HIF-2α Interaction with Ataxin-10 Enhances HIF-2α Binding to Its Target Gene Promoters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
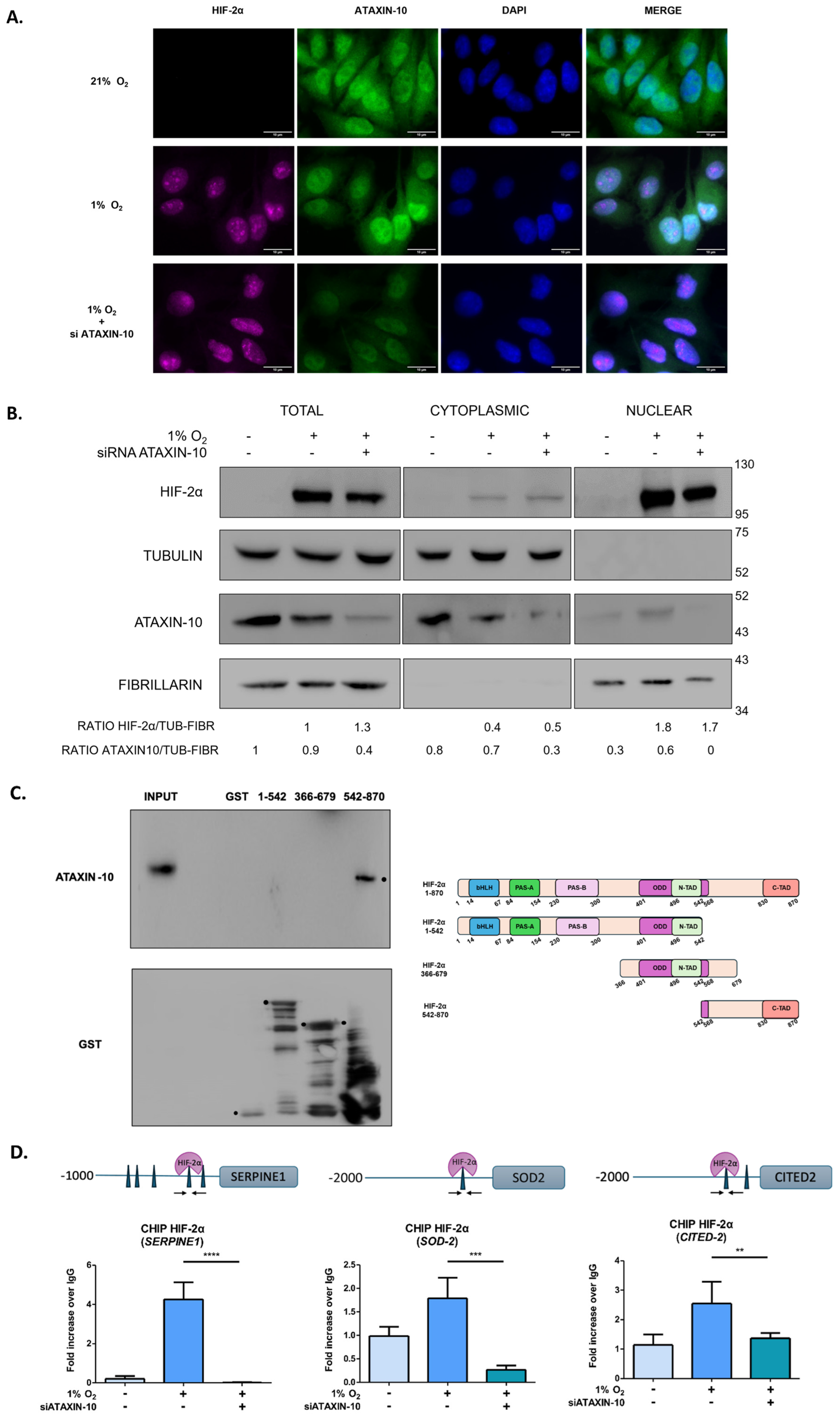
2.1. HIF-2α Interacts with Ataxin-10
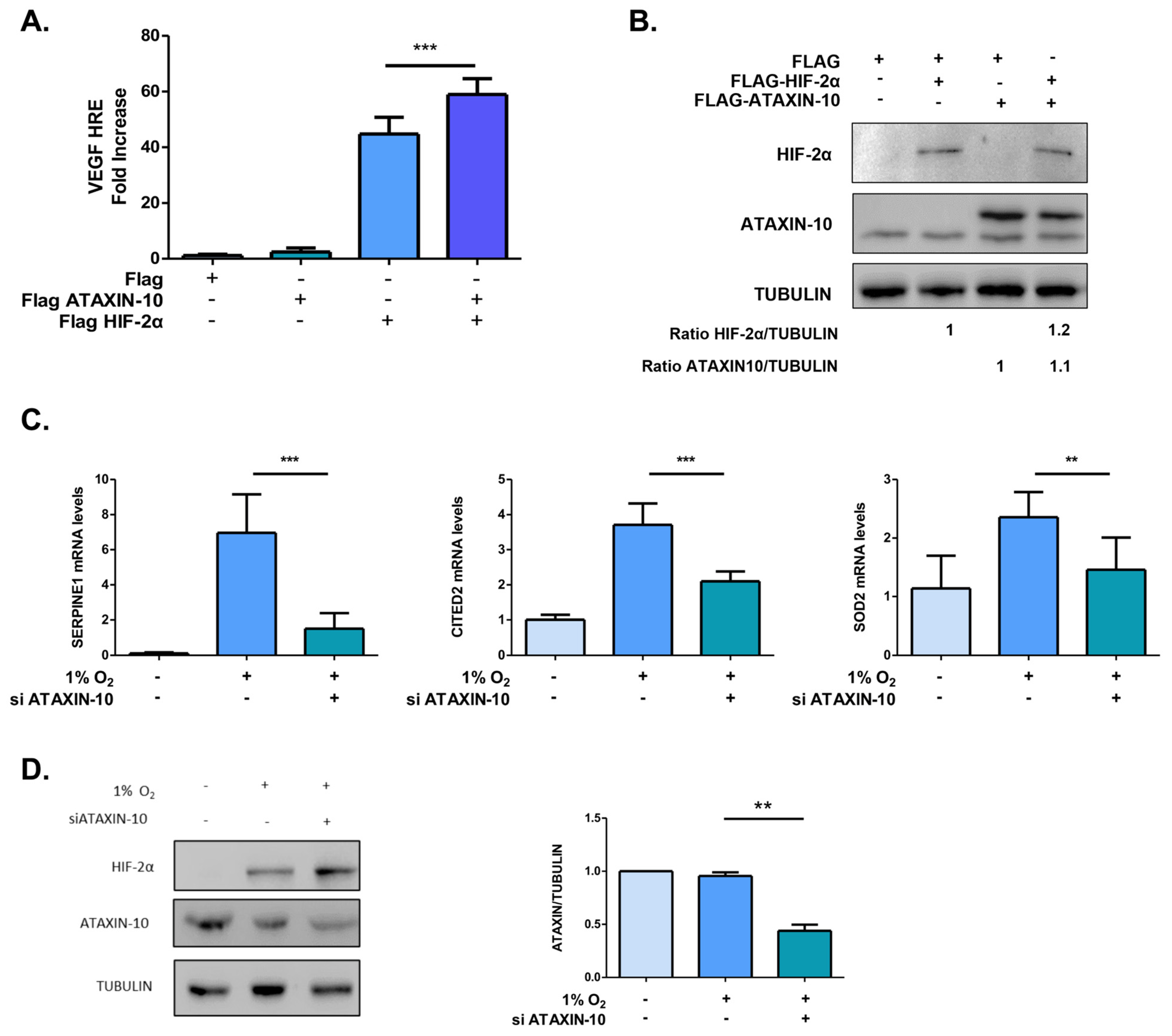
2.2. Under Hypoxic Conditions, Ataxin-10 Upregulates the Expression of HIF-2 Target Genes
2.3. Ataxin-10 Enhances HIF-2α’s Binding to Chromatin but Does Not Affect Its Subcellular Distribution
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Transfection, and Luciferase Assays
4.2. siRNA-Mediated Silencing, RNA Extraction, cDNA Production, and Quantitative PCR
4.3. LC-MS/MS Proteomic Analysis
4.4. Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Subcellular Fractionation
4.6. Western Blot Analysis and Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.7. In Vitro Binding Assays
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP)
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prabhakar, N.R.; Semenza, G.L. Oxygen Sensing and Homeostasis. Physiology 2015, 30, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wei, T.; Sun, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, J.; Bai, X.; Liang, T. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α promotes tumor progression and has crosstalk with Wnt/β-catenin signaling in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covello, K.L.; Simon, M.C.; Keith, B. Targeted replacement of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by a hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha knock-in allele promotes tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2277–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; McKnight, S.L.; Russell, D.W. Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 (EPAS1), a transcription factor selectively expressed in endothelial cells. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flamme, I.; Frölich, T.; Risau, W. Molecular mechanisms of vasculogenesis and embryonic angiogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 1997, 173, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Maltepe, E.; Lu, M.M.; Simon, C.; Bradfield, C. Expression of ARNT, ARNT2, HIF1α, HIF2α and Ah receptor mRNAs in the developing mouse. Mech. Dev. 1998, 73, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesener, M.S.; Jürgensen, J.S.; Rosenberger, C.; Scholze, C.K.; Hörstrup, J.H.; Warnecke, C.; Mandriota, S.J.; Bechmann, I.; Frei, U.A.; Pugh, C.W.; et al. Widespread, hypoxia-inducible expression of HIF-2α in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB J. 2002, 17, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menrad, H.; Werno, C.; Schmid, T.; Copanaki, E.; Deller, T.; Dehne, N.; Brüne, B. Roles of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) versus HIF-2alpha in the survival of hepatocellular tumor spheroids. Hepatology 2010, 51, 2183–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Befani, C.; Liakos, P. The role of hypoxia-inducible factor-2 alpha in angiogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9087–9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco-Price, C.; Zhang, N.; Schnelle, M.; Evans, C.; Katschinski, D.M.; Liao, D.; Ellies, L.; Johnson, R.S. Endothelial Cell HIF-1α and HIF-2α Differentially Regulate Metastatic Success. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Ohneda, K.; Nagano, M.; Miyoshi, C.; Kaneko, N.; Miwa, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Ohneda, O.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Hypoxia-inducible Transcription Factor-2α in Endothelial Cells Regulates Tumor Neovascularization through Activation of Ephrin A1. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18926–18936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schödel, J.; Oikonomopoulos, S.; Ragoussis, J.; Pugh, C.W.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Mole, D.R. High-resolution genome-wide mapping of HIF-binding sites by ChIP-seq. Blood 2011, 117, e207–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skuli, N.; Majmundar, A.J.; Krock, B.L.; Mesquita, R.C.; Mathew, L.K.; Quinn, Z.L.; Runge, A.; Liu, L.; Kim, M.N.; Liang, J.; et al. Endothelial HIF-2α regulates murine pathological angiogenesis and revascularization processes. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1427–1443, Erratum in J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e180863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Eyler, C.; Sathornsumetee, S.; Shi, Q.; Cao, Y.; Lathia, J.; McLendon, R.E.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors regulate tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcelén, M.; Velásquez, C.; Vidal, V.; Gutierrez, O.; Fernandez-Luna, J.L. HIF2α Upregulates the Migration Factor ODZ1 under Hypoxia in Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renfrow, J.J.; Soike, M.H.; Debinski, W.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Mott, R.T.; Frenkel, M.B.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Lesser, G.J.; Strowd, R.E. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α: A novel target in gliomas. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.; Recktenwald, M.; Hutt, E.; Fuller, S.; Briggs, M.; Goel, A.; Daringer, N. Targeting HIF-2α in the Tumor Microenvironment: Redefining the Role of HIF-2α for Solid Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrella, B.L.; Lohi, J.; Brinckerhoff, C. Identification of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase as a target of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in von Hippel–Lindau renal cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2004, 24, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, R.; Vaishampayan, U. Hypoxia Inducible Factor-2α (HIF-2α) Pathway Inhibitors. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2025, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pal, S.K.; Bernard-Tessier, A.; Grell, P.; Gao, X.; Kotecha, R.R.; Picus, J.; de Braud, F.; Takahashi, S.; Wong, A.; Suárez, C.; et al. A Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of the HIF-2 Alpha Inhibitor DFF332 in Patients with Advanced Clear-Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, A.C.; Gleadle, J.M.; McNeill, L.A.; Hewitson, K.S.; O’Rourke, J.; Mole, D.R.; Mukherji, M.; Metzen, E.; Wilson, M.I.; Dhanda, A.; et al. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell 2001, 107, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivan, M.; Kondo, K.; Yang, H.; Kim, W.; Valiando, J.; Ohh, M.; Salic, A.; Asara, J.M.; Lane, W.S.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: Implications for O2 sensing. Science 2001, 292, 464–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaakkola, P.; Mole, D.R.; Tian, Y.M.; Wilson, M.I.; Gielbert, J.; Gaskell, S.J.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Hebestreit, H.F.; Mukherji, M.; Schofield, C.J.; et al. Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 2001, 292, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, R.H.; Stiehl, D.P.; Camenisch, G. Integration of oxygen signaling at the consensus HRE. Sci. STKE 2005, 2005, re12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, M.R.; Wang, L.; Ware, K.; Hu, C.J. Upstream stimulatory factor 2 and hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha (HIF2alpha) cooperatively activate HIF2 target genes during hypoxia. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4595–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlus, M.R.; Wang, L.; Murakami, A.; Dai, G.; Hu, C.J. STAT3 or USF2 contributes to HIF target gene specificity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.M.; Cahill, M.A.; Rupec, R.A.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Nordheim, A. Antioxidants as well as oxidants activate c-fos via Ras-dependent activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 2 and Elk-1. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 244, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Michels, C.L.; Leung, M.K.; Arany, Z.P.; Kung, A.L.; Livingston, D.M. Functional role of p35srj, a novel p300/CBP binding protein, during transactivation by HIF-1. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprelikova, O.; Wood, M.; Tackett, S.; Chandramouli, G.V.; Barrett, J.C. Role of ETS transcription factors in the hypoxia-inducible factor-2 target gene selection. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5641–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmann, B.M.; Burrows, N.; Lobb, I.T.; Arnaiz, E.; Wit, N.; Bailey, P.S.J.; Jordon, L.H.; Lombardi, O.; Peñalver, A.; McCaffrey, J.; et al. The HIF complex recruits the histone methyltransferase SET1B to activate specific hypoxia-inducible genes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkotinakou, I.M.; Befani, C.; Samiotaki, M.; Panayotou, G.; Liakos, P. Novel HIF-2α interaction with Reptin52 impairs HIF-2 transcriptional activity and EPO secretion. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 557, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, T.; Yamagata, T.; Burgess, D.L.; Rasmussen, A.; Grewal, R.P.; Watase, K.; Khajavi, M.; McCall, A.E.; Davis, C.F.; Zu, L.; et al. Large expansion of the ATTCT pentanucleotide repeat in spinocerebellar ataxia type 10. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerman, K.A.; Ruan, H.; Edamura, K.N.; Matsuura, T.; Pearson, C.E.; Wang, Y.H. The ATTCT repeats of spinocerebellar ataxia type 10 display strong nucleosome assembly which is enhanced by repeat interruptions. Gene 2009, 434, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.C.; Gao, R.; Xu, W.; Mandal, S.M.; Lim, J.G.; Hazra, T.K.; Wakamiya, M.; Edwards, S.F.; Raskin, S.; Teive, H.A.; et al. Inactivation of hnRNP K by expanded intronic AUUCU repeat induces apoptosis via translocation of PKCdelta to mitochondria in spinocerebellar ataxia 10. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley-Ford, M.R.; Andersen, R.S.; Croyle, M.J.; Haycraft, C.J.; Clearman, K.R.; Foote, J.B.; Reiter, J.F.; Yoder, B.K. ATXN10 Is Required for Embryonic Heart Development and Maintenance of Epithelial Cell Phenotypes in the Adult Kidney and Pancreas. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 705182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- März, P.; Probst, A.; Lang, S.; Schwager, M.; Rose-John, S.; Otten, U.; Ozbek, S. Ataxin-10, the spinocerebellar ataxia type 10 neurodegenerative disorder protein, is essential for the survival of cerebellar neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 35542–35550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waragai, M.; Nagamitsu, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.J.; Lin, X.; Ashizawa, T. Ataxin 10 induces neuritogenesis via interaction with G-protein beta2 subunit. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 83, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrali, S.S.; März, P.; Ozcan, S. Ataxin-10 interacts with O-GlcNAc transferase OGT in pancreatic beta cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- März, P.; Stetefeld, J.; Bendfeldt, K.; Nitsch, C.; Reinstein, J.; Shoeman, R.L.; Dimitriades-Schmutz, B.; Schwager, M.; Leiser, D.; Ozcan, S.; et al. Ataxin-10 interacts with O-linked beta-N-acetylglucosamine transferase in the brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20263–20270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Hou, W.; Jing, Z.; Tian, C.; Han, Y.; Liao, J.; Dong, M.Q.; Xu, X. Phosphorylation of Ataxin-10 by polo-like kinase 1 is required for cytokinesis. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2946–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Tian, C.; Ding, Y.; Li, Z.; Geng, Q.; Xiahou, Z.; Wang, J.; Hou, W.; Liao, J.; Dong, M.Q.; et al. Aurora B-dependent phosphorylation of Ataxin-10 promotes the interaction between Ataxin-10 and Plk1 in cytokinesis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, T.; Kazlauskas, A.; Poellinger, L.; Ebbesen, P.; Zachar, V. Identification of a tightly regulated hypoxia-response element in the promoter of human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Blood 2002, 99, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sillen, M.; Declerck, P.J. A Narrative Review on Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 and Its (Patho)Physiological Role: To Target or Not to Target? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placencio, V.R.; DeClerck, Y.A. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 in Cancer: Rationale and Insight for Future Therapeutic Testing. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2969–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, M.; Gao, L. Identification and validation of SERPINE1 as a prognostic and immunological biomarker in pan-cancer and in ccRCC. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1213891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphries, B.A.; Buschhaus, J.M.; Chen, Y.-C.; Haley, H.R.; Qyli, T.; Chiang, B.; Shen, N.; Rajendran, S.; Cutter, A.; Cheng, Y.-H.; et al. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor 1 (PAI1) Promotes Actin Cytoskeleton Reorganization and Glycolytic Metabolism in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, F.; Cingoz, A.; Sur-Erdem, İ.; Erguder, N.; Erkent, A.; Uyulur, F.; Esai Selvan, M.; Gümüş, Z.H.; Gönen, M.; Bayraktar, H.; et al. Identification of SERPINE1 as a Regulator of Glioblastoma Cell Dispersal with Transcriptome Profiling. Cancers 2019, 11, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbashevich, K.; Ermlich, L.; Wegner, J.; Pfeiffer, J.; Raz, E. The mitochondrial protein Sod2 is important for the migration, maintenance, and fitness of germ cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1250643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Song, B.R.; Kim, D.H.; Ha, J.; Lee, M.; Choi, S.J.; Oh, W.; Um, S.; Jin, H.J. Up-Regulation of Superoxide Dismutase 2 in 3D Spheroid Formation Promotes Therapeutic Potency of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foty, R. A simple hanging drop cell culture protocol for generation of 3D spheroids. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 51, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.M.; Weber, K.L.; Doucet, M.; Chou, Y.; Brady, K.; Kowalski, J.; Tsai, H.; Yang, J.; Kominsky, S.L. Identification of prospective factors promoting osteotropism in breast cancer: A potential role for CITED2. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minemura, H.; Takagi, K.; Sato, A.; Takahashi, H.; Miki, Y.; Shibahara, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Ishida, T.; Sasano, H.; Suzuki, T. CITED2 in breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic predictor associated with proliferation, migration and chemoresistance. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1898–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagat, M.; Palanichamy, J.K.; Ramalingam, P.; Mudassir, M.; Irshad, K.; Chosdol, K.; Sarkar, C.; Seth, P.; Goswami, S.; Sinha, S.; et al. HIF-2α mediates a marked increase in migration and stemness characteristics in a subset of glioma cells under hypoxia by activating an Oct-4/Sox-2-Mena (INV) axis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 74, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havlis, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diseri, A.; Gkotinakou, I.-M.; Befani, C.; Pappas, I.; Samiotaki, M.; Panayotou, G.; Liakos, P. HIF-2α Interaction with Ataxin-10 Enhances HIF-2α Binding to Its Target Gene Promoters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110417
Diseri A, Gkotinakou I-M, Befani C, Pappas I, Samiotaki M, Panayotou G, Liakos P. HIF-2α Interaction with Ataxin-10 Enhances HIF-2α Binding to Its Target Gene Promoters. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110417
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiseri, Aikaterini, Ioanna-Maria Gkotinakou, Christina Befani, Ioannis Pappas, Martina Samiotaki, George Panayotou, and Panagiotis Liakos. 2025. "HIF-2α Interaction with Ataxin-10 Enhances HIF-2α Binding to Its Target Gene Promoters" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110417
APA StyleDiseri, A., Gkotinakou, I.-M., Befani, C., Pappas, I., Samiotaki, M., Panayotou, G., & Liakos, P. (2025). HIF-2α Interaction with Ataxin-10 Enhances HIF-2α Binding to Its Target Gene Promoters. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10417. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110417







