Association of NOS Gene Polymorphisms with Sepsis-Related Complications in Secondary Peritonitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Group
2.2. Allele and Genotype Frequencies
2.3. Associations of NOS Genotypes with In-Hospital Mortality and Severe Complications
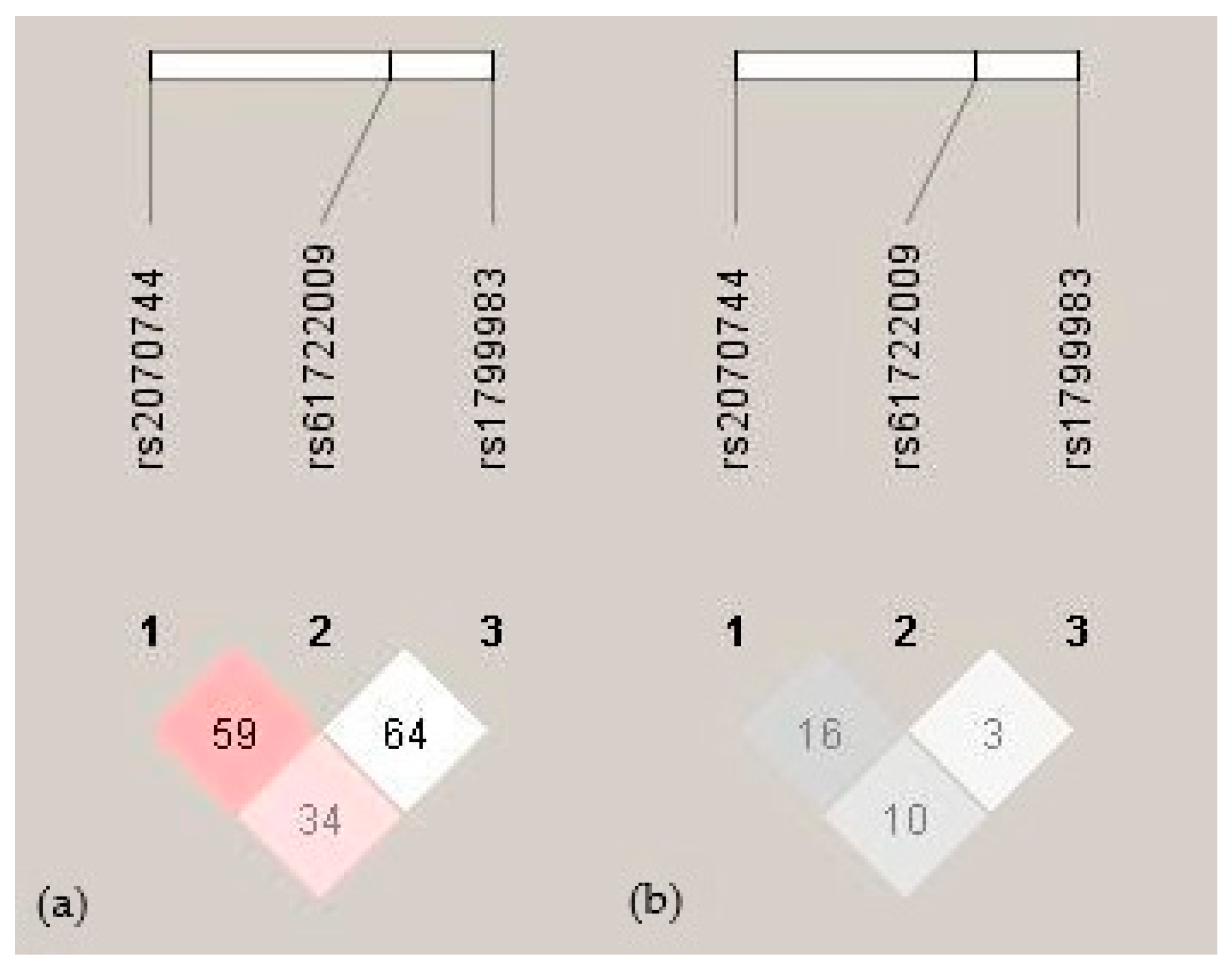
2.4. Haplotype Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
4.2.1. NOS3 Genotyping
4.2.2. NOS2 Genotyping
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ross, J.T.; Matthay, M.A.; Harris, H.W. Secondary Peritonitis: Principles of Diagnosis and Intervention. BMJ 2018, 361, k1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitrascu, C.O.; Gherghe, M.; Costache, M.; Cretu, B.; Cirstoiu, C. The Role of Serum and Peritoneal Biomarkers in Predicting Sepsis and Septic Multiorgan Failure in Patients with Secondary Peritonitis. Cureus 2023, 15, e41724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, T.W.; Tolonen, M.; Ball, C.G.; Kirkpatrick, A.W. Secondary Peritonitis and Intra-Abdominal Sepsis: An Increasingly Global Disease in Search of Better Systemic Therapies. Scand. J. Surg. 2021, 110, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Via, L.; Sangiorgio, G.; Stefani, S.; Marino, A.; Nunnari, G.; Cocuzza, S.; La Mantia, I.; Cacopardo, B.; Stracquadanio, S.; Spampinato, S.; et al. The Global Burden of Sepsis and Septic Shock. Epidemiologia 2024, 5, 456–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA—J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, V.L.; Ercisli, M.F.; Rogobete, A.F.; Boia, E.S.; Horhat, R.; Nitu, R.; Diaconu, M.M.; Pirtea, L.; Ciuca, I.; Horhat, D.; et al. Early Prediction of Sepsis Incidence in Critically Ill Patients Using Specific Genetic Polymorphisms. Biochem. Genet. 2017, 55, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Maca-Meyer, N.; Pérez-Méndez, L.; Flores, C. Bench-to-Bedside Review: Understanding Genetic Predisposition to Sepsis. Crit. Care 2004, 8, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Winkler, M.S.; Kluge, S.; Holzmann, M.; Moritz, E.; Robbe, L.; Bauer, A.; Zahrte, C.; Priefler, M.; Schwedhelm, E.; Böger, R.H.; et al. Markers of Nitric Oxide Are Associated with Sepsis Severity: An Observational Study. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.; Asensi, V.; Montes, A.H.; Collazos, J.; Alvarez, V.; Pérez-Is, L.; Carton, J.A.; Taboada, F.; Valle-Garay, E. Endothelial (NOS3 E298D) and Inducible (NOS2 Exon 22) Nitric Oxide Synthase Polymorphisms, as Well as Plasma NOx, Influence Sepsis Development. Nitric Oxide—Biol. Chem. 2014, 42, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, M.; Günay, N.; Sener, E.F.; Karcıoglu, Ö.; Tahtasakal, R.; Dal, F.; Günay, N.E.; Demiryürek, A.T. Variants in TNF and NOS3 (ENOS) Genes Associated with Sepsis in Adult Patients. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambden, S. Bench to Bedside Review: Therapeutic Modulation of Nitric Oxide in Sepsis—An Update. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2019, 7, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, K.; Yue, M.; Lu, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Y.; Li, P.; Yu, L.; Cai, M.; et al. A Non-Synonymous SNP in the NOS2 Associated with Septic Shock in Patients with Sepsis in Chinese Populations. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raia, L.; Zafrani, L. Endothelial Activation and Microcirculatory Disorders in Sepsis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 907992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vera, S.; Martinez, R.; Gormaz, J.G.; Gajardo, A.; Galleguillos, F.; Rodrigo, R. Novel Relationships between Oxidative Stress and Angiogenesis-Related Factors in Sepsis: New Biomarkers and Therapies. Ann. Med. 2015, 47, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S.; Cox, N.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Hindorff, L.A.; Hunter, D.J.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ramos, E.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Chakravarti, A.; et al. Finding the Missing Heritability of Complex Diseases. Nature 2009, 461, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnello, L.; Ciaccio, M. Biomarkers of Sepsis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierrakos, C.; Vincent, J.L. Sepsis Biomarkers: A Review. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póvoa, P.; Coelho, L.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Ferrer, R.; Huttner, A.; Conway Morris, A.; Nobre, V.; Ramirez, P.; Rouze, A.; Salluh, J.; et al. How to Use Biomarkers of Infection or Sepsis at the Bedside: Guide to Clinicians. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Lacchini, R.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase: From Biochemistry and Gene Structure to Clinical Implications of NOS3 Polymorphisms. Gene 2016, 575, 584–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukada, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Arai, T.; Takemoto, F.; Hara, S.; Yamada, A.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Hosoya, T.; Igari, J. Evidence of Association of the EcNOS Gene Polymorphism with Plasma NO Metabolite Levels in Humans. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 245, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensi, V.; Montes, A.H.; Valle, E.; Ocaña, M.G.; Astudillo, A.; Alvarez, V.; López-Anglada, E.; Solís, A.; Coto, E.; Meana, A.; et al. The NOS3 (27-Bp Repeat, Intron 4) Polymorphism Is Associated with Susceptibility to Osteomyelitis. Nitric Oxide—Biol. Chem. 2007, 16, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Zhu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase 894G→T but Not -786T→C Gene Polymorphism Is Associated with Organ Dysfunction and Increased Mortality in Patients with Severe Sepsis. J. Trauma—Inj. Infect. Crit. Care 2011, 71, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, R.; Hurme, M.; Laine, J.; Eklund, C.; Vuento, R.; Aittoniemi, J.; Huhtala, H.; Syrjänen, J. Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase G894T (GLU298ASP) Polymorphism Is Associated with Hypotension in Patients with E. Coli Bacteremia but Not in Bacteremia Caused by a Gram-Positive Organism. Shock 2009, 31, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, M.C.; Martinez, A.; Mendoza, J.L.; Taxonera, C.; Díaz-Rubio, M.; Fernández-Arquero, M.; De La Concha, E.G.; Urcelay, E. Influence of the Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Gene (NOS2A) on Inflammatory Bowel Disease Susceptibility. Immunogenetics 2007, 59, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S.S.; Mastropaolo, L.A.; Murchie, R.; Griffiths, C.; Thöni, C.; Elkadri, A.; Xu, W.; Mack, A.; Walters, T.; Guo, C.; et al. Higher Activity of the Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Contributes to Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2014, 5, e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Lee, Y.; Kellum, J.A. A New Perspective on NO Pathway in Sepsis and ADMA Lowering as a Potential Therapeutic Approach. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, C.; Módis, K.; Oláh, G.; Brunyánszki, A.; Herzig, D.S.; Sherwood, E.R.; Ungvári, Z.; Szabo, C. Endothelial Dysfunction Is a Potential Contributor to Multiple Organ Failure and Mortality in Aged Mice Subjected to Septic Shock: Preclinical Studies in a Murine Model of Cecal Ligation and Puncture. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.; McLoughlin, R.M.; Brodovitch, A.; Moulin, P.; Brouckaert, P.; Casadei, B.; Feron, O.; Topley, N.; Balligand, J.L.; Devuyst, O. Nitric Oxide Synthase Isoforms Play Distinct Roles during Acute Peritonitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Beckman, J.S.; Liaudet, L. Nitric Oxide and Peroxynitrite in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 315–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, F.; Oliveira Formiga, R.; Fernandes da Silva Coimbra, J.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Cunha, F.Q. Targeting Nitric Oxide as a Key Modulator of Sepsis, Arthritis and Pain. Nitric Oxide—Biol. Chem. 2019, 89, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srdić, T.; Đurašević, S.; Lakić, I.; Ružičić, A.; Vujović, P.; Jevđović, T.; Dakić, T.; Đorđević, J.; Tosti, T.; Glumac, S.; et al. From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Therapy: Understanding Sepsis-Induced Multiple Organ Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Cinel, I. Bench-to-Bedside Review: Nitric Oxide in Critical Illness—Update 2008. Crit. Care 2009, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.H.; Chen, M.H.; Han, F.; Li, Q.; Sun, R.H.; Tu, Y.X. Prognostic Value of the Biomarkers Serum Amyloid A and Nitric Oxide in Patients with Sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 62, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, M.; Mi, B.; Liu, L.; Ma, H.; Jiang, C. Genetic Polymorphisms, Biomarkers and Signaling Pathways Associated with Septic Shock: From Diagnosis to Therapeutic Targets. Burn. Trauma 2024, 12, tkae006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, I.F.; Sertório, J.T.C.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Modulation of Nitric Oxide Formation by Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Gene Haplotypes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, D.; Assreuy, J. Nitric Oxide and Vascular Reactivity in Sepsis. Shock 2008, 30, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Förstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric Oxide Synthases: Regulation and Function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koperna, T. Risk Stratification in Emergency Surgical Patients. Arch. Surg. 2001, 136, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.L.; Ramsay, G. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Intensive Care Med. 2003, 29, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamone, G.; Licari, L.; Falco, N.; Augello, G.; Tutino, R.; Campanella, S.; Guercio, G.; Gulotta, G. Mannheim Peritonitis Index (MPI) and Elderly Population: Prognostic Evaluation in Acute Secondary Peritonitis. G. Chir.—J. Surg. 2016, 27, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.A.; Dykes, D.D.; Polesky, H.F. A Simple Salting out Procedure for Extracting DNA from Human Nucleated Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbocation Corporation False Discovery Rate Online Calculator. Available online: https://tools.carbocation.com/FDR (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and Visualization of LD and Haplotype Maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SNP (rsID) | Location/Type | Reported Functional Effect | Reported Clinical Associations |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOS3 c.-786T>C (rs2070744) | Promoter region | The C allele reduces NOS3 promoter activity and NO synthesis [19]. | Hypertension, endothelial dysfunction, and sepsis [10,19]. |
| NOS3 27 bp VNTR (rs61722009) | Intron 4 | The 4a allele is associated with lower NOS3 expression and plasma NO levels [20]. | Osteomyelitis, hypertension disorders, and obesity [19,21]. |
| NOS3 c.894G>T (rs1799983) | Exon 7, missense variant | The T allele causes eNOS protein instability and reduced NO bioavailability [19]. | Sepsis, hypotension, and cardiovascular risk [9,22,23]. |
| NOS2 c.1823C>T (rs2297518) | Exon 16, missense variant | The T allele may increase iNOS activity and NO production [12]. | Sepsis, septic shock, and inflammatory diseases [12,24,25] |
| Variable | Patients, n (%)/ ± SD | |
|---|---|---|
| Total cases | 202 | |
| Age, years | 56.83 ± 17.7 | |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 111 (55.0) | |
| Female | 91 (45.0) | |
| APACHE II score | 10.63 ± 7.23 | |
| MPI | 20.30 ± 7.46 | |
| Length of ICU stay, days | 2.93 ± 9.35 | |
| Source of peritonitis, n (%) | ||
| Upper gastrointestinal perforation | 42 (21.65) | |
| Small bowel perforation | 48 (24.74) | |
| Large bowel perforation | 21 (10.82) | |
| Appendiceal perforation | 65 (33.51) | |
| Gynecological peritonitis | 2 (1.03) | |
| Biliary peritonitis | 16 (8.25) | |
| Type of peritonitis, n (%) | ||
| Purulent | 155 (80.73) | |
| Stercoral | 23 (11.98) | |
| Biliary | 14 (7.29) | |
| WBC, 109/L | 14.2 ± 7.0 | |
| Neutrophils, % | 84.30 ± 11.75 | |
| PLT, 109/L | 277.33 ± 105.17 | |
| Urea, mmol/L | 8.55 ± 7.16 | |
| Creatinine, µmol/L | 114.02 ± 83.80 | |
| Bilirubin, µmol/L | 18.63 ± 23.75 | |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 168.04 ± 150.71 | |
| SNP (rsID) | Genotype/Allele | Frequency (n, %) |
|---|---|---|
| NOS3 c.-786T>C (rs2070744) | TT | 91 (45.0) |
| TC | 95 (47.0) | |
| CC | 16 (7.9) | |
| T | 0.69 | |
| C | 0.31 | |
| NOS3 27 bp VNTR (rs61722009) | 4b/4b | 136 (67.3) |
| 4a/4b | 62 (30.7) | |
| 4a/4a | 4 (2.0) | |
| 4b | 0.83 | |
| 4a | 0.17 | |
| NOS3 c.894G>T (rs1799983) | GG | 105 (52.0) |
| GT | 80 (39.6) | |
| TT | 17 (8.4) | |
| G | 0.72 | |
| T | 0.28 | |
| NOS2 c.1823C>T (rs2297518) | GG | 119 (58.9) |
| GA | 68 (33.7) | |
| AA | 15 (7.4) | |
| G | 0.76 | |
| A | 0.24 |
| SNP | Genotype Group | Patients, n (%) | Survived, n (%) | Died, n (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOS3 c.-786T>C | TT | 91 (45.0) | 75 (82.4) | 16 (17.6) | 0.700 |
| TC + CC | 111 (55.0) | 101 (91.0) | 10 (9.0) | ||
| NOS3 27 bp VNTR | 4b/4b | 136 (67.3) | 116 (85.3) | 20 (14.7) | 0.264 |
| 4a/4b + 4a/4a | 66 (32.7) | 60 (90.9) | 6 (9.1) | ||
| NOS3 c.894G>T | GG | 105 (52.0) | 90 (85.7) | 15 (14.3) | 0.532 |
| GT + TT | 97 (48.0) | 86 (88.7) | 11 (11.3) | ||
| NOS2 c.1823C>T | GG | 119 (58.9) | 101 (84.9) | 18 (15.1) | 0.252 |
| GA + AA | 83 (41.1) | 75 (90.4) | 8 (9.6) |
| SNP | Genotype Group | ARDS, n (%) | p | MODS, n (%) | p | MOF, N (%) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOS3 c.-786T>C | TT | 15 (16.5) | 0.165 | 19 (20.9) | 0.017 * | 18 (19.8) | 0.008 * |
| TC + CC | 11 (9.9) | 10 (9.0) | 8 (7.2) | ||||
| NOS3 27 bp VNTR | 4b/4b | 19 (14.0) | 0.503 | 22 (16.2) | 0.290 | 20 (14.7) | 0.264 |
| 4a/4b + 4a/4a | 7 (10.6) | 7 (10.6) | 6 (9.1) | ||||
| NOS3 c.894G>T | GG | 17 (16.2) | 0.143 | 17 (16.2) | 0.439 | 16 (15.2) | 0.296 |
| GT + TT | 9 (9.3) | 12 (12.4) | 10 (10.3) | ||||
| NOS2 c.1823C>T | GG | 20 (16.8) | 0.046 * | 22 (18.5) | 0.045 * | 17 (14.3) | 0.472 |
| GA + AA | 6 (7.2) | 7 (8.4) | 9 (10.8) |
| Gene | SNP | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) | PCR Conditions | Product Size (bp) | Reaction Enzyme | Genotypes and Restriction Fragments (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOS3 | c.-786T>C | F: CCCAGCAAGGATGTAGTGAC R: GTGTACCCCACCTGCATTCT | Denaturation: 94 °C for 1 min Annealing: 60 °C for 1 min Extension: 72 °C for 1 min | 306 | Pdil or NaeI (37 °C, 1 h) | TT: 306 CT: 306, 225, 81 CC: 225, 81 |
| 27 bp VNTR | F: CTATGGTAGTGCCTTGGCTGGAGG R: ACC GCC CAG GGA ACT CCG CT | 210/183 | / | 4b4b: 210 4b4a: 210, 183 4a4a: 183 | ||
| c.894G>T | F: AAGGCAGGAGACAGTGGATGG R: CCCAGTCAATCCCTTTGGTGC | 248 | MboI (37 °C, 5–15 min) | GG: 248 GT: 248, 158, 90 TT: 158, 90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rasic, M.; Maksimovic, N.; Grk, M.; Dusanovic Pjevic, M.; Rasic, P.; Svircev, M.; Damnjanovic, T.; Perovic, D.; Djuranovic Uklein, A.; Stojanovski, N.; et al. Association of NOS Gene Polymorphisms with Sepsis-Related Complications in Secondary Peritonitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110306
Rasic M, Maksimovic N, Grk M, Dusanovic Pjevic M, Rasic P, Svircev M, Damnjanovic T, Perovic D, Djuranovic Uklein A, Stojanovski N, et al. Association of NOS Gene Polymorphisms with Sepsis-Related Complications in Secondary Peritonitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110306
Chicago/Turabian StyleRasic, Milica, Nela Maksimovic, Milka Grk, Marija Dusanovic Pjevic, Petar Rasic, Milos Svircev, Tatjana Damnjanovic, Dijana Perovic, Ana Djuranovic Uklein, Natasa Stojanovski, and et al. 2025. "Association of NOS Gene Polymorphisms with Sepsis-Related Complications in Secondary Peritonitis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110306
APA StyleRasic, M., Maksimovic, N., Grk, M., Dusanovic Pjevic, M., Rasic, P., Svircev, M., Damnjanovic, T., Perovic, D., Djuranovic Uklein, A., Stojanovski, N., Pesic, M., Novakovic, I., & Doklestic Vasiljev, K. (2025). Association of NOS Gene Polymorphisms with Sepsis-Related Complications in Secondary Peritonitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10306. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110306





