Stabilization of G-Quadruplexes Modulates the Expression of DNA Damage and Unfolded Protein Response Genes in Canine Lymphoma/Leukemia Cells
Abstract
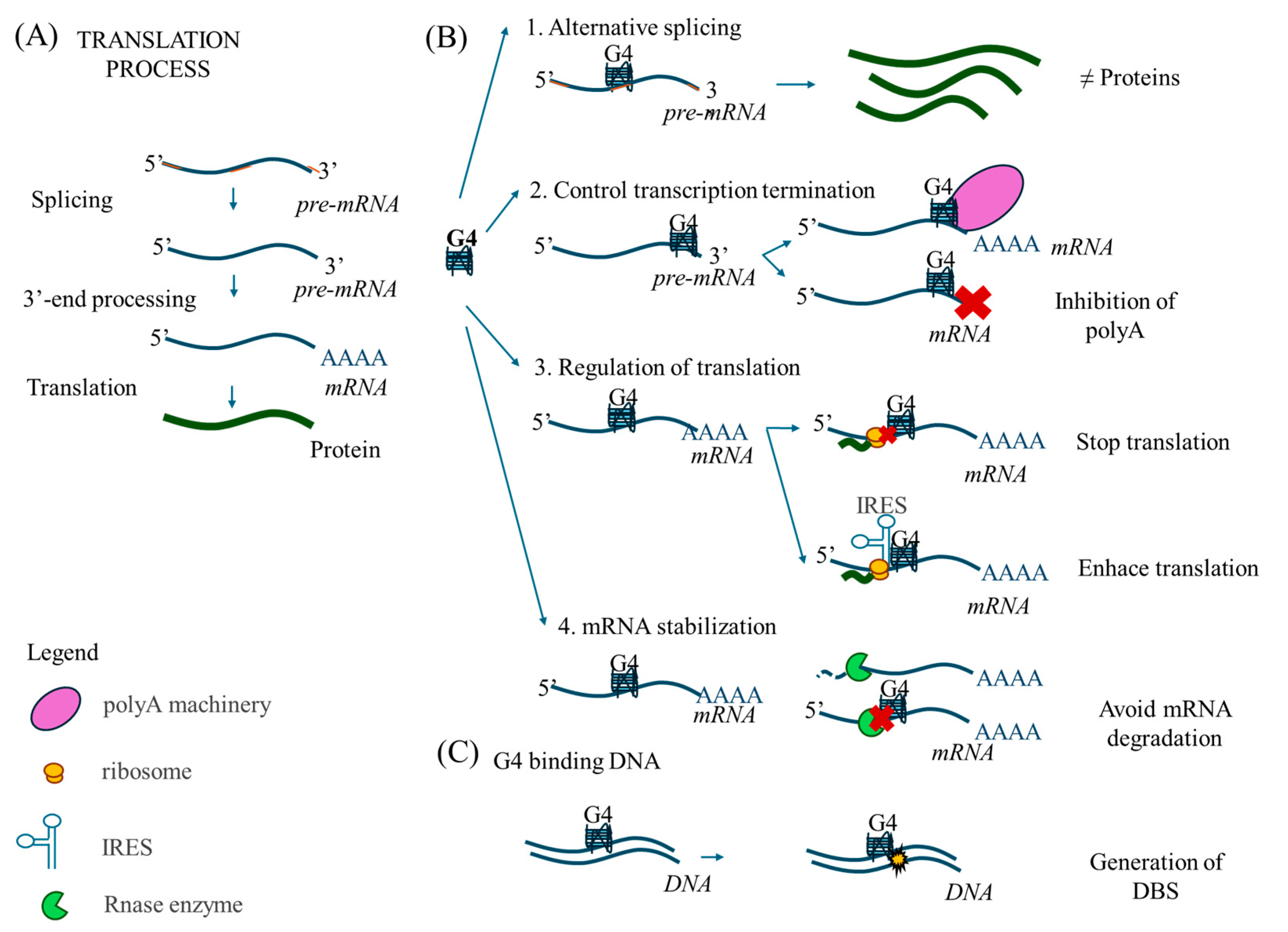
1. Introduction
2. Results
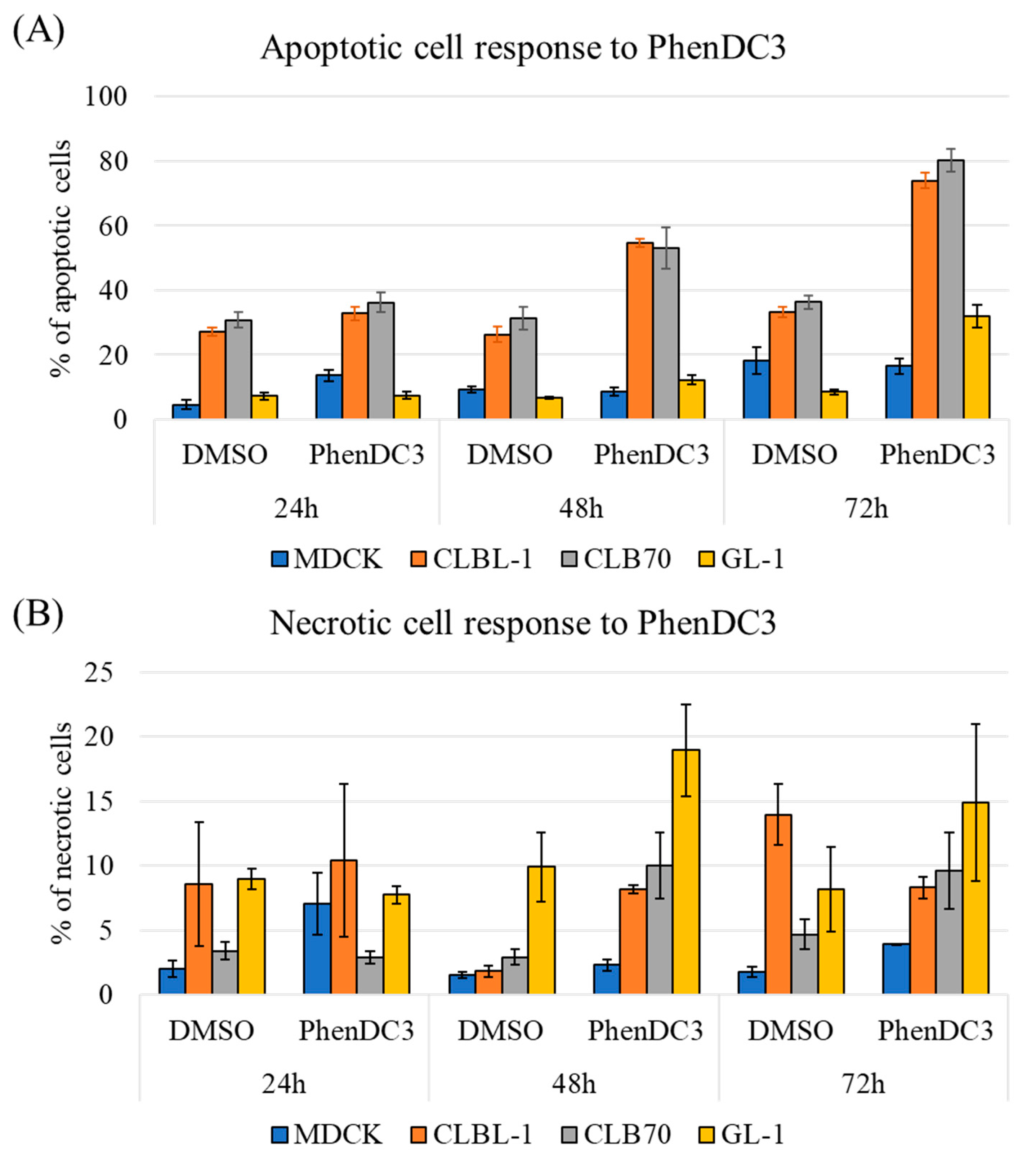
2.1. PhenDC3 Induces Cell Death in Canine Lymphoma and Leukemia Cell Lines
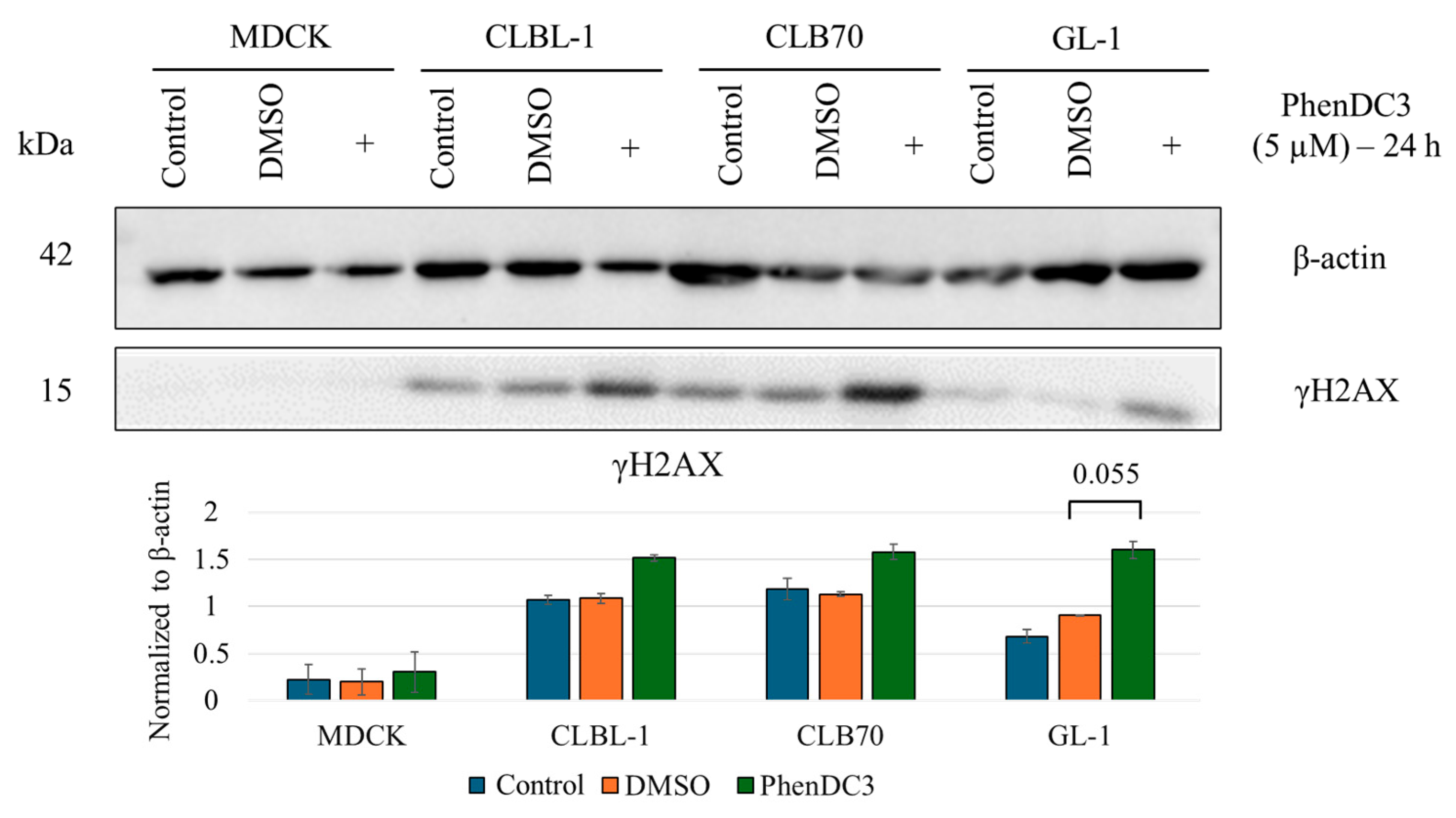
2.2. Confirmation of G4 Structures in Canine Lymphoma and Leukemia Cells
2.3. G4 in DDR and UPR Targets
2.3.1. Database Search to Explore RG4s on DDR and UPR Genes
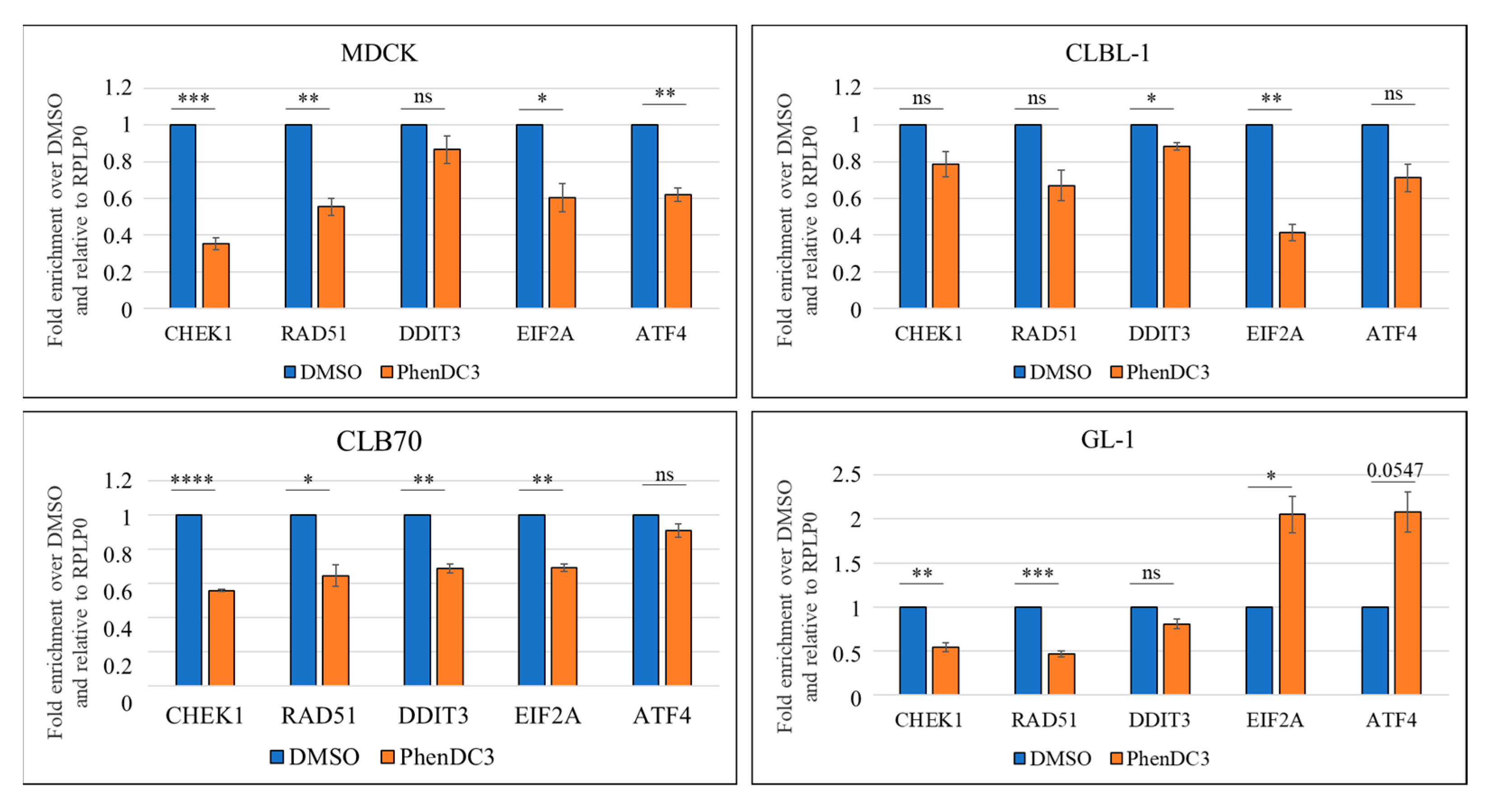
2.3.2. Changes in Canine Cells Observed at the mRNA Level in the DDR and UPR Pathways After Treatment with PhenDC3 at 5 μM for 24 h
2.4. RNA Sequencing Analysis
2.4.1. Quantification Analysis
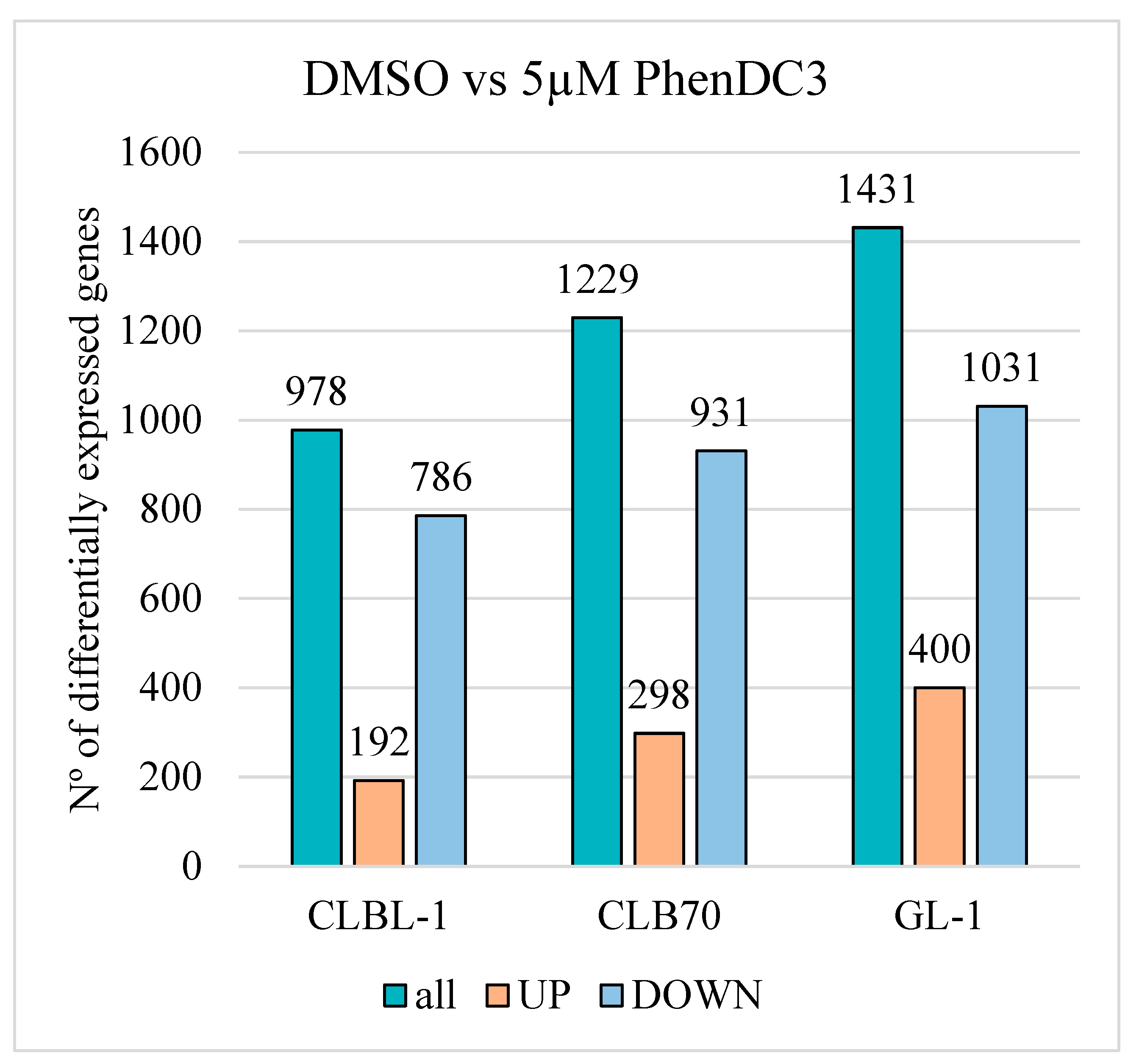
2.4.2. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
Differential Gene Expression Analysis for Each Comparison Across Cell Lines
Alterations in the Activity of the DDR and UPR Pathways Observed Across the Three Analyzed Cell Lines Following Treatment with the G4 Ligand
2.4.3. Enrichments Analysis
Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)
3. Discussion
3.1. PhenDC3 Stabilizes G4 and Induces Mild DNA Damage in Canine Lymphoma/Leukemia Cells
3.2. DDR and UPR Components Are Downregulated or Upregulated Depending on the Cell Type After G4 Stabilization with PhenDC3
3.3. GL-1 Might Be Suffering Oxidative Stress When Treated with PhenDC3
3.4. The Possibility of Using PhenDC3 in Combinational Therapy
- -
- The upregulation of PARP1 observed in GL-1 after blocking the G4s. Many available PARP inhibitors (PARPi) are used in clinics, but many are inducing resistance over time [41], and it has been shown that cancer cells use upregulation of PARP1 as a mechanism to become resistant to PARPi [42]. Treatment with olaparib has been tested in GL-1 and CLBL-1 by our group, showing that both cell lines are dying in a concentration and time-dependent manner, and in fact, GL-1 was less sensitive compared to CLBL-1 to olaparib treatment [43]. One potential avenue for future investigation is the combination of G4 ligands with PARPi in the canine cell lines studied, with GL-1 serving as a promising model for exploring therapeutic strategies in PARP1-upregulated cells.
- -
- DDIT4 overexpression is related to poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) human patients treated only with chemotherapy [44]. The results of the presented study showed that using a G4 ligand reduces DDIT4 expression in CLB70 and GL-1 cell lines, suggesting that the combination of PhenDC3 with the usual chemotherapy could improve the efficiency of the treatment and conditions of the patients. Given the physiological and molecular similarities between humans and canines, it is highly plausible that DDIT4 expression patterns observed in human AML may also be present in canine patients.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Material and Conditions
4.1.1. Cells and Culture
4.1.2. Drugs and Treatments
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.3. Apoptosis Study
4.4. Western Blot
4.5. Immunofluorescence Microscopy—Biotrackers BioCyTASQ
4.6. Database Search for G4 Structures on the Selected Genes
4.7. qPCR
4.7.1. RNA Isolation and Reverse Transcription
4.7.2. Primers Design
4.7.3. Gene Expression Analysis Using Real-Time PCR
4.7.4. Statistical Analysis of qPCR
4.8. RNA-Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| AV/PI | Annexin V/propidium iodide |
| BER | Base excision repair |
| CTCF | Corrected total cell fluorescence |
| DDR | DNA Damage Response |
| DSB | Double Strand Breaks |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| FPKM | Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads |
| G4 | G-quadruplexes |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| HKGs | Housekeeping genes |
| HRD | Homologous Recombination Deficiency |
| IRES | Internal ribosome entry site |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| padj | Adjusted p-value |
| PARPi | PARP inhibitors |
| PCA | Principal Components Analysis |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| polyA | polyadenylation |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TGs | Target genes |
| UPR | Unfolded Protein Response |
References
- Dumas, L.; Herviou, P.; Dassi, E.; Cammas, A.; Millevoi, S. G-Quadruplexes in RNA Biology: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, P.; Pandey, S.; Maiti, S. The Tale of RNA G-Quadruplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 5570–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fay, M.M.; Lyons, S.M.; Ivanov, P. RNA G-Quadruplexes in Biology: Principles and Molecular Mechanisms. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 2127–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodoin, R.; Carrier, J.C.; Rivard, N.; Bisaillon, M.; Perreault, J.-P. G-Quadruplex Located in the 5′UTR of the BAG-1 MRNA Affects Both Its Cap-Dependent and Cap-Independent Translation through Global Secondary Structure Maintenance. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 10247–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammas, A.; Millevoi, S. Survey and Sumary RNA G-Quadruplexes: Emerging Mechanisms in Disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herviou, P.; Le Bras, M.; Dumas, L.; Hieblot, C.; Gilhodes, J.; Cioci, G.; Hugnot, J.-P.; Ameadan, A.; Guillonneau, F.; Dassi, E.; et al. HnRNP H/F Drive RNA G-Quadruplex-Mediated Translation Linked to Genomic Instability and Therapy Resistance in Glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, C.; Seimiya, H. G-Quadruplex in Cancer Biology and Drug Discovery. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 531, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, D.; Spiegel, J.; Zyner, K.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. The Regulation and Functions of DNA and RNA G-Quadruplexes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, R.; Limmer, M.; Juranek, S.; Heine, A.; Paeschke, K. The Relevance of G-Quadruplexes for DNA Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iachettini, S.; Biroccio, A.; Zizza, P. Therapeutic Use of G4-Ligands in Cancer: State-of-the-Art and Future Perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, J.; Tacconi, E.M.C.; Folio, C.; Badie, S.; Porru, M.; Klare, K.; Tumiati, M.; Markkanen, E.; Halder, S.; Ryan, A.; et al. Targeting BRCA1 and BRCA2 Deficiencies with G-Quadruplex-Interacting Compounds. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct Evidence for a G-Quadruplex in a Promoter Region and Its Targeting with a Small Molecule to Repress c- MYC Transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandrini, I.; Recagni, M.; Zaffaroni, N.; Folini, M. On the Road to Fight Cancer: The Potential of G-Quadruplex Ligands as Novel Therapeutic Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Simeone, A.; Shea, A.; Hui, W.W.I.; Zyner, K.G.; Marsico, G.; Rueda, O.M.; Bruna, A.; Martin, A.; Zhang, X.; et al. Landscape of G-Quadruplex DNA Structural Regions in Breast Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyner, K.G.; Mulhearn, D.S.; Adhikari, S.; Martínez Cuesta, S.; Di Antonio, M.; Erard, N.; Hannon, G.J.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Genetic Interactions of G-Quadruplexes in Humans. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzan, E.; Elgendy, R.; Giantin, M.; Dacasto, M.; Sissi, C. Whole-Transcriptome Profiling of Canine and Human in Vitro Models Exposed to a G-Quadruplex Binding Small Molecule. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamm, D.H. Novel Treatments for Lymphoma. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 49, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlak, A.; Henklewska, M. The Role of Bcl-XL Protein Research in Veterinary Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, A.; Ziolo, E.; Kutkowska, J.; Blazejczyk, A.; Wietrzyk, J.; Krupa, A.; Hildebrand, W.; Dziegiel, P.; Dzimira, S.; Obminska-Mrukowicz, B.; et al. A Novel Canine B-Cell Leukaemia Cell Line. Establishment, Characterisation and Sensitivity to Chemotherapeutics. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 1218–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Suárez, B.; Gillespie, D.A.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B.; Pawlak, A. An Initial Characterisation of the Unfolded Protein Response Pathway in Haematopoietic Canine Cancer Cell Lines—A Necessary Step for the Future Development of New Therapies in Dogs with Neoplasia. J. Vet. Res. 2023, 63, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Suárez, B.; Gillespie, D.A.; Dejnaka, E.; Kupczyk, P.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B.; Pawlak, A. Studying the DNA Damage Response Pathway in Hematopoietic Canine Cancer Cell Lines, a Necessary Step for Finding Targets to Generate New Therapies to Treat Cancer in Dogs. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1227683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, I.; Rentoft, M.; Singh, V.; Jamroskovic, J.; Chand, K.; Chorell, E.; Westerlund, F.; Sabouri, N. Stabilization of G-Quadruplex DNA Structures in Schizosaccharomyces Pombe Causes Single-Strand DNA Lesions and Impedes DNA Replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 10998–11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, C.K.; Marsico, G.; Sahakyan, A.B.; Chambers, V.S.; Balasubramanian, S. RG4-Seq Reveals Widespread Formation of G-Quadruplex Structures in the Human Transcriptome. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A New Generation of Protein Database Search Programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, J.C. Venny. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn’s Diagrams (2007–2015). Available online: https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 28 September 2025).
- Biffi, G.; Tannahill, D.; Miller, J.; Howat, W.J.; Balasubramanian, S. Elevated Levels of G-Quadruplex Formation in Human Stomach and Liver Cancer Tissues. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.; Doimo, M.; Andréasson, M.; L’Hôte, V.; Chorell, E.; Wanrooij, S. A Complementary Chemical Probe Approach towards Customized Studies of G-Quadruplex DNA Structures in Live Cells. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdon, S.; Herviou, P.; Dumas, L.; Destefanis, E.; Zen, A.; Cammas, A.; Millevoi, S.; Dassi, E. QUADRatlas: The RNA G-Quadruplex and RG4-Binding Proteins Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D240–D247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Bugaut, A.; Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. An RNA G-Quadruplex in the 5′ UTR of the NRAS Proto-Oncogene Modulates Translation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masud, T.; Soong, C.; Xu, H.; Biele, J.; Bjornson, S.; McKinney, S.; Aparicio, S. Ubiquitin-Mediated DNA Damage Response Is Synthetic Lethal with G-Quadruplex Stabilizer CX-5461. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douarre, C.; Mergui, X.; Sidibe, A.; Gomez, D.; Alberti, P.; Mailliet, P.; Trentesaux, C.; Riou, J.-F. DNA Damage Signaling Induced by the G-Quadruplex Ligand 12459 Is Modulated by PPM1D/WIP1 Phosphatase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 3588–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardinelli, F.; Tanori, M.; Muoio, D.; Buccarelli, M.; di Masi, A.; Leone, S.; Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Pallini, R.; Mancuso, M.; Antoccia, A. G-Quadruplex Ligand RHPS4 Radiosensitizes Glioblastoma Xenograft in Vivo through a Differential Targeting of Bulky Differentiated- and Stem-Cancer Cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micco, M.; Collie, G.W.; Dale, A.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Pazitna, I.; Gunaratnam, M.; Reszka, A.P.; Neidle, S. Structure-Based Design and Evaluation of Naphthalene Diimide G-Quadruplex Ligands As Telomere Targeting Agents in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2959–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, K.; Lian, W.; Zhou, N.; Wu, C.; Bao, J. G-Quadruplex Structures as a “Switch” Regulate ATF4 Expression in Ferroptotic HepG2 Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festjens, N.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Vandenabeele, P. Necrosis, a Well-Orchestrated Form of Cell Demise: Signalling Cascades, Important Mediators and Concomitant Immune Response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2006, 1757, 1371–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A.M.; Ding, Y.; Burrows, C.J. Oxidative DNA Damage Is Epigenetic by Regulating Gene Transcription via Base Excision Repair. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2604–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, H.; Nishimura, S. Hydroxylation of Deoxyguanosine at the C-8 Position by Ascorbic Acid and Other Reducing Agents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, J.; Adhikari, S.; Balasubramanian, S. The Structure and Function of DNA G-Quadruplexes. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Hurley, L.H.; Xu, H. A Synthetic Lethal Approach to Drug Targeting of G-Quadruplexes Based on CX-5461. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2023, 91, 129384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine (U.S.). (2021, August-) Study of CX-5461 in Patients with Solid Tumours and BRCA1/2, PALB2 or Homologous Recombination Deficiency (HRD) Mutation. NCT04890613. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04890613?intr=CX-5461&rank=2 (accessed on 30 March 2024).
- Spiegel, J.O.; Van Houten, B.; Durrant, J.D. PARP1: Structural Insights and Pharmacological Targets for Inhibition. DNA Repair 2021, 103, 103125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gouttia, O.G.; Wang, L.; Peng, A. PARP1 Upregulation in Recurrent Oral Cancer and Treatment Resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 804962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasaol, J.C.; Dejnaka, E.; Mucignat, G.; Bajzert, J.; Henklewska, M.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B.; Giantin, M.; Pauletto, M.; Zdyrski, C.; Dacasto, M.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Olaparib Induces DNA Damage and Acts as a Drug Sensitizer in an in Vitro Model of Canine Hematopoietic Cancer. BMC Vet. Res. 2025, 21, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Dai, Y.; Pang, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cui, L.; Quan, L.; Qian, T.; Zeng, T.; Si, C.; et al. Up-regulation of DDIT4 Predicts Poor Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rütgen, B.C.; Hammer, S.E.; Gerner, W.; Christian, M.; de Arespacochaga, A.G.; Willmann, M.; Kleiter, M.; Schwendenwein, I.; Saalmüller, A. Establishment and Characterization of a Novel Canine B-Cell Line Derived from a Spontaneously Occurring Diffuse Large Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 932–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaichi, M.; Taura, Y.; Kanki, M.; Mamba, K.; Momoi, Y.; Tsujimoto, H.; Nakama, S. Establishment and Characterization of a New Canine B-Cell Leukemia Cell Line. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1996, 58, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, F.J.; Amode, M.R.; Aneja, A.; Austine-Orimoloye, O.; Azov, A.G.; Barnes, I.; Becker, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Bhai, J.; et al. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D933–D941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.A.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and Quantifying Mammalian Transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-Responsive Genes Involved in Oxidative Phosphorylation Are Coordinately Downregulated in Human Diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Bartel, D.P. RNA G-quadruplexes are globally unfolded in eukaryotic cells and depleted in bacteria. Science 2016, 353, 6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| IC50 (µM) | |
|---|---|
| MDCK | 11.90 ± 0.13 |
| CLBL-1 | 8.65 ± 1.63 |
| CLB70 | 7.72 ± 0.64 |
| GL-1 | 7.04 ± 0.80 |
| Predicted * | Experimentally ** | Reference | Alignment with the Dog Sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDR | CHEK1 | 6 | - | 3 | - | |
| RAD51 | 8 | 2 | [23] | 6 | 2 | |
| UPR | DDIT3 | 1 | - | 1 | - | |
| EIF2A | 2 | - | 2 | - | ||
| ATF4 | 15 | - | 6 | - | ||
| Gene | CLBL-1 | CLB70 | GL-1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDR | PARP1 | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| PIK3CB | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | |
| GADD45A | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | |
| UPR | EIF4EBP1 | ↓ | ↑ | ↓ |
| NCK2 | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ | |
| DDIT4 | - | ↓ | ↓ |
| Cell Line | PhenDC3 to DMSO | GO |
|---|---|---|
| CLBL-1 | DOWN | - |
| UP | GPCRs signaling pathway, GPCR activity, transmembrane signaling receptor activity, signaling receptor activity, molecular transducer activity, signal transducer activity | |
| CLB70 | DOWN | - |
| UP | SIGNALING (16/38): GPCR signaling pathway, regulation of signal transduction, regulation of cell communication, regulation of signaling, Ras protein signal transduction, regulation of Ras protein signal transduction, regulation of small GTPase mediated signal transduction, Rho protein signal transduction, regulation of Rho protein signal transduction, small GTPase mediated signal transduction, GPCR activity, signaling receptor activity, transmembrane signaling receptor activity, signal transducer activity, regulation of intracellular signal transduction, regulation of response to stimulus STRUCTURAL AND BIOLOGY FUNCTION (10/38): molecular transducer activity, GTPase binding, protein heterodimerization activity, guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, Ras GTPase binding, small GTPase binding, enzyme binding, Ras guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity, Rho GTPase binding DNA PACKING (6/38): Nucleosome, protein-DNA complex, DNA packaging complex, Chromatin, chromosomal part, chromosome CELL DEATH (6/38): apoptotic process, cell death, programmed cell death, regulation of cell death, regulation of apoptotic process, regulation of programmed cell death | |
| GL-1 | DOWN | ion channel activity, substrate-specific channel activity, channel activity, passive transmembrane transporter activity, GPCR activity, cation channel activity |
| UP | DNA replication, DNA metabolic process |
| Cell Line | PhenDC3 to DMSO | KEGG |
|---|---|---|
| CLBL-1 | DOWN | CANCER TYPES (5/6): Breast cancer, Colorectal cancer, Renal cell carcinoma, Gastric cancer, Endometrial cancer OTHER (1/6): Glutamatergic synapse |
| UP | - | |
| CLB70 | DOWN | - |
| UP | DISEASE OR MEDICAL CONDITION (3/8): Amoebiasis, Alcoholism, Systemic lupus erythematosus STRUCTURAL AND BIOLOGICAL FUNCTION (5/8): Neutrophil extracellular trap formation, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Cell adhesion molecules, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | |
| GL-1 | DOWN | SIGNALING PATHWAYS (5/7): Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption, Chemokine signaling pathway, Axon guidance, Inflammatory mediator regulation of TRP channels ALTERED RESPONSE TO THERAPIES (2/7): Morphine addiction, Endocrine resistance |
| UP | DNA METABOLISM (2/7): Pyrimidine metabolism, Nucleotide metabolism DNA REPLICATION AND REPAIR (4/7): Cell cycle, Base excision repair, DNA replication, Mismatch repair CANCER TYPE (1/7): Bladder cancer |
| Gene Name | Primers 5′–3′ * | Amplicon Size | Gene Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHEK1 | F: TGGTTGACTTTCGGCTCTCT R: AAACCTTCTGGCTGCTCACA | 102 | XM_038503854.1 |
| RAD51 | F: TGTGGAGGCTGTTGCCTATG R: ATCGCCTTTGGTGGAACTCA | 146 | NM_001003043.1 |
| DITT3 | F: AGCCCTCACTCTCCAGATTC R: GCCACTCTGTTTCCGTTTCC | 93 | XM_022424097.2 |
| EIF2A | F: TGCCTTGAATTCTCGCCAAA R: GTATCCCAGCTGTGCCATCT | 82 | XM_038432666.1 |
| ATF4 | F: GCTGGCTTTGGATGGGTTG7 R: CCAATCTGTCCCGGAGAAGG | 70 | XM_038679806.1 |
| CLASPN | F: TGGAATCGATAAGGGCAGCT R: TGCCTTTGGATAGCTCAGTCT | 114 | XM_038687566.1 |
| ACTB | F: ACGGGCAGGTCATCACTATT R: GGTAGTTTCATGGATGCCGC | 104 | NM_01195845.3 |
| RPLP0 | F: AGGGCATCTGGAGAACAACC R: TGAATACAAAACCCACATTCCCC | 74 | XM_038436105.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Suárez, B.; Gillespie, D.A.; Dejnaka, E.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B.; Pawlak, A. Stabilization of G-Quadruplexes Modulates the Expression of DNA Damage and Unfolded Protein Response Genes in Canine Lymphoma/Leukemia Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209928
Hernández-Suárez B, Gillespie DA, Dejnaka E, Obmińska-Mrukowicz B, Pawlak A. Stabilization of G-Quadruplexes Modulates the Expression of DNA Damage and Unfolded Protein Response Genes in Canine Lymphoma/Leukemia Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(20):9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209928
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Suárez, Beatriz, David A. Gillespie, Ewa Dejnaka, Bożena Obmińska-Mrukowicz, and Aleksandra Pawlak. 2025. "Stabilization of G-Quadruplexes Modulates the Expression of DNA Damage and Unfolded Protein Response Genes in Canine Lymphoma/Leukemia Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 20: 9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209928
APA StyleHernández-Suárez, B., Gillespie, D. A., Dejnaka, E., Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B., & Pawlak, A. (2025). Stabilization of G-Quadruplexes Modulates the Expression of DNA Damage and Unfolded Protein Response Genes in Canine Lymphoma/Leukemia Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(20), 9928. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26209928







