Contribution of Cerebellar Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems in Premotor and Early Stages of Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Evaluation and MRS Metabolites
2.2. Neuropsychiatric Evaluation and MRS Metabolites
2.3. Neuropsychological Assessment and MRS Metabolites
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Participants
4.2. Subjects’ Assessment
4.2.1. Clinical Evaluation
4.2.2. Neuropsychiatric Evaluation
4.2.3. Neuropsychological Assessment
4.3. Neuroimaging Procedure
4.3.1. MRI and MRS Acquisition
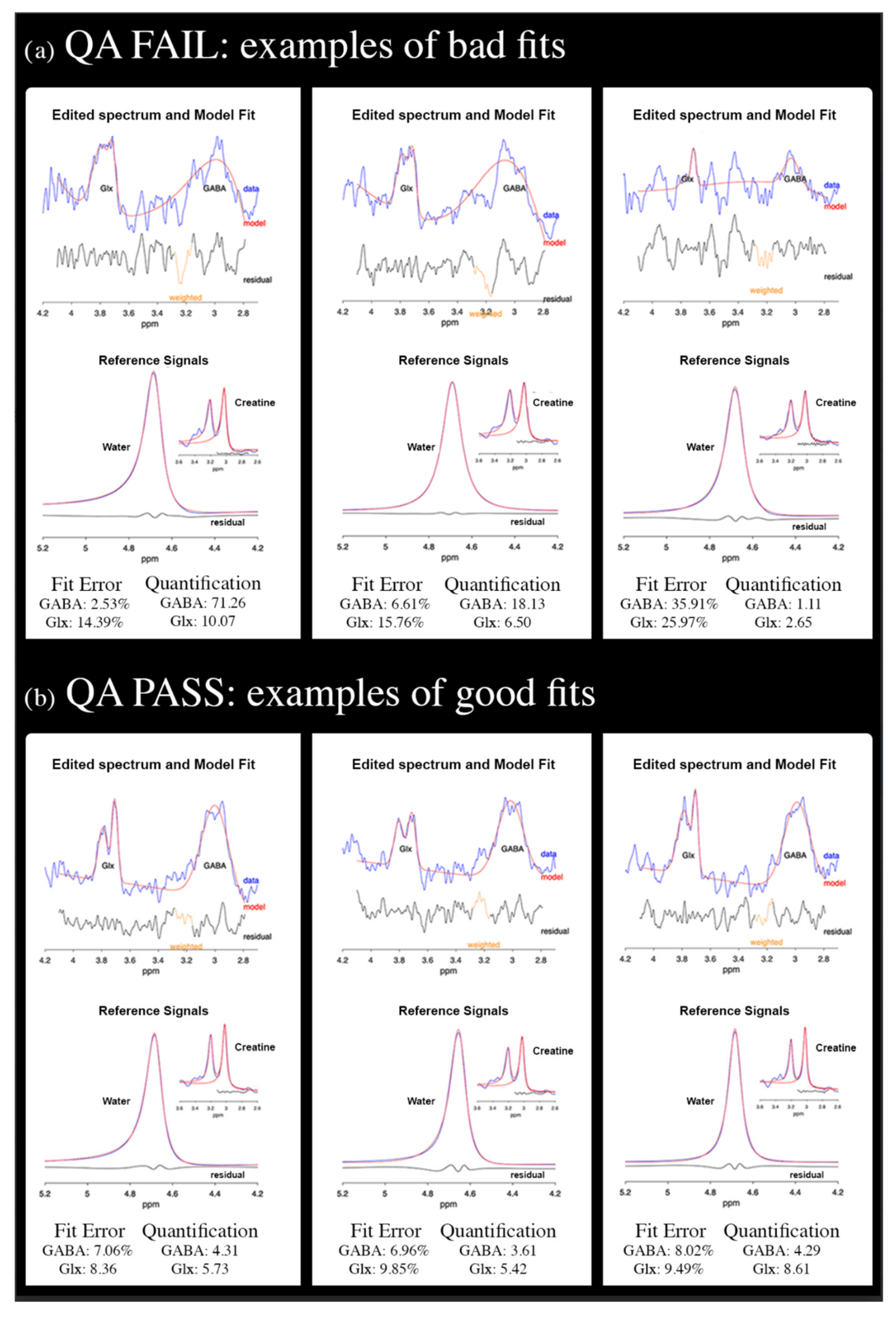
4.3.2. MRS Processing
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bostan, A.C.; Strick, P.L. The Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia Are Interconnected. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2010, 20, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Le, W.; Jankovic, J. Linking the Cerebellum to Parkinson Disease: An Update. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2023, 19, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerestes, R.; Laansma, M.A.; Owens-Walton, C.; Perry, A.; van Heese, E.M.; Al-Bachari, S.; Anderson, T.J.; Assogna, F.; Aventurato, Í.K.; van Balkom, T.D.; et al. Cerebellar Volume and Disease Staging in Parkinson’s Disease: An ENIGMA-PD Study. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 2269–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, X.; Hu, Y.; Sun, J.; Gao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, J.; Doyon, J.; Wu, T.; Chan, P. Altered Cerebellar Resting-State Functional Connectivity in Early-Stage Parkinson’s Disease Patients With Cognitive Impairment. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 678013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Mattis, P.; Tang, C.; Perrine, K.; Carbon, M.; Eidelberg, D. Metabolic Brain Networks Associated with Cognitive Function in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuroimage 2007, 34, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solstrand Dahlberg, L.; Lungu, O.; Doyon, J. Cerebellar Contribution to Motor and Non-Motor Functions in Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of FMRI Findings. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.H.; Chen, B.; He, J.Q.; Qi, Y.M.; Yan, Y.Y.; Jin, S.X.; Chang, Y. Patterns of Cerebellar Cortex Hypermetabolism on Motor and Cognitive Functions in PD. npj Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buddhala, C.; Loftin, S.K.; Kuley, B.M.; Cairns, N.J.; Campbell, M.C.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Kotzbauer, P.T. Dopaminergic, Serotonergic, and Noradrenergic Deficits in Parkinson Disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesman, A.I.; da Silva Castanheira, J.; Fon, E.A.; Baillet, S.; PREVENT-AD Research Group; Quebec Parkinson Network. Structural and Neurophysiological Alterations in Parkinson’s Disease Are Aligned with Cortical Neurochemical Systems. medRxiv Prepr. Serv. Health Sci. 2023, 95, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, B.; Al-kuraishy, H.M.; Al-Gareeb, A.I.; Elekhnawy, E.; Alharbi, H.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Batiha, G.E.S. Role of GABA Pathway in Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson’s Disease: A Bidirectional Circuit. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, A.; Mikkelsen, M.; Edden, R.A.E.; Robertson, C.E. Regional Balance between Glutamate+glutamine and GABA+ in the Resting Human Brain. Neuroimage 2020, 220, 117112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortel, I.; Zhan, L.; Ajilore, O.; Wu, Y.; Mackin, S.; Leow, A. Disrupted Excitation-Inhibition Balance in Cognitively Normal Individuals at Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2023, 95, 1449–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, P.W.; Lui, S.S.Y.; Hung, K.S.Y.; Chan, R.C.K.; Chan, Q.; Sham, P.C.; Cheung, E.F.C.; Mak, H.K.F. In Vivo Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid and Glutamate Levels in People with First-Episode Schizophrenia: A Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 193, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, C.E.; Ratai, E.M.; Kanwisher, N. Reduced GABAergic Action in the Autistic Brain. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasanta, D.; He, J.L.; Ford, T.; Oeltzschner, G.; Lythgoe, D.J.; Puts, N.A. Functional MRS Studies of GABA and Glutamate/Glx—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 144, 104940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klietz, M.; Bronzlik, P.; Nösel, P.; Wegner, F.; Dressler, D.W.; Dadak, M.; Maudsley, A.A.; Sheriff, S.; Lanfermann, H.; Ding, X.Q. Altered Neurometabolic Profile in Early Parkinson’s Disease: A Study with Short Echo-Time Whole Brain MR Spectroscopic Imaging. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, F.; Vecchio, D.; Assogna, F.; Pellicano, C.; Ciullo, V.; Banaj, N.; Edden, R.A.E.; Pontieri, F.E.; Piras, F.; Spalletta, G. Cerebellar GABA Levels and Cognitive Interference in Parkinson’s Disease and Healthy Comparators. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Högl, B.; Stefani, A.; Videnovic, A. Idiopathic REM Sleep Behaviour Disorder and Neurodegeneration—An Update. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, A.; Fernández-Arcos, A.; Tolosa, E.; Serradell, M.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Valldeoriola, F.; Gelpi, E.; Vilaseca, I.; Sánchez-Valle, R.; Lladó, A.; et al. Neurodegenerative Disorder Risk in Idiopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder: Study in 174 Patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, 89741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, A.; Verga, L.; Giora, E.; Zucconi, M.; Ferini-Strambi, L. The Risk of Neurodegeneration in REM Sleep Behavior Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Longitudinal Studies. Sleep Med. Rev. 2019, 43, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereshtehnejad, S.M.; Yao, C.; Pelletier, A.; Montplaisir, J.Y.; Gagnon, J.F.; Postuma, R.B. Evolution of Prodromal Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies: A Prospective Study. Brain 2019, 142, 2051–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, S.V.; Libourel, P.A.; Lazarus, M.; Grassi, D.; Luppi, P.H.; Fort, P. Genetic Inactivation of Glutamate Neurons in the Rat Sublaterodorsal Tegmental Nucleus Recapitulates REM Sleep Behaviour Disorder. Brain 2017, 140, 414–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-Sponsored Revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale Presentation and Clinimetric Testing Results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M. The Assessment Of Anxiety Rating Scale. Br. J. Med. Psychol. 1959, 32, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Beck Depression Inventory-II; Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1966; Volume 78, pp. 490–498. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, P.H.; Claire, S.; Benoit, M.; Koutaich, J.; Bertogliati, C.; Tible, O.; Caci, H.; Borg, M.; Brocker, P.; Bedoucha, P. The Apathy Inventory: Assessment of Apathy and Awareness in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2002, 17, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagby, R.M.; Taylor, G.J.; Parker, J.D.A. The Twenty-Item Toronto Alexithymia Scale-II. Convergent, Discriminant, and Concurrent Validity. J. Psychosom. Res. 1994, 38, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlesimo, G.A.; Caltagirone, C.; Gainotti, G.; Facida, L.; Gallassi, R.; Lorusso, S.; Marfia, G.; Marra, C.; Nocentini, U.; Parnett, L. The Mental Deterioration Battery: Normative Data, Diagnostic Reliability and Qualitative Analyses of Cognitive Impairment. Eur. Neurol. 1996, 36, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, H.E. A Modified Card Sorting Test Sensitive to Frontal Lobe Defects. Cortex 1976, 12, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarra, P.; Vezzadini, G.; Dieci, F.; Zonato, F.; Venneri, A. A Short Version of the Stroop Test: Normative Data in an Italian Population Sample. Nuova Riv. Neurol. 2002, 12, 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieth, P.A. Le Test de Copie d’une Figure Complexe; Contribution à l’étude de La Perception et de La Mémoire. Arch. Psychol. 1944, 30, 206–356. [Google Scholar]
- Carlesimo, G.A.; Buccione, I.; Fadda, L.; Graceffa, A.; Mauri, M.; Lorusso, S.; Bevilacqua, G.; Caltagirone, C. Standardizzazione Di Due Test Di Memoria per Uso Clinico: Breve Racconto e Figura Di Rey. Nuova Riv. Neurol. 2002, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Gong, T.; Xiang, Y.; Mikkelsen, M.; Wang, G.; Edden, R.A.E. Single-Dose L-Dopa Increases Upper Brainstem GABA in Parkinson’s Disease: A Preliminary Study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 422, 117309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashima, H.; Terada, T.; Bunai, T.; Matsudaira, T.; Obi, T.; Ouchi, Y. In Vivo Illustration of Altered Dopaminergic and GABAergic Systems in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 880407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terkelsen, M.H.; Hvingelby, V.S.; Pavese, N. Molecular Imaging of the GABAergic System in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonisms. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2022, 22, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Nuland, A.J.M.; den Ouden, H.E.M.; Zach, H.; Dirkx, M.F.M.; van Asten, J.J.A.; Scheenen, T.W.J.; Toni, I.; Cools, R.; Helmich, R.C. GABAergic Changes in the Thalamocortical Circuit in Parkinson’s Disease. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2020, 41, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Ai, K.; Zhang, B.; Lui, S. The Immediate Alteration of Cerebellar Glx/GABA and Cerebello-Thalamo-Cortical Connectivity in Patients with Schizophrenia after Cerebellar TMS. Schizophrenia 2025, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Herold, C.J.; Cheung, E.F.C.; Chan, R.C.K.; Schröder, J. Neurological Soft Signs and Brain Network Abnormalities in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozza, C.; Baron, J.C.; Eidelberg, D.; Mentis, M.J.; Carbon, M.; Marié, R.M. Executive Processes in Parkinson’s Disease: FDG-PET and Network Analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2004, 22, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firbank, M.J.; Parikh, J.; Murphy, N.; Killen, A.; Allan, C.L.; Collerton, D.; Blamire, A.M.; Taylor, J.P. Reduced Occipital GABA in Parkinson Disease with Visual Hallucinations. Neurology 2018, 91, e675–e685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Qi, Q.; Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Cerebellar Large-Scale Network Connectivity in Parkinson’s Disease: Associations with Emotion, Cognition, and Aging Effects. Brain Imaging Behav. 2025, 19, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chau, S.W.; Chan, J.W.; Chu, W.C.; Abrigo, J.M.; Mok, V.C.; Wing, Y.K. Large-Scale Network Dysfunction in α-Synucleinopathy: A Meta-Analysis of Resting-State Functional Connectivity. eBioMedicine 2022, 77, 103915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, K.; Cattaneo, Z.; Oldrati, V.; Ferrari, C.; Grossman, E.D.; Garcia, J.O. A Modulator of Cognitive Function: Cerebellum Modifies Human Cortical Network Dynamics via Integration. bioRxiv 2024, 612716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, A.; Santamaria, J.; Pujol, J.; Moreno, A.; Deus, J.; Tolosa, E. Brainstem Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Idopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder. Sleep 2002, 25, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, G.; Ueki, Y.; Oishi, N.; Oguri, T.; Fukui, A.; Nakayama, M.; Sano, Y.; Kandori, A.; Kan, H.; Arai, N.; et al. Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Dysfunction and Altered Functional Connectivity in Rem Sleep Behavior Disorder with Mild Motor Impairment. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 435662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauvilliers, Y.; Schenck, C.H.; Postuma, R.B.; Iranzo, A.; Luppi, P.H.; Plazzi, G.; Montplaisir, J.; Boeve, B. REM Sleep Behaviour Disorder. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, P.L.; Peever, J.H. Impaired GABA and Glycine Transmission Triggers Cardinal Features of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7111–7121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assogna, F.; Liguori, C.; Cravello, L.; Macchiusi, L.; Belli, C.; Placidi, F.; Pierantozzi, M.; Stefani, A.; Mercuri, B.; Izzi, F.; et al. Cognitive and Neuropsychiatric Profiles in Idiopathic Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder and Parkinson’s Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, L.; Gagnon, J.F.; Pelletier, A.; Montplaisir, J.Y.; Gagnon, G.; Postuma, R.B. Characterization of Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms in Idiopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 1409–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Assogna, F.; Pellicano, C.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Placidi, F.; Izzi, F.; Camedda, R.; Schillaci, O.; Spalletta, G.; Lombardo, C.; et al. Neuropsychiatric, Neuropsychological, and Neuroimaging Features in Isolated REM Sleep Behavior Disorder: The Importance of MCI. Sleep Med. 2022, 100, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Brok, M.G.H.E.; van Dalen, J.W.; van Gool, W.A.; Moll van Charante, E.P.; de Bie, R.M.A.; Richard, E. Apathy in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.R.T.; Ballenger, J.C.; Lecrubier, Y.; Rickels, K.; Borkovec, T.D.; Stein, D.J.; Nutt, D.J. Pharmacotherapy of Generalized Anxiety Disorder. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2001, 62, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmahmann, J.D. Disorders of the Cerebellum: Ataxia, Dysmetria of Thought, and the Cerebellar Cognitive Affective Syndrome. J. Neuropsychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2004, 16, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggio, M.; Olivito, G. Topography of the Cerebellum in Relation to Social Brain Regions and Emotions. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 154, pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.J.; Guell, X.; Hubbard, N.A.; Siless, V.; Frosch, I.R.; Goncalves, M.; Lo, N.; Nair, A.; Ghosh, S.S.; Hofmann, S.G.; et al. Functional Alterations in Cerebellar Functional Connectivity in Anxiety Disorders. Cerebellum 2021, 20, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stagg, C.J.; Bachtiar, V.; Amadi, U.; Gudberg, C.A.; Ilie, A.S.; Sampaio-Baptista, C.; O’Shea, J.; Woolrich, M.; Smith, S.M.; Filippini, N.; et al. Local GABA Concentration Is Related to Network-Level Resting Functional Connectivity. Elife 2014, 3, e01465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferini-Strambi, L.; Di Gioia, M.R.; Castronovo, V.; Oldani, A.; Zucconi, M.; Cappa, S.F. Neuropsychological Assessment in Idiopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder (RBD): Does the Idiopathic Form of RBD Really Exist? Neurology 2004, 62, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, M.L.; Farini, E.; Ortelli, P.; Zucconi, M.; Manconi, M.; Cappa, S.; Ferini-Strambi, L. Longitudinal Study of Cognitive Function in Idiopathic REM Sleep Behavior Disorder. Sleep 2011, 34, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.; Jo, H.; Chai, Y.; Park, H.R.; Lee, H.; Joo, E.Y.; Kim, H. Static and Dynamic Brain Morphological Changes in Isolated REM Sleep Behavior Disorder Compared to Normal Aging. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1365307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Cai, Y.-C.; Liu, D.-Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Northoff, G.; et al. GABAergic Inhibition in Human HMT+ Predicts Visuo-Spatial Intelligence Mediated through the Frontal Cortex. Elife 2024, 13, e97545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niendam, T.A.; Laird, A.R.; Ray, K.L.; Dean, Y.M.; Glahn, D.C.; Carter, C.S. Meta-Analytic Evidence for a Superordinate Cognitive Control Network Subserving Diverse Executive Functions. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 12, 241–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Z.; Luo, N.; Niu, M.; Li, Y.; Kang, W.; Liu, J. Dynamic Functional Connectivity Impairments in Idiopathic Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 79, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firbank, M.J.; Pasquini, J.; Best, L.; Foster, V.; Sigurdsson, H.P.; Anderson, K.N.; Petrides, G.; Brooks, D.J.; Pavese, N. Cerebellum and Basal Ganglia Connectivity in Isolated REM Sleep Behaviour Disorder and Parkinson’s Disease: An Exploratory Study. Brain Imaging Behav. 2024, 18, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyke, K.; Pépés, S.E.; Chen, C.; Kim, S.; Sigurdsson, H.P.; Draper, A.; Husain, M.; Nachev, P.; Gowland, P.A.; Morris, P.G.; et al. Comparing GABA-Dependent Physiological Measures of Inhibition with Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Measurement of GABA Using Ultra-High-Field MRI. Neuroimage 2017, 152, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucherie, D.E.; Reneman, L.; Ruhé, H.G.; Schrantee, A. Neurometabolite Changes in Response to Antidepressant Medication: A Systematic Review of 1H-MRS Findings. NeuroImage Clin. 2023, 40, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, S.E.; Lees, A.J. Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank, London: Overview and Research. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 1993, 39, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sateia, M.J. International Classification of Sleep Disorders-Third Edition Highlights and Modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Poewe, W.; Rascol, O.; Sampaio, C.; Stebbins, G.T.; Counsell, C.; Giladi, N.; Holloway, R.G.; Moore, C.G.; Wenning, G.K.; et al. Movement Disorder Society Task Force Report on the Hoehn and Yahr Staging Scale: Status and Recommendations. Mov. Disord. 2004, 19, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. DSM 5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 9780890425541. [Google Scholar]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-Mental State”. A Practical Method for Grading the Cognitive State of Patients for the Clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emre, M.; Aarsland, D.; Brown, R.; Burn, D.J.; Duyckaerts, C.; Mizuno, Y.; Broe, G.A.; Cummings, J.; Dickson, D.W.; Gauthier, S.; et al. Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Dementia Associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1689–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, K.R.; Healy, D.G.; Schapira, A.H. Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnosis and Management. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. Beck Depression Inventory-Second Edition (BDI-II)|Men’s Health Initiative; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub, D.; Hoops, S.; Shea, J.A.; Lyons, K.E.; Pahwa, R.; Driver-Dunckley, E.D.; Adler, C.H.; Potenza, M.N.; Miyasaki, J.; Siderowf, A.D.; et al. Validation of the Questionnaire for Impulsive-Compulsive Disorders in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2009, 24, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- First, M.B.; Williams, J.B.W.; Karg, R.S.; Spitzer, R.L. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5®-Research Version; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- First, M.B. SCID-5-PD: Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Personality Disorders: Includes the Self-Report Screener Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-5 Screening Personality Questionnaire (SCID-5-SPQ); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; ISBN 9781585624744. [Google Scholar]
- Reitan, R.M. Trail Making Test, Manual for Administration and Scoring; Reitan Neuropsychology Laboratory: Tucson, AZ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Tkáč, I.; Starčuk, Z.; Choi, I.Y.; Gruetter, R. In Vivo 1H NMR Spectroscopy of Rat Brain at 1 Ms Echo Time. Magn. Reson. Med. 1999, 41, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruetter, R.; Tkáč, I. Field Mapping without Reference Scan Using Asymmetric Echo-Planar Techniques. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 43, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkáč, I.; Gruetter, R. Methodology of 1H NMR Spectroscopy of the Human Brain at Very High Magnetic Fields. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2005, 29, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edden, R.A.E.; Puts, N.A.J.; Harris, A.D.; Barker, P.B.; Evans, C.J. Gannet: A Batch-Processing Tool for the Quantitative Analysis of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid–Edited MR Spectroscopy Spectra. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Near, J.; Edden, R.; Evans, C.J.; Paquin, R.; Harris, A.; Jezzard, P. Frequency and Phase Drift Correction of Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Data by Spectral Registration in the Time Domain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| HC (N = 18) | iRBD (N = 18) | dnPD (N = 20) | t, chi2, F | df | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, mean (sd) | 67 (9.5) | 68.6 (8.3) | 67.1 (10) | 0.154 | 2;53 | 0.858 |
| Sex, male (%) | 11 (61) | 13 (72) | 13 (65) | 0.512 | 2 | 0.774 |
| Years of education, mean (sd) | 13.2 (3.8) | 13.3 (4.3) | 12.8 (4.7) | 0.065 | 2;53 | 0.937 |
| Age of onset, mean (sd) | - | 65.3 (8.5) | 65.7 (9.9) | −0.14 | 36 | 0.889 |
| Age of diagnosis, mean (sd) | - | 67.3 (8.5) | 66.5 (10) | 0.258 | 36 | 0.798 |
| RBD illness duration, (years) mean (sd) | 3.28 (2.1) | - | - | - | ||
| dnPD illness duration, (years) mean (sd) | - | - | 1.45 (1) | - | - | - |
| Antidepressant, yes (%) | 1 (5) | 1 (5.6) | 3 (15) | 1.41 | 2 | 0.494 |
| Benzodiazepines, yes (%) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 3 (15) | 3.32 | 2 | 0.191 |
| MDS-UPDRS I, mean (sd) | - | 5.78 (2.8) | 6.6 (3.6) | −0.779 | 36 | 0.441 |
| MDS-UPDRS II, mean (sd) | - | 0.89 (1.4) | 5.20 (3.2) | −5.261 | 36 | <0.001 * |
| MDS-UPDRS III, mean (sd) | - | 2.55 (2.3) | 25.9 (9.4) | −10.287 | 36 | <0.001 * |
| H&Y, median | - | - | 2 | - | - | - |
| Symptoms laterality, right (%) | - | - | 11 (55) | - | - | - |
| ICDs, no (%) | - | 18 (100) | 19 (95) | 0.924 | 1 | 0.336 |
| NMSS, mean (sd) | - | 28.3 (20.4) | 33.8 (23.1) | −0.778 | 36 | 0.442 |
| HC (N = 18) | iRBD (N = 18) | dnPD (N = 20) | F, H | df | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolite concentrations | ||||||
| GABA_L | 3.71 (0.48) | 3.79 (0.46) | 3.53 (0.46) | 1.59 | 2;52 | 0.214 |
| GABA_R | 3.95 (0.57) | 4.07 (0.74) | 3.95 (0.53) | 0.225 | 2;50 | 0.799 |
| GABAavg | 3.87 (0.35) | 3.96 (0.43) | 3.76 (0.40) | 1.166 | 2;49 | 0.322 |
| Glx_L # | 6.83 (0.75) | 7.27 (1.12) | 6.55 (1.27) | 3.446 | 2 | 0.179 |
| Glx_R | 6.92 (1.23) | 7.15 (1.16) | 7.47 (1.36) | 0.886 | 2;52 | 0.418 |
| Glxavg | 6.95 (0.86) | 7.19 (0.95) | 7.01 (1.13) | 0.248 | 2;50 | 0.781 |
| Glx/GABA_L | 1.88 (0.28) | 1.93 (0.29) | 1.88 (0.36) | 0.174 | 2;51 | 0.841 |
| Glx/GABA_R # | 1.76 (0.24) | 1.77 (0.33) | 1.95 (0.24) | 7.216 | 2 | 0.027 * |
| Glx/GABAavg | 1.81 (0.22) | 1.82 (0.17) | 1.89 (0.19) | 0.943 | 2;48 | 0.396 |
| Neuropsychiatric scores | ||||||
| HARS # | 2.78 (3.26) | 7.83 (4.46) | 8.15 (6.37) | 15.688 | 2 | <0.001 * |
| BDI-Som # | 1.61 (1.33) | 3.67 (2.2) | 3.35 (2.13) | 10.521 | 2 | 0.005 * |
| BDI-Tot # | 3.44 (3.1) | 7.78 (5.9) | 7.20 (6.1) | 8.192 | 2 | 0.017 * |
| Apathy Scale # | 0.94 (1.21) | 3.06 (4.80) | 3.10 (2.81) | 7.136 | 2 | 0.028 * |
| TAS-F1# | 7.9 (1.02) | 9.44 (3.76) | 9.0 (2.86) | 1.276 | 2 | 0.528 |
| TAS-F2 # | 8.67 (3.77) | 8.72 (4.4) | 9.15 (2.9) | 0.777 | 2 | 0.678 |
| TAS-F3 # | 15.44 (4.74) | 15.78 (4.73) | 16.75 (3.53) | 2.436 | 2 | 0.296 |
| TAS Tot. # | 32.11 (7.35) | 34.56 (9.3) | 34.70 (4.3) | 1.965 | 2 | 0.374 |
| Neuropsychological performance | ||||||
| Rey’s 15w Immediate Recall | 48.22 (7.67) | 36.61 (8.08) | 38.85 (9.77) | 9.304 | 2;53 | <0.001 * |
| Rey’s 15w Delayed Recall # | 10.89 (2.63) | 8 (3.05) | 8.45 (2.93) | 9.084 | 2 | 0.011 * |
| WCST-msf Pers. Err. # | 0.44 (0.86) | 1.78 (1.93) | 1.65 (2.28) | 7.473 | 2 | 0.024 * |
| Post Hoc Comparisons | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC vs. iRBD | HC vs. dnPD | iRBD vs. dnPD | |||||||
| Mean Diff. | U, t | p | Mean Diff. | U, t | p | Mean Diff. | U, t | p | |
| Metabolite concentrations | |||||||||
| Glx/GABA_R # | −0.01 | 135 | 0.744 | −0.19 | 86 | 0.017 * | −0.18 | 93 | 0.03 * |
| Neuropsychiatric group differences | |||||||||
| HARS # | −5.05 | 52 | <0.001 * | −5.05 | 66 | <0.001 * | −0.320 | 165 | 0.67 |
| BDI-Som # | −2.06 | 72 | 0.004 * | −2.06 | 89.5 | 0.007 * | 0.320 | 160.5 | 0.564 |
| BDI-Tot # | −4.34 | 79 | 0.008 * | −4.34 | 101 | 0.021 * | 0.580 | 170 | 0.769 |
| Apathy Scale # | −2.12 | 127 | 0.279 | −2.12 | 85.5 | 0.004 * | −0.040 | 145 | 0.317 |
| Neuropsychological groups differences | |||||||||
| Rey’s 15w Immediate Recall | 11.61 | 11.6 | <0.001 * | 11.61 | 9.37 | 0.004 * | −2.240 | −2.24 | 1 (Bonf.p) |
| Rey’s 15w Delayed Recall # | 2.89 | 76.5 | 0.007 * | 2.89 | 97.5 | 0.015 * | −0.450 | 159 | 0.553 (Bonf.p) |
| WCST-msf Pers. Err. # | −1.34 | 89 | 0.012 * | −1.34 | 108 | 0.021 * | 0.130 | 168 | 0.716 (Bonf.p) |
| Correlation Analyses | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glx/GABA_R~Neuropsychiatric Measures | ||||
| Spearman’s Coefficient | R2 | p | ||
| iRBD | HARS # | −0.50 | 0.25 | 0.043 |
| BDI-Som # | −0.63 | 0.40 | 0.007 | |
| BDI-Tot # | −0.60 | 0.36 | 0.010 | |
| TAS-F1 # | −0.52 | 0.27 | 0.032 | |
| dnPD | No significant correlations | |||
| HC | No significant correlations | |||
| Glx/GABA_R~Neuropsychological Measures | ||||
| iRBD | Copy of R-O picture | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.024 |
| WCST-msf Pers. Err | −0.58 | 0.34 | 0.015 | |
| dnPD | No significant correlations | |||
| HC | Rey’s 15w Delayed Recall | 0.51 | 0.26 | 0.038 |
| Copy of R-O picture | 0.58 | 0.34 | 0.015 | |
| SWCT-Color, time | −0.593 | 0.35 | 0.012 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellicano, C.; Vecchio, D.; Giove, F.; Macchiusi, L.; Clemenzi, M.; Marzi, C.; Fernandes, M.; Cirillo, F.; Maio, S.; Liguori, C.; et al. Contribution of Cerebellar Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems in Premotor and Early Stages of Parkinson’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110754
Pellicano C, Vecchio D, Giove F, Macchiusi L, Clemenzi M, Marzi C, Fernandes M, Cirillo F, Maio S, Liguori C, et al. Contribution of Cerebellar Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems in Premotor and Early Stages of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110754
Chicago/Turabian StylePellicano, Clelia, Daniela Vecchio, Federico Giove, Lucia Macchiusi, Marco Clemenzi, Claudia Marzi, Mariana Fernandes, Flavia Cirillo, Silvia Maio, Claudio Liguori, and et al. 2025. "Contribution of Cerebellar Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems in Premotor and Early Stages of Parkinson’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110754
APA StylePellicano, C., Vecchio, D., Giove, F., Macchiusi, L., Clemenzi, M., Marzi, C., Fernandes, M., Cirillo, F., Maio, S., Liguori, C., Piras, F., & Piras, F. (2025). Contribution of Cerebellar Glutamatergic and GABAergic Systems in Premotor and Early Stages of Parkinson’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10754. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110754






