miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Share a Common Seed with Different Functions in Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
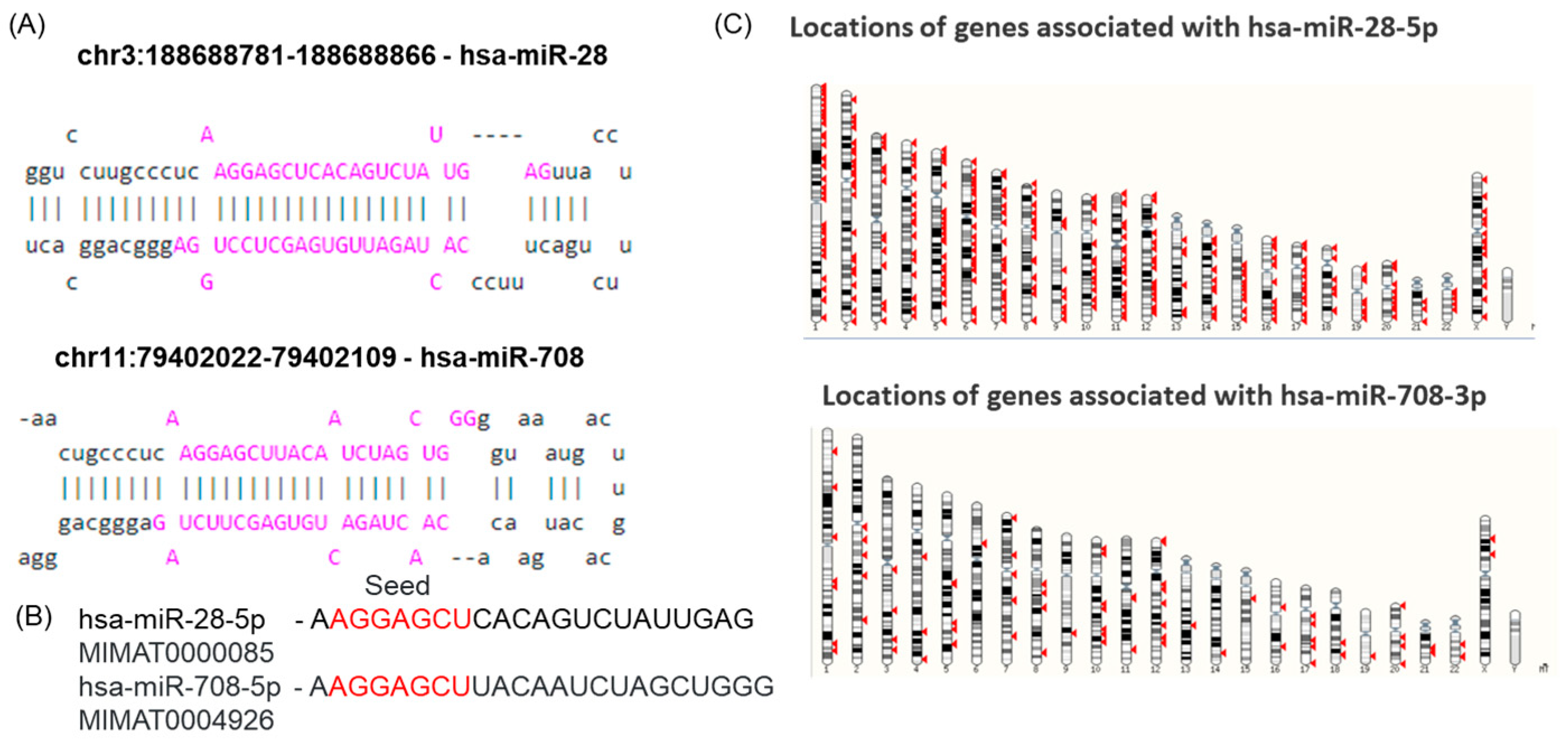
2.1. miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Share a Common Seed Sequence
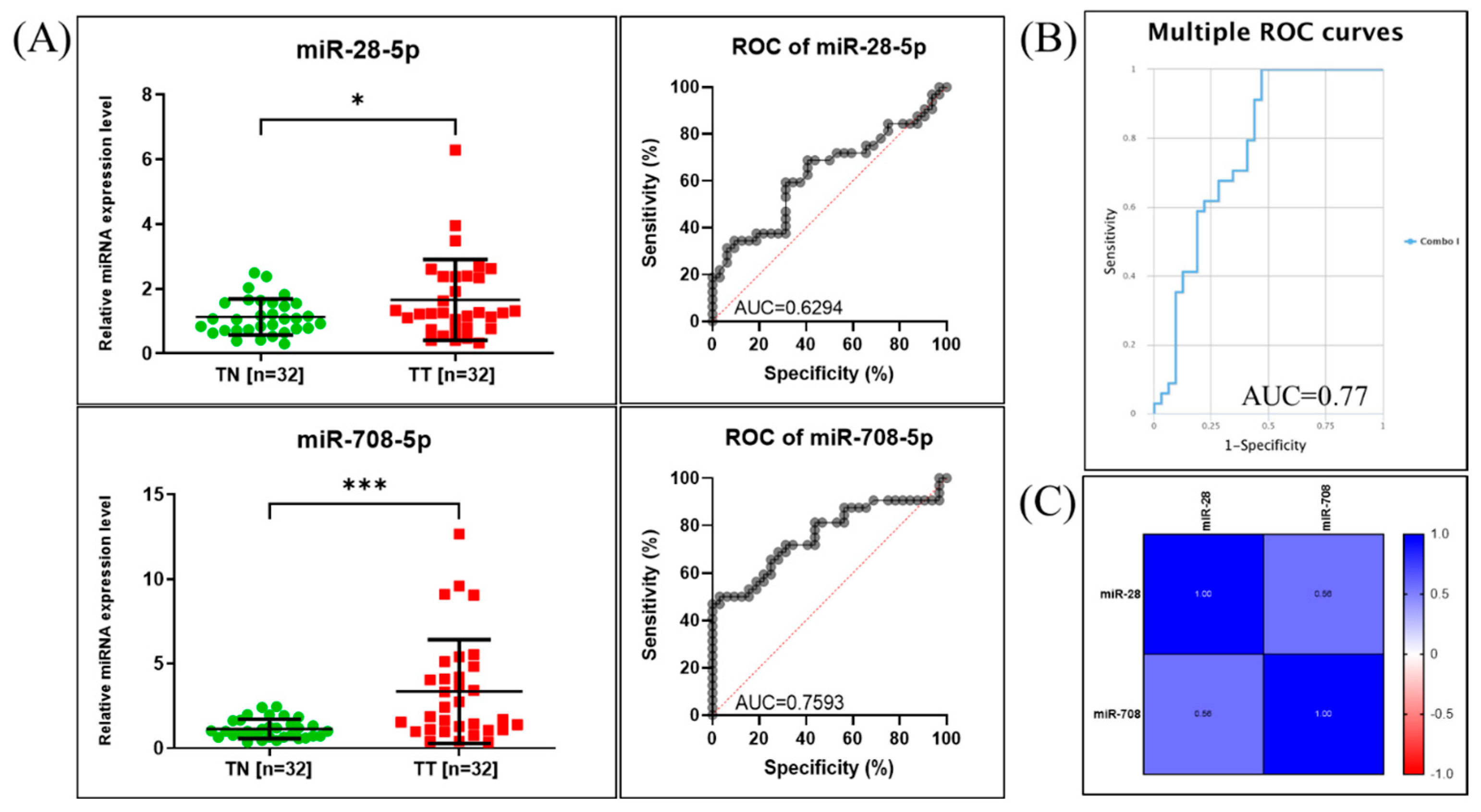
2.2. qRT-PCR for miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Expression Assessment in NSCLC Patients
2.3. Validation of the Expression Levels of miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p in Lung Cancer Using Public Available Datasets
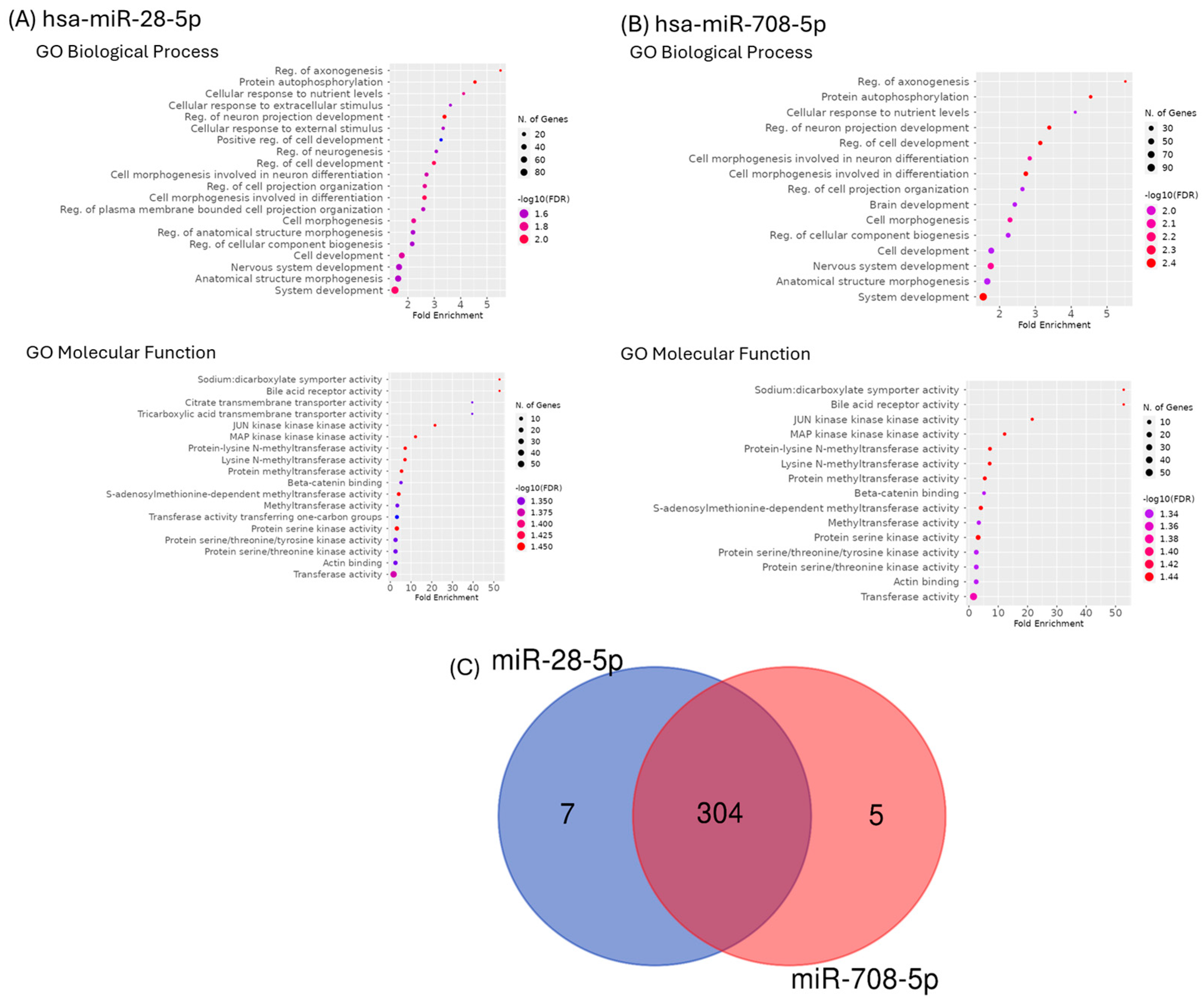
2.4. Functional Classification and Enrichment Analysis of miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Target Genes
2.5. Pathway Analysis for miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p
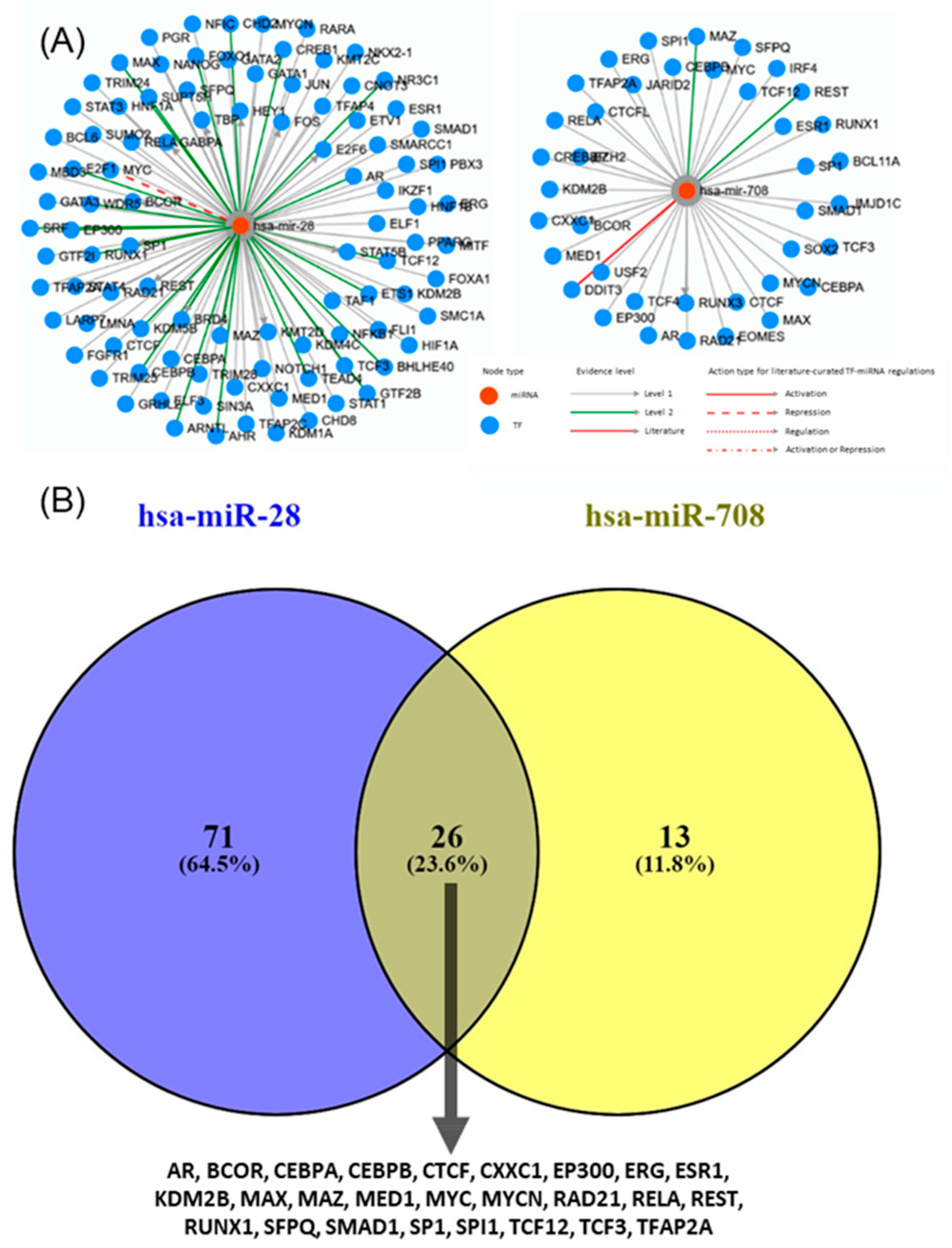
2.6. Transcription Factors and Regulatory Networks
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genomic Localisation and Sequence Analysis
4.2. Patients
4.3. Evaluation of miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (RT-PCR)
4.4. miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Expression Levels in Lung Cancer Public Database
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Predicted Target Genes Enrichment Analysis
4.7. Biological Pathways Associated with miR-28b-5p and miR-708-5p
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, T.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Yu, G. The value of CEP55 gene as a diagnostic biomarker and independent prognostic factor in LUAD and LUSC. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Che, L.; Xie, Z.; Cai, X.; Gong, L.; Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Liu, S. Using biological information to analyze potential miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks in the plasma of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghiorghiesei, O.; Zanoaga, O.; Raduly, L.; Aghiorghiesei, A.I.; Chiroi, P.; Trif, A.; Buiga, R.; Budisan, L.; Lucaciu, O.; Pop, L.A.; et al. Dysregulation of miR-21-5p, miR-93-5p, miR-200c-3p and miR-205-5p in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Potential Biomarkers Panel? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osan, C.; Chira, S.; Nutu, A.M.; Braicu, C.; Baciut, M.; Korban, S.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Connection between MicroRNAs and Oral Cancer Pathogenesis: Emerging Biomarkers in Oral Cancer Management. Genes 2021, 12, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Zimta, A.A.; Harangus, A.; Iurca, I.; Irimie, A.; Coza, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Function of Non-Coding RNAs in Lung Cancer Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2019, 11, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Calin, G.A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. MicroRNAs and cancer therapy—From bystanders to major players. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Zhou, Q.; Xiao, K.; Qian, H. MicroRNA-28 promotes the proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonea, L.; Buse, M.; Gulei, D.; Onaciu, A.; Simon, I.; Braicu, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Decoding the Emerging Patterns Exhibited in Non-coding RNAs Characteristic of Lung Cancer with Regard to their Clinical Significance. Curr. Genom. 2018, 19, 258–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimie, A.I.; Braicu, C.; Sonea, L.; Zimta, A.A.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Tonchev, K.; Mehterov, N.; Diudea, D.; Buduru, S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. A Looking-Glass of Non-coding RNAs in oral cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Sharawat, S.K.; Kumar, S. Role of microRNAs in regulating cell proliferation, metastasis and chemoresistance and their applications as cancer biomarkers in small cell lung cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wu, X.; Xiang, S.; Qiao, M.; Cen, X.; Pan, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Z. Regulatory mechanism of miR-20a-5p expression in Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.H.; Ko, Y.H. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications of microRNAs in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Bica, C.; Gulei, D.; Cojocneanu-Petric, R.; Braicu, C.; Petrut, B.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Understanding the Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Bladder Cancer: From Dark Matter to Valuable Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.; Kang, Y.; Xie, D.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J. Dysregulated expression of microRNA involved in resistance to osimertinib in EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 1978–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.L.; Qu, L.L.; Fu, H.J.; Zheng, X.F.; Tang, C.H.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.X.; Yang, S.X.; Wang, L.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers of ALK-positive nonsmall cell lung cancer and predictors of response to crizotinib therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45399–45414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petkova, V.; Marinova, D.; Kyurkchiyan, S.; Stancheva, G.; Mekov, E.; Kachakova-Yordanova, D.; Slavova, Y.; Kostadinov, D.; Mitev, V.; Kaneva, R. MiRNA expression profiling in adenocarcinoma and squamous cell lung carcinoma reveals both common and specific deregulated microRNAs. Medicine 2022, 101, e30027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, R.; Brattås, P.L.; Sharma, Y.; Jönsson, M.E.; Pircs, K.; Bengzon, J.; Jakobsson, J. LINE-2 transposable elements are a source of functional human microRNAs and target sites. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rfam. Family: Mir-708 (RF00917). Available online: https://rfam.org/family/RF00917 (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Li, J.L.; Li, K.Z.; Xie, M.Z.; Tang, Y.P.; Tang, Y.L.; Hu, B. Clinical Significance and Prognostic Value of miR-28-5p in Colon Cancer. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 3159831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, X.; Wu, G. Strand-specific miR-28-3p and miR-28-5p have differential effects on nasopharyngeal cancer cells proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Wei, D.; Yu, F.; Sun, J. circAGFG1 sponges miR-28-5p to promote non-small-cell lung cancer progression through modulating HIF-1α level. Open Med. 2021, 16, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, N.J.; Lutz, C.S. miR-708-5p: A microRNA with emerging roles in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 71292–71316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Guo, H.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, J. MiR-708-5p inhibits the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting Sirt3. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Nie, R.; Liu, M.; Zhang, X. A Novel Strategy for Identifying NSCLC MicroRNA Biomarkers and Their Mechanism Analysis Based on a Brand-New CeRNA-Hub-FFL Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzara, S.; Rossi, R.L.; Grifantini, R.; Donizetti, S.; Abrignani, S.; Bombaci, M. CombiROC: An interactive web tool for selecting accurate marker combinations of omics data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, A.; Tang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Teschendorff, A.E. dbDEMC 2.0: Updated database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, D812–D818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanker, M.; Willcutts, D.; Roth, J.A.; Ramesh, R. Drug resistance in lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2010, 1, 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zimta, A.A.; Cenariu, D.; Irimie, A.; Magdo, L.; Nabavi, S.M.; Atanasov, A.G.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The Role of Nrf2 Activity in Cancer Development and Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulei, D.; Raduly, L.; Broseghini, E.; Ferracin, M.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The extensive role of miR-155 in malignant and non-malignant diseases. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 70, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braicu, C.; Gulei, D.; Cojocneanu, R.; Raduly, L.; Jurj, A.; Knutsen, E.; Calin, G.A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. miR-181a/b therapy in lung cancer: Reality or myth? Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, R.; Niu, W.; Tang, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X. Integrating microRNA expression, miRNA-mRNA regulation network and signal pathway: A novel strategy for lung cancer biomarker discovery. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.S.; Jeon, H.S.; Sun, Z.; Aubry, M.C.; Tang, H.; Park, C.H.; Rakhshan, F.; Schultz, D.A.; Kolbert, C.P.; Lupu, R.; et al. Increased miR-708 expression in NSCLC and its association with poor survival in lung adenocarcinoma from never smokers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3658–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Chen, W.; Shi, P.; Lian, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, K.; Qian, D.; Xiao, D.; Long, H. Silencing of microRNA-708 promotes cell growth and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by activating the SPHK2/AKT/β-catenin pathway in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Guan, W.; Han, S.; Hong, D.-K.; Kim, L.-S.; Kim, H. MicroRNA-708-3p mediates metastasis and chemoresistance through inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteleone, N.J.; Lutz, C.S. miR-708-5p targets oncogenic prostaglandin E2 production to suppress a pro-tumorigenic phenotype in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2464–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stivarou, T.; Patsavoudi, E. Extracellular molecules involved in cancer cell invasion. Cancers 2015, 7, 238–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltavets, V.; Kochetkova, M.; Pitson, S.M.; Samuel, M.S. The Role of the Extracellular Matrix and Its Molecular and Cellular Regulators in Cancer Cell Plasticity. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Miranda, J.; Gallego-Gutiérrez, H.; Cano-Cortina, M.; Amaya, E. Relationship between apical junction proteins, gene expression and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knights, A.J.; Funnell, A.P.; Crossley, M.; Pearson, R.C. Holding Tight: Cell Junctions and Cancer Spread. Trends Cancer Res. 2012, 8, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chae, Y.K.; Choi, W.M.; Bae, W.H.; Anker, J.; Davis, A.A.; Agte, S.; Iams, W.T.; Cruz, M.; Matsangou, M.; Giles, F.J. Overexpression of adhesion molecules and barrier molecules is associated with differential infiltration of immune cells in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Xie, C.; Lu, N. Crosstalk between Hippo signalling and miRNAs in tumour progression. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaousov, S.; Reuter, J.S.; Seetin, M.G.; Mathews, D.H. RNAstructure: Web servers for RNA secondary structure prediction and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W471–W474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Ren, F.; Liu, C.; He, S.; Sun, G.; Gao, Q.; Yao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Miao, R.; Cao, Y.; et al. dbDEMC: A database of differentially expressed miRNAs in human cancers. BMC Genom. 2010, 11 (Suppl. S4), S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X. miRDB: An online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D127–D131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A graphical gene-set enrichment tool for animals and plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastsoglou, S.; Skoufos, G.; Miliotis, M.; Karagkouni, D.; Koutsoukos, I.; Karavangeli, A.; Kardaras, F.S.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v4.0: Expanding target-based miRNA functional analysis in cell-type and tissue contexts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W154–W159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cui, C. TransmiR v3.0: An updated transcription factor-microRNA regulation database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D318–D323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Siklenka, K.; Arora, S.K.; Ribeiro, P.; Kimmins, S.; Xia, J. miRNet—Dissecting miRNA-target interactions and functional associations through network-based visual analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W135–W141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| miRNA ID | Source ID | Cancer Type | Design | logFC | AveExpr | p Value | adj p Value | Expression Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-28-5p | GSE135918 | lung cancer | cancer vs. normal | −0.74 | 0.44 | 0.000417 | 0.00745 | DOWN |
| hsa-miR-28-5p | GSE74190 | lung cancer | cancer vs. normal | 0.55 | 4.91 | 0.000374 | 0.00304 | UP |
| hsa-miR-28-5p | GSE74190 | lung cancer | cancer vs. normal | 0.93 | 4.91 | 0.0000000398 | 0.000000309 | UP |
| hsa-miR-28-5p | TCGA_LUAD | LUAD | cancer vs. normal | 0.25 | 6.68 | 0.00648 | 0.0163 | UP |
| hsa-miR-28-5p | TCGA_LUSC | LUSC | cancer vs. normal | −0.2 | 6.89 | 0.00566 | 0.0287 | DOWN |
| hsa-miR-708-5p | SRP040720 | lung cancer | cancer vs. normal | 1.83 | 5.79 | 0.000630 | 0.00726 | UP |
| hsa-miR-708-5p | TCGA_LUAD | LUAD | cancer vs. normal | 2.53 | 4.57 | 4.66 × 10−29 | 5.96 × 10−28 | UP |
| hsa-miR-708-5p | TCGA_LUSC | LUSC | cancer vs. normal | 3.24 | 6.47 | 2.34 × 10−51 | 2.47 × 10−49 | UP |
| KEGG Pathway | p-Value | #Genes | #miRNAs | Target Genes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ECM–receptor interaction | 4.46 × 10−13 | 8 | 2 | miR-28-5p: AGRN, HSPG2, COL6A2, COL1A1, COL1A2, LAMC1 |
| miR-708-5p: AGRN, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL1A1, LAMC1 | |||||
| 2 | Adherents junction | 1.44 × 10−5 | 12 | 2 | miR-28-5p: ACTB, CTNND1, LMO7, IQGAP1, IGF1R, EGFR, SMAD4, CTNNB1, FARP2, MAPK1 |
| miR-708-5p: SMAD2, IQGAP1, IGF1R, CTNNB1, PVRL1 | |||||
| 3 | Lysine degradation | 3.70 × 10−5 | 7 | 2 | miR-28-5p: WHSC1L1, NSD1, ASH1L, KMT2D, KMT2A, KMT2B |
| miR-708-5p: NSD1, WHSC1, KMT2A | |||||
| 4 | Hippo signaling pathway | 6.01 × 10−5 | 17 | 2 | miR-28-5p: ACTB, YWHAH, YWHAE, BTRC, CCND2, CSNK1D, DLG4, CCND1, SMAD4, CTNNB1, TEAD1, STK3, PPP2CB, PPP2R1B, BMPR2 |
| miR-708-5p: YWHAH, SMAD2, YWHAE, CCND2, BIRC5, CTNNB1, STK3, BMPR2 |
| Characteristics | No. of Patients (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ≤65 | 16 (50) |
| ≥65 | 16 (50) | |
| T | T2 | 4 (12.5) |
| T3 | 9 (28.1) | |
| T4 | 19 (59.4) | |
| N | N0 | 3 (9.4) |
| N1 | 3 (9.4) | |
| N2 | 21 (65.6) | |
| N3 | 5 (15.6) | |
| M | M0 | 18 (56.3) |
| M1 | 14 (43.7) | |
| Stage | III | 19 (59.4) |
| IV | 13 (40.6) | |
| miRNA | Assay Code | miRNA Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| RNU48 | 0001006 | GATGACCCCAGGTAACTCTGAGTGTGTCGCTGATGCCATCACCGCAGCGCTCTGACC |
| U6 | 001973 | GTGCTCGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAATTGGAACGATACAGAGAAGATTAGCATGGCCCCTGCGCAAGGATGACACGCAAATTCGTGAAGCGTTCCATATTTT |
| miR-28-5p | 000411 | AAGGAGCUCACAGUCUAUUGAG |
| miR-708-5p | 002341 | AAGGAGCUUACAAUCUAGCUGGG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciocan, C.A.; Bica, C.; Budisan, L.; Raduly, L.; Chira, S.; Burz, C.-C.; Farc, O.; Harangus, A.; Simon, M.; Busuioc, C.-I.; et al. miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Share a Common Seed with Different Functions in Lung Cancer Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110364
Ciocan CA, Bica C, Budisan L, Raduly L, Chira S, Burz C-C, Farc O, Harangus A, Simon M, Busuioc C-I, et al. miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Share a Common Seed with Different Functions in Lung Cancer Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110364
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiocan, Cristina Alexandra, Cecilia Bica, Liviuta Budisan, Lajos Raduly, Sergiu Chira, Claudia-Cristina Burz, Ovidiu Farc, Antonia Harangus, Marioara Simon, Constantin-Ioan Busuioc, and et al. 2025. "miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Share a Common Seed with Different Functions in Lung Cancer Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110364
APA StyleCiocan, C. A., Bica, C., Budisan, L., Raduly, L., Chira, S., Burz, C.-C., Farc, O., Harangus, A., Simon, M., Busuioc, C.-I., Strilciuc, S., Braicu, C., & Berindan-Neagoe, I. (2025). miR-28-5p and miR-708-5p Share a Common Seed with Different Functions in Lung Cancer Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10364. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110364








