Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide Mixtures Against hDPSCs: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. hDPSCs Characterization
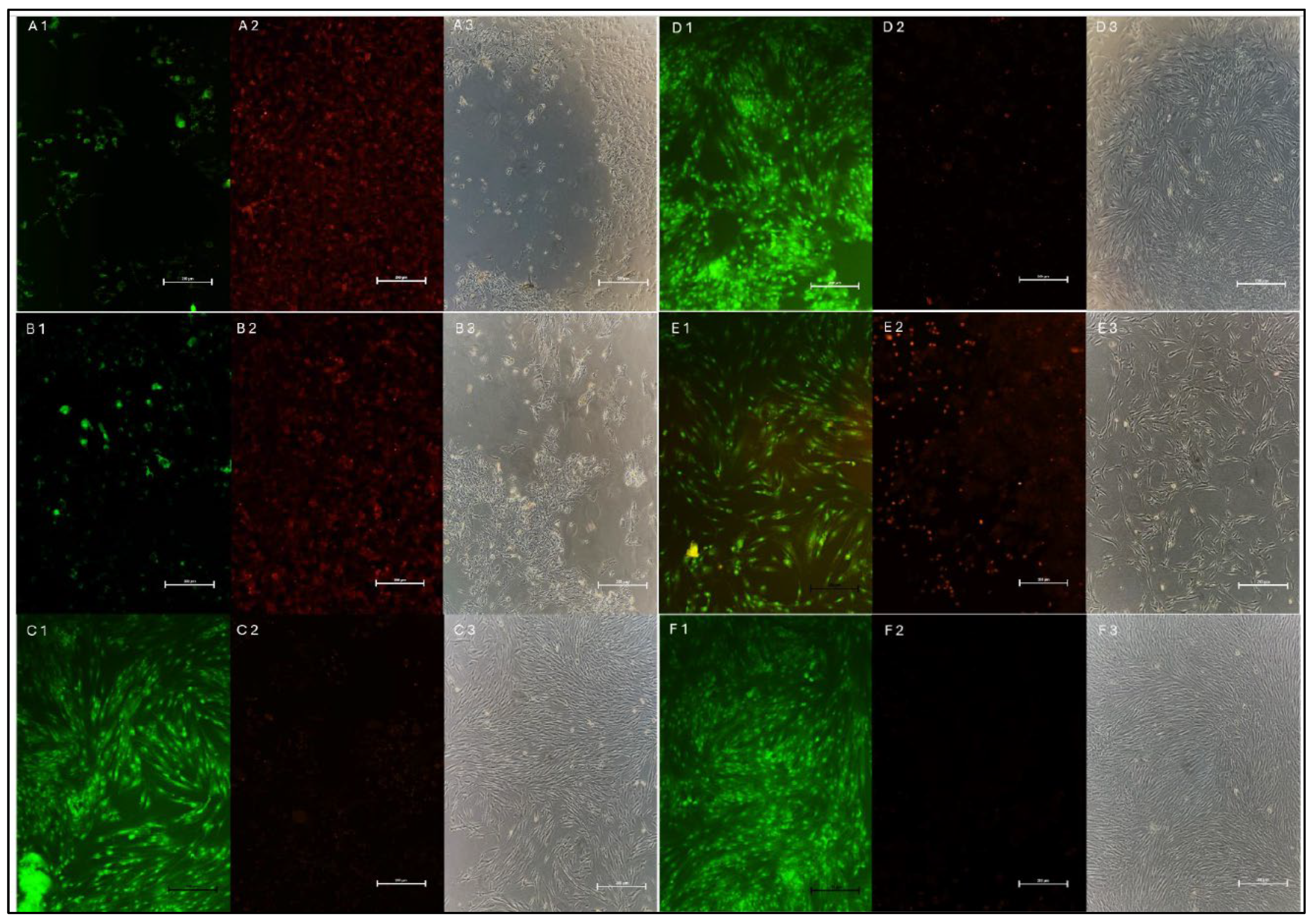
2.2. Cell Viability
2.3. ROS Release
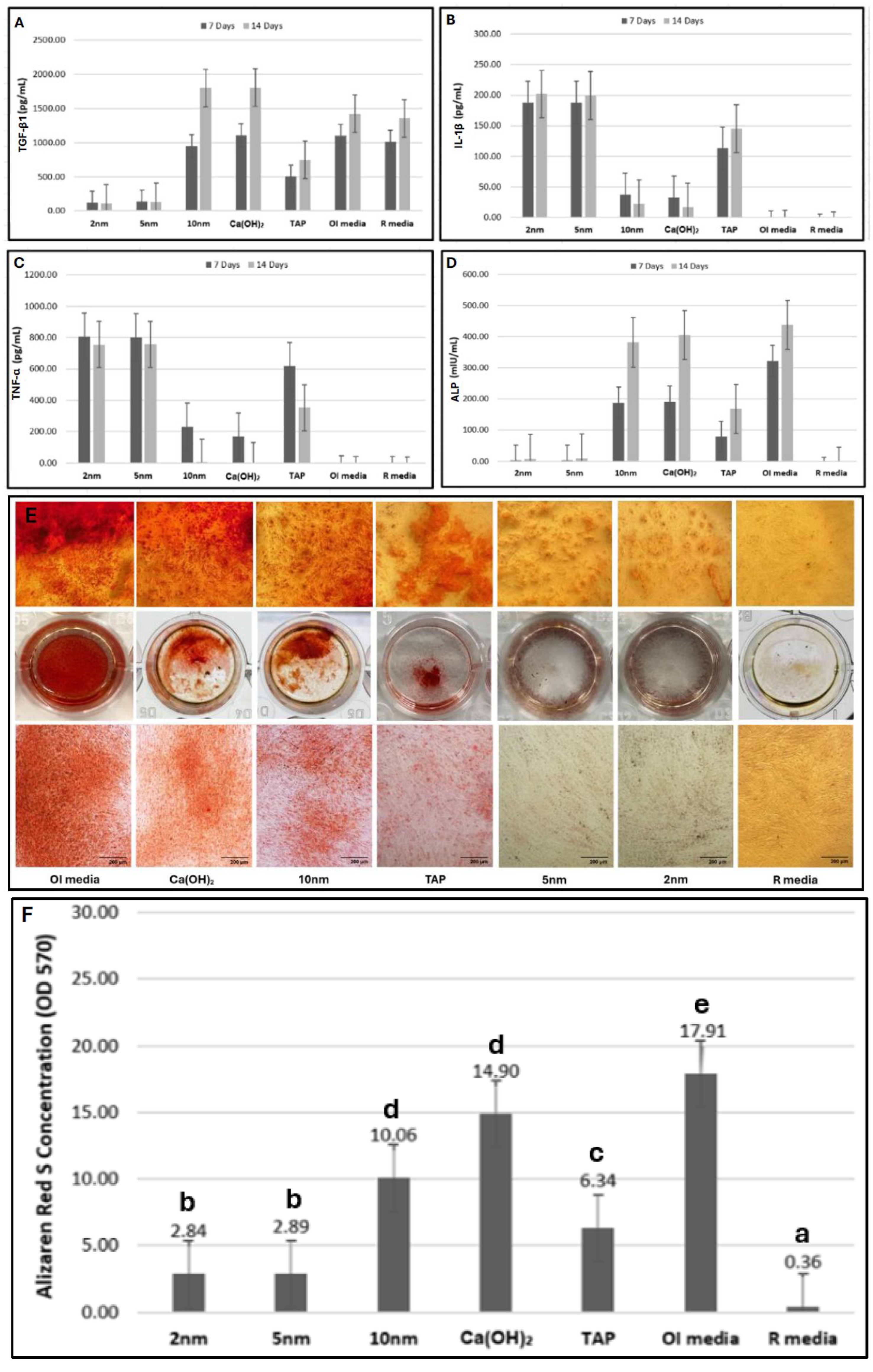
2.4. Proinflammatory/Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
2.5. ALP Production
2.6. Alizarin Red S Staining
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Medicament Preparation
4.2. Culturing of hDPSCs
4.3. Characterization of hDPSCs
4.4. Cell Viability
4.5. ROS Release
4.6. Proinflammatory/Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
4.7. ALP Production
4.8. Alizarin Red S Staining
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trope, M. Treatment of the Immature Tooth with a Non–Vital Pulp and Apical Periodontitis. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 54, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, A.F. Microbial Factors and Antimicrobial Strategies in Dental Pulp Regeneration. J. Endod. 2017, 43, S46–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Sharma, G.; Zilm, P.; Rossi-Fedele, G. Comparison of the Biocidal Efficacy of Sodium Dichloroisocyanurate and Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments over a 7-Day Contact Time: An Ex Vivo Study. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1273–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Association of Endodontists. Clinical Considerations for a Regenerative Endodontic Procedure. Available online: https://www.aae.org/specialty/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2021/08/ClinicalConsiderationsApprovedByREC062921.pdf (accessed on 13 October 2025).
- Distel, J.; Hatton, J.; Gillespie, M. Biofilm Formation in Medicated Root Canals. J. Endod. 2002, 28, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Kishen, A. Antibacterial Nanoparticles in Endodontics: A Review. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1417–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balto, H.; Bukhary, S.; Al-Omran, O.; BaHammam, A.; Al-Mutairi, B. Combined Effect of a Mixture of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide against Enterococcus faecalis Biofilm. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1689–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afkhami, F.; Pourhashemi, S.J.; Sadegh, M.; Salehi, Y.; Fard, M.J.K. Antibiofilm efficacy of silver nanoparticles as a vehicle for calcium hydroxide medicament against Enterococcus faecalis. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGazlan, A.S.; Auda, S.H.; Balto, H.; Alsalleeh, F. Antibiofilm Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Alone or Mixed with Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicaments: An Ex-Vivo Analysis. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakeeha, G.; AlHarbi, S.; Auda, S.; Balto, H. The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles’ Size on Biofilm Eradication. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 75, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diogenes, A.; Hargreaves, K.M. Microbial Modulation of Stem Cells and Future Directions in Regenerative Endodontics. J. Endod. 2017, 43, S95–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, S.; Scherzed, A.; Kessler, M.; Hummel, S.; Technau, A.; Froelich, K.; Ginzkey, C.; Koehler, C.; Hagen, R.; Kleinsasser, N. Silver nanoparticles: Evaluation of DNA damage, toxicity and functional impairment in human mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 201, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengstock, C.; Diendorf, J.; Epple, M.; Schildhauer, T.A.; Köller, M. Effect of silver nanoparticles on human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 2058–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 942916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, H.C.; Wang, T.; Liao, C.Y.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Q.F.; Yan, B.; Jiang, G.B. Impact of silver nanoparticles on human cells: Effect of particle size. Nanotoxicology 2010, 4, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.; Hussain, S.M.; Schrand, A.M.; Braydich-Stolle, L.K.; Hess, K.L.; Jones, R.L.; Schlager, J.J. Unique Cellular Interaction of Silver Nanoparticles: Size-Dependent Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 13608–13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.; Casey, A.; Byrne, G.; Chambers, G.; Howe, O. Silver nanoparticles induce pro-inflammatory gene expression and inflammasome activation in human monocytes. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2016, 36, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Gutierrez, F.; Thi, E.P.; Silverman, J.M.; de Oliveira, C.C.; Svensson, S.L.; Vanden Hoek, A.; Sánchez, E.M.; Reiner, N.E.; Gaynor, E.C.; Pryzdial, E.L.; et al. Antibacterial activity, inflammatory response, coagulation and cytotoxicity effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2012, 8, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Moussa, S.; El Backly, R.; El-Gendy, R. Investigating the residual effect of silver nanoparticles gel as an intra-canal medicament on dental pulp stromal cells. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Walboomers, X.F.; Van Kuppevelt, T.H.; Daamen, W.F.; Van Damme, P.A.; Bian, Z.; Jansen, J. In vivo evaluation of human dental pulp stem cells differentiated towards multiple lineages. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2008, 2, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Ito, K.; Sugito, T.; Yoshimi, R.; Nagasaka, T.; Ueda, M. A Feasibility of Useful Cell-Based Therapy by Bone Regeneration with Deciduous Tooth Stem Cells, Dental Pulp Stem Cells, or Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Clinical Study Using Tissue Engineering Technology. Tissue Eng. A 2010, 16, 1891–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.H.; Song, J.S.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.-S.; Jeon, M.; Kim, S.-O.; Lee, J.-H. Cytokine Expression of Stem Cells Originating from the Apical Complex and Coronal Pulp of Immature Teeth. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 87–92.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.V.; Neigh, A.M.; Vermeulen, J.P.; De La Fonteyne, L.J.; Verharen, H.W.; Briedé, J.J.; Van Loveren, H.; De Jong, W.H. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9810–9817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althumairy, R.I.; Teixeira, F.B.; Diogenes, A. Effect of Dentin Conditioning with Intracanal Medicaments on Survival of Stem Cells of Apical Papilla. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruparel, N.B.; Teixeira, F.B.; Ferraz, C.C.R.; Diogenes, A. Direct Effect of Intracanal Medicaments on Survival of Stem Cells of the Apical Papilla. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, A.Y. Comparison of Cytotoxic Effects of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide on Human Gingival Fibroblasts: An In-vitro Study. J. Dent. Health Oral Res. 2024, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ryu, D. Silver nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress, genotoxicity and apoptosis in cultured cells and animal tissues. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, W.L.F.; de Brito, L.C.N.; Henriques, L.C.F.; Teles, F.R.F.; Teles, R.P.; Vieira, L.Q.; Sobrinho, A.P.R. Effects of Calcium Hydroxide on Cytokine Expression in Endodontic Infections. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 1368–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.J.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, I.H. Inflammasome formation and IL-1β release by human blood monocytes in response to silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6858–6867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Sun, X.; Hargreaves, K.M. Effect of Calcium Hydroxide on Proinflammatory Cytokines and Neuropeptides. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.S.S.; Rossi, M.A.; Cardoso, C.R.; da Silva, J.S.; da Silva, L.A.B.; Kuga, M.C.; Faria, G. Cellular and Molecular Tissue Response to Triple Antibiotic Intracanal Dressing. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galler, K.M.; Buchalla, W.; Hiller, K.A.; Federlin, M.; Eidt, A.; Schiefersteiner, M.; Schmalz, G. Influence of Root Canal Disinfectants on Growth Factor Release from Dentin. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Riggs, B.L.; Boyle, W.J.; Khosla, S. Regulation of osteoclastogenesis and RANK expression by TGF-β1. J. Cell Biochem. 2001, 83, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lee, P.; Lui, V.C.H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Lok, C.N.; To, M.; Yeung, K.; Wong, K.K. Silver nanoparticles promote osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and improve bone fracture healing in osteogenesis mechanism mouse model. Nanomedicine 2015, 11, 1949–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhila, A.; Prabath Singh, V.P.; Varma, K.R.; Vasudevan, S.V.; Sukhithasri, V.; Sasikumar, S. An in-vitro Comparative Evaluation of Quantitative Release of Transforming Growth Factor β-1 from Dentin upon the Action of Endodontic Irrigants, Medicaments, Ultrasonic Activation, and Low-Level Laser Irradiation. Amrita J. Med. 2021, 17, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaunberzins, A.; Gutmann, J.L.; Witherspoon, D.E.; Harper, R.P. TGF-β1 alone and in combination with calcium hydroxide is synergistic to TGF-β1 production by osteoblasts in vitro. Int. Endod. J. 2000, 33, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jin, A.; Huang, X.; Gao, X.; Sun, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Lu, T.; et al. The odontoblastic differentiation of dental mesenchymal stem cells: Molecular regulation mechanism and related genetic syndromes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1174579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Cao, Y.; Shin, S.J.; Shon, W.-J.; Chugal, N.; Kim, R.H.; Kim, E.; Kang, M.K. Revascularization-associated Intracanal Calcification: Assessment of Prevalence and Contributing Factors. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 2025–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizuela, C.; Huang, G.T.J.; Diogenes, A.; Botero, T.; Khoury, M. The Four Pillars for Successful Regenerative Therapy in Endodontics: Stem Cells, Biomaterials, Growth Factors, and Their Synergistic Interactions. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 1580842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iohara, K.; Imabayashi, K.; Ishizaka, R.; Watanabe, A.; Nabekura, J.; Ito, M.; Matsushita, K.; Nakamura, H.; Nakashima, M. Complete Pulp Regeneration After Pulpectomy by Transplantation of CD105 + Stem Cells with Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1. Tissue Eng A 2011, 17, 1911–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, W.L.; Hargreaves, K.M.; Jin, L.; Samaranayake, L.P.; Zhang, C. The Interplay of Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Endothelial Cells in an Injectable Peptide Hydrogel on Angiogenesis and Pulp Regeneration In Vivo. Tissue Eng. A 2015, 21, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, W.L.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, C.; Hargreaves, K.M.; Jin, L.; Tong, E.H.Y. Coculture of Dental Pulp Stem Cells with Endothelial Cells Enhances Osteo-/Odontogenic and Angiogenic Potential In Vitro. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, C.; Xie, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, X. Pulp regeneration in a full-length human tooth root using a hierarchical nanofibrous microsphere system. Acta Biomater. 2016, 35, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Gao, X.; Dong, Y. Characteristics and Effects on Dental Pulp Cells of a Polycaprolactone/Submicron Bioactive Glass Composite Scaffold. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y.; Sasaki, J.I.; Hashimoto, M.; Katata, C.; Hayashi, M.; Imazato, S. Pulp Regeneration by 3-dimensional Dental Pulp Stem Cell Constructs. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, Q.; Zaky, S.H.; Patil, A.; Beniash, E.; Ray, H.; Sfeir, C. Decellularized Swine Dental Pulp Tissue for Regenerative Root Canal Therapy. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1460–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Şahin, F. Stem Cells Derived from Dental Tissues. In Stem Cells Derived from Dental Tissues; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakopoulou, A.; Leyhausen, G.; Volk, J.; Tsiftsoglou, A.; Garefis, P.; Koidis, P.; Geurtsen, W. Comparative analysis of in vitro osteo/odontogenic differentiation potential of human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) and stem cells from the apical papilla (SCAP). Arch. Oral. Biol. 2011, 56, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, P.C.T.; Gomes-Filho, J.E.; Ervolino, E.; Sundefeld, M.L.M.M.; TadahiroWayama, M.; Lodi, C.S.; Dezan-Júnior, E.; Cintra, L.T.A. Histopathological Condition of the Remaining Tissues after Endodontic Infection of Rat Immature Teeth. J. Endod. 2014, 40, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; He, J. Stem Cells from the Apical Papilla (SCAPs): Past, Present, Prospects, and Challenges. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Gaudin, A.; Peters, O.A. A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study biocompatibility of endodontic materials. Int. Endod. J. 2022, 55, 346–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjor, I.A. A comparison of in vivo and in vitro methods for toxicity testing of dental materials. Int. Endod. J. 1980, 13, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmalz, G. Use of cell cultures for toxicity testing of dental materials—Advantages and limitations. J. Dent. 1994, 22, S6–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, L.R.G.; Saunders, W.P. Calcium hydroxide pastes: Classification and clinical indications. Int. Endod. J. 1999, 32, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
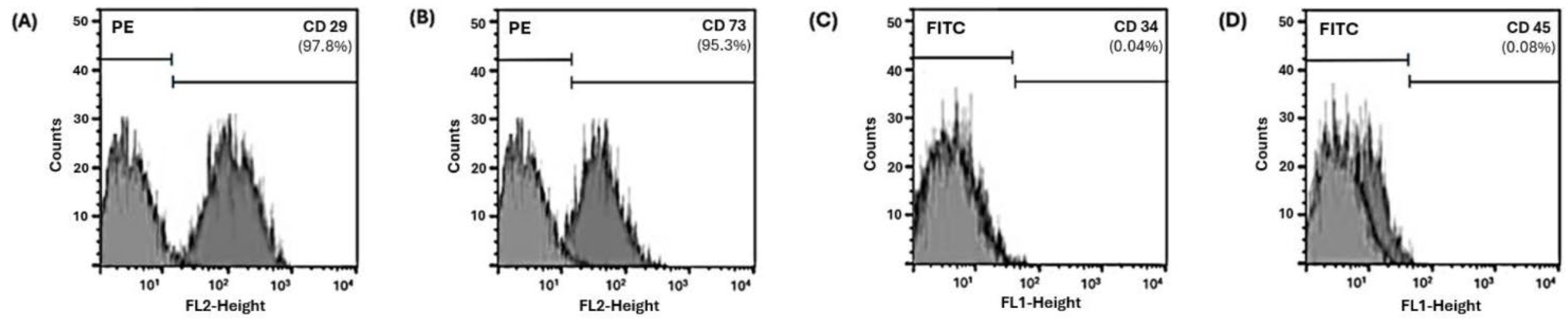
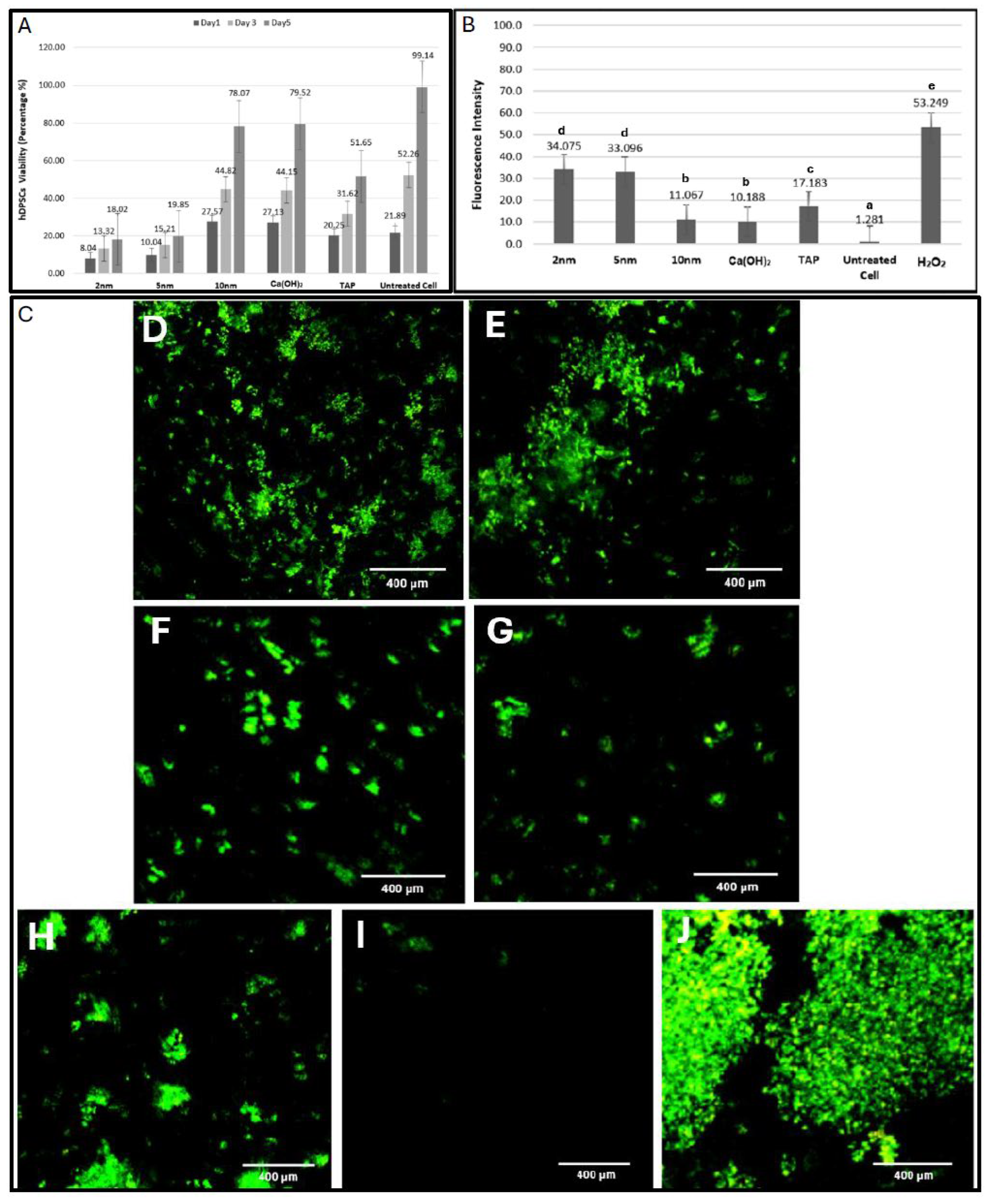

| Group | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 5 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Mean ± SD (%) | Mean Rank | MCT | Median | Mean ± SD (%) | Mean Rank | MCT | Median | Mean ± SD (%) | Mean Rank | MCT | |
| 2 nm | 8.89 | 8.04 ± 4.3 | 10.96 | a ° | 13.78 | 13.32 ± 1.8 | 12.16 | a ° | 18.25 | 18.02 ± 1 | 10.46 | a ° |
| 5 nm | 9.98 | 10.04 ± 3.6 | 14.04 | a ° | 15.29 | 15.21 ± 6.4 | 12.83 | a ° | 19.91 | 19.85 ± 2.9 | 14.54 | a ° |
| 10 nm | 27.88 | 27.57 ± 3.6 | 64.67 | c * | 44.76 | 44.82 ± 1.2 | 50.17 | c 1 | 77.98 | 78.07 ± 10.5 | 47.83 | c 1 |
| Ca(OH)2 | 27.02 | 27.13 ± 2.2 | 56.33 | c * | 44.30 | 44.15± 4.3 | 47.33 | c 1 | 79.43 | 79.52 ± 10 | 49.17 | c 1 |
| TAP | 20.01 | 20.25 ± 2.5 | 30.50 | b | 31.54 | 31.62 ± 3.8 | 30.51 | b | 51.89 | 51.65 ± 6.3 | 30.5 | b |
| Untreated Cells | 21.77 | 21.89 ± 0.2 | 42.50 | b | 52.07 | 52.26 ± 5.4 | 66.01 | d * | 99.24 | 99.14 ± 0.5 | 66.5 | d * |
| p-value | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| Marker | Group | 7 Days | 14 Days | Wilcoxon Paired Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Mean ± SD | Mean Rank | p Value | MCT | Median | Mean ± SD | Mean Rank | p Value | MCT | |||
| TGF-β1 | 2 nm | 125.32 | 121.71 ± 20.37 | 8.50 | 0.00 | a | 109.29 | 110.86 ± 39.05 | 8.44 | 0.00 | a | 0.593 |
| 5 nm | 137.41 | 139.49 ± 37.1 | 10.50 | a | 125.49 | 130.73 ± 35.69 | 10.56 | a | 0.859 | |||
| 10 nm | 951.9 | 953.08 ± 71.25 | 34.39 | c | 1811.34 | 1799.49 ± 92.97 | 54.22 | d | 0.008 | |||
| Ca(OH)2 | 1118.32 | 1111.91 ± 49.74 | 53.72 | d | 1803.43 | 1801.97 ± 107.22 | 54.78 | d | 0.008 | |||
| TAP | 502.53 | 504.98 ± 49.88 | 23.00 | b | 741.31 | 745.24 ± 12.85 | 23.00 | b | 0.008 | |||
| OI media | 1109.01 | 1101.84 ± 41.82 | 53.06 | d | 1430.42 | 1421.71 ± 53.46 | 40.00 | c | 0.008 | |||
| R media | 1020.21 | 1013.35 ± 64.81 | 40.83 | c | 1355.42 | 1352.17 ± 51.58 | 33.00 | c | 0.008 | |||
| TNF-α | 2 nm | 805.54 | 807.19 ± 4.96 | 57.00 | 0.00 | d | 752.63 | 754.5 ± 6.73 | 55.78 | 0.00 | d | 0.008 |
| 5 nm | 800.43 | 802.06 ± 6.4 | 52.00 | d | 752.21 | 757.91 ± 27.35 | 53.22 | d | 0.021 | |||
| 10 nm | 235.28 | 231.12 ± 30.36 | 32.00 | b | 4.89 | 5.91 ± 11.06 | 32.00 | b | 0.008 | |||
| Ca(OH)2 | 171.54 | 169.31 ± 7.18 | 23.00 | b | −116.87 | −18.07 ± 5.06 | 23.00 | b | 0.008 | |||
| TAP | 622.32 | 619.77 ± 27.89 | 41.00 | c | 355.29 | 353.34 ± 36.84 | 41.00 | c | 0.008 | |||
| OI media | −101.23 | −103.71 ± 1.63 | 14.00 | a | −108.01 | −106.32 ± 1.42 | 13.78 | a | 0.008 | |||
| R media | −105.34 | −107.64 ± 0.58 | 5.00 | a | −109.2 | −110.06 ± 2.21 | 5.22 | a | 0.015 | |||
| IL-1β | 2 nm | 190.26 | 188.27 ± 2.05 | 56.28 | 0.00 | d | 202.11 | 201.8 ± 4.13 | 55.44 | 0.00 | d | 0.007 |
| 5 nm | 189.65 | 187.95 ± 2.34 | 52.72 | d | 120.06 | 199.59 ± 2.5 | 53.56 | d | 0.007 | |||
| 10 nm | 35.01 | 37.35 ± 1.94 | 30.00 | b | 20.87 | 21.82 ± 1.47 | 31.56 | b | 0.007 | |||
| Ca(OH)2 | 30.32 | 32.71 ± 4.23 | 25.00 | b | 17.22 | 16.86 ± 2.23 | 23.44 | b | 0.007 | |||
| TAP | 117.43 | 113.38 ± 4.54 | 41.00 | c | 148.02 | 145.15 ± 2.43 | 41.00 | c | 0.007 | |||
| OI media | −24.69 | −24.34 ± 0.57 | 14.00 | a | −28.99 | −27.86 ± 0.18 | 12.33 | a | 0.007 | |||
| R media | −25.59 | −29.8 ± 2.54 | 5.00 | a | −29.23 | −30.24 ± 2.21 | 6.67 | a | 0.257 | |||
| Marker | Group | 7 Days | 14 Days | Wilcoxon Paired Test | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Mean ± SD | Mean Rank | p Value | MCT | Median | Mean ± SD | Mean Rank | p Value | MCT | |||
| ALP | 2 nm | 1.85 | 1.98 ± 0.78 | 16.72 | 0.00 | b | 7.01 | 7.06 ± 2.33 | 16.00 | 0.00 | b | 0.008 |
| 5 nm | 2.24 | 2.28 ± 0.26 | 20.28 | b | 8.41 | 8.87 ± 2.95 | 21.00 | b | 0.008 | |||
| 10 nm | 188.17 | 188.19 ± 8.2 | 44.78 | d | 382.13 | 381.25 ± 6.61 | 43.00 | d | 0.008 | |||
| Ca(OH)2 | 191.88 | 191.08 ± 6.19 | 46.22 | d | 403.98 | 404.3 ± 3.64 | 50.00 | d | 0.008 | |||
| TAP | 78.88 | 78.61 ± 16.1 | 32.00 | c | 168.62 | 168.25 ± 17.42 | 31.00 | c | 0.008 | |||
| OI media | 323.22 | 322.12 ± 13.2 | 59.00 | e | 538.21 | 537.67 ± 13.84 | 62.00 | e | 0.008 | |||
| R media | −36.78 | −36.93 ± 1.19 | 5.00 | a | −32.95 | −33.21 ± 1.73 | 5.00 | a | 0.011 | |||
| Medicament | Chemical Composition | Preparation |
|---|---|---|
| 2 nm mixture | 2 nm AgNPs (0.02%) + 35%Ca(OH)2 | 0.02% of the 2 nm AgNPs colloidal suspension (US Research Nanomaterial, Inc., Houston, TX, USA) was stirred gently and sonicated with 35% Ca(OH)2 paste in a proportion of 1:1, until no lumps observed. |
| 5 nm mixture | 5 nm AgNPs (0.02%) + 35%Ca(OH)2 | 0.02% of the 5 nm AgNPs colloidal suspension (Nano Composix, Inc., Suite K, San Diego, CA, USA) was stirred gently and sonicated with 35% Ca(OH)2 paste in a proportion of 1:1, until no lumps observed. |
| 10 nm mixture | 10 nm AgNPs (0.02%) + 35%Ca(OH)2 | 0.02% of the 10 nm AgNPs colloidal suspension (Nano Composix, Inc., Suite K, San Diego, CA, USA) was stirred gently and sonicated with 35% Ca(OH)2 paste in a proportion of 1:1, until no lumps observed. |
| Ca(OH)2 alone | 35% Ca(OH)2 paste | Ca(OH)2 paste was prepared by levigating 35 gm of pure Ca(OH)2 powder (Somatco, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia) with 65 gm of dense water-soluble viscous vehicle of (propylene glycol: glycerin, 1:1 proportion), until a paste-like consistency was achieved. The formula permits the slow/extended ions release. |
| TAP | 1 mg/mL TAP (metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, and minocycline) | TAP was prepared by dissolving metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, and minocycline powders (Xi’an Sgonek Biological Technology Co., Ltd., Shaanxi, China) in distilled water at a ratio of 1:1:1 (w/w/w) using a magnetic stirrer. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fakeeha, G.; Al-Zamil, L.; Muthurangan, M.; Auda, S.; Balto, H. Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide Mixtures Against hDPSCs: An In Vitro Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110604
Fakeeha G, Al-Zamil L, Muthurangan M, Auda S, Balto H. Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide Mixtures Against hDPSCs: An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110604
Chicago/Turabian StyleFakeeha, Ghazal, Lama Al-Zamil, Manikandan Muthurangan, Sayed Auda, and Hanan Balto. 2025. "Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide Mixtures Against hDPSCs: An In Vitro Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110604
APA StyleFakeeha, G., Al-Zamil, L., Muthurangan, M., Auda, S., & Balto, H. (2025). Size-Dependent Bioactivity of Silver Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide Mixtures Against hDPSCs: An In Vitro Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110604






