarker of Chronological and Biological Ages. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2014, 69, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Chen, L. Proteomics: An In-Depth Review on Recent Technical Advances and Their Applications in Biomedicine. Med. Res. Rev. 2025, 45, 1021–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Cai, Y.; Yao, H.; Lin, C.; Xie, Y.; Tang, S.; Zhang, A. Small Molecule Metabolites: Discovery of Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Gonzalez, F.J. Challenges and Opportunities of Metabolomics. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 2975–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermingham, K.M.; Brennan, L.; Segurado, R.; Barron, R.E.; Gibney, E.R.; Ryan, M.F.; Gibney, M.J.; O’Sullivan, A.M. Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Variation in the Stable Urinary NMR Metabolome over Time: A Classic Twin Study. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 3992–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchel, C.; Becker, S.; Dittrich, J.; Kirsten, H.; Toenjes, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Loeffler, M.; Thiele, H.; Beutner, F.; Thiery, J.; et al. Clinical and Lifestyle Related Factors Influencing Whole Blood Metabolite Levels—A Comparative Analysis of Three Large Cohorts. Mol. Metab. 2019, 29, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, L. High-Throughput Proteomics: A Methodological Mini-Review. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akune-Taylor, Y.; Kon, A.; Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F. In Silico Simulation of Glycosylation and Related Pathways. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 3687–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouka, T.; Akase, S.; Sogabe, I.; Jin, C.; Karlsson, N.G.; Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F. Computational Modeling of O-Linked Glycan Biosynthesis in CHO Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudelj, I.; Lauc, G.; Pezer, M. Immunoglobulin G Glycosylation in Aging and Diseases. Cell. Immunol. 2018, 333, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paton, B.; Suarez, M.; Herrero, P.; Canela, N. Glycosylation Biomarkers Associated with Age-Related Diseases and Current Methods for Glycan Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, R.; Gu, Y.; Xu, X.; Ren, S.; Gu, J. B-Cell-Specific Ablation of β-1,4-Galactosyltransferase 1 Prevents Aging-Related IgG Glycans Changes and Improves Aging Phenotype in Mice. J. Proteom. 2022, 268, 104717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, T.; Zhao, H.; Ren, S. Glycosylation in Aging and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2024, 56, 1208–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrom, M.L.; Bates, D.M. Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models for Repeated Measures Data. Biometrics 1990, 46, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Graffenried, C.L.; Bertozzi, C.R. The Roles of Enzyme Localisation and Complex Formation in Glycan Assembly within the Golgi Apparatus. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2004, 16, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, L.; Banfield, D.K. Localization of Golgi-Resident Glycosyltransferases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Fanayan, S.; Packer, N.H.; Thaysen-Andersen, M. Differential Site Accessibility Mechanistically Explains Subcellular-Specific N-Glycosylation Determinants. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, A.; Kunii, M.; Kurokawa, K.; Sumi, T.; Kanda, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nadanaka, S.; Hirosawa, K.M.; Tokunaga, K.; Tojima, T.; et al. Dynamic Movement of the Golgi Unit and Its Glycosylation Enzyme Zones. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschberg, K.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Secretory Pathway Kinetics and In Vivo Analysis of Protein Traffic from the Golgi Complex to the Cell Surface. FASEB J. 1999, 13, S251–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moles, C.G.; Mendes, P.; Banga, J.R. Parameter Estimation in Biochemical Pathways: A Comparison of Global Optimization Methods. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, A.; Kreutz, C.; Maiwald, T.; Bachmann, J.; Schilling, M.; Klingmüller, U.; Timmer, J. Structural and Practical Identifiability Analysis of Partially Observed Dynamical Models by Exploiting the Profile Likelihood. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raue, A.; Becker, V.; Klingmüller, U.; Timmer, J. Identifiability and Observability Analysis for Experimental Design in Nonlinear Dynamical Models. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2010, 20, 045105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltelli, A.; Annoni, P.; Azzini, I.; Campolongo, F.; Ratto, M.; Tarantola, S. Variance Based Sensitivity Analysis of Model Output. Design and Estimator for the Total Sensitivity Index. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2010, 181, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabitz, H.; Kramer, M.; Dacol, D. Sensitivity Analysis in Chemical Kinetics. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1983, 34, 419–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpakov, F.; Akberdin, I.; Kashapov, T.; Kiselev, L.; Kolmykov, S.; Kondrakhin, Y.; Kutumova, E.; Mandrik, N.; Pintus, S.; Ryabova, A.; et al. BioUML: An Integrated Environment for Systems Biology and Collaborative Analysis of Biomedical Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W225–W233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolpakov, F.; Akberdin, I.; Kiselev, I.; Kolmykov, S.; Kondrakhin, Y.; Kulyashov, M.; Kutumova, E.; Pintus, S.; Ryabova, A.; Sharipov, R.; et al. BioUML—Towards a Universal Research Platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W124–W131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.P.; Bergmann, F.T.; Chandran, D.; Sauro, H.M. Antimony: A Modular Model Definition Language. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2452–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindmarsh, A.C.; Brown, P.N.; Grant, K.E.; Lee, S.L.; Serban, R.; Shumaker, D.E.; Woodward, C.S. SUNDIALS: Suite of Nonlinear and Differential/Algebraic Equation Solvers. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 2005, 31, 363–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebro, A.J.; Durillo, J.J.; Luna, F.; Dorronsoro, B.; Alba, E. MOCell: A Cellular Genetic Algorithm for Multiobjective Optimization. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 726–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Common Parameters | Sources | |
|---|---|---|
| Kinetic reaction rate constants (Supplementary Table S4) | 15 kf and Km parameters for Equation (1) | [31] |
| 22 correction factors for kf | Estimated median values for the Korčula cohort | |
| Distribution coefficients for total enzyme concentrations across Golgi compartments (Supplementary Table S2) | 23 coefficients: 4 per enzyme for GnT II, GnT III, Man II, GalT, and SiaT; plus 2 for GnT I in Golgi compartments III and IV; and 1 for FucT in the final Golgi compartment | [31] |
| 5 coefficients: 3 for FucT across the first three Golgi compartments, plus 2 for GnT I in the first two compartments | Estimated median values for the Korčula cohort | |
| Total enzyme concentrations | Total Man II concentration | An estimated median value for the Korčula cohort |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kutumova, E.; Mandrik, N.; Sharipov, R.; Pučić-Baković, M.; Rapčan, B.; Aulchenko, Y.; Lauc, G.; Kolpakov, F. Quantitative Modeling of IgG N-Glycosylation Profiles from Population Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311495
Kutumova E, Mandrik N, Sharipov R, Pučić-Baković M, Rapčan B, Aulchenko Y, Lauc G, Kolpakov F. Quantitative Modeling of IgG N-Glycosylation Profiles from Population Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311495
Chicago/Turabian StyleKutumova, Elena, Nikita Mandrik, Ruslan Sharipov, Maja Pučić-Baković, Borna Rapčan, Yurii Aulchenko, Gordan Lauc, and Fedor Kolpakov. 2025. "Quantitative Modeling of IgG N-Glycosylation Profiles from Population Data" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311495
APA StyleKutumova, E., Mandrik, N., Sharipov, R., Pučić-Baković, M., Rapčan, B., Aulchenko, Y., Lauc, G., & Kolpakov, F. (2025). Quantitative Modeling of IgG N-Glycosylation Profiles from Population Data. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311495






