Molecular Mimicry Between Toxoplasma gondii B-Cell Epitopes and Human Antigens Related to Schizophrenia: An In Silico Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Autoantigen Analysis
4.2. Modeling Based on Homology
4.3. Epitope Prediction
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ENO2 | Gamma-enolase |
| TPO | Thyroid peroxidase |
| GAD65 | Glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 kDa isoform |
| VRK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 2 |
| DPYP | Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase [NADP(+)] |
| Da | Daltons |
| NADP | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| RMSD | Root Mean Square Deviation index |
References
- Saha, S.; Chant, D.; Welham, J.; McGrath, J. A Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Schizophrenia. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhar, S.; Johnstone, M.; McKenna, P.J. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2022, 399, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radua, J.; Ramella-Cravaro, V.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Reichenberg, A.; Phiphopthatsanee, N.; Amir, T.; Thoo, H.Y.; Oliver, D.; Davies, C.; Morgan, C.; et al. What causes psychosis? An umbrella review of risk and protective factors. World Psychiatry 2018, 17, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Leemput, J.; Hess, J.L.; Glatt, S.J.; Tsuang, M.T. Genetics of Schizophrenia. Adv. Genet. 2016, 96, 99–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Prandovszky, E.; Kannan, G.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Dickerson, F.; Severance, E.G.; Yolken, R.H. Toxoplasma gondii: Biological Parameters of the Connection to Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, K.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Zipp, F. Immunoneuropsychiatry—Novel perspectives on brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolken, R.H.; Torrey, E.F. Are some cases of psychosis caused by microbial agents? A review of the evidence. Mol. Psychiatry 2008, 13, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blomström, Å.; Gardner, R.M.; Dalman, C.; Yolken, R.H.; Karlsson, H. Influence of maternal infections on neonatal acute phase proteins and their interaction in the development of non-affective psychosis. Transl. Psychiatry 2015, 5, e502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrey, E.F.; Bartko, J.J.; Lun, Z.-R.; Yolken, R.H. Antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii in Patients With Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 2007, 33, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.P.; Kaushik, M.; Bristow, G.C.; McConkey, G.A. Toxoplasma gondii infection, from predation to schizophrenia: Can animal behaviour help us understand human behaviour? J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 216, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirotte, C.; Kappeler, P.M.; Ngoubangoye, B.; Bourgeois, S.; Moussodji, M.; Charpentier, M.J.E. Morbid attraction to leopard urine in Toxoplasma-infected chimpanzees. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R98–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, Y.; Gressitt, K.L.; He, H.; Kannan, G.; Schultz, T.L.; Svezhova, N.; Carruthers, V.B.; Pletnikov, M.V.; Yolken, R.H.; et al. Cerebral complement C1q activation in chronic Toxoplasma infection. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 58, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedland, R.P. Mechanisms of Molecular Mimicry Involving the Microbiota in Neurodegeneration. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2015, 45, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westall, F.C. Molecular Mimicry Revisited: Gut Bacteria and Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Múnera, M.; Farak, J.; Pérez, M.; Rojas, J.; Villero, J.; Sánchez, A.; Sánchez, J.; Emiliani, Y. Prediction of molecular mimicry between antigens from Leishmania sp. and human: Implications for autoimmune response in systemic lupus erythematosus. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 148, 104444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, Y.; Garces, J.; Díaz, R.; Escobar, M.; Sanchez, A.; Buendía, E.; Múnera, M. Molecular mimicry among human proteinase 3 and bacterial antigens: Implications for development of c-ANCA associated vasculitis. Oxf. Open Immunol. 2022, 3, iqac009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, C.; Tao, H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Altered Expression of Glucocorticoid Receptor and Neuron-Specific Enolase mRNA in Peripheral Blood in First-Episode Schizophrenia and Chronic Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, J.; Schiltz, K.; Stoecker, W.; Teegen, B.; Dobrowolny, H.; Meyer-Lotz, G.; Pennewitz, M.; Borucki, K.; Frodl, T.; Bernstein, H.G. Association of thyroid peroxidase antibodies with anti-neuronal surface antibodies in health, depression and schizophrenia–Complementary linkage with somatic symptoms of major depression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 90, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, N.; Bartels, C.; Teegen, B.; Wiltfang, J.; Malchow, B. Catatonic Schizophrenia Associated With Cerebrospinal GAD65 Autoantibodies: Case Report and Literature Review. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 829058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, R.; St Clair, D.; Mustard, C.J.; Hallford, P.; Wei, J. Study of Novel Autoantibodies in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 2018, 44, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severance, E.G.; Yolken, R.H. Role of Immune and Autoimmune Dysfunction in Schizophrenia. Handb. Behav. Neurosci. 2016, 23, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Melamud, M.M.; Buneva, V.N.; Ivanova, S.A. Immune System Abnormalities in Schizophrenia: An Integrative View and Translational Perspectives. Front Psychiatry 2022, 13, 880568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G.; Gianniki, M.; Ai-Nhi Truong, A.; Montoya, J.G. Toxoplasmosis and Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence and Associations and Future Directions. Psychiatr. Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 4, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oncu-Oner, T.; Can, S. Meta-analysis of the relationship between Toxoplasma gondii and schizophrenia. Ann. Parasitol. 2022, 68, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, A.; Polcyn, R.; Matzelle, D.; Banik, N.L. New Insights into the Role of Neuron-Specific Enolase in Neuro-Inflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Neuroprotection. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polcyn, R.; Capone, M.; Hossain, A.; Matzelle, D.; Banik, N.L.; Haque, A. Neuron specific enolase is a potential target for regulating neuronal cell survival and death: Implications in neurodegeneration and regeneration. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 4, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Hernández, V.; Ramos-Loyo, J.; Luquin, S.; Sánchez, L.F.C.; García-Estrada, J.; Navarro-Ruiz, A. Increased lipid peroxidation and neuron specific enolase in treatment refractory schizophrenics. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2007, 41, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaper, D.; Prabha, V. Molecular Mimicry: Unravelling the Role of Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Diseases and Infertility. In Biomedical Translational Research; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, A.G.; Limacher, A.; Flückiger, S.; Scheynius, A.; Scapozza, L.; Crameri, R. Analysis of the cross-reactivity and of the 1.5 Å crystal structure of the Malassezia sympodialis Mala s 6 allergen, a member of the cyclophilin pan-allergen family. Biochem. J. 2006, 396, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Saiz, A.; Dalmau, J. GAD antibodies in neurological disorders—Insights and challenges. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bembenek, B.M.; Largiadèr, C.R.; Offer, S.M. Review of Neurologic and Developmental Conditions Associated with Pediatric Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase Deficiency. Adv. Mol. Pathol. 2024, 7, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahata, N.; Kasai, K.; Kawato, M. Computational neuroscience approach to biomarkers and treatments for mental disorders. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 71, 215–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Jin, M.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Jia, N.; Cui, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, G.; Yu, Q. Identification of potential biomarkers and their correlation with immune infiltration cells in schizophrenia using combinative bioinformatics strategy. Psychiatry Res. 2022, 314, 114658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, G.K.; Ramadan, H.K.A.; Elbeh, K.; Haridy, N.A. The role of infections and inflammation in schizophrenia: Review of the evidence. Middle East Curr. Psychiatry 2024, 31, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, M.T.; Heinlen, L.D.; Dennis, G.J.; Roebuck, J.; Harley, J.B.; James, J.A. Early events in lupus humoral autoimmunity suggest initiation through molecular mimicry. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujinami, R.S.; von Herrath, M.G.; Christen, U.; Whitton, J.L. Molecular Mimicry, Bystander Activation, or Viral Persistence: Infections and Autoimmune Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.; Mateen, W.; Khurshid, S.; Malik, J.M.; Agha, Z.; Khan, F.; Ajmal, M.; Ali, S.H.B. A common missense variant rs874881 of PADI4 gene and rheumatoid arthritis: Genetic association study and in-silico analysis. Gene 2023, 854, 147123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Wang, Y.; Duan, T.; Patel, J.; Liggett, T.; Loda, E.; Brahma, S.; Goswami, R.; Grouse, C.; Byrne, R.; et al. Cross-Immunoreactivity between Bacterial Aquaporin-Z and Human Aquaporin-4: Potential Relevance to Neuromyelitis Optica. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 4602–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.J.P.; Parmley, S.F.; Tomavo, S. Evidence for nuclear localisation of two stage-specific isoenzymes of enolase in Toxoplasma gondii correlates with active parasite replication. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1399–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Escobar, M.; Schares, G.; Maksimov, P.; Joeres, M.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Calero-Bernal, R. Toxoplasma gondii Genotyping: A Closer Look Into Europe. Front. Cell. Infect Microbiol. 2022, 12, 842595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Farrell, A.; Niedelman, W.; Melo, M.; Lu, D.; Julien, L.; Marth, G.T.; Gubbels, M.J.; Saeij, J.P. Genetic basis for phenotypic differences between different Toxoplasma gondii type I strains. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanderlugt, C.L.; Miller, S.D. Epitope spreading in immune-mediated diseases: Implications for immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Zhang, P.; LaBaer, J.; Hermjakob, H.; Li, D.; Yu, X. AAgAtlas 1.0: A human autoantigen database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D769–D776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, W.R. An Introduction to Sequence Similarity (“Homology”) Searching. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2013, 42, 3.1.1–3.1.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Bittrich, S.; Chen, L.; Crichlow, G.V.; Christie, C.H.; Dalenberg, K.; Di Costanzo, L.; Duarte, J.M.; et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: Powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D437–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooers, B.H.M. Simplifying and enhancing the use of PyMOL with horizontal scripts. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
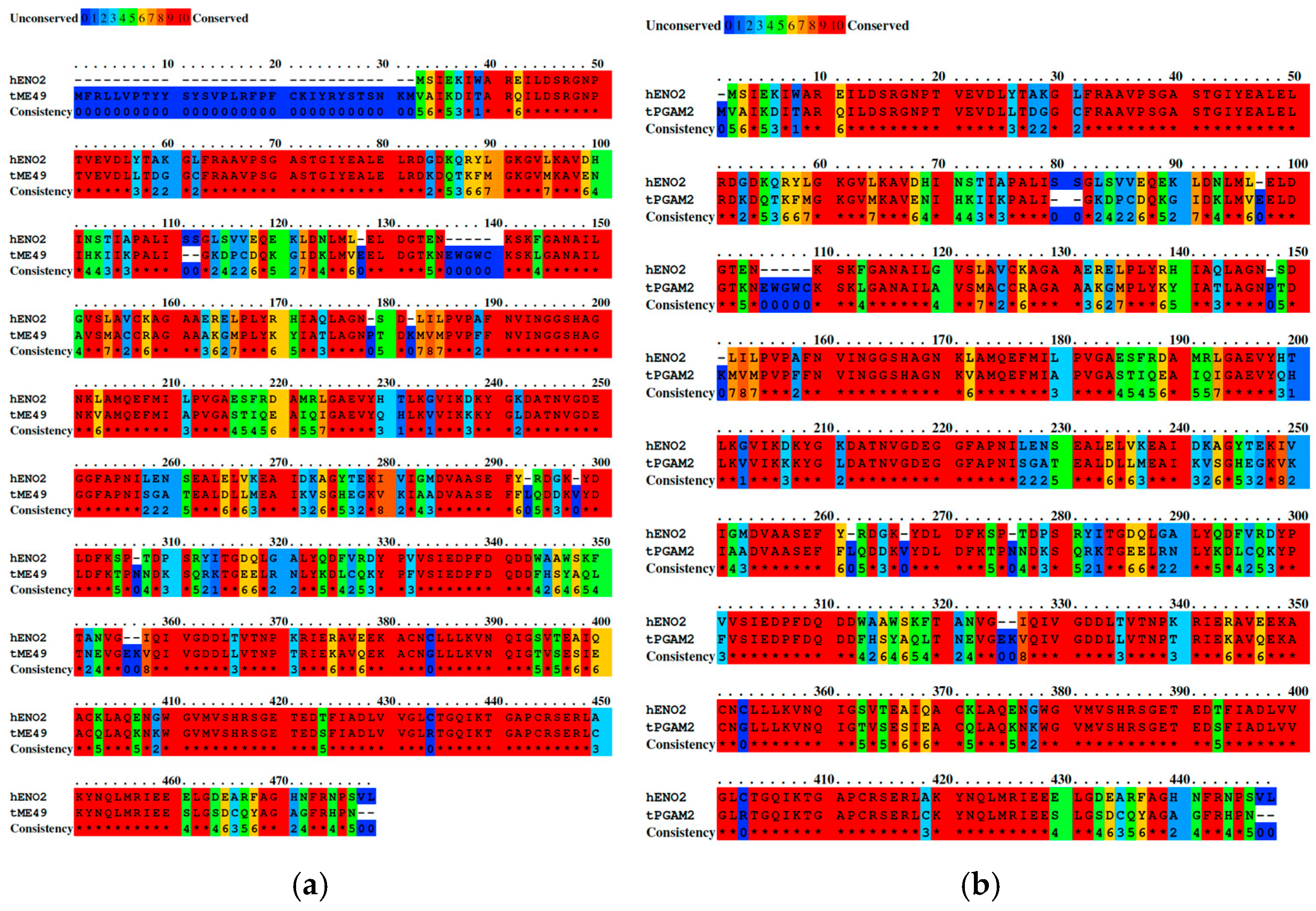
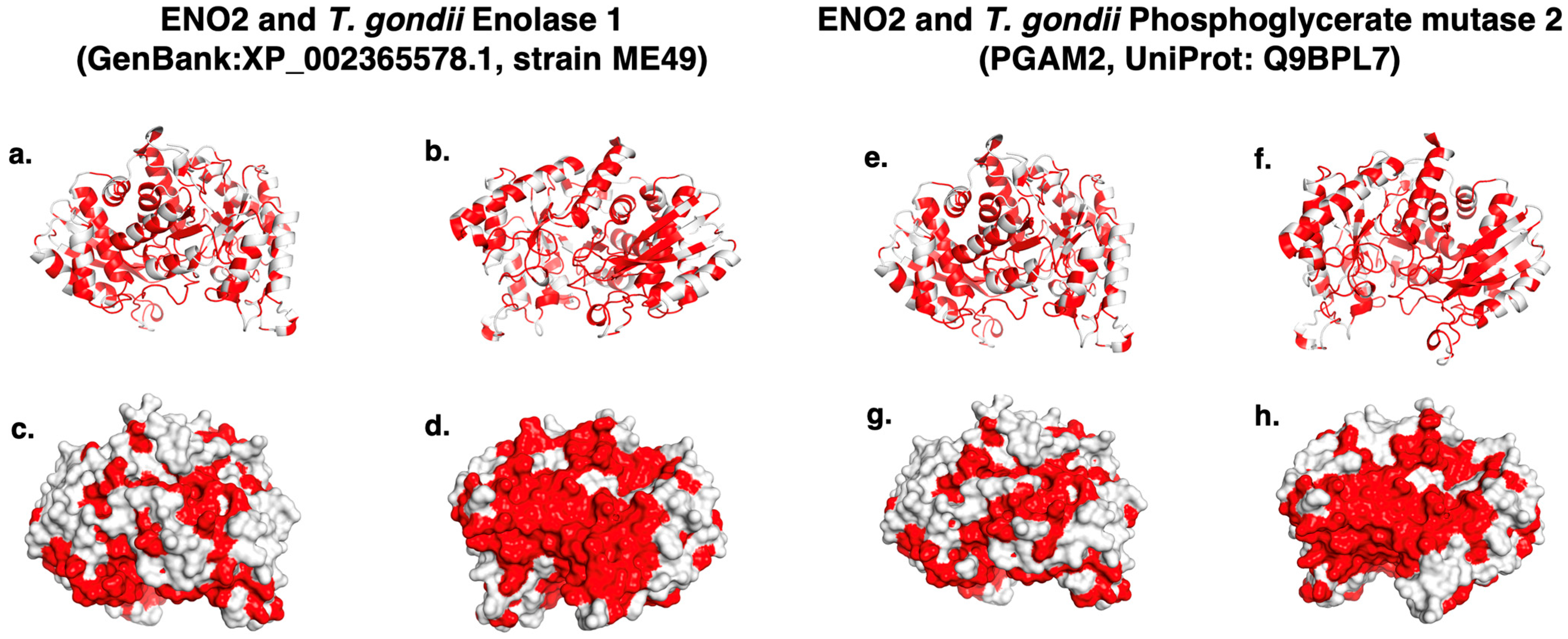
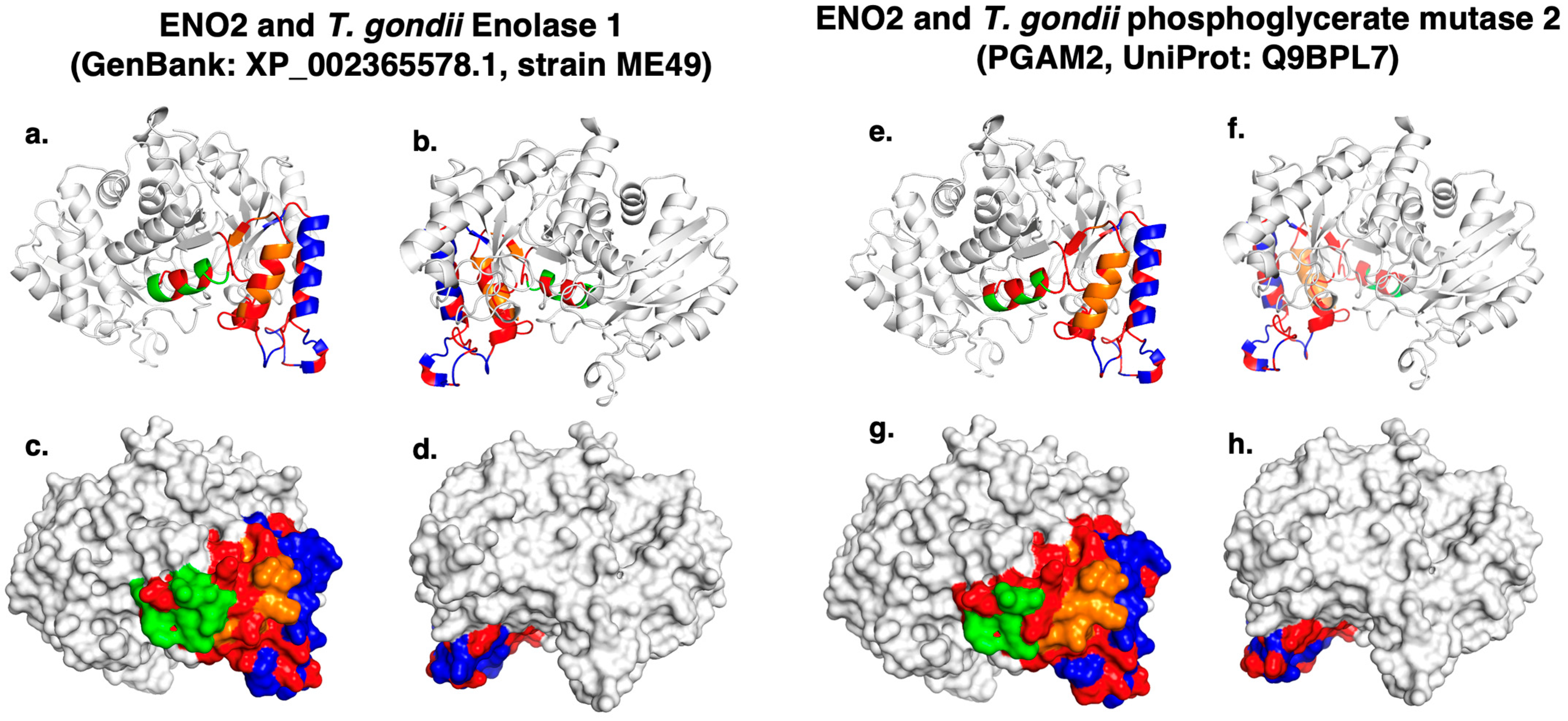
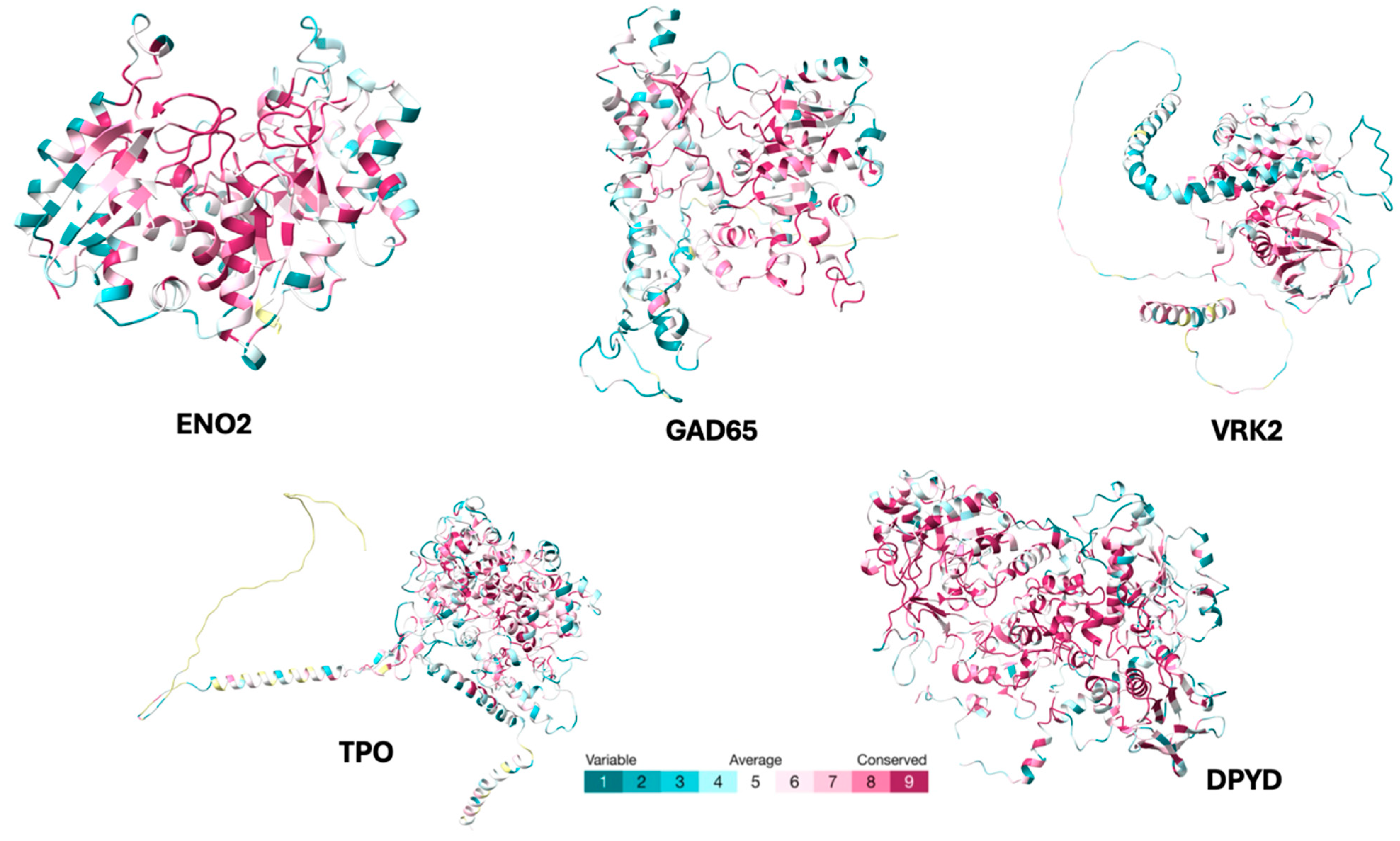
| Autoantigen | Accession | Amino Acids | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENO2 | P09104 | 434 | Liu et al. [18] |
| TPO | P07202 | 933 | Steiner J et al. [19] |
| GAD65 | Q05329 | 585 | Hansen N et al. [20] |
| VRK2 | Q86Y07 | 324 | Whelan R et al. [21] |
| DPYD | Q12882 | 1025 | Whelan R et al. [21] |
| Autoantigen | Nº Epitope | Epitope | T. gondii Protein (Strain) | Accession | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENO2 | 1 | ASEFYRDGKYDLDFKSPTDPSRYITGDQLGA-LYQDFVRDYPVV | Phosphoglycerate mutase 2 (PGAM2, strain ME49) | Q9BPL7 | 68 |
| 2 | TNPKRIERA-VEEKACN | Enolase 1 (strain ME49) | XP_002365578 | 68 | |
| 3 | DPFDQDD-WAAW-SKFTANVGIQI | Enolase 2 (strain ME49) | XP_002365579 | 66 | |
| TPO | 1 | ESVTDHVN-LITPLEKPLQN | Calcium-binding EGF domain-containing protein (strain FOU) | KFG44949 | 29 |
| 2 | TPLPA-NILDWQALN-YEIRGYVII | Calcium-binding EGF domain-containing protein (strain TgCatPRC2) | KYK67774 | 29 | |
| 3 | LRQGYFVEAQPKIV | Calcium-binding EGF domain-containing protein (strain RUB) | KFG63764 | 27 | |
| 4 | QEQDSYGGKFDR | Calcium-binding EGF domain-containing protein (strain VEG) | CEL74380 | 23 | |
| GAD65 | 1 | RFKMFPEV-KEKGMAALPR-LI | Protein kinase (incomplete catalytic triad, strain ME49) | XP_018637623.1 | 37 |
| 2 | WYIPPSLRTLEERMSRLSKVA-PVIKAR | Putative helicase (partial, strain ME49) | PUA92631.1 | 28 | |
| VRK2 | 1 | YCPNGNHKQYQENPRKGHN | Casein kinase (strain CAST) | RQX72942 | 28 |
| 2 | NPHGI-PLGPLDFSTKGQ | Casein kinase (strain COUG) | PIM01748 | 27 | |
| 3 | YLAFPTNKPEKDAR | Casein kinase (strain VEG) | CEL78736 | 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cano, J.F.; Bernal-Valencia, M.A.; Vargas-Acevedo, P.; Mejía-Salgado, G.; Sánchez, A.; Correa-Jiménez, O.; Múnera, M.; de-la-Torre, A. Molecular Mimicry Between Toxoplasma gondii B-Cell Epitopes and Human Antigens Related to Schizophrenia: An In Silico Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110321
Cano JF, Bernal-Valencia MA, Vargas-Acevedo P, Mejía-Salgado G, Sánchez A, Correa-Jiménez O, Múnera M, de-la-Torre A. Molecular Mimicry Between Toxoplasma gondii B-Cell Epitopes and Human Antigens Related to Schizophrenia: An In Silico Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110321
Chicago/Turabian StyleCano, Juan F., Maria Andrea Bernal-Valencia, Pablo Vargas-Acevedo, Germán Mejía-Salgado, Andrés Sánchez, Oscar Correa-Jiménez, Marlon Múnera, and Alejandra de-la-Torre. 2025. "Molecular Mimicry Between Toxoplasma gondii B-Cell Epitopes and Human Antigens Related to Schizophrenia: An In Silico Approach" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110321
APA StyleCano, J. F., Bernal-Valencia, M. A., Vargas-Acevedo, P., Mejía-Salgado, G., Sánchez, A., Correa-Jiménez, O., Múnera, M., & de-la-Torre, A. (2025). Molecular Mimicry Between Toxoplasma gondii B-Cell Epitopes and Human Antigens Related to Schizophrenia: An In Silico Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110321







