Changes in Apolipoprotein A1-Associated Proteomic Composition After Pioglitazone Treatment Versus Weight Loss
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
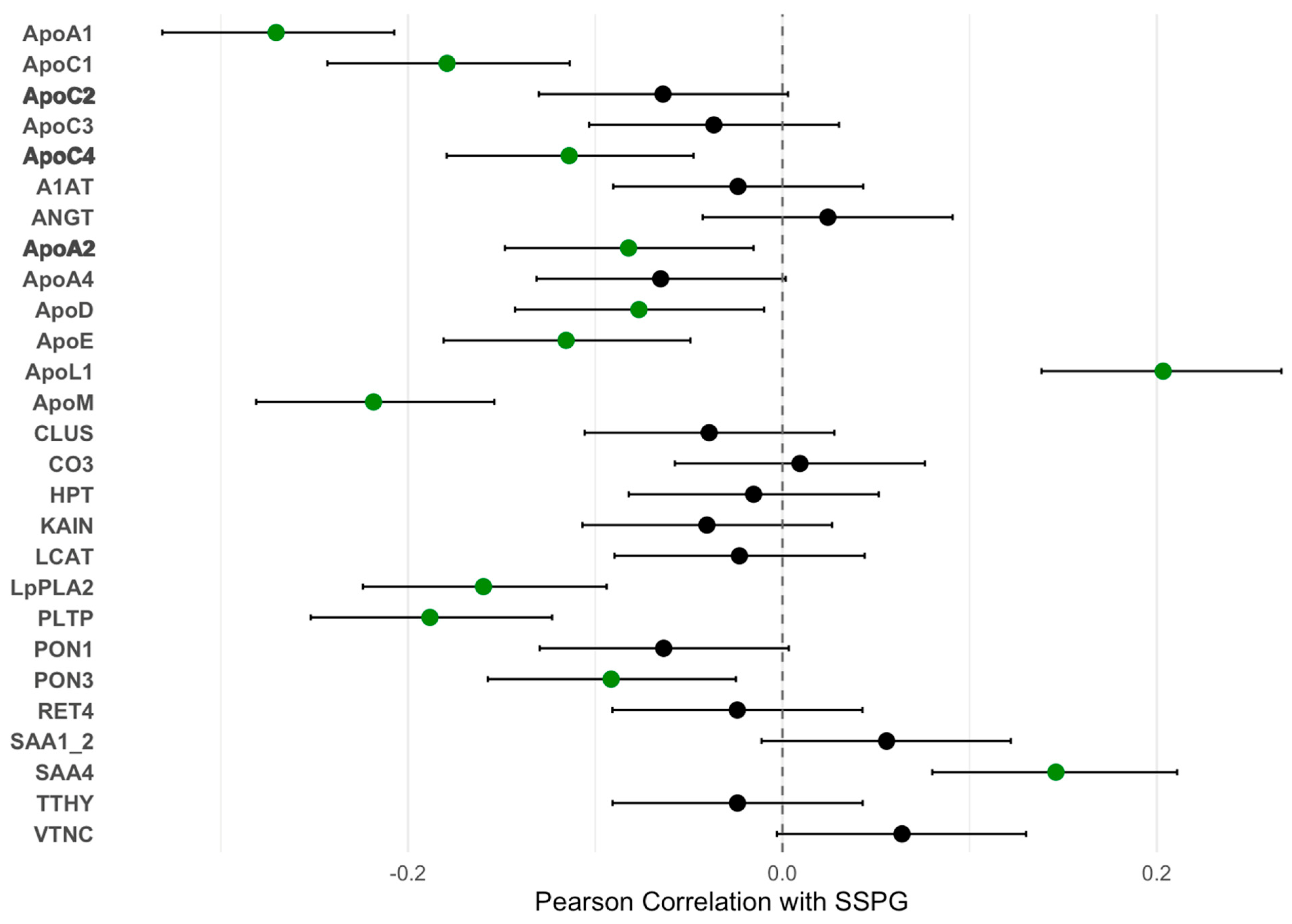
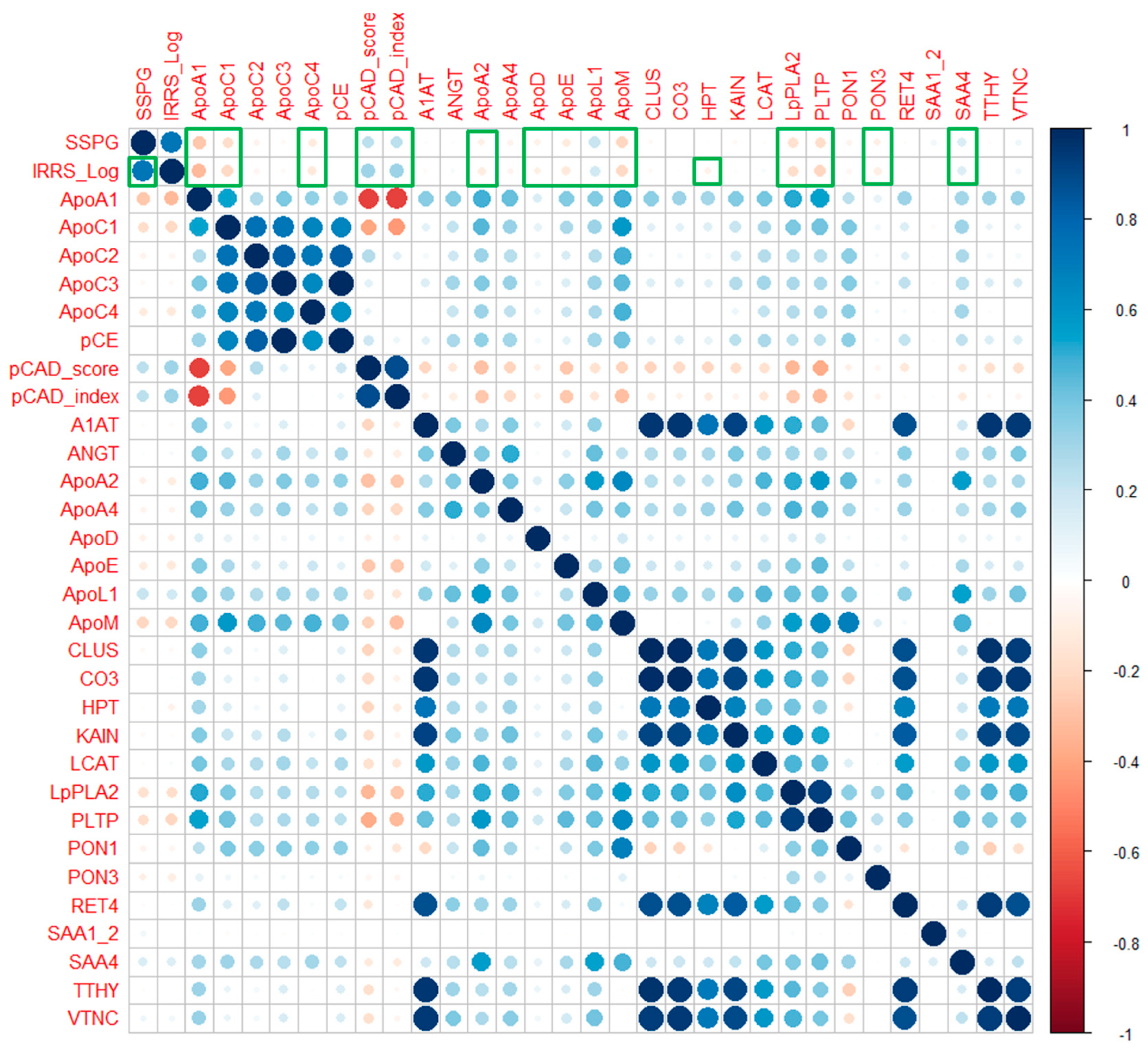
2.2. Baseline Correlations Between IRRS and SSPG and ApoA-I-Associated Proteome
2.3. Intervention Effects on Insulin Resistance and Lipid Levels
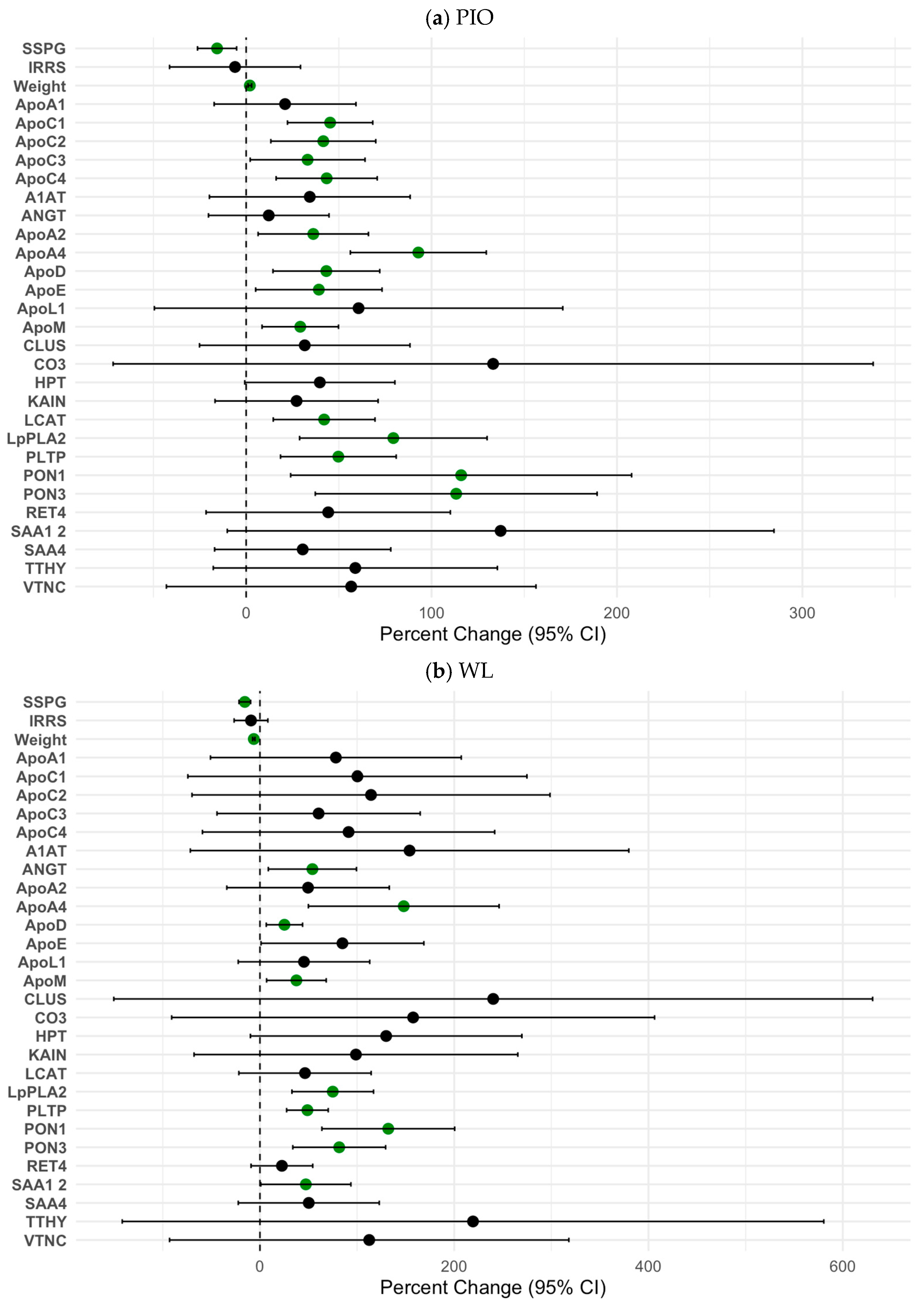
2.4. Changes in ApoA-I-Associated Proteome
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Design and Participants
3.2. Assessment of Insulin Resistance
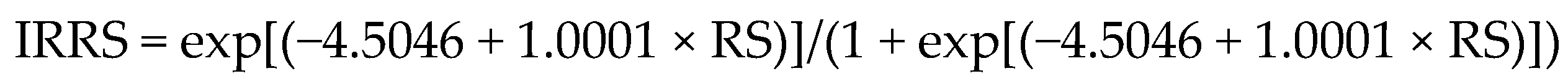
3.3. Measurement of ApoA-I-Associated Proteome
3.4. Sample Preparation
3.5. LC-MS Parameters
3.6. Intervention Groups
3.7. Outcome Measures
3.8. Statistical Analysis
3.9. Power Calculations
3.10. Data Handling and Missing Values
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A1AT | Alpha-1-Antitrypsin |
| ApoA1 | Apolipoprotein A-I |
| ApoAC-22–ApoA4 | Apolipoprotein A-II to A-IV |
| ApoC1–C4 | Apolipoprotein C-I to C-IV |
| ApoD | Apolipoprotein D |
| ApoE | Apolipoprotein E |
| ApoL1 | Apolipoprotein L1 |
| ApoM | Apolipoprotein M |
| ANGT | Angiotensinogen |
| ASCVD | Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| CIMT | Carotid Intima-Media Thickness |
| CLUS | Clusterin |
| CO3 | Complement Component 3 |
| DM | Diabetes Mellitus |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| HDL-C | HDL Cholesterol |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance |
| Hp | Haptoglobin |
| IR | Insulin Resistance |
| IRRS | Insulin Resistance Risk Score |
| KAIN | Kallistatin |
| LCAT | Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| LDL-C | LDL Cholesterol |
| LpPLA2 | Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 |
| LPL | Lipoprotein Lipase |
| PON1/PON3 | Paraoxonase 1/Paraoxonase 3 |
| PCAD | Prediction of Coronary Artery Disease (Score) |
| PIO | Pioglitazone |
| PLTP | Phospholipid Transfer Protein |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma |
| RCT | Reverse Cholesterol Transport |
| RET4 | Retinol-Binding Protein 4 |
| SAA1/2, SAA4 | Serum Amyloid Alpha-1/2, Alpha-4 |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| S1P | Sphingosine-1-Phosphate |
| SSPG | Steady-State Plasma Glucose |
| T2DM | Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| TG/HDL-C | Triglyceride/HDL Cholesterol Ratio |
| TTHY | Transthyretin |
| VTNC | Vitronectin |
| WL | Weight Loss |
References
- Ong, K.L.; Stafford, L.K.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Boyko, E.J.; Vollset, S.E.; Smith, A.E.; Dalton, B.E.; Duprey, J.; Cruz, J.A.; Hagins, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234, Erratum in Lancet 2023, 402, 1132; Erratum in Lancet 2025, 405, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasan, R.S.; Enserro, D.M.; Xanthakis, V.; Beiser, A.S.; Seshadri, S. Temporal trends in the remaining lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease among middle-aged adults over six decades: The Framingham Study. Circulation 2022, 145, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartolano, F.D.C.; Dias, G.D.; de Freitas, M.C.P.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M.; Damasceno, N.R.T. Insulin Resistance Predicts Atherogenic Lipoprotein Profile in Nondiabetic Subjects. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 1018796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin resistance, lipotoxicity, type 2 diabetes and atherosclerosis: The missing links. The Claude Bernard Lecture 2009. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1270–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuñiga, F.A. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, R.; Armitage, J.; Parish, S.; Sleigh, P.; Peto, R.; Heart Protection Study Collaborative Group. MRC/BHF Heart Protection Study of cholesterol-lowering with simvastatin in 5963 people with diabetes: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2003, 361, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.L.; Hess, C.N.; Hiatt, W.R.; Goldfine, A.B. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease and Heart Failure in Type 2 Diabetes—Mechanisms, Management, and Clinical Considerations. Circulation 2016, 133, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.S.; Cooke, A.L.; Swertfeger, D.K.; Shah, A.S. The Difference Between High Density Lipoprotein Subfractions and Subspecies: An Evolving Model in Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Silva, R.A.G.D.; Jerome, W.G.; Kontush, A.; Chapman, M.J.; Curtiss, L.K.; Hodges, T.J.; Davidson, W.S. Apolipoprotein A-I structural organization in high density lipoproteins isolated from human plasma. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Barrett, T.J.; Fisher, E.A. HDL and Reverse Cholesterol Transport: Basic Mechanisms and their Roles in Vascular Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denimal, D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Functions of High-Density Lipoprotein in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Antioxidants 2023, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgila, K.; Vyrla, D.; Drakos, E. Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I), Immunity, Inflammation and Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Song, Z.; Mao, B.; Xu, G. Apolipoprotein A1-Related Proteins and Reverse Cholesterol Transport in Antiatherosclerosis Therapy: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2022, 2022, 4610834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, J.T.; Seckler, H.S. HDL modification: Recent developments and their relevance to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2019, 30, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, T.S.; Jin, Z.; Topbas, C.; Bystrom, C. Rapid Affinity Enrichment of Human Apolipoprotein A-I Associated Lipoproteins for Proteome Analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchior, J.T.; Street, S.E.; Vaisar, T.; Hart, R.; Jerome, J.; Kuklenyik, Z.; Clouet-Foraison, N.; Thornock, C.; Bedi, S.; Shah, A.S.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-I modulates HDL particle size in the absence of apolipoprotein A-II. J. Lipid Res. 2021, 62, 100099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, S.R.; Osme, A.; Ilchenko, S.; Golizeh, M.; Lee, K.; Wang, S.; Bena, J.; Previs, S.F.; Smith, J.D.; Kasumov, T. Glycation Reduces the Stability of ApoAI and Increases HDL Dysfunction in Diet-Controlled Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Gao, X.; Yao, Z.; Xu, Y. Low ApoA1 is associated with insulin resistance in patients with impaired glucose tolerance: A cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenc, K.; Marcinkowski, M.; Olszewski, J.; Kowalczyk, P.; Pilžys, T.; Garbicz, D.; Dib, N.; Świderska, B.; Matyba, P.; Gajewski, Z.; et al. The proteomic profile is altered but not repaired after bariatric surgery in type 2 diabetes pigs. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, P.; Collier, T.S.; Jin, Z.; Lyass, A.; Li, Y.; Ibrahim, N.E.; Mukai, R.; McCarthy, C.P.; Massaro, J.M.; D’aGostino, R.B.; et al. Association of an HDL Apolipoproteomic Score with Coronary Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Death. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, O.; Rohatgi, A.; Louie, J.Z.; Collier, T.S.; McPhaul, M.J.; Abbasi, F. An HDL Proteomic Score Independently Predicts Incident Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. JACC Adv. 2025, 4, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.; Jayyous, A.; Asaad, N.; Helmy, S.; Al-Suwaidi, J. Pioglitazone and cardiovascular risk in T2DM patients: Is it good for all? Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.; Reviriego, J.; Karamanos, V.; del Cañizo, F.J.; Vlachogiannis, N.; Drossinos, V.; ECLA Study Group. Management of cardiovascular risk factors with pioglitazone combination therapies in type 2 diabetes: An observational cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2011, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Neeland, I.J.; McGuire, D.K. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A New Dawn. Circulation 2024, 149, 1621–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, M.; Suraamornkul, S.; Hardies, L.J.; Glass, L.; Musi, N.; DeFronzo, R.A. Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-α and PPAR-γ agonists on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Shen, W.J.; Bittner, S.; Kraemer, F.B.; Azhar, S. PPARs: Regulators of metabolism and as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. Part II: PPAR-β/δ and PPAR-γ. Future Cardiol. 2017, 13, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohm, T.V.; Meier, D.T.; Olefsky, J.M.; Donath, M.Y. Inflammation in obesity, diabetes, and related disorders. Immunity 2022, 55, 31–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, A.C.; Jain, V.; Grandhi, G.R.; Patel, P.; Karagiannis, A.; Patel, N.; Dhindsa, D.S.; Liu, C.; Desai, S.R.; Almuwaqqat, Z.; et al. Does Elevated High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Protect Against Cardiovascular Disease? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, A.N.; Heinecke, J.W. Lipoproteomics: Using mass spectrometry-based proteomics to explore the assembly, structure, and function of lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1967–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, E.; Targher, G.; Alberiche, M.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Saggiani, F.; Zenere, M.B.; Monauni, T.; Muggeo, M. Homeostasis model assessment closely mirrors the glucose clamp technique in the assessment of insulin sensitivity: Studies in subjects with various degrees of glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Diabetes Care 2000, 23, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, D.; Khayamzadeh, M.; Kohansal, K.; Ahanchi, N.S.; Hasheminia, M.; Hadaegh, F.; Tohidi, M.; Azizi, F.; Habibi-Moeini, A.S. Are HOMA-IR and HOMA-B good predictors for diabetes and pre-diabetes subtypes? BMC Endocr. Disord. 2023, 23, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Honda, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Mizoue, T. Should insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), insulin secretion (HOMA-β), and visceral fat area be considered for improving the performance of diabetes risk prediction models. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2024, 12, e003680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanet, D.; O’Shea, P.; Lyons, C.; Shafat, A.; Dunne, F. The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test—Is It Time for a Change?—A Literature Review with an Emphasis on Pregnancy. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Jokelainen, J.; Auvinen, J.; Puukka, K.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Järvelin, M.-R.; Kettunen, J.; Mäkinen, V.-P.; Ala-Korpela, M. Insulin resistance and systemic metabolic changes in oral glucose tolerance test in 5340 individuals: An interventional study. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Gautier, J.F.; Chon, S. Assessment of Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance in Human. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, R.; Lee, S.; Chen, H.; Quon, M.J. Current approaches for assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in vivo: Advantages, limitations, and appropriate usage. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, E15–E26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganath Madan, R.; Varghese, R.T. Assessing Insulin Sensitivity and Resistance in Humans. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278954/ (accessed on 11 February 2025).
- Abbasi, F.; Shiffman, D.; Tong, C.H.; Devlin, J.J.; McPhaul, M.J. Insulin Resistance Probability Scores for Apparently Healthy Individuals. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palavicini, J.P.; Chavez-Velazquez, A.; Fourcaudot, M.; Tripathy, D.; Pan, M.; Norton, L.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Shannon, C.E. The Insulin-Sensitizer Pioglitazone Remodels Adipose Tissue Phospholipids in Humans. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 784391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talbot, C.P.; Plat, J.; Joris, P.J.; Konings, M.; Kusters, Y.H.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Ritsch, A.; Mensink, R.P. HDL cholesterol efflux capacity and cholesteryl ester transfer are associated with body mass, but are not changed by diet-induced weight loss: A randomized trial in abdominally obese men. Atherosclerosis 2018, 274, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffron, S.P.; Lin, B.; Parikh, M.; Scolaro, B.; Adelman, S.J.; Collins, H.L.; Berger, J.S.; Fisher, E.A. Changes in HDL Cholesterol Efflux Capacity following Bariatric Surgery are Procedure Dependent. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, S.; Schlamp, F.; Gildea, M.A.; Lin, B.-X.; Hülsmeier, A.; Chaloemtoem, A.; Falis, M.; Parikh, M.; Fisher, E.A.; Hornemann, T.; et al. High-Density Lipoprotein Lipid and Protein Cargo and Cholesterol Efflux Capacity Before and After Bariatric Surgery. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2025, 45, e48–e62, Erratum in Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025, 45, e163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Farin, H.M.F.; Lamendola, C.; McGraw, L.; McLaughlin, T.; Reaven, G.M. Pioglitazone administration decreases cardiovascular disease risk factors in insulin-resistant smokers. Metabolism 2008, 57, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Abbasi, F.; Kim, S.H.; Ariel, D.; Lamendola, C.; Cardell, J.; Xu, S.; Patel, S.; Tomasso, V.; Mojaddidi, H.; et al. Effect of Pioglitazone on Cardiometabolic Risk in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 119, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, M.; Meyer, P.M.; Haffner, S.; Feinstein, S.; D’aGostino, R.; Kondos, G.T.; Perez, A.; Chen, Z.; Mazzone, T.; D’agostino, S.R. Increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol predicts the pioglitazone-mediated reduction of carotid intima-media thickness progression in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circulation 2008, 117, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bots, M.L.; Visseren, F.L.; Evans, G.W.; Riley, W.A.; Revkin, J.H.; Tegeler, C.H.; Shear, C.L.; Duggan, W.T.; Vicari, R.M.; Grobbee, D.E.; et al. Torcetrapib and carotid intima-media thickness in mixed dyslipidaemia (RADIANCE 2 study): A randomised, double-blind trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornfeldt, K.E. Apolipoprotein C3: Form begets function. J. Lipid Res. 2023, 65, 100475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, D.A.; Medh, J.D. Receptor-mediated mechanisms of lipoprotein remnant catabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 1998, 37, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudet, D.; Gonciarz, M.; Shen, X.; Leohr, J.K.; Beyer, T.P.; Day, J.W.; Mullins, G.R.; Zhen, E.Y.; Hartley, M.; Larouche, M.; et al. Targeting the angiopoietin-like protein 3/8 complex with a monoclonal antibody in patients with mixed hyperlipidemia: A phase 1 trial. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 2632–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvinov, D.; Mahini, H.; Garelnabi, M. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Paraoxonase 1: Implication in Arteriosclerosis Diseases. North Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 4, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffersen, C.; Benn, M.; Christensen, P.M.; Gordts, P.L.S.M.; Roebroek, A.J.M.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Dahlbäck, B.; Nielsen, L.B. The plasma concentration of HDL-associated apoM is influenced by LDL receptor-mediated clearance of apoB-containing particles. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2198–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.W.; Reaven, G.M.; Farquhar, J.W. Comparison of impedance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake in normal subjects and in subjects with latent diabetes. J. Clin. Investig. 1970, 49, 2151–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, J.C.; Matthews, D.R.; Hermans, M.P. Correct Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) Evaluation Uses the Computer Program. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 2191–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.W.; Clarke, N.J.; Chen, Z.; McPhaul, M.J. A high-throughput mass spectrometry assay to simultaneously measure intact insulin and C-peptide. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 455, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Collier, T.S.; Dai, D.L.Y.; Chen, V.; Hollander, Z.; Ng, R.T.; McManus, B.M.; Balshaw, R.; Apostolidou, S.; Penn, M.S.; et al. Development and Validation of Apolipoprotein AI-Associated Lipoprotein Proteome Panel for the Prediction of Cholesterol Efflux Capacity and Coronary Artery Disease. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maravi, J.S.M.; Leszczynski, E.C.; Schwartz, C.S.; Dev, P.K.; Barber, J.L.; Reasons, R.J.; Pearce, R.W.; McPhaul, M.J.; Konrad, R.J.; Robbins, J.M.; et al. Associations of an HDL apolipoproteomic index with cardiometabolic risk factors before and after exercise training in the HERITAGE Family Study. Atherosclerosis 2024, 395, 117587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age, years | 47.3 (11.6) |
| Female * | 564 (65.5) |
| Non-Hispanic White * | 590 (68.5) |
| Hispanic * | 64 (7.4) |
| Black * | 47 (5.5) |
| South Asian * | 83 (9.6) |
| East Asian * | 70 (8.1) |
| American Indian and Alaska Native * | 7 (0.8) |
| Weight, kg | 85.6 (19.6) |
| BMI | 30.2 (6.0) |
| Total Cholesterol, mg/dL | 189.9 (39.5) |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 140.5 (128.5) |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 116.3 (31.6) |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 46.6 (13.4) |
| Fasting Glucose, mg/dL | 96.8 (9.7) |
| Fasting Insulin, mU/L | 10.0 (7.6) |
| SSPG, mg/dL | 164.1 (73.4) |
| Variable | N | r (95% CI) * | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IRRS | 861 | 0.73 (0.69–0.76) | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 861 | 0.67 (0.63–0.71) | <0.001 |
| TG/HDL-C | 662 | 0.41 (0.34–0.47) | <0.001 |
| TG | 662 | 0.35 (0.28–0.41) | <0.001 |
| HDL-C | 662 | −0.37 (−0.43–−0.30) | <0.001 |
| PIO N = 38 | WL N = 70 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years * | 50.3 (8.1) | 49.0 (10.3) | 0.50 |
| Female | 13 (34.2) | 22 (31.4) | 0.94 |
| Non-Hispanic White | 25 (65.8) | 36 (51.4) | 0.283 |
| Hispanic | 2 (5.3) | 5 (7.1) | 0.82 |
| Black | 7 (18.4) | 1 (1.4) | 0.001 |
| South Asian | 1 (2.6) | 20 (28.6) | 0.001 |
| East Asian | 3 (7.9) | 7 (10) | 0.99 |
| Am. Indian and Alaska Native | 0 (0) | 1 (1.4) | 0.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parsa, S.; Collier, T.S.; McPhaul, M.J.; Melander, O.; Knowles, J.W.; Rohatgi, A.; Abbasi, F. Changes in Apolipoprotein A1-Associated Proteomic Composition After Pioglitazone Treatment Versus Weight Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110690
Parsa S, Collier TS, McPhaul MJ, Melander O, Knowles JW, Rohatgi A, Abbasi F. Changes in Apolipoprotein A1-Associated Proteomic Composition After Pioglitazone Treatment Versus Weight Loss. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110690
Chicago/Turabian StyleParsa, Shyon, Timothy S. Collier, Michael J. McPhaul, Olle Melander, Joshua W. Knowles, Anand Rohatgi, and Fahim Abbasi. 2025. "Changes in Apolipoprotein A1-Associated Proteomic Composition After Pioglitazone Treatment Versus Weight Loss" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110690
APA StyleParsa, S., Collier, T. S., McPhaul, M. J., Melander, O., Knowles, J. W., Rohatgi, A., & Abbasi, F. (2025). Changes in Apolipoprotein A1-Associated Proteomic Composition After Pioglitazone Treatment Versus Weight Loss. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110690








