In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of a Novel Multifunctional Cyclic Peptide with Antioxidant, Tyrosinase-Inhibitory, and Extracellular Matrix-Modulating Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
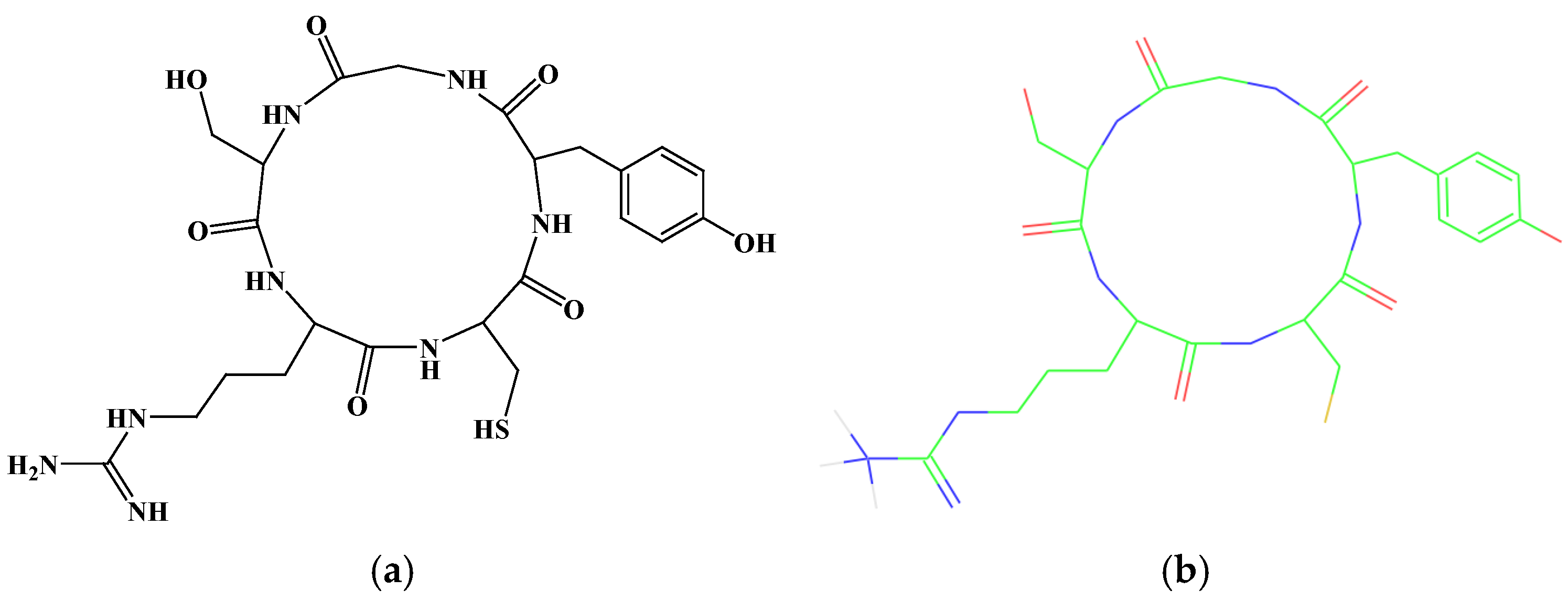
2.1. Stucture of CR5
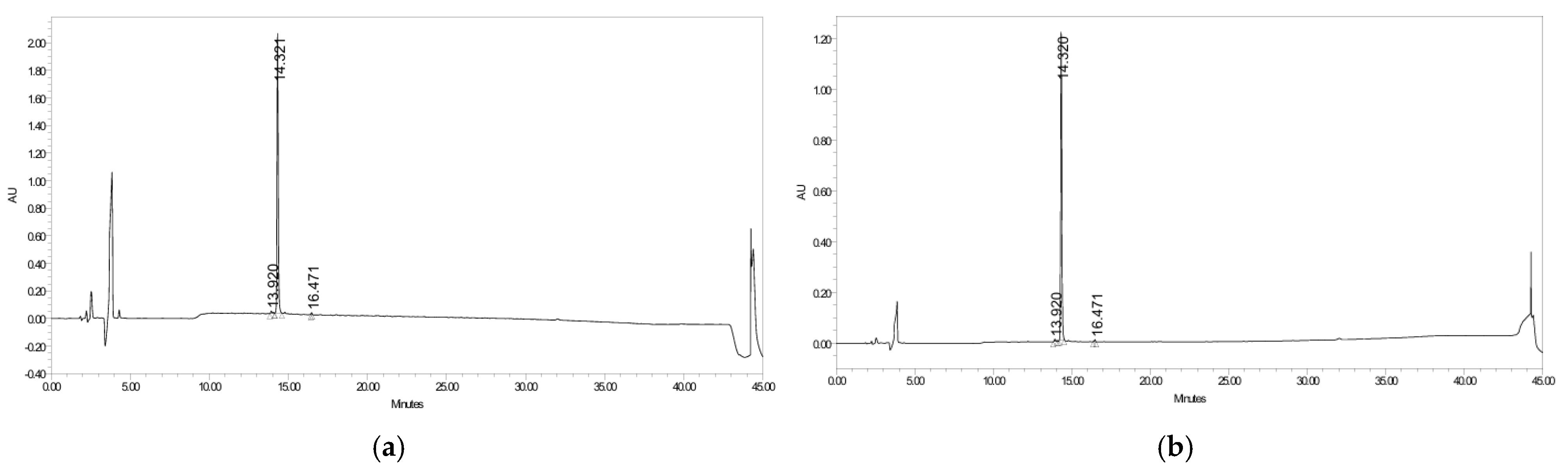
2.2. Purity Analysis of CR5 by HPLC
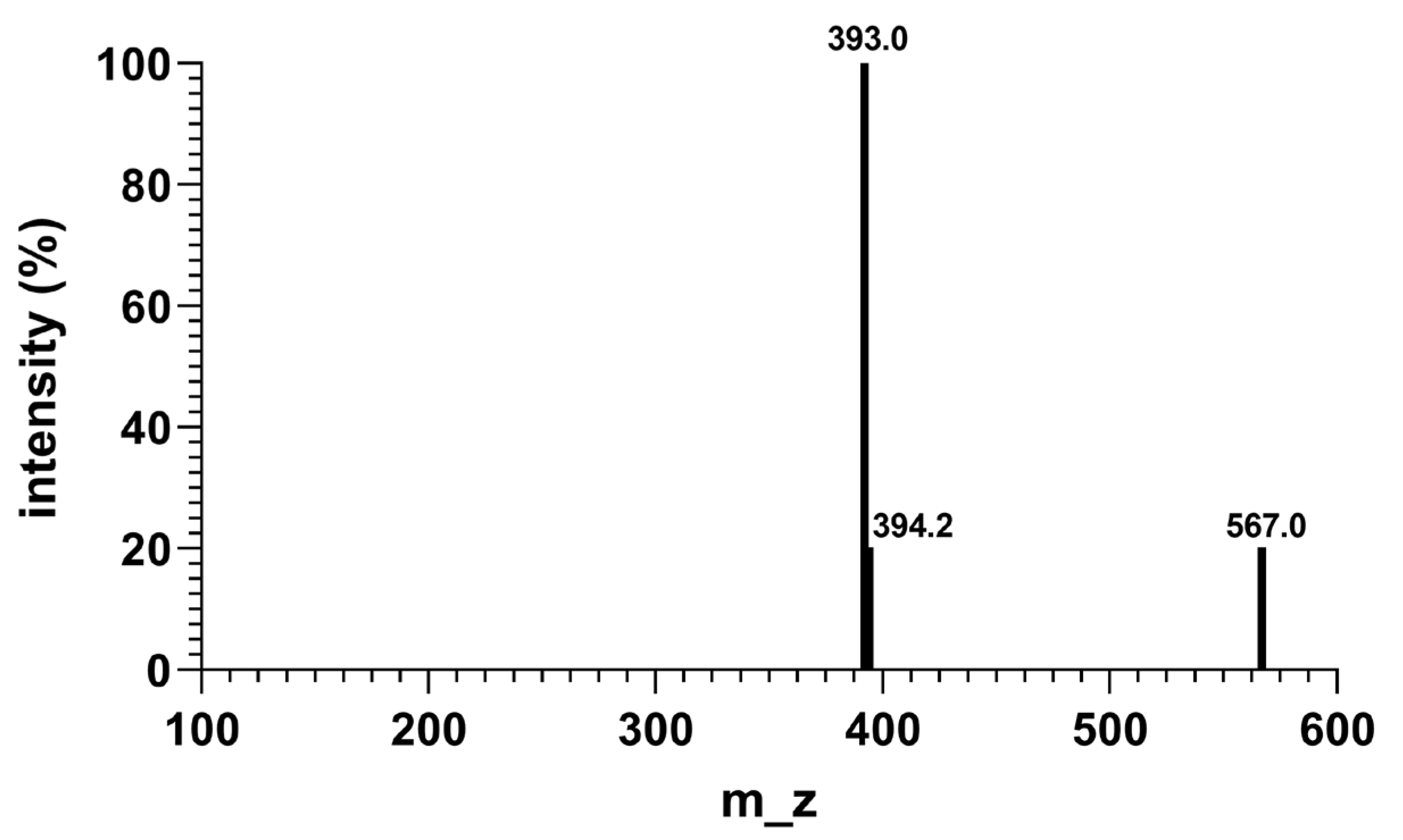
2.3. Molecular Weight Analysis of CR5
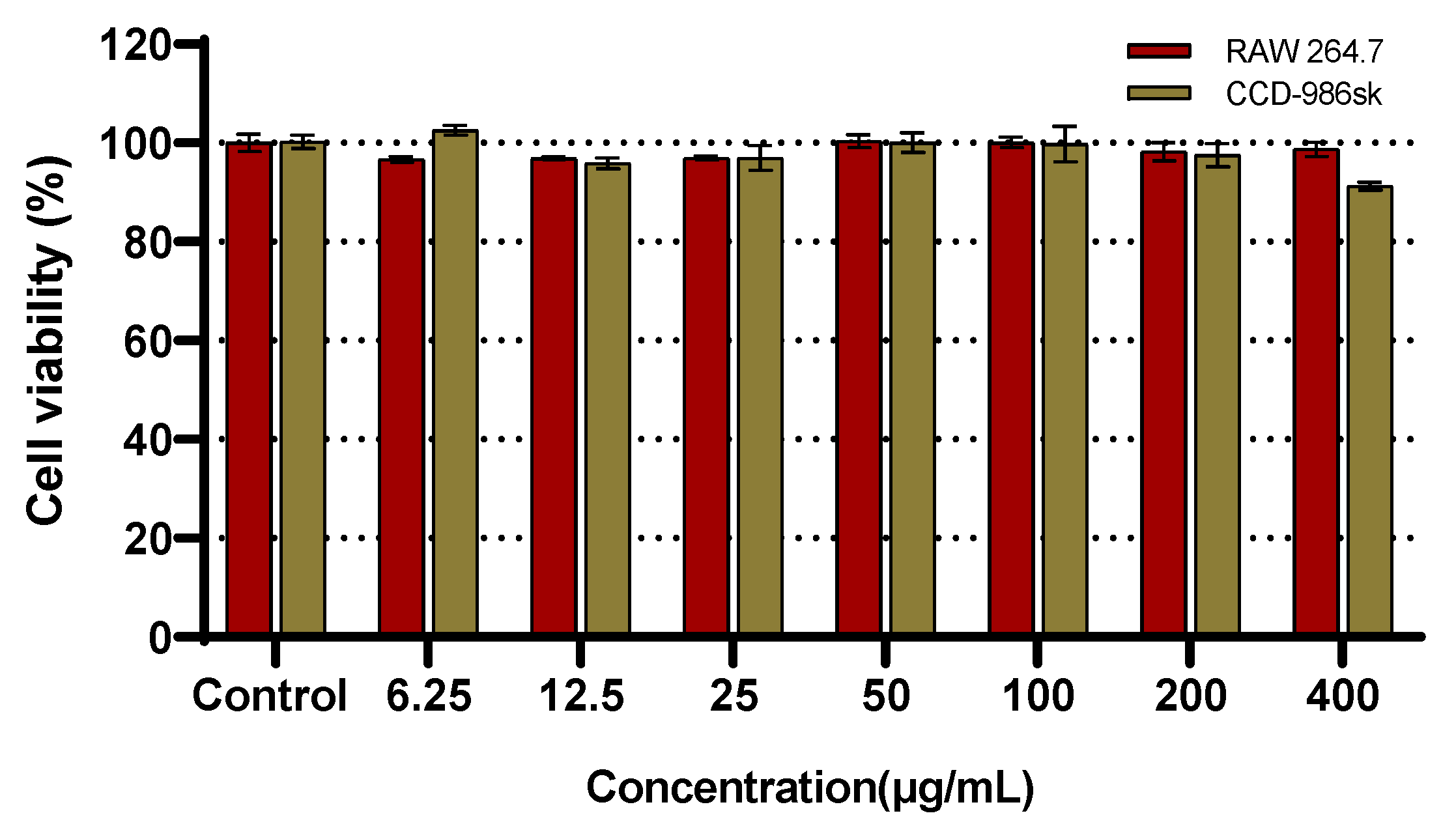
2.4. Cell Viability
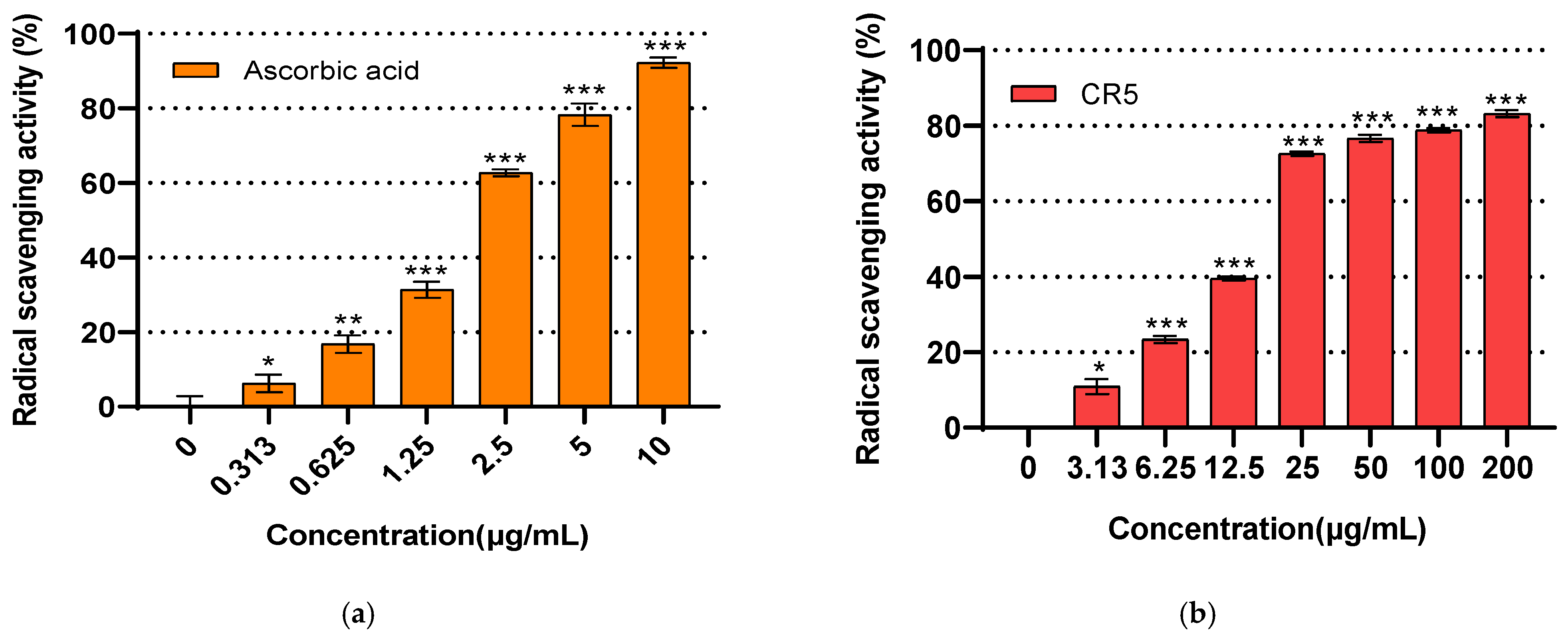
2.5. Antioxidant Activity Assay
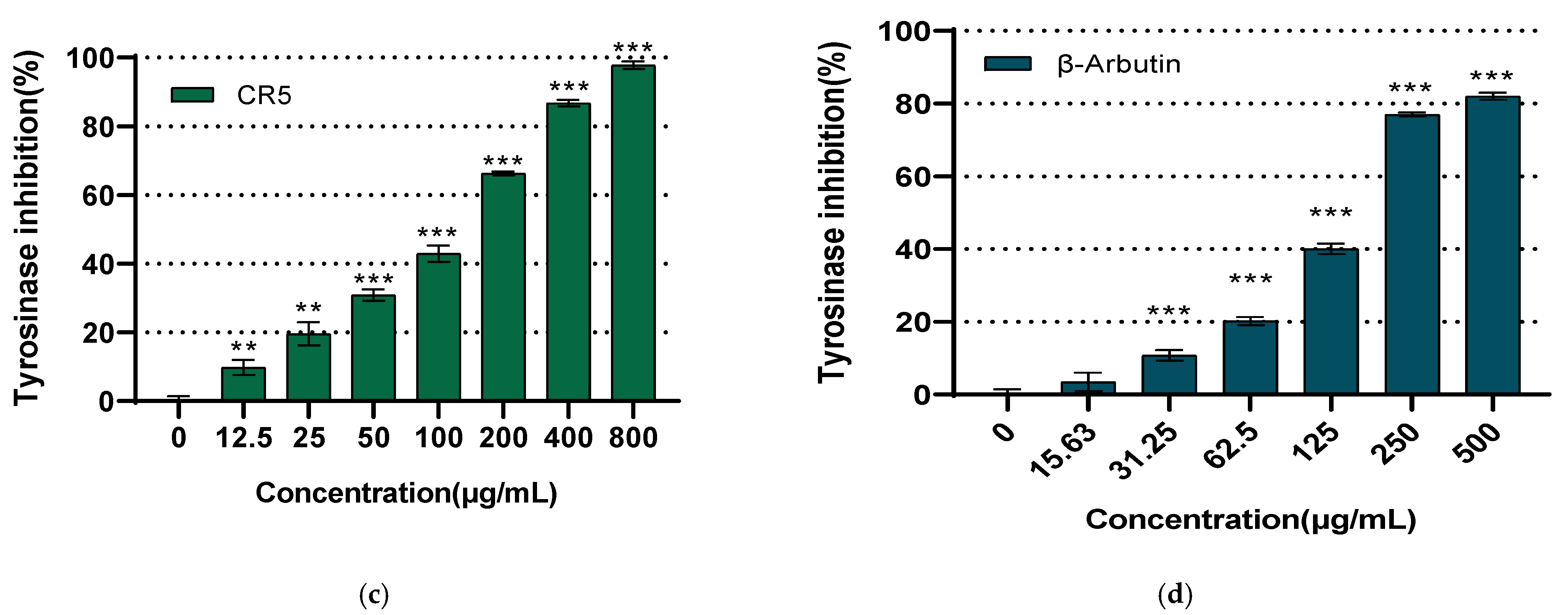
2.6. Whitening Activity Assay
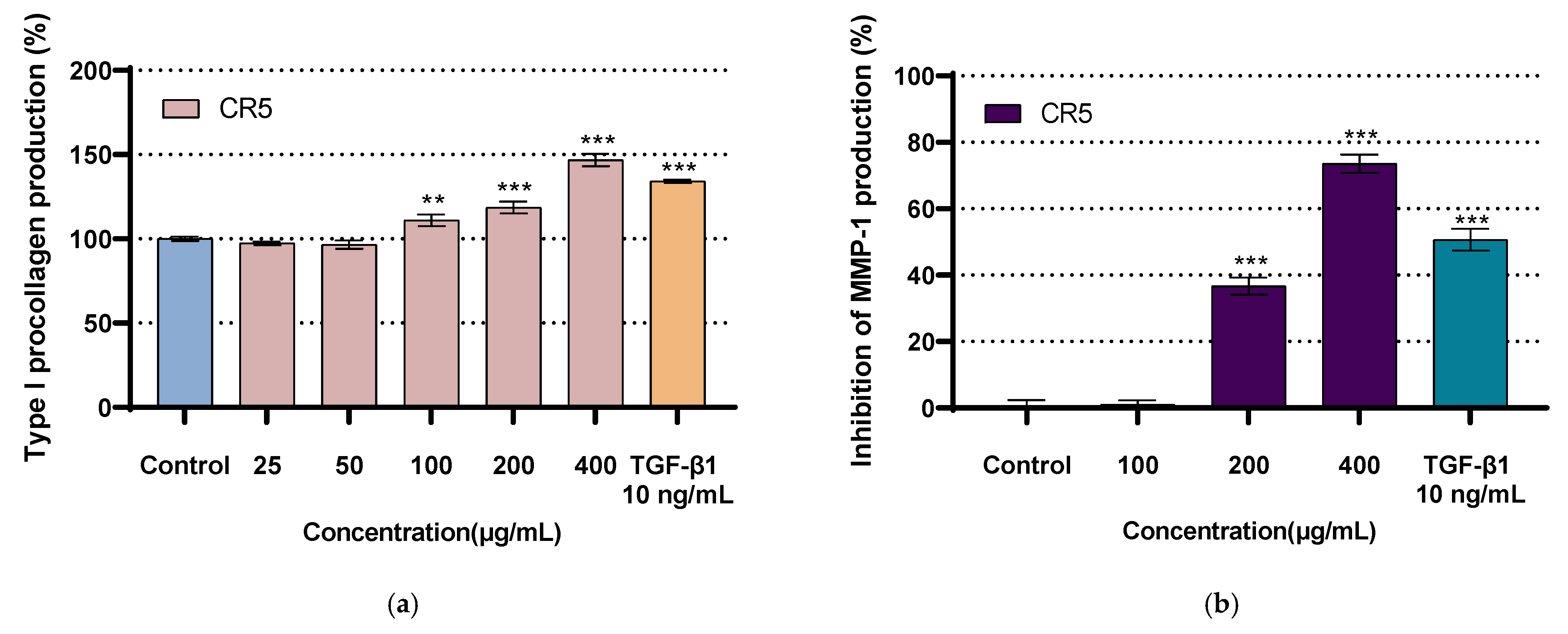
2.7. Type I Procollagen Expression Assay
2.8. Inhibition of MMP-1 Expression Assay
2.9. Molecular Docking of CR5 with Target Enzymes (Tyrosinase and MMP-1)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Cell Lines
4.1.2. Assay Kits
4.1.3. Chemicals
4.1.4. Instruments
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Synthesis of CYGSR Using Fmoc-Chemistry
4.2.2. Cleavage of CYGSR
4.2.3. Cyclization of CYGSR
4.2.4. HPLC Purification and Analysis of CR5
4.2.5. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry (MS) Analysis of CR5
4.2.6. Cell Culture
4.2.7. Cell Viability Assay in RAW 264.7 and CCD-986sk Cells
4.2.8. DPPH Radical-Scavenging Assay
4.2.9. Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
4.2.10. MMP-1 Expression Inhibition Assay
4.2.11. Type I Procollagen Expression Stimulation Assay
4.2.12. Protein Content Analysis
4.2.13. Data Analysis and Statistical Processing
4.2.14. Molecular Docking Simulation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CR5 | Cys-Tyr-Gly-Ser-Arg |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DIEA | N,N-diisopropylethylamine |
| DMF | N,N-dimethylformamide |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s medium |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| HOBt | 1-hydroxybenzotriazole |
| DIC | N,N′-diisopropylcarbodiimide |
| IMDM | Iscove’s Modified Dulbecco’s medium |
| MALDI–TOF | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| PDA | Photodiode array |
| SPPS | Solid-phase peptide synthesis |
| LPPS | Liquid-phase peptide synthesis |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
References
- Surber, C.; Brandt, S.; Cozzio, A.; Kottner, J. Principles of skin care in the elderly. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2015, 150, 699–716. [Google Scholar]
- Nagae, M.; Mitsutake, T.; Sakamoto, M. Impact of skin care on body image of aging people: A quasi-randomized pilot trial. Heliyon 2023, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Tan, T.; Zhang, Y. Novel Tyrosinase Inhibitory Peptide with Free Radical Scavenging Ability. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-G.; Hwang, J.-W.; Kang, H. Antioxidant and Skin-Whitening Efficacy of a Novel Decapeptide (DP, KGYSSYICDK) Derived from Fish By-Products. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hao, Z.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y. Naturally Occurring New Peptides From Velvet Antler of Cervus nippon Temminck: Structural Characterization and Organic Synthesis, Antioxidant and Anti—melanogenic Effects Using In Vitro Cell Models and In Vivo Zebrafish Models. Chem. Biodivers. 2025, 22, e00288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukiatsiri, S.; Wongsrangsap, N.; Kiatwuthinon, P.; Phonphoem, W. Purification and Identification of Novel Antioxidant Peptides Derived from Bombyx Mori Pupae Hydrolysates. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2024, 38, 101707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangtanoo, P.; Srimongkol, P.; Saisavoey, T.; Puthong, S.; Buakeaw, A.; Suttisuwan, R.; Jatupornpipat, M.; Pimtong, W.; Reamtong, O.; Karnchanatat, A. Bee Pollen Peptides as Potent Tyrosinase Inhibitors with Anti-Melanogenesis Effects in Murine B16f10 Melanoma Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Cai, S.; Cui, L.; Yu, T.; Qiao, K.; Su, Y.; Xu, M.; Tang, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, M.; et al. Novel Peptide Inhibitor of Matrix Metalloproteinases-1 from Pufferfish Skin Collagen Hydrolysates and Its Potential Photoprotective Activity via the MAPK/AP-1 Signaling Pathway. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2025, 262, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, E.; Joo, H.; Kim, M.; Kim, D.-U.; Chung, H.-C.; Kim, J.G. Low-Molecular-Weight Collagen Peptide Improves Skin Dehydration and Barrier Dysfunction in Human Dermal Fibrosis Cells and UVB-Exposed SKH-1 Hairless Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintea, A.; Manea, A.; Pintea, C.; Vlad, R.-A.; Bîrsan, M.; Antonoaea, P.; Rédai, E.M.; Ciurba, A. Peptides: Emerging Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Senescence: A Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Mao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Overview of Peptides and Their Potential Roles in Skin Health and Beauty. J. Pept. Sci. 2025, 31, e3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, R.; Saeedi, M.; Akbarzadeh, T. Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Peptides: Efficient Tyrosinase Inhibitors. J. Pept. Sci. 2021, 27, e3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Lin, H.; Gao, J.; Cao, W.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Huang, H. A Novel Tyrosinase Inhibitory Peptide Derived from Sipunculus Nudus Suppresses Melanogenesis in B16F10 Cells by Down-Regulating TRP-1/TRP-2 Expression. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 129, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namjoshi, S.; Benson, H.A.E. Cyclic Peptides as Potential Therapeutic Agents for Skin Disorders. Biopolymers 2010, 94, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashaolu, T.J. Applications of Bioactive Peptides in Cosmeceuticals: A Review. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2025, 26, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errante, F.; Menicatti, M.; Pallecchi, M.; Giovannelli, L.; Papini, A.M.; Rovero, P.; Bartolucci, G. Susceptibility of Cosmeceutical Peptides to Proteases Activity: Development of Dermal Stability Test by LC-MS/MS Analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Nie, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Deng, H. Peptides in Cosmetics: From Pharmaceutical Breakthroughs to Skincare Innovations. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, S. Cyclic Peptide Drugs Approved in the Last Two Decades (2001–2021). RSC Chem. Biol. 2022, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Nielsen, A.L.; Heinis, C. Cyclic Peptides for Drug Development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202308251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Sun, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Nie, J.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A Cyclic Heptapeptide-Based Hydrogel Boosts the Healing of Chronic Skin Wounds in Diabetic Mice and Patients. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fan, H.; Teng, X.; Sun, T.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Exploring Novel Antioxidant Cyclic Peptides in Corn Protein Hydrolysate: Preparation, Identification and Molecular Docking Analysis. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Bi, Y.; Li, T.; Ding, M.; Shao, B.; Li, C. Accelerating Anti-Aging Cyclic Peptide Discovery through Computational Design and Automated Synthesis. Sci. China Chem. 2025, 68, 5074–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechtler, C.; Lamers, C. Macrocyclization Strategies for Cyclic Peptides and Peptidomimetics. RSC Med. Chem. 2021, 12, 1325–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Pang, W.-K.; Xuan, S.; Chan, W.-L.; Leung, K.C.-F. Recent Advances in Peptide Macrocyclization Strategies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 11725–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, P.; Espiritu, M.J.; Cabalteja, C.; Bingham, J.-P. The Emergence of Cyclic Peptides: The Potential of Bioengineered Peptide Drugs. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2014, 20, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, H.C.; Luk, L.Y.P.; Tsai, Y.-H. Approaches for Peptide and Protein Cyclisation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 3983–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, D.; Mori, S.; Chadli, A.; Panda, S.S. Natural Cyclic Peptides: Synthetic Strategies and Biomedical Applications. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Gao, J.; Chen, Z.; Cao, W.; Qin, X.; Zheng, H.; Ji, D.; Liu, H. Inhibitory Mechanism of Tyrosinase Inhibitory Peptides Identified from the Mantle of Pinctada Martensii. J. Funct. Foods 2025, 127, 106759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, T.; Li, X.; Sadiq, F.A.; Mao, K.; Gao, J.; Mi, S.; Liu, X.; Deng, W.; Chitrakar, B.; Sang, Y. Novel Antioxidant Peptides from Protein Hydrolysates of Scallop (Argopecten irradians) Mantle Using Enzymatic and Microbial Methods: Preparation, Purification, Identification and Characterization. LWT 2022, 164, 113636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kang, S.; Kwon, H.; Moon, H.; Park, M.C. Dual Functional Bioactive-peptide, AIMP1-derived Peptide (AdP), for Anti-aging. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Quan, Z.; Xiao, P.; Duan, J.-A. New Insights into Antioxidant Peptides: An Overview of Efficient Screening, Evaluation Models, Molecular Mechanisms, and Applications. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianeti, M.; Maia Campos, P. Efficacy Evaluation of a Multifunctional Cosmetic Formulation: The Benefits of a Combination of Active Antioxidant Substances. Molecules 2014, 19, 18268–18282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rischard, F.; Gore, E.; Flourat, A.; Savary, G. The Challenges Faced by Multifunctional Ingredients: A Critical Review from Sourcing to Cosmetic Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 340, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, R.H.; Nguyen, T.M.; Shim, D.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, J. Development of Multifunctional Cosmetic Cream Using Bioactive Materials from Streptomyces Sp. T65 with Synthesized Mesoporous Silica Particles SBA-15. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Peña, L.; Guzmán, E.; Fernández-Pérez, C.; Barba-Nieto, I.; Ortega, F.; Leonforte, F.; Rubio, R.G.; Luengo, G.S. Study of the Dilution-Induced Deposition of Concentrated Mixtures of Polyelectrolytes and Surfactants. Polymers 2022, 14, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Walraven, N.; FitzGerald, R.J.; Danneel, H.-J.; Amigo-Benavent, M. Bioactive Peptides in Cosmetic Formulations: Review of Current in Vitro and Ex Vivo Evidence. Peptides 2025, 193, 171440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N.; Saito, Y.; Niki, E. Actions of Thiols, Persulfides, and Polysulfides as Free Radical Scavenging Antioxidants. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2023, 39, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Dong, H.; Su, G.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, M. Radical Scavenging Activities of Tyr-, Trp-, Cys- and Met-Gly and Their Protective Effects against AAPH-Induced Oxidative Damage in Human Erythrocytes. Food Chem. 2016, 197, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paz-Lugo, P.; Lupiáñez, J.A.; Meléndez-Hevia, E. High Glycine Concentration Increases Collagen Synthesis by Articular Chondrocytes in Vitro: Acute Glycine Deficiency Could Be an Important Cause of Osteoarthritis. Amino Acids 2018, 50, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppes, S.A.; Kemperman, P.; Van Tilburg, I.; Calkoen-Kwa, F.; Engebretsen, K.A.; Puppels, G.J.; Caspers, P.J.; Kezic, S. Determination of Natural Moisturizing Factors in the Skin: Raman Microspectroscopy versus HPLC. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhong, B.; Qin, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Lou, Z.; Fan, Y.; et al. An Epidermal Serine Sensing System for Skin Healthcare. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, Á.D.P.B.D.; Oliveira, M.M.R.D.; Andrade, R.R.D.; Amorim, R.F.B.D.; Bocca, A.L.; Borin, M.D.F. The in vivo Effect of L-Arginine on Skin Elasticity in Mice. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 53, e00045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Kanazawa, S.; Ichibori, R.; Tanigawa, T.; Magome, T.; Shingaki, K.; Miyata, S.; Tohyama, M.; Hosokawa, K. L-Arginine Stimulates Fibroblast Proliferation through the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt Pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amblard, M.; Fehrentz, J.-A.; Martinez, J.; Subra, G. Methods and Protocols of Modern Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. Mol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; De La Torre, B.G.; Albericio, F. Liquid-Phase Peptide Synthesis (LPPS): A Third Wave for the Preparation of Peptides. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 13516–13546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roxin, Á.; Zheng, G. Flexible Or Fixed: A Comparative Review Of Linear And Cyclic Cancer-Targeting Peptides. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 1601–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martian, P.C.; Tertis, M.; Leonte, D.; Hadade, N.; Cristea, C.; Crisan, O. Cyclic Peptides: A Powerful Instrument for Advancing Biomedical Nanotechnologies and Drug Development. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 252, 116488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putri, S.; Maharani, R.; Maksum, I.; Siahaan, T. Peptide Design for Enhanced Anti-Melanogenesis: Optimizing Molecular Weight, Polarity, and Cyclization. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2025, 19, 645–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Wang, N.; Cai, S.; Yan, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Liang, Z. Research Progress on Peptides That Inhibit Melanin Synthesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2025, 16, 1610623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussen, E.M.; Endalew, S.A. In Vitro Antioxidant and Free-Radical Scavenging Activities of Polar Leaf Extracts of Vernonia amygdalina. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2023, 23, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Cao, Y.; Su, D.; Karrar, E.; Zhang, L.; Chen, C.; Deng, N.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; et al. Preparation and Identification of Antioxidant Peptides from Quasipaa Spinosa Skin through Two-Step Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Molecular Simulation. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anu, O.S.; Ahmed, S.; Islam, M.d.T.; Shah, V.K.; Ahmed, M.d.I.; Rahman, M.d.A. Comparative Investigation of Free Radical Scavenging and Cyclic Voltammetric Analyses to Evaluate the Antioxidant Potential of Selective Green Vegetables Extracts. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 31919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, A.C.; Le, T.M. Improvement of Anti-Tyrosinase Activity in Potential Skin Whitening Products by Combining Herbal Extracts and Reducing Their Tannin Content by Collagen Fibre Adsorption. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 155, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, S.; Koyu, H.; Yilmaz, M.A.; Tarhan, A.; Ozturk, S.B. Antityrosinase Activity and LC-MS/MS Analysis of Optimized Ultrasound-Assisted Condition Extracts and Fractions from Strawberry Tree (Arbutus unedo L.). J. Food Drug Anal. 2024, 32, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Thibeault, S.L. Response of Fibroblasts to Transforming Growth Factor-Β1 on Two-Dimensional and in Three-Dimensional Hyaluronan Hydrogels. Tissue Eng. Part A 2012, 18, 2528–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Cheng, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Li, H. TGF-Β1 Induces Type I Collagen Deposition in Granulosa Cells via the AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway-Mediated MMP1 down-Regulation. Reprod. Biol. 2022, 22, 100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.; Christensen, M.H. MolDock: A New Technique for High-Accuracy Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimori, H.; Hisama, M.; Shibayama, H.; Iwaki, M. Protecting Effect of Phytoncide Solution, on Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts against Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Oleo Sci. 2009, 58, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakyai, W.; Saraphanchotiwitthaya, A.; Viennet, C.; Humbert, P.; Viyoch, J. An In Vitro Model for Fibroblast Photoaging Comparing Single and Repeated UVA Irradiations. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MolDock Score (kcal/mol) | H-Bond Energy (kcal/mol) | Rerank Score | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PDB ID: 2Y9X | −110.023 | −14.8095 | −72.9746 |
| PDB ID: 1HFC | −99.6438 | −9.19535 | 27.7123 |
| Column | YMC-Pack ODS-A-HG (250.00 × 20.00 mm I.D., 10.00 µm, 30.00 nm) | |
| Mobile Phase | Solvent A: H2O + 0.10% TFA Solvent B: Acetonitrile + 0.10% TFA | |
| Time (min) | Solvent A (%) | Solvent B (%) |
| 0.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 10.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 45.0 | 50 | 50 |
| 50.0 | 50 | 50 |
| 50.1 | 0 | 100 |
| 51.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 51.1 | 95 | 5 |
| 55.0 | 95 | 5 |
| Flow Rate | 20.00 mL/min | |
| Detection Wavelength | 210.00 nm or 230.00 nm | |
| Injection Volume | 1.00~5.00 mL | |
| Run Time | 55 min | |
| Column | XBridge C18 column (4.60 × 250.00 mm, 5.00 μm) | |
| Mobile Phase | Solvent A: H2O + 0.10% TFA Solvent B: Acetonitrile + 0.10% TFA | |
| Time (min) | Solvent A (%) | Solvent B (%) |
| 0.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 10.0 | 95 | 5 |
| 35.0 | 35 | 65 |
| 40.0 | 35 | 65 |
| 40.1 | 0 | 100 |
| 41.0 | 0 | 100 |
| 41.1 | 95 | 5 |
| 45.0 | 95 | 5 |
| Flow Rate | 1.00 mL/min | |
| Detection Wavelength | 210.00 nm or 230.00 nm | |
| Injection Volume | 20.00~100.00 μL | |
| Run Time | 45 min | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, G.-H.; Kim, B.-M. In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of a Novel Multifunctional Cyclic Peptide with Antioxidant, Tyrosinase-Inhibitory, and Extracellular Matrix-Modulating Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210878
Kim G-H, Kim B-M. In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of a Novel Multifunctional Cyclic Peptide with Antioxidant, Tyrosinase-Inhibitory, and Extracellular Matrix-Modulating Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(22):10878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210878
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ga-Hyun, and Bo-Mi Kim. 2025. "In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of a Novel Multifunctional Cyclic Peptide with Antioxidant, Tyrosinase-Inhibitory, and Extracellular Matrix-Modulating Activities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 22: 10878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210878
APA StyleKim, G.-H., & Kim, B.-M. (2025). In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation of a Novel Multifunctional Cyclic Peptide with Antioxidant, Tyrosinase-Inhibitory, and Extracellular Matrix-Modulating Activities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(22), 10878. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262210878





